The Effect of Freeze–Thaw Cycles on the Microscopic Properties of Dumpling Wrappers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wheat Flour Samples
2.2. Preparation and Freeze–Thaw Cycles of Dumpling Wrappers
2.3. Textural Properties Analysis
2.4. Particle Size Distribution
2.5. Water Distribution Analysis
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy Observations (SEM)
2.7. Secondary Structure Study
2.8. Thermal Properties Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Textural Properties of Dumpling Wrappers
3.2. Particle Size Distribution in Dumpling Wrappers
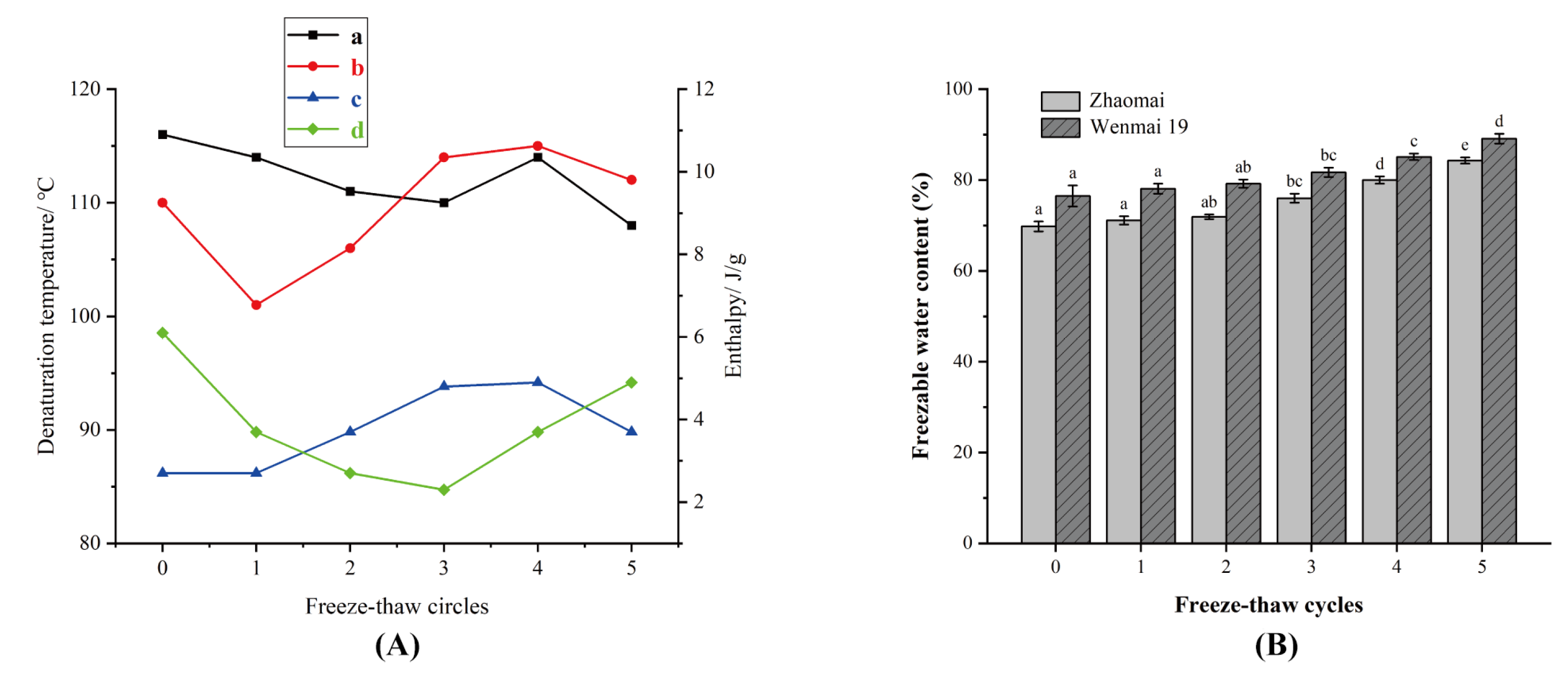
3.3. Water Distribution Analysis
3.4. Microscopic Analysis of Dumpling Wrappers
3.5. Microscopic Analysis of Gliadins
3.6. Secondary Structure of Gliadins
3.7. Thermal Properties of Gliadins
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goesaert, H.; Brijs, K.; Veraverbeke, W.; Courtin, C.; Gebruers, K.; Delcour, J. Wheat flour constituents: How they impact bread quality, and how to impact their functionality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.-N.; Liao, A.-M.; Zhang, F.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.-G.; Huang, J.-H.; Wei, Z.-J. Microstructural, Textural, Sensory Properties and Quality of Wheat–Yam Composite Flour Noodles. Foods 2019, 8, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, T.H.; Day, L. Effect of sodium chloride on gluten network formation, dough microstructure and rheology in relation to breadmaking. J. Cereal Sci. 2013, 57, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, V.; Khatkar, B. Effects of gliadin/glutenin and HMW-GS/LMW-GS ratio on dough rheological properties and bread-making potential of wheat varieties. J. Food Qual. 2015, 38, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D.; Khatkar, B. Effect of compositional variation of gluten proteins and rheological characteristics of wheat flour on the textural quality of white salted noodles. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, F.; Ansari, S.; Yau, P.; Yazar, G.; Ryan, V.; Kokini, J. Distribution and location of ethanol soluble proteins (Osborne gliadin) as a function of mixing time in strong wheat flour dough using quantum dots as a labeling tool with confocal laser scanning microscopy. Food Res. Int. 2014, 66, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Don, C.; Mann, G.; Bekes, F.; Hamer, R. HMW-GS affect the properties of glutenin