Physicochemical and Functional Properties of DND358 (A Hypocholesterolemic Soybean) Protein Isolate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Preparation of SPI
2.3. SDS-PAGE Analysis of SPI
2.4. Isoflavone Analysis
2.5. Detection of Amino Acids
2.6. Single-Factor Experiments and Orthogonal Test
2.7. Water-Holding Capacity
2.8. Oil-Binding Capacity
2.9. Emulsification Property
2.10. Foaming Capacity and Stability
2.11. Gelation Ability
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
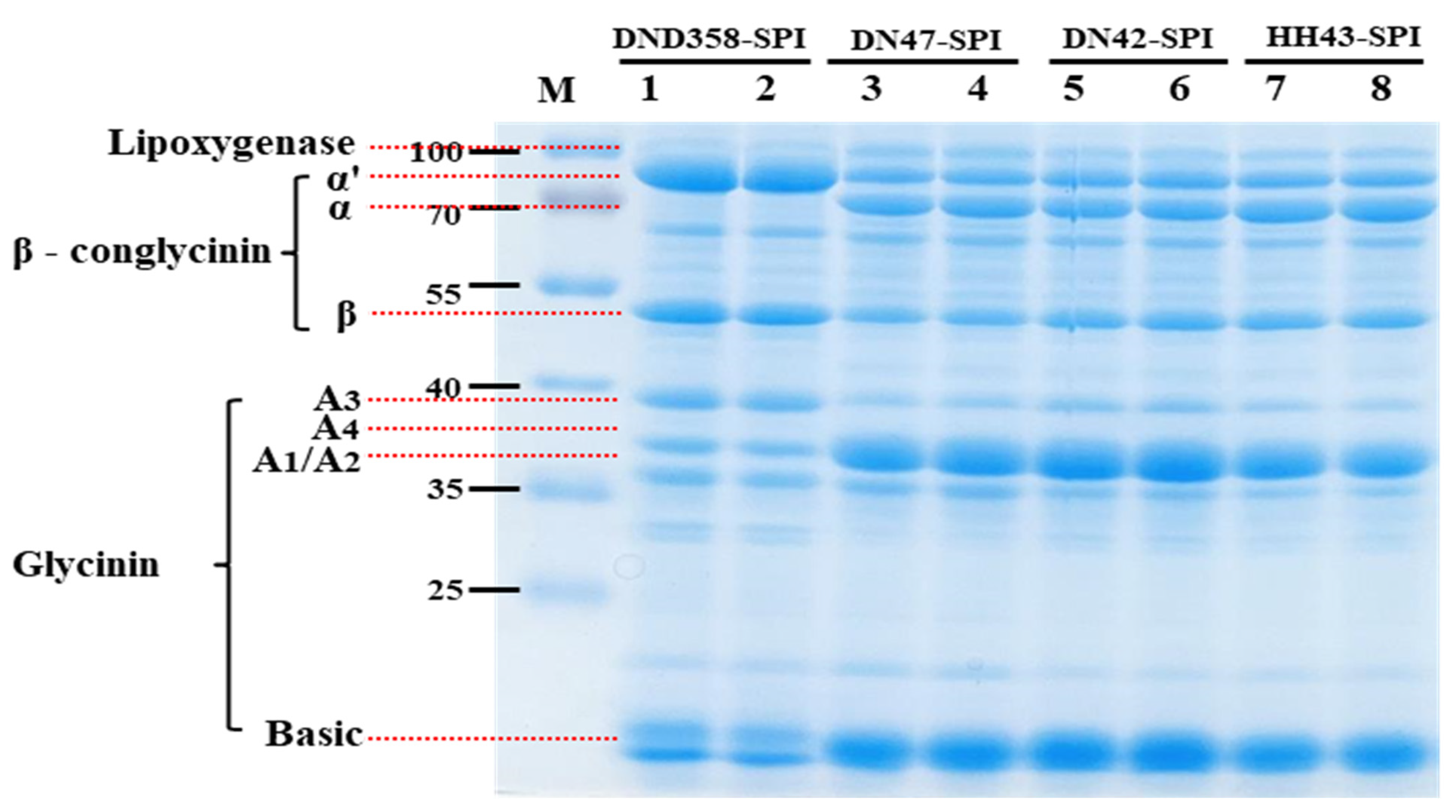
3.1. Identification of Protein Subunit Composition of SPI from DND358
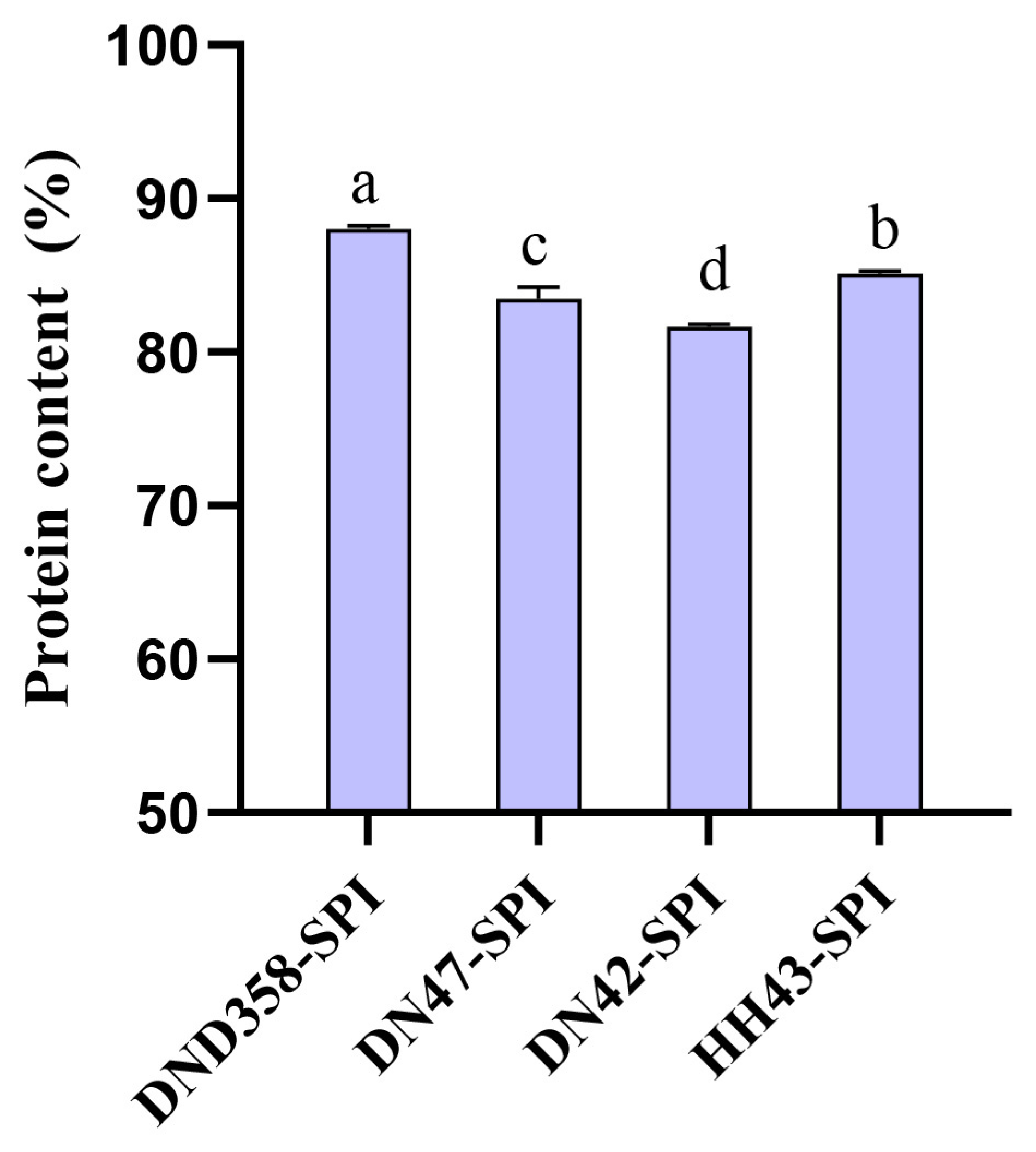
3.2. Characterization of DND358-SPI
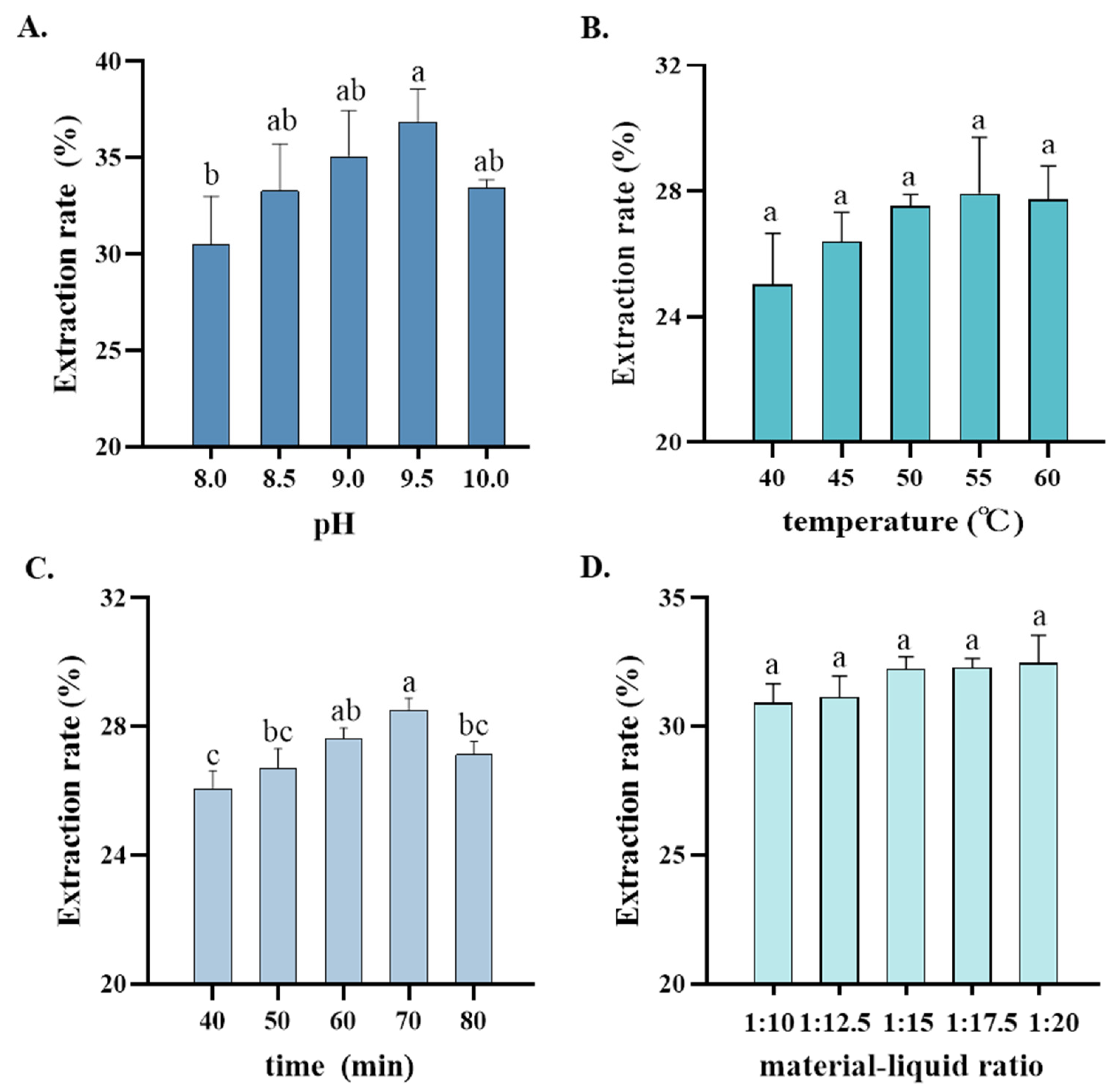
3.3. Orthogonal Test on Optimal Extraction Process for DND358-SPI
3.4. Functional Properties of DND358-SPI
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramdath, D.D.; Padhi, E.M.; Sarfaraz, S.; Renwick, S.; Duncan, A.M. Beyond the Cholesterol–Lowering Effect of Soy Protein: A Review of the Effects of Dietary Soy and Its Constituents on Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2017, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, K.; Tachibana, N.; Wanezaki, S.; Tsuzaki, S.; Takamatsu, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Shimoda, T. Isoflavone–free soy protein prepared by column chromatography reduces plasma cholesterol in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5717–5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taku, K.; Umegaki, K.; Ishimi, Y.; Watanabe, S. Effects of extracted soy isoflavones alone on blood total and LDL cholesterol: Meta–analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaczer, D.; Liska, D.J.; Lerman, R.H.; Darland, G.; Schiltz, B.; Tripp, M.; Bland, J.S. Effect of a low glycemic index diet with soy protein and phytosterols on CVD risk factors in postmenopausal women. Nutrition 2006, 22, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, R.E.; Krehl, W.A.; Stone, D.B.; Lopes, A. Dietary Carbohydrates and Low Cholesterol Diets: Effects on Serum Lipids of Man. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1967, 20, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.W.; Johnstone, B.M.; Cook–Newell, M.E. Meta–analysis of the effects of soy protein intake on serum lipids. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Lei, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Ma, K.Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.Y. 7S protein is more effective than total soybean protein isolate in reducing plasma cholesterol. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, C.; Duranti, M.; Eberini, I.; Scharnag, H.; März, W.; Castiglioni, S.; Lovati, M.R. Subcellular localization of soybean 7S globulin in HepG2 cells and LDL receptor up–regulation by its alpha’ constituent subunit. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 2149–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranti, M.; Lovati, M.R.; Dani, V.; Barbiroli, A.; Scarafoni, A.; Castiglioni, S.; Ponzone, C.; Morazzoni, P. The α′ Subunit from Soybean 7S Globulin Lowers Plasma Lipids and Upregulates Liver β–VLDL Receptors in Rats Fed a Hypercholesterolemic Diet. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, N.; Ma, G.; Zhong, L.; Xu, J. Characterization of Soy Protein Isolate/Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide hydrogel and its immunostimulatory effects on RAW264.7 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 151, 112126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Feng, G.; Li, T.; Wan, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X. Extension Region Domain of Soybean 7S Globulin Contributes to Serum Triglyceride–Lowering Effect via Modulation of Bile Acids Homeostasis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2200883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, A.; Liu, X. Properties of soy protein isolate prepared from aqueous alcohol washed soy flakes. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Lamsal, B.P.; Stepien, V.; Johnson, L.A.; Murphy, P.A. Functionality of soy protein produced by enzyme–assisted extraction. J. Amer. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterlee, L.D.; Bembers, M.; Kendrick, J.G. Functional properties of the Great Northern Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) protein isolate. J. Food Sci. 1975, 40, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, F.; Mcfeeters, R.F. Improvement of the emulsification properties of soy protein by limited pepsin hydrolysis. Lebensm–Wiss Technol. 1978, 11, 42–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bazinet, L.; Lamarche, F.; Labrecque, R.; Ippersiel, D. Effect of number of bipolar membranes and temperature on the performance of bipolar membrane electroacidification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3788–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsen, E.; Ahlstrm, C.; Labba, I.M.; Sandberg, A.; Rayner, M.; Purhagen, J.K. Protein extraction from cold pressed hempseed press cake: From laboratory to pilot scale. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 312–325. [Google Scholar]
