Widely Targeted Lipidomics and Microbiomics Perspectives Reveal the Mechanism of Auricularia auricula Polysaccharide’s Effect of Regulating Glucolipid Metabolism in High-Fat-Diet Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Instruments and Equipment
2.3. Animal Experiment
2.4. Organ Index and Body Weight
2.5. Biochemical Parameter Detection
2.6. Histological Examination
2.7. Analysis of SCFAs
2.8. Amplicon Sequencing
2.9. Wide-Target Lipidomics Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
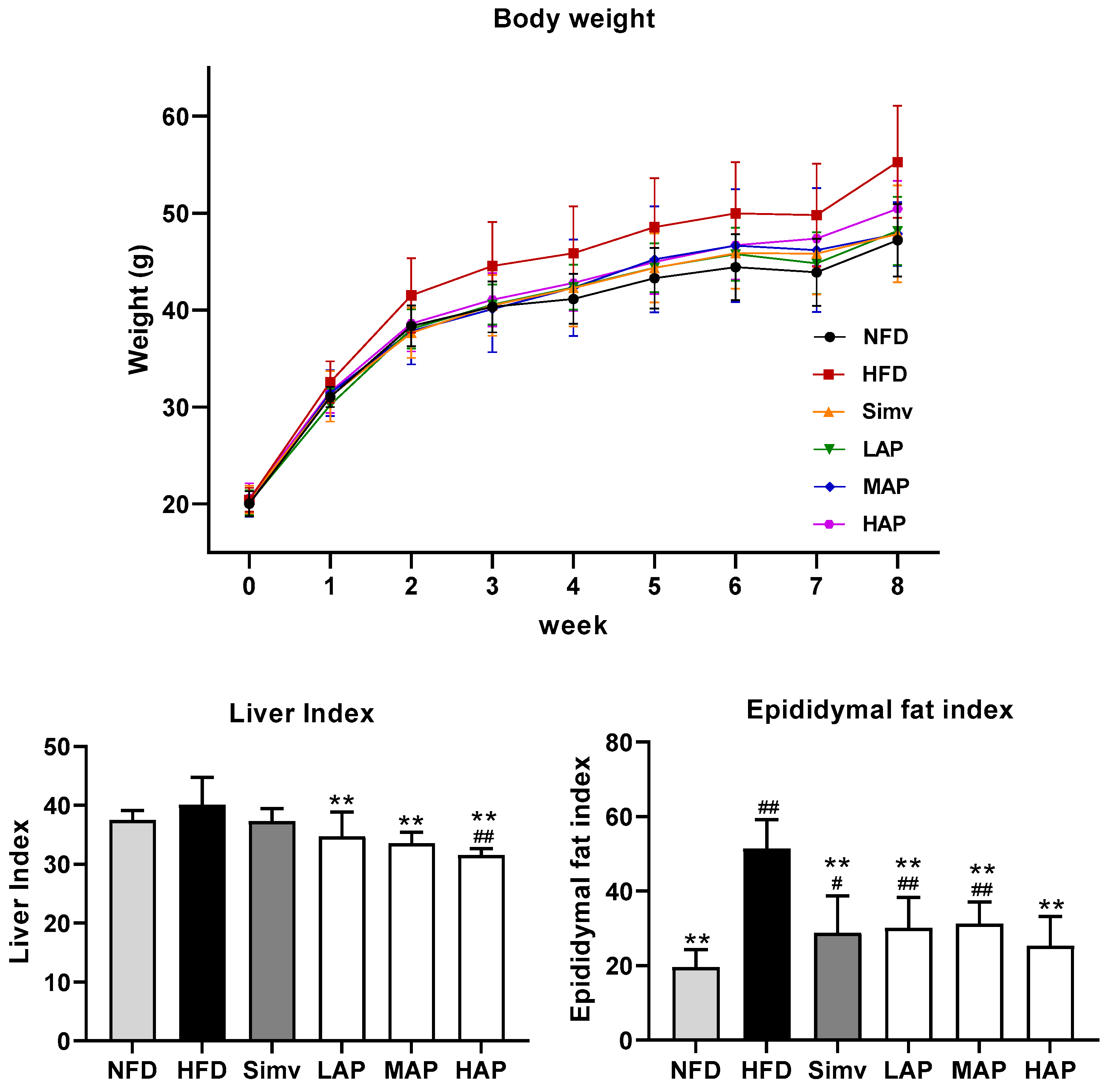
3.1. Body Weight and Organ Index
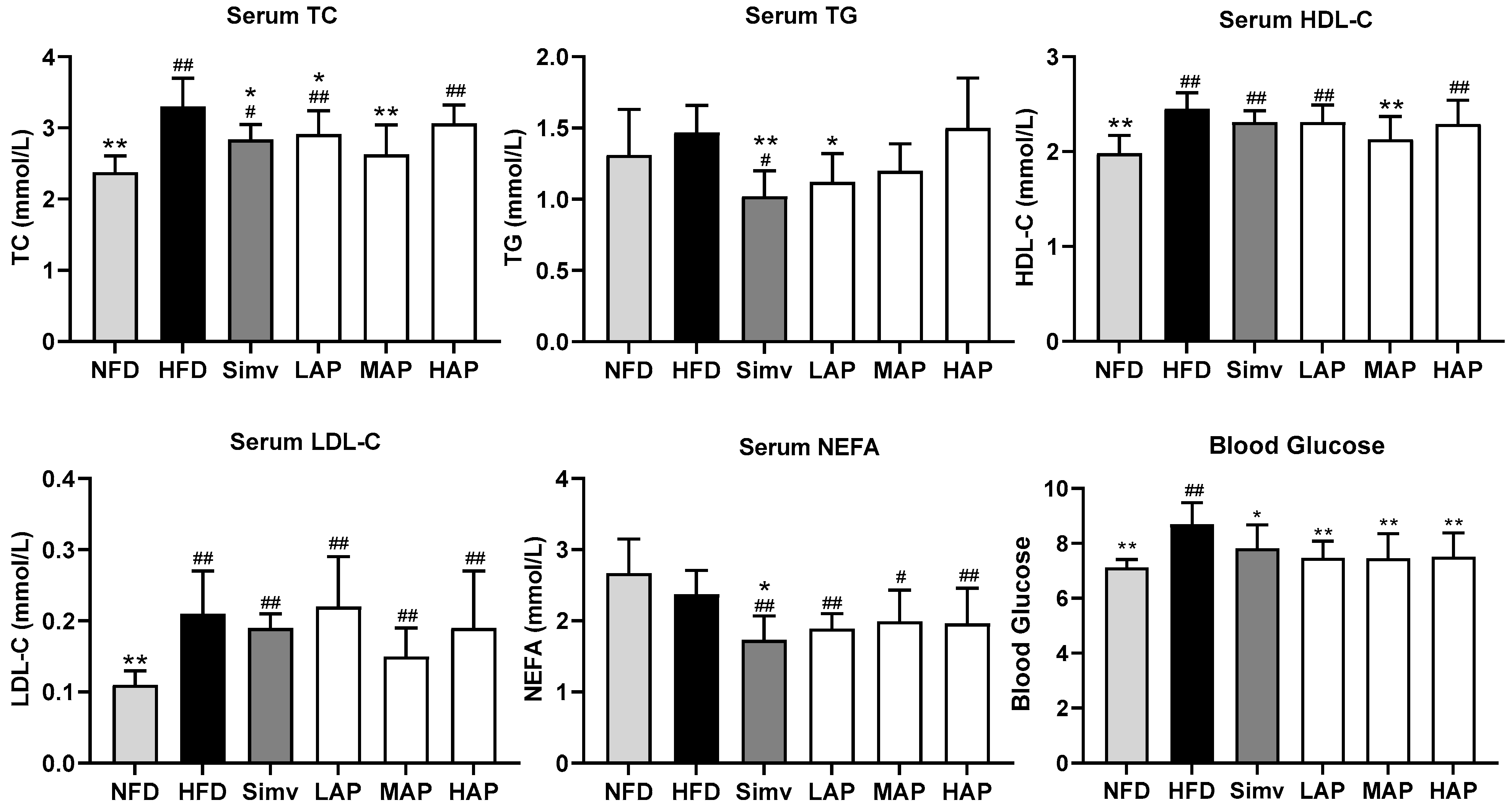
3.2. Serum Biochemical Parameters
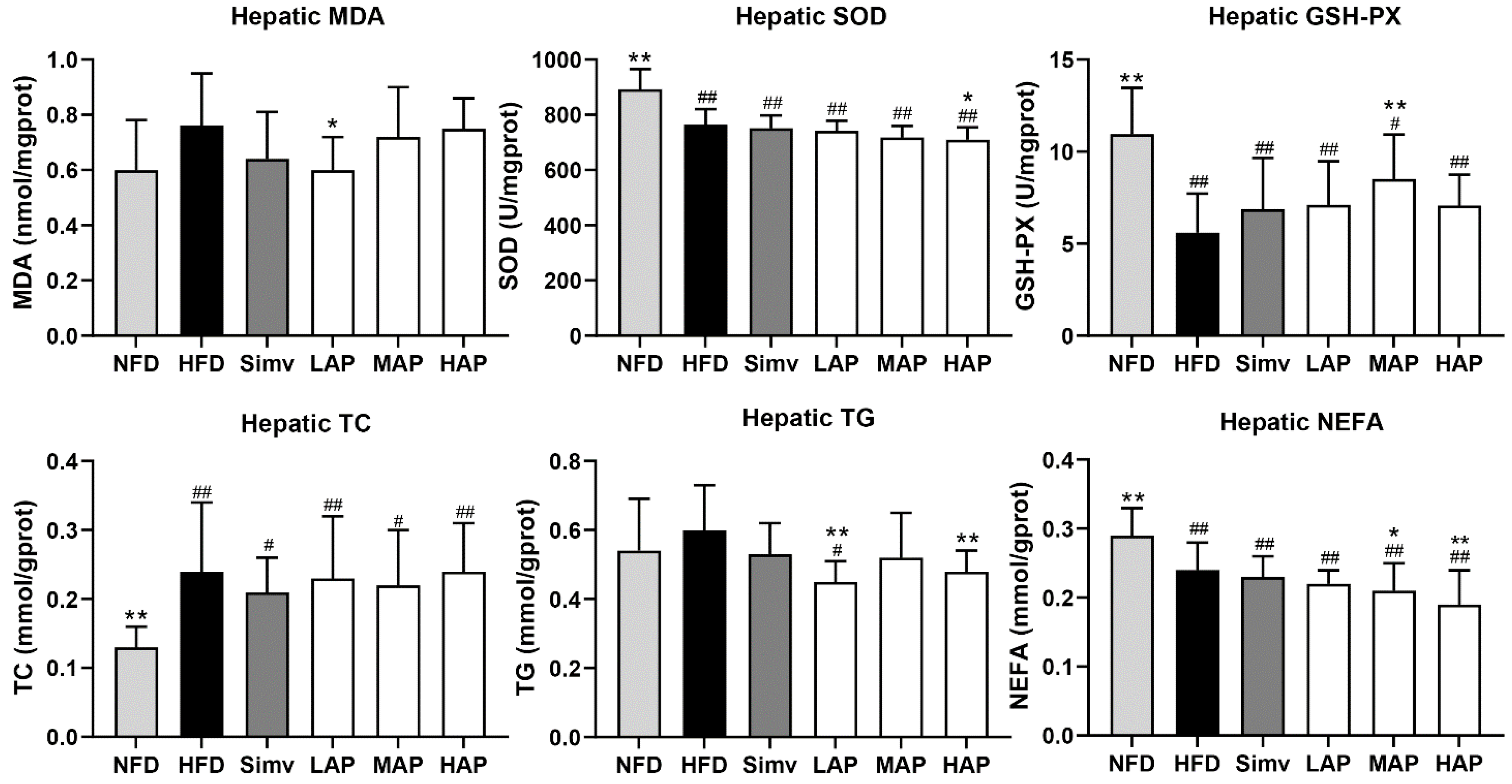
3.3. Liver Biochemical Parameters
3.4. Fecal Biochemical Parameters
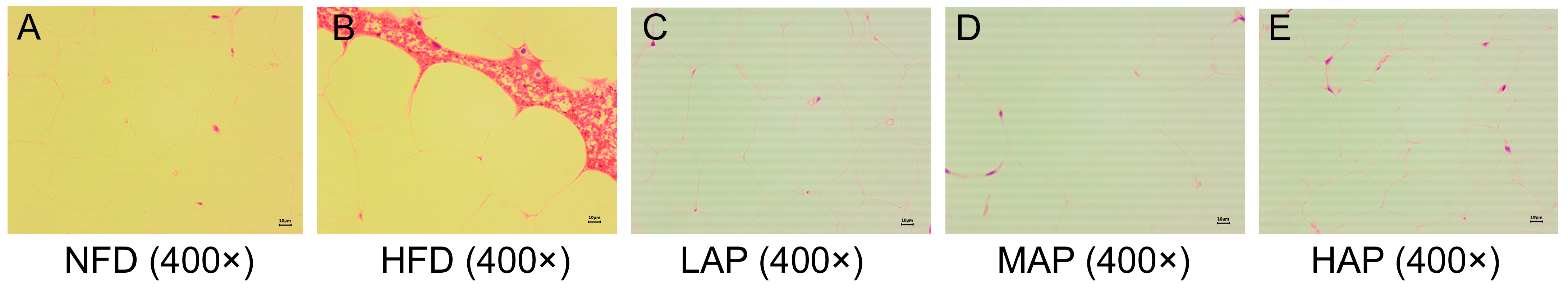
3.5. The Morphology of Liver and Epididymal Adipocytes
3.6. The Composition of Intestinal Microbiota
3.7. Serum Widely Targeted Lipidomics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, K.S.; Kathiravan, M.K.; Somani, R.S.; Shishoo, C.J. The biology and chemistry of hyperlipidemia. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 4674–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Vaart, J.I.; van Eenige, R.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Kooijman, S. Atherosclerosis: An overview of mouse models and a detailed methodology to quantify lesions in the aortic root. Vas. Biol. 2024, 6, e230017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.Y.; Li, Z.; Tian, X.J.; Ren, Y.C. The top 5 causes of death in China from 2000 to 2017. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, S.; Spaccarotella, C.A.M.; Esposito, G.; Indolfi, C. Bempedoic acid: A new player for statin-intolerant patients and beyond. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. 2024, 31, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, J.; He, G. Research progress on hypolipidemic nutraceuticals and functional foods. Food Sci. 2011, 32, 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.C.; Kong, X.H.; Zhang, P.Q.; Liu, J.N.; Ma, Y.P.; Dai, X.D.; Han, Z.H.; Ma, Q.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Yu, L.P. Identification of a new fungal pathogen causing white villous disease on the fruiting body of the culinary-medicinal mushroom Auricularia auricula-judae (Agaricomycetes) in China. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2017, 19, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, T.; Ganesan, K.; Xu, B. Insights into health-promoting effects of Jew’s ear (Auricularia auricula-judae). Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 114, 552–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Luo, Y.C.; Ji, B.P.; Li, B.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, W.; Xiao, Z.L. Effect of polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula on blood lipid metabolism and lipoprotein lipase activity of ICR mice fed a cholesterol-enriched diet. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, H103–H108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhao, X.; Yin, H.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z. Hypolipemic effect of acidic polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula on hyperlipidemia mice. Food Sci. 2016, 37, 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Zhao, W.; Xie, B.; Liu, H. Effects of Auricularia auricula and its polysaccharide on diet-induced hyperlipidemia rats by modulating gut microbiota. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 72, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.F.; Yue, Z.L.; Wang, Y.N.; Li, Y.D.; Li, C.; Liu, X.T.; Shi, R.H.; Huo, N.N.; Li, D.D.; Gao, S.; et al. Synergistic effect of polysaccharides and flavonoids on lipid and gut microbiota in hyperlipidemic rats. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Tang, B.; Lai, P.; Li, Y.; Weng, M.; Chen, J. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted and pectinase-added extraction for uronic acid from Auricularia auricula (L.ex Hook)Underw. Fujian J. Agri. Sci. 2019, 34, 719–729. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Z.J.; Yao, L.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lin, S.Y. Isolation, purification, characterization, and immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula on RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Wang, M.Q.; Ma, W.T.; Li, N.; Huang, J.W.; Jiang, X.J.; Wu, W.H.; Zhang, C.Y. In vitro antioxidant activity of the polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula and its structural characterisation. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Wu, Q.; Liang, B.; Wang, J.M.; Wu, D.; Shang, X.Z. The current state and future prospects of Auricularia auricula’s polysaccharide processing technology portfolio. Molecules 2023, 28, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Weng, M.; Zheng, H.; Lai, P.; Tang, B.; Chen, J.; Li, Y. Hypoglycemic effect of okra aqueous extract on streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 40, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chou, W.C.; Lai, Y.J.; Liang, K.X.; Tam, J.W.; Brickey, W.J.; Chen, L.; Montgomery, N.D.; Li, X.; Bohannon, L.M.; et al. Multi-omics analyses of radiation survivors identify radioprotective microbes and metabolites. Science 2020, 370, eaay9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muguruma, Y.; Tsutsui, H.; Noda, T.; Akatsu, H.; Inoue, K. Widely targeted metabolomics of Alzheimer’s disease postmortem cerebrospinal fluid based on 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate derivatized ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1091, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Qi, X.; Liu, X.; Guo, X. Metabolomic detection between pancreatic cancer and liver metastasis nude mouse models constructed by using the PANC1-KAI1/CD82 cell line. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masenga, S.K.; Kabwe, L.S.; Chakulya, M.; Kirabo, A. Mechanisms of oxidative stress in metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.P.; Wu, S.L.; Wu, M.W.; Yang, C.L.; Jiang, Y.J.; Chen, B.Z. Regulatory effect of ethanol extracts from Auricularia heimuer on liver and intestinal flora in high fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 22, 161–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Intervention Mechanism of Auricularia auricula Polysaccharides on High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity; Northwestern Polytechnical University: Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.M.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, K. Cheong-sang-gyeon-tong-tang improves hepatic steatosis by regulating cholesterol metabolism. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Ijaz, M.; Shu, Y.S.; Wang, P.; Ma, L.; Wang, P.; Ding, H.L.; Shahbaz, M.; Shi, H.Y. The in vivo study on antioxidant activity of wendan decoction in treating hyperlipidemia: A pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) model. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1260603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.N.; Chen, M.Y.; Song, J.N.