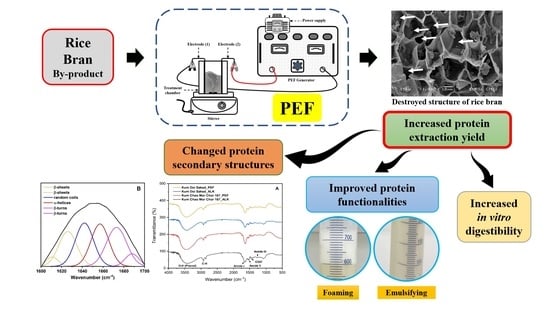
Impacts of Electroextraction Using the Pulsed Electric Field on Properties of Rice Bran Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Rice Bran Preparation
2.3. Electroextraction of Rice Bran Protein Using Pulsed Electric Field (PEF)
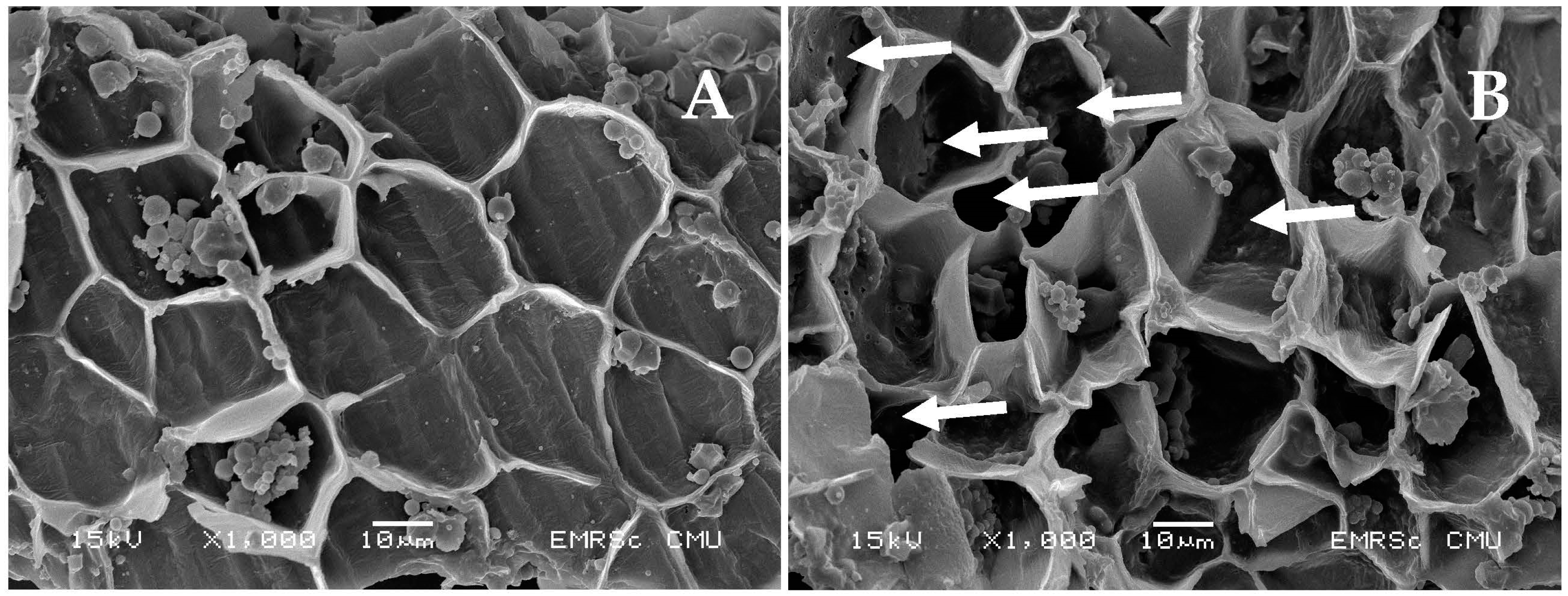
2.4. Rice Bran Morphology Analysis
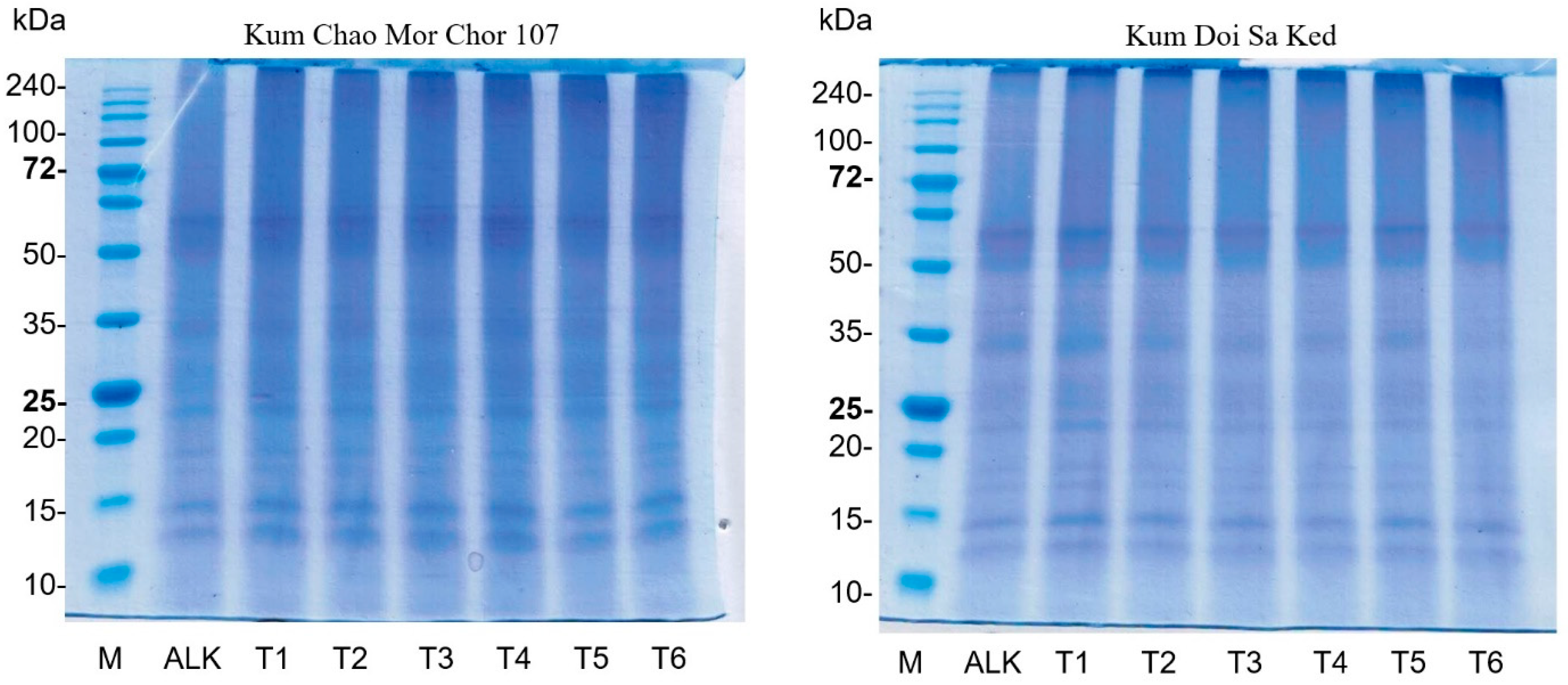
2.5. Protein Pattern Using SDS-PAGE
2.6. Amino Acid Composition Analysis
2.7. Functional Properties Determinations
2.7.1. Oil Holding Capacity
2.7.2. Foaming Properties
2.7.3. Emulsifying Properties
2.8. Secondary Structure Changes Using Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.9. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion
2.10. Antioxidant Activity Determinations
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of PEF Treatment on Protein Extraction
3.2. Effect of PEF on Amino Acid Composition
3.3. Effect of PEF on Protein Pattern
3.4. Effect of PEF on Secondary Structure
3.5. Effect of PEF on Functional Properties
3.6. In Vitro Digestibility and Antioxidant Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imsanguan, P.; Roaysubtawee, A.; Borirak, R.; Pongamphai, S.; Douglas, S.; Douglas, P.L. Extraction of α-tocopherol and γ-oryzanol from rice bran. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hua, N.; Godber, J.S. Antioxidant activity of tocopherols, tocotrienols, and γ-oryzanol components from rice bran against cholesterol oxidation accelerated by 2, 2 ‘-azobis (2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2077–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, C.; Ju, Y.H. A review on rice bran protein: Its properties and extraction methods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surin, S.; Surayot, U.; Seesuriyachan, P.; You, S.G.; Phimolsiripol, Y. Antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of sulphated polysaccharides from purple glutinous rice bran (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Food Sci. 2017, 53, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongthai, S.; D’Amico, S.; Schoenlechner, R.; Rawdkuen, S. Fractionation and antioxidant properties of rice bran protein hydrolysates stimulated by in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongthai, S.; Lim, S.T.; Rawdkuen, S. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of rice bran protein using response surface methodology. J. Food Biochem. 2016, 41, e12314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongthai, S.; Lim, S.T.; Rawdkuen, S. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of rice bran protein and its hydrolysates properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 70, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanasiritham, L.; Theerakulkait, C.; Wickramasekara, S.; Maier, C.S.; Stevens, J.F. Isolation and identification of antioxidant peptides from enzymatically hydrolyzed rice bran protein. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phongthai, S.; Singsaeng, N.; Nhoo-ied, R.; Suwannatrai, T.; Schönlechner, R.; Unban, K.; Klunklin, W.; Laokuldilok, T.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Rawdkuen, S. Properties of peanut (KAC431) protein hydrolysates and their impact on the quality of gluten-free rice bread. Foods 2020, 9, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaessen, E.M.J.; Timmermans, R.A.H.; Tempelaars, M.H.; Schutyser, M.A.I.; Den Besten, H.M.W. Reversibility of membrane permeabilization upon pulsed electric field treatment in Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lyu, X.; Arshad, R.N.; Aadil, R.M.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yang, R. Pulsed electric field as a promising technology for solid foods processing: A review. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, R.N.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Roobab, U.; Munir, M.A.; Naderipour, A.; Qureshi, M.I.; Bekhit, A.E.D.; Liu, Z.W.; Aadil, R.M. Pulsed electric field: A potential alternative towards a sustainable food processing. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, M.M.A.; Kanwal, R.; Shafique, B.; Arshad, R.N.; Irfan, S.; Kieliszek, M.; Aadil, R.M. A critical review on pulsed electric field: A novel technology for the extraction of phytoconstituents. Molecules 2021, 26, 4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Q.; Roginski, H.; Williams, R.P.W.; Versteeg, C.; Wan, J. Effect of pulsed electric field and thermal treatment on the physicochemical and functional properties of whey protein isolate. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.J.; Jiang, W.; Qian, J.Y. Effect of pulsed electric field on functional and structural properties of canola protein by pretreating seeds to elevate oil yield. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhao, X.D.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Wu, C.; Ding, X.; Qian, J.Y. Assessment of impact of pulsed electric field on functional, rheological and structural properties of vital wheat gluten. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 147, 111536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.J.; Ma, L.J.; Wang, L.J.; Jiang, W. Effect of pulsed electric field on structural properties of protein in solid state. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Wang, J.M.; Gong, Q.; Yang, X.Q.; Yin, S.W.; Qi, J.R. Characterization and in vitro digestibility of rice protein prepared by enzyme-assisted microfluidization: Comparison to alkaline extraction. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 56, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psarianos, M.; Dimopoulos, G.; Ojha, S.; Ana Clara MorenoCavinia, A.C.M.; Bußler, S.; Taoukis, P.; Schlüter, O.K. Effect of pulsed electric fields on cricket (Acheta domesticus) flour: Extraction yield (protein, fat and chitin) and techno-functional properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 76, 102908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Käferböck, A.; Smetana, S.; Vos, R.; Schwarz, C.; Toepfl, S.; Parniakov, O. Sustainable extraction of valuable components from Spirulina assisted by pulsed electric fields technology. Algal Res. 2020, 48, 101914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, L.; Ju, H.; Bao, Z.; Zeng, X.; Lin, S. Research advances and application of pulsed electric field on proteins and peptides in food. Food Res. Int. 2020, 139, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, G.P.; Postma, P.R.; Fernandes, D.A.; Timmermans, R.A.H.; Vermuë, M.H.; Barbosa, M.J.; Eppink, M.H.M.; Wijffels, R.H.; Olivieri, G. Pulsed electric field for protein release of the microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and Neochloris oleoabundans. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, L.; Mathys, A. Perspective on pulsed electric field treatment in the bio-based industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Mason, S.L.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A. Pulsed electric field: Role in protein digestion of beef Biceps femoris. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 50, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Mason, S.L.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A.; Mungure, T.E. Pulsed electric field: Effect on in-vitro simulated gastrointestinal protein digestion of deer Longissimus dorsi. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Mason, S.L.; Jayawardena, S.R.; Bekhit, A.E.D.A. Pulsed electric field: A new way to improve digestibility of cooked beef. Meat Sci. 2019, 155, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhao, W.; Yang, R.; Chen, X. Effects of pulsed electric fields processing on stability of egg white proteins. J. Food Eng. 2014, 139, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, M.; Wang, P.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Physicochemical and structural properties of myofibrillar proteins isolated from pale, soft, exudative (PSE)-like chicken breast meat: Effects of pulsed electric field (PEF). Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 59, 102277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X. Secondary structure changes induced by pulsed electric field affect antioxidant activity of pentapeptides from pine nut (Pinus koraiensis) protein. Food Chem. 2018, 254, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chungchunlam, S.M.D.; Henare1, J.S.; Ganesh, S.; Moughan, P.J. Effect of whey protein and a free amino acid mixture simulating whey protein on measures of satiety in normal weight women. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1666–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, R.; Tang, Y.; Lu, R. Combined effects of heat and PEF on microbial inactivation and quality of liquid egg whites. Int. J. Food Eng. 2007, 3, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | Treatment Time (min) PEF/ALK | Extracted Protein (mg) | Protein Increment (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kum Chao Mor Chor 107 | Kum Doi Saket | Kum Chao Mor Chor 107 | Kum Doi Saket | ||