- Elsohaimy, S.A.; Refaay, T.M.; Zaytoun, M.A.M. Physicochemical and functional properties of quinoa protein isolate. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2015, 60, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, L. Physicochemical, rheological and digestive characteristics of soy protein isolate gel induced by lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Eng. 2021, 292, 110243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butteiger, D.N.; Hibberd, A.A.; McGraw, N.J.; Napawan, N.; Hall–Porter, J.M.; Krul, E.S. Soy protein compared with milk protein in a western diet increases gut microbial diversity and reduces serum lipids in golden syrian hamsters. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, E.; Aguilar, J.M.; Bengoechea, C.; Lopez, M.L.; Guerrero, A. Rheology and water absorption properties of Alginate–Soy Protein composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmedna, M.; Prinyawiwatkul, W.; Rao, R.M. Solubilized wheat protein isolate: Functional properties and potential food applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshala, R.; Khan, N.; Chitneni, M.; Darwis, Y. Formulation and in vivo evaluation of ondansetron orally disintegrating tablets using different superdisintegrants. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 1945–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, G.M.; Mougeot, E. Creation and characterisation of aerated food products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Sit, N. Effect of ultrasonication on functional properties of tamarind seed protein isolates. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; He, Z.; Zeng, M.; Qin, F.; Chen, J. Effects of soy protein composition in recombined soy–based cream on the stability and physical properties of whipping cream. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2732–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taktak, W.; Nasri, R.; Hamdi, M.; Gomez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Lopez-Rubio, A.; Li, S.; Nasri, M.; Chaâbouni, M.K. Physicochemical, textural, rheological and microstructural properties of protein isolate gels produced from Europeaneel (Anguilla anguilla) by heat–induced gelation process. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 82, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, S.K.; Mcclements, D.J. Influence of Cosolvent Systems on the Gelation Mechanism of Globular Protein: Thermodynamic, Kinetic, and Structural Aspects of Globular Protein Gelation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2005, 4, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Oehrle, N.W.; Liu, S.; Krishnan, H.B. Development and Characterization of a Soybean Experimental Line Lacking the α’ Subunit of β-Conglycinin and G1, G2, and G4 Glycinin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Qiu, Z.; Li, M.; Luo, T.; Wu, Q.; Krishnan, H.B.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S. Breeding of ‘DND358’: A new soybean cultivar for processing soy protein isolate with a hypocholesterolemic effect similar to that of fenofibrate. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 90, 104979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuchat, L.R. Functional and electrophoretic characteristics of succinylated peanut flour protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1977, 25, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klompong, V.; Benjakul, S.; Kantachote, D.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidative activity and functional properties of protein hydrolysate of yellow stripe trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as influenced by the degree of hydrolysis and enzyme type. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrassia, R.; Palazolo, G.G.; Risso, P.H.; Wagner, J.R. Glycosylation, denaturation, and aggregation of soy proteins in defatted soy flakes flour: Influence of thermal and homogenization treatments. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 10, 2358–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varfolomeyeva, E.P.; Danilenko, A.N.; Bikbov, T.M.; Grinberg, V.Y.; Leontiev, A.L.; Tolstoguzov, V.B. The rheological properties of diluted solutions of 11 S-glogulin isolated from soybeans by using selective thermal denaturation of 2S- and 7S globulins. Die Nahr. 1986, 30, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.S.; Chang, S.K.; Li, L.T.; Tatsumi, E. Effect of selective thermal denaturation of soybean proteins on soymilk viscosity and tofu’s physical properties. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, B.; Lin, L.; Chen, B.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, J. Hydration properties and binding capacities of dietary fibers from bamboo shoot shell and its hypolipidemic effects in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, G.S.; Cui, W.; Eskin, N.A.M. Effect of saponin on the surface properties of quinoa proteins. Int. J. Food Prop. 1999, 2, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumiya, K.; Murray, B.S. Soybean protein isolate gel particles as foaming and emulsifying agents. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.P.; Chen, X.W.; Guo, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.M.; Yang, X.Q. Stabilization of foam and emulsion by subcritical water-treated soy protein: Effect of aggregation state. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.R.; Gueguen, J. Surface functional properties of native, acid-treated, and reduced soy glycinin. 2. Emulsifying properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, D. Structures of plant storage proteins and their functions. Food Rev. Int. 1999, 7, 353–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žilić, S.M.; Barać, M.B.; Pešić, M.B.; Mladenović Drinić, S.D.; Ignjatović-Micić, D.D.; Srebrić, M.B. Characterization of proteins from kernel of different soybean varieties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Dong, Y.; Niu, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. Study on the gel properties and secondary structure of soybean protein isolate/egg white composite gels. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, H.G. Changes in quality characteristics of tofu with freezing treatment of soybeans. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Amino Acid (%) | DND358-SPI | DN47-SPI | DN42-SPI | HH43-SPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAAs | ||||
| Met | 1.17 ± 0.01 a | 1.20 ± 0.01 a | 1.08 ± 0.03 b | 0.98 ± 0.02 c |
| Val | 3.65 ± 0.02 a | 3.51 ± 0.03 b | 3.40 ± 0.04 c | 3.00 ± 0.03 d |
| Lys | 5.39 ± 0.03 a | 5.16 ± 0.06 b | 4.80 ± 0.09 c | 4.52 ± 0.08 d |
| Ile | 3.77 ± 0.01 b | 3.92 ± 0.05 a | 3.39 ± 0.08 c | 3.39 ± 0.05 c |
| Phe | 4.38 ± 0.01 a | 4.33 ± 0.03 b | 3.92 ± 0.04 b | 3.83 ± 0.07 b |
| Leu | 6.40 ± 0.01 b | 6.70 ± 0.05 a | 6.29 ± 0.12 b | 6.28 ± 0.10 b |
