Highly Sensitive Immunochromatographic Detection of Porcine Myoglobin as Biomarker for Meat Authentication Using Prussian Blue Nanozyme
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Synthesis of AuNPs and PBNPs
2.3. Conjugation of AuNPs and PBNPs with Mab
2.4. Obtaining of Immunochromatographic Test Strips
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.6. LFIAs of MG
3. Results and Discussion
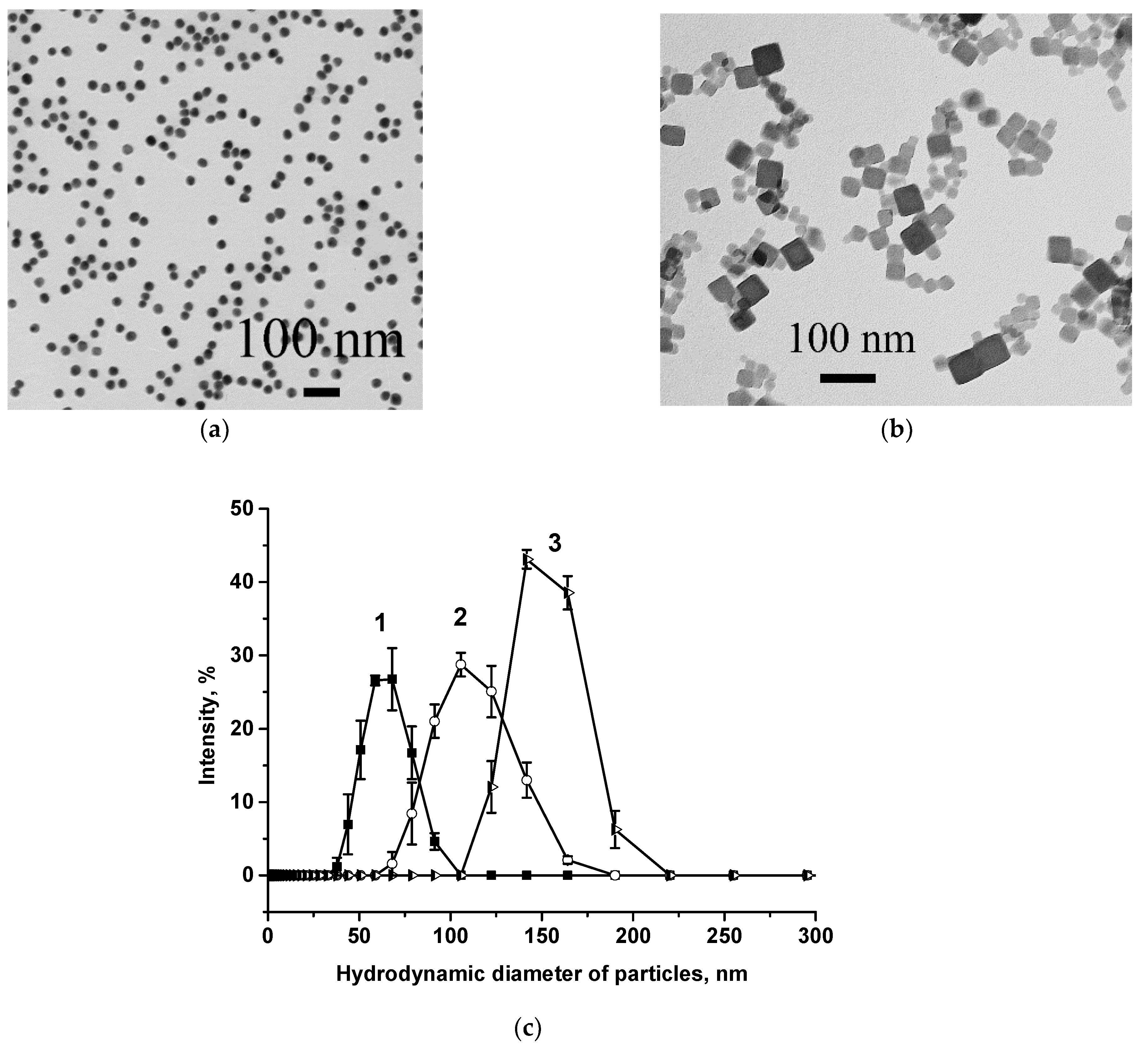
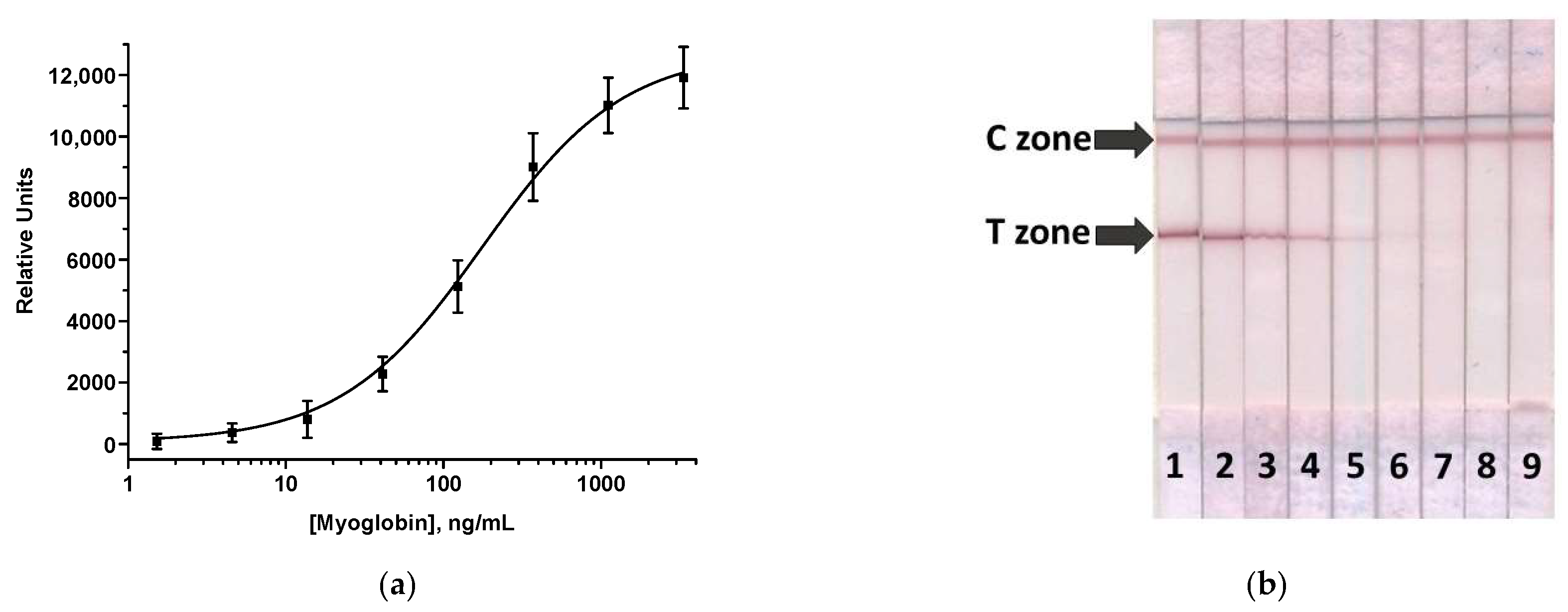
3.1. Preparation of Key LFIA Reagents and Their Characterization
3.2. Principle of the LFIA
3.3. AuNPs-Based LFIA of MG
3.4. Enhanced LFIA of MG
3.4.1. Extinguishing of Non-Specific Interactions
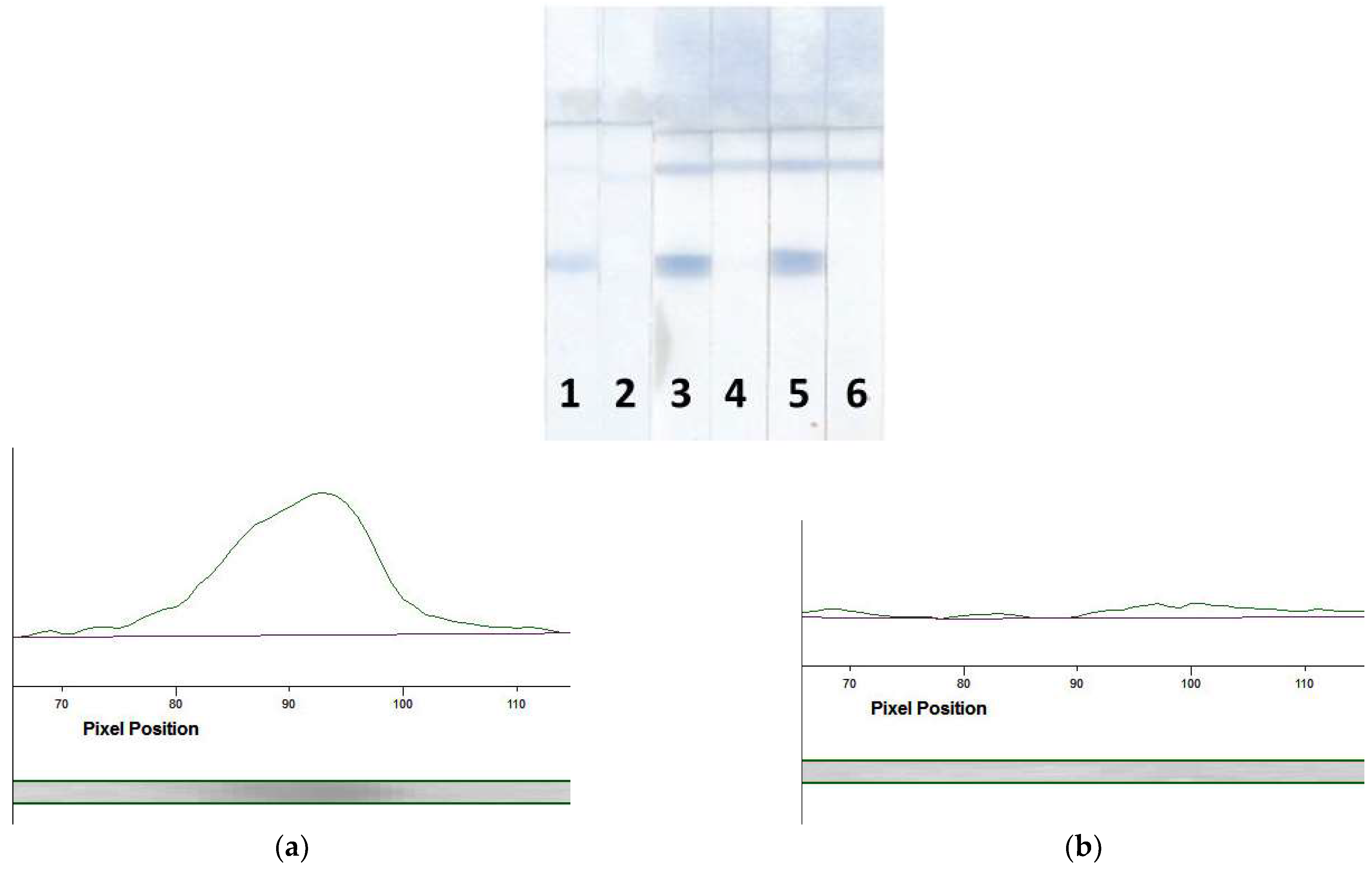
3.4.2. Selection of the Labeled Conjugate
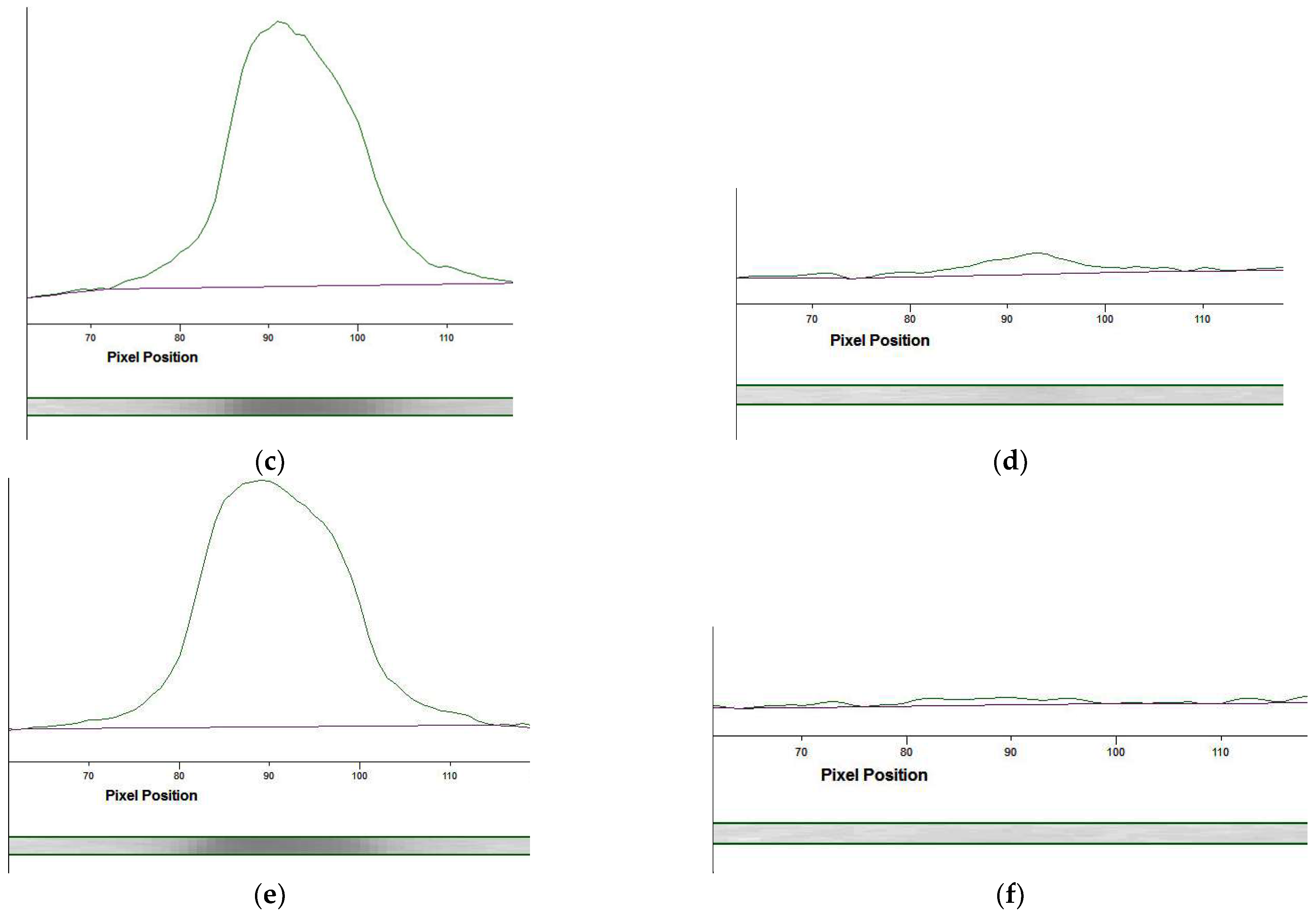
3.4.3. Optimization of the LFIA
3.5. Determination of MG in Meat Samples
3.6. Comparison with Other Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fung, F.; Wang, H.S.; Menon, S. Food safety in the 21st century. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font-I-Furnols, M. Meat consumption, sustainability and alternatives: An overview of motives and barriers. Foods 2023, 12, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, H.H.; Brown, L.C.; Romero, M.R.; Donarski, J.A. Review: Methods to determine offal adulteration in meat products to support enforcement and food security. Food Chem. 2023, 399, 133818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Liu, S.Y.; Meng, F.B.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.M. Comparative review and the recent progress in detection technologies of meat product adulteration. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2256–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, S.; Singh, A.; Mangal, M.; Mangal, A.K.; Kumar, S. Food adulteration: Sources, health risks, and detection methods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1174–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja Nhari, R.M.H.; Soh, J.H.; Khairil Mokhtar, N.F.; Mohammad, N.A.; Mohd Hashim, A. Halal authentication using lateral flow devices for detection of pork adulteration in meat products: A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2023, 40, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.C.; Ahmad Ruslan, N.A.S.; Chin, L.X.; Ahmad, M.; Abu Hanifah, S.; Abdullah, Z.; Khor, S.M. Recent advances in halal food authentication: Challenges and strategies. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 8–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.M.; Uddin, S.M.K.; Sultana, S.; Wahab, Y.A.; Sagadevan, S.; Johan, M.R.; Ali, M.E. Authentication of Halal and Kosher meat and meat products: Analytical approaches, current progresses and future prospects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 285–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, Q.; Alawami, M.; Mokhtar, N.F.K.; Nhari, R.M.H.R.; Hanish, I. Current analytical methods for porcine identification in meat and meat products. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavin, C.; Cottenet, G.; Cooper, K.M.; Zbinden, P. Meat vulnerabilities to economic food adulteration require new analytical solutions. Chimia 2018, 72, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, S.H.; Yuswan, M.H.; Aizat, W.M.; Mansor, M.K.; Desa, M.N.M.; Yusof, Y.A.; Song, L.K.; Mustafa, S. Comparative database search engine analysis on massive tandem mass spectra of pork-based food products for halal proteomics. J. Proteom. 2021, 241, 104240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gagaoua, M.; Mullen, A.M.; Viala, D.; Rai, D.K.; Kelly, A.L.; Sheehan, D.; Hamill, R.M. Shotgun proteomics for the preliminary identification of biomarkers of beef sensory tenderness, juiciness and chewiness from plasma and muscle of young Limousin-sired bulls. Meat Sci. 2021, 176, 108488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhong, G.; Zhou, S.; Guo, Y.; Pan, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Xia, Q.; Cai, Z. Detection and characterization of meat adulteration in various types of meat products by using a high-efficiency multiplex polymerase chain reaction technique. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 979977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muflihah; Hardianto, A.; Kusumaningtyas, P.; Prabowo, S.; Hartati, Y.W. DNA-based detection of pork content in food. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Ju, S.; Zhou, S.; Zeng, X.; Wu, Z.; Pan, D.; Zhong, G.; Cai, Z. Heat-treated meat origin tracing and authenticity through a practical multiplex polymerase chain reaction approach. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qi, J.; Zhao, W.; Gu, J.; Guo, W.; Li, Y. Screening of specific quantitative peptides of beef by LC-MS/MS coupled with OPLS-DA. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachniuk, A.; Sumara, A.; Montowska, M.; Fornal, E. LC-QTOF-MS identification of rabbit-specific peptides for authenticating the species composition of meat products. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shin, M.S.; Shin, J.; Kim, H.M.; Pham, X.H.; Park, S.M.; Kim, D.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Jun, B.H. Recent trends in lateral flow immunoassays with optical nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Guo, J.; Zhang, G. Lateral flow immunoassays for antigens, antibodies and haptens detection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, O.D.; Zvereva, E.A.; Vostrikova, N.L.; Chernukha, I.M.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Zherdev, A.V. Lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of undeclared chicken meat in meat products. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, O.D.; Zvereva, E.A.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Zherdev, A.V. Sensitive lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of pork additives in raw and cooked meat products. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R.; Maheswarappa, N.B.; Biswas, S.; Dasoju, S.; Barbuddhe, S.; Rajan, V.M.; Patra, G.; Bhattacharyya, D. Lateral flow immunoassay-based absolute point-of-care technique for authentication of meat and commercial meat products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, Q.; Li, M.; Lu, S. Identification of potential sex-specific biomarkers in pigs with low and high intramuscular fat content using integrated bioinformatics and machine learning. Genes 2023, 14, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tukiran, N.A.; Ismail, A.; Mustafa, S.; Hamid, M. Enzyme immunoassay for the detection of porcine gelatine in edible bird’s nests. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2015, 32, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Wu, M.; Dong, W.; Rao, Q.; Huo, H.; Han, Q. Monoclonal antibody-based sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for porcine hemoglobin quantification. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachniuk, A.; Trzpil, A.; Kozub, A.; Montowska, M.; Fornal, E. Pork liver tissue-specific peptide markers for food authenticity testing and adulteration detections. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 135013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagaoua, M.; Suman, S.P.; Purslow, P.P.; Lebret, B. The color of fresh pork: Consumers expectations, underlying farm-to-fork factors, myoglobin chemistry and contribution of proteomics to decipher the biochemical mechanisms. Meat Sci. 2023, 206, 109340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkholi, I.E.; Elsherbiny, M.E.; Emara, M. Myoglobin: From physiological roles to potential implications in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.-W.; Lo, C.; Chu, C.-S.; Chin, L.-T.; Wang, Y.-T.; Yang, W.-C. Development of a colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic test strip for detection of cetacean myoglobin. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 113, 53433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, O.D.; Zvereva, E.A.; Pridvorova, S.M.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Zherdev, A.V. The use of Au@Pt nanozyme to perform ultrasensitive immunochromatographic detection of banned pork additives in meat products. Food Control 2023, 154, 110013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvereva, E.A.; Byzova, N.A.; Hendrickson, O.D.; Popravko, D.S.; Belichenko, K.A.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Zherdev, A.V. Immunochromatographic detection of myoglobin as a specific biomarker of porcine muscle tissues in meat products. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panferov, V.G.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Post-assay chemical enhancement for highly sensitive lateral flow immunoassays: A critical review. Biosensors 2023, 13, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, J.; Ma, X. Nanomaterial labels in lateral flow immunoassays for point-of-care-testing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 60, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirica, A.C.; Stan, D.; Chelcea, I.C.; Mihailescu, C.M.; Ofiteru, A.; Bocancia-Mateescu, L.A. Latest trends in lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) detection labels and conjugation process. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 922772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, R.; Wang, D.; Arain, H.; Mohan, C. Design of gold nanoparticle vertical flow assays for point-of-care testing. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric and electrochemical sensors for the detection of illegal food additives. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 28, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Nanozymes: Classification, catalytic mechanisms, activity regulation, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4357–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, M.; Liu, C.; Xu, C. Activity regulating strategies of nanozymes for biomedical applications. Small 2023, 19, 2207142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyakin, A.A. Catalytic properties of peroxidase mimicking nanozymes. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2023, 92, RCR5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Cheng, N.; Ruan, X.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Review—Nanozyme-based immunosensors and immunoassays: Recent developments and future trends. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 037508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, P.; Lu, L.; Han, L.; Hai, X. Recent advances in the immunoassays based on nanozyme. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xianyu, Y. Nanobody and Nanozyme-enabled immunoassays with enhanced specificity and sensitivity. Small Methods 2022, 6, e2101576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, F.; Mohd-Naim, N.F.; Chandrawati, R.; Cozzolino, D.; Ahmed, M.U. Nanozyme-based sensors for detection of food biomarkers: A review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 26160–26175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Ying, R.; Su, E. The recent development of nanozymes for food quality and safety detection. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, O.D.; Zvereva, E.A.; Panferov, V.G.; Solopova, O.N.; Zherdev, A.V.; Sveshnikov, P.G.; Dzantiev, B.B. Application of Au@Pt nanozyme as enhancing label for the sensitive lateral flow immunoassay of okadaic acid. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, L.; Xiao, X.; Peng, J.; Guo, P.; Zhang, W.; Lai, W. Synthesis of PDA-mediated magnetic bimetallic nanozyme and its application in immunochromatographic assay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Long, M.; Duan, Y.; Gu, N. Prussian blue nanozymes: Progress, challenges, and opportunities. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 12818–12839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estelrich, J.; Busquets, M.A. Prussian blue: A nanozyme with versatile catalytic properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Zhu, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Gu, N. Progress in the preparation of Prussian blue-based nanomaterials for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 5272–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busquets, M.A.; Estelrich, J. Prussian blue nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface modification, and biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frens, G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Xie, W.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Li, C.M.; Liu, Y. A sensitive lateral flow immunochromatographic strip with Prussian blue nanoparticles mediated signal generation and cascade amplification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvereva, E.A.; Kovalev, L.I.; Ivanov, A.V.; Kovaleva, M.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Shishkin, S.S.; Lisitsyn, A.B.; Chernukha, I.M.; Dzantiev, B.B. Enzyme immunoassay and proteomic characterization of troponin I as a marker of mammalian muscle compounds in raw meat and some meat products. Meat Sci. 2015, 105, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; 900p. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, T.; Bai, F.; Sun, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, S.; He, K.; Wang, X.; Jia, P.; Wang, L. An innovative Prussian blue nanocubes decomposition-assisted signal amplification strategy suitable for competitive lateral flow immunoassay to sensitively detect aflatoxin B1. Food Chem. 2021, 34415, 128711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hua, Q.; Wang, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, X.; Lei, H.; Li, X. Prussian blue immunochromatography with portable smartphone-based detection device for zearalenone in cereals. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 131008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Huang, Q.; Dou, L.; Bu, T.; Chen, K.; Yang, Q.; Yan, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Prussian blue nanoparticles based lateral flow assay for high sensitive determination of clenbuterol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 275, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Shen, D.; Cui, X.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, H.; Eremin, S.A.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, S. Prussian blue nanoparticles with peroxidase-mimicking properties in a dual immunoassays for glycocholic acid. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 1875, 113317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Shen, X.; Xu, Z.; Lei, H.; Huang, X.; Li, X. Two kinds of lateral flow immunoassays based on multifunctional magnetic Prussian blue nanoenzyme and colloidal gold for the detection of 38 β-agonists in swine urine and pork. Food Chem. 2023, 417, 135897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, X.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Z.; Ma, M.; Shi, F. Rapid vertical flow technique for the highly sensitive detection of Brucella antibodies with Prussian blue nanoparticle labeling and nanozyme-catalyzed signal amplification. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Dou, L.; Yao, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, M.; Yin, X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. Nanozyme amplification mediated on-demand multiplex lateral flow immunoassay with dual-readout and broadened detection range. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 1691, 112610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Ji, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. Functional nanozyme mediated multi-readout and label-free lateral flow immunoassay for rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 127224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.-S.; Chen, Y.-T.; Hsu, Y.-P.; Pang, H.-H.; Huang, C.-Y.; Shiue, Y.-L.; Wei, K.-C.; Yang, H.-W. Mobile healthcare system based on the combination of a lateral flow pad and smartphone for rapid detection of uric acid in whole blood. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 164, 112309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

