Differences in the Chromogenic Effect of Corn Starch and Potato Starch on Paprika Red Pigment and Structural Characterisation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Starch-Paprika Red Pigment Complexes
2.3. Colour Evaluation of Starch-Paprika Red Pigment Complexes
2.4. Determination of Reflectance and Scattering Rate of Starch-Paprika Red Pigment Complexes
2.5. Analysis of Pigments Adsorbed by Starch in Paprika Red Pigment
2.5.1. Pretreatment of Samples
2.5.2. Analysis of Pigments Content in CS-P and PS-P
2.6. Determination of Complexing Index (CI) of Samples
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.8. Particle Size Analysis
2.9. Mercury Porosimetry Analysis
2.10. Fourier Transform Infra Red (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.11. X-ray Diffraction
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CS-P and PS-P Colour Comparison
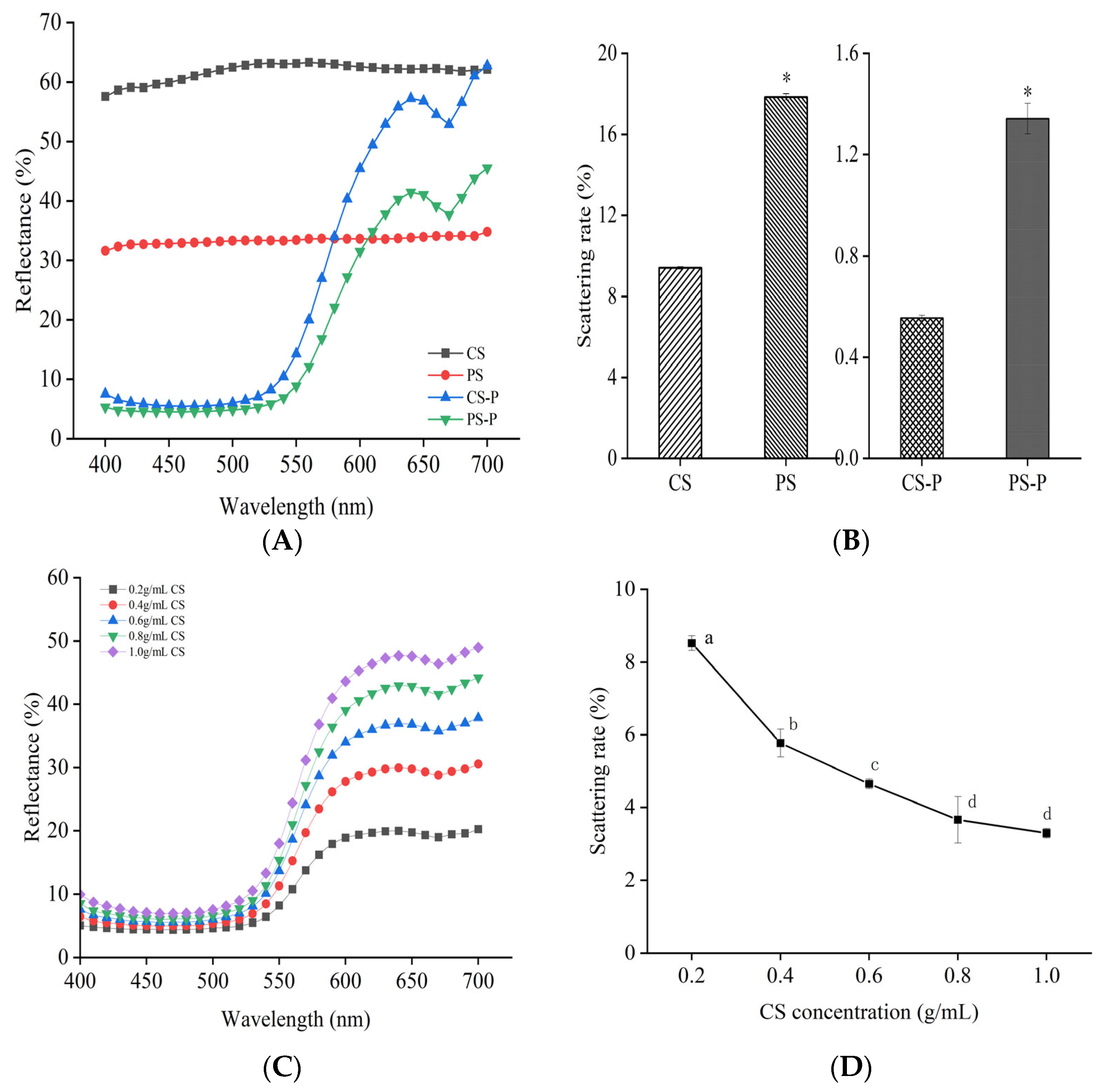
3.2. Analysis of the Optical Properties of Starches and Starch-Paprika Red Pigment Complexes
3.3. HPLC Analysis of Adsorption of Paprika Red Pigment from CS and PS
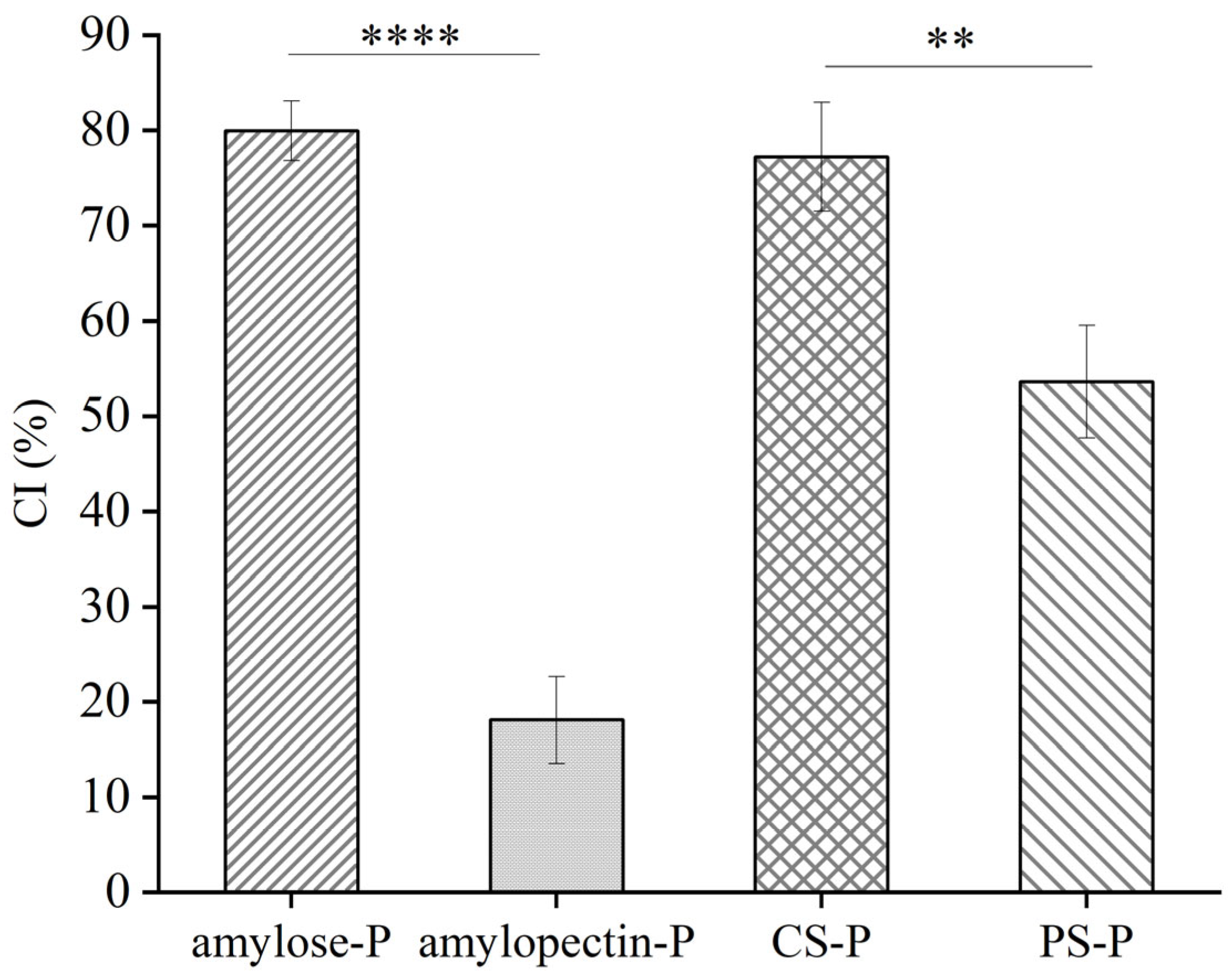
3.4. CI values of the Starch-Paprika Red Pigment Complexes
3.5. Particle Size Analysis of Starches and Starch-Paprika Red Pigment Complexes
3.6. Pore Analysis of Starches and Starch-Paprika Red Pigment Complexes
3.7. Structural Characterisation of Starchs and Starch-Paprika Red Pigment Complexes
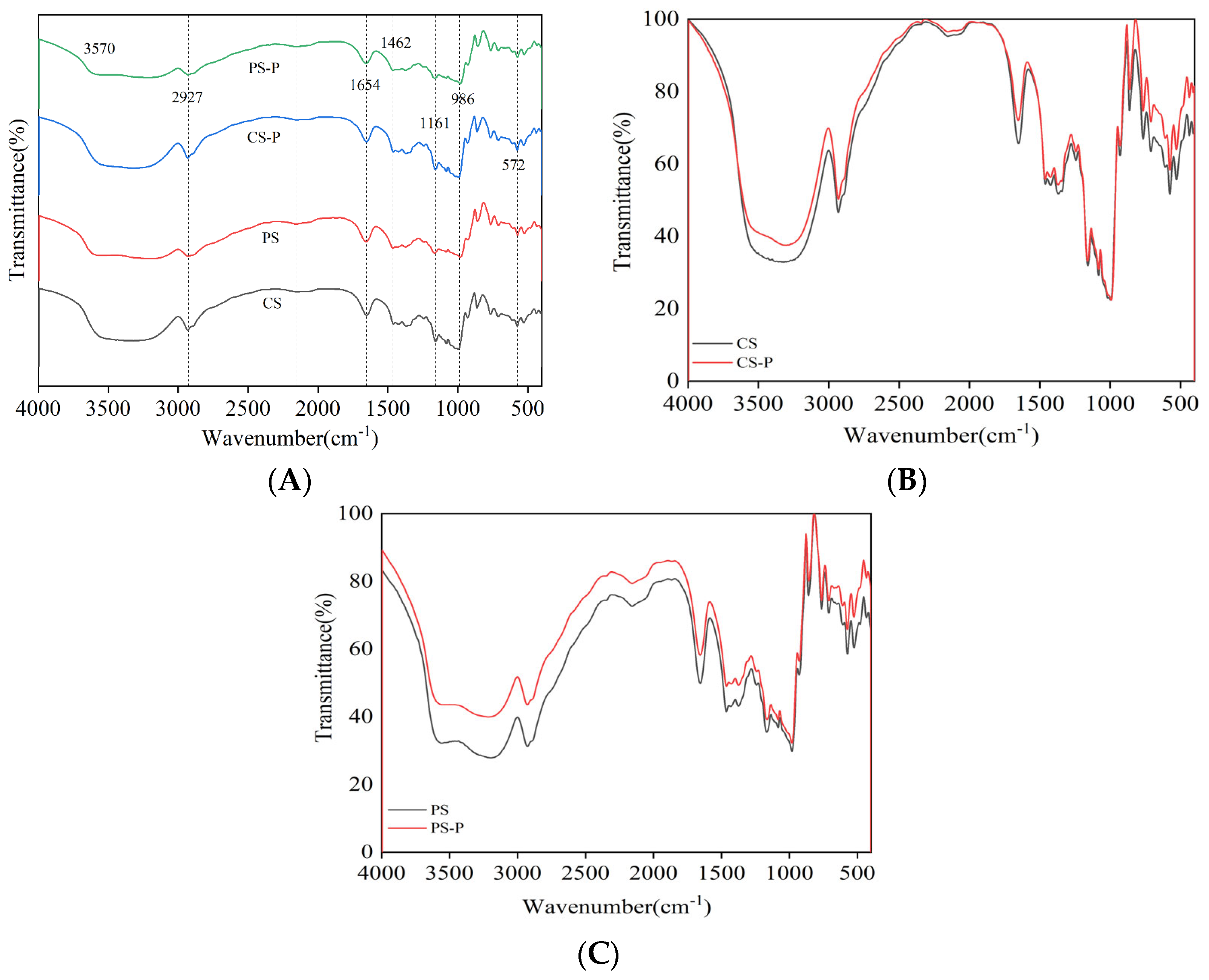
3.7.1. FT-IR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.7.2. X-Diffraction Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arimboor, R.; Natarajan, R.B.; Menon, K.R.; Chandrasekhar, L.P.; Moorkoth, V. Red pepper (Capsicum annuum) carotenoids as a source of natural food colors: Analysis and stability—A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 1258–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, W.R.; Witty, C.F.; Daniel, J.M.; Dohanich, G.P. Choline acetyltransferase in the hippocampus is associated with learning strategy preference in adult male rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 289, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, W.M.; Rhee, H.C.; Kim, S. Red paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) and its main carotenoids, capsanthin and beta-carotene, prevent hydrogen peroxide-induced inhibition of gap-junction intercellular communication. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 254, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, R.; Alvarez-Orti, M.; Pardo, J.E. Influence of the paprika type on redness loss in red line meat products. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Ha, T.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.J.; Ahn, J.Y. Red paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) and its main carotenoid capsanthin ameliorate impaired lipid metabolism in the liver and adipose tissue of high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 31, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echegaray, N.; Guzel, N.; Kumar, M.; Guzel, M.; Hassoun, A.; Lorenzo, J.M. Recent advancements in natural colorants and their application as coloring in food and in intelligent food packaging. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vertzoni, M.; Kartezini, T.; Reppas, C.; Archontaki, H.; Valsami, G. Solubilization and quantification of lycopene in aqueous media in the form of cyclodextrin binary systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 309, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, N.; Cheng, C.; McClements, D.J.; Chen, X.; Zou, L.; Liu, W. Encapsulation of hydrophobic capsaicin within the aqueous phase of water-in-oil high internal phase emulsions: Controlled release, reduced irritation, and enhanced bioaccessibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.X.; Huang, G.Q.; Wang, S.Q.; Sun, Y.T. Microencapsulation of capsanthin by soybean protein isolate-chitosan coacervation and microcapsule stability evaluation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 131, 39671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Yang, Z.; Tan, K.B.; Chen, J.; Huang, J.; Li, Q. Preparation and characterization of ethyl cellulose film modified with capsaicin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Gao, Y.; Mei, X.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with capsaicin and their oxidation resistance in meat preservation. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balde, A.; Kim, S.K.; Benjakul, S.; Nazeer, R.A. Pulmonary drug delivery applications of natural polysaccharide polymer derived nano/micro-carrier systems: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 220, 1464–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, L.M.M.; Petito, N.; Costa, V.G.; Falcão, D.Q.; de Lima Araújo, K.G. Inclusion complexes of red bell pepper pigments with β-cyclodextrin: Preparation, characterisation and application as natural colorant in yogurt. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.T.; Hadinoto, K. A new solubility enhancement strategy of capsaicin in the form of high-payload submicron capsaicin-chitosan colloidal complex. Colloid Surf. A 2017, 520, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, Z.; Tang, D.; Lv, C.; Luo, K.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. Development and Identification of SSR Markers Associated with Starch Properties and β-Carotene Content in the Storage Root of Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Hu, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhu, X.; Chen, D.; Zhuang, H.; Yao, L.; Song, S.; Wang, H.; Sun, M. Emulsion-based delivery systems for curcumin: Encapsulation and interaction mechanism between debranched starch and curcumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Lv, J.; Jiang, S.W.; Niu, B.C.; Pang, M.; Jiang, S.T. Preparation and characterization of porous corn starch