Differences and Mechanism of Waxy Corn Starch and Normal Corn Starch in the Preparation of Recrystallized Resistant Starch (RS3)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Resistant Starch (RS)
2.3. Determination of RS Content
2.4. Determination of Amylose Content in RS
2.5. Determination of Moisture Content in RS
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis of RS (DSC)
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy of RS (FTIR)
2.8. X-ray Diffraction of RS (XRD)
2.9. Determination of Amylopectin Chain Length Distribution in RS
2.10. Observation by Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differences in RS Content and Moisture Content of the Two RS Type
3.2. Differences in Thermal Properties of the Two RS Type
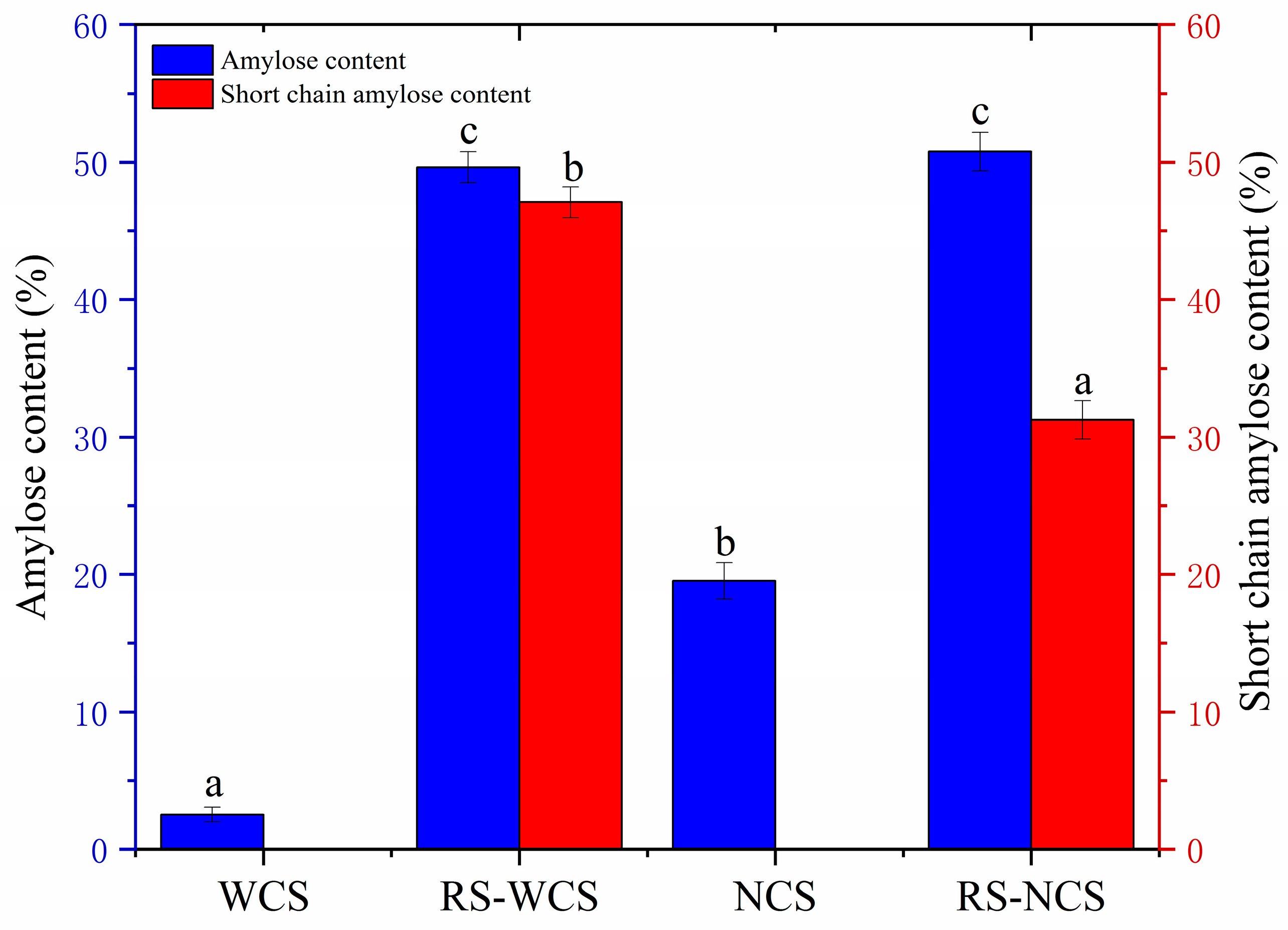
3.3. Influence of Amylose Content on RS Content
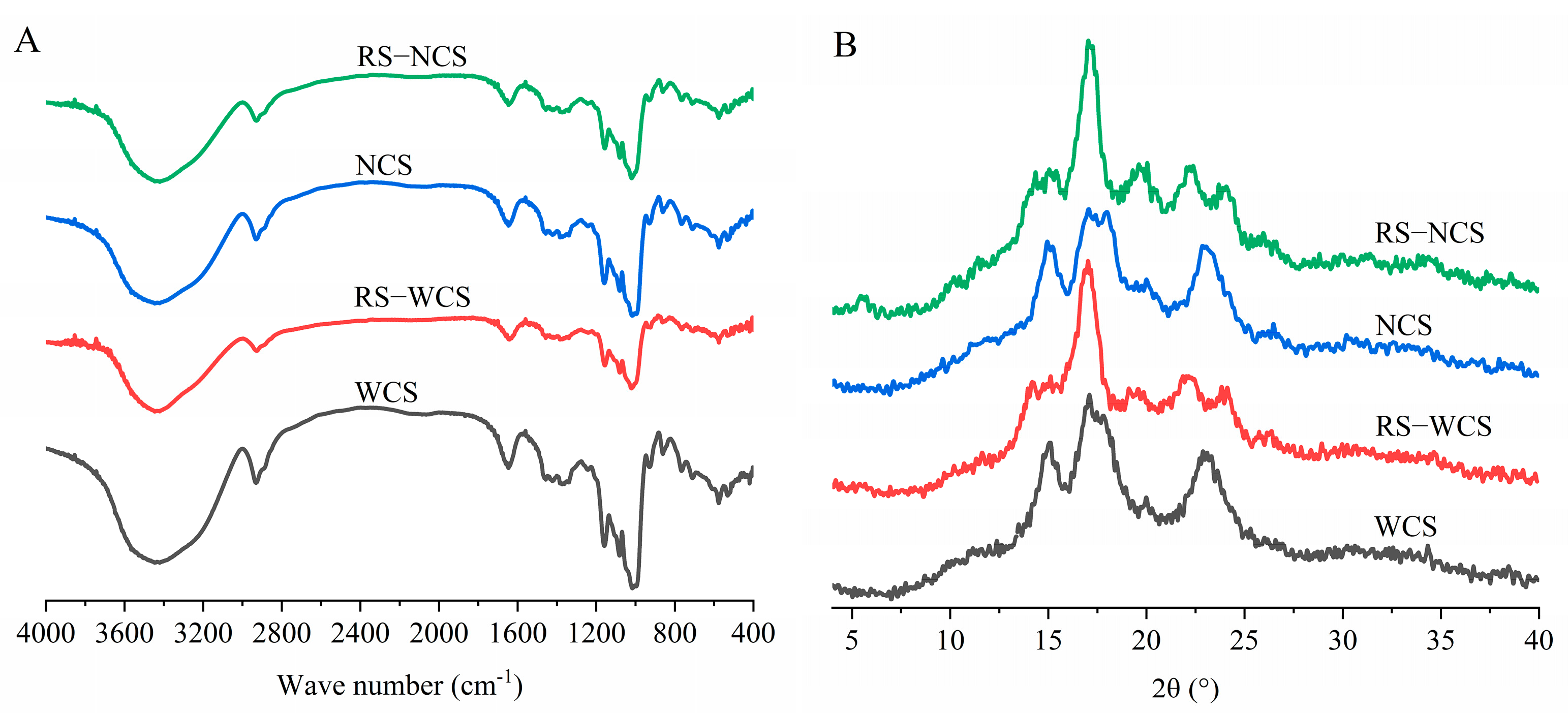
3.4. Differences in Chemical Structure of RS
3.5. Differences in Crystal Structure and Crystallinity between the Two RS Types
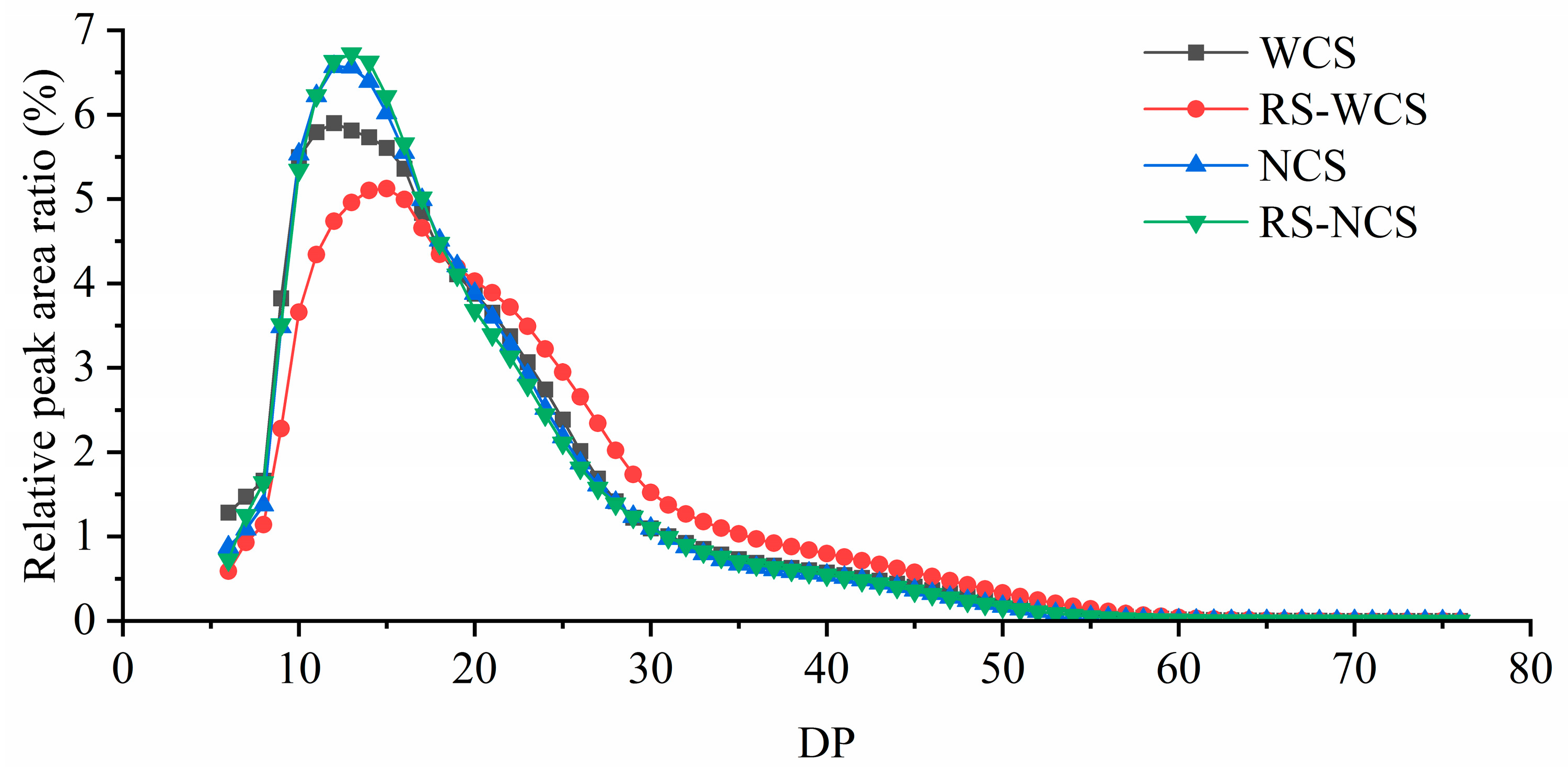
3.6. Changes in Branched Chain Length Distribution of Amylopectin between the Two RS Types
3.7. Changes in Branched Chain Length Distribution of Amylopectin between the Two RS Types
3.8. Microstructure Changes of RS
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bojarczuk, A.; Skąpska, S.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Marszałek, K. Health benefits of resistant starch: A review of the literature. J. Funct. Foods. 2022, 93, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Liu, J.; Ji, F.; Fu, L.; Xu, K.; Yang, Y.; Ma, A. Hypoglycemic effect of recrystallized resistant starch on high-fat diet- and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice via gut microbiota modulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261, 129812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Kan, J. Effects of resistant starch III on the serum lipid levels and gut microbiota of Kunming mice under high-fat diet. FSHW 2023, 12, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Shi, Y.