The Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on the Structural and Functional Properties of Tenebrio molitor Myofibrillar Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction of MP
2.3. Ultrasonic Treatment of MP
2.4. Physicochemical Properties of MP after Ultrasonic Treatment
2.4.1. Particle Size
2.4.2. Total Sulfhydryl Content
2.4.3. Carbonyl Content
2.4.4. Turbidity
2.4.5. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.4.6. Emulsifying Properties
2.5. Intrinsic Fluorescence Spectra
2.6. Fourier Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.7. Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE)
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
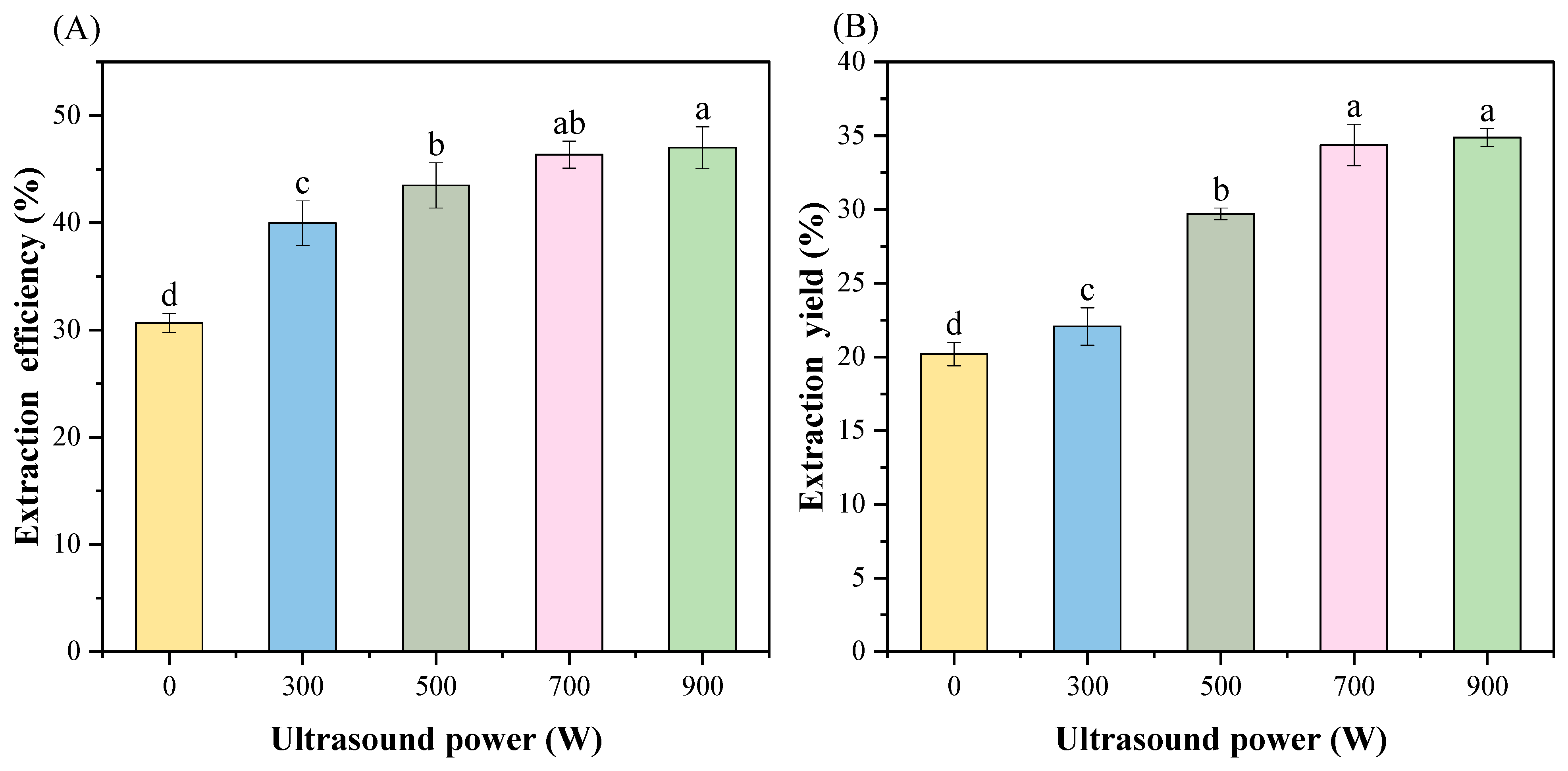
3.1. Extraction Efficiency and Yield
3.2. Particle Size
3.3. Total Sulfhydryl Group
3.4. Carbonyl Group
3.5. Turbidity
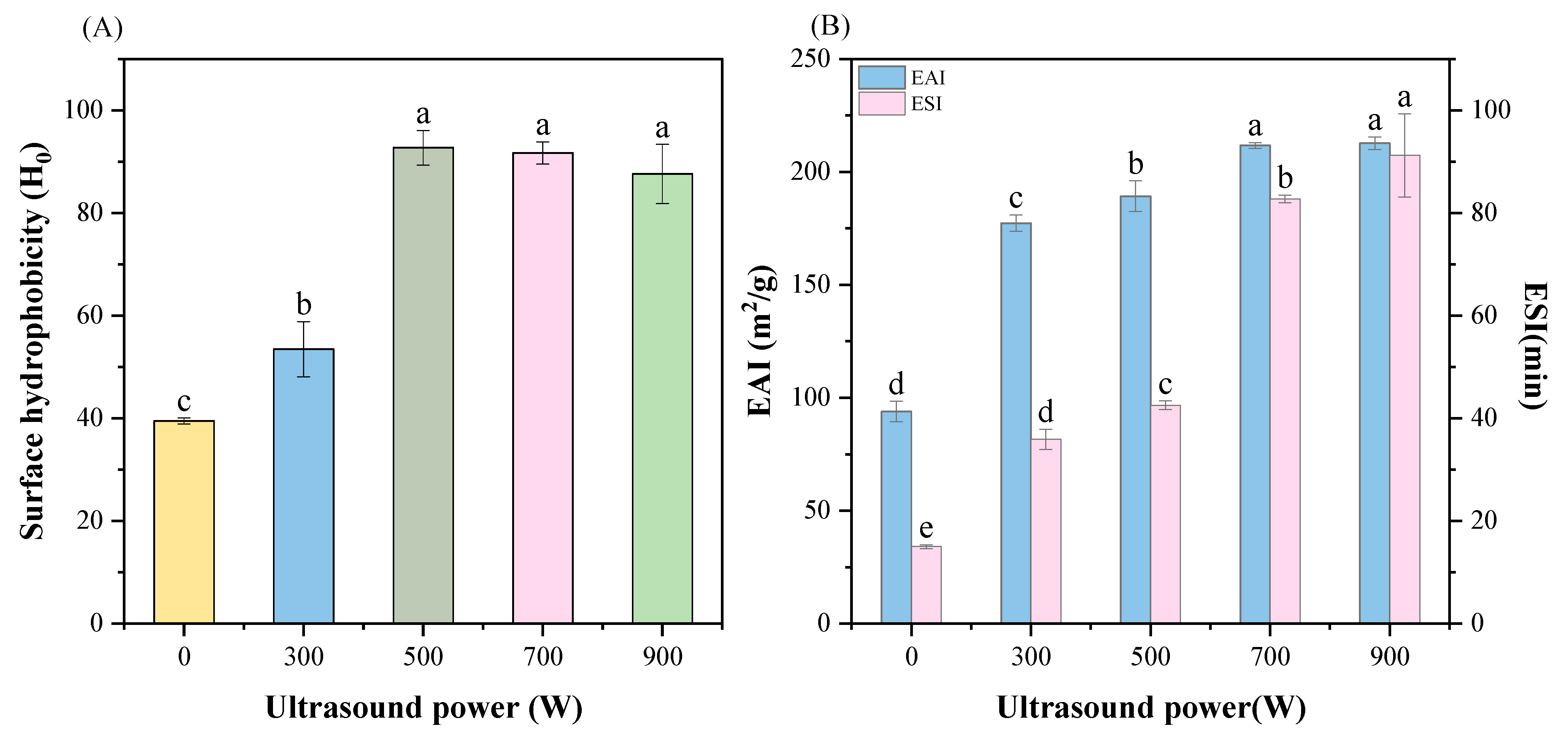
3.6. Surface Hydrophobicity
3.7. Emulsifying Properties
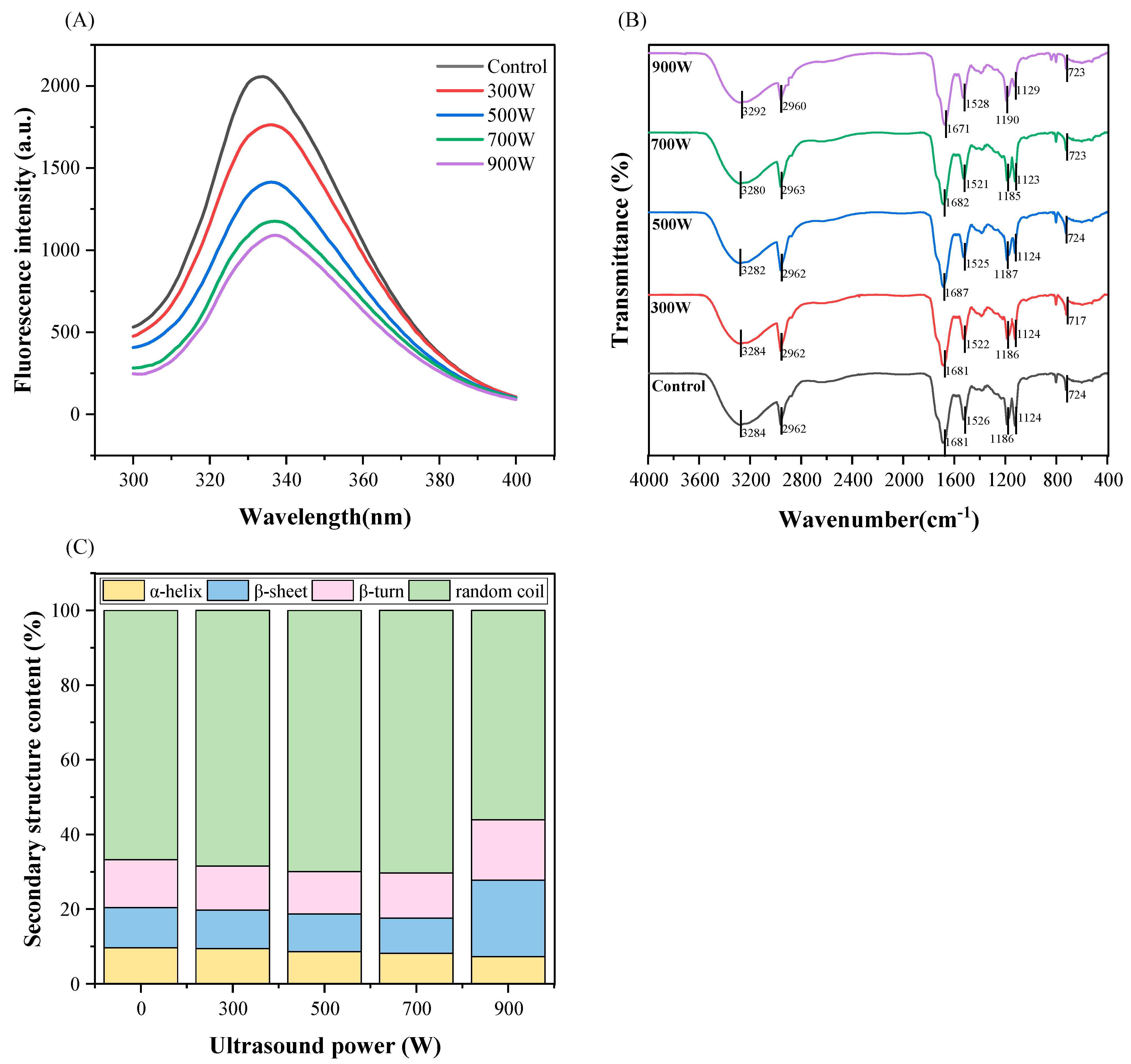
3.8. Intrinsic Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.9. FTIR
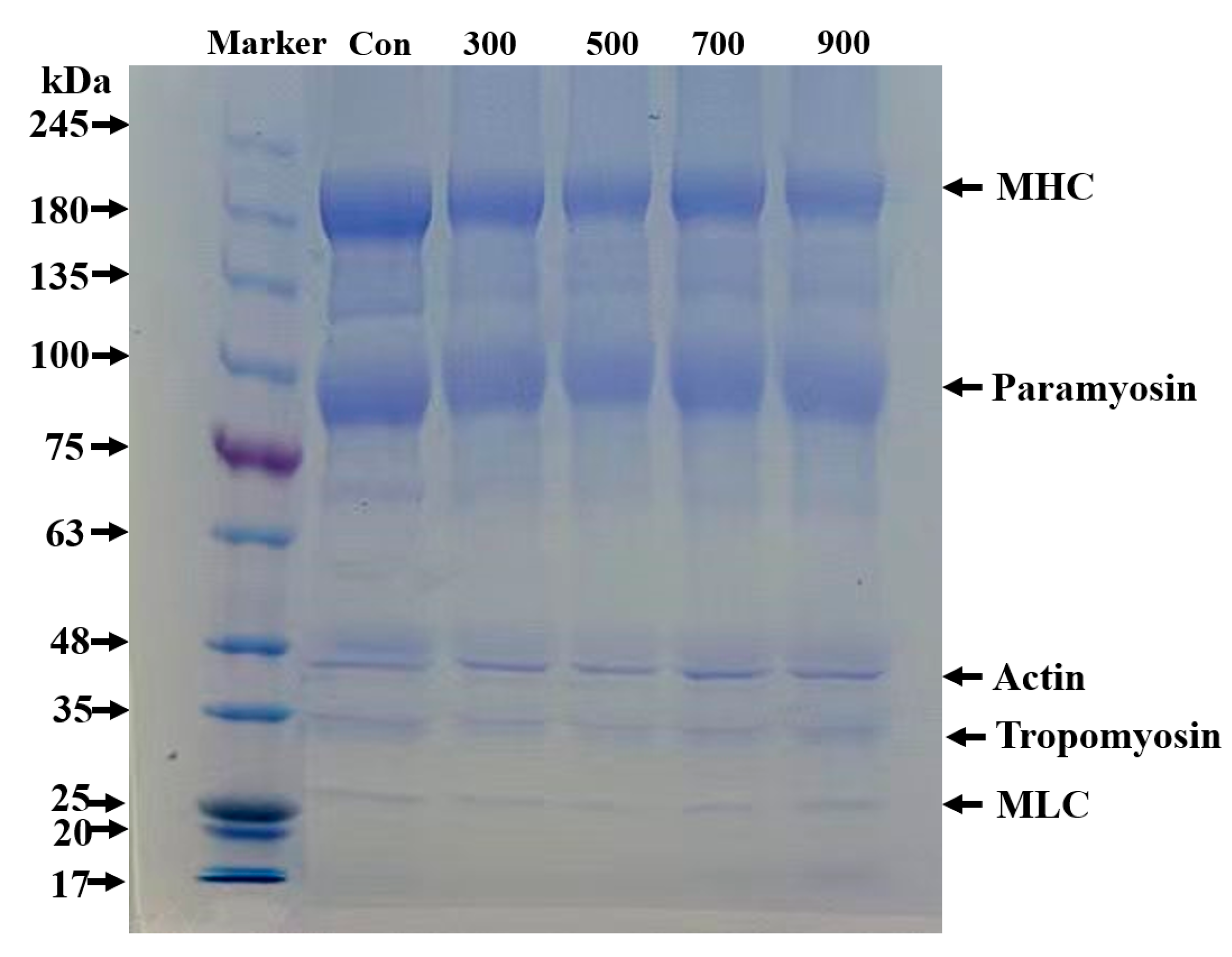
3.10. SDS–PAGE
3.11. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gould, J.; Wolf, B. Interfacial and emulsifying properties of mealworm protein at the oil/water interface. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie-Luke, E. Alternative protein sources: Science powered startups to fuel food innovation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Q.; Min, C.; Shen, L.L.; Sun, Q.C.; Yang, P.Y.; Rui, G.; Wang, S.J.; Duan, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.H.; Haile, M. Ultrasound Pretreatment Increases the Bioavailability of Dietary Proteins by Dissociating Protein Structure and Composition. Food Biophys. 2020, 15, 409–415. [Google Scholar]
- Higuera-Barraza, O.A.; Del Toro-Sanchez, C.L.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Effects of high-energy ultrasound on the functional properties of proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Guo, Z.H.; Wang, Z.R.; Yang, B.; Chen, X.H.; Wen, L.Y.; Yang, Q.Q.; Kan, J.Q. Structural and physicochemical properties of the different ultrasound frequency modified Qingke protein. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 94, 106338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.H.; Zhang, X.; Fu, M.Y.; Chen, X.; Pius, B.A.; Xu, X.L. Ultrasound-assisted covalent reaction of myofibrillar protein: The improvement of functional properties and its potential mechanism. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Sharifian, P.; Soltanizadeh, N. Application of ultrasound treatment for improving the physicochemical, functional and rheological properties of myofibrillar proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Safety of dried yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor larva) as a novel food pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. Efsa J. 2021, 19, e06778. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, L.A.; Pereira, S.M.S.; Dias, K.A.; Paes, S.d.S.; Grancieri, M.; Jimenez, L.G.S.; de Carvalho, C.W.P.; de Oliveira, E.E.; Martino, H.S.D.; Della Lucia, C.M. Nutritional content, amino acid profile, and protein properties of edible insects (Tenebrio molitor and Gryllus assimilis) powders at different stages of development. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 125, 105804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Huang, M.; Wang, K.; Shao, J.H.; Sun, J.X. Effects of Tenebrio molitor protein emulsion on the properties, and structure of myofibrillar protein gel. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 189, 115511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Zhao, X.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X. An unfolding/aggregation kinetic instructed rational design towards improving graft degree of glycation for myofibrillar protein. Food Chem. 2024, 446, 138876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambrak, A.R.; Lelas, V.; Mason, T.J.; Kresic, G.; Badanjak, M. Physical properties of ultrasound treated soy proteins. J. Food Eng. 2009, 93, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.-H.; Ni, X.-X.; Han, J.-H.; Yao, W.-H.; Fang, Y.-J.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, M.-F. High-intensity ultrasound modified the functional properties of Neosalanx taihuensis myofibrillar protein and improved its emulsion stability. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 97, 106458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.-C.; Zou, Y.-H.; Cheng, Y.-P.; Xing, L.-J.; Zhou, G.-H.; Zhang, W.-G. Effects of power ultrasound on oxidation and structure of beef proteins during curing processing. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 33, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Cao, L.W.; Xiong, S.B.; You, J.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R. Effects of pH on self-assembly of silver carp myosin at low temperature. Food Biosci. 2019, 30, 100420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolandani; Ma, H.L.; Li, Y.L.; Liu, D.D.; Zhou, H.C.; Liu, X.S.; Wan, Y.M.; Zhao, X.X. Ultrasound-assisted limited enzymatic hydrolysis of high concentrated soy protein isolate: Alterations on the functional properties and its relation with hydrophobicity and molecular weight. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 95, 106414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, N.; Tan, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, D. Effects of calcium chloride on the gelling and digestive characteristics of myofibrillar protein in Litopenaeus vannamei. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, F.; Li, Y.; Kong, B.; Liu, Q. Effect of freeze—Thaw cycles on the emulsion activity and structural characteristics of soy protein isolate. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 1607–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Ma, H.L.; Wang, K.; Azam, S.M.R.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhou, J.; Qu, W.J. Ultrasound frequency effect on soybean protein: Acoustic field simulation, extraction rate and structure. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 145, 111320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.Q.; Hong, H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Monto, A.R.; Gao, R.C.; Bao, Y.L. Oxidation affects pH buffering capacity of myofibrillar proteins via modification of histidine residue and structure of myofibrillar proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 260, 129532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.L.; Puolanne, E.; Ertbjerg, P. Effect of oxygen concentration in modified atmosphere packaging on color and texture of beef patties cooked to different temperatures. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Yuan, L.; Kong, Y.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, C.; Jin, W.; Monto, A.R.; Gao, R. Towards higher-quality low salt surimi gels: Significance of the combinatorial effects of chickpea protein with transglutaminase on their micro-structures. LWT 2024, 199, 116103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewbangkerd, K.; Hamzeh, A.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of collagen from broiler chicken trachea and its biochemical characterization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 95, 106372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.L.; Yuan, Y.W.; Xie, T.F.; Tang, G.W.; Song, G.S.; Li, L.; Yuan, T.L.; Zheng, F.P.; Gong, J.Y. Ultrasound-assisted aqueous enzymatic extraction of gardenia fruits (Gardenia jasminoides Ellis) oil: Optimization and quality evaluation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 191, 116021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Sharma, H.K.; Saini, C.S. High intensity ultrasound