A Review of Recent Developments in Edible Films and Coatings-Focus on Whey-Based Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
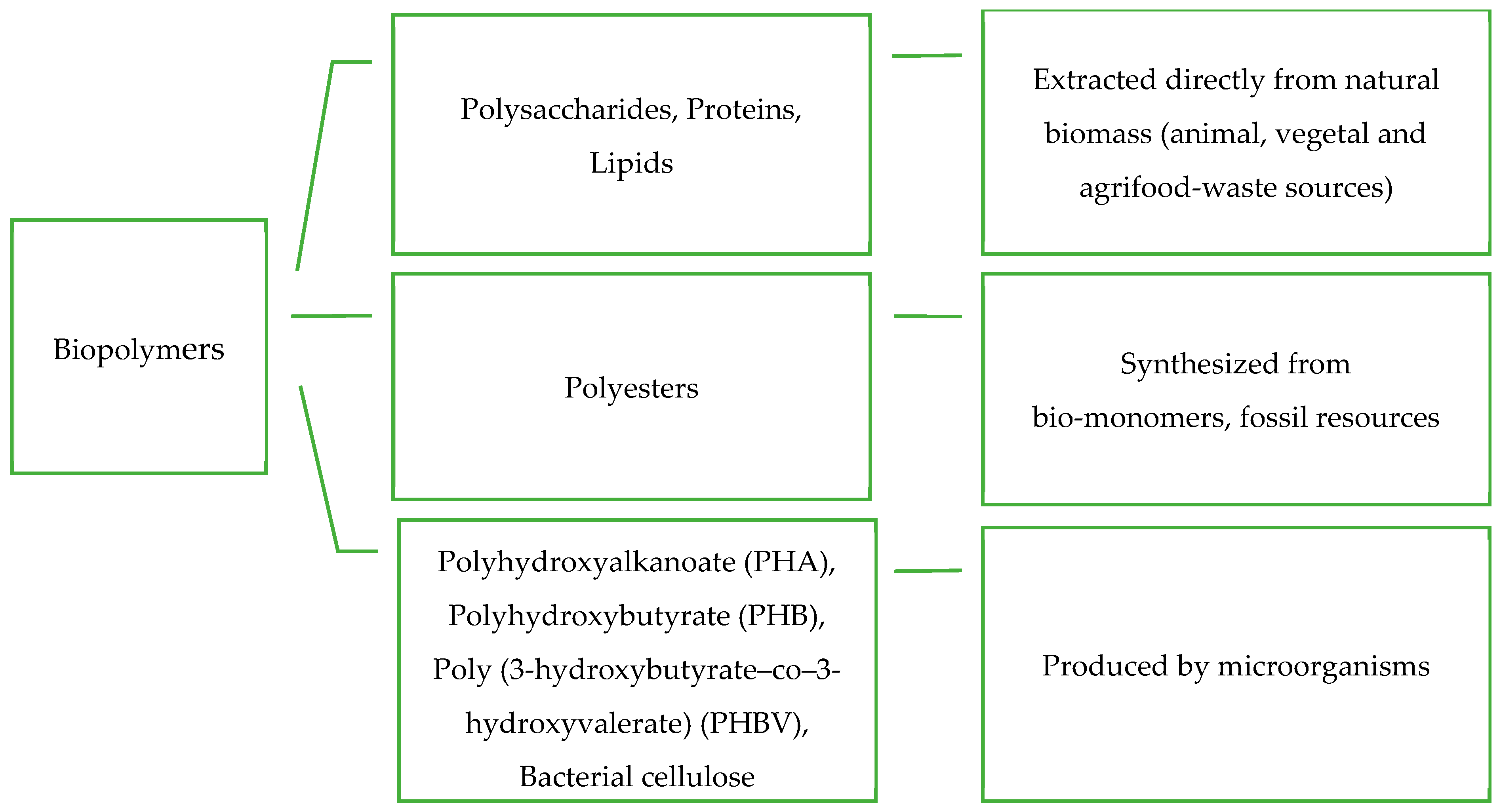
2. Biopolymer Based Edible Films and Coatings
2.1. Base Materials Used to Produce Biopolymers
2.1.1. Polysaccharide Based Films and Coatings
2.1.2. Lipid-Based Films and Coatings
2.1.3. Protein-Based Films and Coatings
2.1.4. Composite and Nanocomposite Films and Coatings
2.2. Plasticizers Used in Edible Films and Coatings
3. Edible Protein-Based Films and Coatings’ Properties
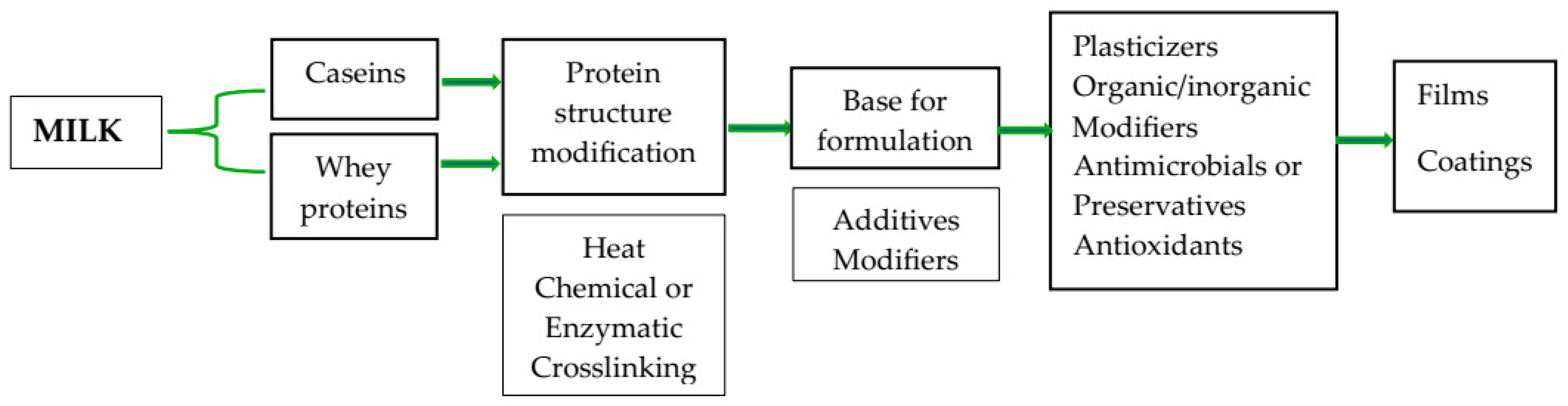
4. Whey Protein-Based Films and Coatings
4.1. Methods to Obtain Whey Protein Films and Coatings
4.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Whey Films and Coatings
4.3. Improvement of Protein Film’s Properties
5. Additives for Whey Based Functional Films and Coatings
5.1. Prebiotics and/or Probiotics Incorporated in Edible Films and Coatings
5.2. Antioxidants, Antibacterial and Antifungal Compounds
| Additives | Coatings/Films | Plasticizer | Main Properties | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PREBIOTICS AND PROBIOTICS | ||||
| Lactobacillus paracasei CIDCA 8339 and Kluyveromyces marxianus CIDCA 8154 | Whey proteins and kefiran | Glycerol | Probiotic activity | [92] |
| Lactobacillus curvatus 54M16 | Whey protein/inulin/gelatin | Glycerol | Antimicrobial activity | [93] |
| Bifidobacterium animalis Bb-12® and Lactobacillus casei-01 | WPI | Glycerol | Antimicrobial activity, probiotic activity | [42] |
| Inulin, fructooligosaccharides, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 | WPI and alginate | Glycerol | Probiotic activity | [94] |
| Lactobacillus casei | WPI | Glycerol | Anti-ripening process | [95] |
| Lactic acid bacteria (LAB), Lactobacillus buchneri | Protein-based films and coatings | Glycerol | Antifungal properties | [96] |
| ESSENTIAL OILS | ||||
| Almond and walnut oil | WPI | Glycerol | Emulsified films showed a more hydrophobic nature, decrease the water vapor permeability and increase the contact angle values. | [24] |
| Oregano, garlic oils nisin, and natamycin | WPI | Glycerol and Candelilla wax | Antimicrobial activity | [97] |
| Laurus nobilis L. and Salvia officinalis | WPI | Glycerol | antioxidant properties | [79] |
| Oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) | WPC and Lepidium perfoliatum L. gum (LPG) | Glycerol | Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties | [28] |
| Oregano (Origanum compactum) and Salvia (Salvia sclarea) | Sheep’s second cheese whey (SCW) | Glycerol | Protective coating cheese | [83] |
| Thyme (Thymus vulgaris) | Tamarind starch and WPC | Glycerol | Antimicrobial Agents. | [98] |
| Lemon and bergamot | WPI | Glycerol | Antimicrobial activity. | [81] |
| Tarragon (Artemisia dracunculus) | WPI | Glycerol | Antimicrobial properties | [99] |
| Oregano, clove, tea tree, coriander, mastic thyme, laurel, rosemary, and sage | WPI | Glycerol | Antimicrobial activity | [100] |
| Cinnamomum cassia, Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Rosmarinus officinalis | WPC | Glycerol | Antioxidant | [101] |
| PLANT EXTRACTS | ||||
| Curcumin | WPI | Glycerol | Antiviral, antioxidant, anti-infection, and antimicrobial activities | [102] |
| Urtica dioica L. | Whey protein isolate (WPI) | Glycerol | Antioxidant and antibacterial | [103] |
| Tarbush (Fluorensia cernua) | Whey protein | Glycerol and candelilla wax | Inhibiting the growth of pathogenic fungi | [104] |
| Fireweed extract (Epilobium angustifolium L.) | Gelatin and WPI | Glycerol | Phytoantioxidants | [105] |
| Yerba mate and white tea | Furcellaran/WPI | Glycerol | Antioxidant properties | [106] |
| Rosemary and sage extracts | WPC | Glycerol | Antioxidant activity | [107] |
| Garlic (Allium sativum) and white pepper (Piper nigrum L.) | WPI | Glycerol | Storage stability | [108] |
| Green tea extract | WPC | Glycerol | Retarding the lipid oxidation | [109] |
| OTHER ADDITIVES | ||||
| Liquid smoke | WPC | Glycerol | Antimicrobial, colouring, and flavouring properties | [110] |
| Spent coffee grounds | Whey protein | Glycerol | Antioxidants | [111] |
| γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) | WPI | Glycerol | Regulates blood pressure and insulin, protects the nervous system, fights diabetes and cancer | [37] |
| Liquid smoke | WPC | Glycerol | Antimicrobial and preservation | [112] |