particles in GMP and thus flour quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 44, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Dynamic rheological properties of wheat flour dough and proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D.; Khatkar, B. Influence of gliadin and glutenin fractions on rheological, pasting, and textural properties of dough. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, B.; Barak, S.; Mudgil, D. Effects of gliadin addition on the rheological, microscopic and thermal characteristics of wheat gluten. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 53, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D.; Khatkar, B. Relationship of gliadin and glutenin proteins with dough rheology, flour pasting and bread making performance of wheat varieties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, P.; Gao, Y.; Chen, P.; Lv, C.; Zhao, G. Recent Advances in the Study of Wheat Protein and Other Food Components Affecting the Gluten Network and the Properties of Noodles. Foods 2022, 11, 3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, N.; Virdi, A.S.; Dangi, P.; Khatkar, B.S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Singh, N. Protein, thermal and functional properties of α-, γ- and ω-gliadins of wheat and their effect on bread making characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Guo, W.; Rossi, V.; Xin, M.; Du, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. An elite γ-gliadin allele improves end-use quality in wheat. New Phytol. 2023, 239, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jekle, M.; Becker, T. Dough microstructure: Novel analysis by quantification using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Kokawa, M.; Nango, N.; Miura, M.; Araki, T.; Yamada, M.; Takeya, K.; Sagara, Y. Development of a quantification method of the gluten matrix in bread dough by fluorescence microscopy and image analysis. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Du, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z. Did Wheat Breeding Simultaneously Improve Grain Yield and Quality of Wheat Cultivars Releasing over the Past 20 Years in China? Agronomy 2022, 12, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H.; Antes, S.; Seilmeier, W. Quantitative determination of gluten protein types in wheat flour by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yu, C.; Yang, Z.; Xing, J.; Guo, X.; Zhu, K. Impact of gluten quality on textural stability of cooked noodles and the underlying mechanism. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, J.E.; Damodaran, S. Bran-induced changes in water structure and gluten conformation in model gluten dough studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannou, V.; Tzia, C. Addition of vital wheat gluten to enhance the quality characteristics of frozen dough products. Foods 2016, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier-Schenk, A.; Handschin, S.; Von Schönau, M.; Bittermann, A.; Bächi, T.; Conde-Petit, B. In situ observation of the freezing process in wheat dough by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM): Formation of ice and changes in the gluten network. J. Cereal Sci. 2005, 42, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.; Ragaee, S.; Abdel-Aal, E.S.M. Effect of β-glucan–rich barley flour fraction on rheology and quality of frozen yeasted dough. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, E2470–E2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belorio, M.; Sahagún, M.; Gómez, M. Influence of Flour Particle Size Distribution on the Quality of Maize Gluten-Free Cookies. Foods 2019, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, H.; Wang, P.; Wu, F.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Particle size distribution of wheat starch granules in relation to baking properties of frozen dough. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; Guan, C.; Qian, J.; Zhou, X. Effect of barley antifreeze proteinon dough and bread during Freezing and Freeze-Thaw cycles. Foods 2020, 9, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Yang, Z.; Guo, X.-N.; Xing, J.-J.; Zhu, K.-X. Effect of NaHCO3 and freeze–thaw cycles on frozen dough: From water state, gluten polymerization and microstructure. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tao, H.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. The final established physicochemical properties of steamed bread made from frozen dough: Study of the combined effects of gluten polymerization, water content and starch crystallinity on bread firmness. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 63, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhao, L. Impact of xanthan gum on gluten microstructure and bread quality during the freeze-thaw storage. LWT 2022, 162, 113450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zounis, S.; Quail, K.; Wootton, M.; Dickson, M. Studying frozen dough structure using low-temperature scanning electron microscopy. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 35, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xu, L.; Nikoo, M.; Ocen, D.; Wu, F.; Yang, N.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of frozen storage on the conformational, thermal and microscopic properties of gluten: Comparative studies on gluten-, glutenin- and gliadin-rich fractions. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Huang, W.; Rayas-Duarte, P.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Hydration, polymerization and rheological properties of frozen gluten-water dough as influenced by thermostable ice structuring protein extract from Chinese privet (Ligustrum vulgare) leaves. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 59, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tao, H.; Wu, F.; Yang, N.; Chen, F.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of frozen storage on the foaming properties of wheat gliadin. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markgren, J.; Hedenqvist, M.; Rasheed, F.; Skepö, M.; Johansson, E. Glutenin and Gliadin, a Piece in the Puzzle of their Structural Properties in the Cell Described through Monte Carlo Simulations. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Qi, X.; Xiao, J. Effect of barley antifreeze protein on thermal properties and water state of dough during freezing and freeze-thaw cycles. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 47, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Langstaff, T.M.; Berzonsky, W.A. Effect of frozen storage and freeze–thaw cycles on the rheological and baking properties of frozen doughs. Food Res. Int. 2003, 36, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J. A study on the relationship between rheological properties of wheat flour, gluten structure, and dumpling wrapper quality. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 1566–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.-L.; Liu, J.-J.; Xiao, Y.-G.; Sun, Q.-X.; He, Z.-H. The relationship between chinese raw dumpling quality and flour characteristics of Shandong winter wheat cultivars. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 1792–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
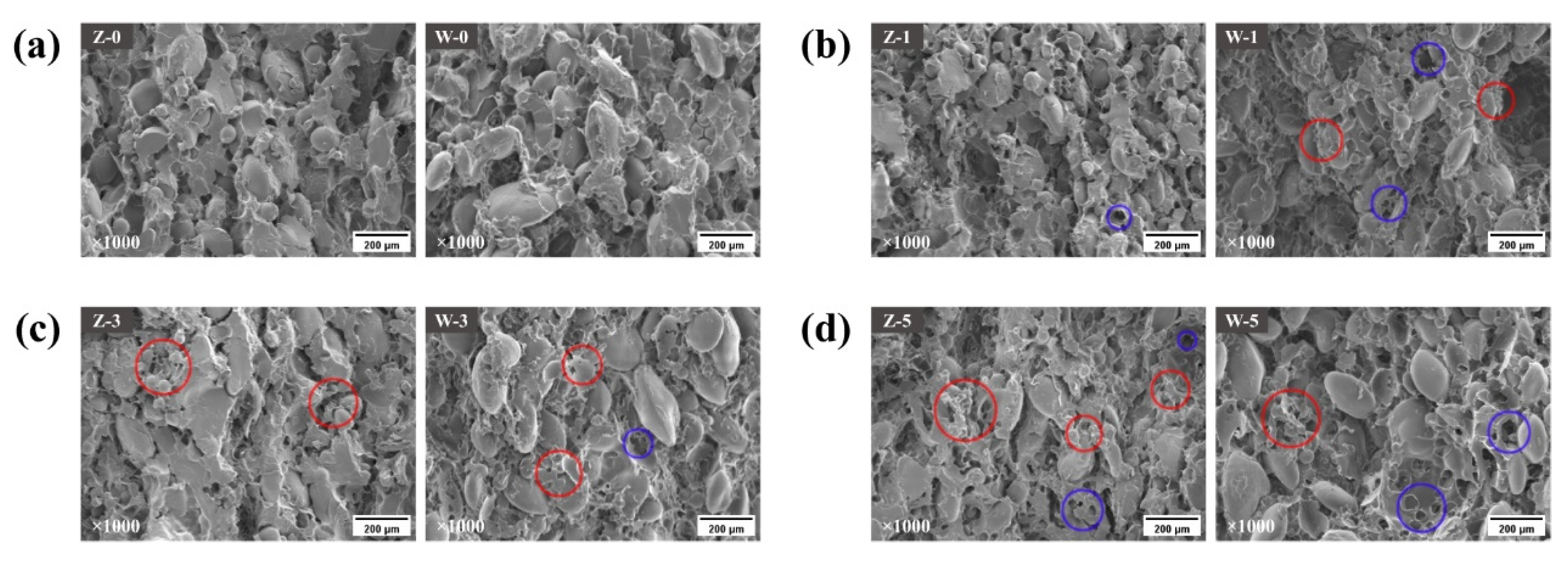
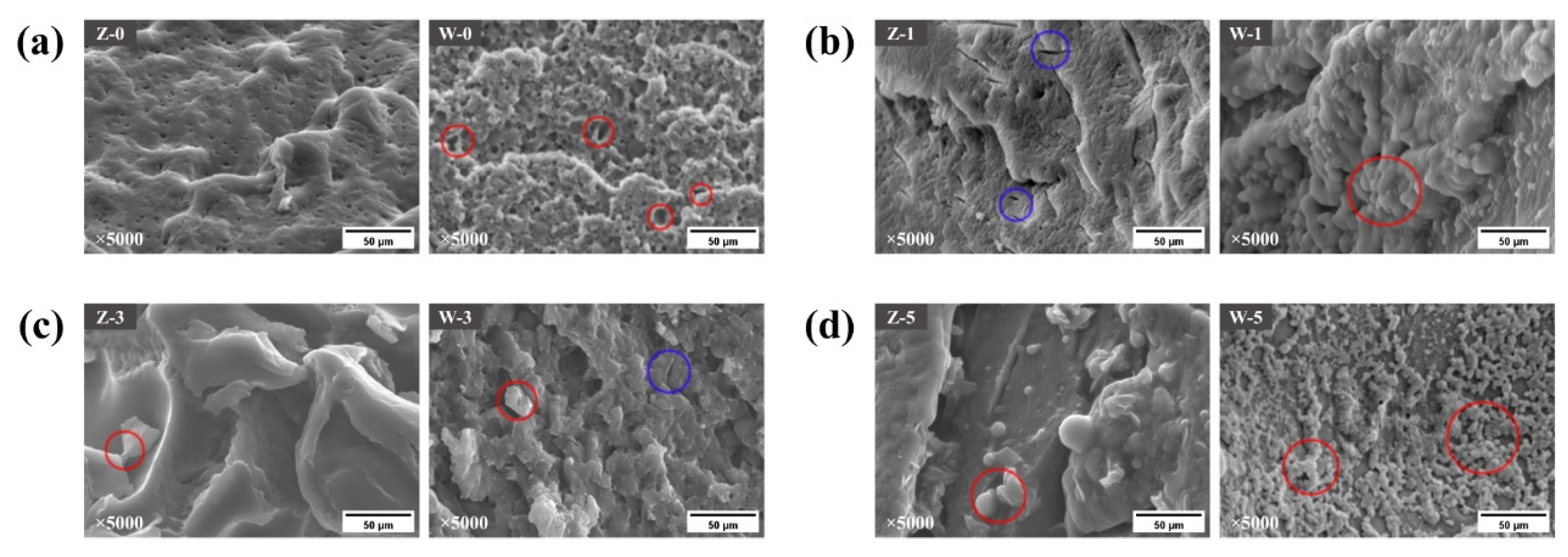
