Determination of Opium Alkaloid Content in Poppy Seeds Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with a Mass Spectrometer with a Time-of-Flight Analyzer (UPLC-TOF-HRMS)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Reagents
2.2. Research Material
2.3. Sample Preparation (OAs Measurement)
2.4. LC/MS Analysis
2.5. Method Validation
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Method’s Evaluation
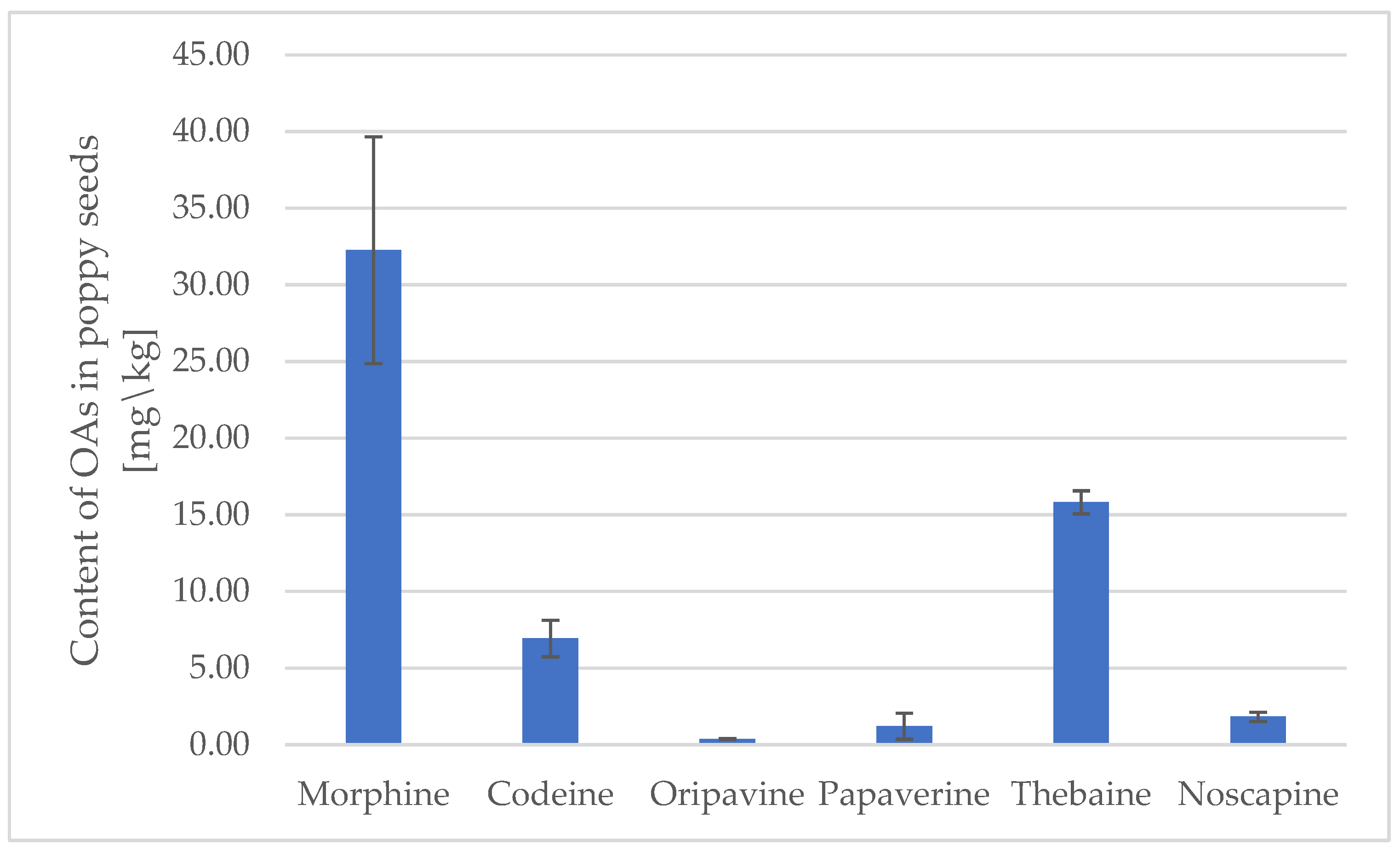
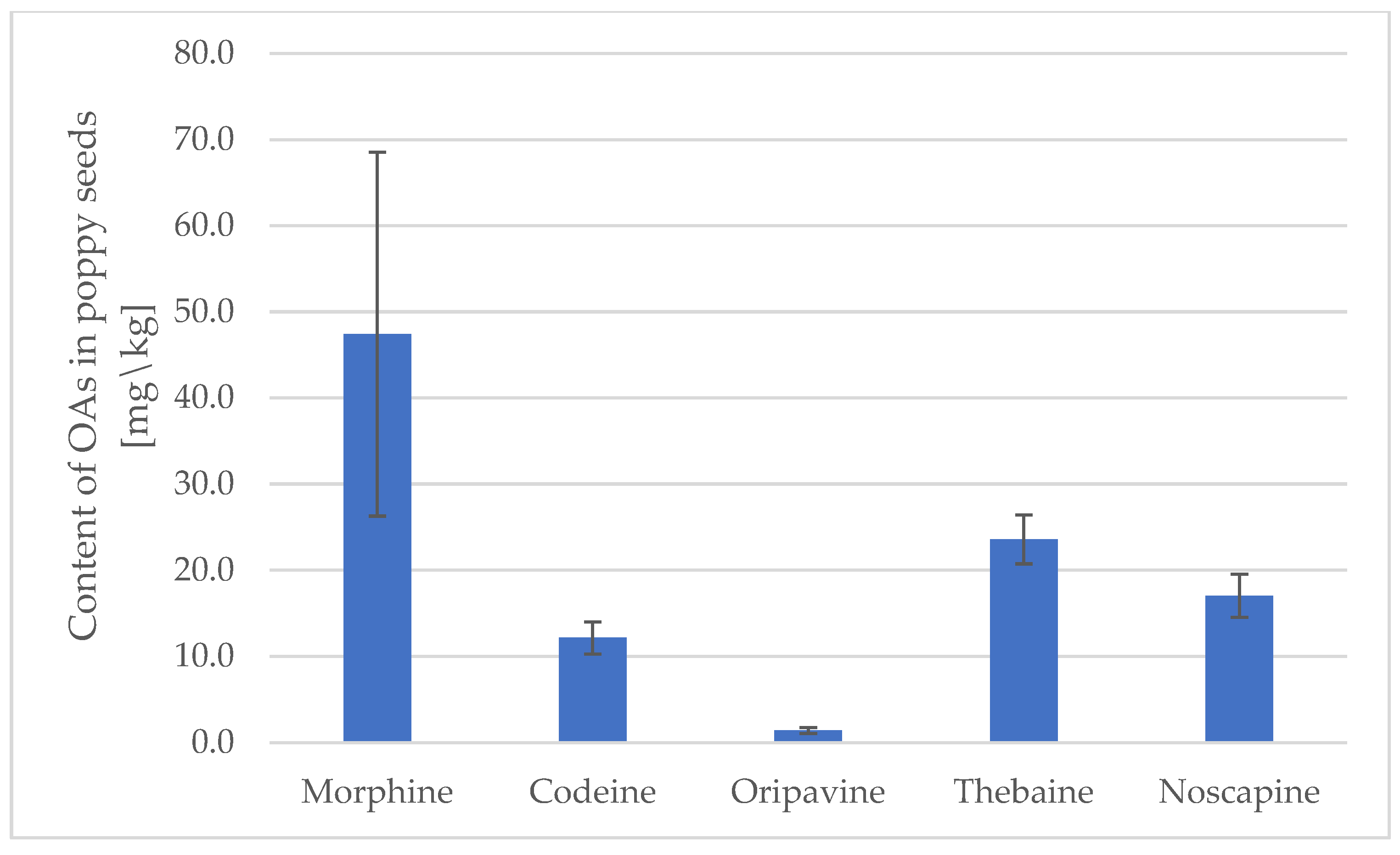
3.2. The Concentration of OAs in Poppy Seeds
3.3. Methods of Reduction of OA Contamination on Poppy Seed Surfaces
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Červeň, J.; Vrbovský, V.; Horáček, J.; Bartas, M.; Endlová, L.; Pečinka, P.; Čurn, V. New Low Morphine Opium Poppy Genotype Obtained by TILLING Approach. Plants 2023, 12, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngernsaengsaruay, C.; Leksungnoen, N.; Chanton, P.; Andriyas, T.; Thaweekun, P.; Rueansri, S.; Tuntianupong, R.; Hauyluek, W. Morphology, Taxonomy, Anatomy, and Palynology of the Opium Poppy (Papaver somniferum L.) Cultivation in Northern Thailand. Plants 2023, 12, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczak, M.; Sałaga, M.; Storr, M.A.; Fichna, J. Physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of opioid receptors and their ligands in the gastrointestinal tract: Current concepts and future perspectives. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetge, S.A.; Dzakovich, M.P.; Cooperstone, J.L.; Kleinmeier, D.; Redan, B.W. Concentrations of the Opium Alkaloids Morphine, Codeine, and Thebaine in Poppy Seeds are Reduced after Thermal and Washing Treatments but are Not Affected when Incorporated in a Model Baked Product. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5241–5248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Swortwood, M.J.; Yu, J. Determination of morphine, codeine, and thebaine concentrations from poppy seed tea using magnetic carbon nanotubes facilitated dispersive micro-solid phase extraction and GC-MS analysis. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 329, 111052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, N.; Casado-Hidalgo, G.; González-Gómez, L.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Sierra, I. Insight into the Impact of Food Processing and Culinary Preparations on the Stability and Content of Plant Alkaloids Considered as Natural Food Contaminants. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, M.G.; Dean, J.R.; Ames, J.M. Opium Alkaloids in Harvested and Thermally Processed Poppy Seeds. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Hidalgo, G.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Sierra, I. Mesostructured Silica-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles to Extract Six Opium Alkaloids in Poppy Seeds Prior to Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Hidalgo, G.; Perestelo, R.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Câmara, J.S.; Sierra, I. Evaluation of the Transfer and Occurrence of Opium Alkaloids in Poppy Seed Teas Using Preconcentrations with µSPEed followed by GC-MS Analysis. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM); Knutsen, H.K.; Alexander, J.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; et al. Update of the Scientific Opinion on opium alkaloids in poppy seeds. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2023/915 of 25 April 2023 on Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Food and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2023/915/oj (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Yan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. The effect of opioids on gastrointestinal function in the ICU. Crit Care 2021, 25, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntz, M.; Golombek, P.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Reduction of Morphine During Baking? Response: Commentary: Opium Alkaloids in Harvested and Thermally Processed Poppy Seeds. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 692045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakhaee, S.; Ghasemi, S.; Karimzadeh, K. The effects of opium on the cardiovascular system: A review of side effects, uses, and potential mechanisms. Subst. Abus. Treat. Prev. Policy 2020, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maino, A.; Sadeghian, S.; Mancini, I.; Abbasi, S.H.; Poorhosseini, H.; Boroumand, M.A. Opium as a risk factor for early-onset coronary artery disease: Results from the Milano-Iran (MIran) study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado-Hidalgo, G.; Martinez-Garcia, G.