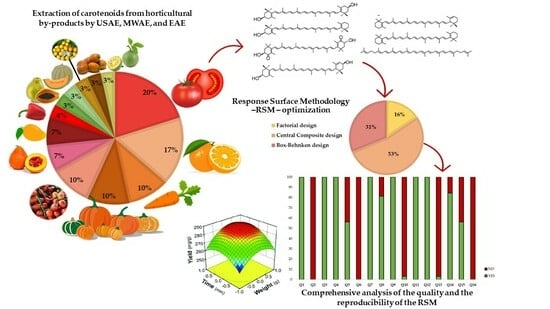
Response Surface Methodology to Optimize the Extraction of Carotenoids from Horticultural By-Products—A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. A Short Overview of Response Surface Methodology Applied in By-Products Revalorization Area
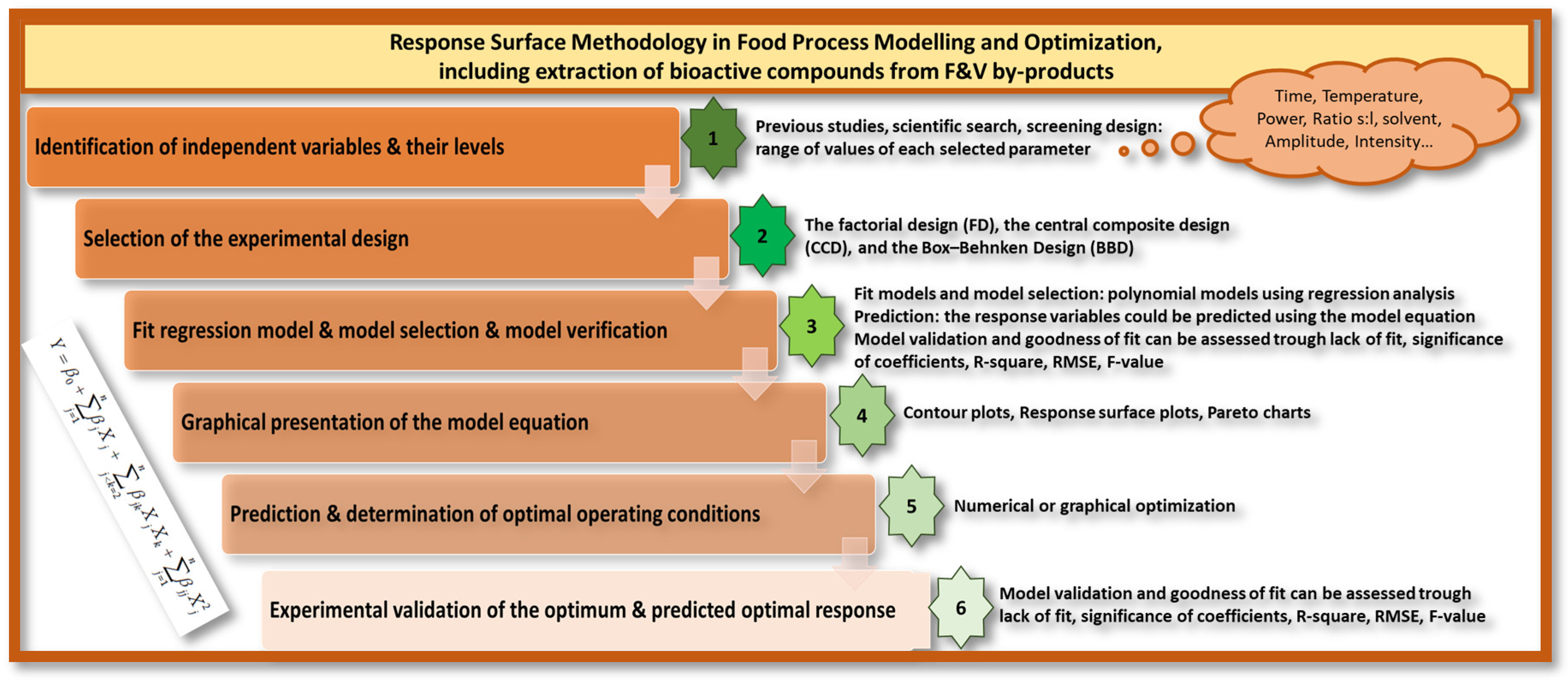
1.1. Steps for Properly Implementing Experimental Response Surface Methodology
1.1.1. Identification of Inputs and Their Levels
1.1.2. Selection of the Experimental Response Surface Methodology Design
- Factorial design
- Central composite design
- Box–Behnken design
1.1.3. Selection of a Regression Model and Prediction and Verification of Model Equation
1.1.4. Graphical Presentation of the Model Equation
1.1.5. Prediction and Determination of Optimal Operating Conditions
2. Importance of Carotenoids from Horticultural By-Products
3. Methodology
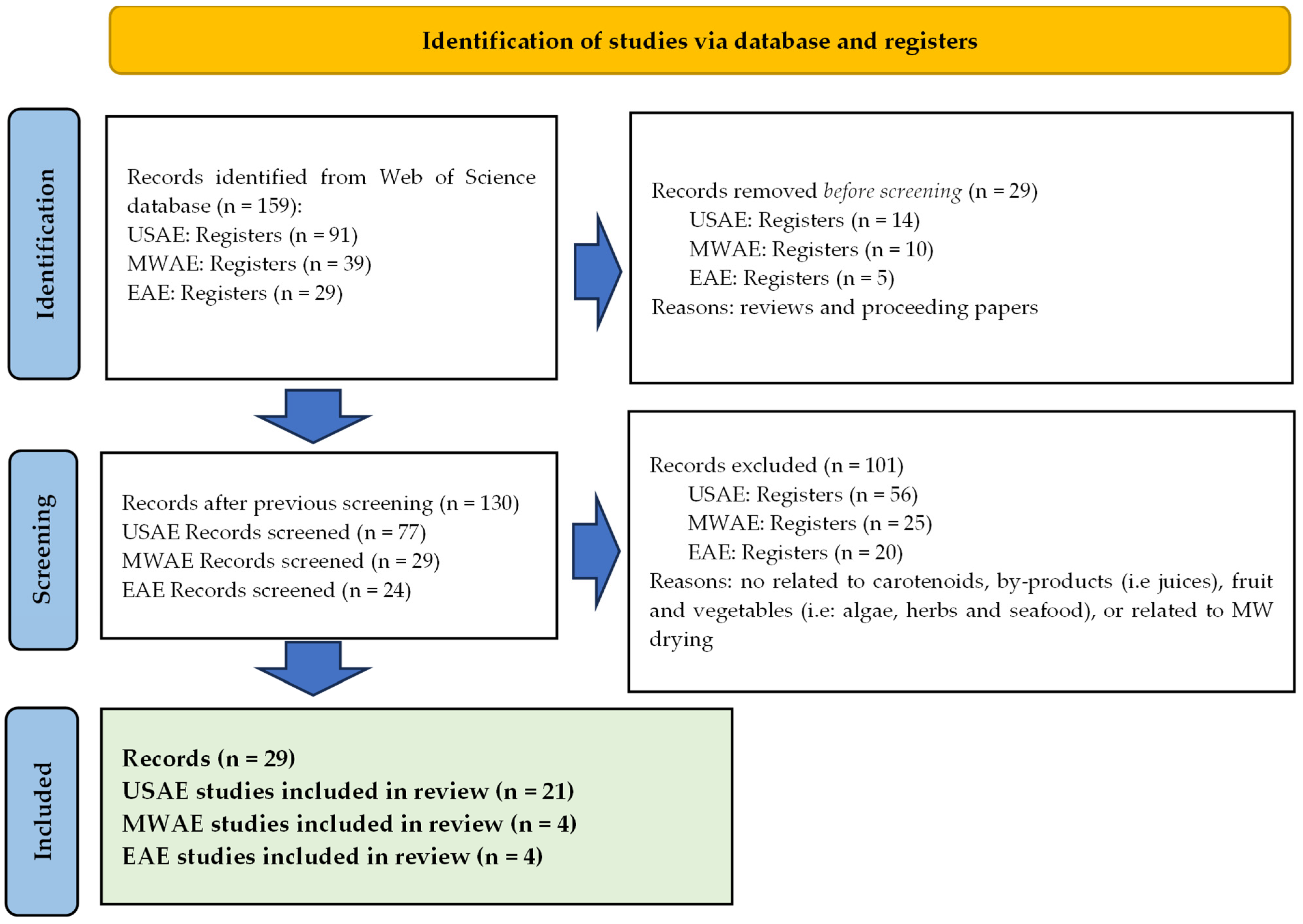
3.1. Search and Eligibility Criteria
3.2. Data Synthesis: PRISMA Flow Diagram
3.3. Data Collection Process and Quality Criteria
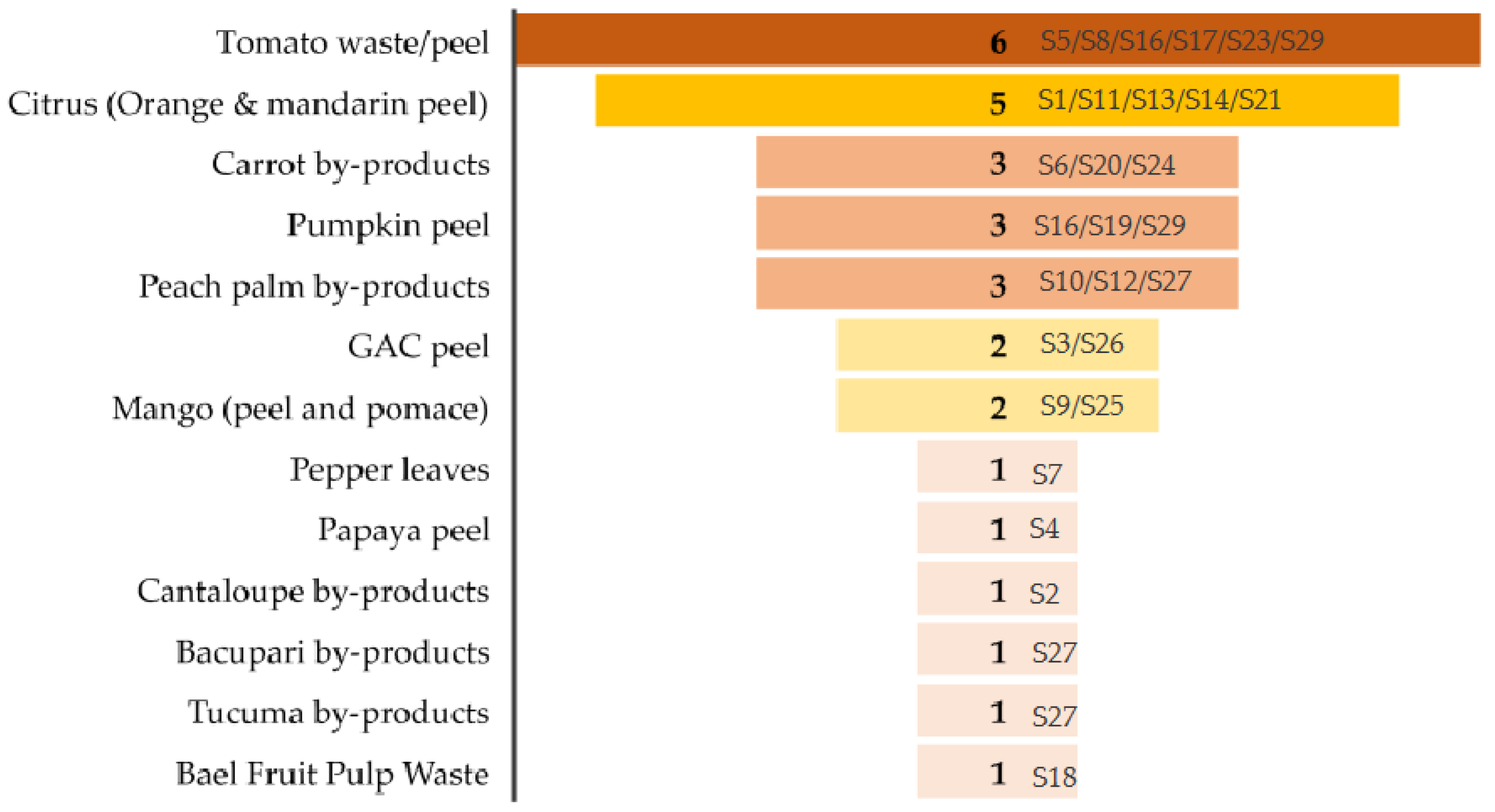
4. Application of RSM to Carotenoids Extraction from Horticultural By-Products
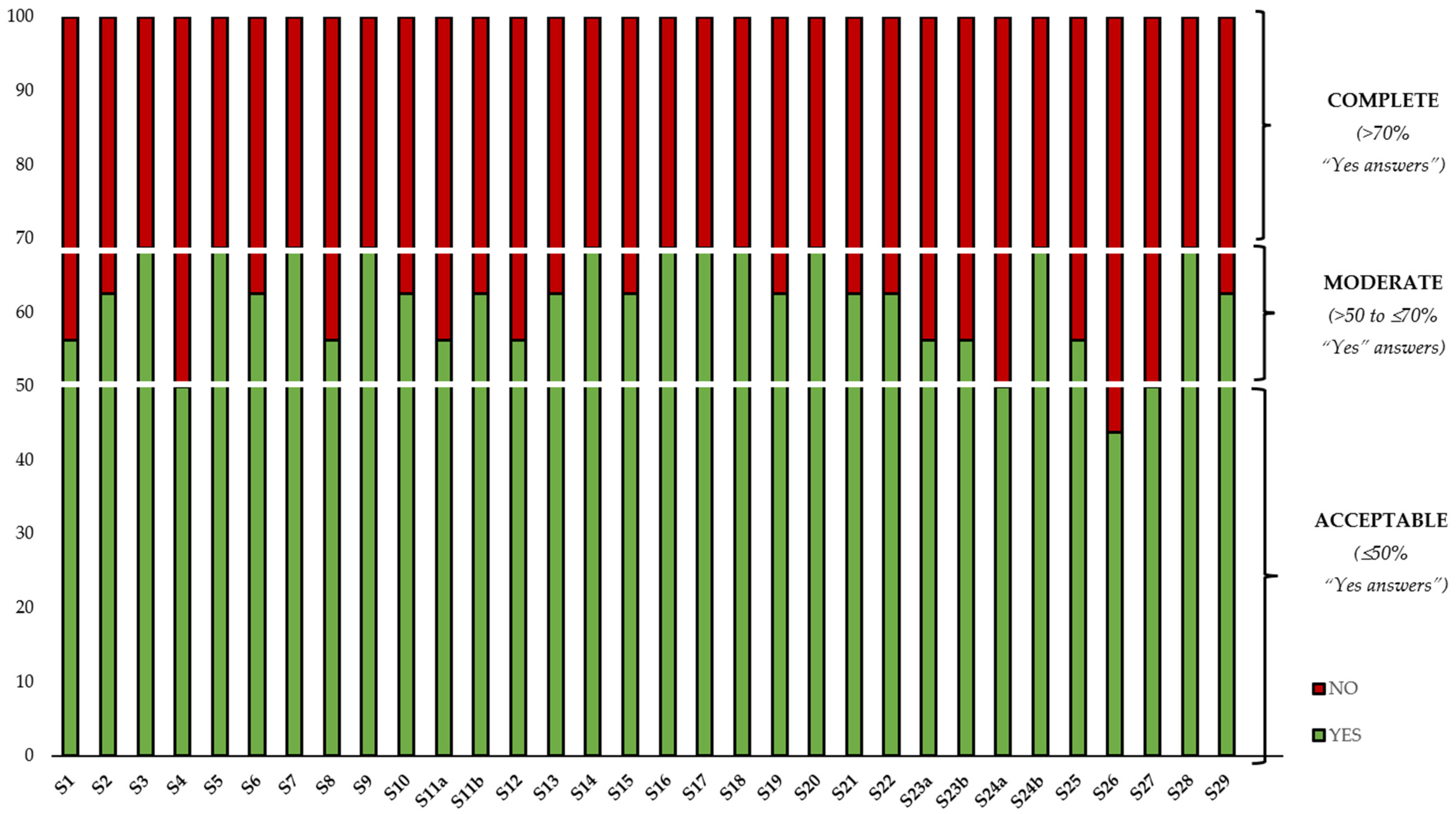
Quality Criteria of the Selected Papers and Breakdown of the Quality Criteria
| Technique | Study | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Q5 | Q6 | Q7 | Q8 | Q9 | Q10 | Q11 | Q12 | Q13 | Q14 | Q15 | Q16 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USAE | S1 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [27] |
| S2 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [28] | |
| S3 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [29] | |
| S4 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | NO | [22] | |
| S5 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [30] | |
| S6 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | NO | [31] | |
| S7 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [32] | |
| S8 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | NO | [33] | |
| S9 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [34] | |
| S10 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [35] | |
| S11a | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | NO | [36] | |
| S11b | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | NO | [36] | |
| S12 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | NO | [37] | |
| S13 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | NO | [38] | |
| S14 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [39] | |
| S15 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [40] | |
| S16 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [41] | |
| S17 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [42] | |
| S18 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [43] | |
| S19 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [44] | |
| S20 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [45] | |
| S21 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [46] | |
| MWAE | S22 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [47] |
| S23a | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | NO | [48] | |
