A Colorimetric Sensor Enabled with Heterogeneous Nanozymes with Phosphatase-like Activity for the Residue Analysis of Methyl Parathion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Synthesis of Nanozymes
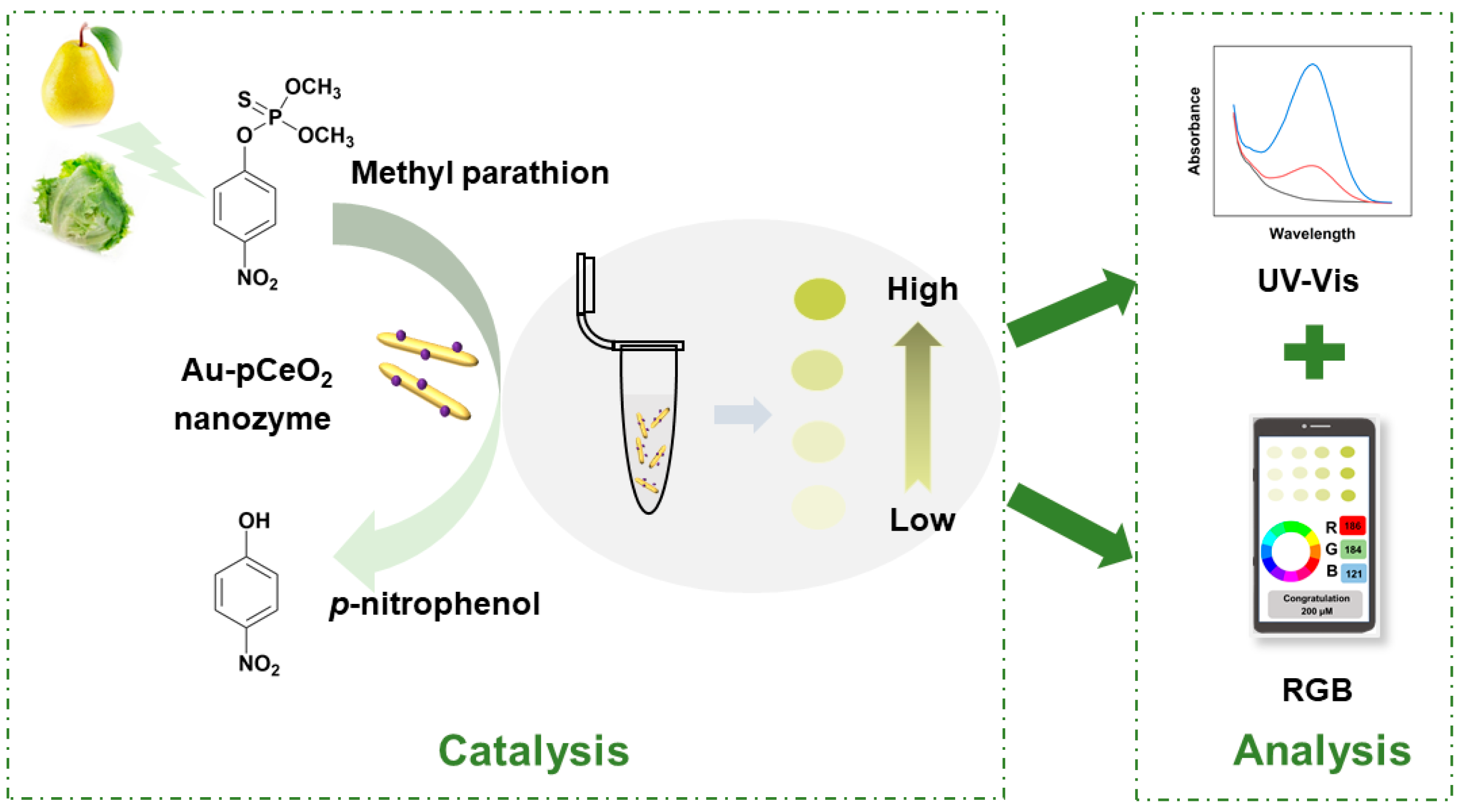
2.3. Detection of MP
2.4. Real Sample Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Comparison of CeO2, pCeO2, and Au-CeO2 Nanozymes
3.2. Optimization and Characterization of Au-CeO2 Nanozymes
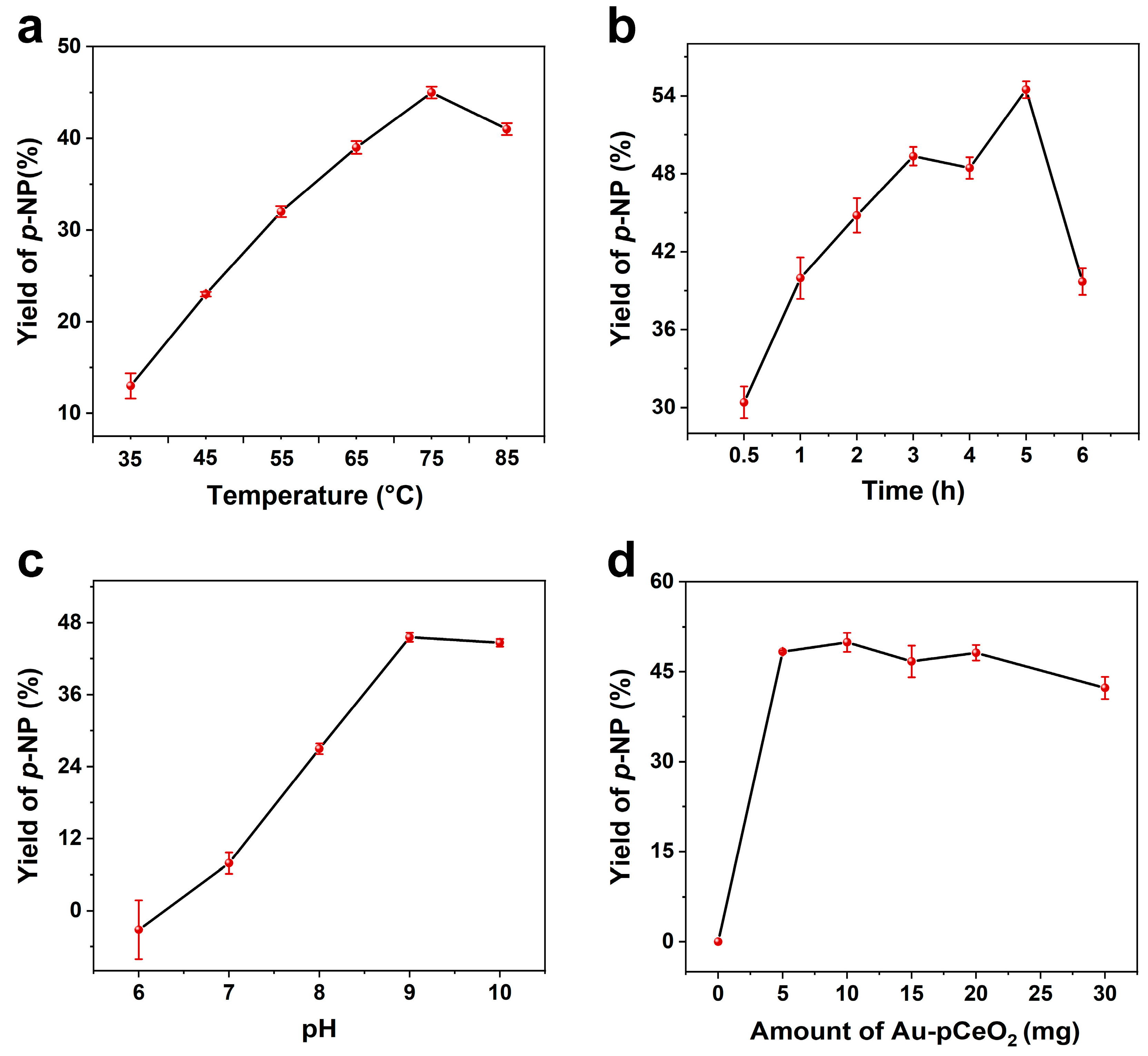
3.3. Catalytic Conditions of Au-pCeO2 Nanozyme
3.4. Detection Performance for MP
3.5. Selectivity, Interference, Stability, and Recoverability
3.6. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhattu, M.; Verma, M.; Kathuria, D. Recent advancements in the detection of organophosphate pesticides: A review. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4390–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, G.K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Datta, S.; Singh, J. Toxicity, monitoring and biodegradation of organophosphate pesticides: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1135–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloo, K.V.; Ibrahim, N.A.S. Analytical Extraction Methods and Sorbents’ Development for Simultaneous Determination of Organophosphorus Pesticides’ Residues in Food and Water Samples: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, M.; Li, B.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, F. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Laser-Induced Graphene for Carbendazim Detection in Water. Foods 2023, 12, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Tan, P.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z. Advances in organophosphorus pesticides pollution: Current status and challenges in ecotoxicological, sustainable agriculture, and degradation strategies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424 Pt B, 127494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, J.; Ying, Y.; She, Y.; Wang, J.; Ping, J. Carbon nanomaterial-enabled pesticide biosensors: Design strategy, biosensing mechanism, and practical application. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 106, 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Liu, G.; Ping, J. Nanozyme-based biosensor for organophosphorus pesticide monitoring: Functional design, biosensing strategy, and detection application. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 165, 117152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Alvarez, I.; Andrade, R.J. Organophosphate pesticides: Another silent liver hazard? Liver Int. 2023, 43, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar-Flores, J.; Lomeli-Martinez, S.M.; Ceja-Galvez, H.R.; Torres-Jasso, J.H.; Torres-Reyes, L.A.; Torres-Sanchez, E.D. Impacts of Pesticides on Oral Cavity Health and Ecosystems: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatunsin, O.T.; Oyeyiola, A.O.; Moshood, M.O.; Akanbi, L.M.; Fadahunsi, D.E. Dietary risk assessment of organophosphate and carbamate pesticide residues in commonly eaten food crops. Sci. Afr. 2020, 8, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwevura, H.; Kylin, H.; Vogt, T.; Bouwman, H. Dynamics of organochlorine and organophosphate pesticide residues in soil, water, and sediment from the Rufiji River Delta, Tanzania. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 41, 101607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Lan, L.; Jiang, C.; Ping, J. Metallic Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Nanosheets as an Effective and Biocompatible Transducer for Electrochemical Detection of Pesticide. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11658–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, E.F.; André, L.C.; Menezes, H.C.; Cardeal, Z.L.; Llorent Mart Nez, E.J. Development of a Simple Integrative Carbon Nanomaterial Microextraction Method with GC-MS for Assessing Pesticide Residues in Apples. J. Chem. 2023, 2023, 5561490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmand, M.; Saghafifar, H.; Alijanianzadeh, M.; Soltanolkotabi, M. A sensitive tapered-fiber optic biosensor for the label-free detection of organophosphate pesticides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Sun, M.; Liu, H.; Yu, G.; Gao, F. Palladium-copper nanowires-based biosensor for the ultrasensitive detection of organophosphate pesticides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 982, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Barbieri, M.V.; Chino, M.; Manco, G.; Febbraio, F. A FRET Approach to Detect Paraoxon among Organophosphate Pesticides Using a Fluorescent Biosensor. Sensors 2022, 22, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Tao, L.; Song, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, F. Amorphous metal boride as a novel platform for acetylcholinesterase biosensor development and detection of organophosphate pesticides. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 055501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yang, L. Development of enzymatic electrochemical biosensors for organophosphorus pesticide detection. J. Environ. Sci. Health B. 2021, 56, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Bandyopadhyay, D.; Singh, P.K. A simple and convenient choline oxidase inhibition based colorimetric biosensor for detection of organophosphorus class of pesticides. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 118258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y. A lanthanide-based ratiometric fluorescent biosensor for the enzyme-free detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhou, B.; Wang, X.; Shen, J.; Zhao, B. Detection of organophosphorus pesticides by nanogold/mercaptomethamidophos multi-residue electrochemical biosensor. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, U.J.; Fermin, C.D.; Kim, M. Immobilized Enzymes in Biosensor Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; He, J.; Li, X.; Bai, Y.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. Smart plant-wearable biosensor for in-situ pesticide analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 170, 112636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsawiset, S.; Sansenya, S.; Teepoo, S. Nanozymes paper-based analytical device for the detection of organophosphate pesticides in fruits and vegetables. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1267, 341377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Wan, Y.; Mao, D.; Deng, R.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Y.; Tan, W. A colorimetric smartphone-based platform for pesticides detection using Fe-N/C single-atom nanozyme as oxidase mimetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen Prasad, S.; Bansal, V.; Ramanathan, R. Detection of pesticides using nanozymes: Trends, challenges and outlook. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 144, 116429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, C.; Lan, L.; Ping, J.; Ye, Z.; Ying, Y. Nanomaterial-based biosensors for agro-product safety. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, P.; Pu, L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, D.; Li, F. CeO2@NC nanozyme with robust dephosphorylation ability of phosphotriester: A simple colorimetric assay for rapid and selective detection of paraoxon. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 220, 114841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Jiang, Z.W.; Li, W.; Li, C.M.; Huang, C.Z.; Li, Y.F. In Situ Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles/Metal-Organic Gels Hybrids with Excellent Peroxidase-Like Activity for Sensitive Chemiluminescence Detection of Organophosphorus Pesticides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 28868–28876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guo, J.; Yang, L.; Gao, Z.; Song, Y.Y. Construction of Peroxidase-like Metal-Organic Frameworks in TiO2 Nanochannels: Robust Free-Standing Membranes for Diverse Target Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9486–9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Li, F. Two-Dimensional MnO2 Nanozyme-Mediated Homogeneous Electrochemical Detection of Organophosphate Pesticides without the Interference of H2O2 and Color. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 4084–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Yang, L.; Luo, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, P. Nanozyme-assisted technique for dual mode detection of organophosphorus pesticide. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 179, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Yu, L.; Hou, T.; Hu, R.; Li, F. Direct and Specific Detection of Glyphosate Using a Phosphatase-like Nanozyme-Mediated Chemiluminescence Strategy. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 4479–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Xu, C.; Guo, R.; Lin, C.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.; Lin, Y. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-90 Nanoparticles as Nanozymes to Mimic Organophosphorus Hydrolase. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 3345–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wanyan, Y.; Zeng, J.; Fang, H.; Li, Z.; Dong, Y.; Qin, R.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, M.; et al. Surface Engineering Protocol To Obtain an Atomically Dispersed Pt/CeO2 Catalyst with High Activity and Stability for CO Oxidation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14054–14062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Qi, C.; Han, Q.; Xiao, W.; Cai, S.; Wang, C.; Yang, R. Sensitive colorimetric detection of ascorbic acid using Pt/CeO2 nanocomposites as peroxidase mimics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 479, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Yuan, X.; Yan, C.; Ma, Q.; Wang, B.; Du, J.; Zheng, B.; Xiao, D. Dual-readout performance of Eu3+-doped nanoceria as a phosphatase mimic for degradation and detection of organophosphate. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 4747–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, C.; Shao, Y.; Barcelo, D.