-C. Preparation, structure, and digestibility of crystalline A- and B-type aggregates from debranched waxy starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 105, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G.; Cheng, L.; Li, J. Effects of composition, starch structural orders, and kernel structure on starch in vitro digestion of highland barley. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 301, 120274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, K.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W. Changes in structural, physicochemical, and digestive properties of normal and waxy wheat starch during repeated and continuous annealing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovino, S.; Quiquero, M.; De Arcangelis, E.; Cuomo, F.; Trivisonno, M.C.; Messia, M.C.; Marconi, E. Physico-chemical and nutritional properties of different high-amylose wheat breads. J. Cereal Sci. 2024, 117, 103919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddappa, S.B.; Muthusamy, V.; Zunjare, R.U.; Chhabra, R.; Talukder, Z.A.; Maman, S.; Chand, G.; Pal, D.; Kumar, R.; Mehta, B.K.; et al. Composition of kernel-amylose and -resistant starch among subtropically adapted maize. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 119, 105392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xue, W.; Li, T.; Wang, L. Understanding the Relationship between the Molecular Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Soft Rice Starch. Foods 2023, 12, 3611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cota-López, R.; Velazquez, G.; Méndez-Montealvo, G.; Pérez-Ramírez, I.F.; Murúa-Pagola, B.; Espinoza-Mellado, R.; Hernández-Gama, R. Effect of adding high concentrations of retrograded starch with different amylose content on the physicochemical properties and sensory attributes of Greek-style yogurt. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Liu, K.; Gao, Q. Effects of Heat-Moisture Treatment on the Digestibility and Physicochemical Properties of Waxy and Normal Potato Starches. Foods 2022, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiatponglarp, W.; Tongta, S.; Rolland-Sabaté, A.; Buléon, A. Crystallization and chain reorganization of debranched rice starches in relation to resistant starch formation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klostermann, C.E.; Buwalda, P.L.; Leemhuis, H.; de Vos, P.; Schols, H.A.; Bitter, J.H. Digestibility of resistant starch type 3 is affected by crystal type, molecular weight and molecular weight distribution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 265, 118069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Luo, F.; Lin, Q.J.F.C. Insights into the relations between the molecular structures and digestion properties of retrograded starch after ultrasonic treatment. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worawikunya, K.; Supagorn, R.; Agnès, R.-S.; Alain, B.; Sunanta, T. Spherulitic self-assembly of debranched starch from aqueous solution and its effect on enzyme digestibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Jin, Z.; Tian, Y. Insights into the structural, morphological, and thermal property changes in simulated digestion and fermentability of four resistant starches from high amylose maize starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 142, 108770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Sweedman, M.C.; Shi, Y.-C. Structure, birefringence and digestibility of spherulites produced from debranched waxy maize starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, D.; Wu, Z.; Tian, J.; Xu, E.; Liu, D. Rearranged supramolecular structure of resistant starch with polymorphic microcrystals prepared in high-solid enzymatic system. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Resistant Starch in Starch and Plant Materials, Enzymatic Digestion, First Action 2002; AOAC: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Park, I.; Mannaa, M. Assessing Amylose Content with Iodine and Con A Methods, In Vivo Digestion Profile, and Thermal Properties of Amylosucrase-Treated Waxy Corn Starch. Foods 2024, 13, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.K.; Blazek, J.; Flanagan, B.M.; Dhital, S.; Larroque, O.; Morell, M.K.; Gilbert, E.P.; Gidley, M.J.J.C.P. Molecular, mesoscopic