| S23b | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | NO | [48] | |
| S24a | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | NO | [23] | |
| S24b | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [23] | |
| S25 | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | NO | [24] | |
| EAE | S26 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | NO | NO | [49] |
| S27 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | NO | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | NO | NO | [25] | |
| S28 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | NO | NO | [26] | |
| S29 | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | YES | YES | NO | [50] |
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barton, R.R. Response Surface Methodology. In Encyclopedia of Operations Research and Management Science; Gass, S.I., Fu, M.C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 1307–1313. ISBN 978-1-4419-1153-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yolmeh, M.; Jafari, S.M. Applications of Response Surface Methodology in the Food Industry Processes. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2017, 10, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Artés-Hernández, F. By-Products Revalorization with Non-Thermal Treatments to Enhance Phytochemical Compounds of Fruit and Vegetables Derived Products: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Jiménez, F.-J.; Fernández-Ochoa, Á.; Cádiz-Gurrea, M.d.l.L.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Oliver-Simancas, R.; Alañón, M.E.; Castangia, I.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Arráez-Román, D. Application of Response Surface Methodologies to Optimize High-Added Value Products Developments: Cosmetic Formulations as an Example. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shina, S. Three-Level Factorial Design and Analysis Techniques. In Industrial Design of Experiments: A Case Study Approach for Design and Process Optimization; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 187–215. ISBN 978-3-030-86267-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ait-Amir, B.; Pougnet, P.; El Hami, A. 6 - Meta-Model Development. In Embedded Mechatronic Systems 2; El Hami, A., Pougnet, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 151–179. ISBN 978-1-78548-014-0. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, A.; Fathy, S.; Kutlu, O.; Niikura, F.; Inayat, A.; Mustafa, M.; Abdellatief, T.M.M.; Bokhari, A.; Samuel, O.D.; Pastore, C.; et al. Cleaner and Sustainable Synthesis of High-Quality Monoglycerides by Use of Enzyme Technologies: Techno-Economic and Environmental Study for Monolaurin. Clean. Technol. Environ. Policy 2023, 25, 3263–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidane, S.W. Application of Response Surface Methodology in Food Process Modeling and Optimization. In Response Surface Methodology in Engineering Science; Kayaroganam, P., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alkiayat, M. A Practical Guide to Creating a Pareto Chart as a Quality Improvement Tool. Glob. J. Qual. Saf. Healthc. 