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. Self-reduction bimetallic nanoparticles on ultrathin MXene nanosheets as functional platform for pesticide sensing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gia-Thien Ho, T.; Do, B.L.; Pham, B.V.; Nguyen, T.T.V.; Phan, H.P.; Nguyen, H.B.; Vo, P.P.T.; Tri, N. High-efficiency reduction of p-nitrophenol on green-synthesized gold nanoparticles decorated on ceria nanorods. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 25753–25763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Zhou, L.; Jia, C.-J.; Sun, L.-D.; Yan, C.-H. Pt-embedded-CeO2 hollow spheres for enhancing CO oxidation performance. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, J. Self-limited Phosphatase-mimicking CeO2 Nanozymes. ChemNanoMat 2020, 6, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y. Phosphatase-like Activity of Porous Nanorods of CeO2 for the Highly Stabilized Dephosphorylation under Interferences. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yang, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, S.; Li, P. Fluorometric determination of pesticides and organophosphates using nanoceria as a phosphatase mimic and an inner filter effect on carbon nanodots. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Chen, F.F.; Li, C.X.; Luo, X.J.; Chen, Q.; Bai, Y.P.; Xu, J.H. Improved efficiency of a novel methyl parathion hydrolase using consensus approach. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2016, 93–94, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | Samples | Added (µM) | Found (µM) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%, n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV-Vis | Pear | 25 | 26.21 ± 0.71 | 104.83 | 2.69 |
| 50 | 49.22 ± 0.83 | 98.45 | 1.69 | ||
| 100 | 87.47 ± 1.76 | 87.47 | 2.01 | ||
| Lettuce | 25 | 25.78 ± 0.56 | 103.12 | 2.15 | |
| 50 | 46.67 ± 0.80 | 93.33 | 1.72 | ||
| 100 | 95.92 ± 1.16 | 95.92 | 1.21 | ||
| RGB | Pear | 25 | 28.97 ± 0.57 | 115.87 | 1.96 |
| 50 | 42.63 ± 1.60 | 85.27 | 3.76 | ||
| 100 | 94.40 ± 4.85 | 94.40 | 5.14 | ||
| Lettuce | 25 | 23.67 ± 0.85 | 94.67 | 3.59 | |
| 50 | 44.07 ± 2.73 | 88.13 | 6.20 | ||
| 100 | 93.23 ± 2.31 | 93.23 | 2.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, F.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, M. A Colorimetric Sensor Enabled with Heterogeneous Nanozymes with Phosphatase-like Activity for the Residue Analysis of Methyl Parathion. Foods 2023, 12, 2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152980
Zhao F, Li M, Wang L, Wang M. A Colorimetric Sensor Enabled with Heterogeneous Nanozymes with Phosphatase-like Activity for the Residue Analysis of Methyl Parathion. Foods. 2023; 12(15):2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152980
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Fengnian, Mengyue Li, Li Wang, and Min Wang. 2023. "A Colorimetric Sensor Enabled with Heterogeneous Nanozymes with Phosphatase-like Activity for the Residue Analysis of Methyl Parathion" Foods 12, no. 15: 2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152980
APA StyleZhao, F., Li, M., Wang, L., & Wang, M. (2023). A Colorimetric Sensor Enabled with Heterogeneous Nanozymes with Phosphatase-like Activity for the Residue Analysis of Methyl Parathion. Foods, 12(15), 2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152980