and microscopic structure evolution during amylase digestion of maize starch granules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villas-Boas, F.; Facchinatto, W.M.; Colnago, L.A.; Volanti, D.P.; Franco, C.M.L. Effect of amylolysis on the formation, the molecular, crystalline and thermal characteristics and the digestibility of retrograded starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, M.; Xiuxiu, Y.; Xinzhong, H.; Xiaoping, L.; Liu, L.; Joyce, I.B. Structural characterization of resistant starch isolated from Laird lentils (Lens culinaris) seeds subjected to different processing treatments. Food Chem. 2018, 263, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J.; Gui, Y.; Tao, H.; Zou, F.; Liu, P.; Janaswamy, S.; Cui, B. The effects of wheat amylose ratios on the structural and physicochemical properties of waxy rice starch using branching enzyme and glucoamylase. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, T. Effect of pullulanase debranching and recrystallization on structure and digestibility of waxy maize starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Banerjee, R. Increase of resistant starch content by hydrolysis of potato amylopectin and its microstructural studies by 2D and 3D imaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 223, 1674–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Zhu, S.; Chen, F.; Gao, Q.; Yu, S. Effect of different drying methods on the structure and digestibility of short chain amylose crystals. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Herbuger, K.; Petersen, B.L.; Cui, Y.; Blennow, A.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y. High-pressure pasting performance and multilevel structures of short-term microwave-treated high-amylose maize starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 322, 121366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | RS Content (%) | Moisture Content (%) |
|---|---|---|
| WCS | 0.36 ± 0.08 a | 11.48 ± 0.03 c |
| RS-WCS | 57.80 ± 0.91 c | 9.99 ± 0.18 b |
| NCS | 1.06 ± 0.10 a | 12.80 ± 0.08 d |
