Integrated Analysis of Ginsenoside Content and Biomarker Changes in Processed Ginseng: Implications for Anti-Cancer Mechanisms
Abstract
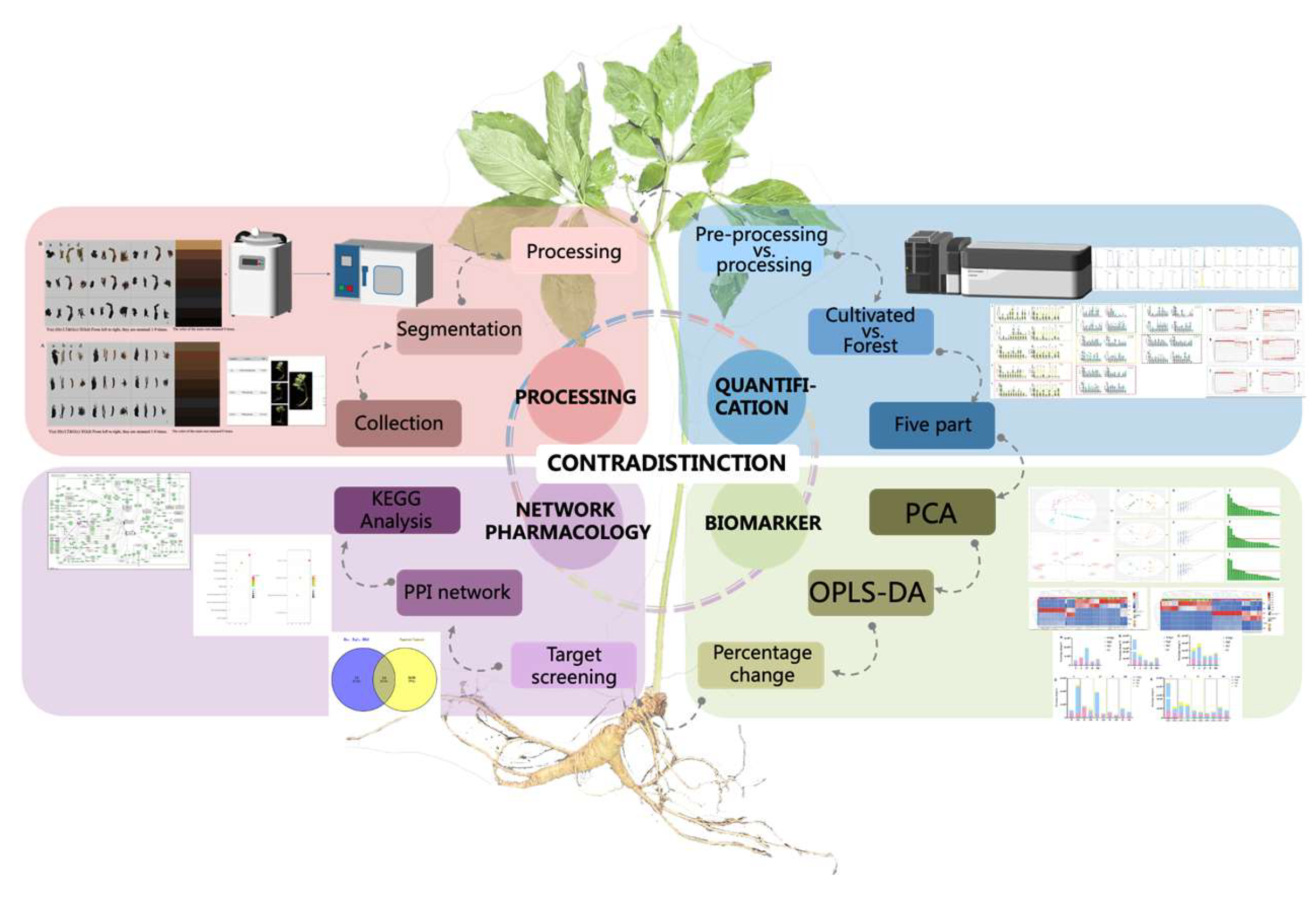
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
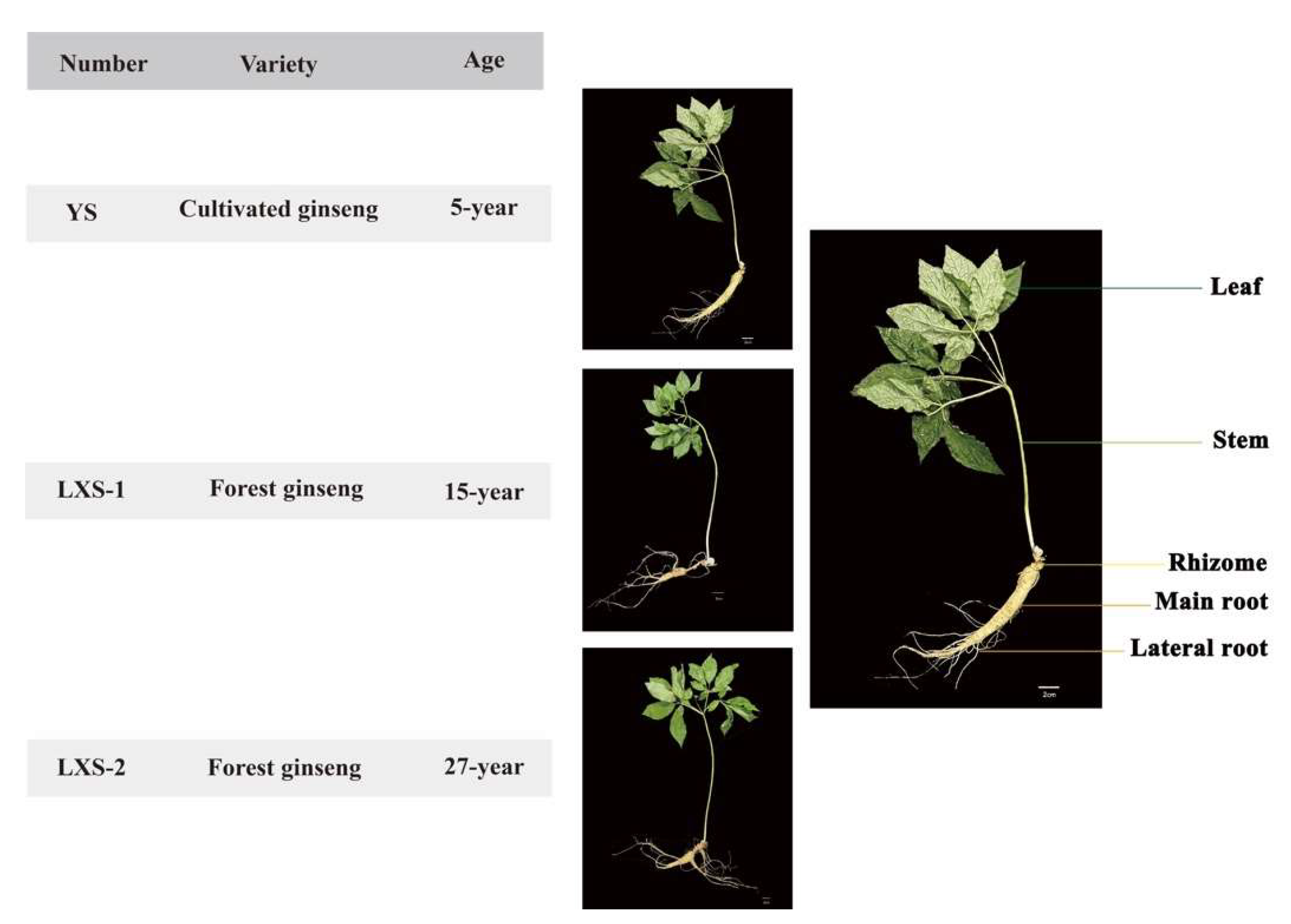
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Preparation of Stock Solutions of Standards and Samples
2.3.1. Preparation of Standard Stock and Working Solutions
2.3.2. Preparation of Samples for UPLC-MS/MS Analysis
2.4. UPLC-MS/MS Conditions
2.5. Method Validation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Network Pharmacology
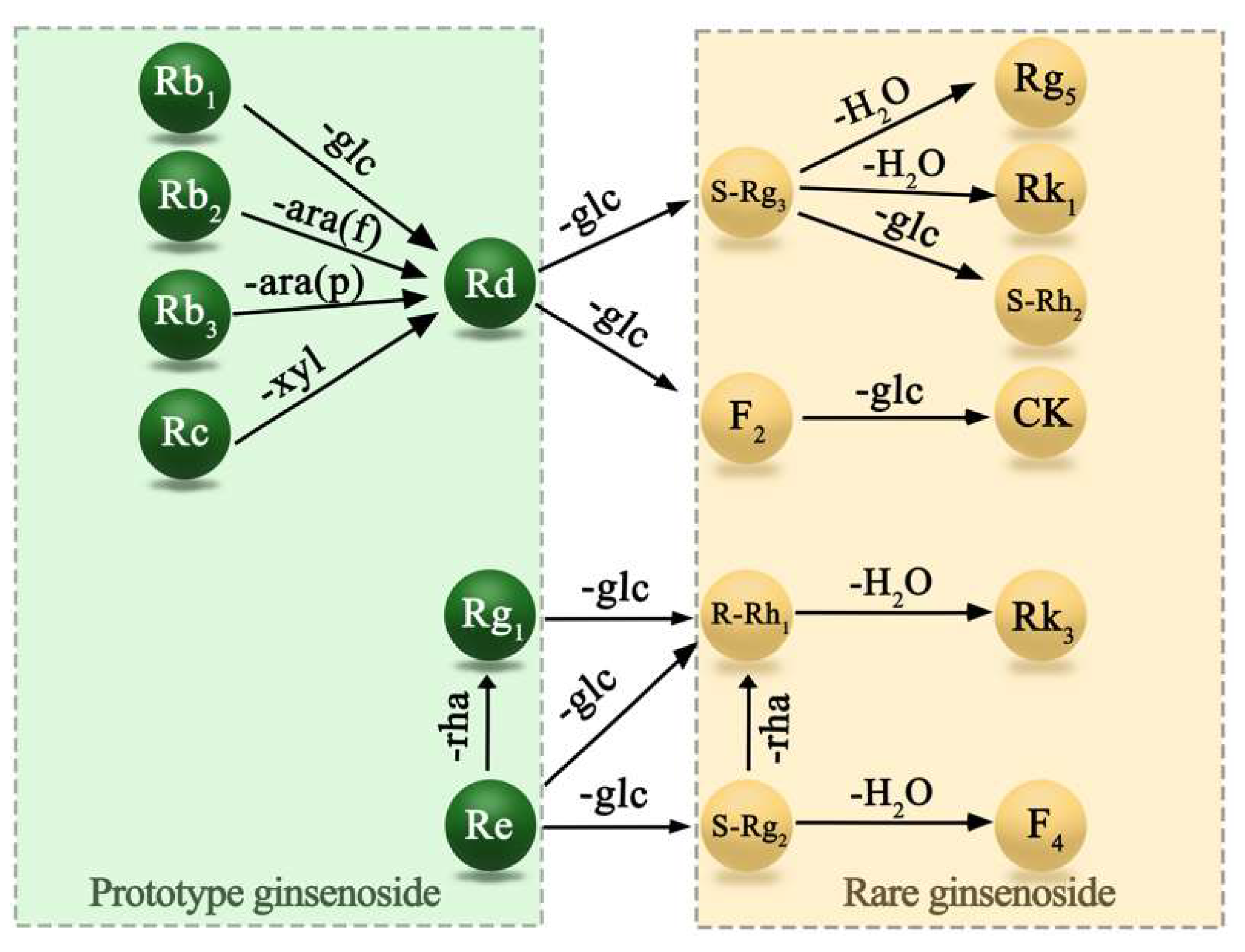
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of Ginseng Content before and after Processing
3.1.1. Comparison of Ginsenoside Content before and after Processing
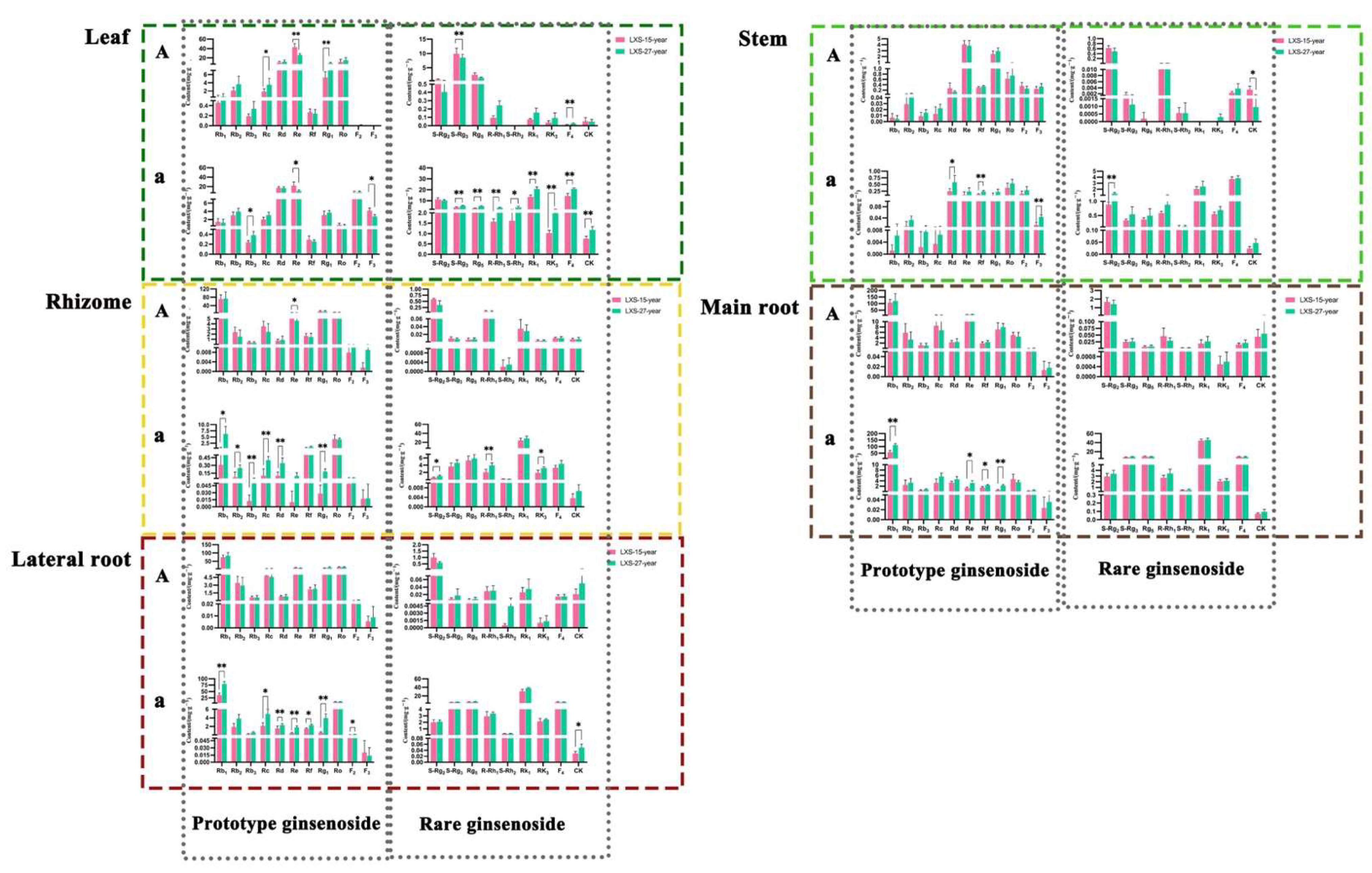
3.1.2. Comparison of Ginsenoside Content with Different Cultivation Ages
3.1.3. Comparison of Ginsenoside Content with Different Cultivation Methods
3.1.4. Comparison of Ginsenoside Content in Different Parts of Black Ginseng
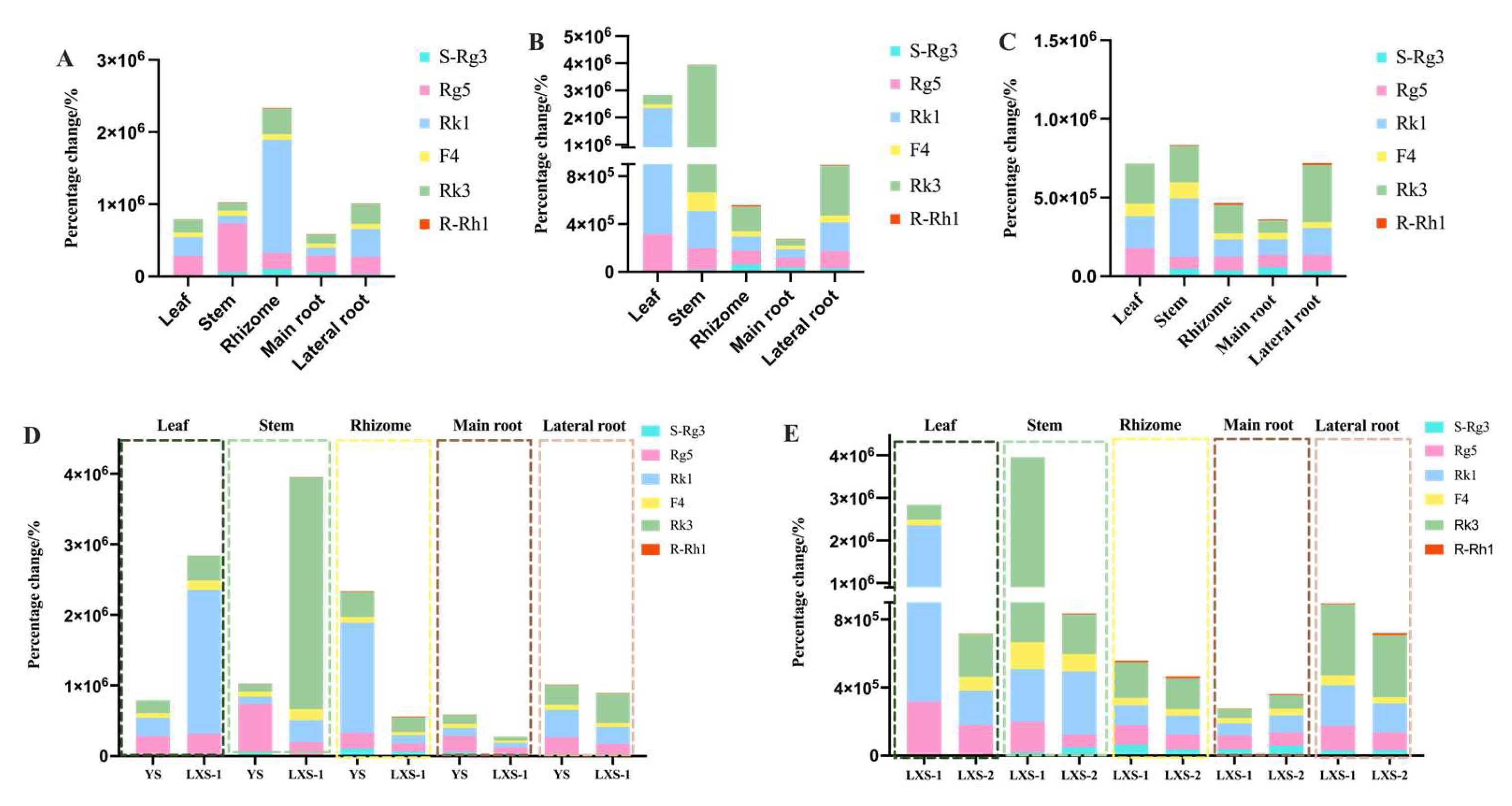
3.2. Exploration of Biomarkers of Ginseng before and after Processing Based on Chemometric Analysis
3.3. Percentage Changes of Biomarkers of Ginseng before and after Processing
3.4. Prediction of Anti-Cancer Mechanisms of Ginseng Biomarkers Based on Network Pharmacology
3.4.1. Target Screening and PPI Network Construction
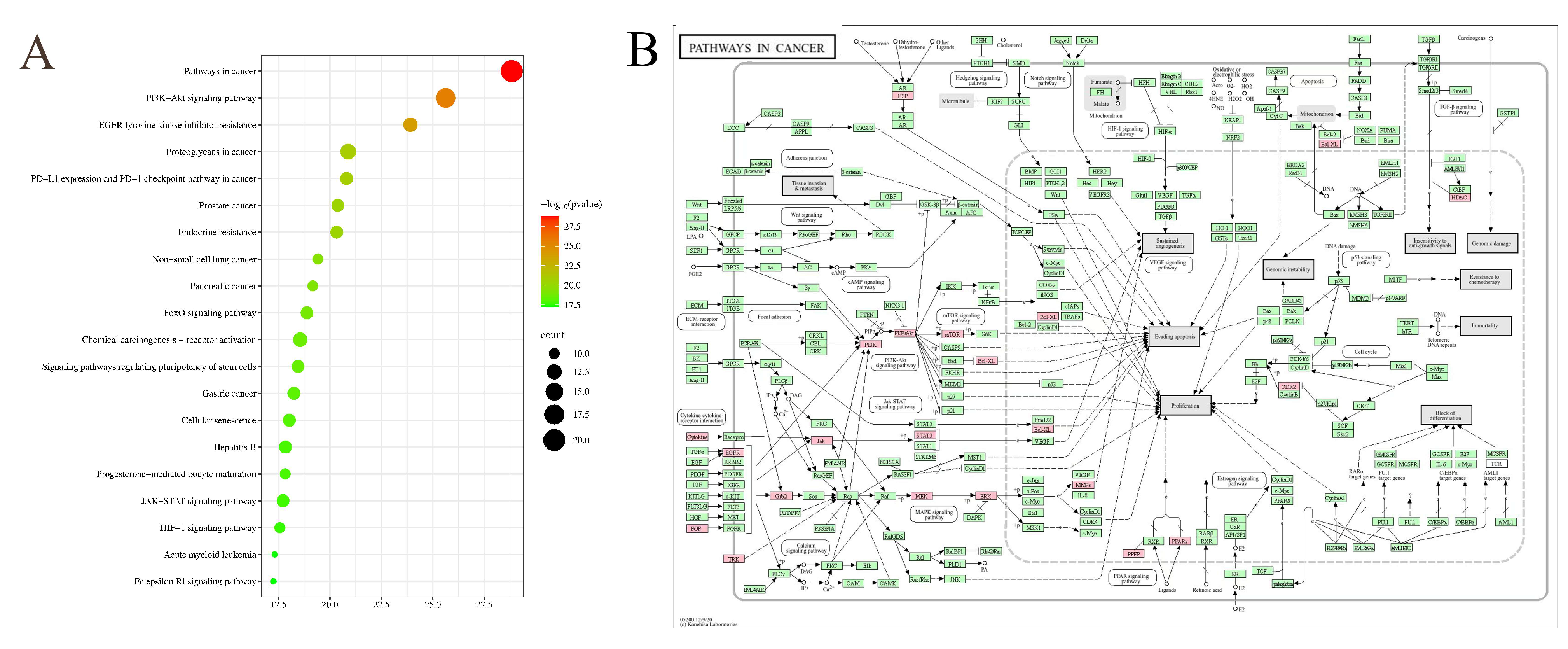
3.4.2. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y. Traditional uses, chemical diversity and biological activities of Panax L. (Araliaceae): A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 112792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Pharmacopoeia Committee. Chinese Pharmacopoeia; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Balan, P.; Popovich, D.G. Comparison of Ginsenoside Components of Various Tissues of New