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. New Validated Method for the Determination of Six Opium Alkaloids in Poppy Seed-Containing Bakery Products by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry after Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Guidance Document on Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation Procedures for Pesticide Residues and Analysis in Food and Feed; SANTE/12682/2019. 2019. Available online: https://www.eurl-pesticides.eu/userfiles/file/EurlALL/AqcGuidance_SANTE_2019_12682.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- Avula, B.; Katragunta, K.; Adams, S.J.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Khan, I.A. Applicability of LC-QToF and Microscopical Tools in Combating the Sophisticated, Economically Motivated Adulteration of Poppy Seeds. Foods 2023, 12, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, P.; Pereboom-de Fauw, D.P.; Mulder, P.P.; Spanjer, M.; de Stoppelaar, J.; Mol, H.G.; de Nijs, M. Straightforward analytical method to determine opium alkaloids in poppy seeds and bakery products. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zentai, A.; Sali, J.; Szeitzné-Szabó, M.; Szabó, I.J.; Ambrus, Á. Exposure of consumers to morphine from poppy seeds in Hungary. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenreich, A.; Sachse, B.; Gürtler, R.; Dusemund, B.; Lindtner, O.; Schäfer, B. What do we know about health risks related to thebaine in food? Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproll, C.; Perz, R.C.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Optimized LC/MS/MS Analysis of Morphine and Codeine in Poppy Seed and Evaluation of Their Fate during Food Processing as a Basis for Risk Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5292–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Baquero, F.L.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Sierra, I. Evaluation of Thermal Degradation of Tropane and Opium Alkaloids in Gluten-Free Corn Breadsticks Samples Contaminated with Stramonium Seeds and Baked with Poppy Seeds under Different Conditions. Foods 2022, 11, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Recommendation 2014/662/EU of 10 September 2014 on Good Practices to Prevent and to Reduce the Presence of Opium Alkaloids in Poppy Seeds and Poppy Seed Products. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reco/2014/662/oj (accessed on 26 March 2024).
