γ-Conglutin Immunoreactivity Is Differently Affected by Thermal Treatment and Gastrointestinal Digestion in Lupine Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Mixtures Preparation
2.2. Protein Extraction and Quantification
2.3. SDS-PAGE Analysis
2.4. Immunoblotting Analysis
2.5. Indirect ELISA
2.6. Gastrointestinal Digestion
3. Results
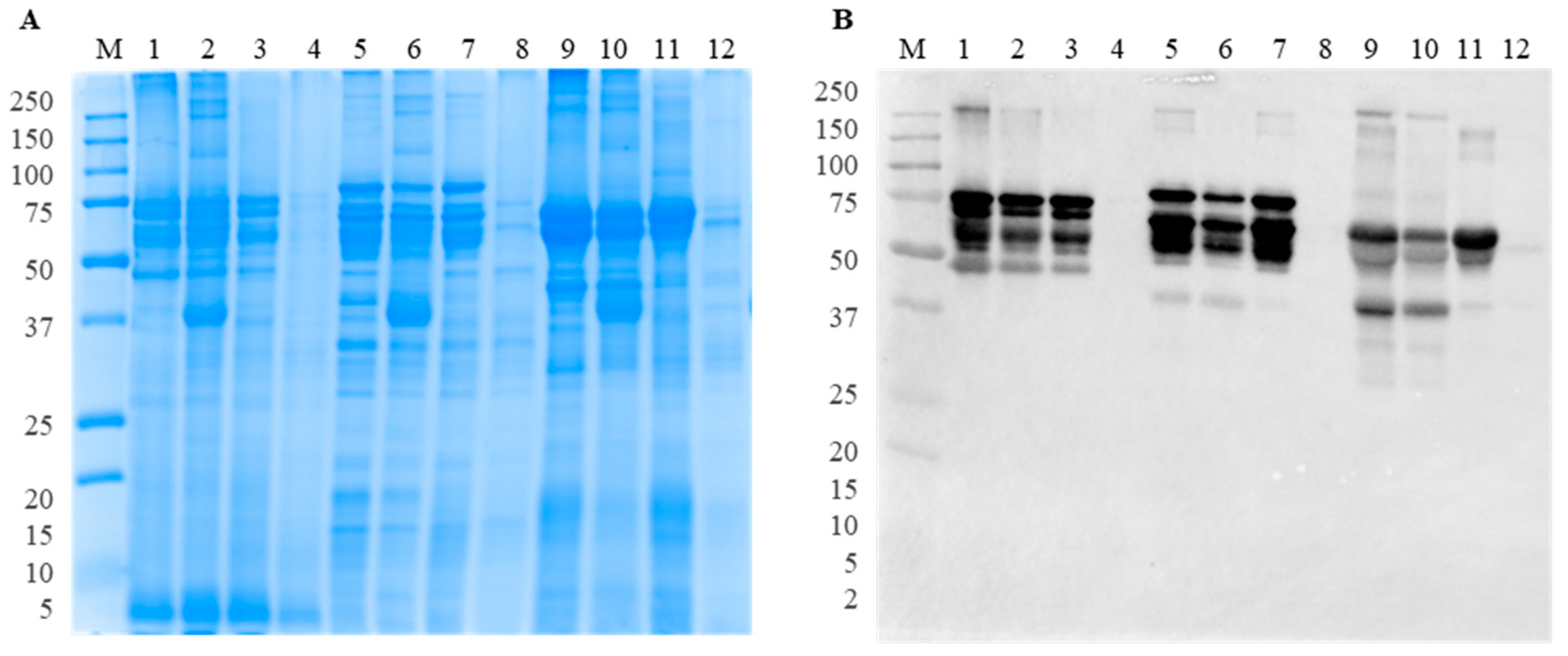
3.1. Effect of Thermal Treatment
3.1.1. SDS-PAGE and Immunoblotting with Polyclonal Antibodies
3.1.2. Indirect ELISA
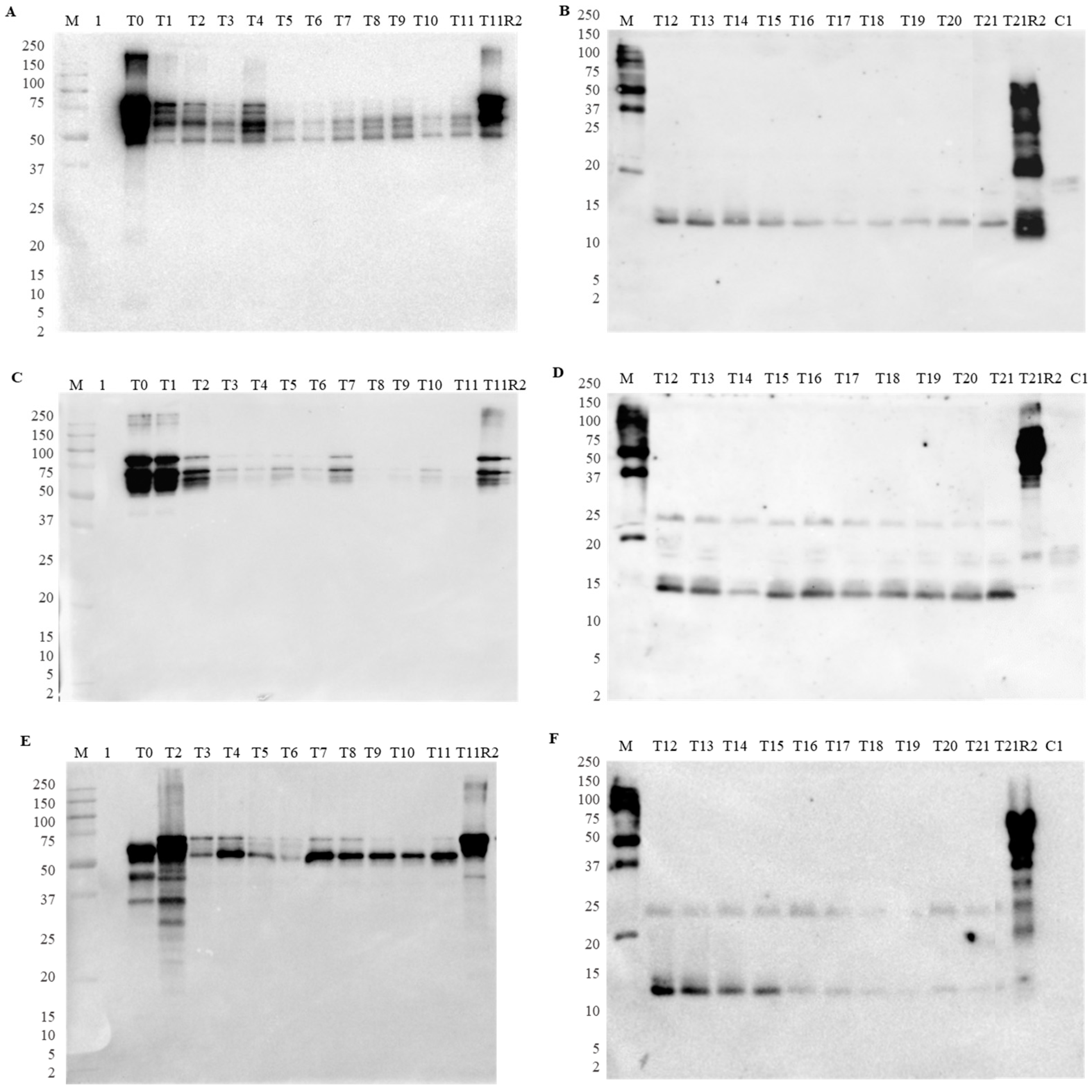
3.2. Effect of Gastrointestinal Digestion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boukid, F.; Pasqualone, A. Lupine (Lupinus spp.) proteins: Characteristics, safety and food applications. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohajdova, Z.; Karovičova, J.; Schmidt, Š. Lupin composition and possible use in bakery—A review. Czech J. Food Sci. 2011, 29, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations—Statistics Division. 2021. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Sanz, M.L.; De Las Marinas, M.D.; Fernández, J.; Gamboa, P.M. Lupin allergy: A hidden killer in the home. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, C.; Moura, M.B.M.V.; Costa, J.; Mafra, I. Immunoreactivity of lupine and soybean allergens in foods as affected by thermal processing. Foods 2020, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefle, S.L.; Lemanske, R.F., Jr.; Bush, R.K. Adverse reaction to lupine-fortified pasta. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 94, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of 25 October 2011 on the Provision of Food Information to Consumers, Amending Regulations (EC) No 1924/2006 and (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and Repealing Commission Directive 87/250/EEC, Council Directive 90/496/EEC, Commission Directive 1999/10/EC, Directive 2000/13/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Directives 2002/67/EC and 2008/5/EC and Commission Regulation (EC) No 608/2004. L304, 18–63. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=celex%3A32011R1169 (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Villa, C.; Costa, J.; Mafra, I. Lupine allergens: Clinical relevance, molecular characterization, cross-reactivity, and detection strategies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3886–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ALLERGEN. World Health Organization/International Union of Immunological Societies (WHO/IUIS) Allergen Nomenclature Sub-Committee. Available online: http://allergen.org/ (accessed on 3 February 2024).