Zealand Forest-Grown Asian Ginseng (Panax ginseng) and American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolium L.). Biomolecules 2020, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Zanuso, B.; de Oliveira Dos Santos, A.; Miola, V.; Guissoni Campos, L.; Spilla, C.; Barbalho, S. Panax ginseng and aging related disorders: A systematic review. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 161, 111731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.N.; Hong, H.G.; Son, J.S.; Kwon, Y.O.; Lee, H.H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Son, M.J.; Oh, J.G.; Yoon, M.H. Investigation of Ginsenosides and Antioxidant Activities in the Roots, Leaves, and Stems of Hydroponic-Cultured Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer). Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 24, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.P.; Lin, Y.P.; Hu, Y.Z.; Liu, C.X.; Lan, K.; Jia, W. Phytochemistry, Metabolism, and Metabolomics of Ginseng. Chin. Herb. Med 2015, 7, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.X.; Yang, Y.P.; Li, C.N.; Zhang, K.Y.; Gao, X.C.; Shen, J.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Cheng, D.D.; Lv, J.W.; Sun, J.M. Based on 1H NMR and LC-MS metabolomics reveals biomarkers with neuroprotective effects in multi-parts ginseng powder. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engwa, G. The pharmacological effects of topical ginseng root and leaf extracts (Panax ginseng) on the intraoccular pressure of experimental Rabbits. Indian E-J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 1, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jeon, J.-N.; Wang, C.; Min, J.-W.; Noh, H.-Y.; Yang, D.-C. Effect of White, Red and Black Ginseng on Physicochemical Properties and Ginsenosides. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2015, 70, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chang, Z.; Wei, K.