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tavares, L.; Souza, H.K.; Gonçalves, M.P.; Rocha, C.M. Physicochemical and microstructural properties of composite edible film obtained by complex coacervation between chitosan and whey protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packaging Market Size & Share Analysis—Growth Trends & Forecasts (2024–2029). Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/global-packaging-market (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Flexible Packaging Facts and Figures. Available online: https://www.flexpack.org/facts-and-figures (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Calva-Estrada, S.J.; Jiménez-Fernández, M.; Lugo-Cervantes, E. Protein-based films: Advances in the development of biomaterials applicable to food packaging. Food Eng. Rev. 2019, 11, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerna, S.; D’Incecco, P.; Limbo, S.; Sindaco, M.; Pellegrino, L. Strategies for Exploiting Milk Protein Properties in Making Films and Coatings for Food Packaging: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hedayati, S.; Tarahi, M.; Karaca, A.C.; Hadidi, M.; Assadpour, E.; Jafari, S.M. Advances in transglutaminase cross-linked protein-based food packaging films; a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, C.; Hafeez, M.A.; Wang, Q.; Farooq, S.; Huang, Q.; Tian, W.; Xiao, J. Biopolymer-based functional films for packaging applications: A review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1000116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Savino, I.; Locaputo, V.; Uricchio, V.F. A detailed review study on potential effects of microplastics and additives of concern on human health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavli, F.; Tassou, C.; Nychas, G.-J.E.; Chorianopoulos, N. Probiotic incorporation in edible films and coatings: Bioactive solution for functional foods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, S.; Yoo, J.; Yun, J.; Kang, H.-B.; Seol, K.-H.; Kim, H.-W.; Ham, J.-S. Application of whey protein-based edible films and coatings in food industries: An updated overview. Coatings 2021, 11, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirpan, A.; Ainani, A.F.; Djalal, M. A Review on Biopolymer-Based Biodegradable Film for Food Packaging: Trends over the Last Decade and Future Research. Polymers 2023, 15, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, Ó.L.; Reinas, I.; Silva, S.I.; Fernandes, J.C.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Pereira, R.N.; Vicente, A.A.; Poças, M.F.; Pintado, M.E.; Malcata, F.X. Effect of whey protein purity and glycerol content upon physical properties of edible films manufactured therefrom. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.; Dutta, S.; Moses, J.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Utilization of food waste streams for the production of biopolymers. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.; Yaqoob, M.; Aggarwal, P. An overview of biodegradable packaging in food industry. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, K.; Vishvakarma, R.; Sharma, P.; Singh, A.; Gaur, V.K.; Varjani, S.; Srivastava, J.K. Production of biopolymers from food waste: Constrains and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Rosas, J.; Cruz-Galvez, A.M.; Gomez-Aldapa, C.A.; Falfan-Cortes, R.N.; Guzman-Ortiz, F.A.; Rodríguez-Marín, M.L. Biopolymer films and the effects of added lipids, nanoparticles and antimicrobials on their mechanical and barrier properties: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Bian, H.; Pan, Y.; Sun, J.; Han, W. Application of protein-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Polymers 2019, 11, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, L.M.; Piccirilli, G.N.; Delorenzi, N.J.; Verdini, R.A. Effect of different combinations of glycerol and/or trehalose on physical and structural properties of whey protein concentrate-based edible films. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukoulis, C.; Behboudi-Jobbehdar, S.; Macnaughtan, W.; Parmenter, C.; Fisk, I.D. Stability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG incorporated in edible films: Impact of anionic biopolymers and whey protein concentrate. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, M.C.; Braga, M.E. Edible films and coatings based on agrifood residues: A new trend in the food packaging research. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 50, 101006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, O.L.; Pop, C.R.; Dufrechou, M.; Vodnar, D.