The In Vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion Affects the Bioaccessibility and Bioactivity of Beta vulgaris Constituents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Sample Preparation
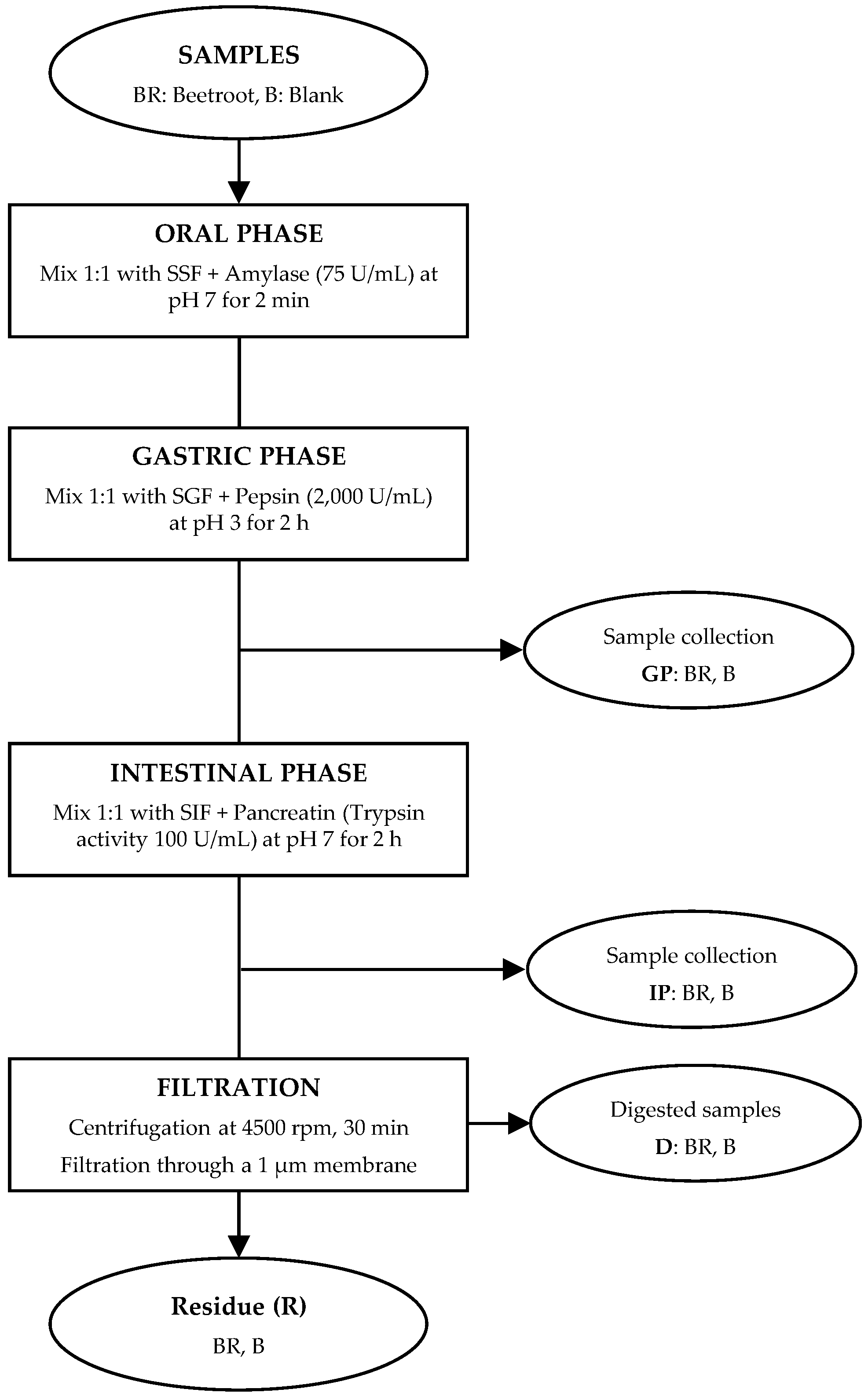
2.2. Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion
2.3. Measurement of Water Content and Activity
2.4. Mineral Content Determination
2.5. Organic Acid Analysis
2.6. Betacyanin Analysis
2.7. Antioxidant Activity Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Water Content and Activity
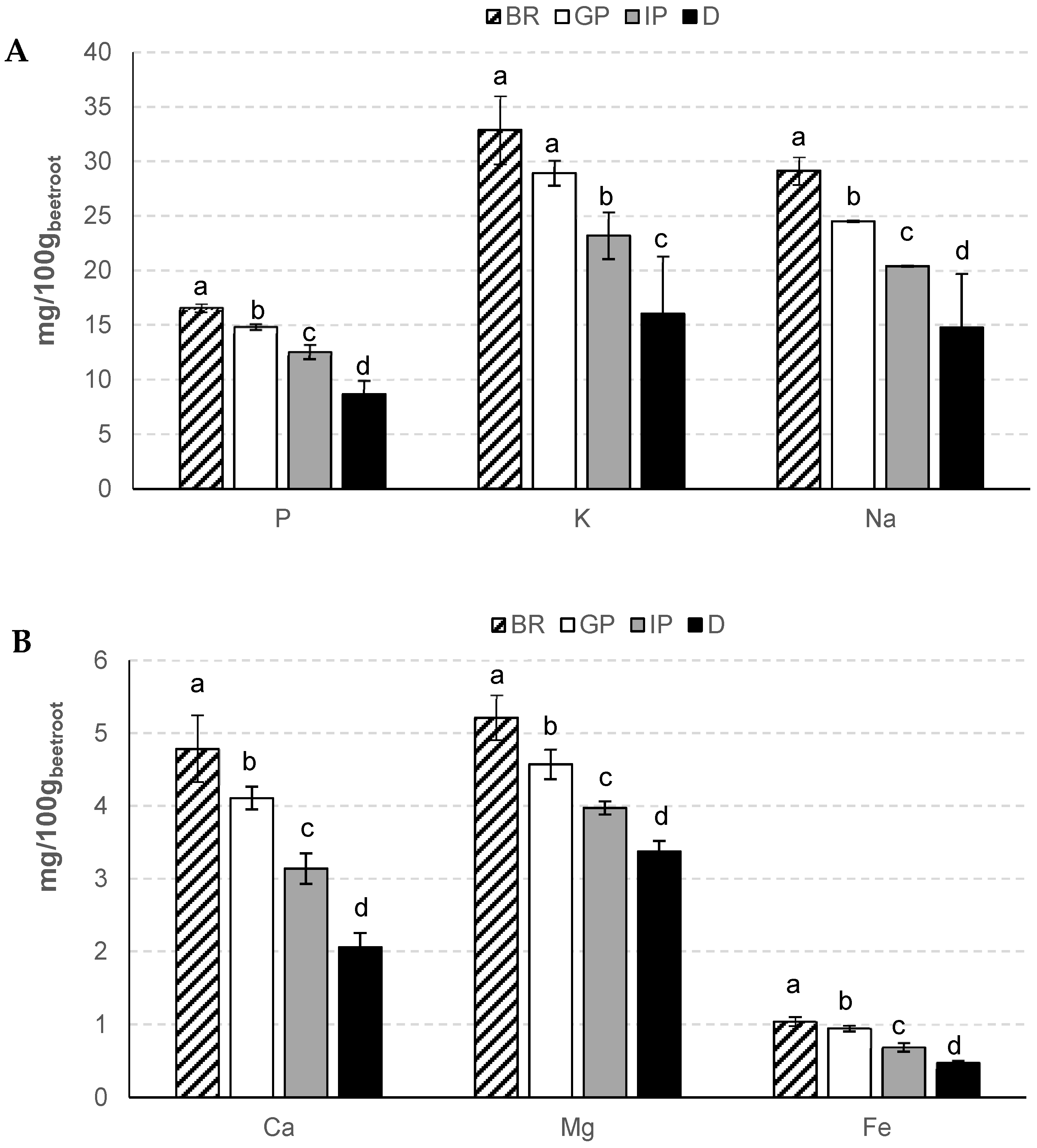
3.2. Mineral Elements
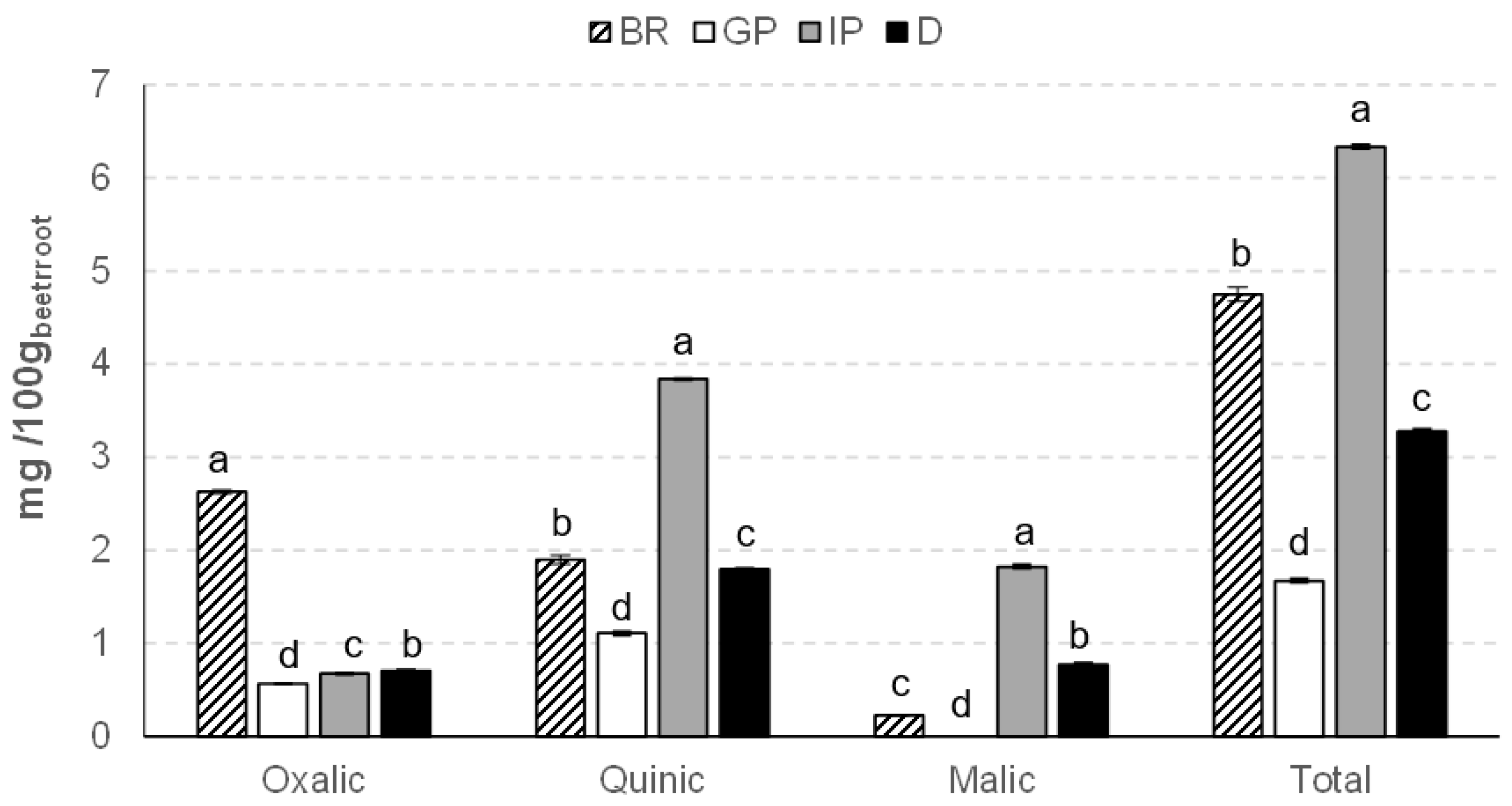
3.3. Organic Acids
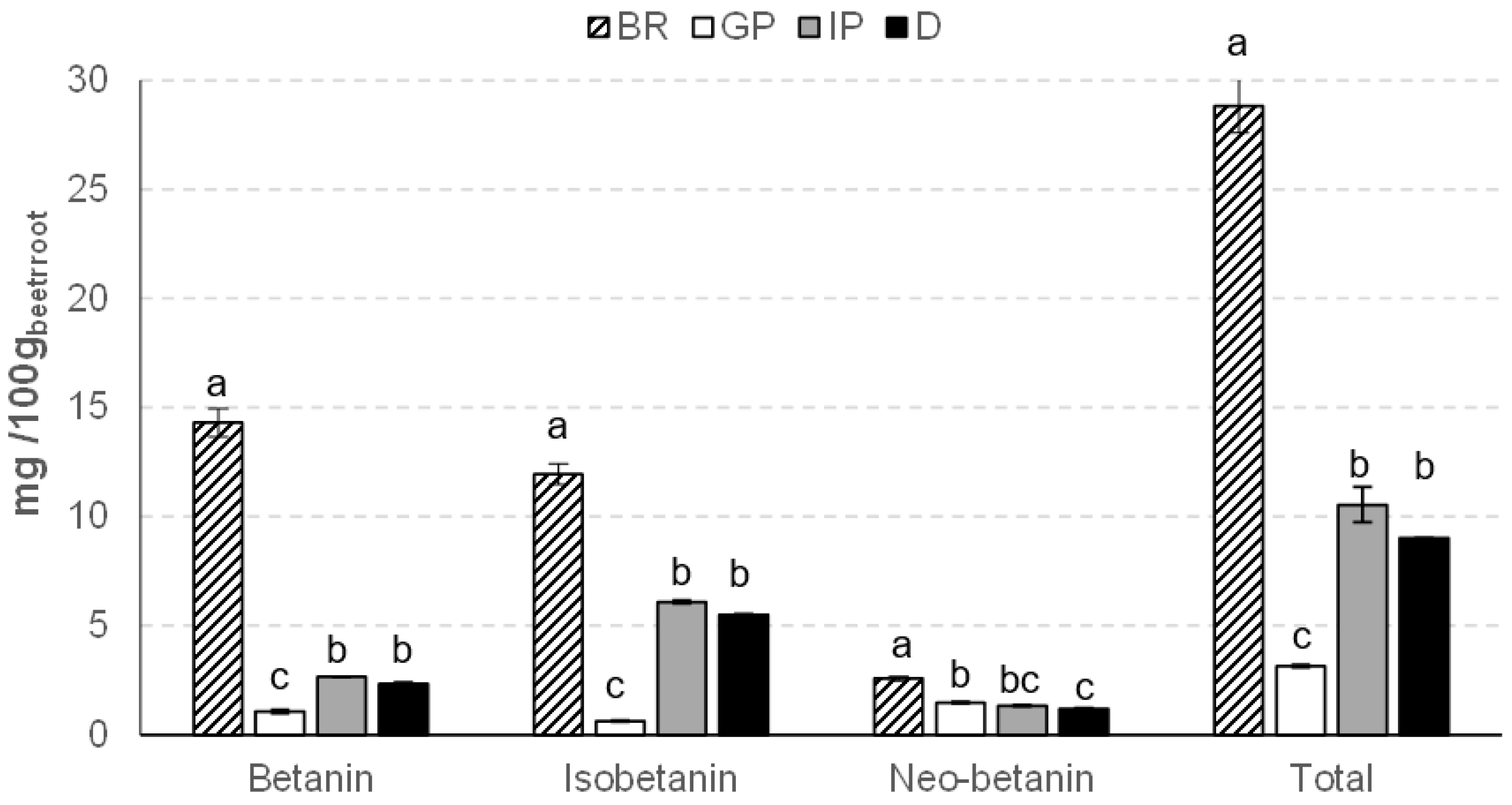
3.4. Betacyanins
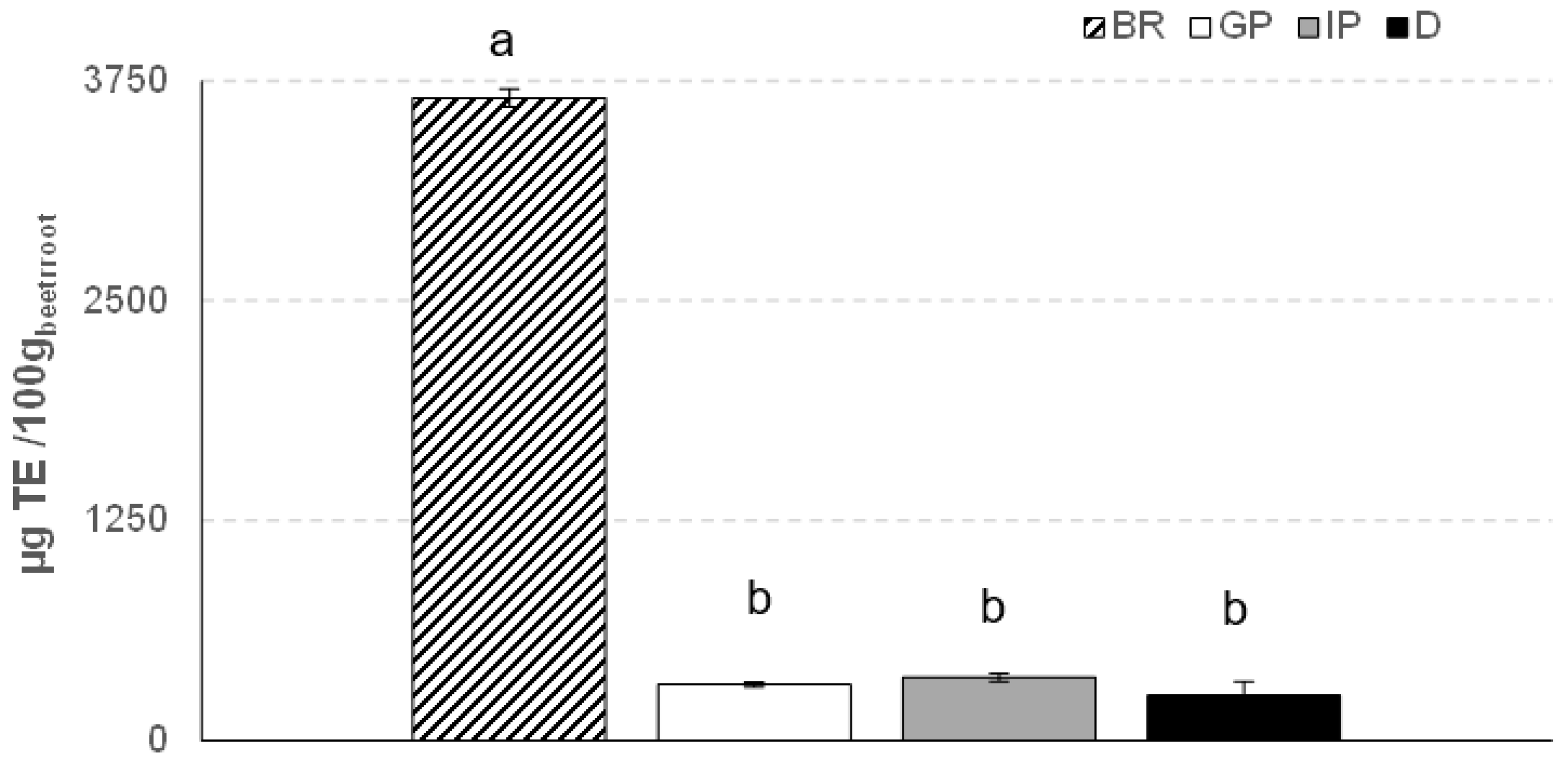
3.5. Antioxidant Activity
3.6. Contribution to Mineral Requirements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wascher, F.L.; Stralis-Pavese, N.; McGrath, J.M.; Schulz, B.; Himmelbauer, H.; Dohm, J.C. Genomic Distances Reveal Relationships of Wild and Cultivated Beets. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulwinder, K.; Singh, A.K. Drying Kinetics and Quality Characteristics of Beetroot Slices under Hot Air Followed by Microwave Finish Drying. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 9, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panghal, A.; Virkar, K.; Kumar, V.; Dhull, S.B.; Gat, Y.; Chhikara, N. Development of Probiotic Beetroot Drink. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 5, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiel, A. Drying Kinetics and Quality of Beetroots Dehydrated by Combination of Convective and Vacuum-Microwave Methods. J. Food Eng. 2010, 98, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, S.J.; Łechtańska, J.M. Drying of Red Beetroot after Osmotic Pretreatment: Kinetics and Quality Considerations. Chem. Process. Eng. 2015, 36, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, S.V.; Lele, S.S. Betalain Content and Antioxidant Activity of Beta vulgaris: Effect of Hot Air Convective Drying and Storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2014, 38, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.; Dias, M.I.; Pinela, J.; Roriz, C.L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barros, L. Betalains. In Nutraceutical and Functional Food Components; Galanakis, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 461–507. [Google Scholar]