treatment of protein isolate extracted from dephenolized sunflower meal: Effect on physicochemical and functional properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silventoinen, P.; Sozer, N. Impact of Ultrasound Treatment and pH-Shifting on Physicochemical Properties of Protein-Enriched Barley Fraction and Barley Protein Isolate. Foods 2020, 9, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.J.; Li, W.J.; Li, G.N.; Zhang, W.Y.; Chen, H.R.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D.P. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the physicochemical properties of Tenebrio Molitor Protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Xue, D.; Nian, Y.; Zhao, D.; Shan, K.; Dai, C.; Li, C. Ultrasound treatment can increase digestibility of myofibrillar protein of pork with modified atmosphere packaging. Food Chem. 2022, 377, 131811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, K.-X.; Du, J.-Y.; Tan, Z.-F.; Xu, Y.-P.; Liu, X.-Y.; Zhou, D.-Y.; Li, D.-Y. High-intensity ultrasound improved the physicochemical and gelling properties of Litopenaeus vannamei myofibrillar protein. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 90, 106217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, X.; Tang, D.; Yang, H.; Zhu, M. Oxidation and nitrosation in Cantonese sausage during processing and storage-The impact of adding Prunus mume polyphenol. Food Control 2024, 167, 110789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, Q.; Shi, W. Ultrasound-assisted processing: Changes in gel properties, water-holding capacity, and protein aggregation of low-salt Hypophthalmichthys molitrix surimi by soy protein isolate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 92, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Li, N.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, D. Improving the gelation and digestive properties of myofibrillar protein in Litopenaeus vannamei by ultra-high pressure. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xing, L.; Kang, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Effects of ultrasound-assisted vacuum tumbling on the oxidation and physicochemical properties of pork myofibrillar proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 74, 105582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanjun, X.; Qingqing, Y.; Yaqi, Z.; Yu, F.; Qiaoyu, C.; Ruichang, G.; Yulong, B. Insight into the mechanism of the decrease in mechanical strength and water-holding capacity of gels made from oxidized gelatin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 258, 