| Freeze–Thaw Cycles | Hardness (g) | Springness | Cohesiveness | Firmness (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhaomai | 0 | 15,277 ± 964 a | 0.992 ± 0.002 a | 0.843 ± 0.019 ab | 927 ± 154 a |
| 1 | 14,811 ± 1124 a | 0.992 ± 0.002 a | 0.849 ± 0.007 a | 879 ± 3 ab | |
| 2 | 15,940 ± 1231 a | 0.990 ± 0 a | 0.837 ± 0.011 ab | 907 ± 24 a | |
| 3 | 16,105 ± 589 a | 0.993 ± 0.001 a | 0.824 ± 0.009 b | 767 ± 33 b | |
| 4 | 14,619 ± 220 a | 0.990 ± 0 a | 0.834 ± 0.005 ab | 875 ± 15 ab | |
| 5 | 11,505 ± 545 b | 0.973 ± 0.019 b | 0.849 ± 0.013 a | 804 ± 14 ab | |
| Wenmai 19 | 0 | 9000 ± 1165 a | 0.953 ± 0.009 a | 0.903 ± 0.006 a | 471 ± 48 ab |
| 1 | 8404 ± 660 ab | 0.937 ± 0.044 a | 0.891 ± 0.005 a | 504 ± 81 a | |
| 2 | 7337 ± 589 bc | 0.948 ± 0.013 a | 0.877 ± 0.017 a | 439 ± 72 ab | |
| 3 | 6995 ± 406 cd | 0.889 ± 0.070 a | 0.845 ± 0.017 b | 403 ± 98 ab | |
| 4 | 7396 ± 785 bc | 0.957 ± 0.014 a | 0.881 ± 0.020 a | 403 ± 23 ab | |
| 5 | 5866 ± 295 d | 0.938 ± 0.043 a | 0.900 ± 0.031 a | 368 ± 5 b |
| Freeze–Thaw Cycles | D10 (μm) | D50 (μm) | D90 (μm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhaomai | 0 | 10.48 ± 1.53 c | 23.27 ± 1.92 ab | 44.04 ± 0.62 a |
| 1 | 13.86 ± 0.35 b | 26.19 ± 1.46 a | 40.86 ± 0.37 abc | |
| 2 | 16.36 ± 2.46 a | 25.03 ± 1.55 a | 35.24 ± 0.8 cd | |
| 3 | 8.91 ± 0.11 c | 20.49 ± 0.25 c | 33.12 ± 0.36 cd | |
| 4 | 10.65 ± 1.18 c | 20.48 ± 3.44 c | 36.52 ± 3.38 bcd | |
| 5 | 11.48 ± 1.2 bc | 20.46 ± 1.81 c | 42.16 ± 2.48 ab | |
| Wenmai 19 | 0 | 16.52 ± 0.08 a | 27.27 ± 0.76 a | 45.06 ± 2.63 a |
| 1 | 13.35 ± 1.03 b | 20.58 ± 0.12 b | 34.33 ± 1.3 b | |
| 2 | 11.85 ± 0.87 bc | 18.92 ± 0.68 c | 32.91 ± 2.51 b | |
| 3 | 10.46 ± 1.46 cd | 18.51 ± 0.36 c | 29.07 ± 1.38 c | |
| 4 | 9.51 ± 0.37 d | 18.56 ± 0.36 c | 41.81 ± 1.61 a | |
| 5 | 11.63 ± 0.5 bc | 18.61 ± 0.62 c | 29.31 ± 1.69 c |
| Freeze–Thaw Cycles | T21 (ms) | T22 (ms) | A21 | A22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhaomai | 0 | 1.05 ± 0.07 c | 44.49 ± 0.01 c | 2716.17 ± 29.64 a | 15,888.18 ± 35.20 c |
| 1 | 1.08 ± 0.03 c | 45.90 ± 0.04 c | 2607.52 ± 16.96 a | 16,094.73 ± 37.48 c | |
| 2 | 1.10 ± 0.02 c | 48.36 ± 0.01 c | 2553.20 ± 22.13 b | 16,364.83 ± 25.49 b | |
| 3 | 1.16 ± 0.01 b | 50.95 ± 0.02 b | 2444.55 ± 19.44 c | 16,682.59 ± 33.43 b | |
| 4 | 1.31 ± 0.04 a | 52.53 ± 0.04 b | 2254.42 ± 18.22 d | 17,318.12 ± 37.94 a | |
| 5 | 1.53 ± 0.03 a | 51.03 ± 0.01 a | 2145.77 ± 17.56 e | 17,635.88 ± 30.86 a | |