- Slavov, A.; Karagyozov, V.; Denev, P.; Kratchanova, M.; Kratchanov, C. Antioxidant Activity of Red Beet Juices Obtained after Microwave and Thermal Pretreatments. Czech J. Food Sci. 2013, 31, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaimainen, M.; Laaksonen, O.; Järvenpää, E.; Sandell, M.; Huopalahti, R. Consumer Acceptance and Stability of Spray Dried Betanin in Model Juices. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.N.; Sharma, M.; Chikara, N.; Anand, T.; Bansal, S. Quality Characteristics of Vegetable-Blended Wheat-Pearl Millet Composite Pasta. Agric. Res. 2014, 3, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panghal, A.; Yadav, D.N.; Khatkar, B.S.; Sharma, H.; Kumar, V.; Chhikara, N. Post-Harvest Malpractices in Fresh Fruits and Vegetables: Food Safety and Health Issues in India. Nutr. Food Sci. 2018, 48, 561–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Nagababu, B.H. Applications of Food Color and Bio-Preservatives in the Food and Its Effect on the Human Health. Food Chem. Adv. 2022, 1, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-García, E.; Carvajal-Lérida, I.; Pérez-Gálvez, A. In Vitro Bioaccessibility Assessment as a Prediction Tool of Nutritional Efficiency. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada, J.; Aguilera, J.M. Food Microstructure Affects the Bioavailability of Several Nutrients. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R21–R32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, R.; Sawate, A.; Kshirsagar, R.; Patil, B.; Mane, R. Studies on Evaluation of Physical and Chemical Composition of Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.). Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2018, 6, 2977–2979. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sohaimy, S.A.; Abdo, E.; Shaltout, O.; Abdalla, A.; Zeitoun, A. Nutritional Evaluation of Beetroots (Beta vulgaris L.) and Its Potential Application in a Functional Beverage. Plants 2020, 9, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberal, Â.; Pinela, J.; Vívar-Quintana, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barros, L. Fighting Iron-Deficiency Anemia: Innovations in Food Fortificants and Biofortification Strategies. Foods 2020, 9, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A Standardised Static In Vitro Digestion Method Suitable for Food—An International Consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST Static In Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Food Digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, E.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Giménez, B.; Cebrián, R.; Maqueda, M.; Parada, J.; Martínez-Férez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Robert, P. Role of Maltodextrin and Inulin as Encapsulating Agents on the Protection of Oleuropein during In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, A.P.; Niccolai, A.; Fradinho, P.; Fragoso, S.; Bursic, I.; Rodolfi, L.; Biondi, N.; Tredici, M.R.; Sousa, I.; Raymundo, A. Microalgae Biomass as an Alternative Ingredient in Cookies: Sensory, Physical and Chemical Properties, Antioxidant Activity and In Vitro Digestibility. Algal. Res. 2017, 26, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; Latimer, G.W., Ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Sánchez-Mata, M.C.; Cámara, M.; Torija, M.E.; Chaya, C.; Galiana-Balaguer, L.; Roselló, S.; Nuez, F. Internal Quality Characterization of Fresh Tomato Fruits. HortScience 2004, 39, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Wandurraga, Z.N.; Igual, M.; García-Segovia, P.; Martínez-Monzó, J. In Vitro Bioaccessibility of Minerals from Microalgae-Enriched Cookies. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2186–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.; Barros, L.; Carvalho, A.