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Gong, P.; Chen, X.F. Effects of Auricularia auricula polysaccharides on gut microbiota composition in type 2 diabetic mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Jia, Y.Z.; Xu, N.; Tang, L.H.; Chang, Y.N. Auricularia auricula-judae (Bull.) polysaccharides improve obesity in mice by regulating gut microbiota and TLR4/JNK signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.C.K. The hypocholesterolemic effect of two edible mushrooms: Auricularia auricula (tree-ear) and Tremella fuciformis (white jelly-leaf) in hypercholesterolemic rats. Nutr. Res. 1996, 16, 1721–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.Y.; Zhu, C.L.; Li, H.; Yin, M.M.; Pan, C.; Huang, L.S.; Kong, C.; Wang, X.C.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, S.; et al. Dysbiosis signatures of gut microbiota along the sequence from healthy, young patients to those with overweight and obesity. Obesity 2018, 26, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daddi, L.; Dorsett, Y.; Geng, T.T.; Bokoliya, S.; Yuan, H.S.; Wang, P.H.; Xu, W.L.; Zhou, Y.J. Baseline gut microbiome signatures correlate with immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kwon, Y.M.; Kim, I.S.; Kim, J.A.; Yu, D.Y.; Adhikari, B.; Lee, S.S.; Choit, I.S.; Cho, K.K. Effects of the brown seaweed Laminaria japonica supplementation on serum concentrations of IgG, triglycerides, and cholesterol, and intestinal microbiota composition in rats. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Liang, N.N.; Zhang, X.X.; Han, C.X.; Nan, X.I. Functional differentiation related to decomposing complex carbohydrates of intestinal microbes between two wild zokor species based on 16SrRNA sequences. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Qian, Y.; Li, G.; Fu, F.; Shan, Y. Effect of orlistat on gut microbiota of rats fed with high-fat diet. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 48, 585–593. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liu, J.J.; Yan, C.C.; Zhang, C.; Pan, W.J.; Zhang, W.N.; Lu, Y.M.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y. Sarcodon aspratus polysaccharides ameliorated obesity-induced metabolic disorders and modulated gut microbiota dysbiosis in mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2588–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Jiang, W.B.; Tian, Z.; Wu, H.Y.; Ning, H.; Yan, G.C.; Zhang, Z.W.; Li, Z.X.; Dong, F.; Sun, Y.Z.; et al. Fecal g. Streptococcus and g. Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes_group combined with sphingosine to modulate the serum dyslipidemia in high-fat diet mice. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4234–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.H.; Strazar, M.; Mohamed, A.M.T.; Pacheco, J.A.; Walker, R.L.; Lebar, T.; Zhao, S.J.; Lockart, J.; Dame, A.; Thurimella, K.; et al. Gut microbiome and metabolome profiling in Framingham heart study reveals cholesterol-metabolizing bacteria. Cell 2024, 187, 1834–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, W.N.; Tian, F.; Shen, H.Y.; Zhou, M.M. A combination of quercetin and resveratrol reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed rats by modulation of gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 4644–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; You, J.M.; Wang, Z.R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, B.; Du, M.; Zou, T.D. Curcumin alleviates high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis and obesity in association with modulation of gut microbiota in mice. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourosh, A.; Luna, R.A.; Balderas, M.; Nance, C.; Anagnostou, A.; Devaraj, S.; Davis, C.M. Fecal microbiome signatures are different in food-allergic children compared to siblings and healthy children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 29, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farsi, D.N.; Gallegos, J.L.; Koutsidis, G.; Nelson, A.; Finnigan, T.J.A.; Cheung, W.; Muñoz-Muñoz, J.L.; Commane, D.M. Substituting meat for mycoprotein reduces genotoxicity and increases the abundance of beneficial microbes in the gut: Mycomeat, a randomised crossover control trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, W.H.; Zhang, B.W.; Yin, J.; Liuqi, S.; Wang, J.; Peng, B.; Wang, S. Fucoidan ameliorated dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis by modulating gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 14864–14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.L.; Cao, Y.J.; You, S.Z.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Han, J.Z.; Lv, X.C.; Rao, P.F.; Ai, L.Z.; Ni, L. Ganoderic acids-rich ethanol extract from Ganoderma lucidum protects against alcoholic liver injury and modulates intestinal microbiota in mice with excessive alcohol intake. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuge, A.X.; Li, S.J.; Yuan, Y.; Li, B.; Li, L.J. The synergy of dietary supplements Lactobacillus salivarius LI01 and Bifidobacterium longum TC01 in alleviating liver failure in rats treated with d-galactosamine. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 10239–10252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, H.B.; Melo, T.; Guerra, I.M.S.; Moreira, A.S.P.; Laranjeira, P.; Paiva, A.; Goracci, L.; Bonciarelli, S.; Domingues, P.; Domingues, M.R. Whole blood and plasma-based lipid profiling reveals distinctive metabolic changes in systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic sclerosis. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 2995–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowda, S.G.B.; Gao, Z.-J.; Chen, Z.; Abe, T.; Hori, S.; Fukiya, S.; Ishizuka, S.; Yokota, A.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S.-P. Untargeted lipidomic analysis of plasma from high-fat diet-induced obese rats using UHPLC–linear trap Quadrupole–Orbitrap MS. Anal. Sci. 2020, 36, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amunugama, K.; Ford, D.A. Lipidomic profiling of host-pathogen interactions using untargeted and targeted lipidomics approaches in a sepsis cell culture model. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojo, L.; Santos-González, E.; Riera, L.; Aguilera, A.; Barahona, R.; Pellicer, P.; Buxó, M.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Fernandez-Balsells, M.; Fernández-Real, J.-M. Plasma lipidomics profiles highlight the associations of the dual antioxidant/pro-oxidant molecules sphingomyelin and phosphatidylcholine with subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with type 1 diabetes. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Legido-Quigley, C.; Mason, A.J. Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers Discovery Using Metabolomics Approach; King’s College: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdani, A.; Yazdani, A.; Liu, X.; Boerwinkle, E. Identification of rare variants in metabolites of the carnitine pathway by whole genome sequencing analysis. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhao, H.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Jiang, L. Integrated multi-omics analysis reveals the positive leverage of citrus flavonoids on hindgut microbiota and host homeostasis by modulating sphingolipid metabolism in mid-lactation dairy cows consuming a high-starch diet. Microbiome 2023, 11, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anesi, A.; Di Minno, A.; Calcaterra, I.; Cavalca, V.; Tripaldella, M.; Porro, B.; Di Minno, M.N.D. An untargeted lipidomic analysis reveals depletion of several phospholipid classes in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia on treatment with evolocumab. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurila, P.-P.; Wohlwend, M.; Imamura de Lima, T.; Luan, P.; Herzig, S.; Zanou, N.; Crisol, B.; Bou-Sleiman, M.; Porcu, E.; Gallart-Ayala, H. Sphingolipids accumulate in aged muscle, and their reduction counteracts sarcopenia. Nat. Aging 2022, 2, 1159–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.X.; Li, C.R.; Kan, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Rao, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, P. Hypolipidemic and antithrombotic effect of 6′-o-caffeoylarbutin from Vaccinium dunalianum based on zebrafish model, network pharmacology, and molecular docking. Molecules 2024, 29, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Tang, B.; Weng, M.; Shen, H.; Chen, J.; Lai, P. Widely Targeted Lipidomics and Microbiomics Perspectives Reveal the Mechanism of Auricularia auricula Polysaccharide’s Effect of Regulating Glucolipid Metabolism in High-Fat-Diet Mice. Foods 2024, 13, 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172743
Wu L, Li Y, Chen S, Yang Y, Tang B, Weng M, Shen H, Chen J, Lai P. Widely Targeted Lipidomics and Microbiomics Perspectives Reveal the Mechanism of Auricularia auricula Polysaccharide’s Effect of Regulating Glucolipid Metabolism in High-Fat-Diet Mice. Foods. 2024; 13(17):2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172743
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Li, Yibin Li, Shouhui Chen, Yanrong Yang, Baosha Tang, Minjie Weng, Hengsheng Shen, Junchen Chen, and Pufu Lai. 2024. "Widely Targeted Lipidomics and Microbiomics Perspectives Reveal the Mechanism of Auricularia auricula Polysaccharide’s Effect of Regulating Glucolipid Metabolism in High-Fat-Diet Mice" Foods 13, no. 17: 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172743
APA StyleWu, L., Li, Y., Chen, S., Yang, Y., Tang, B., Weng, M., Shen, H., Chen, J., & Lai, P. (2024). Widely Targeted Lipidomics and Microbiomics Perspectives Reveal the Mechanism of Auricularia auricula Polysaccharide’s Effect of Regulating Glucolipid Metabolism in High-Fat-Diet Mice. Foods, 13(17), 2743. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172743





