Soy Protein Isolate Gel Subjected to Freezing Treatment: Influence of Methylcellulose and Sodium Hexametaphosphate on Gel Stability, Texture and Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SPI Gel
2.3. Treatment by Freezing
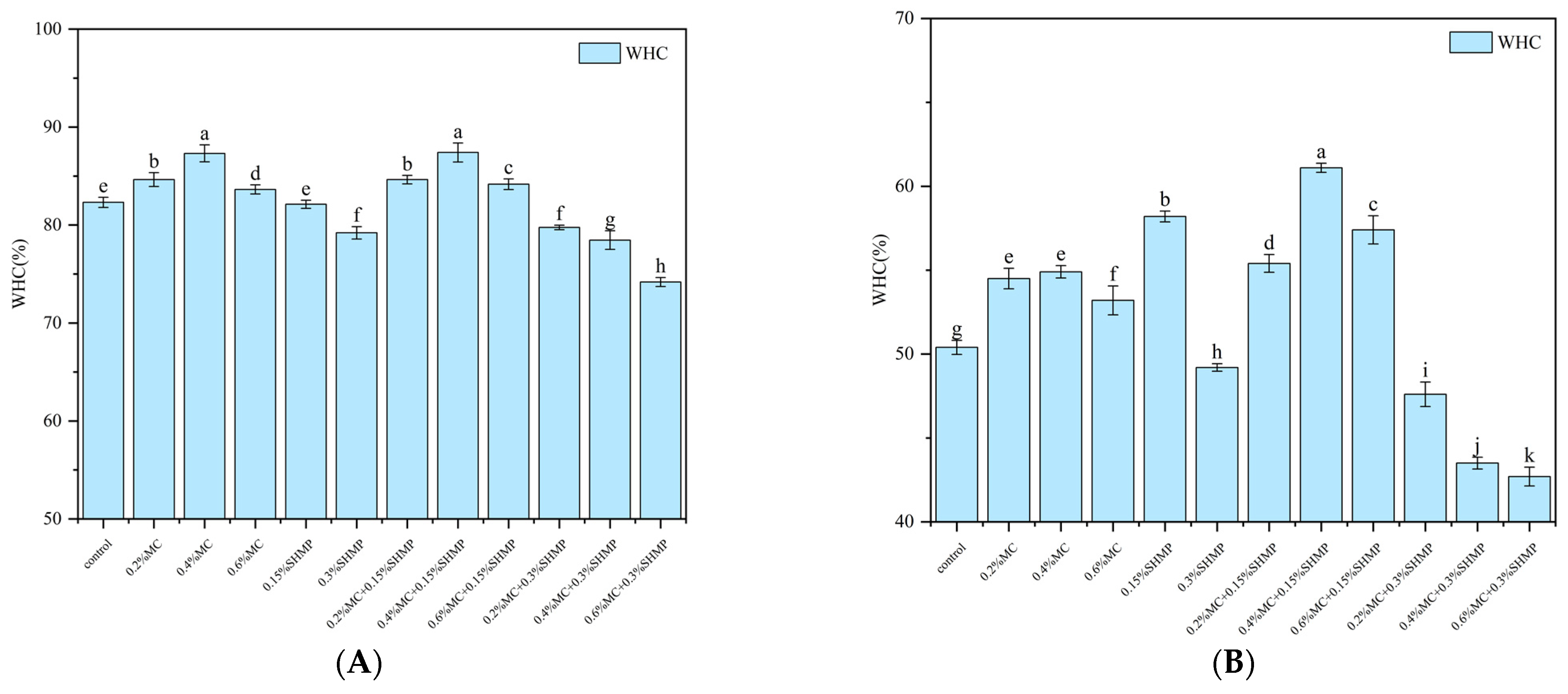
2.4. Water-Holding Capacity
2.5. Texture Properties (TPA)
2.6. Viscoelasticity Analyses
2.7. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR)
2.8. Intermolecular Force
2.9. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
2.10. Microscopy
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water-Holding Capacity
3.2. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
3.3. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA)
3.4. Rheological Properties
3.5. Protein Secondary Structures
3.6. Intermolecular Force
3.7. Microscopy
3.8. Heat Map
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicole, T.Z.H.; Nichelle, T.S.; Elizabeth, T.E.; Yuliarti, O. Formulation of functional crackers enriched with fermented soybean (tempeh) paste: Rheological and microstructural properties. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xiong, Y.L.; Wang, Q.; Shang, K.; Zhang, D. Site-specific incorporation of sodium tripolyphosphate into myofibrillar protein from mantis shrimp (Oratosquilla oratoria) promotes protein crosslinking and gel network formation. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Lee, P.R.; Yang, H.S. Kappa-carrageenan improves the gelation and structures of soy protein isolate through the formation of hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 140, 108585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jiang, L.Z.; Sui, X.N. Incorporating chitin nanocrystal yields stronger soy protein gel: Insights into linear and nonlinear rheological behaviors by oscillatory shear tests. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Sun, L.; Guan, C.X.; Ren, T.; Zhang, Q.L.; Pan, S.H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H. Preparation and properties of salecan-soy protein isolate composite hydrogel induced by thermal treatment and transglutaminase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.J.; He, M.Y.; Yang, H.D.; Wang, N.; Kong, Y.; Li, Y.; Teng, F. Effect of soybean lipophilic protein-methyl cellulose complex on the stability and digestive properties of water-in-oil-in-water emulsion containing vitamin B12. Colloid Surf. A 2021, 629, 127364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, M.L.; Liberman, L.; Ertem, S.P.; Edmund, J.; Bates, F.S.; Lodge, T.P. Methyl cellulose solutions and gels: Fibril formation and gelation properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 112, 101324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudyal, R.L.; Rika, K.; Toru, S.; Watanabe, M. Effect of different freezing and storage condition on the physical properties of protein coagulum (Firm Tofu). Int. J. Refrig. 2019, 107, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Wang, B.; Li, H.J.; Liu, H.T.; Shi, S.; Feng, J.; Pan, N.; Xia, X.F. Research progress on quality deterioration mechanism and control technology of frozen muscle foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 4812–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.B.; Yu, J.; Chen, S.; Ge, H.G.; Jiang, L.Z. Freeze-thaw stability of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by soy protein isolate-dextran conjugates. LWT 2017, 78, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, N.; Mehdi, V.; Fatemeh, A. Licorice extract/whey protein isolate/sodium alginate ternary complex-based bioactive food foams as a novel strategy to substitute fat and sugar in ice cream. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, H.Z.; Lin, W.F.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.H. Freeze-thaw-stable high internal phase emulsions stabilized by soy protein isolate and chitosan complexes at pH 3.0 as promising mayonnaise replacers. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Bakry, A.M.; Zeng, S.W.; Xiong, S.B.; Yin, T.; You, J.; Fan, M.C.; Huang, Q.L. Effect of phosphates on gelling characteristics and water mobility of myofibrillar protein from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Food Chem. 2019, 272, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.B.; Chen, J.H.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, L. Impact of phosphates on heat-induced egg white gel properties: Texture, water state, micro-rheology and microstructure. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 110, 106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M. Texture analyzers for food quality evaluation. Eval. Technol. Food Qual. 2019, 17, 441–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanger, C.; Andlinger, D.J.; Brümmer-Rolf, A.; Engel, J.; Kulozik, U. Quantification of protein-protein interactions in highly denatured whey and potato protein gels. Methods X 2021, 8, 101243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.X.; Lei, Y.C.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J. Rheological and structural properties of sodium caseinate as influenced by locust bean gum and κ-carrageenan. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Y.; Sun, F.D.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.H. Modification of gel properties of soy protein isolate by freeze-thaw cycles are associated with changes of molecular force involved in the gelation. Process Biochem. 2017, 52, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Liu, J.N.; Wang, G.R.; Zhang, A.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.H. Effect of freeze-thaw treatment on the structure and texture of soy protein-dextran conjugate gels crosslinked by transglutaminase. LWT 2022, 153, 112443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Guo, C.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y.R. Acid-induced mixed methylcellulose and casein gels: Structures, physical properties and formation mechanism. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Yu, L.; Duan, Q.; Miao, S.; Liu, H.; Shen, W.; Jin, W. Morphology and rheology of a cool-gel (protein) blended with a thermo-gel (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose). Foods 2022, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Q.; Xiong, G.Y.; Fun, L.; Liu, S.L. Water distribution of raw and heat-induced gelation of minced pork paste prepared by soy protein isolates and carrageenan: Ingredients modify the gelation of minced pork. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2019, 43, e14221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Wang, J.; Zhai, J.L.; Gu, L.P.; Su, Y.J.; Chang, C.H.; Yang, Y.J. Improving gelling properties of diluted whole hen eggs with sodium chloride and sodium tripolyphosphate: Study on intermolecular forces, water state and microstructure. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.H.; Wang, W.; Jia, Z.H.; Yi, S.M.; Li, J.R.; Li, X.P.; Guo, X.H.; Yu, J.Y.; Luo, M.J. Water retention mechanism of phosphate and its research progress on water retention effect of aquatic products. J. Food Saf. Food Qual. 2020, 11, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Yu, M.Q.; Wang, Z.Z.; Luo, K.Y.; Adhikari, B.; Miao, S.T.; Liu, S.T. Modulation of soy protein isolate gel properties by a novel “two-step” gelation process: Effects of pre-aggregation with different divalent sulfates. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaewruang, P.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T. Characteristics and gelling property of phosphorylated gelatin from the skin of unicorn leatherjacket. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Fan, X.K.; Gao, X.; Zhou, C.L. Injection of L-arginine or L-lysine before freezing delays the emulsifying and gelling properties deterioration of myofibrillar proteins of frozen porcine Longissimus lumborum muscle. Food Chem. 2023, 427, 136736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorat, A.A.; Munjal, B.; Geders, T.W.; Suryanarayanan, R. Suryanarayanan. Freezing-induced protein aggregation-Role of pH shift and potential mitigation strategies. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyawaki, O.; Omote, C.; Matsuhira, K. Matsuhira. Thermodynamic Analysis of Sol-Gel Transition of Gelatin in Terms of Water Activity in Various Solutions. Biopolymers 2015, 103, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klangmuang, P.; Sothornvit, R. Combination of beeswax and nanoclay on barriers, sorption isotherm and mechanical properties of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-based composite films. LWT 2016, 65, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.W.; He, D.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Duan, X.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Yue, Y.; Zhan, F.C.; Li, B.; Teng, Y.T. Adenosine monophosphate boosts the cryoprotection of ultrasound-assisted freezing to frozen surimi: Insights into protein structures and gelling behaviors. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.R.; Zang, M.W.; Zhao, B.; Wang, S.W.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhu, N.; Liu, M.; Li, S.; Lv, G.; Liu, B.; et al. Effect of citrus fiber on the phosphate-mediated gel properties of myofibrillar protein and partial replacement of phosphate. LWT 2023, 173, 114274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Ye, S.Q.; Han, K.; Zhu, G.L.; Ma, M.H.; Cai, Z.X. Consequences of phosphorylation on the structural and foaming properties of ovalbumin under wet-heating conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Ni, Y.Y.; Hu, X.S.; Li, Q.H. Effect of phosphorylation on antioxidant activities of pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo, Lady godiva) polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Wi, G.; Choi, M.J. The rheological properties and stability of gelled emulsions applying to x-carrageenan and methyl cellulose as an animal fat replacement. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 136, 108243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.S.; Jin, Y.G.; Sheng, L. Impact of microwave assisted phosphorylation on the physicochemistry and rehydration behaviour of egg white powder. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Heublein, B.; Fink, H.P.; Bohn, A. Cellulose: Fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3358–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouda, M.; Zhang, S.S.; Liu, Y.Y.; Sheng, L.; Ma, M.H. Effects of four natural antioxidant phenyl terpenes on emulsifying and rheological properties of egg yolk. LWT 2017, 83, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Wang, X.Q.; Zeng, Q.M. Research progress on oxidation process, mechanism, detection technology and influencing factors of vegetable oil. Food Ferment. Ind. 2016, 42, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Magalhaes, S.; Alves, L.; Antunes, F.; Miguel, M.; Lindman, B.; Medronho, B. Cellulose-based edible films for probiotic entrapment. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 88, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, N.; Abbasi, S.; Azarikia, F.; Azizi, M.H. Solubilization of concentrated protein dispersion: Effect of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP). Food Chem. 2023, 400, 133980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.W.; Liu, J.N.; Wang, G.R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, A.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.B. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on freeze-thaw stability of soy protein isolate gel. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, M.A.; Wright, A.J.; Marangoni, A.G. Nanostructuring fiber morphology and solvent inclusions in 12-hydroxystearic acid/canola oil organogels. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 14, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.J.; Zhou, Q.; Dai, Y.M.; Lei, C.G.; Ding, L.Y. Effect of different thawing methods and antifreeze treatment on the quality of frozen sea bass (Percafluviatilis) fillets. Food Ferment. Ind. 2020, 46, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cao, Y.; Yin, T.; Huang, Q.L. Inhibitive effect of trehalose and sodium pyrophosphate on oxidation and structural changes of myofibrillar proteins in silver carp surimi during frozen storage. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 184361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabizadeh, M.; Jamali, S. Life and death of colloidal bonds control the rate-dependent rheology of gels. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Zeng, Q.H.; Liang, M.; Wang, L.; Cheng, S. Effects of xanthan gum on rheological properties and microstructure of soy protein isolate gel. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2022, 43, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Li, P.J.; Xu, B.C. Insight into the mechanism of textural deterioration of myofibrillar protein gels at high temperature conditions. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S. Tribo-rheometry behaviour and gel strength of κ-carrageenan and gelatin solutions at concentrations, pH and ionic conditions used in dairy products. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozinsky, V.I.; Damshkaln, L.G.; Brown, R.; Norton, I.T. Study of cryostructuration of polymer systems. XVIII. Freeze-thaw influence on water-solubilized artificial mixtures of amylopectin and amylose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 78, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhang, M.Q.; Zhai, Y.H.; Zhou, B.; Su, Y.J.; Yang, Y.J. Effects of selected phosphate salts on gelling properties and water state of whole egg gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, P.; Salminen, H.; Stadtmueller, L.; Schmitt, C.; Weiss, J. Comparison of binding properties of a laccase-treated pea protein-sugar beet pectin mixture with methylcellulose in a bacon-type meat analogue. Foods 2023, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Wang, Q.M.; Tang, Y.W.; Li, F.H.; Zhao, J.C.; Zhang, Y.H.; Ming, J. Combined effect of carboxymethylcellulose and salt on structural properties of wheat gluten proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Y.B.; Zhou, R.; Wang, H.J.; Ma, Q.Y. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of in-situ multi-component carbides reinforced FeCoNi alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 886, 161215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, S.M.; Xie, B.J.; Xiong, S.B. Contribution of protein conformation and intermolecular bonds to fish and pork gelation properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.L.; Ertbjerg, P.; Estevez, M.; Yuan, L.; Gao, R.C. Freezing of meat and aquatic food: Underlying mechanisms and implications on protein oxidation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5548–5569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupper, N.; Rabin, Y.; Rosenbluh, M. Multiple stages in the aging of a physical polymer gel. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3983–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.J.; Gu, L.P.; Chang, C.H.; Yang, Y.J. Phase separation in ternary composite cold-set gel of egg yolk/κ-carrageenan/xanthan: Study on rheological and proton mobility properties. LWT 2019, 116, 108497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, J.; Langton, M.; Stading, M.; Hermansson, A.M. Simultaneous analysis of the structural and mechanical changes during large deformation of whey protein isolate/gelatin gels at the macro and micro levels. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayase, G.; Yamazaki, K.; Kodaira, T. Fabrication of boehmite nanofiber aerogels by a phosphate gelation process for optical applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2022, 104, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.R.; Rebelo, S.; da Cruz e Silva, O.A.B.; Lopes-da-Silva, J.A. The influence of galactomannans with different amount of galactose side chains on the gelation of soy proteins at neutral pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 33, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memic, A.; Colombani, T.; Eggermont, L.J.; Rezaeeyazdi, M.; Steingold, J.; Rogers, Z.J.; Navare, K.J.; Mohammed, H.S.; Bencherif, S.A. Latest advances in cryogel technology for biomedical applications. Adv. Ther. 2019, 2, 1800114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, C.H. Comparative analysis of 3D printability and rheological properties of surimi gels via LF-NMR and dielectric characteristics. J. Food Eng. 2021, 292, 110278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample Addition | α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Corner | Random Coil | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unfrozen Gel | Frozen Gel | Unfrozen Gel | Frozen Gel | Unfrozen Gel | Frozen Gel | Unfrozen Gel | Frozen Gel | |
| control | 25.32 h | 23.34 j | 34.27 j | 32.88 k | 18.42 f | 22.45 a | 21.98 c | 21.32 d |
| 0.2% MC | 27.51 d | 25.57 e | 37.77 d | 35.44 d | 14.42 k | 20.21 h | 17.31 j | 18.78 h |
| 0.4% MC | 29.49 b | 26.18 d | 37.88 c | 36.82 c | 13.73 l | 19.32 l | 20.90 g | 17.67 j |
| 0.6% MC | 26.25 g | 24.43 g | 38.79 a | 34.32 h | 15.92 h | 19.71 j | 19.04 h | 21.54 c |
| 0.15% SHMP | 27.65 c | 26.76 b | 36.71 f | 36.97 b | 18.46 e | 19.93 i | 17.18 k | 16.33 k |
| 0.3% SHMP | 20.53 l | 24.94 f | 35.84 h | 35.22 f | 22.19 b | 20.32 f | 21.43 e | 19.52 g |
| 0.2% MC + 0.15% SHMP | 30.56 a | 26.56 c | 36.56 g | 35.42 e | 15.11 i | 19.39 k | 17.77 i | 18.62 i |
| 0.4% MC + 0.15% SHMP | 31.44 f | 27.32 a | 37.53 e | 37.94 a | 14.99 j | 20.23 g | 16.04 f | 14.50 l |
| 0.6% MC + 0.15% SHMP | 27.38 e | 24.38 h | 38.56 b | 34.29 i | 17.78 g | 20.95 d | 16.29 l | 20.37 f |
| 0.2% MC + 0.3% SHMP | 21.56 k | 23.56 i | 35.48 i | 34.83 g | 21.11 c | 21.02 c | 21.86 d | 20.60 e |
| 0.4% MC + 0.3% SHMP | 23.44 i | 20.98 k | 33.45 k | 32.98 j | 19.61 d | 21.42 b | 23.50 a | 24.61 b |
| 0.6% MC + 0.3% SHMP | 22.42 j | 18.24 l | 32.43 l | 31.37 l | 22.58 a | 20.45 e | 22.57 b | 29.95 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, X.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Qu, M.; Liu, L.; Sun, B.; Zhu, X. Soy Protein Isolate Gel Subjected to Freezing Treatment: Influence of Methylcellulose and Sodium Hexametaphosphate on Gel Stability, Texture and Structure. Foods 2024, 13, 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132117
Xia X, Zhang B, Huang Y, Zhu Y, Qu M, Liu L, Sun B, Zhu X. Soy Protein Isolate Gel Subjected to Freezing Treatment: Influence of Methylcellulose and Sodium Hexametaphosphate on Gel Stability, Texture and Structure. Foods. 2024; 13(13):2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132117
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Xiaoyu, Binyang Zhang, Yuyang Huang, Ying Zhu, Min Qu, Linlin Liu, Bingyu Sun, and Xiuqing Zhu. 2024. "Soy Protein Isolate Gel Subjected to Freezing Treatment: Influence of Methylcellulose and Sodium Hexametaphosphate on Gel Stability, Texture and Structure" Foods 13, no. 13: 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132117
APA StyleXia, X., Zhang, B., Huang, Y., Zhu, Y., Qu, M., Liu, L., Sun, B., & Zhu, X. (2024). Soy Protein Isolate Gel Subjected to Freezing Treatment: Influence of Methylcellulose and Sodium Hexametaphosphate on Gel Stability, Texture and Structure. Foods, 13(13), 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132117




