Behavior of Spoilage Bacterial Communities in Different Cuts of Enshi Black Pork under Refrigerated Storage (4 °C)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Preparation
2.2. Total Viable Count (TVC) Analysis
2.3. Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) Content Analysis
2.4. Bacterial DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.6. Spoilage Bacteria Isolation and Identification
2.7. Spoilage Potential Evaluation of Isolated Strains
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
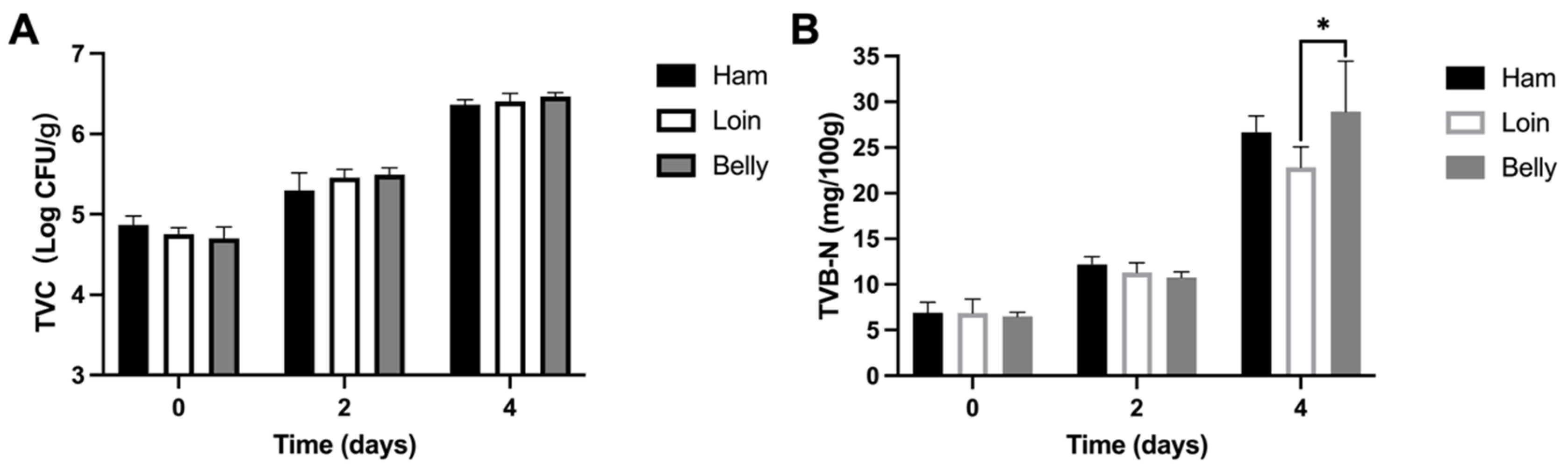
3.1. Spoiled Black Pork Quality
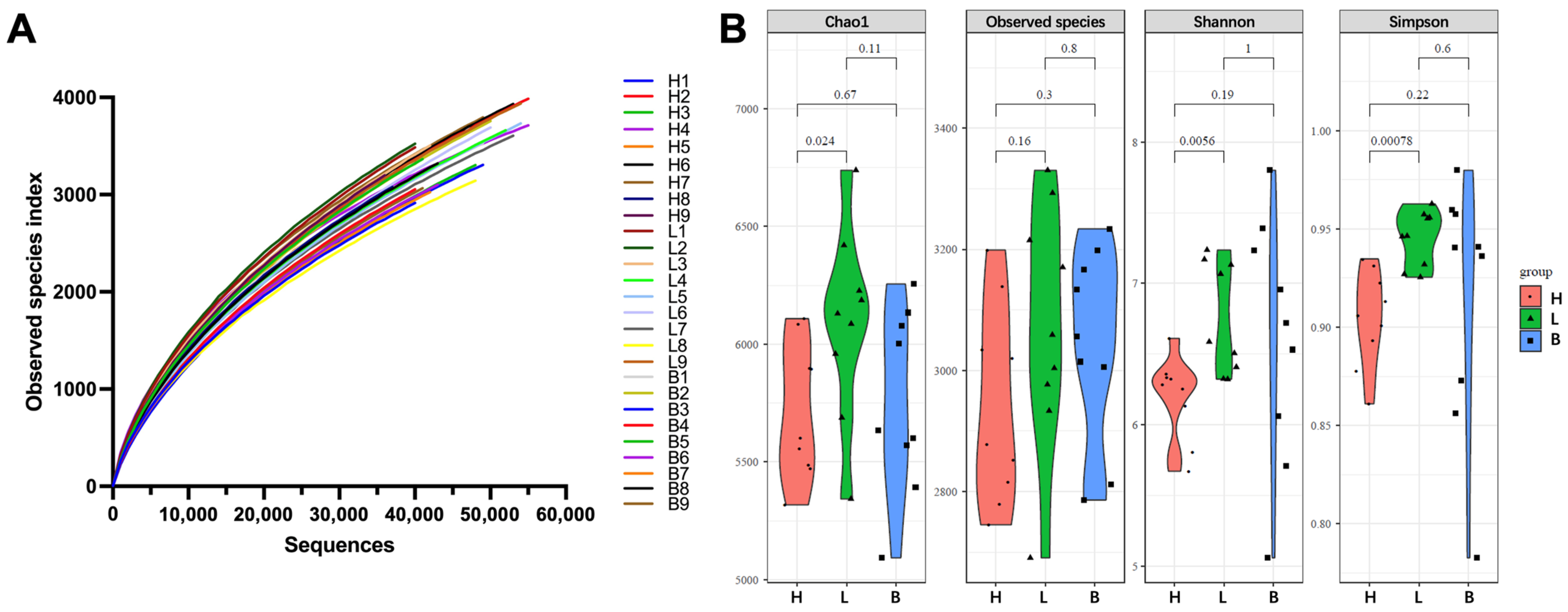
3.2. Sequencing Results and Diversity Indices of Black Pork
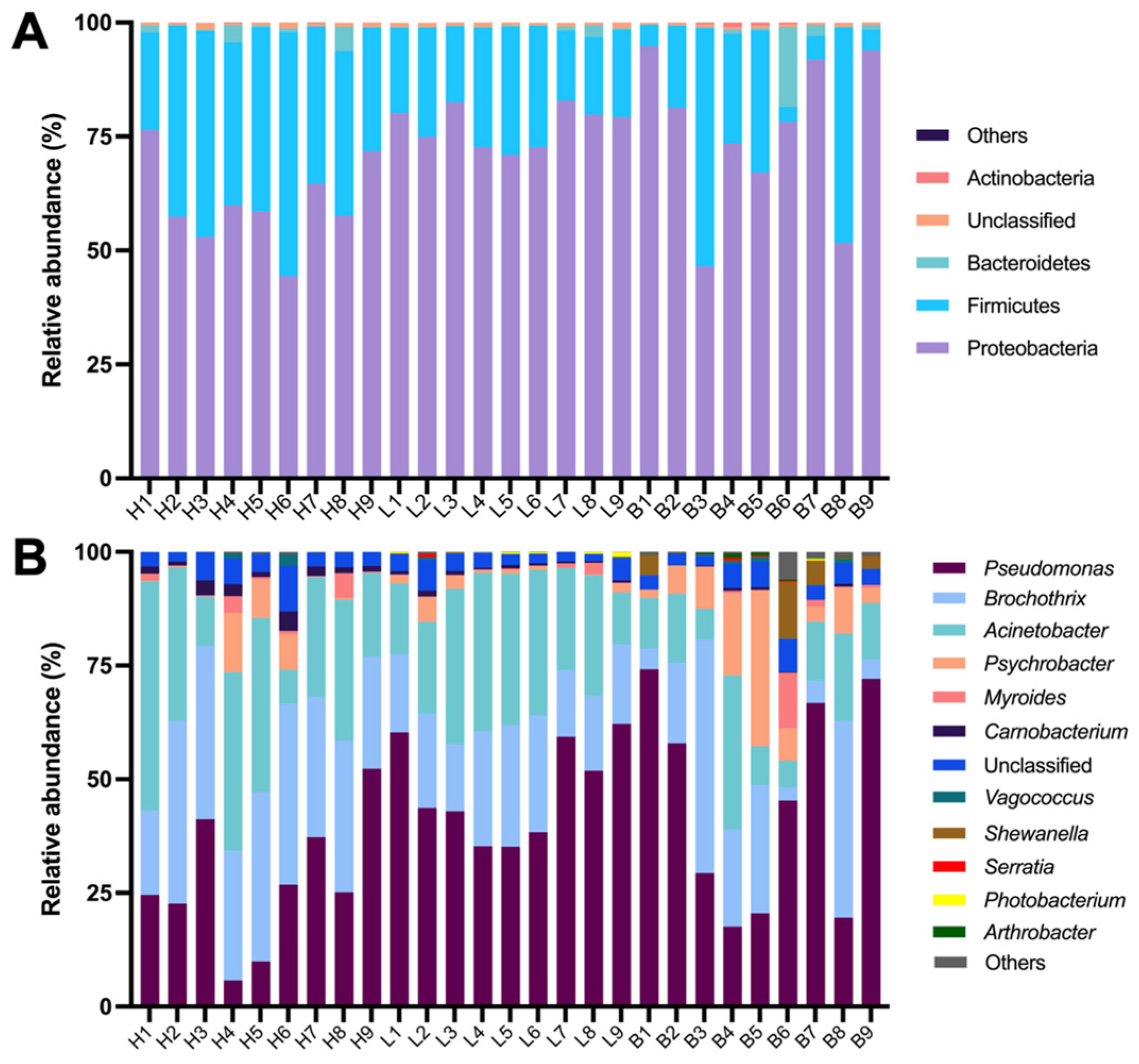
3.3. Bacterial Community Composition of Black Pork
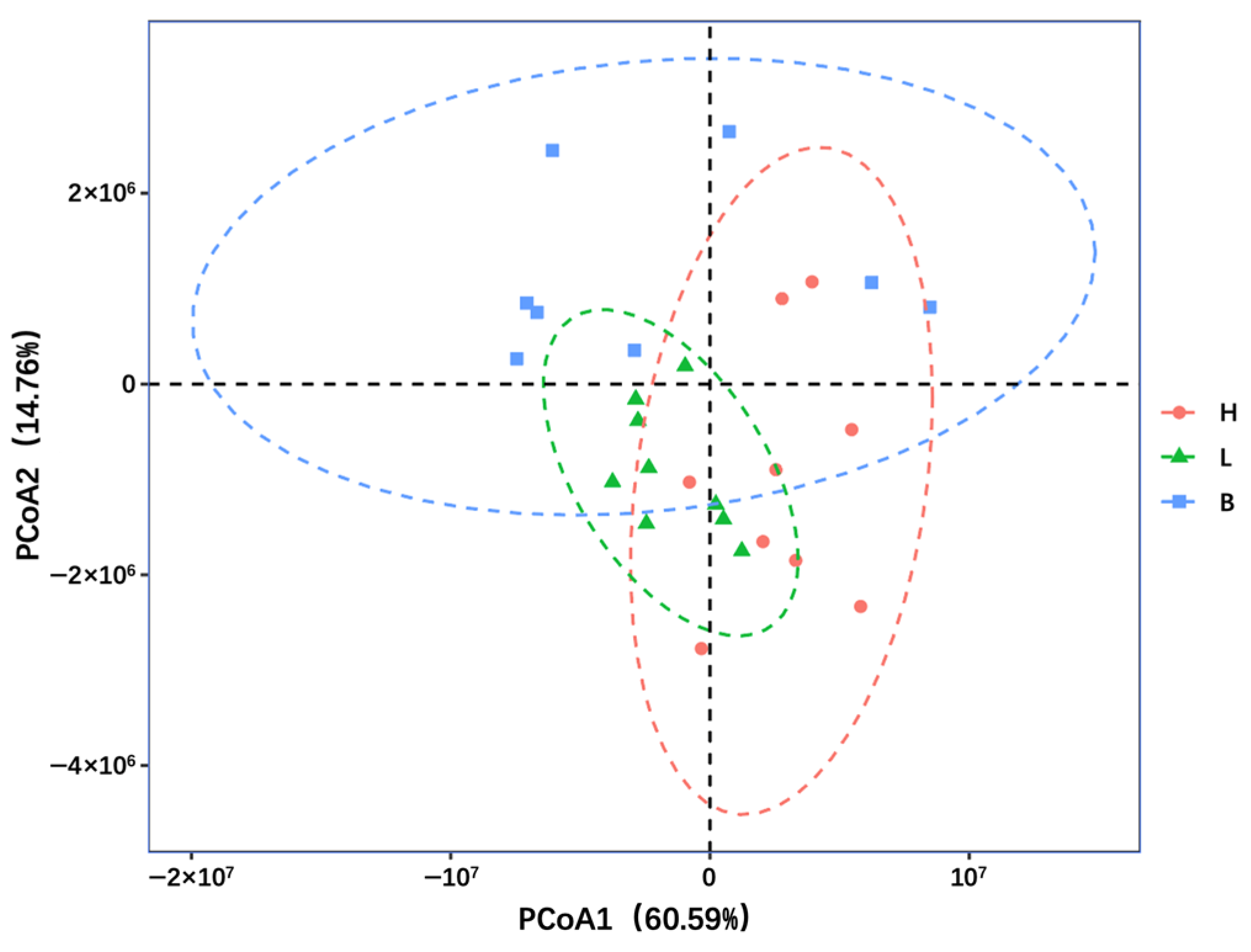
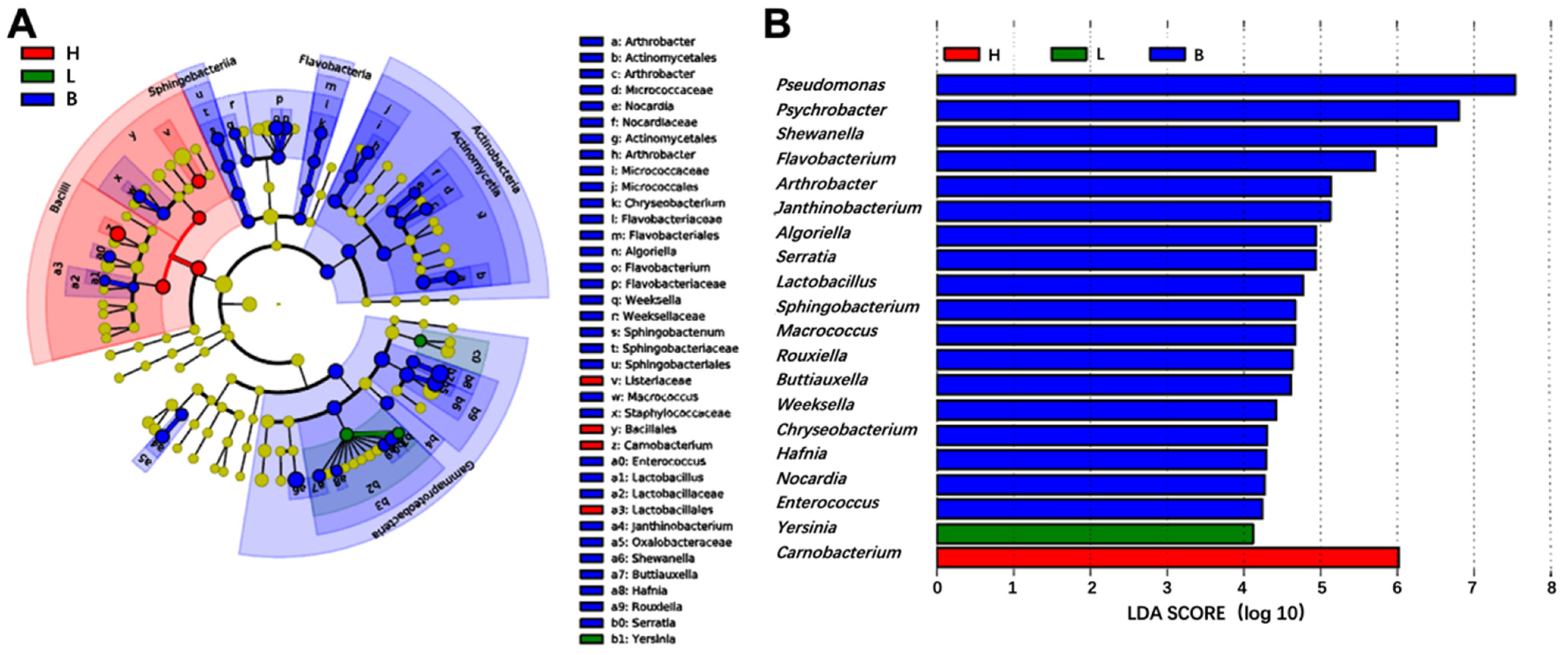
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Bacterial Community
3.5. Isolation and Identification of Strains in Spoiled Black Pork
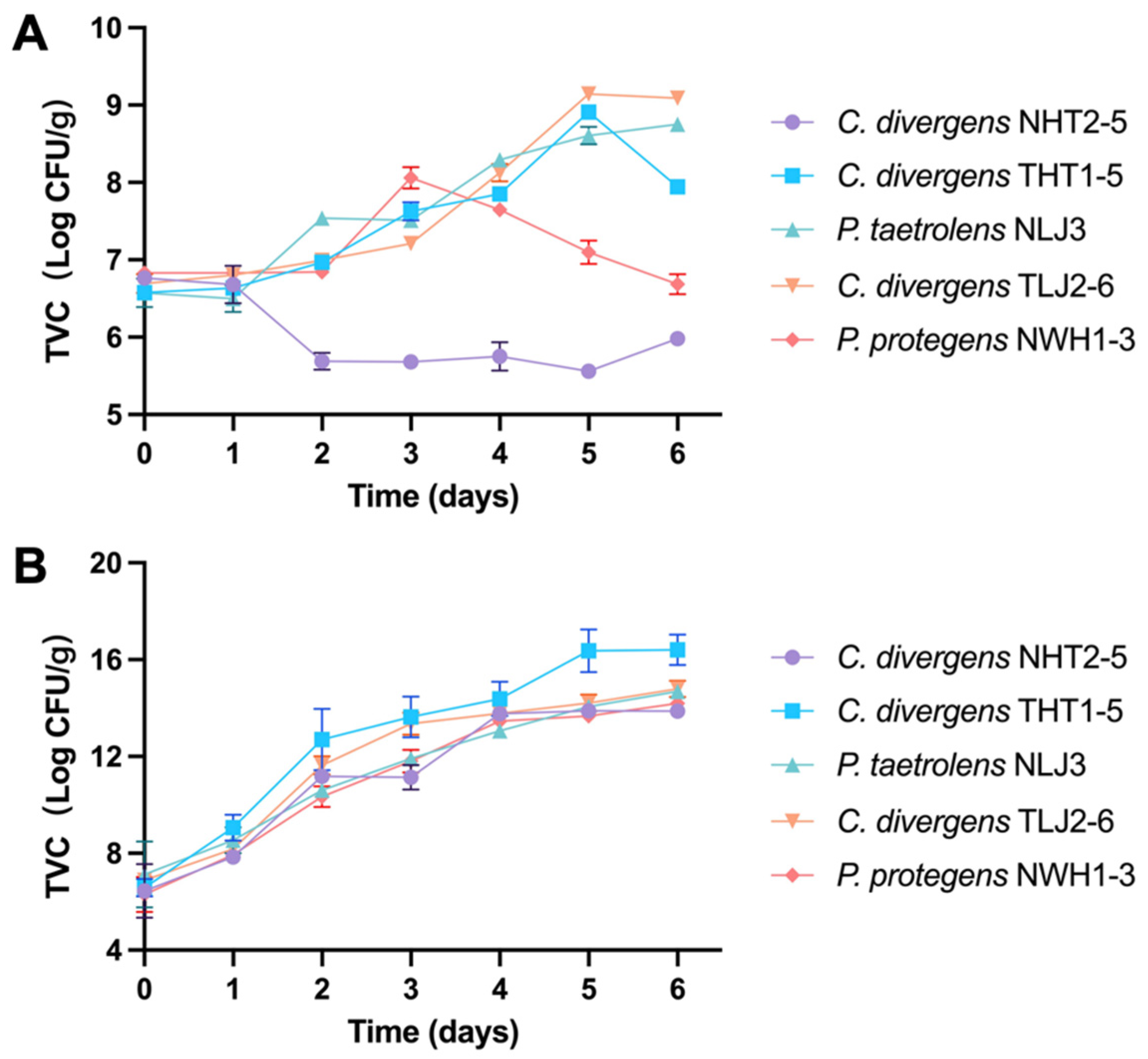
3.6. Spoilage Potential of Isolated Strains
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Datlow, L.Y.; Leventhal, M.; King, J.; Wallace, T.C. Consumption patterns and the nutritional contribution of total, processed, fresh, and fresh-lean pork to the U.S. diet. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaslyng, M.D.; Meinert, L. Meat flavour in pork and beef—From animal to meal. Meat Sci. 2017, 132, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R. Drivers of consumer liking for beef, pork, and lamb: A review. Foods 2020, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Q.; Verkuil, J.M.; Reinbach, H.C.; Meinert, L. Which product characteristics are preferred by Chinese consumers when choosing pork? A conjoint analysis on perceived quality of selected pork attributes. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Martin, W. Factors affecting households’ meat purchase and future meat consumption changes in China: A demand system approach. J. Ethn. Foods 2018, 5, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Qiao, S.; Ying, R. Agricultural industrial scale, price random fluctuation, and profitability levels: Evidence from China’s pig industry. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1291743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, T.; Jia, J.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Xia, N.; Qin, Q.; Peng, H.; et al. Comparison of nutrition and flavor characteristics of five breeds of pork in China. Foods 2022, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Guo, M.; Liao, E.; Wang, Q.; Peng, L.; Jin, W.; Wang, H. Effects of repeated freezing and thawing on myofibrillar protein and quality characteristics of marinated Enshi black pork. Food Chem. 2022, 378, 131994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Tang, Q.; Tian, S.; Jin, L.; Chen, J.; Li, M.; Li, C. Genomic analysis reveals selection in Chinese native black pig. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Cai, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, D.; Pan, X.; Zhi, X. Study of meat quality and flavour in different cuts of Duroc-Bamei binary hybrid pigs. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wang, Y. Antimicrobial and antioxidant effects of kappa-carrageenan coatings Enriched with cinnamon essential oil in pork meat. Foods 2022, 11, 2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellissery, A.J.; Vinayamohan, P.G.; Amalaradjou, M.A.R.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Spoilage bacteria and meat quality. In Meat Quality Analysis, 1st ed.; Biswas, A.K., Mandal, P.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 307–334. [Google Scholar]