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Dulf, F.V.; Minervini, F.; Suharoschi, R. Edible films and coatings functionalization by probiotic incorporation: A review. Polymers 2019, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Montes, E.; Castro-Muñoz, R. Edible films and coatings as food-quality preservers: An overview. Foods 2021, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltzer, M.A.; Salvay, A.G.; Delgado, J.F.; Wagner, J.R. Use of edible films and coatings for functional foods developments: A review. In Functional Foods Sources, Health Effects and Future Perspectives; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Galus, S.; Kadzińska, J. Whey protein edible films modified with almond and walnut oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghita Puscaselu, R.; Besliu, I.; Gutt, G. Edible Biopolymers-Based Materials for Food Applications—The Eco Alternative to Conventional Synthetic Packaging. Polymers 2021, 13, 3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.; Gupta, S.; Santhosh, R.; Syed, I.; Sarkar, P. Biopolymer-based edible films and coatings for food applications. In Food, Medical, and Environmental Applications of Polysaccharides; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 81–107. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, K.; Thirunavookarasu, N.; Chidanand, D. Recent advances in edible coating of food products and its legislations: A review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 12, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, A.; Rahaiee, S.; Litkohi, H.R.; Jamali, S.N.; Jafari, S.M. Development and optimization of whey protein-Lepidium perfoliatum gum packaging films: An approach towards antimicrobial and biodegradable films. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 196, 116447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanapathiranage, A.; Dassanayake, R.S.; Gamage, A.; Karri, R.R.; Manamperi, A.; Evon, P.; Jayakodi, Y.; Madhujith, T.; Merah, O. Recent Developments in Edible Films and Coatings for Fruits and Vegetables. Coatings 2023, 13, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zibaei, R.; Hasanvand, S.; Hashami, Z.; Roshandel, Z.; Rouhi, M.; de Toledo Guimarães, J.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Sarlak, Z.; Mohammadi, R. Applications of emerging botanical hydrocolloids for edible films: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinika, I.; Verma, D.K.; Balia, R.; Utama, G.L.; Patel, A.R. Potential of cheese whey bioactive proteins and peptides in the development of antimicrobial edible film composite: A review of recent trends. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalca, V.; Kerezsi, A.D.; Weber, A.; Gruber-Traub, C.; Schmucker, J.; Vodnar, D.C.; Dulf, F.V.; Socaci, S.A.; Fărcaș, A.; Mureșan, C.I. Protein-based films and coatings for food industry applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Velasco, C.E.; Pérez-Pérez, J.C.; Varillas-Torres, J.M.; Navarro-Cruz, A.R.; Hernández-Carranza, P.; Munguía-Pérez, R.; Cid-Pérez, T.S.; Avila-Sosa, R. Starch edible films/coatings added with carvacrol and thymol: In vitro and in vivo evaluation against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Foods 2021, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.; El-Sakhawy, M.; El-Sakhawy, M.A.-M. Polysaccharides, protein and lipid-based natural edible films in food packaging: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Ng, P.K. Natural biopolymer-based nanocomposite films for packaging applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sothornvit, R.; Krochta, J.M. Plasticizers in edible films and coatings. In Innovations in Food Packaging; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 403–433. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Ameliorating effect of γ-aminobutyric acid on the physical performance of whey protein films. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.; Gastineau, F.A.; Gregorski, K.S.; Tillin, S.J.; Pavlath, A.E. Chitosan-lipid films: Microstructure and surface energy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Hasan, M.; Mangaraj, S.; Pravitha, M.; Verma, D.K.; Srivastav, P.P. Trends in edible packaging films and its prospective future in food: A review. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100118. [Google Scholar]