| ALK | 0/60 | 2060.28 ± 80.94 D | 2427.51 ± 16.52 e | - | - |
| 15/45 | 2281.70 ± 50.10 C | 2618.28 ± 24.78 d | 10.78 ± 1.92 D | 7.87 ± 1.75 c | |
| 1.3 kV/cm | 20/40 | 2323.50 ± 68.74 B,C | 2775.66 ± 57.23 c | 12.80 ± 1.09 C | 14.35 ± 2.49 a,b |
| 25/35 | 2407.13 ± 65.60 A,B | 2875.81 ± 75.71 b,c | 16.86 ± 1.41 B | 18.47 ± 2.97 a | |
| 15/45 | 2289.20 ± 40.47 C | 2687.35 ± 50.73 c,d | 11.16 ± 2.40 C,D | 10.70 ± 1.58 b | |
| 2.3 kV/cm | 20/40 | 2367.89 ± 50.58 B,C | 2691.43 ± 14.58 c | 14.97 ± 2.06 C | 10.87 ± 0.87 b |
| 25/35 | 2485.82 ± 35.25 A | 2980.73 ± 29.78 a | 20.71 ± 3.03 A | 22.80 ± 2.04 a | |
| Amino Acid | Kum Chao Mor Chor 107 | Kum Doi Sa Ket | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALK | PEF | ALK | PEF | |
| Essential amino acids (EAA) | ||||
| Histidine | 640.20 ± 48.63 | 684.25 ± 109.96 | 722.04 ± 8.75 | 736.90 ± 13.93 |
| Isoleucine | 634.17 ± 77.90 | 672.08 ± 130.79 | 660.82 ± 6.23 | 739.26 ± 7.14 |
| Leucine | 1658.21 ± 252.24 | 1607.07 ± 306.33 | 1630.98 ± 27.83 | 1762.62 ± 12.49 |
| Lysine | 1073.06 ± 215.67 | 1028.56 ± 191.76 | 1127.11 ± 21.00 | 1112.95 ± 20.48 |
| Methionine | 287.60 ± 9.09 | 314.78 ± 74.47 | 342.34 ± 1.81 | 358.22 ± 2.23 |
| Phenylalanine | 998.18 ± 92.44 | 958.00 ± 186.67 | 958.68 ± 8.76 | 1058.55 ± 7.19 |
| Threonine | 856.49 ± 174.24 | 672.21 ± 103.87 | 751.54 ± 64.08 | 715.86 ± 5.02 |
| Valine | 1356.95 ± 21.41 | 1353.54 ± 273.08 | 1324.88 ± 2.33 | 1516.78 ± 3.34 |
| Sum | 7504.86 | 7290.49 | 7518.39 | 8001.14 |
| Non-essential amino acids(Non-EEA) | ||||
| Aspartic acid | 2022.32 ± 417.52 | 1762.14 ± 331.80 | 1846.45 ± 71.62 | 1936.99 ± 18.28 |
| Serine | 1059.88 ± 141.71 | 995.36 ± 194.39 | 1023.90 ± 23.69 | 1096.07 ± 14.58 |
| Glutamic acid | 3017.71 ± 157.71 | 3180.24 ± 609.82 | 3299.06 ± 4.39 | 3522.90 ± 25.40 |
| Proline | 722.95 ± 180.74 | 488.39 ± 65.75 | 1978.46 ± 116.23 | 1931.47 ± 3.76 |
| Glycine | 1228.99 ± 107.95 | 1267.13 ± 242.40 | 1327.04 ± 3.32 | 1403.36 ± 8.17 |
| Alanine | 1501.72 ± 222.36 | 1412.67 ± 279.68 | 1427.34 ± 8.17 | 1564.39 ± 15.99 |
| L-Cystine | 84.11 ± 36.20 | 62.98 ± 9.75 | 82.95 ± 10.18 | 68.06 ± 1.98 |
| Tyrosine | 579.68 ± 165.46 | 559.94 ± 92.45 | 592.01 ± 26.43 | 597.44 ± 4.19 |
| Arginine | 1869.05 ± 32.71 | 2016.62 ± 402.38 | 2127.96 ± 5.39 | 2250.20 ± 3.32 |
| Sum | 12,086.41 | 11,745.47 | 13,705.17 | 14,370.88 |
| EAA:Non-EAA ratio | 0.62 ± 0.01 ns | 0.62 ± 0.01 ns | 0.55 ± 0.08 ns | 0.55 ± 0.06 ns |
| % Essential amino acid | 38.31 ± 0.07 ns | 38.29 ± 0.08 ns | 35.42 ± 0.40 ns | 35.76 ± 0.02 ns |
