Benefits of Combining Sonchus brachyotus DC. Extracts and Synbiotics in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. NAFLD and Its Treatment
2.1. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
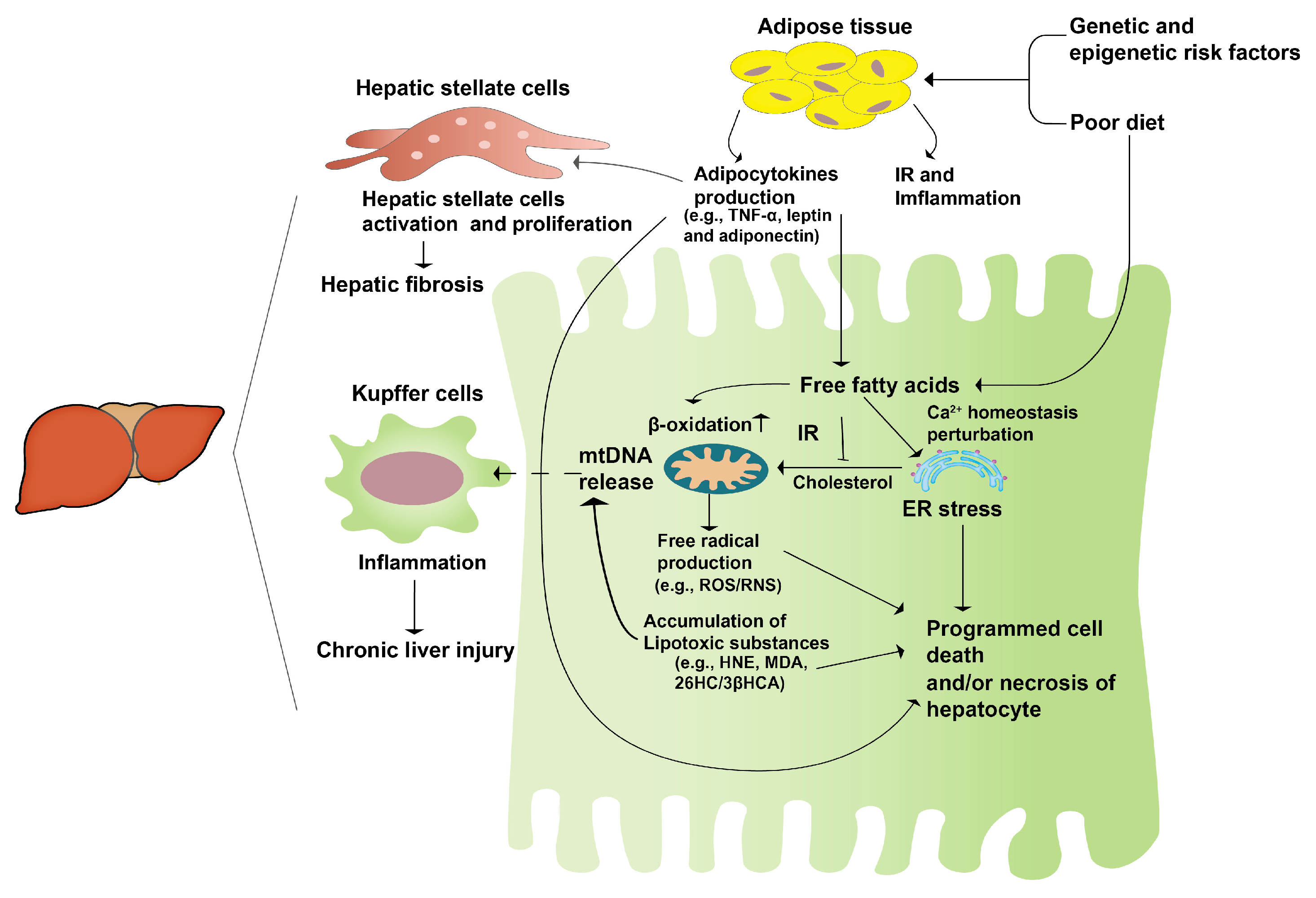
2.2. The Pathogenesis of NAFLD
2.3. The Treatment for NAFLD
3. Definition and Function of, and Research into, Synbiotics
3.1. Definition
3.2. Functions of Synbiotics
3.3. Gut Microecology and NAFLD
4. Sonchus brachyotus DC.
5. Synbiotic Compounds for NAFLD Treatment
5.1. Synbiotic Compounds
5.2. Animal Experiment
5.3. Efficacy of SBE in Combination of Synbiotics in Alleviating NAFLD
5.4. Clinical Research
6. Possible Mechanisms of Synbiotics in NAFLD
7. Future Prospective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, D.H.; Forbes, J.M.; Angus, P.W.; Herath, C.B. Development and Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Role of Advanced Glycation End Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Chander Sharma, B.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Liao, X.; Zhong, B. Epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in some regions of China. J. Clin. Hepatol. 2020, 36, 1370–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, S.; Rustgi, V.K. Current Pharmacologic Therapy for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Y.; Sun, J.; He, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, R.; Chen, H. Effect of Probiotics on Glycemic Control: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marengo, A.; Rosso, C.; Bugianesi, E. Liver Cancer: Connections with Obesity, Fatty Liver, and Cirrhosis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.F.; Oral, E.A.; Dufour, S.; Befroy, D.; Ariyan, C.; Yu, C.; Cline, G.W.; DePaoli, A.M.; Taylor, S.I.; Gorden, P.; et al. Leptin reverses insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in patients with severe lipodystrophy. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimia, J.M.; Meyer, C.M.; Segvich, D.M.; Surendran, S.; DePaoli-Roach, A.A.; Morral, N.; Roach, P.J. Lack of liver glycogen causes hepatic insulin resistance and steatosis in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 10455–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.P.; James, O.F. Steatohepatitis: A tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Tian, R.; She, Z.; Cai, J.; Li, H. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 116–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metab. Clin. Exp. 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeda-Valdés, P.; Cuevas-Ramos, D.; Alberto Aguilar-Salinas, C. Metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2009, 8, S18–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rector, R.S.; Thyfault, J.P.; Wei, Y.; Ibdah, J.A. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the metabolic syndrome: An update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capanni, M.; Calella, F.; Biagini, M.R.; Genise, S.; Raimondi, L.; Bedogni, G.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; Sofi, F.; Milani, S.; Abbate, R.; et al. Prolonged n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation ameliorates hepatic steatosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masterton, G.S.; Plevris, J.N.; Hayes, P.C. Review article: Omega-3 fatty acids—A promising novel therapy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, S.; Dasarathy, J.; Khiyami, A.; Yerian, L.; Hawkins, C.; Sargent, R.; McCullough, A.J. Double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial of omega 3 fatty acids for the treatment of diabetic patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 49, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.V.; McCullough, A.; Diehl, A.M.; Bass, N.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Lavine, J.E.; Tonascia, J.; Unalp, A.; et al. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1185–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearlman, M.; Loomba, R. State of the art: Treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 30, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiaghamohammadi, A.A.; Ziaee, A.; Oveisi, S.; Masroor, H. Effects of metformin, pioglitazone, and silymarin treatment on non-alcoholic Fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled pilot study. Hepat. Mon. 2012, 12, e6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.N.; Wang, J.; Muralidharan, S.; Chalasani, S.; Fullenkamp, A.M.; Wilson, L.A.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kowdley, K.V.