Determination of Coenzyme Q10 Content in Food By-Products and Waste by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Diode Array Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
- -
- Freezing conditions: freezing temperature −80 °C and freezing time 24 h;
- -
- Sublimation conditions: vacuum pressure 0.01 mbar, sublimation temperature −55 °C, and sublimation time ~3 days (until a constant weight (±0.005 g)). The lyophilization yield was 22.1%.
2.2. Reagents and Standards
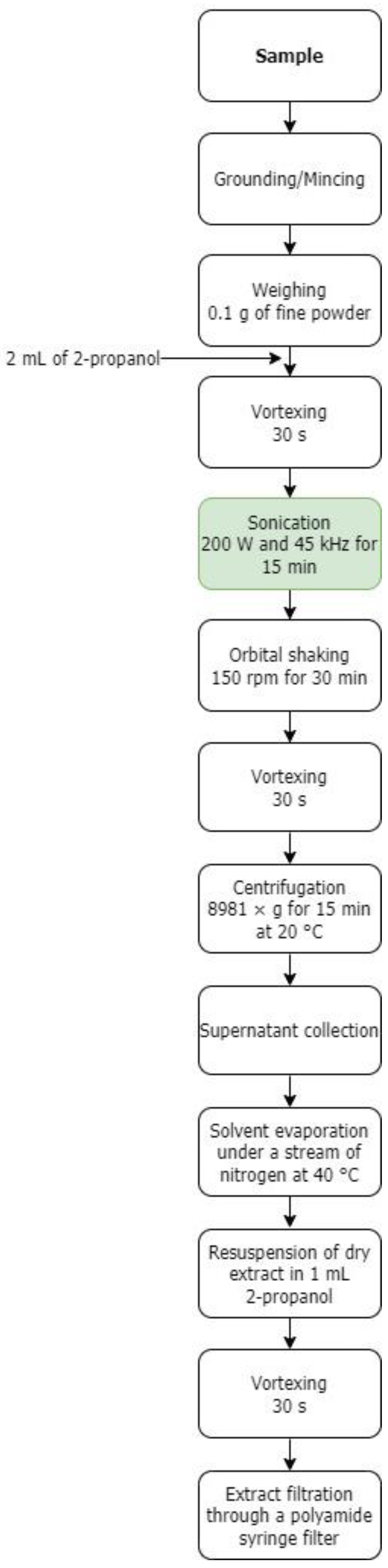
2.3. Preparation of 2-Propanol Extracts
2.4. HPLC-DAD Analysis of the Extracts
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Linearity and Measuring Range, Limits of Detection (LOD), and Quantification (LOQ)
3.2. Levels of CoQ10 in Food By-Products and Waste
3.3. Accuracy (Trueness and Precision)
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez-Estrada, M.T.; Poerio, A.; Mandrioli, M.; Lercker, G.; Trinchero, A.; Tosi, M.R.; Tugnoli, V. Determination of coenzyme Q10 in functional and neoplastic human renal tissues. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 357, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkowicz, M.J.; Karpińska, J. Analytical problems with the determination of coenzyme Q10 in biological samples. BioFactors 2013, 39, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atla, S.R.; Raja, B.; Dontamsetti, B.R. A new method of synthesis of coenzyme Q10 from isolated solanesol from tobacco waste. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 499–502. [Google Scholar]
- Niklowitz, P.; Döring, F.; Paulussen, M.; Menke, T. Determination of coenzyme Q10 tissue status via high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection in swine tissues (Sus scrofa domestica). Anal. Biochem. 2013, 437, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.; Shen, G.; Xu, G. Ultrasonic assisted extraction of coenzyme Q10 from litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) pericarp using response surface methodology. J. Food Process Eng. 2011, 34, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, K.; Zhang, C.; Xie, S.; Feng, G.; Liao, S.; Cai, L.; He, J.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, C. A simple and accurate method for the determination of related substances in coenzyme Q10 soft capsules. Molecules 2019, 24, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.L.; Xu, Y.T.; Zhang, G.M.; Xie, S.M.; Dong, Y.M.; Ito, Y. Purification of coenzyme Q10 from fermentation extract: High-speed counter-current chromatography versus silica gel column chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1127, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, M.; Semeniuc, C.A.; Boselli, E.; Rodriguez-Estrada, M.T. Ubiquinone in Italian high-quality raw cow milk. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2018, 30, 144–155. [Google Scholar]
- Podar, A.S.; Semeniuc, C.A.; Ionescu, S.R.; Socaciu, M.-I.; Fogarasi, M.; Fărcaș, A.C.; Vodnar, D.C.; Socaci, S.A. An overview of analytical methods for quantitative determination of coenzyme Q10 in foods. Metabolites 2023, 13, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeu, I.; Dobre, A.A.; Cucu, E.M.; Mustățea, G.; Belc, N.; Ungureanu, E.L. Byproducts from the vegetable oil industry: The challenges of safety and sustainability. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilakan, K.; Sultana, K.; Radhakrishna, K.; Bawa, A.S. Utilization of byproducts and waste materials from meat, poultry and fish processing industries: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Socaciu, M.-I.; Fogarasi, M.; Simon, E.L.; Semeniuc, C.A.; Socaci, S.A.; Podar, A.S.; Vodnar, D.C. Effects of whey protein isolate-based film incorporated with tarragon essential oil on the quality and shelf-life of refrigerated brook trout. Foods 2021, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattila, P.; Lehtonen, M.; Kumpulainen, J. Comparison of in-line connected diode array and electrochemical detectors in the high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of coenzymes Q(9) and Q(10) in food materials. JAFC 2000, 48, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, P.; Kumpulainen, J. Coenzymes Q9 and Q10: Contents in foods and dietary intake. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2001, 14, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souchet, N.; Laplante, S. Seasonal variation of Co-enzyme Q10 content in pelagic fish tissues from Eastern Quebec. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2007, 20, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, S.; Souchet, N.; Bryl, P. Comparison of low-temperature processes for oil and coenzyme Q10 extraction from mackerel and herring. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2009, 111, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Yue, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, F. Analysis of coenzyme Q10 in bee pollen using online cleanup by accelerated solvent extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Pizarro, V.; Fernández-Romero, J.M.; Gómez-Hens, A. Automatic determination of coenzyme Q10 in food using cresyl violet encapsulated into magnetoliposomes. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemistry LibreTexts. Available online: https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Analytical_Chemistry/Instrumental_Analysis_(LibreTexts)/01%3A_Introduction/1.04%3A_Selecting_an_Analytical_Method (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority. Guidelines for the Validation of Analytical Methods for Active Constituent, United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime. Guidance for the Validation of Analytical Methodology and Calibration of Equipment used for Testing of Illicit Drugs in Seized Materials and Biological Specimens; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2009. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/validation_E.pdf (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. ICH Topic Q 2 (R1). Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology-Step 5; EMEA: London, UK, 1995; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-q-2-r1-validation-analytical-procedures-text-methodology-step-5_en.pdf (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Kubo, H.; Fujii, K.; Kawabe, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Kishida, H.; Hosoe, K. Food content of ubiquinol-10 and ubiquinone-10 in the Japanese diet. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2008, 21, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiff, M.R.; Weissinger, A.K.; Danehower, D.A. Analysis of CoQ10 in cultivated tobacco by a high-performance liquid chromatography–ultraviolet method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 9054–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. Type of Green Solvents Used in Separation and Preconcentration Methods. In New Generation Green Solvents for Separation and Preconcentration of Organic and Inorganic Species, 1st ed.; Soylak, M., Yilmaz, E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 207–266. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, L. A rapid and sensitive LC-MS/MS method for determination of coenzyme Q10 in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) leaves. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union. Directive 2009/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States on extraction solvents used in the production of foodstuffs and food ingredients. Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2009, L141, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, R.; Barlow, S.; Boskou, D.; Castle, L.; Crebelli, R.; Dekant, W.; Engel, K.-H.; Forsythe, S.; Grunow, W.; Larsen, J.C.; et al. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Food Additives, Flavourings, Processing Aids and Materials in Contact with Food on a request from the Commission related to Propan-2-ol as a carrier solvent for Flavourings. EFSA J. 2005, 202, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- González, C.M.; Llorca, M.; Quiles, A.; Hernando, I.; Moraga, G. Water sorption and glass transition in freeze-dried persimmon slices. Effect on physical properties and bioactive compounds. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 130, 109633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercan, P.; El, S.N. Changes in content of coenzyme Q10 in beef muscle, beef liver and beef heart with cooking and in vitro digestion. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, B.D.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Hamill, R.; Kerry, J.P. Effect of cooking and in vitro digestion on the stability of co-enzyme Q10 in processed meat products. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczka, P.; Namiesnik, J. Quality Assurance and Quality Control in the Analytical Chemical Laboratory: A Practical Approach, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 131–213. [Google Scholar]
