The Potential of Co-Fermentation of Whole-Plant Cassava with Piper sarmentosum: A Comprehensive Study of Fermentation Quality, Antioxidant Activity, Bacterial Community Structure, and Microbial Ecological Networks in Novel Foods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Antioxidant Activity, Culture-Based Microbial, and Fermentation Index Analysis
2.3. Microbial Community and Function Profile Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Fresh Whole-Plant Cassava and PS
3.2. Nutrition Composition, Fermentation Characteristics, and Antioxidant Capacity of Co-Fermented Whole-Plant Cassava and PS
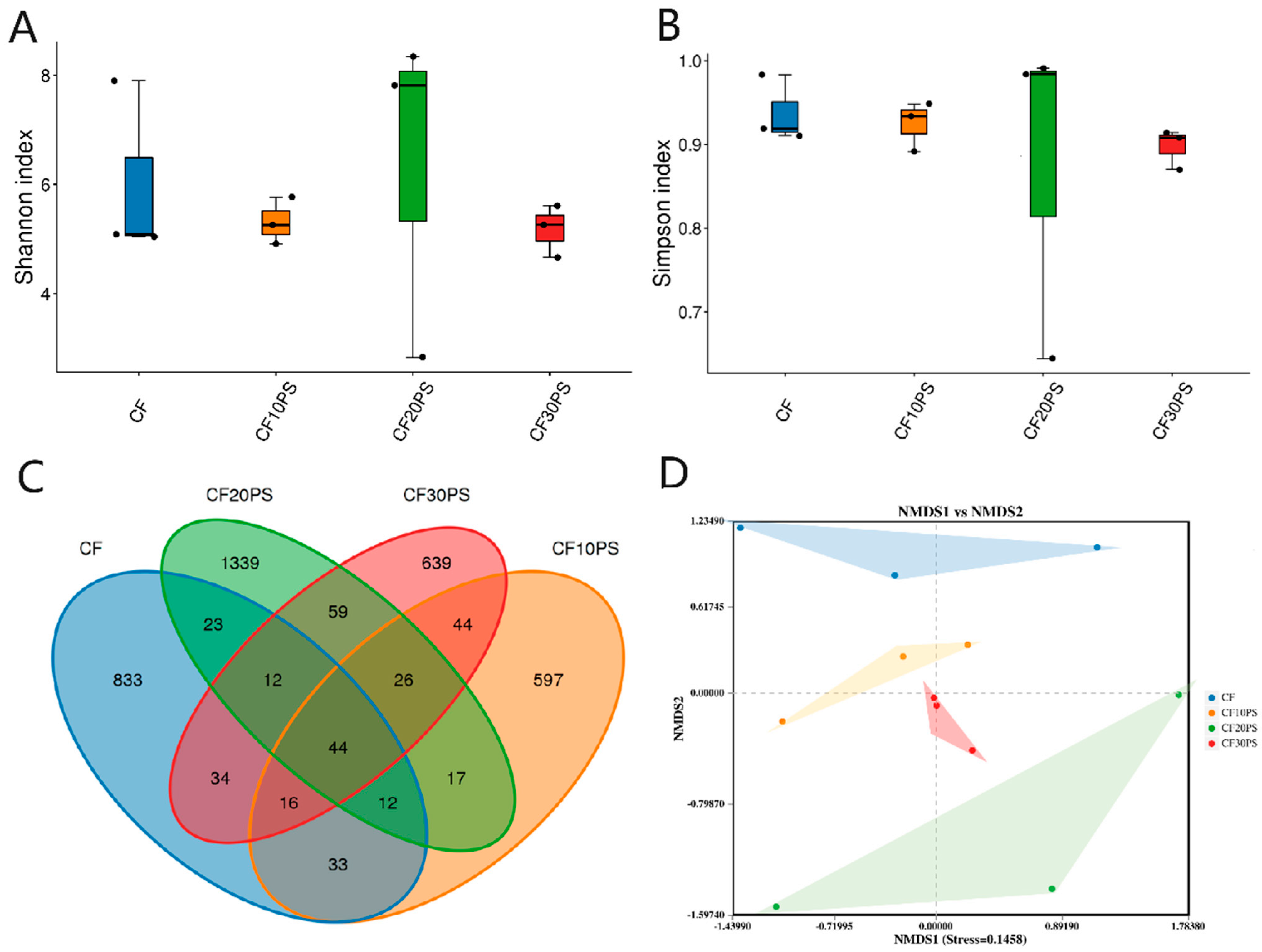
3.3. Bacterial Community Structure and Predicted Functions in Co-Fermented Whole-Plant Cassava and PS
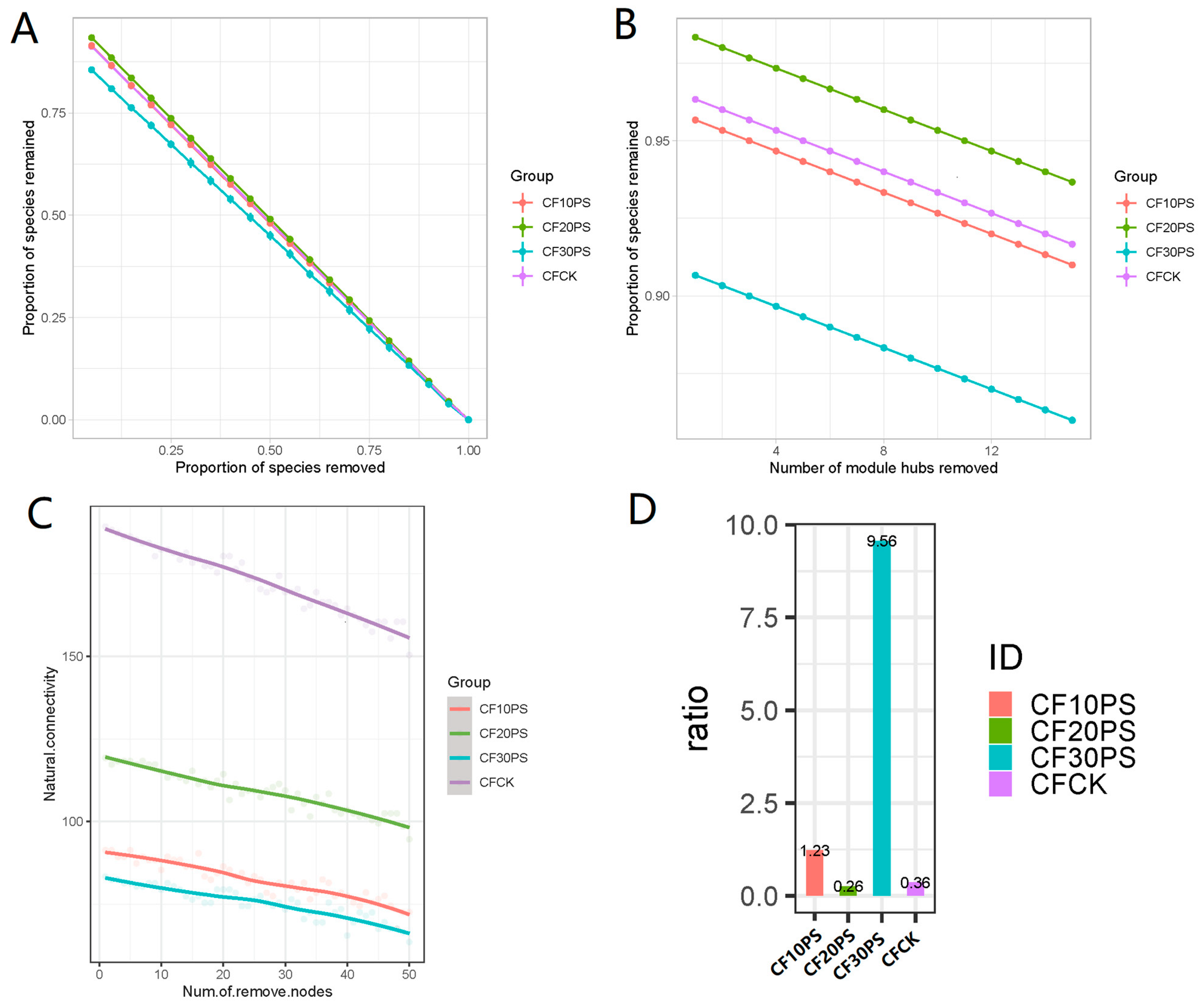
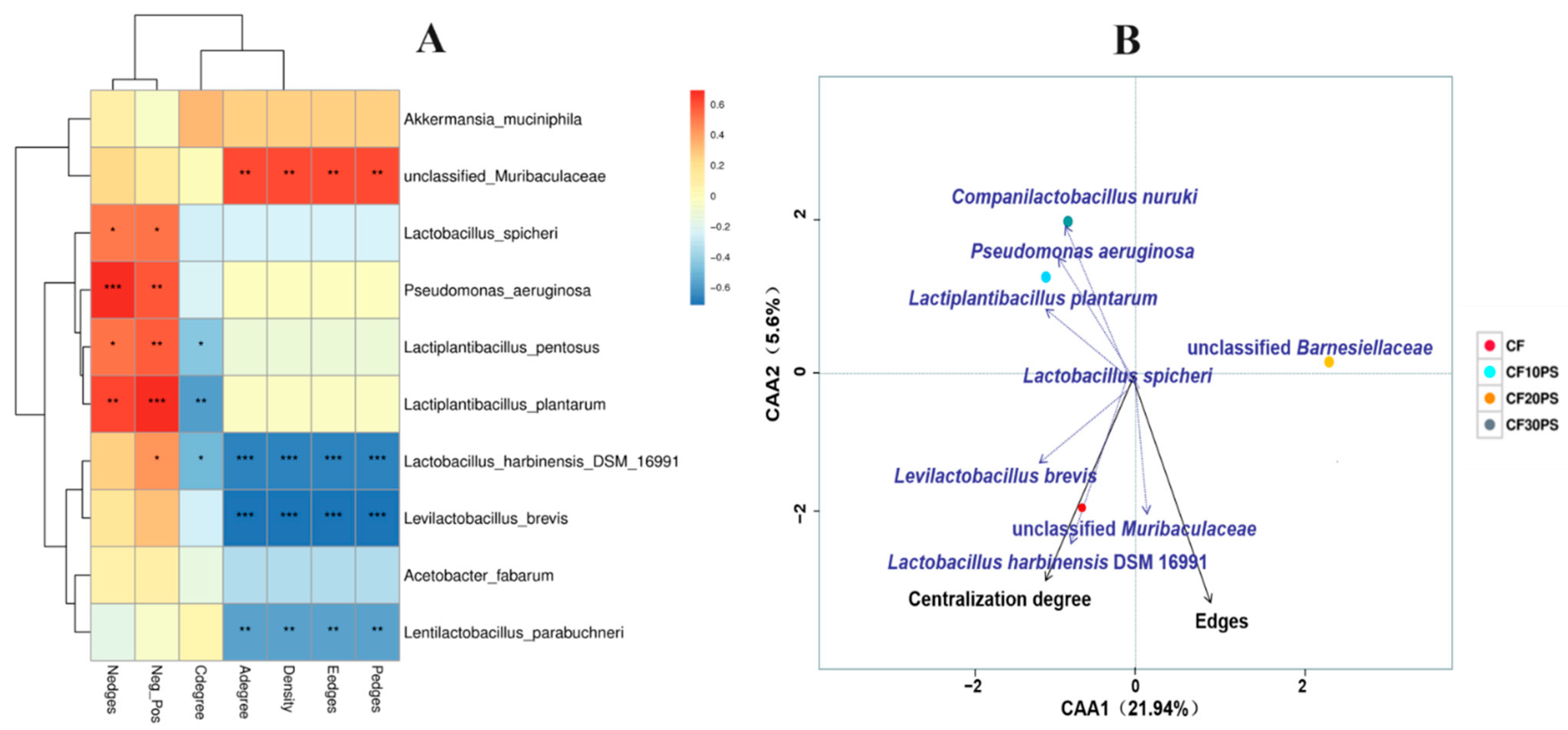
3.4. Bacterial Co-Occurrence Network, Network Modules, and Stability in Co-Fermented Whole-Plant Cassava and PS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malik, A.I.; Kongsil, P.; Nguyễn, V.A.; Ou, W.; Sholihin; Srean, P.; Sheela, M.N.; Becerra López-Lavalle, L.A.; Utsumi, Y.; Lu, C.; et al. Cassava breeding and agronomy in Asia: 50 years of history and future directions. Breed. Sci. 2020, 70, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyanwu, C.N.; Ibeto, C.N.; Ezeoha, S.L.; Ogbuagu, N.J. Sustainability of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) as industrial feedstock, energy and food crop in Nigeria. Renew. Energy 2015, 81, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampa, M.; Sutthanut, K.; Weerapreeyakul, N.; Tukummee, W.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S. Multiple Bioactivities of Manihot esculenta Leaves: UV Filter, Anti-Oxidation, Anti-Melanogenesis, Collagen Synthesis Enhancement, and Anti-Adipogenesis. Molecules 2022, 27, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laya, A.; Koubala, B.B.; Negi, P.S. Antidiabetic (α-amylase and α-glucosidase) and anti-obesity (lipase) inhibitory activities of edible cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) as measured by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion: Effects of phenolics and harvested time. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, I.; Apiamu, A.; Egbune, E.O.; Tonukari, N.J. Biochemical Characterization of Solid-State Fermented Cassava Stem (Manihot esculenta Crantz-MEC) and Its Application in Poultry Feed Formulation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2620–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, N.S.; Torres-Mendoza, L.J.; Abelilla, J.J.; Stein, H.H. Chemical composition of cassava-based feed ingredients from South-East Asia. Anim. Biosci. 