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Brunt, E.M.; et al. Relationship between adipose tissue insulin resistance and liver histology in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A pioglitazone versus vitamin E versus placebo for the treatment of nondiabetic patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis trial follow-up study. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Inui, H.; Fukusato, T. Current pharmacological therapies for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3777–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Harrison, S.A.; Belfort-Aguilar, R.; Hardies, L.J.; Balas, B.; Schenker, S.; Cusi, K. Importance of changes in adipose tissue insulin resistance to histological response during thiazolidinedione treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promrat, K.; Lutchman, G.; Uwaifo, G.I.; Freedman, R.J.; Soza, A.; Heller, T.; Doo, E.; Ghany, M.; Premkumar, A.; Park, Y.; et al. A pilot study of pioglitazone treatment for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2004, 39, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K. Role of obesity and lipotoxicity in the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 711–725.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavine, J.E.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Van Natta, M.L.; Molleston, J.P.; Murray, K.F.; Rosenthal, P.; Abrams, S.H.; Scheimann, A.O.; Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; et al. Effect of vitamin E or metformin for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: The TONIC randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2011, 305, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Gosho, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ishii, N.; Ohashi, T.; Nakade, Y.; Ito, K.; Fukuzawa, Y.; Yoneda, M. Vitamin E has a beneficial effect on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrition 2015, 31, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Qv, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, B.; Berglund, B.; Li, L. An Update on the Efficacy and Functionality of Probiotics for the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Engineering 2021, 7, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Pan, J.J.G.T.C.M. The hepatoprotective effect of semen cassiae extract by antagonizing insulin resistance and inhibiting oxidative-glycation in rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Glob. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 8, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.-C.; Zheng, J.-Y.; Qiu, Y.-H.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Miao, X.-L.; Lu, X.-Y. Salvianolic acid B ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting hepatic lipid accumulation and NLRP3 inflammasome in ob/ob mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 111, 109099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F. Effects of geniposide on inflammation and oxidative stress of ApoE knockout mice with atherosclerosis and none-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Tradit. Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 26, 581–586. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Introducing the concept of prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, M.L.; Sanders, M.E.; Gänzle, M.; Arrieta, M.C.; Cotter, P.D.; De Vuyst, L.; Hill, C.; Holzapfel, W.; Lebeer, S.; Merenstein, D.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on fermented foods. Nat. Reviews. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E. Probiotics in 2015: Their Scope and Use. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 49, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, A.L.; Rajkumar, C.; Cooke, J.; Bulpitt, C.J. Probiotics in prevention of antibiotic associated diarrhoea: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2002, 324, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, G.; Rao, S.; Patole, S.; Bulsara, M. Updated meta-analysis of probiotics for preventing necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm neonates. Pediatrics 2010, 125, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zuo, Z.X.; Mao, A.P. Effect of probiotics on inducing remission and maintaining therapy in ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and pouchitis: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, Y.; Liu, G.; Wan, C. Efficacy of probiotics in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adult and children: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2016, 46, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Buys, N.J. Glucose- and glycaemic factor-lowering effects of probiotics on diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preidis, G.A.; Versalovic, J. Targeting the human microbiome with antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics: Gastroenterology enters the metagenomics era. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 2015–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Tang, R.; Li, B.; Ma, X.; Schnabl, B.; Tilg, H. Gut microbiome, liver immunology, and liver diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Song, Z.; Xi-xiang, A. Study on the relationship between immune system stability of intestinal microecological flora and insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Community Med. 2022, 20, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Han, R.; Cao, Y.; Hua, W.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pang, X.; Wei, C.; et al. Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet relevant to development of metabolic syndromes in mice. ISME J. 2010, 4, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Gill, C.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Gill, S.R. Characterization of gut microbiomes in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: A connection between endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 2013, 57, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpton, S.R.; Maraj, B.; Harding-Theobald, E.; Vittinghoff, E.; Terrault, N.A. Gut microbiome-targeted therapies in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, V.; Mosca, A.; Alterio, T.; Cardile, S.; Putignani, L. Fighting Fatty Liver Diseases with Nutritional Interventions, Probiotics, Symbiotics, and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1125, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorletti, E.; Byrne, C.D. Extrahepatic Diseases and NAFLD: The Triangular Relationship between NAFLD, Type 2-Diabetes and Dysbiosis. Dig. Dis. 2016, 34 (Suppl. S1), 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Cai, M.; Shen, B.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, X. Synbiotics and Gut Microbiota: New Perspectives in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Foods 2022, 11, 2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Su, Y.; Li, M.; Xie, X.; Su, J. Complete Chloroplast Genome Sequence of Sonchus brachyotus Helps to Elucidate Evolutionary Relationships with Related Species of Asteraceae. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 9410496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque-Souza, E.; Sahingur, S.E. Periodontitis, chronic liver diseases, and the emerging oral-gut-liver axis. Periodontology 2000 2022, 89, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, J.; Chang, S.H.; Ko, Y.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Young, J.D.; Ojcius, D.M. Gut barrier disruption and chronic disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2022, 33, 247–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, Z.; Gérard, P. The links between the gut microbiome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2019, 76, 1541–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, M.L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.H.; Wang, M.H. Sonchus asper extract inhibits LPS-induced oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in RAW264.7 macrophages. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2015, 9, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, D.Z.; Yu, X.F.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Zou, Z.D. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of six edible wild plants (Sonchus spp.) in China. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.C.; Zhou, Y.G.; Gao, F.; Liu, H.C.; Chen, S.F. Paenibacillus sonchi sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing species isolated from the rhizosphere of Sonchus oleraceus. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2656–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paula Filho, G.X.; Barreira, T.F.; Pinheiro-Sant’Ana, H.M. Chemical Composition and Nutritional Value of Three Sonchus Species. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 2022, 4181656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Vilela, F.; Soncini, R.; Giusti-Paiva, A. Anxiolytic-like effect of Sonchus oleraceus L. in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 124, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Yang, P.-L. Research progress of Sonchus species. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliak, N.; Abenavoli, L.