and its adsorption toward grape seed proanthocyanidins. Starch-Starke 2016, 68, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, M.; Aleixandre, A.; Sineiro, J.; Rosell, C.M.; Moreira, R. Interactions between Ascophyllum nodosum Seaweeds Polyphenols and Native and Gelled Corn Starches. Foods 2022, 11, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Fan, Y.; Yokoyama, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L. Characterization of milk proteins-lutein complexes and the impact on lutein chemical stability. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, F.; Awika, J.M.; Rooney, L.W. Interaction of tannins and other sorghum phenolic compounds with starch and effects on in vitro starch digestibility. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11609–11617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yifan, L.; Bo, Z.; Huishan, S.; Xiangzhen, G.; Xiangxiang, S.; Qian, Z.; Xiuyun, Z.; Zhuangzhuang, S.; Wenhao, L. Sodium caseinate and acetylated mung bean starch for the encapsulation of lutein: Enhanced solubility and stability of lutein. Foods 2021, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Du, Q.L.; Miao, T.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Jia, D.Y. Interaction between potato starch and polysaccharide. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yue, M.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Ma, C. Interaction between potato starch and barley β-glucan and its influence on starch pasting and gelling properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Zhan, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, B.; Chen, P. Preparation, characterization and evaluation of capsaicin-loaded indica rice starch nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaschar-Ovdat, S.; Shani-Levi, C.; Lesmes, U. Capsaicin stability and bio-accessibility affected by complexation with high-amylose corn starch (HACS). Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6992–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Baranyai, L.; Gottschalk, K.; Zude, M. An Approach for Monitoring the Moisture Content Changes of Drying Banana Slices with Laser Light Backscattering Imaging. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2008, 1, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; An, C.G.; Park, J.S.; Lim, Y.P.; Kim, S. Carotenoid profiling from 27 types of paprika (Capsicum annuum L.) with different colors, shapes, and cultivation methods. Food Chem. 2016, 201, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo, E.; Turcsi, E.; Szabo, I.; Mosquera, Y.; Agocs, A.; Nagy, V.; Gulyas-Fekete, G.; Deli, J. Carotenoid Composition of the Fruit of Red Mamey (Pouteria sapota). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7148–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chao, C.; Cai, J.; Niu, B.; Copeland, L.; Wang, S. Starch-lipid and starch-lipid-protein complexes: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1056–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeyinka, S.A.; Singh, S.; Ma, Y.; Amonsou, E.O. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on structural, thermal and rheological properties of bambara starch complexed with different fatty acids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 80174–80180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włodarczyk-Stasiak, M.; Mazurek, A.; Jamroz, J.; Hajnos, M.; Sokołowska, Z. Influence of physico-chemical modification of waxy corn starch on changes in its structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Lian, W.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, H.; Rao, Z.; Wang, L. Evaluation of the physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of the complex formed between rice starch and a novel pigment from Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. leaf. Food Chem. 2021, 374, 131627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebenyuk, P.E.; Chmutin, A.M.; Chuiko, V.A. Algorithm for Hue contrast transformation in the Lab color space. Izv. Vysših Učebnyh Zaved. Priborostr. 2018, 61, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, H. The interaction between tea polyphenols and rice starch during gelatinization. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2011, 17, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueli, A.M.; Bonfiglio, G.; Pasquale, S.; Troja, S.O. Effect of Particle Size on Pigments Colour. Color Res. Appl. 2017, 42, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntrallou, K.; Gika, H.; Tsochatzis, E. Analytical and Sample Preparation Techniques for the Determination of Food Colorants in Food Matrices. Foods 2020, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiyalagan, S.; Mandal, B.K.; Ling, Y.C. Determination of synthetic and natural colorants in selected green colored foodstuffs through reverse phase-high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choung, M.G. Determination of curcuminoid colouring principles in commercial foods by HPLC. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Tan, J.; Tang, S.H.; Jiang, Z.T.; Di, S.D.; Geng, Y. Simultaneous determination of synthetic edible pigments in beverages by titania-based RP-HPLC. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 3875–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cui, D.P.; Liu, M.Z.; Gong, H.H.; Huang, Y.J.; Han, F. Corn porous starch: Preparation, characterization and adsorption property. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Cui, R. Comparison of physicochemical properties of oca (Oxalis tuberosa), potato, and maize starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, H.; Liang, Q.; Ameer, K.; Ma, H.; Ren, X. Dual-frequency power ultrasound effects on the complexing index, physicochemical properties, and digestion mechanism of arrowhead starch-lipid complexes. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 84, 105978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, S.; Bertoft, E. The molecular structures of starch components and their contribution to the architecture of starch granules: A comprehensive review. Starch-Starke 2010, 62, 389–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, S. Effect of fatty acids on functional properties of normal wheat and waxy wheat starches: A structural basis. Food Chem. 2015, 190, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hong, Y.; Gu, Z.B.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.F.; Li, C.M. Stabilization of Pickering emulsions using starch nanocrystals treated with alkaline solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunaratne, R.; Zhu, F. Physicochemical interactions of maize starch with ferulic acid. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Yue, P.X.; Chi, J.P.; Liang, J.; Gao, X.L. Formation and stability of anthocyanins-loaded nanocomplexes prepared with chitosan hydrochloride and carboxymethyl chitosan. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 74, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, B. The structure property and adsorption capacity of new enzyme-treated potato and sweet potato starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 144, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujka, M.; Jamroz, J. Characteristics of pores in native and hydrolyzed starch granules. Starch-Starke 2010, 62, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.Y.; Fang, K.; Li, J.B.; Du, N.; Hu, D.B.; Cao, D.Y.; Tian, R.; Deng, L.G.; Li, K. Competitive adsorption mechanisms of pigments in sugarcane juice on starch-based magnetic nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 231, 123134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tian, Y.; Sun, B.; Cai, C.; Ma, R.; Jin, Z. Measurement and characterization of external oil in the fried waxy maize starch granules using ATR-FTIR and XRD. Food Chem. 2017, 242, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jivan, M.J.; Madadlou, A.; Yarmand, M. An attempt to cast light into starch nanocrystals preparation and cross-linking. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1661–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.M.; Fowler, P.A.; Sayers, C.; Williams, P.A. The chemical modification of a range of starches under aqueous reaction conditions. Carbohyd. Polym. 2003, 55, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, F.J.; Gidley, M.J.; Flanagan, B.M. Infrared spectroscopy as a tool to characterise starch ordered structure—A joint FTIR–ATR, NMR, XRD and DSC study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 139, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Deng, Z.; Tang, C.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, S.J.; Chen, T.T.; Hu, X.T. Formation, structure and properties of the starch-polyphenol inclusion complex: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, I.; Zhuo, G.