- Jafarzadeh, S.; Forough, M.; Amjadi, S.; Javan Kouzegaran, V.; Almasi, H.; Garavand, F.; Zargar, M. Plant protein-based nanocomposite films: A review on the used nanomaterials, characteristics, and food packaging applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 9667–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, S.; Nafchi, A.M.; Salehabadi, A.; Oladzad-Abbasabadi, N.; Jafari, S.M. Application of bio-nanocomposite films and edible coatings for extending the shelf life of fresh fruits and vegetables. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 291, 102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.O.; Soares, J.; Sousa, S.; Madureira, A.R.; Gomes, A.; Pintado, M. Edible films as carrier for lactic acid bacteria. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, O.; Ferreiro, T.; Rodríguez-Otero, J.L.; Cobos, Á. Characterization of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) flour films: Effects of pH and plasticizer concentration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, Ó.L.; Fernandes, J.C.; Silva, S.I.; Pintado, M.E.; Malcata, F.X. Edible films and coatings from whey proteins: A review on formulation, and on mechanical and bioactive properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntrakul, K.; Harnkarnsujarit, N. Effects of plasticizers on water sorption and aging stability of whey protein/carboxy methyl cellulose films. J. Food Eng. 2020, 272, 109809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Y.A.; Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Anwer, M.K.; Khan, M.R.; Jawad, M.; Akram, N.; Faisal, Z. Mechanical Properties of Protein-Based Food Packaging Materials. Polymers 2023, 15, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, R.; Zo, S.M.; Kanan, B.N.; Purohit, S.; Gupta, M.K.; Han, S.S. Recent development of protein-based biopolymers in food packaging applications: A review. Polym. Test. 2023, 124, 108097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrieta-Martínez, C.; Soto-Valdez, H.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Rodríguez-Felix, F.; Márquez Ríos, E. Edible protein films: Sources and behavior. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2018, 31, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalrazeq, M.; Giosafatto, C.V.L.; Esposito, M.; Fenderico, M.; Di Pierro, P.; Porta, R. Glycerol-plasticized films obtained from whey proteins denatured at alkaline pH. Coatings 2019, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxabide, A.; Arregi, M.; Cabezudo, S.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Whey Protein Films for Sustainable Food Packaging: Effect of Incorporated Ascorbic Acid and Environmental Assessment. Polymers 2023, 15, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazón, P.; Velazquez, G.; Ramírez, J.A.; Vázquez, M. Polysaccharide-based films and coatings for food packaging: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaashikaa, P.; Kamalesh, R.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A.; Vijayasri, K.; Rangasamy, G. Recent advances in edible coatings and their application in food packaging. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matloob, A.; Ayub, H.; Mohsin, M.; Ambreen, S.; Khan, F.A.; Oranab, S.; Rahim, M.A.; Khalid, W.; Nayik, G.A.; Ramniwas, S. A review on edible coatings and films: Advances, composition, production methods, and safety concerns. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 28932–28944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhumal, C.V.; Sarkar, P. Composite edible films and coatings from food-grade biopolymers. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 4369–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.; Tan, G.; Gomes, D.; Pereira-Dias, S.; Díaz, O.; Cobos, A.; Pereira, C. Application of Ultrafiltration to Produce Sheep’s and Goat’s Whey-Based Synbiotic Kefir Products. Membranes 2023, 13, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.F.; Marnotes, N.G.; Rubio, O.D.; Garcia, A.C.; Pereira, C.D. Dairy by-products: A review on the valorization of whey and second cheese whey. Foods 2021, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.; Pires, A.; Gomes, D.; Viegas, J.; Pereira-Dias, S.; Pintado, M.E.; Henriques, M.; Pereira, C.D. Sheep’s Butter and Correspondent Buttermilk Produced with Sweet Cream and Cream Fermented by Aromatic Starter, Kefir and Probiotic Culture. Foods 2023, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonyali, B.; Cikrikci, S.; Oztop, M.H. Physicochemical and microstructural characterization of gum tragacanth added whey protein based films. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-J.; Weng, Y.-M. Novel edible composite films fabricated with whey protein isolate and zein: Preparation and physicochemical property evaluation. LWT 2019, 101, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammann, F.; Schmid, M. Determination quantification of molecular interactions in protein films: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 7975–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Müller, K. Whey protein-based packaging films and coatings. In Whey Proteins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 407–437. [Google Scholar]