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Feng, B. Chemical Differentiation and Quantitative Analysis of Black Ginseng Based on an LC-MS Combined with Multivariate Statistical Analysis Approach. Molecules 2023, 28, 5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.W.; Li, C.S.; Zhang, H.X.; Li, Q.; Cheng, S.Q.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.; Ren, H.M.; Xia, L.J.; Wang, X.X.; et al. Saponins of ginseng products: A review of their transformation in processing. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1177819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Han, K.-M.; Kim, Y.-S.; Kwon, E.; Paek, S.-H.; Seo, Y.-K.; Yun, J.-W.; Kang, B.-C. Efficacy and safety evaluation of black ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Mey.) extract (CJ EnerG): Broad spectrum cytotoxic activity in human cancer cell lines and 28-day repeated oral toxicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Pan, J.H.; Cho, H.T.; Kim, Y.J. Black Ginseng Extract Counteracts Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, E.; Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.-H.; Hong, S.-B.; Rhee, M.H. A comparative study on immune-stimulatory and antioxidant activities of various types of ginseng extracts in murine and rodent models. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, M.Y.; Lee, S.R.; Hwang, H.J.; Yoon, J.G.; Lee, H.J.; Cho, J.A. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Korean Black Ginseng Extract through ER Stress Pathway. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, B.K.; Kwon, S.W.; Park, J.H. Chemical diversity of ginseng saponins from Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Ma, M.; Wu, Z.; Liang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Li, D.; An, T.; Wang, G. Advances in the biosynthesis and metabolic engineering of rare ginsenosides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Park, S.; Long, N.P.; Min, J.E.; Kim, H.M.; Yang, E.; Lee, S.J.