128842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.S.; Zhou, L.K.; Zhao, L.W.; Wang, D.L.; Yuan, T.L.; Li, L.; Gong, J.Y. Analysis of non-covalent interaction between β-lactoglobulin and hyaluronic acid under ultrasound-assisted treatment: Conformational structures and interfacial properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Xue, S.; Xu, X. Effects of ultrasound frequency mode on myofibrillar protein structure and emulsifying properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Bao, A.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Song, G.; Yuan, T.; Gong, J. Whey protein isolate-stabilized gardenia fruit oil nanoemulsions: Ultrasonic preparation, characterization and applications in nutraceuticals delivery. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 212, 118345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.Z.; Xu, J.W.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Effects of flexibility and surface hydrophobicity on emulsifying properties: Ultrasound-treated soybean protein isolate. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 142, 110881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, S.; Javanmardi, F.; Mohammadi, M.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A. Effects of ultrasound on the techno-functional properties of milk proteins: A systematic review. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 83, 105938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.N.; Li, L. Effects of ultrasound pretreatment on functional property, antioxidant activity, and digestibility of soy protein isolate nanofibrils. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 90, 106193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, C.-M.; Bian, X.; Ren, L.-K.; Liu, B.-X.; Ai, L.-Z.; Zhang, N. The improvement of the oxidative oat (Avena sativa L.) protein based on ultrasound treatment: Study of structural, emulsifying, and rheological properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 144, 109047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Hayat, K.; Kurtz, N.C.; Wu, X.; Ahmad, M.; Zheng, F. Ultrasound-assisted alkaline proteinase extraction enhances the yield of pecan protein and modifies its functional properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 80, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Boateng, I.D.; Zhang, W.; Jia, S.; Wang, T.; Huang, L. Effect of ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid pretreatment on the structure and interfacial properties of soy protein isolate. Process Biochem. 