| Total amino acid contents | 19,591.27 | 19,035.96 | 21,223.56 | 22,372.72 |
| Properties | Kum Chao Mor Chor 107 | Kum Doi Sa Ket | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALK | PEF | ALK | PEF | |
| Secondary Structures | ||||
| α-helices (portion, %) | 23.47 ± 0.06 B | 24.37 ± 0.06 A | 24.29 ± 0.06 b | 24.64 ± 0.06 a |
| β-sheets (portion, %) | 22.84 ± 0.05 B | 29.94 ± 0.06 A | 24.87 ± 0.06 b | 27.13 ± 0.05 a |
| β-turns (portion, %) | 29.64 ± 0.07 A | 23.15 ± 0.06 B | 26.48 ± 0.06 a | 25.63 ± 0.06 b |
| Random coils (portion, %) | 24.23 ± 0.06 A | 22.54 ± 0.06 B | 24.01 ± 0.06 a | 22.95 ± 0.06 b |
| Functional properties | ||||
| Oil binding capacity (g oil/g sample) | 2.65 ± 0.06 B | 3.25 ± 0.02 A | 2.76 ± 0.02 b | 3.32 ± 0.06 a |
| Foaming ability (%) | 4.7 ± 0.30 B | 13.4 ± 0.30 A | 4.7 ± 0.10 b | 11.7 ± 1.90 a |
| Foaming stability (%) | 55.6 ± 7.90 B | 100 ± 0.00 A | 33.3 ± 23.60 b | 61.1± 7.90 a |
| Emulsifying ability (%) | 96.7 ± 0.90 B | 100 ± 0.00 A | 94.7 ± 1.90 b | 100 ± 0.00 a |
| Emulsifying stability (%) | 69.0 ± 1.40 B | 75.6± 1.00 A | 68.4 ± 2.40 b | 76.6 ± 0.20 a |
| Antioxidant properties | ||||
| DPPH radical-scavenging activity (% Increment, after in vitro digestion) | 22.37 ± 0.01 B | 37.84 ± 0.01 A | 28.75 ± 0.01 b | 40.45 ± 0.01 a |
| ABTS radical-scavenging activity(% Increment, after in vitro digestion) | 12.75 ± 0.07 B | 37.86 ± 0.03 A | 3.94 ± 0.04 b | 28.46 ± 0.03 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thongkong, S.; Klangpetch, W.; Unban, K.; Tangjaidee, P.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Rachtanapun, P.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Schönlechner, R.; Thipchai, P.; Phongthai, S. Impacts of Electroextraction Using the Pulsed Electric Field on Properties of Rice Bran Protein. Foods 2023, 12, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040835
Thongkong S, Klangpetch W, Unban K, Tangjaidee P, Phimolsiripol Y, Rachtanapun P, Jantanasakulwong K, Schönlechner R, Thipchai P, Phongthai S. Impacts of Electroextraction Using the Pulsed Electric Field on Properties of Rice Bran Protein. Foods. 2023; 12(4):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040835
Chicago/Turabian StyleThongkong, Saban, Wannaporn Klangpetch, Kridsada Unban, Pipat Tangjaidee, Yuthana Phimolsiripol, Pornchai Rachtanapun, Kittisak Jantanasakulwong, Regine Schönlechner, Parichat Thipchai, and Suphat Phongthai. 2023. "Impacts of Electroextraction Using the Pulsed Electric Field on Properties of Rice Bran Protein" Foods 12, no. 4: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040835
APA StyleThongkong, S., Klangpetch, W., Unban, K., Tangjaidee, P., Phimolsiripol, Y., Rachtanapun, P., Jantanasakulwong, K., Schönlechner, R., Thipchai, P., & Phongthai, S. (2023). Impacts of Electroextraction Using the Pulsed Electric Field on Properties of Rice Bran Protein. Foods, 12(4), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040835