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.W. Research Quality-Based Multivariate Modeling for Comparison of the Pharmacological Effects of Black and Red Ginseng. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, Y.; Ahn, S.; Kim, S.; Yang, B.; Lee, E.; Kang, C. Analysis of Ginsenosides and Non-Saponin Components of Red Ginseng from Landraces and New Varieties. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Moore, R.; Gao, Y.; Chen, P.; Yu, L.; Zhang, M.; Sun, J. Comparison of Phytochemical Profiles of Wild and Cultivated American Ginseng Using Metabolomics by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2022, 28, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Xiao, H. Effects of growth years on ginsenoside biosynthesis of wild ginseng and cultivated ginseng. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Yi, L.W.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Guo, F.; Huo, Y.S.; Zhao, D.Q.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Cai, S.Q. 177 Saponins, Including 11 New Compounds in Wild Ginseng Tentatively Identified via HPLC-IT-TOF-MS(n), and Differences among Wild Ginseng, Ginseng under Forest, and Cultivated Ginseng. Molecules 2021, 26, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales, C.; Mamdouh, Z.M.; List, M.; Kiel, C.; Casas, A.I.; Schmidt, H. Network pharmacology: Curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Cui, Z.; Chu, J.; Du, G. UPLC-MS/MS and Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis of Bioactive Anti-Depression Compounds in Betel Nut. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2021, 15, 4827–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.P.; Yue, H.; Chen, C.B.; Liu, S.Y. Multicomponent assessment and ginsenoside conversions of Panax quinquefolium L. roots before and after steaming by HPLC-MS(n). J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Luo, J.P.; Zhang, W.J.; Mu, Q. Variation of Ginsenosides in Ginseng of Different Ages. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 739–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.F.; Cheng, X.L.; Lin, Q.H.; Li, S.S.; Jia, Z.; Han, T.; Lin, R.C.; Wang, D.; Wei, F.; Li, X.R. Identification of mountain-cultivated ginseng and cultivated ginseng using UPLC/oa-TOF MSE with a multivariate statistical sample-profiling strategy. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.E.; Kim, Y.S.; Yi, M.J.; Park, W.G.; Yi, J.S.; Chun, S.R.; Han, S.S.; Lee, S.J. Physiological and chemical characteristics of field-and mountain-cultivated ginseng roots. J. Plant Biol. 2007, 50, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xiang, Y.; Deng, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. Simultaneous analysis of anthocyanin and non-anthocyanin flavonoid in various tissues of different lotus (Nelumbo) cultivars by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS(n). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Doh, E.J.; Lee, G. Quantitative Comparison of the Marker Compounds in Different Medicinal Parts of Morus alba L. Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detector with Chemometric Analysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Chen, L.; Guo, Y.H.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y. Simultaneous Determination and Analysis of Major Ginsenosides in Wild American Ginseng Grown in Tennessee. Chem. Biodivers. 2019, 16, e1900203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.S.; Gu, L.J.; Fang, Z.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, Z.; Lee, M.R.; Li, Z.; Li, J.J.; Sung, C.K. Simultaneous quantification of 19 ginsenosides in black ginseng developed from Panax ginseng by HPLC-ELSD. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Ji, S.H.; Choi, B.R.; Choi, D.J.; Lee, Y.G.