- ALLERGOME. Allergome Database, the Platform for Allergen Knowledge; ALLERGOME: Latina, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Magni, C.; Ballabio, C.; Restani, P.; Sironi, E.; Scarafoni, A.; Poiesi, C.; Duranti, M. Two-dimensional electrophoresis and Western-blotting analyses with anti Ara h 3 basic subunit IgG evidence the cross-reacting polypeptides of Arachis hypogaea, Glycine max, and Lupinus albus seed proteomes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2275–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, M.; Consonni, A.; Magni, C.; Sessa, F.; Scarafoni, A. The major proteins of lupin seed: Characterisation and molecular properties for use as functional and nutraceutical ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Insunza, R.; Iturriaga, C.; Mariñanco, A.; Venegas, L.; Aravena, G.; Perez-Mateluna, G.; Baptista-Dias, N.; Borzutzky, A.; Wandersleben, T. High prevalence of lupin allergy among patients with peanut allergy: Identification of γ-conglutin as major allergen. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 130, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Bavaro, S.L.; Benedé, S.; Diaz-Perales, A.; Bueno-Diaz, C.; Gelencser, E.; Klueber, J.; Larré, C.; Lozano-Ojalvo, D.; Lupi, R.; et al. Are physicochemical properties shaping the allergenic potency of plant allergens? Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 62, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loza, A.; Lampart-Szczapa, E. Allergenicity of lupine proteins—A review. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2008, 58, 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Bøgh, K.L.; Madsen, C.B. Food allergens: Is there a correlation between stability to digestion and allergenicity? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 1545–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czubiński, J.; Siger, A.; Lampart-Szczapa, E. Digestion susceptibility of seed globulins isolated from different lupin species. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bio-Rad. Mini-PROTEAN® Tetra Cell Instruction Manual. Available online: https://www.biorad.com/webroot/web/pdf/lsr/literature/10007296D.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Bio-Rad. Trans-Blot® Turbo™ Transfer System Instruction Manual. Available online: https://www.bio-rad.com/sites/default/files/webroot/web/pdf/lsr/literature/10000071567.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2024).