2021, 4, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grané, A.; Jach, A. Applications of Principal Component Analysis (PCA) in Food Science and Technology. In Mathematical and Statistical Methods in Food Science and Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 55–86. ISBN 9781118434635. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, M.S. Natural Antioxidants: Sources, Compounds, Mechanisms of Action, and Potential Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorente, B.; Martinez-Garcia, J.F.; Stange, C.; Rodriguez-Concepcion, M. Illuminating Colors: Regulation of Carotenoid Biosynthesis and Accumulation by Light. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 37, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rocío Gómez-García, M.; Ochoa-Alejo, N. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Carotenoid Biosynthesis in Chili Peppers (Capsicum spp.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19025–19053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, F.; Hartmann, L.; Dubois-Laurent, C.; Welsch, R.; Huet, S.; Hamama, L.; Briard, M.; Peltier, D.; Gagné, S.; Geoffriau, E. Carotenoid Gene Expression Explains the Difference of Carotenoid Accumulation in Carrot Root Tissues. Planta 2017, 245, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.C.; de Camargo, B.A.F.; de Araújo, J.T.C.; Chorilli, M. Lycopene: From Tomato to Its Nutraceutical Use and Its Association with Nanotechnology. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meléndez-Martínez, A.J.; Mandić, A.I.; Bantis, F.; Böhm, V.; Borge, G.I.A.; Brnčić, M.; Bysted, A.; Cano, M.P.; Dias, M.G.; Elgersma, A.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on Carotenoids in Foods and Feeds: Status Quo, Applications, Patents, and Research Needs. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; An, C.G.; Park, J.S.; Lim, Y.P.; Kim, S. Carotenoid Profiling from 27 Types of Paprika (Capsicum Annuum L.) with Different Colors, Shapes, and Cultivation Methods. Food Chem. 2016, 76, C193–C198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, F.A.; Rashid, R.; Jabeen, A.; Brochier, B.; Yadav, S.; Aijaz, T.; Makroo, H.A.; Dar, B.N. Valorisation of Food Wastes to Produce Natural Pigments Using Non-Thermal Novel Extraction Methods: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 4823–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Zamora, L.; Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Artés-Hernández, F.; Castillejo, N. Flavonoid Extracts from Lemon By-Products as a Functional Ingredient for New Foods: A Systematic Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, P.B.V.; Brenelli, L.B.; Mariutti, L.R.B. Waste and By-Products as Sources of Lycopene, Phytoene, and Phytofluene - Integrative Review with Bibliometric Analysis. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Abia, S.; Welti-Chanes, J.; Cano, M.P. Effect of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Carotenoids from Papaya (Carica Papaya L. Cv. Sweet Mary) Using Vegetable Oils. Molecules 2022, 27, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Subramanian, J.; Singh, A. Green Extraction of Bioactive Components from Carrot Industry Waste and Evaluation of Spent Residue as an Energy Source. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Erazo, E.M.; Pasquel-Reátegui, J.L.; Dorronsoro-Guerrero, O.H.; Martínez-Correa, H.A. Phenolics and Carotenoids Recovery from Agroindustrial Mango Waste Using Microwave-Assisted Extraction: Extraction and Modeling. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, P.H.S.; Morais, R.A.; Sousa, H.M.S.; da Silva Gualberto, L.; Freitas, B.C.B.; Asquieri, E.R.; Martins, G.D.S.; de Barros Vilas Boas, E.V.; Damiani, C. Effects of Pectinase Treatment on the Optimization and Extraction of Pigments from Bacupari, Tucumã, and Peach Palm Using Response Surface Methodology. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2023, 00, e-20230124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sogi, D.S. Optimization of Enzyme Aided Pigment Extraction from Pumpkin (Cucurbita Maxima Duch) Using Response Surface Methodology. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiadis, V.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Kotsou, K.; Palaiogiannis, D.; Bozinou, E.; Lalas, S.I. Optimization of the Extraction Parameters for the Isolation of Bioactive Compounds from Orange Peel Waste. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmeziane, A.; Boulekbache-Makhlouf, L.; Mapelli-Brahm, P.; Khaled Khodja, N.; Remini, H.; Madani, K.; Meléndez-Martínez, A.J. Extraction of Carotenoids from Cantaloupe Waste and Determination of Its Mineral Composition. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuyen, H.V.; Roach, P.D.; Golding, J.B.; Parks, S.E.; Nguyen, M.H. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of GAC Peel: An Optimization of Extraction Conditions for Recovering Carotenoids and Antioxidant Capacity. Processes 2020, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eh, A.L.-S.; Teoh, S.-G. Novel Modified Ultrasonication Technique for the Extraction of Lycopene from Tomatoes. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Tomao, V.; Cravotto, G.; Chemat, F. Green Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Carotenoids Based on the Bio-Refinery Concept Using Sunflower Oil as an Alternative Solvent. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Li, J.; Ding, D.; Xie, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Ma, Y.; Gao, F.; Niu, T.; Wang, C.; et al. Optimum Parameters for Extracting Three Kinds of Carotenoids from Pepper Leaves by Response Surface Methodology. Separations 2021, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luengo, E.; Condón-Abanto, S.; Condón, S.; Álvarez, I.; Raso, J. Improving the Extraction of Carotenoids from Tomato Waste by Application of Ultrasound under Pressure. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 136, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado-Mercado, G.; Montalvo-González, E.; Sánchez-Burgos, J.A.; Velázquez-Estrada, R.M.; Álvarez-Parrilla, E.; González-Aguilar, G.A.; Sáyago-Ayerdi, S.G. Optimization of β-carotene from ‘ataulfo’ mango (mangifera indica L.) by-products using ultrasound-assisted extraction. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quim. 2019, 18, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MONTEIRO, S.F.; COSTA, E.L.N.; FERREIRA, R.S.B.; CHISTÉ, R.C. Simultaneous Extraction of Carotenoids and Phenolic Compounds from Pulps of Orange and Yellow Peach Palm Fruits (Bactris Gasipaes) by Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e34021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murador, D.C.; Braga, A.R.C.; Martins, P.L.G.; Mercadante, A.Z.; de Rosso, V. Ionic Liquid Associated with Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction: A New Approach to Obtain Carotenoids from Orange Peel. Food Res. Int. 2019, 126, 108653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordóñez-Santos, L.E.; Pinzón-Zarate, L.X.; González-Salcedo, L.O. Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction of Total Carotenoids from Peach Palm Fruit (Bactris Gasipaes) by-Products with Sunflower Oil Using Response Surface Methodology. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 27, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordóñez-Santos, L.E.; Esparza-Estrada, J.; Vanegas-Mahecha, P. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Total Carotenoids from Mandarin Epicarp and Application as Natural Colorant in Bakery Products. LWT 2021, 139, 110598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, A.; Panesar, P.S.; Bera, M.B. Valuation of Citrus Reticulata (Kinnow) Peel for the Extraction of Lutein Using Ultrasonication Technique. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 11, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebdani, M.M.; Abbasi, H. Green Extraction of Carotenoids from Pumpkin with Ultrasound-Assisted Method; Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.A.; Ferreira, T.A.P.C.; Celli, G.B.; Brooks, M.S. Optimization of Lycopene Extraction from Tomato Processing Waste Using an Eco-Friendly Ethyl Lactate–Ethyl Acetate Solvent: A Green Valorization Approach. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 2851–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.A.; Ferreira, T.A.P.C.; Jiao, G.; Brooks, M.S. Sustainable Approach for Lycopene Extraction from Tomato Processing By-Product Using Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonawane, A.; Pathak, S.S.; Pradhan, R.C. Bioactive Compounds in Bael Fruit Pulp Waste: Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction, Characterization, Modeling, and Optimization Approaches. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2020, 11, 9318–9334. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Yang, Q.; Huang, W.; Xiao, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, C. Optimization of Trans Lutein from Pumpkin (Cucurbita Moschata) Peel by Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 107, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair, M.; Jabbar, S.; Nasiru, M.M.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Abid, M.; Murtaza, M.A.; Kieliszek, M.; Zhao, L. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Carotenoids from Carrot Pomace and Their Optimization through Response Surface Methodology. Molecules 2021, 26, 6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viñas-Ospino, A.; López-Malo, D.; Esteve, M.J.; Frígola, A.; Blesa, J. Improving Carotenoid Extraction, Stability, and Antioxidant Activity from Citrus Sinensis Peels Using Green Solvents. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 2349–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elik, A.; Yanık, D.K.; Göğüş, F. Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Carotenoids from Carrot Juice Processing Waste Using Flaxseed Oil as a Solvent. LWT 2020, 123, 109100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.K.H.Y.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Liceaga, A.M.; San Martín-González, M.F. Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Lycopene in Tomato Peels: Effect of Extraction Conditions on All-Trans and Cis-Isomer Yields. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.C.; Truong, V.N.X.; Debaste, F. Optimisation of Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Oil Rich in Carotenoids from Gac Fruit (Momordica Cochinchinensis Spreng.). Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 51, 488–499. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, Q.T.N.; Nguyen, H.V.H. Optimization of Enzyme-Assisted Lycopene Extraction from Tomato (Lycopersicon Esculentum) Peel Using Rice Bran Oil. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 5154–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weremfo, A.; Abassah-Oppong, S.; Adulley, F.; Dabie, K.; Seidu-Larry, S. Response Surface Methodology as a Tool to Optimize the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Plant Sources. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K. Prospective Sustainable Agriculture Principles Inspired by Green Chemistry. Found. Chem. 2022, 24, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, P.R.; Jambrak, A.R.; Arya, S.S. Green, Environment-Friendly and Sustainable Techniques for Extraction of Food Bioactive Compounds and Waste Valorization. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 296–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
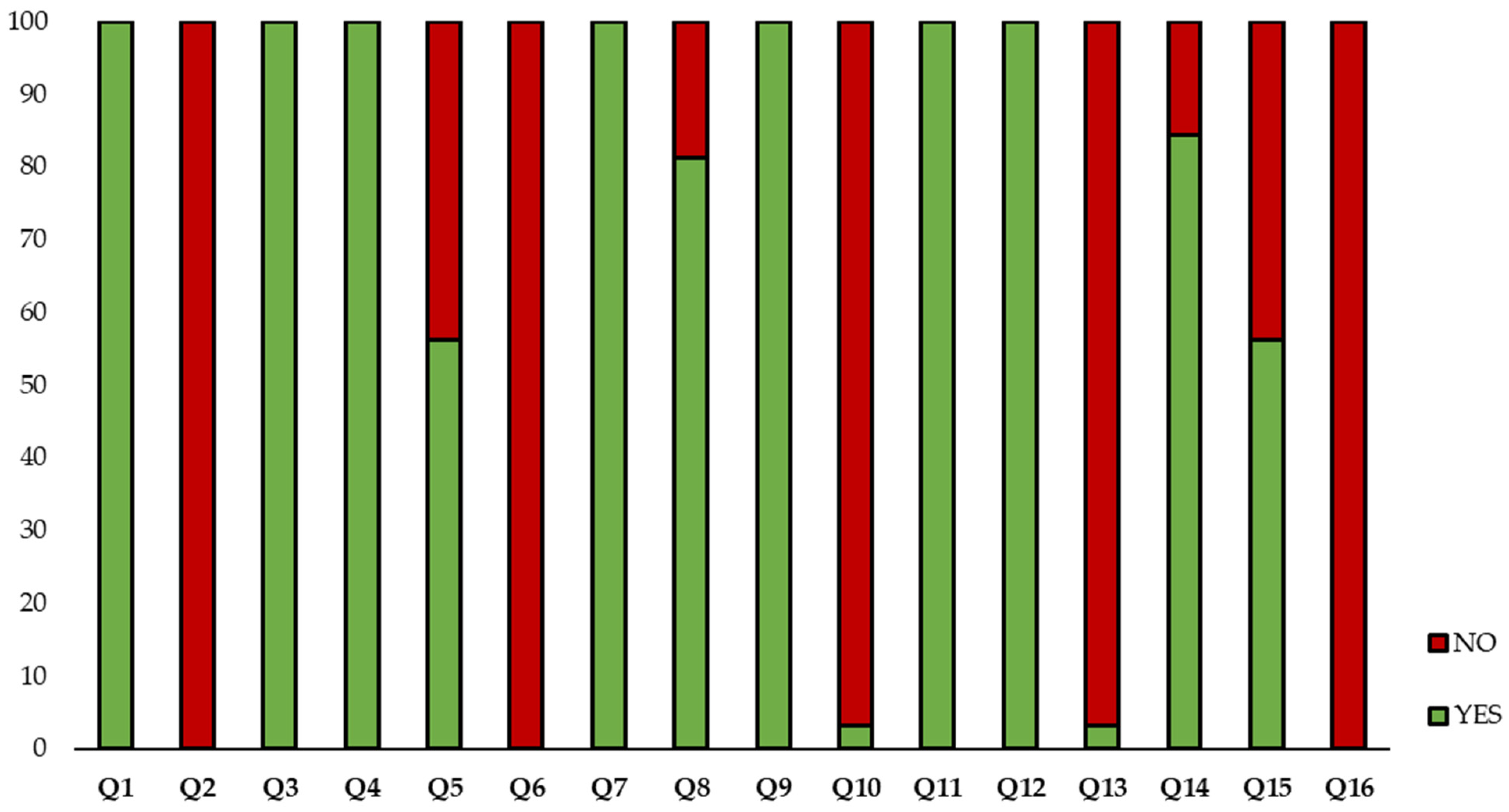
| Q1 | Does the article include an experimental design based on response surface methodology? |
| Q2 | Does the article explain the reason for the experimental design selection? |
| Q3 | Does the article define input factors and output responses? |
| Q4 | Does the article include factor levels? |
| Q5 | Does the article describe how the factor levels were selected? |
| Q6 | Do the authors report a transformation of the response data? |
| Q7 | Does the article include the number of experiments? |
| Q8 | Does the article show the experimental runs? |
| Q9 | Does the article show the measure of response in graphs? |
| Q10 | Are the data available? |
| Q11 | Are indicators for the quality of fit of the response surface included? |
| Q12 | Is a discussion about the significance of each factor’s effect included? |
| Q13 | Does the paper mention whether the statistical hypothesis of the model was checked? |
| Q14 | Does the article include the process optimization? |