- Zink, J.; Wyrobnik, T.; Prinz, T.; Schmid, M. Physical, chemical and biochemical modifications of protein-based films and coatings: An extensive review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, M.; Stading, M.; Hermansson, A.-M. Aging of whey protein films and the effect on mechanical and barrier properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, N.; Monahan, F.; O’riordan, E.; O’sullivan, M. Physical properties of WPI films plasticized with glycerol, xylitol, or sorbitol. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.; Sakanaka, L.S.; Yamashita, F.; Grossmann, M. Water sorption and mechanical properties of cassava starch films and their relation to plasticizing effect. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares-Castañeda, A.; Sánchez-Chino, X.M.; de las Mercedes Gómez y Gómez, Y.; Jiménez-Martínez, C.; Martínez Herrera, J.; Cid-Gallegos, M.S.; Corzo-Ríos, L.J. Cereal and legume protein edible films: A sustainable alternative to conventional food packaging. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 3197–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purewal, S.S.; Kaur, A.; Bangar, S.P.; Singh, P.; Singh, H. Protein-Based Films and Coatings: An Innovative Approach. Coatings 2023, 14, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriani, F.; Aprilia, S.; Arahman, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Suhaimi, H.; Huda, N. Properties of biocomposite film based on whey protein isolate filled with nanocrystalline cellulose from pineapple crown leaf. Polymers 2021, 13, 4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, B.G.; Kaya, S. Characterization and application of novel composite films based on soy protein isolate and sunflower oil produced using freeze drying method. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jiang, S.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, S.Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Facile fabrication of tough, strong, and biodegradable soy protein-based composite films with excellent UV-blocking performance. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 211, 108645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chai, Z.; Leng, X. Study of the physical properties of whey protein isolate and gelatin composite films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5100–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravartula, S.S.N.; Soccio, M.; Lotti, N.; Balestra, F.; Dalla Rosa, M.; Siracusa, V. Characterization of composite edible films based on pectin/alginate/whey protein concentrate. Materials 2019, 12, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Merzbacher, S.; Brzoska, N.; Müller, K.; Jesdinszki, M. Improvement of food packaging-related properties of whey protein isolate-based nanocomposite films and coatings by addition of montmorillonite nanoplatelets. Front. Mater. 2017, 4, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Benbettaïeb, N.; Debeaufort, F.; Karbowiak, T. Bioactive edible films for food applications: Mechanisms of antimicrobial and antioxidant activity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3431–3455. [Google Scholar]
- Sogut, E.; Filiz, B.E.; Seydim, A. Whey protein isolate-and carrageenan-based edible films as carriers of different probiotic bacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 4829–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Leu, R.K.; Hu, Y.; Brown, I.L.; Woodman, R.J.; Young, G.P. Synbiotic intervention of Bifidobacterium lactis and resistant starch protects against colorectal cancer development in rats. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyedzade Hashemi, S.; Khorshidian, N.; Mohammadi, M. An insight to potential application of synbiotic edible films and coatings in food products. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 875368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, M.; Rojas-Graü, M.; Rodríguez, F.; Ramírez, J.; Carmona, A.; Martin-Belloso, O. Alginate-and gellan-based edible films for probiotic coatings on fresh-cut fruits. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, E190–E196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akcan, T.; Estévez, M.; Serdaroğlu, M. Antioxidant protection of cooked meatballs during frozen storage by whey protein edible films with phytochemicals from Laurus nobilis L. and Salvia officinalis. LWT 2017, 77, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, H.; Moradi, M.; Sharafi, K. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the use of plant essential oils and extracts in the development of antimicrobial edible films for dairy application. Vet. Res. Forum 2023, 14, 179–194. [Google Scholar]