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mane, S.P.; Johnson, S.K.; Duranti, M.; Pareek, V.K.; Utikar, R.P. Lupin seed γ-conglutin: Extraction and purification methods—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 73, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czubinski, J.; Barciszewski, J.; Gilski, M.; Szpotkowski, K.; Debski, J.; Lampart-Szczapa, E.; Jaskolski, M. Structure of γ-conglutin: Insight into the quaternary structure of 7S basic globulins from legumes. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. 2015, 71, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czubiński, J.; Montowska, M.; Fornal, E. Post-translational cleavage pattern of Lupinus angustifolius γ-conglutin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5212–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapadia, M.; Johnson, S.; Utikar, R.; Newsholme, P.; Carlessi, R. Antidiabetic effects and mechanisms of action of γ-conglutin from lupin seeds. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 87, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Álvarez, J.; Guillamón, E.; Crespo, J.F.; Cuadrado, C.; Burbano, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Fernández, C.; Muzquiz, M. Effects of extrusion, boiling, autoclaving, and microwave heating on lupine allergenicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranti, M.; Sessa, F.; Scarafoni, A.; Bellini, T.; Dallocchio, F. Thermal stabilities of lupin seed conglutin γ protomers and tetramers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Hijazo, B.; Garcés, M.M.; Caballero, M.L.; Alloza, P.; Moneo, I. Unsuspected lupin allergens hidden in food. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 2006, 141, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirtori, E.; Resta, D.; Brambilla, F.; Zacherl, C.; Arnoldi, A. The effects of various processing conditions on a protein isolate from Lupinus angustifolius. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, L.; Sletten, G.; Lindvik, H.; Fæste, C.; Dooper, M. Characterization of IgE binding to lupin, peanut and almond with sera from lupin-allergic patients. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 2008, 146, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czubinski, J.; Lattová, E.; Zdráhal, Z.; Strasser, R. Characteristics of N-glycosylation and its impact on the molecular behavior of Lupinus angustifolius γ-conglutin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 7359–7369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiarea, S.; Arnoldi, L.; Fanelli, R.; De Combarieu, E.; Chiabrando, C. In-depth glycoproteomic characterization of γ-conglutin by high-resolution accurate mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czubinski, J.; Dwiecki, K.; Siger, A.; Neunert, G.; Lampart-Szczapa, E. Characterisation of different digestion susceptibility of lupin seed globulins. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czubinski, J.; Montowska, M.; Springer, E.; Pospiech, E.; Lampart-Szczapa, E. Immunoreactivity changes during lupin seed storage proteins digestion. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capraro, J.; Magni, C.; Scarafoni, A.; Duranti, M. Susceptibility of lupin γ-conglutin, the plasma glucose-lowering protein of lupin seeds, to proteolytic enzymes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8612–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Treatment | γ-Conglutin (mg/mL) | Coefficient of Variation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L. luteus | Raw pasta | 2.47 ± 0.11 | 4.54 |
| Boiled pasta | 1.50 ± 0.24 | 15.6 | |
| Boiling water | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 9.12 | |
| Gastric digestion (T11) | 0.023 ± 0.001 | 6.22 | |
| Intestinal digestion (T21) | n.d. * | - | |
| L. angustifolius | Raw pasta | 1.23 ± 0.14 | 11.2 |
| Boiled pasta | 1.22 ± 0.06 | 5.07 | |
| Boiling water | 0.001 ± 0.000 | 24.8 | |
| Gastric digestion (T11) | 0.027 ± 0.001 | 4.73 | |
| Intestinal digestion (T21) | n.d. * | - | |
| L. albus | Raw pasta | 0.023 ± 0.001 | 4.61 |
| Boiled pasta | 1.17 ± 0.10 | 8.73 | |
| Boiling water | 0.0004 ± 0.0001 | 27.1 | |
| Gastric digestion (T11) | 0.024 ± 0.003 | 14.5 | |
| Intestinal digestion (T21) | n.d. * | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villa, C.; Carriço-Sá, B.; Teixeira, C.S.S.; Dias, C.; Costa, R.; M. Pereira, C.; Mafra, I.; Costa, J. γ-Conglutin Immunoreactivity Is Differently Affected by Thermal Treatment and Gastrointestinal Digestion in Lupine Species. Foods 2024, 13, 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152330
Villa C, Carriço-Sá B, Teixeira CSS, Dias C, Costa R, M. Pereira C, Mafra I, Costa J. γ-Conglutin Immunoreactivity Is Differently Affected by Thermal Treatment and Gastrointestinal Digestion in Lupine Species. Foods. 2024; 13(15):2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152330
Chicago/Turabian StyleVilla, Caterina, Bruno Carriço-Sá, Carla S. S. Teixeira, Catarina Dias, Renata Costa, Carlos M. Pereira, Isabel Mafra, and Joana Costa. 2024. "γ-Conglutin Immunoreactivity Is Differently Affected by Thermal Treatment and Gastrointestinal Digestion in Lupine Species" Foods 13, no. 15: 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152330
APA StyleVilla, C., Carriço-Sá, B., Teixeira, C. S. S., Dias, C., Costa, R., M. Pereira, C., Mafra, I., & Costa, J. (2024). γ-Conglutin Immunoreactivity Is Differently Affected by Thermal Treatment and Gastrointestinal Digestion in Lupine Species. Foods, 13(15), 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152330