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Use of UFLC-PDA for the Analysis of Organic Acids in Thirty-Five Species of Food and Medicinal Plants. Food Anal. Methods 2013, 6, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roriz, C.L.; Barros, L.; Prieto, M.A.; Morales, P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Floral Parts of Gomphrena Globosa L. as a Novel Alternative Source of Betacyanins: Optimization of the Extraction Using Response Surface Methodology. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockowandt, L.; Pinela, J.; Roriz, C.L.; Pereira, C.; Abreu, R.M.V.; Calhelha, R.C.; Alves, M.J.; Barros, L.; Bredol, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Chemical Features and Bioactivities of Cornflower (Centaurea cyanus L.) Capitula: The Blue Flowers and the Unexplored Non-Edible Part. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 128, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisen, S.; Fernández, J.A. Prediction of the Total Tract Digestibility of Energy in Feedstuffs and Pig Diets by In Vitro Analyses. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 1997, 68, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Ojeda, A.M.; Moreno-Rojas, R.; Cámara-Martos, F. Mineral and Trace Element Content in Legumes (Lentils, Chickpeas and Beans): Bioaccesibility and Probabilistic Assessment of the Dietary Intake. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 73, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, D.; Vedrina Dragojević, I.; Šebečić, B. Bioaccessibility of Ca, Mg, Mn and Cu from Whole Grain Tea-Biscuits: Impact of Proteins, Phytic Acid and Polyphenols. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siener, R.; Seidler, A.; Voss, S.; Hesse, A. The Oxalate Content of Fruit and Vegetable Juices, Nectars and Drinks. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 45, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, A.A. Flavor Quality of Fruits and Vegetables. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 1863–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Pu, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Recent Progress in the Study of Taste Characteristics and the Nutrition and Health Properties of Organic Acids in Foods. Foods 2022, 11, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Galdón, B.; Tascón Rodríguez, C.; Rodríguez