| Q15 | If an optimum is found, was a further experiment carried out to validate the expected results? |
| Q16 | Is the code for data analysis available? |
| Tech. | Study | RSM Design | Levels | Experiments | Centers | Axial Points | Graphical Presentation | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USAE | S1 | FD: FrFD (SD) * | 5 | 20 | No data | - | Response surface plots and PCA | [27] |
| S2 | CCD | 5 | 30 | 6 | - | Response surface plots | [28] | |
| S3 | BBD | 3 | 15 | 3 | - | Response surface plots | [29] | |
| S4 | CCD | 5 | 16 | 2 | - | Response surface plots | [22] | |
| S5 | CCD: rotatable | 5 | 20 | 6 | - | Response surface plots | [30] | |
| S6 | CCD | 3 | 20 | 6 | - | Pareto chart | [31] | |
| S7 | CCD | 5 | 29 | 4 | - | Contour plots and response surface plots | [32] | |
| S8 | CCD | 5 | No data | No data | - | Response surface plots | [33] | |
| S9 | FD: FrFD | 3 | 9 | No data | - | Response surface plots | [34] | |
| S10 | CCD: rotatable | 5 | 18 | 4 | 6 | Contour plots | [35] | |
| S11a | FD: FrFD (SD) | 3 | 19 | 3 | - | Normal graph | [36] | |
| S11b | CCD | 3 | 11 | 3 | - | Contour plots and response surface plots | [36] | |
| S12 | BBD | 3 | 15 | 3 | - | Contour plots and response surface plots | [37] | |
| S13 | CCD | 3 | 20 | 6 | - | Response surface plots | [38] | |
| S14 | BBD | 3 | 29 | 5 | - | Response surface plots | [39] | |
| S15 | CCD | 5 | 20 | 6 | - | Response surface plots | [40] | |
| S16 | BBD | 3 | 30 | 6 | - | Response surface plots | [41] | |
| S17 | BBD | 3 | 30 | 6 | - | Response surface plots | [42] | |
| S18 | BBD | 3 | 17 | 5 | - | Response surface plots | [43] | |
| S19 | CCD: Face-centred | 3 | 20 | 6 | - | Response surface plots | [44] | |
| S20 | CCD | 5 | 17 | 4 | - | Response surface plots | [45] | |
| S21 | BBD | 3 | 15 | 4 | - | Response surface plots | [46] | |
| MWAE | S22 | CCD: rotatable | 5 | 20 | 6 | 6 | Response surface plots | [47] |
| S23a | BBD | 3 | 27 | 3 | - | Response surface plots | [48] | |
| S23b | CCD | 3 | 10 | 2 | - | Response surface plots | [48] | |
| S24a | EXP2. FD: FrFD (HFD) | 3 | 8 | 3 | - | Pareto chart | [23] | |
| S24b | EXP3. CCD: rotatable | 5 | 19 | 6 | 6 | Response surface plots | [23] | |
| S25 | BBD | 3 | 18 | 6 | - | Response surface plots | [24] | |
| EAE | S26 | CCD | 5 | 31 | No data | - | Contour plots and response surface plots | [49] |
| S27 | FD: FFD | 3 | 10 | No data | - | Response surface plots | [25] | |
| S28 | CCD | 5 | 31 | 7 | - | Contour plots and response surface plots | [26] | |
| S29 | BBD | 3 | 15 | 3 | - | Response surface plots and PCA | [50] |
| Tech. | Study | Inputs | I1 * | I2 | I3 | I4 | I5 | I6 | I7 | I8 | I9 | I10 | I11 | I12 | I13 | I14 | I15 | I16 | I17 | I18 | I19 | Responses | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USAE | S1 | 4 | 5 | [27] | |||||||||||||||||||