2022, 115, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; Zhu, W.; Wu, J. Effect of ultrasonic vacuum drying on the structural characteristics of whole-egg protein powder. LWT 2024, 191, 115490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wan, J.; Shah, B.R.; Pei, Y.; Zhou, B.; Li, J.; Li, B. High intensity ultrasound modified ovalbumin: Structure, interface and gelation properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 31, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Chen, C.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Duan, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, M. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on the structure and functional characteristics of myofibrillar proteins from black soldier fly. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 135057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Tu, Y.G.; Zhang, G.W.; Xin, X.J.; Hu, H.; Qiu, W.; Ruan, D.D.; Zhao, Y. Mechanism of ultrasound and tea polyphenol assisted ultrasound modification of egg white protein gel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 81, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakash, G.; Chawla, P.; Sridhar, K.; Bains, A. Interactions of legume phenols-rice protein concentrate towards improving vegan food quality: Development of a protein-phenols enriched fruit smoothie. Food Res. Int. 2023, 171, 113075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Zhao, H.B.; Tao, H.T.; Yu, B.; Cui, B.; Wang, Y. Ultrasound improves the physicochemical and foam properties of whey protein microgel. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1140737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.Y.; Tian, G.F.; Wang, X.H.; Deng, W.Y.; Mao, K.M.; Sang, Y.X. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on the structure and functional properties of mantle proteins from scallops (Patinopecten yessoensis). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 79, 105770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monto, A.R.; Yuan, L.; Xiong, Z.; Shi, T.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Jin, W.; Li, J.; Gao, R. Effect of α-tocopherol, soybean oil, and glyceryl monostearate oleogel on gel properties and the in-vitro digestion of low-salt silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) surimi. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-X.; Li, Y.-Q.; Sun, G.-J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liang, Y.; Hua, D.-L.; Chen, L.; Mo, H.-Z. The improvement and mechanism of gelation properties of mung bean protein treated by ultrasound. LWT 2023, 182, 114811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbour, M.; Alenyorege, E.A.; Mintah, B.; He, R.; Jiang, H.; Ma, H. Proteolysis kinetics and structural characterization of ultrasonic pretreated sunflower protein. Process Biochem. 