Preparation and Characterization of Lutein Co-Amorphous Formulation with Enhanced Solubility and Dissolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Co-Amorphous Mixtures
2.3. Solubility Study
2.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.7. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
2.8. Dissolution Test
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
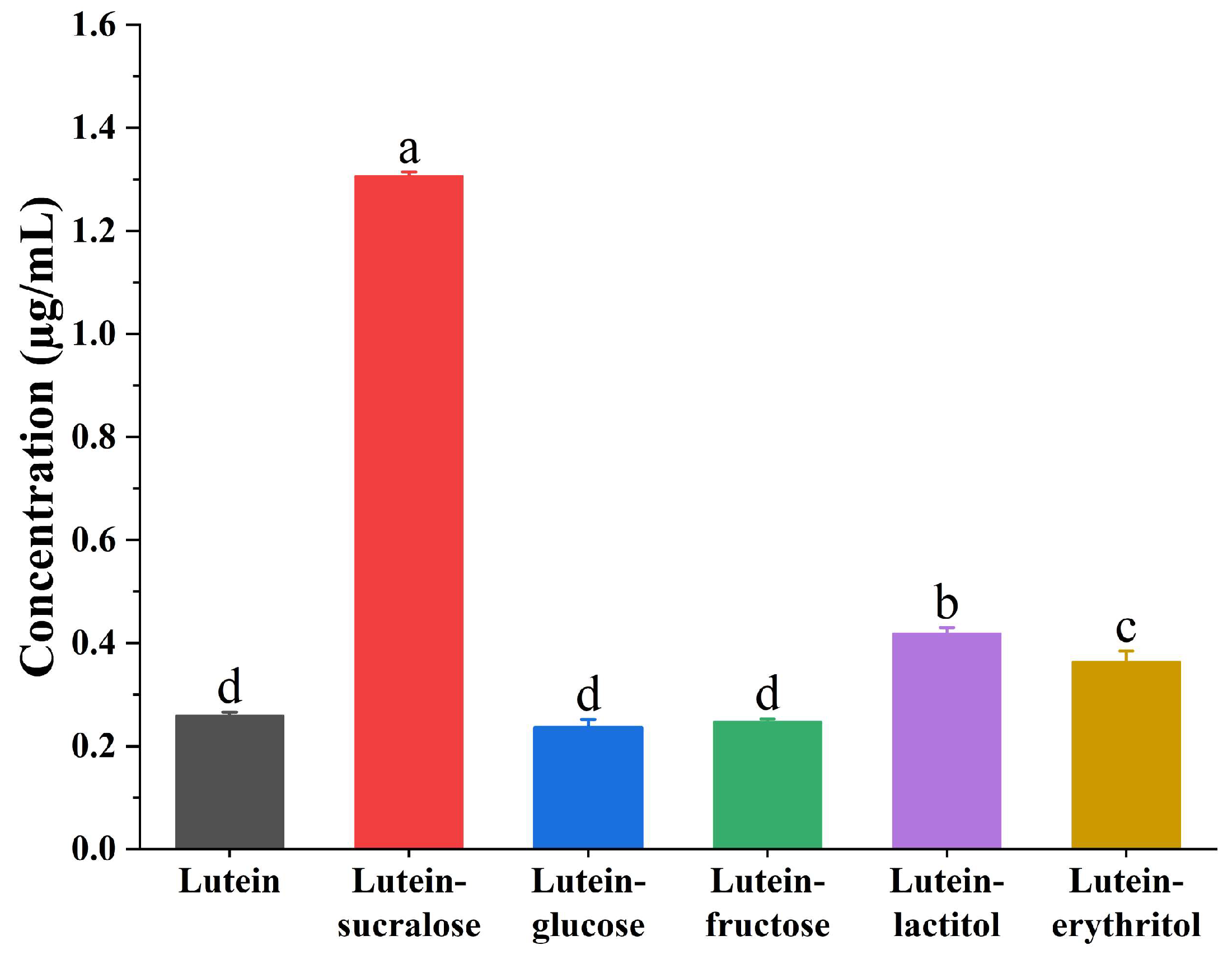
3.1. Co-Former Screening
3.2. Solid State Characterization
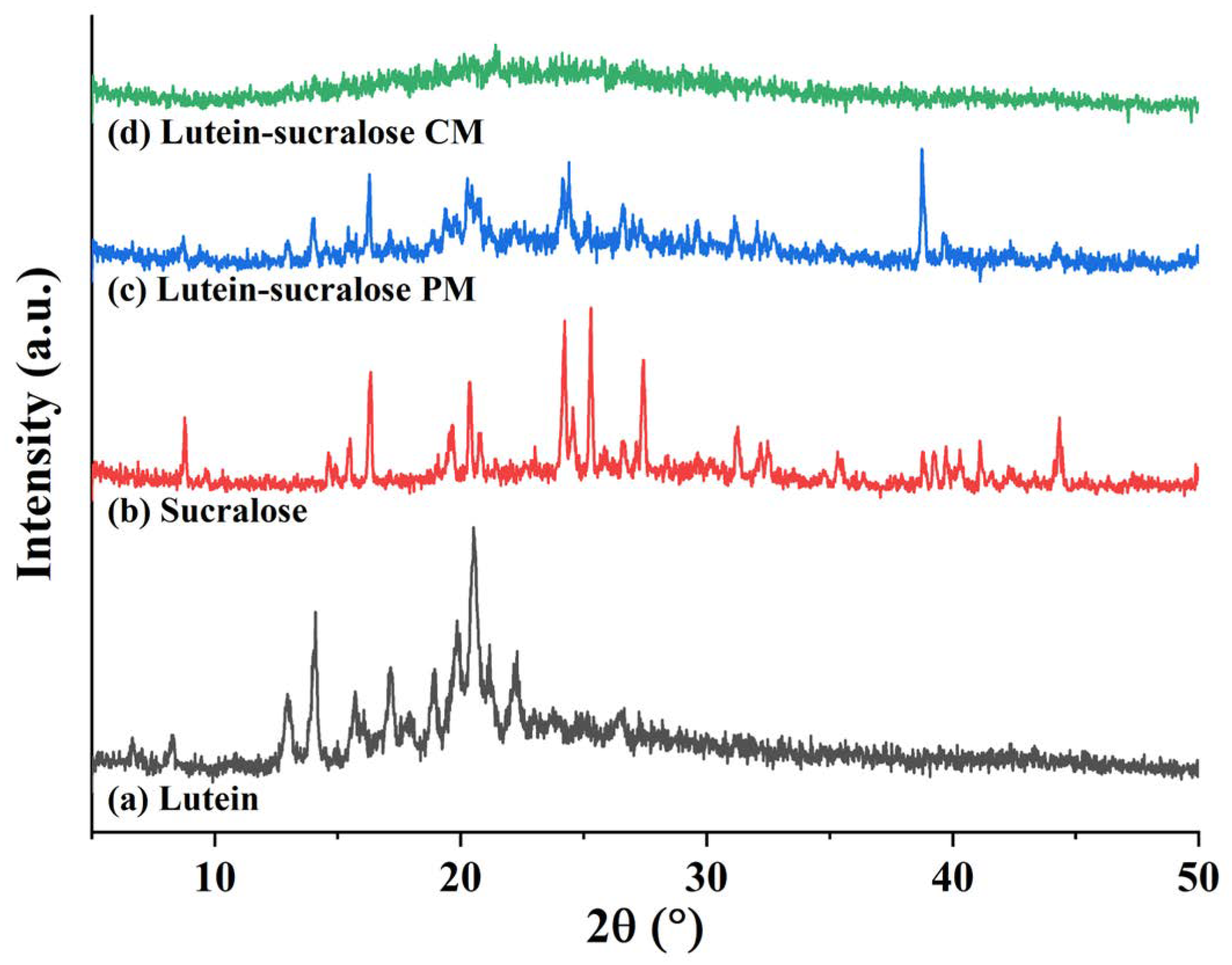
3.2.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
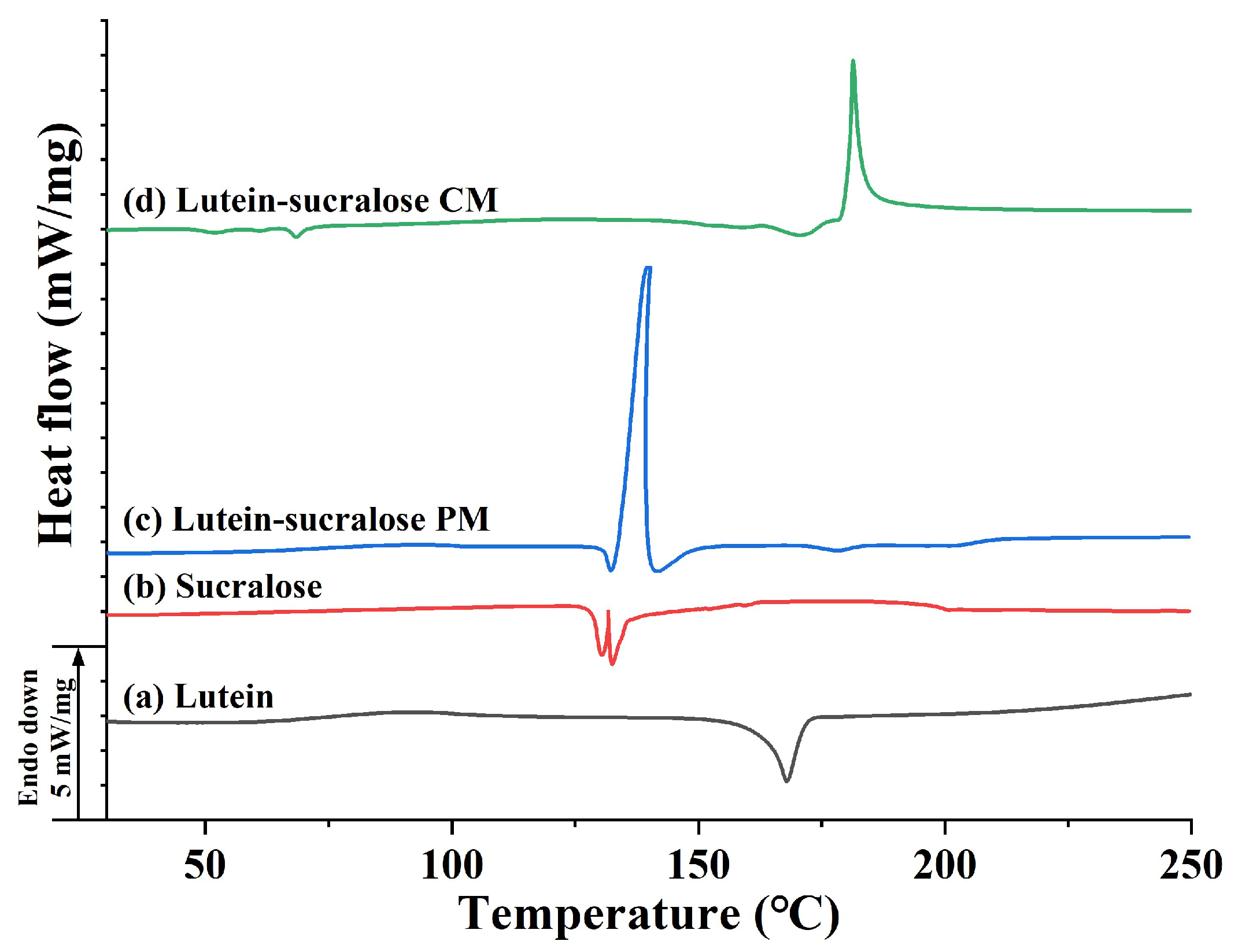
3.2.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
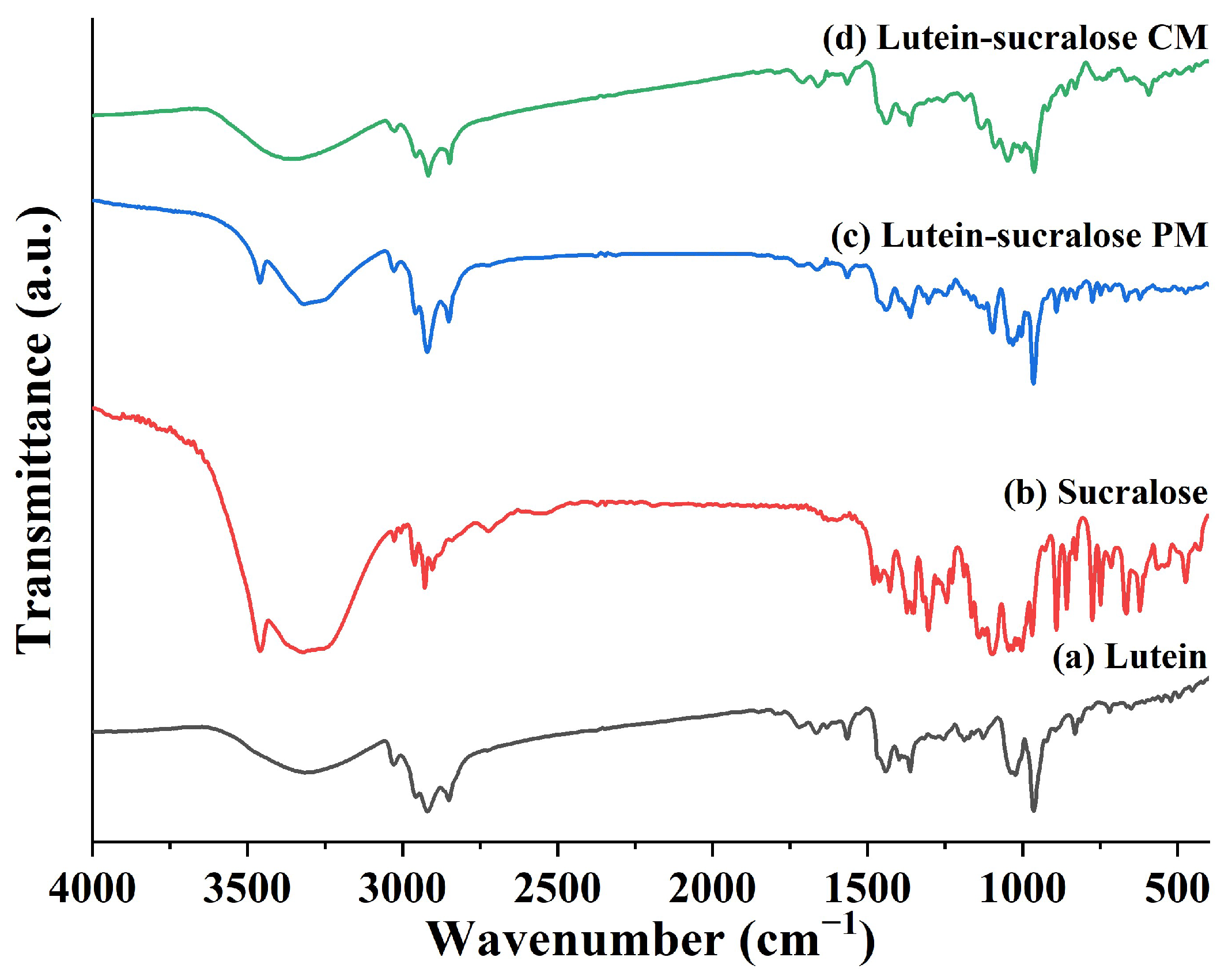
3.2.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
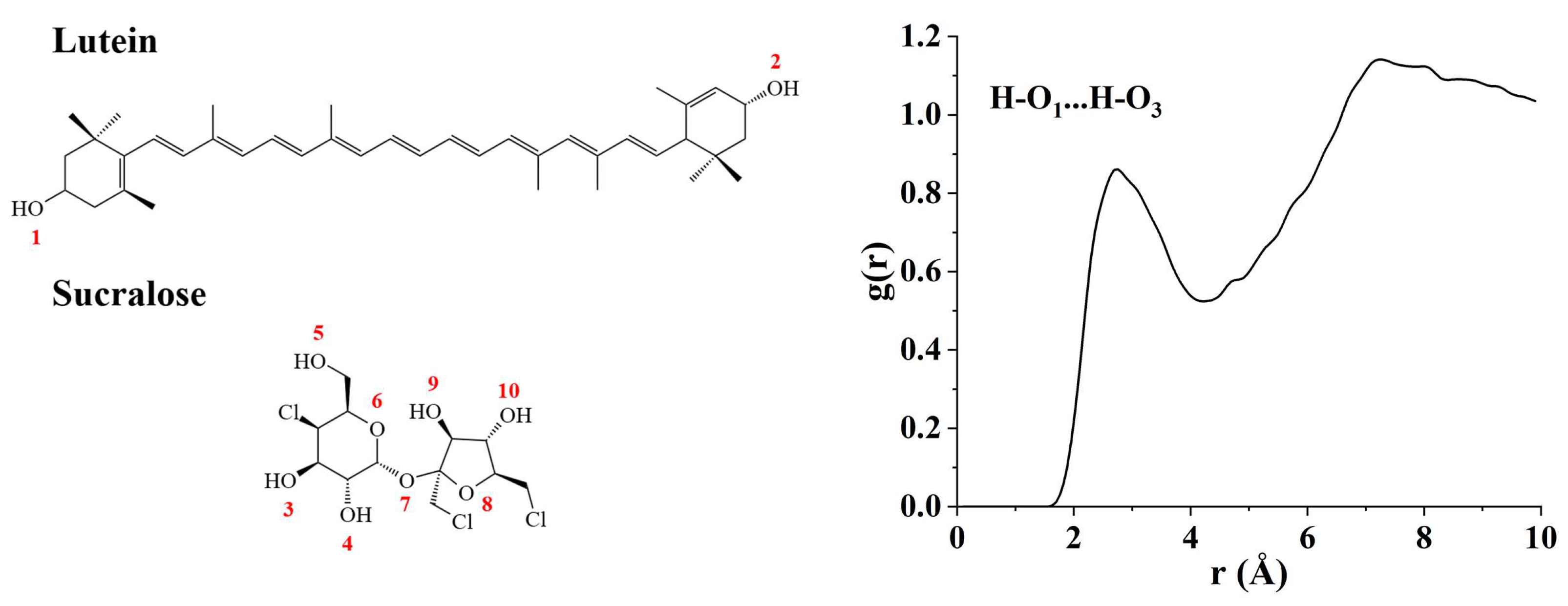
3.2.4. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
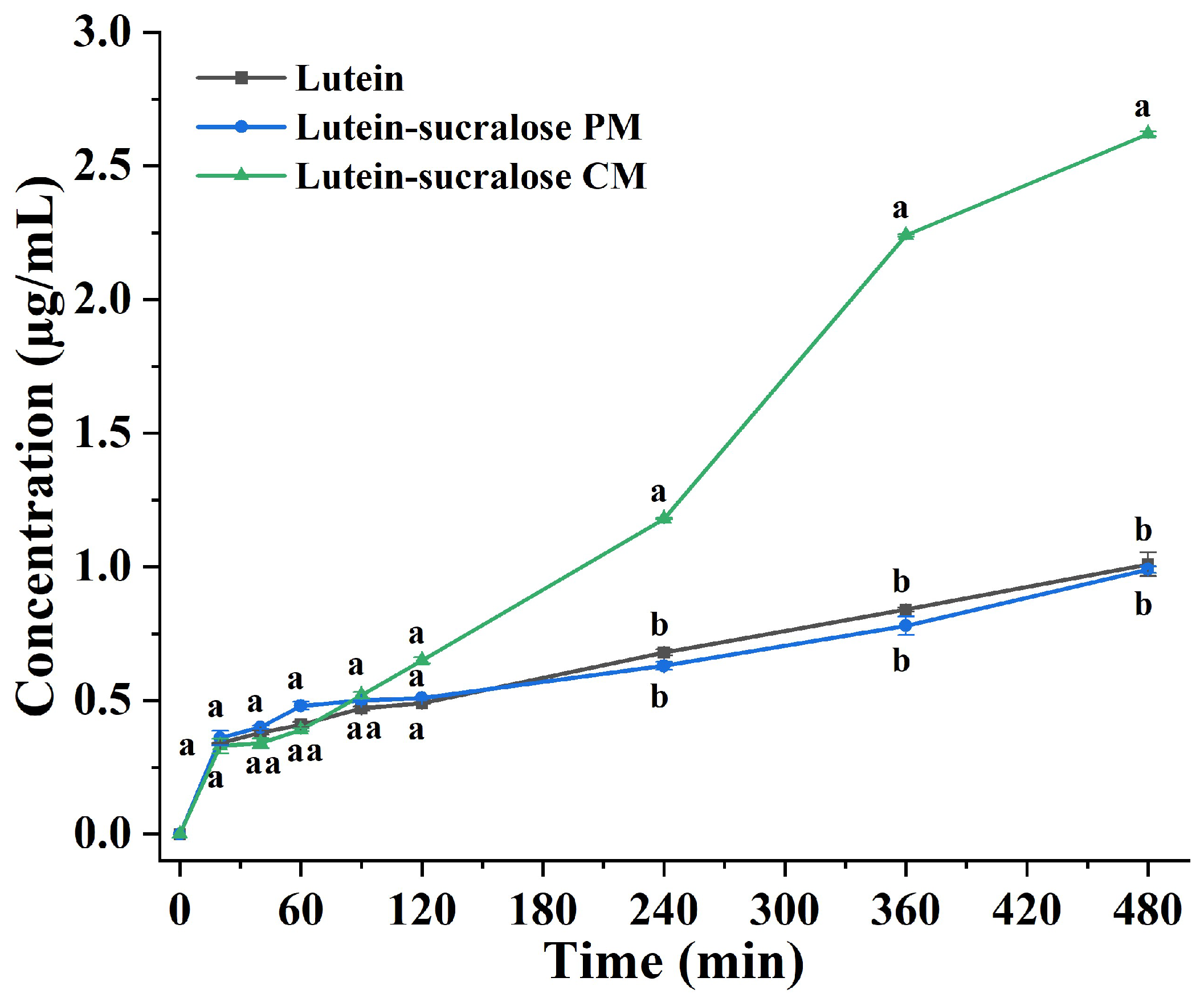
3.3. Dissolution Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steiner, B.M.; McClements, D.J.; Davidov-Pardo, G. Encapsulation systems for lutein: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 82, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa Becerra, M.; Mojica Contreras, L.; Hsieh Lo, M.; Mateos Díaz, J.; Castillo Herrera, G. Lutein as a functional food ingredient: Stability and bioavailability. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 66, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Lee, J.C.; Leung, H.H.; Lam, W.C.; Fu, Z.; Lo, A. Lutein supplementation for eye diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dawson, R.; Kong, L. Roles of macular carotenoids in brain function throughout the lifespan: A review of recent research. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscemi, S.; Corleo, D.; Di Pace, F.; Petroni, M.L.; Satriano, A.; Marchesini, G. The effect of lutein on eye and extra-eye health. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, I.; Yathisha, U.G.; Karunasagar, I.; Mamatha, B.S. Nutraceutical approach to enhance lutein bioavailability via nanodelivery systems. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 709–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, L.M.; Tharmarajah, S.; Jia, Y.; Semba, R.D.; Schaumberg, D.A.; Robinson, K.A. The effect of lutein/zeaxanthin intake on human macular pigment optical density: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 2244–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Lin, J.J.; Chee, X.; Liu, M.H.; Khan, S.A.; Kim, J.E. Encapsulation of lutein via microfluidic technology: Evaluation of stability and in vitro bioaccessibility. Foods 2021, 10, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Kang, J.K.; Jung, C.E.; Sim, T.; Her, J.; Kang, K.; Lee, E.S.; Youn, Y.S.; Choi, H.G.; Oh, K.T. Preparation and characterisation of a lutein solid dispersion to improve its solubility and stability. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algan, A.H.; Gungor-Ak, A.; Karatas, A. Nanoscale delivery systems of lutein: An updated review from a pharmaceutical perspective. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Jin, S.H.; Hong, S.H.; Ha, E.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.S.; Baek, I.H.; Kim, M.S.; Hwang, S.J. Characterisation and therapeutic efficacy evaluation of glimepiride and L-arginine co-amorphous formulation prepared by supercritical antisolvent process: Influence of molar ratio and preparation methods. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 581, 119232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Martins, I.; Rades, T. Recent advances in co-former screening and formation prediction of multicomponent solid forms of low molecular weight drugs. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Moinuddin, S.M.; Cai, T. Advances in coamorphous drug delivery systems. APSB 2019, 9, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayanfar, A.; Ghavimi, H.; Hamishekar, H.; Jouyban, A. Coamorphous atorvastatin calcium to improve its physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 16, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samipillai, M.; Mirmehrabi, M.; Rohani, S. Co-amorphous solids of dasatinib and olanzapine by saccharin with promising physicochemical properties. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.D.; Chen, X.; Li, D.X.; Zhang, H.L.; Duan, Y.W.; Huang, Y. Tranilast-matrine co-amorphous system: Strong intermolecular interactions, improved solubility, and physiochemical stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J. Interaction of sucralose with whey protein: Experimental and molecular modeling studies. Spectrochim. Acta A 2017, 187, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grice, H.C.; Goldsmith, L.A. Sucralose—An overview of the toxicity data. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2000, 38, S1–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Monteagudo, S.I.; Enteshari, M.; Metzger, L. Lactitol: Production, properties, and applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzechonek, D.A.; Dobrowolski, A.; Rymowicz, W.; Mirończuk, A.M. Recent advances in biological production of erythritol. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, M.; Liu, T.; Gao, Z.; Ye, Q.; Tan, X.; Hou, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; He, Z. Co-amorphous solid dispersion systems of lacidipine-spironolactone with improved dissolution rate and enhanced physical stability. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, Z.; Aeri, V. Enhancement of lutein content in Calendula officinalis Linn. By solid-state fermentation with lactobacillus species. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 4794–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Feng, Y.; Yuan, D.; Xu, R.J.; Jiang, C.P.; Xiao, X.C.; Lu, S. Design and molecular insights of drug-active metabolite based co-amorphous formulation: A case study of toltrazuril-ponazuril co-amorphous. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 615, 121475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangid, A.K.; Jain, P.; Medicherla, K.; Pooja, D.; Kulhari, H. Solid-state properties, solubility, stability and dissolution behaviour of co-amorphous solid dispersions of baicalin. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 6128–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Hu, Y.; Wu, T.; Feng, Y.; Jiang, C.; Du, H.; Lu, S. Apigenin-oxymatrine binary co-amorphous mixture: Enhanced solubility, bioavailability, and anti-inflammatory effect. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Han, J.; Wang, R.; Zhao, X.; Qiao, H.; Chen, L.; Li, W.; Di, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, J. Surfactant-free solid dispersion of BCS class IV drug in an amorphous chitosan oligosaccharide matrix for concomitant dissolution in vitro—Permeability increase. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 130, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarlagadda, D.L.; Sai Krishna Anand, V.; Nair, A.R.; Navya Sree, K.S.; Dengale, S.J.; Bhat, K. Considerations for the selection of co-formers in the preparation of co-amorphous formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 602, 120649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelke, R.; Velagacherla, V.; Nayak, U.Y. Recent advances in dual-drug co-amorphous systems. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Li, L.; Su, M.; Heng, W.; Wei, Y.; Gao, Y.; Qian, S. Deaggregation and crystallization inhibition by small amount of polymer addition for a co-amorphous curcumin-magnolol system. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Ahn, D.U. Enhanced lutein stability under UV-Light and high temperature by loading it into alginate-chitosan complex. LWT 2022, 164, 113663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avadhani, K.S.; Manikkath, J.; Tiwari, M.; Chandrasekhar, M.; Godavarthi, A.; Vidya, S.M.; Hariharapura, R.C.; Kalthur, G.; Udupa, N.; Mutalik, S. Skin delivery of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) and hyaluronic acid loaded nano-transfersomes for antioxidant and anti-aging effects in UV radiation induced skin damage. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalawade, P.; Gajjar, A. Preparation and characterisation of spray dried complexes of lutein with cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2015, 83, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, A.; Strachan, C.J.; Gordon, K.C.; Rades, T. Analysis of solid-state transformations of pharmaceutical compounds using vibrational spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 971–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Duan, Y.; Huang, Y. Sustained release of co-amorphous matrine-type alkaloids and resveratrol with anti-COVID-19 potential. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Liang, D.; Xu, D.; Cao, Y.; Sun, B. The improvement of the physicochemical properties and bioaccessibility of lutein microparticles by electrostatic complexation. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizuela, A.B.; Raschi, A.B.; Castillo, M.V.; Leyton, P.; Romano, E.; Brandán, S.A. Theoretical structural and vibrational properties of the artificial sweetener sucralose. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2013, 1008, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, S.; Boateng, J.S. In vitro, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation of taste masked low dose acetylsalicylic acid loaded composite wafers as platforms for buccal administration in geriatric patients with dysphagia. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hu, Y.; Yang, G.; Shi, W.; Lu, S.; Cao, Y. Improving physicochemical properties and pharmacological activities of ternary co-amorphous systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 181, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vullendula, S.K.A.; Nair, A.R.; Yarlagadda, D.L.; Navya Sree, K.S.; Bhat, K.; Dengale, S.J. Polymeric solid dispersion vs. co-amorphous technology: A critical comparison. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 78, 103980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczko, D.; Hachuła, B.; Maksym, P.; Kamiński, K.; Zięba, A.; Orszulak, L.; Paluch, M.; Kamińska, E. The effect of various poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP) polymers on the crystallization of flutamide. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Han, J.; Jiang, A.; Huang, R.; Fu, T.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Li, W.; Li, J. Involvement of metabolism-permeability in enhancing the oral bioavailability of curcumin in excipient-free solid dispersions co-formed with piperine. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 561, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, X.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Preparation and Characterization of Lutein Co-Amorphous Formulation with Enhanced Solubility and Dissolution. Foods 2024, 13, 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132029
Song X, Luo Y, Zhao W, Liu S, Wang Y, Zhang H. Preparation and Characterization of Lutein Co-Amorphous Formulation with Enhanced Solubility and Dissolution. Foods. 2024; 13(13):2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132029
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Xuening, Yingting Luo, Wenduo Zhao, Simiao Liu, Yuzhuo Wang, and Hao Zhang. 2024. "Preparation and Characterization of Lutein Co-Amorphous Formulation with Enhanced Solubility and Dissolution" Foods 13, no. 13: 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132029
APA StyleSong, X., Luo, Y., Zhao, W., Liu, S., Wang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2024). Preparation and Characterization of Lutein Co-Amorphous Formulation with Enhanced Solubility and Dissolution. Foods, 13(13), 2029. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13132029