| S2 | 3 | 1 | [28] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S3 | 3 | 2 | [29] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S4 | 3 | 1 | [22] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S5 | 3 | 1 | [30] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S6 | 3 | 1 | [31] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S7 | 4 | 3 | [32] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S8 | 2 | 1 | [33] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S9 | 3 | 1 | [34] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S10 | 3 | 2 | [35] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S11a | 5 | 1 | [36] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S11b | 3 | 1 | [36] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S12 | 3 | 1 | [37] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S13 | 3 | 1 | [38] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S14 | 4 | 1 | [39] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S15 | 3 | 10 | [40] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S16 | 4 | 1 | [41] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S17 | 4 | 1 | [42] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S18 | 3 | 4 | [43] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S19 | 3 | 3 | [44] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S20 | 3 | 4 | [45] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S21 | 3 | 3 | [46] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| MWAE | S22 | 3 | 1 | [47] | |||||||||||||||||||
| S23a | 4 | 5 | [48] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S23b | 2 | 5 | [48] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S24a | 4 | 4 | [23] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S24b | 3 | 4 | [23] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S25 | 3 | 4 | [24] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| EAE | S26 | 4 | 2 | [49] | |||||||||||||||||||
| S27 | 2 | 1 | [25] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S28 | 4 | 1 | [26] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| S29 | 3 | 1 | [50] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cano-Lamadrid, M.; Martínez-Zamora, L.; Mozafari, L.; Bueso, M.C.; Kessler, M.; Artés-Hernández, F. Response Surface Methodology to Optimize the Extraction of Carotenoids from Horticultural By-Products—A Systematic Review. Foods 2023, 12, 4456. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12244456
Cano-Lamadrid M, Martínez-Zamora L, Mozafari L, Bueso MC, Kessler M, Artés-Hernández F. Response Surface Methodology to Optimize the Extraction of Carotenoids from Horticultural By-Products—A Systematic Review. Foods. 2023; 12(24):4456. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12244456
Chicago/Turabian StyleCano-Lamadrid, Marina, Lorena Martínez-Zamora, Laleh Mozafari, María Carmen Bueso, Mathieu Kessler, and Francisco Artés-Hernández. 2023. "Response Surface Methodology to Optimize the Extraction of Carotenoids from Horticultural By-Products—A Systematic Review" Foods 12, no. 24: 4456. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12244456
APA StyleCano-Lamadrid, M., Martínez-Zamora, L., Mozafari, L., Bueso, M. C., Kessler, M., & Artés-Hernández, F. (2023). Response Surface Methodology to Optimize the Extraction of Carotenoids from Horticultural By-Products—A Systematic Review. Foods, 12(24), 4456. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12244456