| Thr | 3.24 ± 0.01 a | 2.97 ± 0.03 b | 2.52 ± 0.05 d | 2.75 ± 0.05 c |
| Total EAAs | 28.01 ± 0.06 a | 27.80 ± 0.25 a | 25.40 ± 0.33 b | 24.74 ± 0.39 b |
| Non-essential AAs | ||||
| Asp | 9.74 ± 0.01 b | 9.64 ± 0.11 b | 10.23 ± 0.09 a | 8.04 ± 0.10 c |
| Ser | 4.35 ± 0.01 a | 4.35 ± 0.07 a | 3.52 ± 0.06 c | 3.99 ± 0.08 b |
| Glu | 16.57 ± 0.07 a | 16.42 ± 0.13 a | 15.75 ± 0.29 b | 14.98 ± 0.20 c |
| Gly | 3.39 ± 0.01 a | 3.35 ± 0.04 a | 3.39 ± 0.01 a | 2.90 ± 0.05 b |
| Ala | 3.04 ± 0.02 b | 3.41 ± 0.03 a | 2.80 ± 0.13 c | 2.99 ± 0.04 b |
| Cys | 1.11 ± 0.01 a | 1.00 ± 0.02 b | 0.79 ± 0.04 d | 0.85 ± 0.01 c |
| Tyr | 3.14 ± 0.01 a | 3.11 ± 0.02 a | 2.73 ± 0.05 b | 2.65 ± 0.04 b |
| His | 2.67 ± 0.01 a | 2.10 ± 0.02 b | 2.06 ± 0.03 b | 1.89 ± 0.04 c |
| Arg | 6.12 ± 0.02 ab | 6.18 ± 0.06 a | 5.79 ± 0.10 c | 5.98 ± 0.06 b |
| Pro | 4.42 ± 0.08 a | 4.18 ± 0.04 b | 3.10 ± 0.13 d | 3.91 ± 0.08 c |
| Total AAs | 82.57 ± 0.24 a | 81.54 ± 0.75 a | 75.55 ± 1.24 b | 72.92 ± 1.04 c |
| Cultivar-SPI | Daidzein (µg/g) | Glycitein (µg/g) | Genistein (µg/g) | Total Isoflavones (µg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DND358-SPI | 787.84 ± 2.27 a | 254.14 ± 3.53 a | 1713.44 ± 1.60 c | 2755.41 ± 5.42 b |
| DN47-SPI | 669.58 ± 1.01 c | 116.63 ± 0.47 c | 1801.71 ± 0.71 b | 2587.91 ± 2.13 c |
| DN42-SPI | 647.97 ± 2.58 d | 103.48 ± 0.41 d | 1366.81 ± 1.34 d | 2118.25 ± 4.28 d |
| HH43-SPI | 759.68 ± 1.05 b | 145.64 ± 2.96 b | 1897.80 ± 1.86 a | 2803.13 ± 5.52 a |
| Level | pH | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Material–Liquid Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | 50 | 60 | 1:15 |
| 2 | 9.5 | 55 | 70 | 1:17.5 |
| 3 | 10 | 60 | 80 | 1:20 |
| No. | Factor | Extraction Rate (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 31.20 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 35.33 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 37.33 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 37.07 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 33.47 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 35.33 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 35.73 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 37.33 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 30.53 |
| K1 | 103.86 | 104.00 | 103.86 | 95.20 | |
| K2 | 105.87 | 106.13 | 102.93 | 106.39 | |
| K3 | 103.59 | 103.19 | 106.53 | 111.73 | |
| Rj | 2.28 | 2.94 | 3.60 | 16.53 | |