- Casado-Hidalgo, G.; Morante-Zarcero, S.; Pérez-Quintanilla, D.; Sierra, I. Influence of fermentation and storage on the content of opium alkaloids in poppy seed yoghurt. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 121, 105412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapaśnik, A.; Sokołowska, B.; Bryła, M. Role of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Food Preservation and Safety. Foods 2022, 11, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinmeier, D.; Pettengill, E.; Redan, B.W. Commentary: Opium Alkaloids in Harvested and Thermally Processed Poppy Seeds. Front. Chem. 2021, 8, 622488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Analyte | Range Calibration Curve (ng/mL) | Range of Linearity (mg/kg) | Coefficient of Linear Determination (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphine | 0.63–160 | 0.13–32 | 0.9914 |
| Codeine | 0.63–160 | 0.13–32 | 0.9802 |
| Oripavine | 0.63–160 | 0.13–32 | 0.9942 |
| Papaverynine | 0.63–160 | 0.13–32 | 0.9880 |
| Thebaine | 0.63–160 | 0.13–32 | 0.9912 |
| Noscapine | 0.63–800 | 0.13–16 | 0.9840 |
| Analyte | Fortification Level * | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 mg/kg | 2.5 mg/kg | 7.5 mg/kg | 22.5 mg/kg | |||||
| R% | RSD% | R% | RSD% | R% | RSD% | R% | RSD% | |
| Morphine | 100 | 8.2 | 108 | 4.8 | 109 | 3.3 | 110 | 12.1 |
| Codeine | 99 | 14.1 | 115 | 3.7 | 115 | 1.8 | 114 | 12.0 |
| Oripavine | 94 | 11.7 | 108 | 12.5 | 91 | 16.3 | 90 | 18.0 |
| Papaverine | 93 | 18.8 | 110 | 2.2 | 113 | 2.1 | 117 | 8.7 |
| Thebaine | 107 | 11.0 | 107 | 9.1 | 103 | 3.5 | 101 | 11.5 |
| Noscapine | 95 | 19.1 | 116 | 4.5 | 117 | 2.8 | 120 | 9.8 |
| Commercially Available Poppy Series | Poppy Seeds from Local Producers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Positive Samples | Average [mg/kg] | Median | Min–Max | % Positive Samples | Average [mg/kg] | Median | Min–Max | |
| Morphine | 6/6 | 32.26 ± 7.4 | 15.81 | 12.46–102.86 | 59/59 | 47.41 ± 21.13 | 46.7 | 1.1–110.1 |
| Codeine | 6/6 | 6.93 ± 1.19 | 2.36 | 0.25–37.05 | 59/59 | 12.16 ± 1.87 | 12.9 | 1.3–24.3 |
| Oripavine | 2/6 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.38 | 0.37–0.39 | 36/59 | 1.41 ± 0.35 | 1.2 | <LOQ *–5.7 |
| Papaverine | 4/6 | 1.22 ± 0.85 | 0.37 | <LOQ *–7142 | 0/59 | <LOQ * | <LOQ * | <LOQ * |
| Thebaine | 3/6 | 15.82 ± 0.76 | 15.78 | <LOQ *–32.67 | 59/59 | 23.57 ± 2.84 | 23.5 | 1.1–68.8 |
| Noscapine | 6/6 | 1.83 ± 0.30 | 1.88 | 0.31–4.54 | 59/59 | 17.05 ± 2.49 | 19.5 | 0.4–29.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zapaśnik, A.; Pierzgalski, A.; Bryła, M. Determination of Opium Alkaloid Content in Poppy Seeds Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with a Mass Spectrometer with a Time-of-Flight Analyzer (UPLC-TOF-HRMS). Foods 2024, 13, 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172826
Zapaśnik A, Pierzgalski A, Bryła M. Determination of Opium Alkaloid Content in Poppy Seeds Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with a Mass Spectrometer with a Time-of-Flight Analyzer (UPLC-TOF-HRMS). Foods. 2024; 13(17):2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172826
Chicago/Turabian StyleZapaśnik, Agnieszka, Adam Pierzgalski, and Marcin Bryła. 2024. "Determination of Opium Alkaloid Content in Poppy Seeds Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with a Mass Spectrometer with a Time-of-Flight Analyzer (UPLC-TOF-HRMS)" Foods 13, no. 17: 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172826
APA StyleZapaśnik, A., Pierzgalski, A., & Bryła, M. (2024). Determination of Opium Alkaloid Content in Poppy Seeds Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with a Mass Spectrometer with a Time-of-Flight Analyzer (UPLC-TOF-HRMS). Foods, 13(17), 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172826