-Y.; Chakraborty, I.; Melanthota, S.K.; Mal, S.S.; Sarmah, B.; Baruah, V.J.; Mahato, K.K.; Mazumder, N. Investigation of structural and physico-chemical properties of rice starch with varied amylose content: A combined microscopy, spectroscopy, and thermal study. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.; Orlova, Y.; Kovalev, M.; Ungar, Y.; Shimoni, E. Structural and functional properties of amylose complexes with genistein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4212–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| L* | a* | b* | ΔE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS-P | 42.63 ± 0.41 b | 22.45 ± 1.84 b | 20.83 ± 1.40 b | 6.75 ± 0.58 |
| CS-P | 46.01 ± 0.41 a | 26.90 ± 0.23 a | 25.39 ± 0.50 a | 12.57 ± 0.63 *** |
| CS-P-SC | 38.80 ± 0.11 c | 18.44 ± 0.67 c | 15.69 ± 0.47 c | - |
| Adsorption Capacity (μg/g) | Adsorption Ratio/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | capsorubin | 3.56 ± 0.03 e | 4.57 ± 0.50 d |
| capsanthin | 40.63 ± 0.65 a | 48.24 ± 1.79 a | |
| zeaxanthin | 6.50 ± 0.08 d | 8.78 ± 1.37 cd | |
| β-cryptoxanthin | 10.00 ± 0.15 c | 11.85 ± 1.87 c | |
| β-carotene | 24.75 ± 0.19 b | 29.81 ± 4.84 b | |
| Total | 85.44 ± 1.10 | 100 | |
| PS | capsorubin | 0.40 ± 0.01 d | 7.37 ± 1.20 c |
| capsanthin | 2.75 ± 0.25 a | 42.61 ± 2.94 a | |
| zeaxanthin | 0.48 ± 0.08 cd | 9.09 ± 1.90 c | |
| β-cryptoxanthin | 0.75 ± 0.06 c | 11.60 ± 2.24 c | |
| β-carotene | 2.27 ± 0.30 b | 34.14 ± 5.36 b | |
| Total | 6.65 ± 1.53 | 100 |
| Particle Size (µm) | Pore Area (m2) | Porosity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CS | 10.16 ± 0.12 b | 0.48 ± 0.06 a | 55.44 ± 0.65 a |
| PS | 27.54 ± 0.28 a | 0.19 ± 0.05 b | 40.44 ± 0.75 c |
| CS-P | 5.27 ± 0.60 c | 0.48 ± 0.02 a | 46.05 ± 2.12 b |
| PS-P | 26.34 ± 0.22 a | 0.25 ± 0.06 b | 41.63 ± 1.81 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, F.; Wu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S. Differences in the Chromogenic Effect of Corn Starch and Potato Starch on Paprika Red Pigment and Structural Characterisation. Foods 2024, 13, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020191
Su F, Wu Y, Cao Y, Wang S. Differences in the Chromogenic Effect of Corn Starch and Potato Starch on Paprika Red Pigment and Structural Characterisation. Foods. 2024; 13(2):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020191
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Fan, Yongqiang Wu, Yanping Cao, and Shaojia Wang. 2024. "Differences in the Chromogenic Effect of Corn Starch and Potato Starch on Paprika Red Pigment and Structural Characterisation" Foods 13, no. 2: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020191
APA StyleSu, F., Wu, Y., Cao, Y., & Wang, S. (2024). Differences in the Chromogenic Effect of Corn Starch and Potato Starch on Paprika Red Pigment and Structural Characterisation. Foods, 13(2), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13020191