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, K.; Lee, Y.H.; Baek, N.I.; et al. UPLC-QTOF/MS-Based Metabolomics Applied for the Quality Evaluation of Four Processed Panax ginseng Products. Molecules 2018, 23, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.F.; Gao, Y.; Xu, S.Y.; Liu, H.; Xue, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.N.; Xiong, H.; Lin, R.C.; et al. Remarkable impact of steam temperature on ginsenosides transformation from fresh ginseng to red ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Balan, P.; Popovich, D.G. Changes of Ginsenoside Composition in the Creation of Black Ginseng Leaf. Molecules 2020, 25, 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, S.J.; Jun, M.; Qiujie, Q.; Qing, Y.; Wei, W.; Ying, L.S. Identification of ginsenosides Rc, Rb2, Rb3 and related malonyl-ginsenosides in Panax ginseng extracts by using RRLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Human Health and Biomedical Engineering, Jilin, China, 19–22 August 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, X.M.; Huo, Y.; Kang, J.P.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D.U.; Kim, M.; Yang, D.C.; Kang, S.C.; Wang, Y.P. Diversity of Ginsenoside Profiles Produced by Various Processing Technologies. Molecules 2020, 25, 4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Qu, C.Y.; Li, J.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, W.; Wang, C.Z.; Wang, D.S.; Song, J.; Sun, G.Z.; Yuan, C.S. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Malonyl Ginsenosides from American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) on Type 2 Diabetic Mice. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 33652–33664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xia, J.; Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, J.Q.; Ruan, C.C.; Sun, G.Z.; Yuan, C.S. Remarkable Impact of Acidic Ginsenosides and Organic Acids on Ginsenoside Transformation from Fresh Ginseng to Red Ginseng. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5389–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, W.; Jung, J.; Na, H.; Hwang-Bo, J.; Kim, H.-G.; Yoon, D.; Choi, B.-R.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, G.-S.; Baek, N.-I.; et al. Identification and quantification of major malonyl ginsenosides isolated from Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J. Appl. Chem. 2019, 62, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Guan, Y.; Yang, J.; Quan, J.; Yan, H.; Hou, W.; Zhang, G. Growth age of mountain cultivated ginseng affects its chemical composition. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 101, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Li, G.; Jiang, C.; Yang, B.; Yang, H.J.; Xu, H.Y.; Huang, L.Q. Tissue-specific distribution of ginsenosides in different aged ginseng and antioxidant activity of ginseng leaf. Molecules 2014, 19, 17381–17399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, H.N.; Dandin, V.S.; Park, S.Y.; Paek, K.Y. Quality, safety and efficacy profiling of ginseng adventitious roots produced in vitro. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7309–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Yang, P.; Jing, C.; Fu, B.; Teng, X.; Zhao, D.; Sun, L. Comparison of the metabolomic and proteomic profiles associated with triterpene and phytosterol accumulation between wild and cultivated ginseng. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 195, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, M.; Sun, M. Diversity and structure of the rhizosphere microbial communities of wild and cultivated ginseng. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Kim, H.-Y.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, S.H. Transcriptome analysis of Panax ginseng response to high light stress. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, L.; Yi-xin, Y.; Dong-yue, Z.; Wan-long, D. Influence of Allelochemicals on Microbial Community in Ginseng Cultivating Soil. Chin. Herb. Med. 2014, 6, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rg5 induces apoptosis and autophagy via the inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway against breast cancer in a mouse model. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 5513–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Su, Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, W. Ginsenoside-Rg5 Inhibits Retinoblastoma Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis through Suppressing BCL2 Expression. Chemotherapy 2018, 63, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, T.; Wu, W.; Yan, Z.; Li, X. Anticancer effect and molecular mechanism of ginsenoside Rg3 in various cancer types. Intell. Pharm. 2023, 1, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, B.; Liang, Y.; Fu, B.; Luo, J.; Zhou, X.; Ji, R.; He, X. Integrated Analysis of Ginsenoside Content and Biomarker Changes in Processed Ginseng: Implications for Anti-Cancer Mechanisms. Foods 2024, 13, 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162497
Guo B, Liang Y, Fu B, Luo J, Zhou X, Ji R, He X. Integrated Analysis of Ginsenoside Content and Biomarker Changes in Processed Ginseng: Implications for Anti-Cancer Mechanisms. Foods. 2024; 13(16):2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162497
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Biyu, Yingli Liang, Biru Fu, Jiayi Luo, Xingchen Zhou, Ruifeng Ji, and Xin He. 2024. "Integrated Analysis of Ginsenoside Content and Biomarker Changes in Processed Ginseng: Implications for Anti-Cancer Mechanisms" Foods 13, no. 16: 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162497
APA StyleGuo, B., Liang, Y., Fu, B., Luo, J., Zhou, X., Ji, R., & He, X. (2024). Integrated Analysis of Ginsenoside Content and Biomarker Changes in Processed Ginseng: Implications for Anti-Cancer Mechanisms. Foods, 13(16), 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162497