- Çakmak, H.; Özselek, Y.; Turan, O.Y.; Fıratlıgil, E.; Karbancioğlu-Güler, F. Whey protein isolate edible films incorporated with essential oils: Antimicrobial activity and barrier properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 179, 109285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, L.; Balagué, C.; Rubiolo, A.; Verdini, R. Evaluation of the biocide properties of whey-protein edible films with potassium sorbate to control non-O157 shiga toxinproducing Escherichia coli. Procedia Food Sci. 2011, 1, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, M.; Santos, G.; Rodrigues, A.; Gomes, D.; Pereira, C.D.; Gil, M. Replacement of conventional cheese coatings by natural whey protein edible coatings with antimicrobial activity. J. Hyg. Eng. Des. 2013, 3, 34–47. [Google Scholar]
- Mileriene, J.; Serniene, L.; Henriques, M.; Gomes, D.; Pereira, C.; Sekmokiene, D.; Kondrotiene, K.; Kasetiene, N.; Lauciene, L.; Andruleviciute, V.; et al. Effect of liquid whey protein concentrate–based edible coating enriched with cinnamon carbon dioxide extract on the quality and shelf life of Eastern European curd cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1504–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, A.; Pietruszka, H.; Bożek, A.; Szkolnicka, K.; Gomes, D.; Díaz, O.; Cobos, A.; Pereira, C. Sheep’s Second Cheese Whey Edible Coatings with Oregano and Clary Sage Essential Oils Used as Sustainable Packaging Material in Cheese. Foods 2024, 13, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabee, M.Z.; Abdou, E.S. Chitosan based edible films and coatings: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1819–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Tebar, N.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A.; Fernández-López, J.; Viuda-Martos, M. Chitosan Edible Films and Coatings with Added Bioactive Compounds: Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties and Their Application to Food Products: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavinatto, A.; de Almeida Mattos, A.V.; Malpass, A.C.G.; Okura, M.H.; Balogh, D.T.; Sanfelice, R.C. Coating with chitosan-based edible films for mechanical/biological protection of strawberries. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braber, N.L.V.; Di Giorgio, L.; Aminahuel, C.A.; Vergara, L.I.D.; Costa, A.O.M.; Montenegro, M.A.; Mauri, A.N. Antifungal whey protein films activated with low quantities of water soluble chitosan. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Varoni, E.M.; Iriti, M.; Martorell, M.; Setzer, W.N.; del Mar Contreras, M.; Salehi, B.; Soltani-Nejad, A.; Rajabi, S.; Tajbakhsh, M. Carvacrol and human health: A comprehensive review. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, H.; Tian, B.; Jiang, B.; Xu, J.; Li, D.; Feng, Z.; Liu, C. Novel edible coating with antioxidant and antimicrobial activities based on whey protein isolate nanofibrils and carvacrol and its application on fresh-cut cheese. Coatings 2019, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliarini, N.; Diosma, G.; Garrote, G.L.; Abraham, A.G.; Piermaria, J. Whey protein-kefiran films as driver of probiotics to the gut. LWT 2019, 105, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Storia, A.; Di Giuseppe, F.A.; Volpe, S.; Oliviero, V.; Villani, F.; Torrieri, E. Physical properties and antimicrobial activity of bioactive film based on whey protein and Lactobacillus curvatus 54M16 producer of bacteriocins. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odila Pereira, J.; Soares, J.; Costa, E.; Silva, S.; Gomes, A.; Pintado, M. Characterization of edible films based on alginate or whey protein incorporated with Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 and prebiotics. Coatings 2019, 9, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianina, I.B.; Jrb, A.G.O.; Pimentelc, T.C.; Hernandesa, N.F.; Costaa, G.N. Edible biofilms formulated with whey protein isolate and L. casei probiotic culture: Characterization and application in tomatoes and grapes. Chem. Eng 2019, 75, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, A.; Ramos, Ó.; Cerqueira, M.; Venâncio, A.; Abrunhosa, L. Active whey protein edible films and coatings incorporating Lactobacillus buchneri for Penicillium nordicum control in cheese. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2020, 13, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydim, A.C.; Sarikus-Tutal, G.; Sogut, E. Effect of whey protein edible films containing plant essential oils on microbial inactivation of sliced Kasar cheese. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoshal, G. Thyme essential oil nano-emulsion/Tamarind starch/Whey protein concentrate novel edible films for tomato packaging. Food Control 2022, 138, 108990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socaciu, M.-I.; Fogarasi, M.; Semeniuc, C.A.; Socaci, S.A.; Rotar, M.A.; Mureşan, V.; Pop, O.L.; Vodnar, D.C. Formulation and characterization of antimicrobial edible films based on whey protein isolate and tarragon essential oil. Polymers 2020, 12, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pan, I.; Royo, M.; Ignacio Mate, J. Antimicrobial activity of whey protein isolate edible films with essential oils against food spoilers and foodborne pathogens. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, M383–M390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Santos, R.; de Melo, N.R.; Andrade, M.; Azevedo, G.; Machado, A.V.; Carvalho-Costa, D.; Sanches-Silva, A. Whey protein active films incorporated with a blend of essential oils: Characterization and effectiveness. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2018, 31, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevij, H.T.; Salami, M.; Mohammadian, M.; Khodadadi, M. Fabrication and investigation of physicochemical, food simulant release, and antioxidant properties of whey protein isolate-based films activated by loading with curcumin through the pH-driven method. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Moghaddam, A.D.; Sharifan, A.; Dabaghi, P.; Hadi, S. Structural, physico-mechanical, and bio-functional properties of whey protein isolate-based edible films as affected by enriching with nettle (Urtica dioica L.) leaf extract. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 4051–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Perez, O.B.; Ventura-Sobrevilla, J.M.; Torres-León, C.; Rojas-Molina, R.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Aguilar-González, M.A.; Aguilar, C.N. Development and characterization of whey protein films incorporated with tarbush polyphenols and candelilla wax. Food Biosci. 2022, 45, 101505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, D.; Szymanowska, U.; Skrzypek, T.; Basiura-Cembala, M.; Bartkowiak, A.; Łupina, K. A comprehensive study on gelatin-and whey protein isolate-based edible films as carriers of fireweed (Epilobium angustifolium L.) Extract. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022, 15, 2547–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta-Kubica, A.; Jamróz, E.; Kawecka, A.; Juszczak, L.; Krzyściak, P. Active edible furcellaran/whey protein films with yerba mate and white tea extracts: Preparation, characterization and its application to fresh soft rennet-curd cheese. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogianni, V.G.; Kasapidou, E.; Mitlianga, P.; Mataragas, M.; Pappa, E.; Kondyli, E.; Bosnea, L. Production, characteristics and application of whey protein films activated with rosemary and sage extract in preserving soft cheese. LWT 2022, 155, 112996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ket-On, A.; Pongmongkol, N.; Somwangthanaroj, A.; Janjarasskul, T.; Tananuwong, K. Properties and storage stability of whey protein edible film with spice powders. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2933–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robalo, J.; Lopes, M.; Cardoso, O.; Sanches Silva, A.; Ramos, F. Efficacy of whey protein film incorporated with Portuguese green tea (Camellia sinensis L.) extract for the preservation of Latin-style fresh cheese. Foods 2022, 11, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirilli, G.N.; Soazo, M.; Perez, L.M.; Delorenzi, N.J.; Verdini, R.A. Effect of storage conditions on the physicochemical characteristics of edible films based on whey protein concentrate and liquid smoke. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadaki, A.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Lappa, I.K.; Andriotis, H.; Eriotou, E.; Mandala, I.; Kopsahelis, N. Tuning the physical and functional properties of whey protein edible films: Effect of pH and inclusion of antioxidants from spent coffee grounds. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 27, 100700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soazo, M.; Pérez, L.M.; Piccirilli, G.N.; Delorenzi, N.J.; Verdini, R.A. Antimicrobial and physicochemical characterization of whey protein concentrate edible films incorporated with liquid smoke. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 72, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, L.J.L.; Rovina, K.; Vonnie, J.M.; Matanjun, P.; Erna, K.H.; ‘Aqilah, N.M.N.; Felicia, W.X.L.; Funk, A.A. The emergence of edible and food-application coatings for food packaging: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Gao, L.; Dai, L.; Ji, N.; Qin, Y.; Shi, R.; Qiao, Y.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Hydrophobic biopolymer-based films: Strategies, properties, and food applications. Food Eng. Rev. 2023, 15, 360–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Kajla, P.; Kumari, P.; Trif, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Milk protein-based active edible packaging for food applications: An eco-friendly approach. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 942524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-López, M.E.; Calva-Estrada, S.d.J.; Gradilla-Hernández, M.S.; Barajas-Álvarez, P. Current trends in biopolymers for food packaging: A review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1225371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Dallmann, K.; Bugnicourt, E.; Cordoni, D.; Wild, F.; Lazzeri, A.; Noller, K. Properties of whey-protein-coated films and laminates as novel recyclable food packaging materials with excellent barrier properties. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2012, 2012, 562381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han Wen, H.; Shao, X. Understanding consumers’ acceptance of edible food packaging: The role of consumer innovativeness. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2024, 80, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Materials | Example of Materials | Properties | Functionality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polysaccharides | Alginate, Pectin, Cellulose, Starch, Chitosan, Agar | Thickeners Gellants Emulsifiers Stabilizers Coating | Polysaccharides form the structure of a solid polymer matrix and improve gas barrier properties. |
| Proteins | Whey Protein, Gelatin, Casein, Collagen, Ovalbumin Soy Protein | Gellants Thickeners Stabilizers Foaming Firmness Coating | Transport of antimicrobials and antioxidants. They control the transport of gases (oxygen). |
| Lipids | Waxes Paraffin Glycerides | Coating | Avoid drying or dehydration and give flexibility. Prevent moisture migration and water vapor transmission. |
| Protein Source | TS (MPa) | EAB (%) | YM (MPa) | WVP (g·mm/m2 h kPa) | Thickness (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soy * | 1.59–8.05 | 105.3 | 87.4 | - | 82 |
| Zein | 4 | 118 | - | 4 | - |
| Milk Casein | 2–77 | 2–130 | - | 1.6–11 | - |
| WPC | 0.7–0.9 | 18 | - | 6.2–12.8 | 132 |
| WPI | 0.9–8.20 | 33–72.4 | 24.71 | 4.57 | 119.86 |
| Grass Pea * | 8.59 | 68.3 | 483.0 | - | 110 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pires, A.F.; Díaz, O.; Cobos, A.; Pereira, C.D. A Review of Recent Developments in Edible Films and Coatings-Focus on Whey-Based Materials. Foods 2024, 13, 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162638
Pires AF, Díaz O, Cobos A, Pereira CD. A Review of Recent Developments in Edible Films and Coatings-Focus on Whey-Based Materials. Foods. 2024; 13(16):2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162638
Chicago/Turabian StylePires, Arona Figueroa, Olga Díaz, Angel Cobos, and Carlos Dias Pereira. 2024. "A Review of Recent Developments in Edible Films and Coatings-Focus on Whey-Based Materials" Foods 13, no. 16: 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162638
APA StylePires, A. F., Díaz, O., Cobos, A., & Pereira, C. D. (2024). A Review of Recent Developments in Edible Films and Coatings-Focus on Whey-Based Materials. Foods, 13(16), 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162638







