Extraction of Lipids and Functional Properties of Defatted Egg Yolk Powder Obtained Using a One-Step Organic Solvent Lipid Extraction Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Lipid Extraction Process
2.2. Fatty Acid Analysis—Lipid Layer Only
2.2.1. Extraction of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters
2.2.2. Gas Chromatography–Flame Ionization Detection
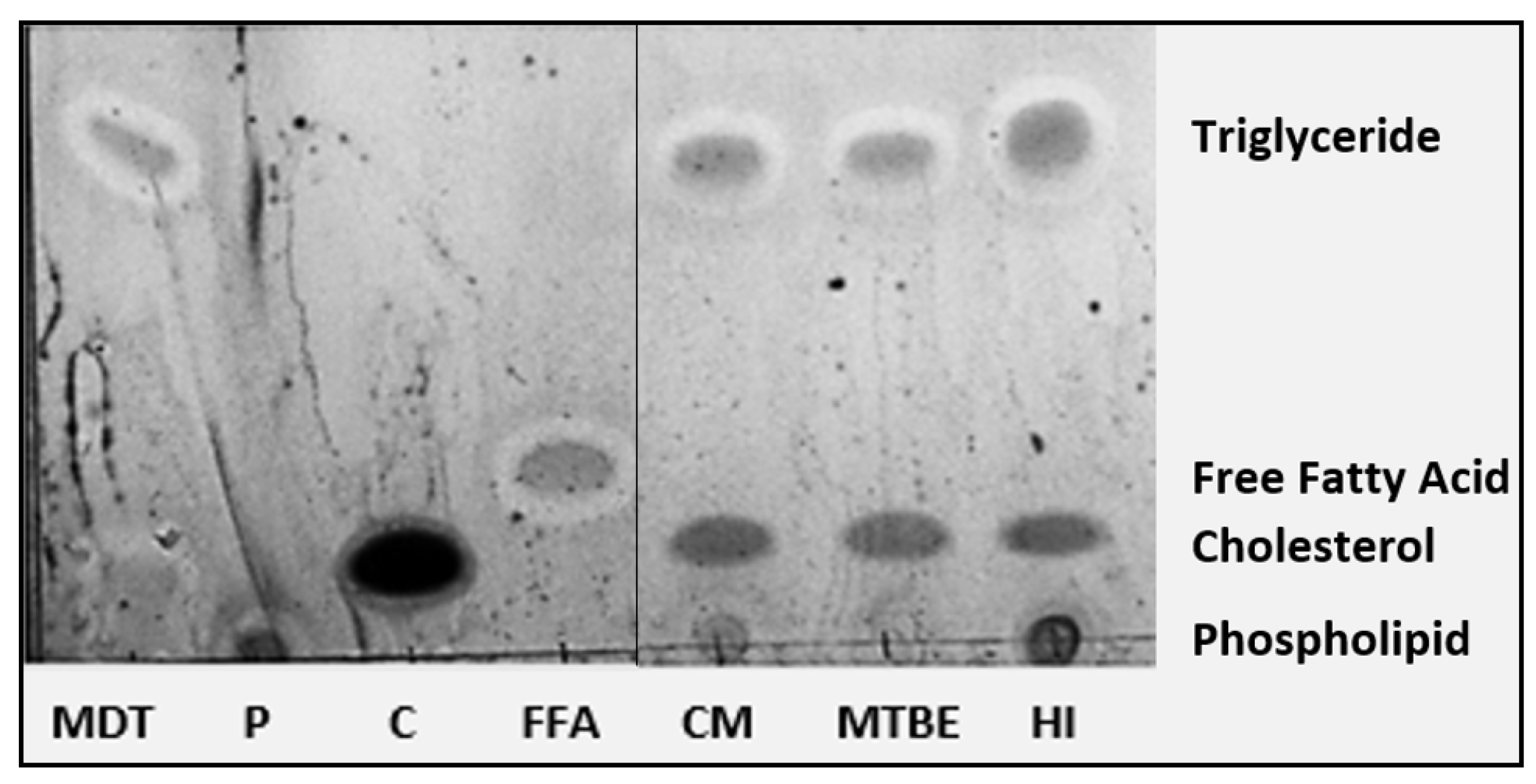
2.3. Thin Layer Chromatography—Lipid Layer Only
2.4. Proximate Composition
2.5. Protein Solubility
2.6. Gelling Properties
2.7. Texture Profile Analysis of Gels
2.8. Water-Holding Capacity of Gels
2.9. Color Analysis of Gels
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Lipid Extraction Efficiency, Fatty Acid Profile, and Classes of Extracted Lipids
3.2. Yield and Proximate Composition of Defatted Egg Yolk
3.3. Protein Solubility
3.4. Protein Gel Formation and Texture Profile Analysis
3.5. Water-Holding Capacity
3.6. Color
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 28. US Dept of Ag Research Services, Nutrient Data Laboratory. 2016. Agricultural Research Service. FoodData Central. Egg, Yolk, Dried. 2019. Available online: https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/173428/nutrients (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Anton, M. Composition and Structure of Hen Egg Yolk. In Bioactive Egg Compounds; Huopalahti, R., López-Fandiño, R., Anton, M., Schade, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Available online: https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2F978-3-540-37885-3_1.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane, S. A simple method for isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, A.; Jaczynski, J.; Matak, K. Extraction of lipids from insect powders using a one-step organic solvent extraction process. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Showman, C.; Ku, K.M.; Jaczynski, J.; Matak, K. Characterization of protein concentrates by defatting cricket, locust, and silkworm powders using a one-step organic solvent extraction. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 182, 114876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.; Showman, C.; Shen, C.; Jaczynski, J.; Matak, K. Effect of organic solvent on the extraction of lipids from krill powders using a one-step extraction process. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 16, 101072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalcuks, A.; Duma, M. Solvent extraction of egg oil from liquid egg yolk. In Proceedings of the 9th Baltic Conference on Food Science and Technology-Food for Consumer Well-Being: Foodbalt, Jelgava, Latvia, 3–5 May 2014; pp. 253–256. Available online: https://lbtufb.lbtu.lv/conference/foodbalt/2014/FoodBalt_Proceedings_2014-253-256.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Matyash, V.; Liebisch, G.