2020, 94, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Shi, T.; Jin, W.; Li, J.; Yuan, L.; Gao, R. Investigation of the enhancement mechanism of ethanol addition on the gel performance of heat-induced surimi. J. Food Eng. 2023, 355, 111581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, K.; Yang, F.; Shu, W.; Ma, J.; Huang, Y.; Cao, X.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, Y. Modification of myofibrillar protein structural characteristics: Effect of ultrasound-assisted first-stage thermal treatment on unwashed Silver Carp surimi gel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 107, 106911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.S.; Yang, F.; Zhao, K.Y.; Zhang, W.W.; Liu, Q.Q.; Yuan, Y.J. Regulation of Protein Flexibility and Promoting the Cod Protein Gel Formation Using Ultrasound Treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 18601–18612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, R.; Saini, C.S. High-Intensity Ultrasound (HIUS) Treatment of Sunnhemp Protein Isolate (Crotalaria juncea L.): Modification of Functional, Structural, and Microstructural Properties. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 1464–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Ni, X.; Duan, C.; Li, R.; Jiang, X.; Xu, M.; Yu, R. The Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on the Structural and Functional Properties of Tenebrio molitor Myofibrillar Protein. Foods 2024, 13, 2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172817
Wang X, Ni X, Duan C, Li R, Jiang X, Xu M, Yu R. The Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on the Structural and Functional Properties of Tenebrio molitor Myofibrillar Protein. Foods. 2024; 13(17):2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172817
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiu, Xiangxiang Ni, Chaoyi Duan, Ruixi Li, Xiao’e Jiang, Mingfeng Xu, and Rongrong Yu. 2024. "The Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on the Structural and Functional Properties of Tenebrio molitor Myofibrillar Protein" Foods 13, no. 17: 2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172817
APA StyleWang, X., Ni, X., Duan, C., Li, R., Jiang, X., Xu, M., & Yu, R. (2024). The Effect of Ultrasound Treatment on the Structural and Functional Properties of Tenebrio molitor Myofibrillar Protein. Foods, 13(17), 2817. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172817