- Sabow, A.B.; Sazili, A.Q.; Aghwan, Z.A.; Zulkifli, I.; Goh, Y.M.; Ab Kadir, M.Z.; Nakyinsige, K.; Kaka, U.; Adeyemi, K.D. Changes of microbial spoilage, lipid-protein oxidation and physicochemical properties during post mortem refrigerated storage of goat meat. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.M.; Kaur, M.; Pillidge, C.J.; Torley, P.J. Evaluation of the potential of protective cultures to extend the microbial shelf-life of chilled lamb meat. Meat Sci. 2021, 181, 108613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, H. Advances in understanding the predominance, phenotypes, and mechanisms of bacteria related to meat spoilage. Trends. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillet, A.; Bouju-Albert, A.; Roblin, S.; Vaissié, P.; Leuillet, S.; Dousset, X.; Jaffrès, E.; Combrisson, J.; Prévost, H. Impact of DNA extraction and sampling methods on bacterial communities monitored by 16S rDNA metabarcoding in cold-smoked salmon and processing plant surfaces. Food Microbiol. 2021, 95, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China, State Administration of Market Supervision and Administration National Food Safety Standard-Food Microbiological Examination: Determination of Total Viable Count, GB 4789.2-2022. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=MuRVhOLgpmvnh8_EtLfOo3ZUO1kWpWGqQnKAUPLHkyqsnP7WilpNZRMb5yWtdXuo0jkIU3K-fchv_EeYpsdefEtTNg8Elqwe5C-mblSgT-4QBUGU2XZ9kh6ummdYB42DgwkLr7bBQX0=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. National Food Safety Standard-Determination of Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen in Foods, GB 5009.228-2016. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=MuRVhOLgpms4C3qhFe_tBui1_d0JX6Yp4YJc0vczOwNKjwjsM2UjaDsbfUpV2DKw2UieUQeafE3Bs3tx-zrcax3TRAF_5EfdQ3BtZuUFlCoJi4bXrZmHAfXiD_ThriuGiC52P57Szng=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Xie, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Q. Vertical and horizontal biogeographic patterns and major factors affecting bacterial communities in the open South China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golob, J.L.; Margolis, E.; Hoffman, N.G.; Fredricks, D.N. Evaluating the accuracy of amplicon-based microbiome computational pipelines on simulated human gut microbial communities. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.M. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, L.; Wang, X.; Yi, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lü, X. Isolation of thermostable lignocellulosic bacteria from chicken manure compost and a M42 family endocellulase cloning from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans Y7. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 26, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassey, A.P.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Odeyemi, O.A.; Gao, T.; Olusola, O.O.; Ye, K.; Li, C.; Zhou, G. Evaluation of spoilage indexes and bacterial community dynamics of modified atmosphere packaged super-chilled pork loins. Food Control 2021, 130, 108383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Gu, Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J. High-throughput sequencing analysis of bacterial community composition and quality characteristics in refrigerated pork during storage. Food Microbiol. 2019, 83, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China National Standard-Fresh and Frozen Pork Lean, Cuts, GB/T 9959.2-2008. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=MuRVhOLgpmuU0XUfR8zUafx9D98qnbWOakraEC3nMPsIhwboHsM3sEZVDPb8mx57_439-JyO_W0DTLETVMGkzsomE4YoEaqRw_NGPlVJ2fsCbkCwkLqb87xRtTmlvJRBpJgjQ6NqzJU=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Tian, X.; Wu, W.; Yu, Q.; Hou, M.; Gao, F.; Li, X.; Dai, R. Bacterial diversity analysis of pork longissimus lumborum following long term ohmic cooking and water bath cooking by amplicon sequencing of 16S rRNA gene. Meat Sci. 2017, 123, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, G.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, C. Effects of different storage temperatures on bacterial communities and functional potential in pork meat. Foods 2022, 11, 2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, A.; Pérez, E.; de Faria, C.T.; Ferrús, M.A.; Carrascosa, C. Food spoilage by Pseudomonas spp.—An overview. In Foodborne Pathogens and Antibiotic Resistance, 2nd ed.; Singh, O.V., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 41–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sah, S.; Krishnani, S.; Singh, R. Pseudomonas mediated nutritional and growth promotional activities for sustainable food security. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2021, 2, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Franzetti, L.; Kaushal, A.; Kumar, D. Pseudomonas fluorescens: A potential food spoiler and challenges and advances in its detection. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanborough, T.; Fegan, N.; Powell, S.M.; Tamplin, M.; Chandry, P.S. Insight into the genome of Brochothrix thermosphacta, a problematic meat spoilage bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e02786–e02816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höll, L.; Hilgarth, M.; Geissler, A.J.; Behr, J.; Vogel, R.F. Metatranscriptomic analysis of modified atmosphere packaged poultry meat enables prediction of Brochothrix thermosphacta and Carnobacterium divergens in situ metabolism. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafei, R.; Hamze, M.; Pailhories, H.; Eveillard, M.; Marsollier, L.; Joly-Guillou, M.L.; Dabboussi, F.; Kempf, M. Extrahuman epidemiology of Acinetobacter baumannii in Lebanon. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2359–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Xiong, G.; Shi, L.; Wu, W.; Li, X.; Qiao, Y.; Liao, L.; Ding, A.; Wang, L. Application of HVEF treatment in bacteriostasis against Acinetobacter radioresistens. Food Control 2021, 124, 107914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Burke, C.M.; Bolch, C.J.S.; Stanley, R. Evaluation of spoilage potential and volatile metabolites production by Shewanella baltica isolated from modified atmosphere packaged live mussels. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruzy, M.F.; Murru, N.; Yu, Z.; Cnockaert, M.; Joossens, M.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Houf, K. Determination of the microbiological contamination in minced pork by culture dependent and 16S amplicon sequencing analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 290, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Ban, G.H.; Hong, Y.W.; Jeong, K.C.; Bae, D.; Kim, S.A. Bacterial profile of pork from production to retail based on high-throughput sequencing. Food Res. Int. 2024, 176, 113745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Alegbeleye, O.O.; Strateva, M.; Stratev, D. Understanding spoilage microbial community and spoilage mechanisms in foods of animal origin. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ning, X.; He, X.; Sun, X.; Yu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, R.Q.; Wu, Y. Fatty acid composition analyses of commercially important fish species from the Pearl River Estuary, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Zou, M.; Li, M.; Liu, D.; Guan, W.; Hao, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Jing, H.; Li, Y.; et al. Prevalence, antimicrobial resistance and phylogenetic characterization of Yersinia enterocolitica in retail poultry meat and swine feces in parts of China. Food Control 2018, 93, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzy, M.F.; Aponte, M.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Capuano, F.; Cristiano, D.; Delibato, E.; Houf, K.; Murru, N. Yersinia enterocolitica detection in pork products: Evaluation of isolation protocols. Food Microbiol. 2020, 92, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Samples | Numbers of Isolated Strains | Strain Identification | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genera | Species | Strains | ||
| Ham | 20 | Pseudomonas | P. versuta | THT2-3 |
| Acinetobacter | A. wanghuae | THT2-1 | ||
| Carnobacterium | C. divergens | NHT2-5, THT1-5, NHT1-1 | ||
| C. maltaromaticum | TWH1-2 | |||
| Serratia | S. liquefaciens | NHT1-5, NHT4 | ||
| Bacillus | B. licheniformis | THT3-5 | ||
| Buttiauxella | B. gaviniae | NHT3-2-2, PHT3 | ||
| Hafnia | H. alvei | PHT5 | ||
| H. paralvei | NHT3-4, THT1-4 | |||
| Klebsiella | K. quasivariicola | NHT2-4 | ||
| Kocuria | K. rhizophila | NHT2-1, NHT1-4 | ||
| Micrococcus | M. luteus | THT2-2 | ||
| Staphylococcus | S. saprophyticus | THT3-1, NHT3-5 | ||
| Loin | 14 | Pseudomonas | P. taetrolens | NLJ3 |