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Mykhalchyshyn, G.; Boccuto, L.; Kononenko, L.; Kyriienko, D.; Komisarenko, I.; Dynnyk, O. Beneficial effects of probiotic combination with omega-3 fatty acids in NAFLD: A randomized clinical study. Minerva Medica 2018, 109, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oscarsson, J.; Önnerhag, K.; Risérus, U.; Sundén, M.; Johansson, L.; Jansson, P.A.; Moris, L.; Nilsson, P.M.; Eriksson, J.W.; Lind, L. Effects of free omega-3 carboxylic acids and fenofibrate on liver fat content in patients with hypertriglyceridemia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2018, 12, 1390–1403.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šmíd, V.; Dvořák, K.; Šedivý, P.; Kosek, V.; Leníček, M.; Dezortová, M.; Hajšlová, J.; Hájek, M.; Vítek, L.; Bechyňská, K.; et al. Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Lipid Metabolism in Patients With Metabolic Syndrome and NAFLD. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1336–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.N.; Kang, J.; Jeong, E.J.; Rho, J.R. Sesquiterpene Lactones with Anti-Inflammatory Activity from the Halophyte Sonchus brachyotus DC. Molecules 2023, 28, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qie, P.; Duan, X.; Wang, M.; Li, X. Antioxidant activity of each polar composition from methanol extracts of Sonchus brachyotus DC. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2016, 37, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, B.-L.; Deng, Y.-R. Comparison of Six Flavonoid Components of Closely-Related Plants Agrimonia pilosa, Potentilla chinensis and Potentilla discolor. Zhong Yao Cai = Zhongyaocai = J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2016, 39, 991–995. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, W.W.; Shi, D.D.; Pan, F.F.; Sun, W.W.; Yang, P.L.; Li, X.M. The Interaction between Oxidative Stress Biomarkers and Gut Microbiota in the Antioxidant Effects of Extracts from Sonchus brachyotus DC. in Oxazolone-Induced Intestinal Oxidative Stress in Adult Zebrafish. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guil-Guerrero, J.L.; Giménez-Giménez, A.; Rodríguez-García, I.; Torija-Isasa, M.E. Nutritional composition of Sonchus species (S asperL, S oleraceusL and S tenerrimusL). J. Sci. Food Agric. 1998, 76, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krog-Mikkelsen, I.; Hels, O.; Tetens, I.; Holst, J.J.; Andersen, J.R.; Bukhave, K. The effects of L-arabinose on intestinal sucrase activity: Dose-response studies in vitro and in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibanuma, K.; Degawa, Y.; Houda, K. Determination of the transient period of the EIS complex and investigation of the suppression of blood glucose levels by L-arabinose in healthy adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2011, 50, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, T.; Lou, J.; Liu, J. L-Arabinose Elicits Gut-Derived Hydrogen Production and Ameliorates Metabolic Syndrome in C57BL/6J Mice on High-Fat-Diet. Nutrients 2019, 11, 3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Pan, H.; Liu, J.X.; Li, T.; Liu, S.; Shi, W.; Sun, C.; Fan, M.; Xue, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. L-Arabinose Inhibits Colitis by Modulating Gut Microbiota in Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13299–13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zuo, Q.; Hai, Y.; Sun, X.J. Lactulose: An indirect antioxidant ameliorating inflammatory bowel disease by increasing hydrogen production. Med. Hypotheses 2011, 76, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Tian, C.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Wei, X.; Lin, W.; Zheng, N.; Jiang, A.; Feng, R.; et al. Targeting the Gut Microbiota to Investigate the Mechanism of Lactulose in Negating the Effects of a High-Salt Diet on Hypertension. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1800941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Liao, Y.; Li, J.; Pei, Z.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Peng, H.; Tan, Y.; Li, C.; Bai, H.; et al. Lactobacillus plantarum GX17 benefits growth performance and improves functions of intestinal barrier/intestinal flora among yellow-feathered broilers. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1195382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jha, R.; Li, A.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhai, Q.; Zhang, J. Probiotics (Lactobacillus plantarum HNU082) Supplementation Relieves Ulcerative Colitis by Affecting Intestinal Barrier Functions, Immunity-Related Gene Expression, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolic Pathways in Mice. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0165122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Zhang, X.; Tong, L.; Liu, Q.; Liang, X.; Bu, Y.; Gong, P.; Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Xia, Y.; et al. Effect of Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Lactobacillus plantarum Q7 on Gut Microbiota and Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 777147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Cao, F.; Lai, S.; Zhuge, H.; Chang, K.; Valencak, T.G.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Ren, D. Lactobacillus plantarum ZY08 relieves chronic alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis and liver injury in mice via restoring intestinal flora homeostasis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Tian, W.; Song, J.; Wang, J. Antihyperlipidaemic effect of microencapsulated Lactobacillus plantarum LIP-1 on hyperlipidaemic rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.X.; Liu, K.; Gao, D.W.; Hao, J.K. Protective effects of two Lactobacillus plantarum strains in hyperlipidemic mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 3150–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, H.H.; Tsai, G.J. Development of Fermented Shrimp Shell Product with Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects on Diabetic Rats. Metabolites 2022, 12, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, P.M.; Teles Filho, R.V.; Azevêdo, L.H.S.; Queiroz, V.C.J.; Costa, P. Inflammatory cytokines and lipid profile in children and adolescents with nephrotic syndrome receiving L. Plantarum: A randomized, controlled feasibility trial. Rev. Assoc. Medica Bras. (1992) 2020, 66, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.C.; Luo, X.G.; Wang, C.X.; Ma, D.Y.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.Y.; Li, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, T.C. Cloning and analysis of bile salt hydrolase genes from Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC No. 8198. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Gao, L.; Lin, H.; Wu, Y.; Han, X.; Zhu, Y.; Li, J. Luteolin improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in db/db mice by inhibition of liver X receptor activation to down-regulate expression of sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Pan, R.; Ding, L.; Zhang, F.; Hu, L.; Ding, B.; Zhu, L.; Xia, Y.; Dou, X. Rutin exhibits hepatoprotective effects in a mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by reducing hepatic lipid levels and mitigating lipid-induced oxidative injuries. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Lin, M.C.; Wang, H.C.; Yang, M.Y.; Jou, M.J.; Wang, C.J. Rutin inhibits oleic acid induced lipid accumulation via reducing lipogenesis and oxidative stress in hepatocarcinoma cells. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, T65–T72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuwamongkolwiwat, P.; Suzuki, T.; Hira, T.; Hara, H. Fructooligosaccharide augments benefits of quercetin-3-O-β-glucoside on insulin sensitivity and plasma total cholesterol with promotion of flavonoid absorption in sucrose-fed rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofidi, F.; Yari, Z.; Poustchi, H.; Merat, S.; Nourinayyer, B.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Effects of Synbiotics Supplementation in Lean Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Study Protocol of a Pilot Randomized Double-blind Clinical Trial. Arch. Iran. Med. 2016, 19, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laue, C.; Papazova, E.; Pannenbeckers, A.; Schrezenmeir, J. Effect of a Probiotic and a Synbiotic on Body Fat Mass, Body Weight and Traits of Metabolic Syndrome in Individuals with Abdominal Overweight: A Human, Double-Blind, Randomised, Controlled Clinical Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferolla, S.M.; Couto, C.A.; Costa-Silva, L.; Armiliato, G.N.; Pereira, C.A.; Martins, F.S.; Ferrari Mde, L.; Vilela, E.G.; Torres, H.O.; Cunha, A.S.; et al. Beneficial Effect of Synbiotic Supplementation on Hepatic Steatosis and Anthropometric Parameters, But Not on Gut Permeability in a Population with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslamparast, T.; Poustchi, H.; Zamani, F.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic supplementation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorletti, E.; Afolabi, P.R.; Miles, E.A.; Smith, D.E.; Almehmadi, A.; Alshathry, A.; Moyses, H.E.; Clough, G.F.; Wright, M.; Patel, J.; et al. Design and rationale of the INSYTE study: A randomised, placebo controlled study to test the efficacy of a synbiotic on liver fat, disease biomarkers and intestinal microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2018, 71, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorletti, E.; Afolabi, P.R.; Miles, E.A.; Smith, D.E.; Almehmadi, A.; Alshathry, A.; Childs, C.E.; Del Fabbro, S.; Bilson, J.; Moyses, H.E.; et al. Synbiotics Alter Fecal Microbiomes, But Not Liver Fat or Fibrosis, in a Randomized Trial of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1597–1610.