2023, 36, 908–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isamah, G.K.; Asagba, S.O.; Ekakitie, A.O. Lipid peroxidation, activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase during post-harvest deterioration of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) root tubers. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2003, 52, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayode, B.I.; Kayode, R.M.O.; Salami, K.O.; Obilana, A.O.; George, T.T.; Dudu, O.E.; Adebo, O.A.; Njobeh, P.B.; Diarra, S.S.; Oyeyinka, S.A. Morphology and physicochemical properties of starch isolated from frozen cassava root. LWT 2021, 147, 111546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogale, S.; Haile, A.; Berhanu, B.; Beshir, H.M. Cassava production practices in Ethiopia and its use as Ingredient for injera making. Future Foods 2022, 6, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, L.T.; Silva, J.J.; Soto, T.S.; Doná, S.; Iamanaka, B.T.; Fungaro, M.H.P.; Taniwaki, M.H. Fungal communities in Brazilian cassava tubers and food products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 384, 109909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbune, E.O.; Ezedom, T.; Orororo, O.C.; Egbune, O.U.; Avwioroko, O.J.; Aganbi, E.; Anigboro, A.A.; Tonukari, N.J. Solid-state fermentation of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz): A review. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ananga, A.; Ukuku, D.O.; Aryee, A.N.A. High Salt Concentration Affects the Microbial Diversity of Cassava during Fermentation, as Revealed by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing. Fermentation 2023, 9, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesulu-Dahunsi, A.T.; Dahunsi, S.O.; Ajayeoba, T.A. Co-occurrence of Lactobacillus Species During Fermentation of African Indigenous Foods: Impact on Food Safety and Shelf-Life Extension. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 684730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.L.; Bressani, A.P.P.; Batista, N.N.; Martinez, S.J.; Dias, D.R.; Schwan, R.F. Indigenous fermented foods: Nutritional and safety aspects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 53, 101075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Ni, K.; Yang, F. Innovative utilization of herbal residues: Exploring the diversity of mechanisms beneficial to regulate anaerobic fermentation of alfalfa. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhou, W.; Wu, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Dynamic changes in the bacterial communities and metabolites of Moringa oleifera leaves during fermentation with or without pyroligneous acid. LWT 2023, 177, 114593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, H.; Hou, G. Chemical composition and anti-inflammatory activity of n-butanol extract of Piper sarmentosum Roxb. In the intestinal porcine epithelial cells (IPEC-J2). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 269, 113723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Zhou, H. Metabolic profiling of two medicinal Piper species. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 139, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Lyu, J.K.; Chen, X. Alkaloids from leaves of Piper sarmentosum. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2023, 35, 231–235. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.M.; Guo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, N.; Ning, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Climate warming enhances microbial network complexity and stability. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Xie, P.; Yang, S.; Niu, G.; Liu, X.; Ding, Z.; Xue, C.; Liu, Y.-X.; Shen, Q.; Yuan, J. ggClusterNet: An R package for microbiome network analysis and modularity-based multiple network layouts. iMeta 2022, 1, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zi, X.; Sun, R.; Ou, W.; Chen, S.; Hou, G.; Zhou, H. Co-Ensiling Whole-Plant Cassava with Corn Stalk for Excellent SilageProduction: Fermentation Characteristics, Bacterial Community, Function Profile, and Microbial Ecological Network Features. Agronomy 2024, 14, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ding, Z.; Su, R.; Wang, M.; Cheng, M.; Xie, D.; Guo, X. Storage Temperature Is More Effective than Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculations in Manipulating Fermentation and Bacterial Community Diversity, Co-Occurrence and Functionality of the Whole-Plant Corn Silage. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0010122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Shi, W.; Sun, J.; Xia, T.; Huang, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Teng, K.; Zhong, J. Dynamic Changes in Fermentation Quality and Structure and Function of the Microbiome during Mixed Silage of Sesbania cannabina and Sweet Sorghum Grown on Saline-Alkaline Land. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0248322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Dong, D.; Shao, T. Diurnal Variation of Epiphytic Microbiota: An Unignorable Factor Affecting the Anaerobic Fermentation Characteristics of Sorghum-Sudangrass Hybrid Silage. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0340422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; AOAC: Arlington, VA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Franco, M.; Ding, Z.; Hao, L.; Ke, W.; Wang, M.; Xie, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, L.; et al. Effect of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus subtilis on fermentation, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts of whole-plant corn silage. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Usman, S.; Ding, Z.; Hao, L.; Guo, X. Probiotic effect of feruloyl esterase-producing Lactobacillus plantarum inoculated alfalfa silage on digestion, antioxidant, and immunity status of lactating dairy goats. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 11, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Li, X.; Guan, H.; Yang, W.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Du, Z.; Li, X.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. Dynamic microbial diversity and fermentation quality of the mixed silage of corn and soybean grown in strip intercropping system. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Shi, S.; Cai, Y. Characteristics of isolated lactic acid bacteria and their effectiveness to improve stylo (Stylosanthes guianensis Sw.) silage quality at various temperatures. Anim. Sci. J. 2012, 83, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, W.; Dai, W.; Xin, H.; Rahmand, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L.; Han, T. Piper sarmentosum Roxb.: A review on its botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 112897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouassi, K.B.; Nindjin, C.; Kouassi, K.N.; Amani, N.G.G. Specific qualities of pressed fermented cassava doughs used for attiéké production based on their geographical origin in Côte d’Ivoire. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 2617–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Wang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Su, R.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J. Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zi, X.; Zhou, H.; Lv, R.; Tang, J.; Cai, Y. Effect of lactic acid bacteria, molasses, and their combination on the fermentation quality and bacterial community of cassava foliage silage. Anim. Sci. J. 2021, 92, e13635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Franco, M.; Cai, Y.; Yu, Z. Dynamics of fermentation profile and bacterial community of silage prepared with alfalfa, whole-plant corn and their mixture. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 270, 114702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.S.; Ke, W.C.; Ding, W.R.; Ding, L.M.; Xu, D.M.; Wang, W.W.; Zhang, P.; Yang, F.Y. Profiling of metabolome and bacterial community dynamics in ensiled Medicago sativa inoculated without or with Lactobacillus plantarum or Lactobacillus buchneri. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, S.; Zou, X.; Ruan, S.; Kholif, A.E.; Hu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W. Effects of Neolamarckia cadamba leaves extract on methanogenesis, microbial community in the rumen and digestibility of stylo silage. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effect of cellulase and Lactobacillus casei on ensiling characteristics, chemical composition, antioxidant activity, and digestibility of mulberry leaf silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9919–9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeledo, E.; Latif, S.; Abass, A.; Müller, J. Antioxidant potential of extracts from peels and stems of yellow-fleshed and white cassava varieties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dike, K.S.; Okafor, C.P.; Ohabughiro, B.N.; Maduwuba, M.C.; Ezeokoli, O.T.; Ayeni, K.I.; Okafor, C.M.; Ezekiel, C.N. Analysis of bacterial communities of three cassava-based traditionally fermented Nigerian foods (abacha, fufu and garri). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 74, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lv, R.; Zhou, H.; Zi, X. Dynamics and correlations of chlorophyll and phytol content with silage bacterial of different growth heights Pennisetum sinese. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 996970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zi, X.; Lv, R.; Tang, J.; Zhou, H. Impacts of Citric Acid and Malic Acid on Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Cassava Foliage Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 595622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, N.; Rinne, M.; Ke, W.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Da, M.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, X. The bacterial community and metabolome dynamics and their interactions modulate fermentation process of whole crop corn silage prepared with or without inoculants. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Sun, L.; Lin, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, F.; Cai, Y. Use of Napier grass and rice straw hay as exogenous additive improves microbial community and fermentation quality of paper mulberry silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2022, 285, 115219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thébault, E.; Fontaine, C. Stability of ecological communities and the architecture of mutualistic and trophic networks. Science 2010, 329, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toju, H.; Yamamichi, M.; Guimarães, P.R., Jr.; Olesen, J.M.; Mougi, A.; Yoshida, T.; Thompson, J.N. Species-rich networks and eco-evolutionary synthesis at the metacommunity level. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Items | Abbreviation | Whole-Plant Cassava | Piper sarmentosum | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry matter (g/kg FM) | DM | 312.5 ± 17.18 a | 192.4 ± 15.34 b | <0.05 | |
| Crude protein (g/kg DM) | CP | 158.6 ± 9.64 a | 41.9 ± 2.55 b | <0.05 | |
| Acid detergent fiber (g/kg DM) | ADF | 116.8 ± 8.73 a | 62.5 ± 4.38 b | <0.05 | |
| Neutral detergent fiber (g/kg DM) | NDF | 158.9 ± 16.41 a | 86.1 ± 6.04 b | <0.05 | |
| Water soluble carbohydrates (g/kg DM) | WSC | 177.2 ± 22.5 a | 38.7 ± 3.59 b | <0.05 | |
| Starch (g/kg DM) | 215.9 ± 14.6 a | 12.4 ± 0.83 b | <0.05 | ||
| Lactic acid bacteria (Log cfu/g FM) | LAB | 5.76 ± 0.45 | 5.28 ± 0.66 | >0.05 | |
| Mold (Log cfu/g FM) | 2.43 ± 0.18 a | 1.52 ± 0.12 b | <0.05 | ||
| Enterobacter (Log cfu/g FM) | 2.68 ± 0.23 a | 1.73 ± 0.17 b | <0.05 |
| Items | Treatments | SEM | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFCK | CF10PS | CF20PS | CF30PS | T | L | ||
| Nutrition composition, g/kgDM | |||||||
| DM (g/kg FM) | 301.3 ± 20.7 a | 294.0 ± 15.6 b | 283.5 ± 17.6 c | 269.2 ± 18.1 d | 7.0 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| CP (DM) | 142.5 ± 7.1 a | 131.8 ± 8.0 b | 121.6 ± 9.6 c | 111.7 ± 7.9 d | 6.6 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| ADF | 94.1 ± 6.2 a | 89.3 ± 4.3 a | 85.7 ± 8.3 b | 81.8 ± 3.9 b | 2.6 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| NDF | 132.4 ± 10.7 a | 125.8 ± 7.9 ab | 120.6 ± 11.4 b | 115.4 ± 6.3 c | 3.6 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| WSC | 92.0 ± 6.6 a | 84.8 ± 3.4 b | 76.5 ± 7.0 c | 70.4 ± 4.5 d | 4.7 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Starch | 155.4 ± 14.8 a | 138.6 ± 9.2 b | 125.2 ± 13.5 c | 109.7 ± 7.9 d | 9.7 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
| Fermentation characteristics, g/kg DM | |||||||