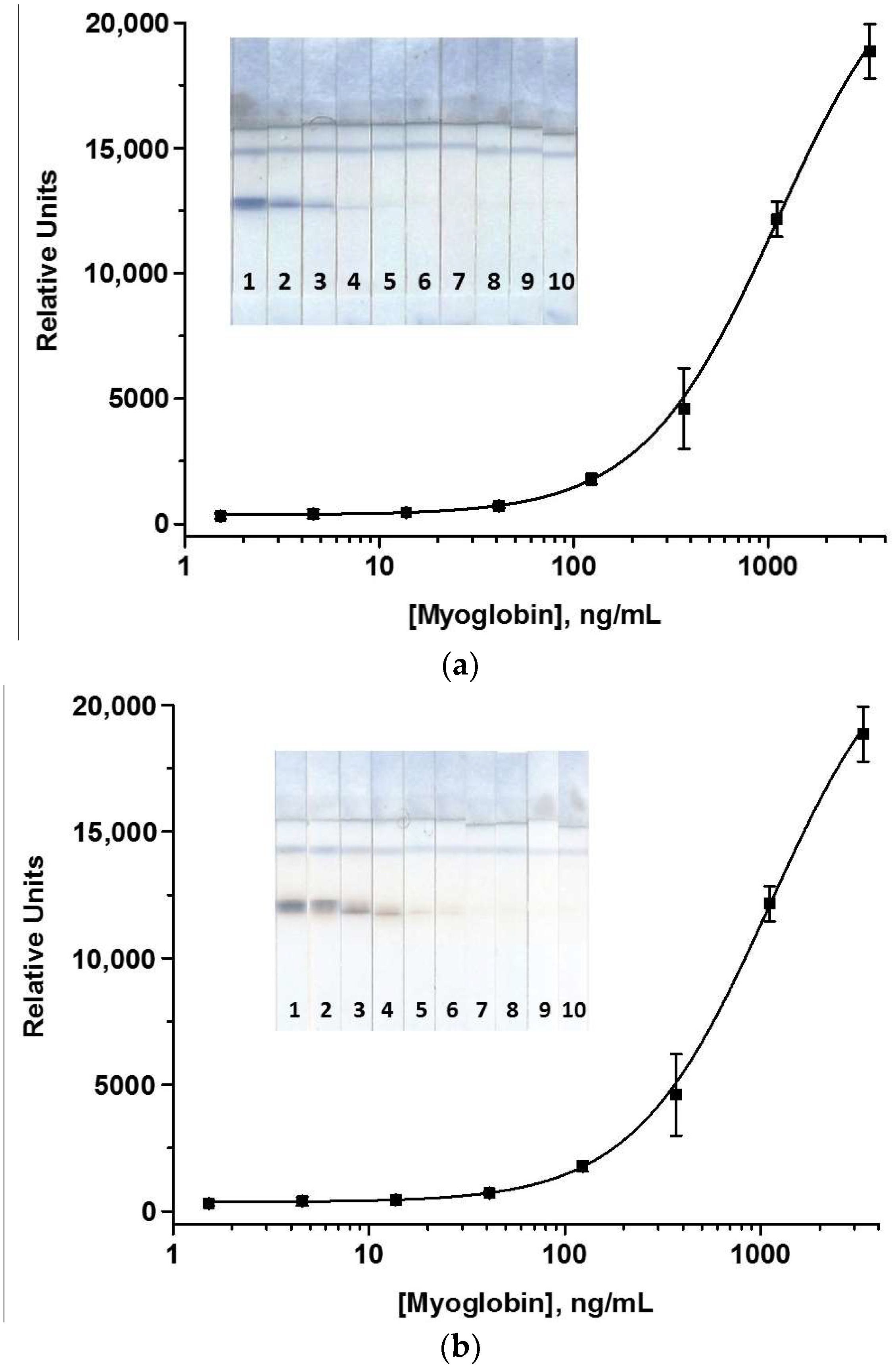
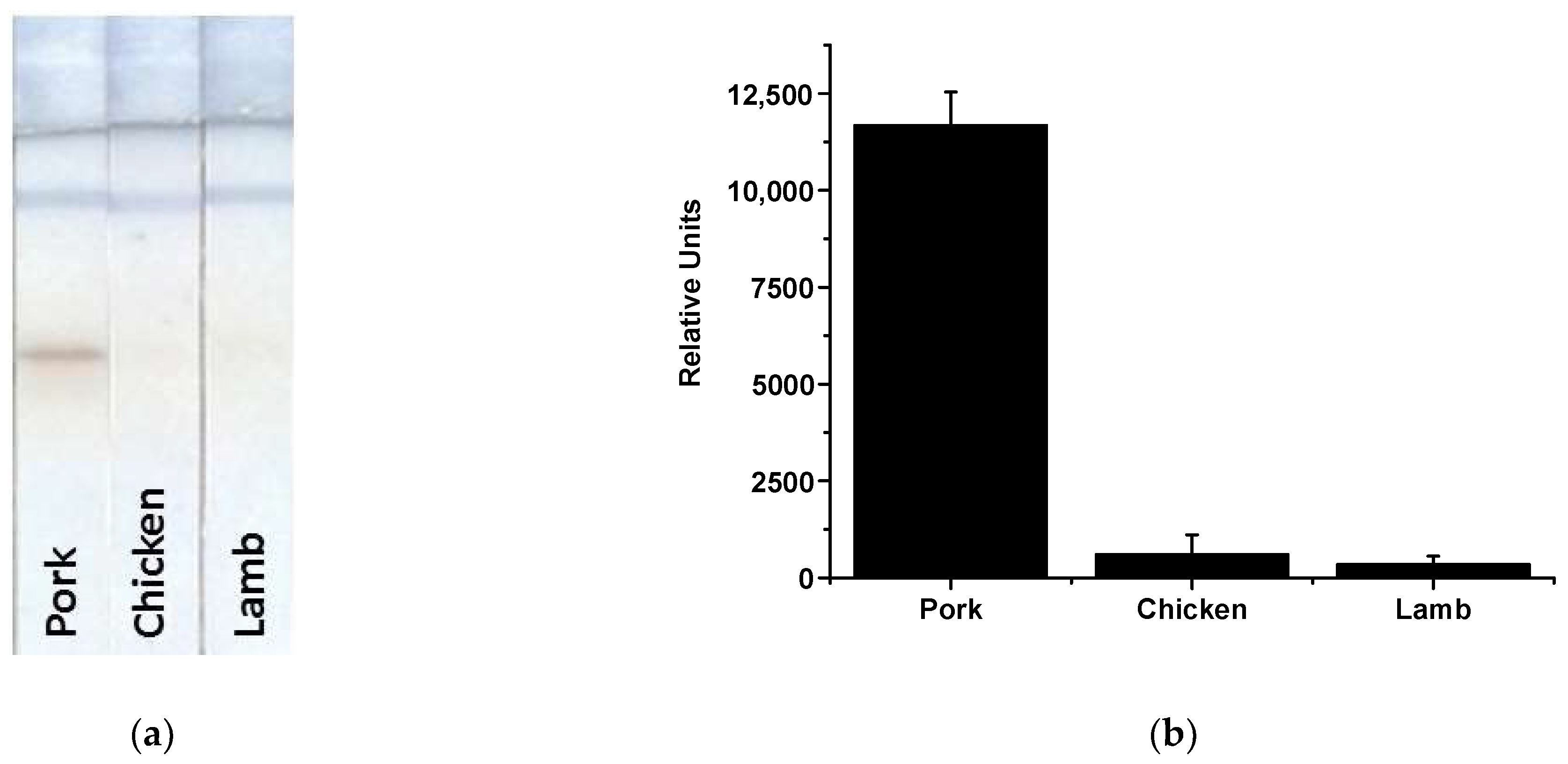

| Analyte | Compound for Amplification (If Used) | Assay Duration, min | LOD | Gain in Sensitivity Compared to AuNP-Based LFIA | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbit IgG/ochratoxin A | TMB | 30 | 0.01 ng/mL/10 ng/mL | 2–3 orders/n.p. * | [52] |
| Aflatoxin B1 | NaOH | 28 | 0.023 ng/mL | 8-fold | [55] |
| Zearalenone | n.u. ** | 6 | 10 µg/kg | 5-fold | [56] |
| Clenbuterol | n.u. | 15 | 1 ng/mL | 5-fold | [57] |
| Glycocholic acid | TMB | 10 | 10 ng/mL | n.p. | [58] |
| β-Agonists | DAB | 20 | 0.3–0.5 μg/kg | 10-fold | [59] |
| Brucella antibodies | TMB | 2–3 | 40 IU/mL | n.p. | [60] |
| Ractopamine/ clenbuterol | TMB | 10 | 6/12 ng/mL | n.p. | [61] |
| Escherichia coli O157:H7 | TMB | 25 | 102 CFU/mL | n.p. | [62] |
| Uric acid | TMB | n.p. | Detection range = 15–85 μg/mL | n.p. | [63] |
| MG | DAB | 30 | 1.5 ng/mL | 9-fold | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hendrickson, O.D.; Zvereva, E.A.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Zherdev, A.V. Highly Sensitive Immunochromatographic Detection of Porcine Myoglobin as Biomarker for Meat Authentication Using Prussian Blue Nanozyme. Foods 2023, 12, 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234252
Hendrickson OD, Zvereva EA, Dzantiev BB, Zherdev AV. Highly Sensitive Immunochromatographic Detection of Porcine Myoglobin as Biomarker for Meat Authentication Using Prussian Blue Nanozyme. Foods. 2023; 12(23):4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234252
Chicago/Turabian StyleHendrickson, Olga D., Elena A. Zvereva, Boris B. Dzantiev, and Anatoly V. Zherdev. 2023. "Highly Sensitive Immunochromatographic Detection of Porcine Myoglobin as Biomarker for Meat Authentication Using Prussian Blue Nanozyme" Foods 12, no. 23: 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234252
APA StyleHendrickson, O. D., Zvereva, E. A., Dzantiev, B. B., & Zherdev, A. V. (2023). Highly Sensitive Immunochromatographic Detection of Porcine Myoglobin as Biomarker for Meat Authentication Using Prussian Blue Nanozyme. Foods, 12(23), 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234252