| Wenmai 19 | 0 | 1.12 ± 0.00 e | 54.79 ± 0.02 d | 2447.99 ± 14.50 a | 16,641.55 ± 37.02 c |
| 1 | 1.14 ± 0.01 e | 56.57 ± 0.01 d | 2350.07 ± 18.73 a | 16,891.17 ± 29.51 c | |
| 2 | 1.19 ± 0.04 d | 59.84 ± 0.06 c | 2301.11 ± 25.62 b | 17,307.21 ± 32.82 b | |
| 3 | 1.25 ± 0.02 c | 62.40 ± 0.03 b | 2178.11 ± 26.66 c | 17,640.04 ± 26.87 b | |
| 4 | 1.43 ± 0.05 b | 64.33 ± 0.02 b | 2007.35 ± 17.46 d | 18,305.71 ± 35.26 a | |
| 5 | 1.72 ± 0.05 a | 70.13 ± 0.03 a | 1909.43 ± 19.71 e | 18,638.54 ± 25.39 a |
| Freeze–Thaw Cycles | α-Helix (%) | β-Turn (%) | β-Sheet (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhaomai | 0 | 24.12% ± 0.23% c | 22.21% ± 0.72% c | 15.90% ± 0.31% a |
| 1 | 26.62% ± 0.22% a | 22.44% ± 0.55% c | 12.48% ± 0.66% d | |
| 2 | 26.17% ± 0.07% b | 23.69% ± 0.81% b | 12.95% ± 0.51% cd | |
| 3 | 26.03% ± 0.18% b | 24.68% ± 0.07% a | 13.70% ± 0.16% bc | |
| 4 | 26.04% ± 0.12% b | 23.35% ± 0.25% b | 13.34% ± 0.40% bc | |
| 5 | 26.18% ± 0.13% b | 25.01% ± 0.20% a | 13.91% ± 0.20% b | |
| Wenmai 19 | 0 | 28.00% ± 0.37% a | 26.08% ± 0.57% ab | 15.05% ± 0.47% a |
| 1 | 26.72% ± 1.37% a | 23.73% ± 0.96% c | 14.79% ± 1.29% ab | |
| 2 | 27.63% ± 0.45% a | 26.04% ± 0.40% ab | 14.60% ± 0.66% ab | |
| 3 | 27.56% ± 0.46% a | 25.30% ± 0.24% b | 14.35% ± 1.05% ab | |
| 4 | 27.95% ± 0.21% a | 26.97% ± 0.46% a | 14.76% ± 0.11% ab | |
| 5 | 26.90% ± 0.29% a | 24.30% ± 0.20% c | 13.31% ± 0.74% b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Z.; Bai, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, M.; Huang, Z. The Effect of Freeze–Thaw Cycles on the Microscopic Properties of Dumpling Wrappers. Foods 2023, 12, 3388. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183388
Pan Z, Bai Y, Xu L, Zhang Y, Lei M, Huang Z. The Effect of Freeze–Thaw Cycles on the Microscopic Properties of Dumpling Wrappers. Foods. 2023; 12(18):3388. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183388
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Zhili, Yibo Bai, Lina Xu, Yanjie Zhang, Mengmeng Lei, and Zhongmin Huang. 2023. "The Effect of Freeze–Thaw Cycles on the Microscopic Properties of Dumpling Wrappers" Foods 12, no. 18: 3388. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183388
APA StylePan, Z., Bai, Y., Xu, L., Zhang, Y., Lei, M., & Huang, Z. (2023). The Effect of Freeze–Thaw Cycles on the Microscopic Properties of Dumpling Wrappers. Foods, 12(18), 3388. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12183388