| pH | 4.27 ± 0.1 a | 4.08 ± 0.07 b | 4.33 ± 0.12 a | 4.03 ± 0.06 b | 0.1 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| Lactic acid | 46.93 ± 4.5 b | 58.24 ± 2.7 a | 40.7 ± 3.6 c | 61.8 ± 3.1 a | 2.8 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| Acetic acid | 19.28 ± 1.5 b | 11.2 ± 0.8 c | 30.5 ± 2.5 a | 9.7 ± 0.7 c | 5.8 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| Propionic acid | 4.16 ± 0.12 a | 1.5 ± 0.05 b | 1.8 ± 0.06 b | 1.6 ± 0.05 b | 0.1 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| Butyric acid | 0.88 ± 0.07 a | N | N | N | N | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| NH3-N/Total N | 85.78 ± 6.1 a | 45.4 ± 2.7 c | 61.2 ± 3.2 b | 47.3 ± 2.8 c | 4.3 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| Antioxidant capacity, U/g FM | |||||||
| T-AOC | 112 ± 16 b | 267 ± 20 a | 283 ± 19 a | 274 ± 17 a | 40.8 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| SOD | 347 ± 25 b | 725 ± 46 a | 740 ± 33 a | 751 ± 50 a | 98.1 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| GSH-Px | 408 ± 28 b | 954 ± 38 a | 893 ± 44 a | 931 ± 52 a | 130.1 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| CAT | 15.6 ± 1.3 a | 8.3 ± 0.8 b | 7.9 ± 0.5 b | 8.6 ± 0.6 b | 1.8 b | <0.05 | >0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Lv, R.; Ou, W.; Chen, S.; Zhou, H.; Hou, G.; Zi, X. The Potential of Co-Fermentation of Whole-Plant Cassava with Piper sarmentosum: A Comprehensive Study of Fermentation Quality, Antioxidant Activity, Bacterial Community Structure, and Microbial Ecological Networks in Novel Foods. Foods 2024, 13, 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132126
Li M, Lv R, Ou W, Chen S, Zhou H, Hou G, Zi X. The Potential of Co-Fermentation of Whole-Plant Cassava with Piper sarmentosum: A Comprehensive Study of Fermentation Quality, Antioxidant Activity, Bacterial Community Structure, and Microbial Ecological Networks in Novel Foods. Foods. 2024; 13(13):2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132126
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mao, Renlong Lv, Wenjun Ou, Songbi Chen, Hanlin Zhou, Guanyu Hou, and Xuejuan Zi. 2024. "The Potential of Co-Fermentation of Whole-Plant Cassava with Piper sarmentosum: A Comprehensive Study of Fermentation Quality, Antioxidant Activity, Bacterial Community Structure, and Microbial Ecological Networks in Novel Foods" Foods 13, no. 13: 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132126
APA StyleLi, M., Lv, R., Ou, W., Chen, S., Zhou, H., Hou, G., & Zi, X. (2024). The Potential of Co-Fermentation of Whole-Plant Cassava with Piper sarmentosum: A Comprehensive Study of Fermentation Quality, Antioxidant Activity, Bacterial Community Structure, and Microbial Ecological Networks in Novel Foods. Foods, 13(13), 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132126