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Shevchenko, A.; Schwudke, D. Lipid extraction by methyl-tert-butyl ether for high-throughput lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Where Can I Locate Information about Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether (MTBE)? 2022. Chemicals and Toxics—General FAQs. 2022. Available online: https://usepa.servicenowservices.com/ecss?id=kb_article_view&sys_kb_id=65ee4d541bb64518cb91a759bc4bcb5e (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis, 16th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D 2974-87; Standard Test Methods for Moisture, Ash, and Organic Matter of Peat and Other Organic Soils. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1993. Available online: http://gsrpdf.lib.msu.edu/ticpdf.py?file=/1990s/1993/930331.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Anton, M. Egg yolk: Structures, functionalities, and processes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2871–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.K.; Prasad, P.; Shang, X.; Keum, Y.-S. Advances in Lipid Extraction Methods—A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, D.; Cho, S.; Kim, O.-H.; Song, J.; Hwang, K.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.-H.; Choi, H.; Hong, H.; Seo, H.; et al. Superior gallstone dissolubility and safety of tert-amyl ethyl ether over methyl-tertiary butyl ether. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5936–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezig, L.; Chibani, F.; Chouaibi, M.; Dalgalarrondo, M.; Hessini, K. Pumpkin (Curcurbita maxima) seed proteins: Sequential extraction processing and fraction characterization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7715–7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| CM | MTBE | HI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid Extraction Efficiency | 31.96 ± 1.70 | 30.42 ± 4.16 | 28.13 ± 4.81 |
| Fatty Acids | |||
| C14:0 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.00 |
| C16:0 | 40.96 ± 1.48 | 39.41 ± 1.54 | 40.70 ± 0.08 |
| C16:1n9 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.04 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| C17:1n10 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 |
| C18:0 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 |
| C18:1n9t | 2.36 ± 0.11 | 2.16 ± 0.24 | 2.23 ± 0.01 |
| C18:1n9 | 41.06 ± 1.67 b | 43.54 ± 0.56 a | 39.74 ± 0.25 b |
| C18:2n6 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.00 |
| C18:3n3 | 0.05 ± 0.07 b | 0.33 ± 0.12 a | 0.34 ± 0.01 a |
| C20:0 | 14.46 ± 0.06 | 14.00 ± 0.11 | 14.75 ± 0.16 |
| C20:2n6 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.02 ± 0.02 |
| C20:4n6 | 1.31 ± 0.10 | 1.00 ± 0.41 | 1.26 ± 0.04 |
| C20:4n3 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| C20:5n3 (EPA) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.0 |
| C22:0 | 0.45 ± 0.12 | 0.35 ± 0.15 | 0.10 ± 0.03 |
