Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Multiple Polyphenols from Spice on Acrolein during High-Temperature Processing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Determination of the Inhibitory Activities and IC50 of Polyphenols on ACR
2.3. Inhibitory Effects on ACR of Polyphenols Individually or in Binary Combination That Were Incubated
2.4. Analysis of the Inhibitory Effect and Mechanism of CAR, ALP, PIN, and CUR in Quaternary Combination in Capturing ACR by Using LC–MS/MS
2.5. Inhibitory Effect on ACR of [CAR + ALP + PIN] at the Fixed Proportion in AKH and CUR in Quaternary Combination in the Model
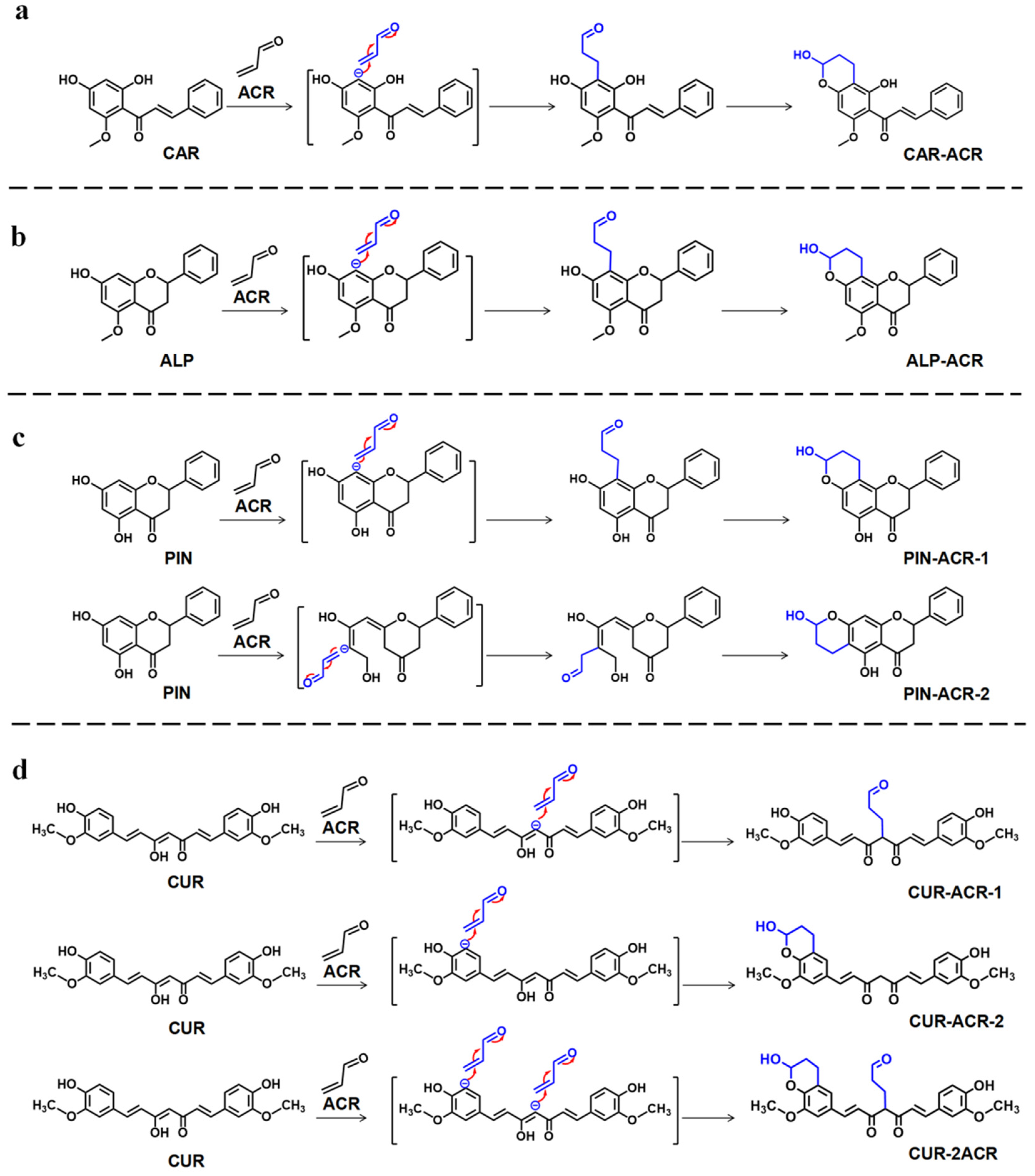
2.6. Quantitative Analysis of the ACR Adducts of CAR, ALP, PIN, and CUR
2.7. ACR Inhibitory Activities of AKH and CUR Individually and in Combination in Roasted Pork
2.8. LC–MS/MS Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scavenging Capability of the Eight Polyphenols on ACR
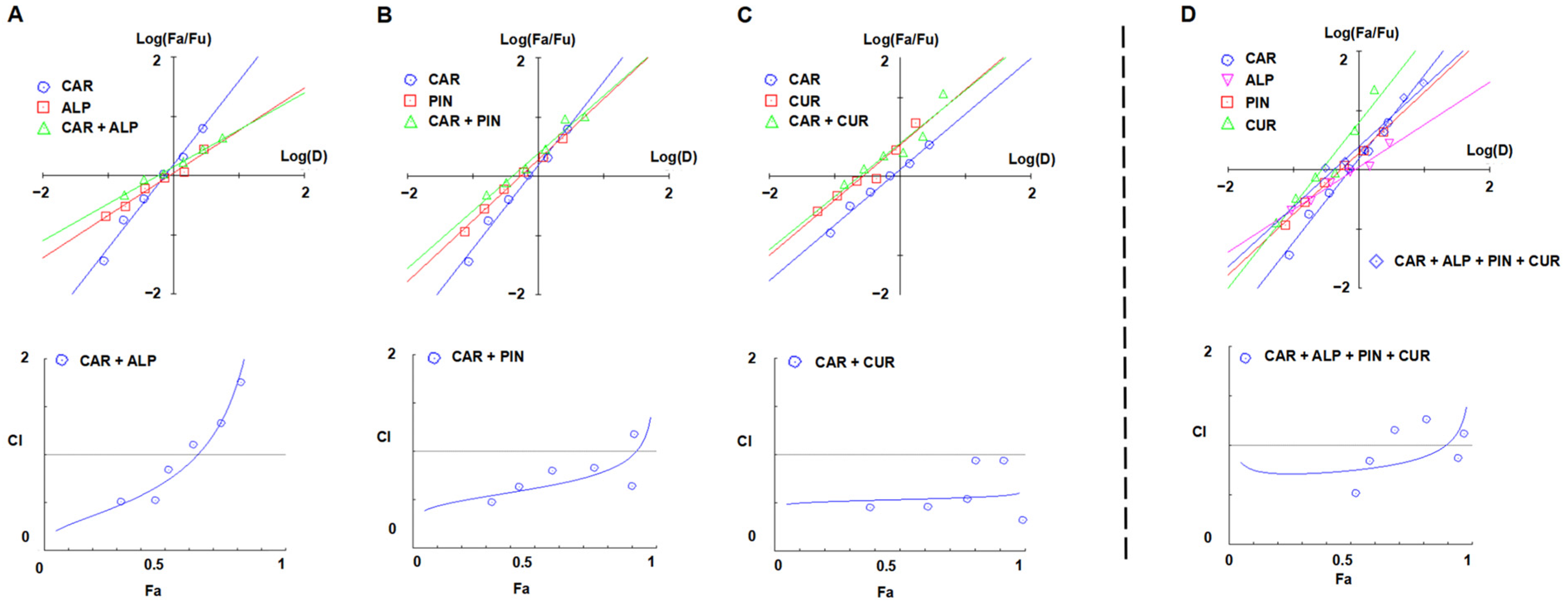
3.2. Scavenging Effects on ACR of Eight Polyphenols in Binary Combination
3.3. Scavenging Effect on ACR of CAR, ALP, PIN, and CUR in Quaternary Combination
3.4. Synergistic Scavenging Mechanism on ACR of the Quaternary Combination of CAR, ALP, PIN, and CUR
3.5. Quantitative Analysis of the Synergistic Effect on ACR of Three Flavonoids (Fixed Proportion in AKH) and CUR in Combination in the Model
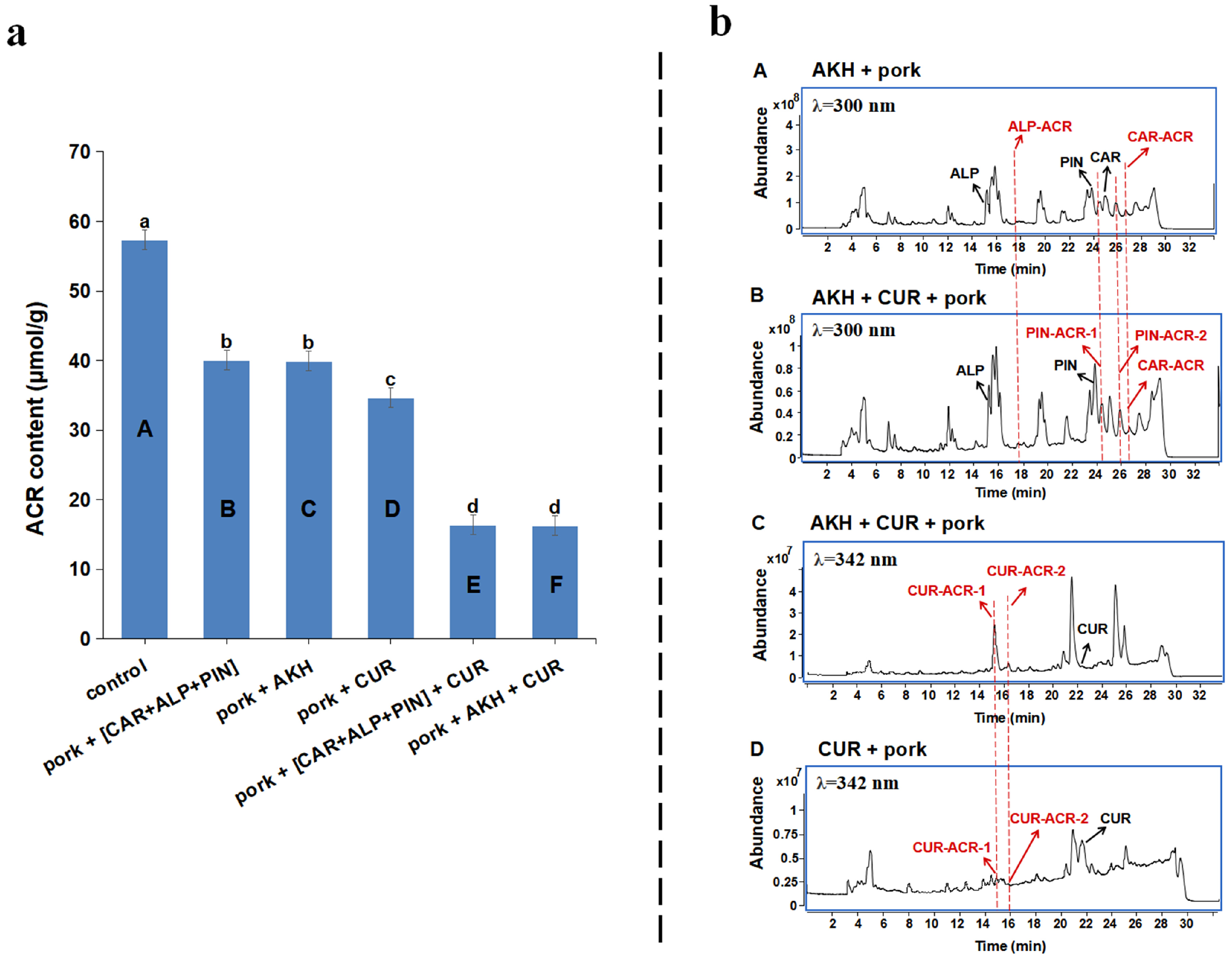
3.6. Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of AKH and CUR in Combination on ACR in Roasted Pork
3.7. Synergistic Scavenging Mechanism on ACR of AKH and CUR in Combination in Roasted Pork
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Abraham, K.; Andres, S.; Palavinskas, R.; Berg, K.; Appel, K.E.; Lampen, A. Toxicology and Risk Assessment of Acrolein in Food. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Tomitori, H.; Machi, Y.; Hagihara, M.; Higashi, K.; Goda, H.; Ohya, T.; Niitsu, M.; Kashiwagi, K.; Igarashi, K. Acrolein Toxicity: Comparison with Reactive Oxygen Species. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 378, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzimenti, S.; Ciamporcero, E.; Daga, M.; Pettazzoni, P.; Arcaro, A.; Cetrangolo, G.; Minelli, R.; Dianzani, C.; Lepore, A.; Gentile, F.; et al. Interaction of Aldehydes Derived from Lipid Peroxidation and Membrane Proteins. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarkovic, N.; Cipak, A.; Jaganjac, M.; Borovic, S.; Zarkovic, K. Pathophysiological Relevance of Aldehydic Protein Modifications. J. Proteom. 2013, 92, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Hu, Y.; Tong, D.; Huang, J.; Gu, L.Y.; Wu, X.R.; Chung, F.L.; Li, G.M.; Tang, M.S. Effect of Carcinogenic Acrolein on DNA Repair and Mutagenic Susceptibility. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12379–12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristova, M.; Heuvelmans, S.; van der Vliet, A. Gsh-Dependent Regulation of Fas-Mediated Caspase-8 Activation by Acrolein. Febs. Lett. 2007, 581, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.J.; Luo, C.; Long, H.A.; Wei, D.Z.; Liu, H.K. Acrolein Is a Mitochondrial Toxin: Effects on Respiratory Function and Enzyme Activities in Isolated Rat Liver Mitochondria. Mitochondrion 2006, 6, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, J.C.; Kehrer, J.P. Acrolein-Induced Cell Death: A Caspase-Influenced Decision between Apoptosis and Oncosis/Necrosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2002, 139, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.D.; Wang, W.X.; Huang, Q.J.; Hu, C.L.; Sang, S.M. Metabolic Investigation on the Interaction Mechanism between Dietary Dihydrochalcone Intake and Lipid Peroxidation Product Acrolein Reduction. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJarnett, N.; Conklin, D.J.; Riggs, D.W.; Myers, J.A.; O’Toole, T.E.; Hamzeh, I.; Wagner, S.; Chugh, A.; Ramos, K.S.; Srivastava, S.; et al. Acrolein Exposure Is Associated with Increased Cardiovascular Disease Risk. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.H.; Hu, W.W.; Hu, Y.; Tang, M.S. Acrolein Is a Major Cigarette-Related Lung Cancer Agent: Preferential Binding at P53 Mutational Hotspots and Inhibition of DNA Repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15404–15409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feroe, A.G.; Attanasio, R.; Scinicariello, F. Acrolein Metabolites, Diabetes and Insulin Resistance. Environ. Res. 2016, 148, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majchrzak, T.; Marc, M.; Wasik, A. Understanding the Early-Stage Release of Volatile Organic Compounds from Rapeseed Oil During Deep-Frying of Tubers by Targeted and Omics-Inspired Approaches Using Ptr-Ms and Gas Chromatography. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.Y.; Lang, C.H.; Lin, P.C.; Kuo, Y.C. Effects of Cooking Method, Cooking Oil, and Food Type on Aldehyde Emissions in Cooking Oil Fumes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Sakai, K.; Fujiya, N.; Fujii, H.; Mano, J. Catechins in Green Tea Powder (Matcha) Are Heat-Stable Scavengers of Acrolein, a Lipid Peroxide-Derived Reactive Carbonyl Species. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.S.H.; Yu, J.Z.; Chu, K.W.; Yeung, L.L. Carbonyl Emissions from Commercial Cooking Sources in Hong Kong. J. Air Waste Manag. 2006, 56, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosetti, F.; Chiuminatto, U.; Mazzucco, E.; Robotti, E.; Calabrese, G.; Gennaro, M.C.; Marengo, E. Simultaneous Determination of Thirteen Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Twelve Aldehydes in Cooked Food by an Automated on-Line Solid Phase Extraction Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6308–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakula, S.; Novotni, D.; Mustac, N.C.; Voucko, B.; Krpan, M.; Hruskar, M.; Curic, D. A Simple Hs-Spme/Gc-Ms Method for Determination of Acrolein from Sourdough to Bread. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 2582–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootveld, M.; Percival, B.C.; Leenders, J.; Wilson, P.B. Potential Adverse Public Health Effects Afforded by the Ingestion of Dietary Lipid Oxidation Product Toxins: Significance of Fried Food Sources. Nutrients 2020, 12, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.F.; Maier, C.S. Acrolein: Sources, Metabolism, and Biomolecular Interactions Relevant to Human Health and Disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghrib, F.; Lahrich, S.; El Mhammedi, M.A. Review-Recent Advances in Direct and Indirect Methods for Sensing Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes in Environment and Foodstuffs. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Y.; Zhao, L.Y.; Chen, X.; Nie, L.; Shi, A.J.; Bai, H.H.; Li, G.A. A Comprehensive Study of Volatile Organic Compounds from the Actual Emission of Chinese Cooking. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 53821–53830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Liu, F.; Zheng, J.; Ou, J.Y.; Zhao, D.Y.; Ou, S.Y. Origin and Fate of Acrolein in Foods. Foods 2022, 11, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, R.; Meek, M.E. World Health Organization & international Programme on Chemical Safety; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Capuano, E.; Fogliano, V. Acrylamide and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF): A review on metabolism, toxicity, occurrence in food and mitigation strategies. LWT 2011, 44, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bercu, J.P.; Galloway, S.M.; Parris, P.; Teasdale, A.; Masuda-Herrera, M.; Dobo, K.; Heard, P.; Kenyon, M.; Nicolette, J.; Vock, E.; et al. Potential Impurities in Drug Substances: Compound-Specific Toxicology Limits for 20 Synthetic Reagents and by-Products, and a Class-Specific Toxicology Limit for Alkyl Bromides. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 94, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.L.; Lu, Y.; Si, B.; Lu, Y.L.; Zhang, Q.T.; Lv, L.S. Inhibitory Effect on Acrolein by Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside and Its Acrolein Adducts from the Pigment of Mynica Red. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11937–11946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.M.; Jiang, X.Y.; Xiao, L.B.; Lu, Y.L.; Sang, S.M.; Lv, L.S.; Dong, W.J. Mechanistic Studies of Inhibition on Acrolein by Myricetin. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Yang, R.; Yao, H.; Wu, Y.; Pan, W.; Jia, A.Q. Inhibiting the Formation of Advanced Glycation End-Products by Three Stilbenes and the Identification of Their Adducts. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Mei, X.; Tang, Z.; Cao, X.; Liu, J. Exploring the Molecular Mechanisms of the Inhibition of Acrolein-Induced Beas-2b Cytotoxicity by Luteolin Using Network Pharmacology and Cell Biology Technology. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 160, 112779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tong, A.Q.; Zhang, C.X.; Duan, Y.; Lu, Y.L.; Lv, L.S. Dual Effects of Cardamonin/Alpinetin and Their Acrolein Adducts on Scavenging Acrolein and Anti-Bacteria from Alpinia Katsumadai Hayata as a Spice in Roasted Meat. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 7088–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X.G.; Hu, Z.D. Separation and Determination of Alpinetin and Cardamonin in Alpinia Katsumadai Hayata by Flow Injection-Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography. Talanta 2007, 71, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Lv, H.F.; Lu, Y.; Lu, Y.L.; Lv, L.S. Trapping of Acrolein by Curcumin and the Synergistic Inhibition Effect of Curcumin Combined with Quercetin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, T.; Sang, S.; Lv, L. Scavenging of Acrolein by Food-Grade Antioxidant Propyl Gallate in a Model Reaction System and Cakes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8520–8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tong, A.Q.; Lu, Y.L.; Lv, L.S. Interconversion and Acrolein-Trapping Capacity of Cardamonin/Alpinetin and Their Metabolites in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11926–11936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Theoretical Basis, Experimental Design, and Computerized Simulation of Synergism and Antagonism in Drug Combination Studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Wang, S.P.; Yang, A.L.; Li, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Dai, L.; Tao, Y.F.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J.Y. Systematic Screening and Characterization of Cardamonin Metabolites Using Uhplc-Q-Exactive Orbitrap Ms after Oral Administration to Rats. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 8768–8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, B.C. Cultivation and Utilization of Alpinia Katsumadi Hayata. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 21, 144–145. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.; Shi, S. The Discussion on the Application of Spices in Meat Products. Chem. Condlm. 2010, 35, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Belardo, G.; Cenciarelli, O.; La Frazia, S.; Rossignol, J.F.; Santoro, M.G. Synergistic Effect of Nitazoxanide with Neuraminidase Inhibitors against Influenza a Viruses in Vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chem. 2015, 59, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.F.; Liu, S.; Yin, Z.; Liang, P.J.; Wang, C.H.; Zhu, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Ou, S.Y.; Li, G.Q. Rutin Alleviated Acrolein-Induced Cytotoxicity in Caco-2 and Ges-1 Cells by Forming a Cyclic Hemiacetal Product. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 976400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, Q. In Vitro Attenuation of Acrolein-Induced Toxicity by Phloretin, a Phenolic Compound from Apple. Planta Med. 2012, 78, PD69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Compound | IC50 | IC75 | IC75 | IC75 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monotherapy (mmol/L) | Combination (mmol/L) | CI | Monotherapy (mmol/L) | Combination (mmol/L) | CI | |
| [CAR + ALP + PIN] | 0.169 | 0.047 | 0.383 | 0.764 | 0.184 | 0.386 |
| CUR | 0.379 | 0.041 | 1.119 | 0.162 | ||
| Compound | Adduct | Single Content (mg/L) | Complex Content (mg/L) | Increase Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAR | CAR-ACR | 41.3 ± 10.2 ab | 43.5 ± 12.4 bc | 5.4 ± 1.2 d |
| ALP | ALP-ACR | 14.9 ± 7.1 c | 40.2 ± 8.9 bc | 170.0 ± 23.4 b |
| PIN | PIN-ACR-1 | 28.1 ± 3.9 b | 31.1 ± 1.7 c | 10.9 ± 4.2 d |
| PIN-ACR-2 | 51.1 ± 13.9 a | 55.2 ± 11.8 bc | 8.1 ± 2.5 d | |
| CUR | CUR-ACR-1 | 56.6 ± 1.6 a | 96.9 ± 10.6 a | 71.3 ± 13.4 c |
| CUR-ACR-2 | 41.7 ± 15.2 ab | 70.9 ± 33.6 ab | 70.2 ± 13.5 c | |
| CUR-2ACR | 2.9 ± 0.4 d | 12.8 ± 2.1 d | 338.1 ± 7.4 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Si, B.; Tong, A.; Lu, Y.; Lv, L. Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Multiple Polyphenols from Spice on Acrolein during High-Temperature Processing. Foods 2023, 12, 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122326
Liu J, Lu Y, Si B, Tong A, Lu Y, Lv L. Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Multiple Polyphenols from Spice on Acrolein during High-Temperature Processing. Foods. 2023; 12(12):2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122326
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Juan, Yongling Lu, Bo Si, Anqi Tong, Yang Lu, and Lishuang Lv. 2023. "Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Multiple Polyphenols from Spice on Acrolein during High-Temperature Processing" Foods 12, no. 12: 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122326
APA StyleLiu, J., Lu, Y., Si, B., Tong, A., Lu, Y., & Lv, L. (2023). Synergistic Inhibitory Effect of Multiple Polyphenols from Spice on Acrolein during High-Temperature Processing. Foods, 12(12), 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122326