Rodríguez, E.; Díaz Romero, C. Organic Acid Contents in Onion Cultivars (Allium cepa L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6512–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, J.A. Handbook of Phytochemical Constituents of Grass, Herbs and Other Economic Plants: Herbal Reference Library; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; Volume 2000, ISBN 9780849338656. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, M.D.; Almeida, M.C.; Lopes, N.P.; de Souza, G.E.P. Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic and Antipyretic Activities of the Natural Polyphenol Chlorogenic Acid. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 2236–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, V.; Faucher, M.; Perreault, V.; Serre, E.; Dubé, P.; Boutin, Y.; Bazinet, L. Evolution of Cranberry Juice Compounds during In Vitro Digestion and Identification of the Organic Acid Responsible for the Disruption of In Vitro Intestinal Cell Barrier Integrity. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedreño, M.A.; Escribano, J. Correlation between Antiradical Activity and Stability of Betanine from Beta vulgaris L. Roots under Different PH, Temperature and Light Conditions. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbach, K.M.; Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R. Impact of Thermal Treatment on Color and Pigment Pattern of Red Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Preparations. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, C491–C498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Santiago, E.; Yahia, E.M. Identification and Quantification of Betalains from the Fruits of 10 Mexican Prickly Pear Cultivars by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5758–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumbas Šaponjac, V.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.; Ćetković, G.; Jakišić, M.; Djilas, S.; Vulić, J.; Stajčić, S.D.S. Encapsulation of Beetroot Pomace Extract: RSM Optimization, Storage and Gastrointestinal Stability. Molecules 2016, 21, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesoriere, L.; Fazzari, M.; Angileri, F.; Gentile, C.; Livrea, M.A. In Vitro Digestion of Betalainic Foods. Stability and Bioaccessibility of Betaxanthins and Betacyanins and Antioxidative Potential of Food Digesta. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10487–10492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel-Sánchez, M.; García-Cayuela, T.; Gómez-Maqueo, A.; García, H.S.; Cano, M.P. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Stability, Bioaccessibility and Potential Biological Activities of Betalains and Phenolic Compounds in Cactus Berry Fruits (Myrtillocactus geometrizans). Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeredo, H.M.C. Betalains: Properties, Sources, Applications, and Stability—A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbach, K.M.; Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R. Betalain Stability and Degradation—Structural and Chromatic Aspects. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, R41–R50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.V.T.; dos Santos Baião, D.; de Oliveira Silva, F.; Alves, G.; Perrone, D.; del Aguila, E.M.; Flosi Paschoalin, V.M. Betanin, a Natural Food Additive: Stability, Bioavailability, Antioxidant and Preservative Ability Assessments. Molecules 2019, 24, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, F.; Santos Dorneles, M.; Pelayo Zapata Noreña, C. Accelerated Stability Testing and Simulated Gastrointestinal Release of Encapsulated Betacyanins and Phenolic Compounds from Bougainvillea glabra Bracts Extract. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Roque, M.J.; Rojas-Graü, M.A.; Elez-Martínez, P.; Martín-Belloso, O. Changes in Vitamin C, Phenolic, and Carotenoid Profiles throughout In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion of a Blended Fruit Juice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Roque, M.J.; de Ancos, B.; Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Cano, M.P.; Elez-Martínez, P.; Martín-Belloso, O. Impact of Food Matrix and Processing on the In Vitro Bioaccessibility of Vitamin C, Phenolic Compounds, and Hydrophilic Antioxidant Activity from Fruit Juice-Based Beverages. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowska-Bartosz, I.; Bartosz, G. Biological Properties and Applications of Betalains. Molecules 2021, 26, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igual, M.; García-Martínez, E.; Martín-Esparza, M.E.; Martínez-Navarrete, N. Effect of Processing on the Drying Kinetics and Functional Value of Dried Apricot. Food Res. Int. 2012, 47, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igual, M.; Cebadera, L.; Cámara, R.M.A.; Agudelo, C.; Martínez-Navarrete, N.; Cámara, M. Novel Ingredients Based on Grapefruit Freeze-Dried Formulations: Nutritional and Bioactive Value. Foods 2019, 8, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Parliament & Council of the European Union. Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the Provision of Food Information to Consumers. Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, 50, 19–63. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32011R1169&from=ES (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Turck, D.; Castenmiller, J.; de Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Kearney, J.; Knutsen, H.K.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Pelaez, C.; et al. Dietary reference values for sodium. EFSA J. 2019, 17, e05778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackenzie, E.L.; Iwasaki, K.; Tsuji, Y. Intracellular iron transport and storage: From molecular mechanisms to health implications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciudad-Mulero, M.; Pinela, J.; Carvalho, A.M.; Barros, L.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Sánchez-Mata, M.C.; Morales, P. Bioaccessibility of Macrominerals and Trace Elements from Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Farmers’ Varieties. Foods 2022, 11, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Peak | Rt (min) | λmax (nm) | [M-H]− (m/z) | MS2 (m/z) | Tentative Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17.4 | 533 | 551 | 389(100), 345(6), 150(8) | Betanidin-5-O-glucoside (betanin) |
| 2 | 18.8 | 531 | 551 | 389(100), 345(7), 150(10) | Isobetanidin-5-O-glucoside (isobetanin) |