| C22:1n9 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.05 |
| C22:6n3 (DHA) | 0.39 ± 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.14 | 0.38 ± 0.01 |
| Lipid Classes (TLC) | |||
| Triglycerides | 53.84 ± 3.89 b | 56.03 ± 5.39 b | 63.87 ± 4.97 a |
| Phospholipids | 25.54 ± 2.83 a | 15.72 ± 3.36 b | 16.32 ± 1.34 b |
| Cholesterol | 20.63 ± 1.08 b | 28.26 ± 2.97 a | 19.80 ± 3.64 b |
| Free Fatty Acids | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Initial Powder | CM | MTBE | HI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield | N.A. | 46.55 ± 0.51 b | 55.61 ± 1.77 a | 57.12 ± 1.68 a |
| Crude Protein | 36.09 ± 0.16 c | 66.19 ± 0.55 a | 57.93 ± 0.39 b | 57.27 ± 0.63 b |
| Crude Lipid | 49.47 ± 0.93 a | 25.67 ± 0.40 c | 24.29 ± 0.77 c | 27.70 ± 0.64 b |
| Ash | 6.31 ± 0.04 c | 9.17 ± 0.41 ab | 8.71 ± 0.17 b | 9.38 ± 0.12 a |
| Moisture | 3.15 ± 0.12 c | 5.15 ± 0.19 ab | 5.44 ± 0.10 a | 4.80 ± 0.27 b |
| Initial Powder | CM | MTBE | HI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (g) | 183.65 ± 10.34 b | n.d. | 654.74 ± 75.41 a | 642.70 ± 81.95 a |
| Springiness (mm) | 0.59 ± 0.02 c | n.d. | 0.83 ± 0.03 a | 0.73 ± 0.03 b |
| Cohesiveness (ratio) | 0.57 ± 0.01 c | n.d. | 0.66 ± 0.01 a | 0.60 ± 0.01 b |
| Gumminess (g) | 97.77 ± 7.89 c | n.d. | 406.32 ± 43.94 a | 359.55 ± 52.43 b |
| Resilience (ratio) | 0.50 ± 0.01 a | n.d. | 0.48 ± 0.01 a | 0.39 ± 0.01 b |
| L* | 90.98 ± 0.75 a | 77.25 ± 1.40 c | 84.62 ± 1.33 b | 86.06 ± 0.92 b |
| a* | −4.89 ± 0.34 a | 0.39 ± 0.25 a | −5.77 ± 0.17 c | −4.54 ± 0.30 b |
| b* | 39.89 ± 1.42 a | 29.45 ± 0.83 c | 30.75 ± 0.47 c | 32.66 ± 1.24 b |
| Whiteness | 58.80 ± 1.35 c | 62.77 ± 1.15 b | 65.12 ± 0.80 a | 64.19 ± 1.00 ab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Showman, C.; Rose, A.; Shen, C.; Jaczynski, J.; Matak, K. Extraction of Lipids and Functional Properties of Defatted Egg Yolk Powder Obtained Using a One-Step Organic Solvent Lipid Extraction Process. Foods 2024, 13, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132113
Showman C, Rose A, Shen C, Jaczynski J, Matak K. Extraction of Lipids and Functional Properties of Defatted Egg Yolk Powder Obtained Using a One-Step Organic Solvent Lipid Extraction Process. Foods. 2024; 13(13):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132113
Chicago/Turabian StyleShowman, Casey, Alleda Rose, Cangliang Shen, Jacek Jaczynski, and Kristen Matak. 2024. "Extraction of Lipids and Functional Properties of Defatted Egg Yolk Powder Obtained Using a One-Step Organic Solvent Lipid Extraction Process" Foods 13, no. 13: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132113
APA StyleShowman, C., Rose, A., Shen, C., Jaczynski, J., & Matak, K. (2024). Extraction of Lipids and Functional Properties of Defatted Egg Yolk Powder Obtained Using a One-Step Organic Solvent Lipid Extraction Process. Foods, 13(13), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132113