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayari, S.; Neishaboori, H.; Jameshorani, M. Combined effects of synbiotic and sitagliptin versus sitagliptin alone in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2018, 24, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofidi, F.; Poustchi, H.; Yari, Z.; Nourinayyer, B.; Merat, S.; Sharafkhah, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Hekmatdoost, A. Synbiotic supplementation in lean patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshimoghaddam, F.; Shateri, K.; Sina, M.; Hashemian, M.; Alizadeh, M. Daily Consumption of Synbiotic Yogurt Decreases Liver Steatosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhari, K.; Saadati, S.; Yari, Z.; Hosseini, H.; Hedayati, M.; Abhari, S.; Alavian, S.M.; Hekmatdoost, A. The effects of Bacillus coagulans supplementation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 39, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrouz, V.; Jazayeri, S.; Aryaeian, N.; Zahedi, M.J.; Hosseini, F. Effects of Probiotic and Prebiotic Supplementation on Leptin, Adiponectin, and Glycemic Parameters in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Middle East J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 9, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, M.; Vacante, M.; Antic, T.; Giordano, M.; Chisari, G.; Acquaviva, R.; Mastrojeni, S.; Malaguarnera, G.; Mistretta, A.; Li Volti, G.; et al. Bifidobacterium longum with fructo-oligosaccharides in patients with non alcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavakhi, A.; Minakari, M.; Firouzian, H.; Assali, R.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Ferns, G. Effect of a Probiotic and Metformin on Liver Aminotransferases in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Double Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 531–537. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Monem, S.M. Probiotic Therapy in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Zagazig University Hospitals. Euroasian J. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 2017, 7, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aller, R.; De Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Conde, R.; Gonzalez Sagrado, M.; Primo, D.; De La Fuente, B.; Gonzalez, J. Effect of a probiotic on liver aminotransferases in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: A double blind randomized clinical trial. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 15, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat. Reviews. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Vitetta, L.J.H. Could butyrate be incorporated with Farnesoid X receptor agonist cilofexor to enhance primary sclerosing cholangitis treatment? Hepatology 2020, 72, 1497–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Vitetta, L. Butyrate in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Therapy. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A.; et al. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltzman, E.T.; Palacios, T.; Thomsen, M.; Vitetta, L. Intestinal Microbiome Shifts, Dysbiosis, Inflammation, and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roy, T.; Llopis, M.; Lepage, P.; Bruneau, A.; Rabot, S.; Bevilacqua, C.; Martin, P.; Philippe, C.; Walker, F.; Bado, A.; et al. Intestinal microbiota determines development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Gut 2013, 62, 1787–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.C.; Ching, Y.H.; Li, Y.P.; Liu, J.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Huang, Y.W.; Yang, S.S.; Huang, W.C.; Chuang, H.L. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Exacerbated in High-Fat Diet-Fed Gnotobiotic Mice by Colonization with the Gut Microbiota from Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Zúñiga, V.; Bartolí, R.; Planas, R.; Hofmann, A.F.; Viñado, B.; Hagey, L.R.; Hernández, J.M.; Mañé, J.; Alvarez, M.A.; Ausina, V.; et al. Oral bile acids reduce bacterial overgrowth, bacterial translocation, and endotoxemia in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 2003, 37, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, Y.; Nishi, M.; Nakayama, H.; Kuwahara, T.; Ohnishi, Y.; Tashiro, S. Role of bile in intestinal barrier function and its inhibitory effect on bacterial translocation in obstructive jaundice in rats. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 115, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xia, J.; Jiang, C.J.L.R. Role of gut microbiota in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Res. 2019, 3, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, J.D.; Guo, G.L. Pharmacologic Modulation of Bile Acid-FXR-FGF15/FGF19 Pathway for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2019, 256, 325–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, E.; Fu, L.; John, L.; Hultgren, B.; Huang, X.; Renz, M.; Stephan, J.P.; Tsai, S.P.; Powell-Braxton, L.; French, D.; et al. Transgenic mice expressing human fibroblast growth factor-19 display increased metabolic rate and decreased adiposity. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Sola, G.; Uriarte, I.; Latasa, M.U.; Fernandez-Barrena, M.G.; Urtasun, R.; Elizalde, M.; Barcena-Varela, M.; Jiménez, M.; Chang, H.C.; Barbero, R.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 15/19 (FGF15/19) protects from diet-induced hepatic steatosis: Development of an FGF19-based chimeric molecule to promote fatty liver regeneration. Gut 2017, 66, 1818–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y.; Pathak, P.; Liu, H.; Donepudi, A.; Ferrell, J.; Boehme, S. Intestinal Farnesoid X Receptor and Takeda G Protein Couple Receptor 5 Signaling in Metabolic Regulation. Dig. Dis. 2017, 35, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoviran, O.F.; Li, D.; Toombs Smith, S.; Raji, M.A. Effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists on comorbidities in older patients with diabetes mellitus. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2019, 10, 2040622319862691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Manchester, J.K.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, H.; Sakoda, H.; Kushiyama, A.; Fujishiro, M.; Nakatsu, Y.; Fukushima, T.; Matsunaga, Y.; Kamata, H.; Asahara, T.; Yoshida, Y.; et al. Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota protects against nonalcoholic steatohepatitis development in a rodent model. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G911–G918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, M.S. Characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum PH04, a potential probiotic bacterium with cholesterol-lowering effects. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 113, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Duan, C.; Yang, G.; Niu, C.; Li, S. Lactobacillus plantarum NA136 ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating gut microbiota, improving intestinal barrier integrity, and attenuating inflammation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 5273–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Groups Assignment | Symbiotic Components | Supplementation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental Group | 30% Lactulose | 30% Arabinose | 40% Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC 8198 | 2.0 g/kg SBE |
| Control Group 1 | 30% Lactulose | 30% Arabinose | 40% Lactobacillus plantarum CGMCC 8198 | \ |
| Control Group 2 | \ | \ | \ | 2.0 g/kg SBE |
| Groups | Liver Wet Weight | Liver Coefficient |
|---|---|---|
| Blank Group (NC) | 1.137 | 0.0433 |
| Model Group (NAFLD) | 2.274 | 0.0477 |
| Experimental Group (NAFLD+Synb+SBE) | 1.347 | 0.0426 |
| Control Group 1 (NAFLD+Synb) | 1.663 | 0.0481 |
| Control Group 2 (NAFLD+SBE) | 1.408 | 0.0447 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, W.; Shen, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, X. Benefits of Combining Sonchus brachyotus DC. Extracts and Synbiotics in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Foods 2023, 12, 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183393
Huang W, Shen B, Li X, Zhang T, Zhou X. Benefits of Combining Sonchus brachyotus DC. Extracts and Synbiotics in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Foods. 2023; 12(18):3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183393
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Wenwu, Boyuan Shen, Xiumei Li, Tongcun Zhang, and Xiang Zhou. 2023. "Benefits of Combining Sonchus brachyotus DC. Extracts and Synbiotics in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease" Foods 12, no. 18: 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183393
APA StyleHuang, W., Shen, B., Li, X., Zhang, T., & Zhou, X. (2023). Benefits of Combining Sonchus brachyotus DC. Extracts and Synbiotics in Alleviating Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Foods, 12(18), 3393. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183393