| Sample | WHC (g/g) | OBC (g/g) | FC (%) | FS (%) | EAI (m2/g) | ESI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DND358-SPI | 4.73 ± 0.03 a | 3.00 ± 0.03 a | 14.67 ± 1.15 b | 61.61 ± 4.64 b | 10.67 ± 0.45 a | 18.37 ± 2.78 c |
| DN47-SPI | 2.11 ± 0.12 c | 1.98 ± 0.12 b | 22.33 ± 2.52 a | 74.58 ± 1.68 a | 10.89 ± 1.30 a | 35.44 ± 2.18 ab |
| DN42-SPI | 2.44 ± 0.10 b | 1.84 ± 0.14 b | 10.67 ± 1.15 b | 62.22 ± 3.85 b | 11.27 ± 1.32 a | 36.30 ± 2.62 a |
| HH43-SPI | 2.75 ± 0.18 b | 2.03 ± 0.11 b | 14.33 ± 1.53 b | 65.34 ± 3.49 ab | 11.13 ± 0.90 a | 30.20 ± 1.13 b |
| Sample | Hardness (g) | Springiness (mm) | Cohesiveness | Gumminess (g) | Chewiness (mj) | Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DND358-SPI | 159.27 ± 0.35 a | 3.70 ± 0.17 a | 1.22 ± 0.07 a | 186.07 ± 5.76 a | 6.78 ± 0.16 a | 1.88 ± 0.04 a |
| DN47-SPI | 121.60 ± 5.50 b | 4.06 ± 0.06 a | 1.10 ± 0.01 a | 177.50 ± 9.13 a | 4.90 ± 0.31 b | 1.62 ± 0.11 b |
| DN42-SPI | 49.57 ± 2.47 d | 3.86 ± 0.36 a | 1.10 ± 0.05 a | 53.93 ± 1.67 c | 2.19 ± 0.21 c | 1.30 ± 0.03 c |
| HH43-SPI | 101.73 ± 1.33 c | 3.90 ± 0.27 a | 1.15 ± 0.08 a | 110.53 ± 5.98 b | 4.38 ± 0.24 b | 1.35 ± 0.07 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, T.; Fan, Y.; Fan, M.; Li, M.; Qiu, Z.; Du, Q.; Ma, C.; Liu, C.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of DND358 (A Hypocholesterolemic Soybean) Protein Isolate. Foods 2024, 13, 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13203236
Luo T, Fan Y, Fan M, Li M, Qiu Z, Du Q, Ma C, Liu C, Peng Y, Zhang S, et al. Physicochemical and Functional Properties of DND358 (A Hypocholesterolemic Soybean) Protein Isolate. Foods. 2024; 13(20):3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13203236
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Tingting, Yuanhang Fan, Mengmeng Fan, Ming Li, Zhendong Qiu, Qiuyan Du, Chongxuan Ma, Chang Liu, Yuhan Peng, Shuzhen Zhang, and et al. 2024. "Physicochemical and Functional Properties of DND358 (A Hypocholesterolemic Soybean) Protein Isolate" Foods 13, no. 20: 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13203236
APA StyleLuo, T., Fan, Y., Fan, M., Li, M., Qiu, Z., Du, Q., Ma, C., Liu, C., Peng, Y., Zhang, S., Liu, S., & Song, B. (2024). Physicochemical and Functional Properties of DND358 (A Hypocholesterolemic Soybean) Protein Isolate. Foods, 13(20), 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13203236