| RS-NCS | 41.46 ± 0.87 b | 7.41 ± 0.03 a |
| Sample | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WCS | 61.40 ± 1.15 a | 69.13 ± 0.40 a | 74.17 ± 1.55 a | 4.29 ± 0.28 a |
| RS-WCS | 100.40 ± 2.13 c | 102.97 ± 1.62 b | 113.50 ± 1.10 b | 16.79 ± 0.29 c |
| NCS | 65.67 ± 1.15 b | 71.07 ± 1.06 a | 75.77 ± 0.72 a | 4.58 ± 0.31 a |
| RS-NCS | 98.77 ± 1.30 c | 101.00 ± 1.41 b | 112.30 ± 0.70 b | 15.01 ± 0.58 b |
| Sample | DP 6–12 | DP 13–24 | DP 25–36 | DP36–76 | IR1047/1022 | IR995/1022 | Relative Crystallinity % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WCS | 25.43 | 52.55 | 14.82 | 7.20 | 0.866 ± 0.009 a | 0.995 ± 0.006 a | 36.38 ± 0.887 b |
| RS-WCS | 17.68 | 51.72 | 20.14 | 10.46 | 0.934 ± 0.006 bc | 0.952 ± 0.010 b | 42.31 ± 1.28 d |
| NCS | 25.15 | 54.43 | 14.08 | 6.34 | 0.914 ± 0.008 b | 0.994 ± 0.003 a | 22.81 ± 1.43 a |
| RS-NCS | 25.33 | 54.25 | 14.05 | 6.37 | 0.930 ± 0.005 c | 0.950 ± 0.001 b | 27.23 ± 0.99 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Q.; Chen, L.; Sun, L.; Liu, K.; Gong, K. Differences and Mechanism of Waxy Corn Starch and Normal Corn Starch in the Preparation of Recrystallized Resistant Starch (RS3). Foods 2024, 13, 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132039
Su Q, Chen L, Sun L, Liu K, Gong K. Differences and Mechanism of Waxy Corn Starch and Normal Corn Starch in the Preparation of Recrystallized Resistant Starch (RS3). Foods. 2024; 13(13):2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132039
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Qing, Lirong Chen, Linlin Sun, Kaichang Liu, and Kuijie Gong. 2024. "Differences and Mechanism of Waxy Corn Starch and Normal Corn Starch in the Preparation of Recrystallized Resistant Starch (RS3)" Foods 13, no. 13: 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132039
APA StyleSu, Q., Chen, L., Sun, L., Liu, K., & Gong, K. (2024). Differences and Mechanism of Waxy Corn Starch and Normal Corn Starch in the Preparation of Recrystallized Resistant Starch (RS3). Foods, 13(13), 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132039