| Carnobacterium | C. divergens | TLJ2-6, NLJ1, PLJ1, PLJ2 | ||
| C. maltaromaticum | TLJ3-4 | |||
| Serratia | S. liquefaciens | NLJ7, TLJ1-5, TLJ2-4, TLJ1-3 | ||
| Hafnia | H. alvei | NLJ4, TLJ1-2 | ||
| Kocuria | K. rhizophila | TLJ1-1, NLJ2 | ||
| Belly | 16 | Pseudomonas | P. protegens | NWH1-3 |
| Acinetobacter | A. wanghuae | PWH1-1 | ||
| Carnobacterium | C. divergens | NWH3-3, NWH1-5 | ||
| Serratia | S. liquefaciens | PWH1-3, PWH2-1, TWH2-4 | ||
| S. quinivorans | NWH3-4 | |||
| Aeromonas | A. caviae | NWH2-2 | ||
| A. media | NWH1-1 | |||
| A. salmonicida | NWH1-4, NWH3-5, TWH2-3 | |||
| Kurthia | K. zopfii | NWH2-5 | ||
| Macrococcus | M. caseolyticus | NWH1-2, TWH2-1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Peng, L.; Liao, E.; Wang, H. Behavior of Spoilage Bacterial Communities in Different Cuts of Enshi Black Pork under Refrigerated Storage (4 °C). Foods 2024, 13, 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132081
Zhang Y, Yang J, Peng L, Liao E, Wang H. Behavior of Spoilage Bacterial Communities in Different Cuts of Enshi Black Pork under Refrigerated Storage (4 °C). Foods. 2024; 13(13):2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132081
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ying, Jiang Yang, Lijuan Peng, E Liao, and Haibin Wang. 2024. "Behavior of Spoilage Bacterial Communities in Different Cuts of Enshi Black Pork under Refrigerated Storage (4 °C)" Foods 13, no. 13: 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132081
APA StyleZhang, Y., Yang, J., Peng, L., Liao, E., & Wang, H. (2024). Behavior of Spoilage Bacterial Communities in Different Cuts of Enshi Black Pork under Refrigerated Storage (4 °C). Foods, 13(13), 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132081