| 3 | 22.8 | 462 | 549 | 389(100) | 14,15-Dehydrobetanin (neobetanin) |
| Samples | P (% Contribution) | K (% Contribution) | Na (% Contribution) | Ca (% Contribution) | Mg (% Contribution) | Fe (% Contribution) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR | 2.37 ± 0.05 | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 1.46 ± 0.05 | 0.60 ± 0.05 | 1.39 ± 0.07 | 7.4 ± 0.4 |
| GP | 2.12 ± 0.03 (−10%) | 1.45 ± 0.05 (−12%) | 1.23 ± 0.01 (−16%) | 0.51 ± 0.02 (−14%) | 1.22 ± 0.04 (−12%) | 6.7 ± 0.2 (−9%) |
| IP | 1.79 ± 0.08 (−24%) | 1.16 ± 0.09 (−29%) | 1.02 ± 0.01 (−30%) | 0.39 ± 0.02 (−34%) | 1.06 ± 0.02 (−24%) | 4.9 ± 0.4 (−34%) |
| D | 1.24 ± 0.02 (−48%) | 0.80 ± 0.07 (−51%) | 0.74 ± 0.06 (−49%) | 0.26 ± 0.02 (−57%) | 0.90 ± 0.03 (−35%) | 3.4 ± 0.2 (−54%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Igual, M.; Fernandes, Â.; Dias, M.I.; Pinela, J.; García-Segovia, P.; Martínez-Monzó, J.; Barros, L. The In Vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion Affects the Bioaccessibility and Bioactivity of Beta vulgaris Constituents. Foods 2023, 12, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020338
Igual M, Fernandes Â, Dias MI, Pinela J, García-Segovia P, Martínez-Monzó J, Barros L. The In Vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion Affects the Bioaccessibility and Bioactivity of Beta vulgaris Constituents. Foods. 2023; 12(2):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020338
Chicago/Turabian StyleIgual, Marta, Ângela Fernandes, Maria Inês Dias, José Pinela, Purificación García-Segovia, Javier Martínez-Monzó, and Lillian Barros. 2023. "The In Vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion Affects the Bioaccessibility and Bioactivity of Beta vulgaris Constituents" Foods 12, no. 2: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020338
APA StyleIgual, M., Fernandes, Â., Dias, M. I., Pinela, J., García-Segovia, P., Martínez-Monzó, J., & Barros, L. (2023). The In Vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion Affects the Bioaccessibility and Bioactivity of Beta vulgaris Constituents. Foods, 12(2), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020338