- Michiu, D.; Socaciu, M.-I.; Fogarasi, M.; Jimborean, A.M.; Ranga, F.; Mureşan, V.; Semeniuc, C.A. Implementation of an analytical method for spectrophotometric evaluation of total phenolic content in essential oils. Molecules 2022, 27, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuc, C.A.; Mandrioli, M.; Tura, M.; Socaci, B.S.; Socaciu, M.-I.; Fogarasi, M.; Michiu, D.; Jimborean, A.M.; Mureşan, V.; Ionescu, S.R.; et al. Impact of lavender flower powder as a flavoring ingredient on volatile composition and quality characteristics of Gouda-type cheese during ripening. Foods 2023, 12, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Acuña, R.; Brenne, E.; Lacoste, F. Determination of coenzyme Q10 and Q9 in vegetable oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6241–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşbozan, O.; Gökçe, M.A. Fatty Acids in Fish. In Fatty Acids; Catala, A., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2017; pp. 143–159. [Google Scholar]
- Temova Rakuša, Ž.; Kristl, A.; Roškar, R. Stability of reduced and oxidized coenzyme Q10 in finished products. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Bermejo, D.; Temelli, F. Extraction of oil rich in coenzyme Q10 from chicken by-products using supercritical CO2. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2021, 174, 105242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassanelli, M.; Prosapio, V.; Norton, I.; Mills, T. Design of a cost-reduced flexible plant for supercritical fluid-assisted applications. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ISO 5725-4:2020; Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results Part 4: Basic Methods for the Determination of the Trueness of a Standard Measurement Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. Available online: www.iso.org/standard/69421.html (accessed on 22 January 2023).
- Manzi, P.; Durazzo, A. Rapid determination of coenzyme Q10 in cheese using high-performance liquid chromatography. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Commission. Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation Procedures for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed SANTE 11312/2021; SANTE: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2022-02/pesticides_mrl_guidelines_wrkdoc_2021-11312.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2023).
- Agricultural and Veterinary Chemical Products; APVMA: Kingston, Australia, 2004. Available online: https://apvma.gov.au/sites/default/files/docs/guideline-69-analytical-methods.pdf (accessed on 22 January 2023).

| Sample/MC (%) | 1st Day of Measurement | 2nd Day of Measurement | Mean ± σpooled (µg CoQ10/g Sample) | RSDpooled (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± σ (µg CoQ10/g Sample) | RSD (%) | Mean ± σ (µg CoQ10/g Sample) | RSD (%) | |||
| RPC/10.4% | 57.06 ± 2.316 | 4.1 | 56.47 ± 1.717 | 3.0 | 56.77 ± 1.664 d | 2.9 |
| SPC/9.8% | 48.80 ± 1.386 | 2.8 | 49.78 ± 1.480 | 3.0 | 49.29 ± 1.171 e | 2.4 |
| PPC/9.9% | 84.30 ± 0.978 | 1.2 | 85.29 ± 2.151 | 2.5 | 84.80 ± 1.364 c | 1.6 |
| LPC/10.7% | 53.50 ± 0.913 | 1.7 | 53.89 ± 0.906 | 1.7 | 53.70 ± 0.743 de | 1.4 |
| WPC/9.8% | 36.56 ± 0.845 | 2.3 | 36.56 ± 0.352 | 1.0 | 36.56 ± 0.528 f | 1.4 |
| HPC/11.2% | n.d. | - | n.d. | - | n.d. | - |
| WF/69.0% | n.d. | - | n.d. | - | n.d. | - |
| LWF/3.4% | n.d. | - | n.d. | - | n.d. | - |
| CH/77.0% | 119.95 ± 11.141 | 10.0 | 116.83 ± 11.419 | 9.8 | 114.39 ± 9.211 b | 8.1 |
| LCH/3.2% | 384.52 ± 0.680 | 0.2 | 381.97 ± 0.872 | 0.2 | 383.25 ± 0.639 a | 0.2 |
| Sample | Spiking Concentration (µg CoQ10/mL) | Found Concentration (µg CoQ10/mL) | RSD (%) | Recovery Rate (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPC | - | 12.05 ± 0.042 | 0.4 | - | - |
| 0.5 | 14.56 ± 0.042 | 0.3 | 116.0 ± 0.054 | 0.05 | |
| 1.5 | 15.63 ± 0.042 | 0.3 | 115.4 ± 0.053 | 0.05 | |
| 5.0 | 17.21 ± 0.084 | 0.5 | 100.9 ± 0.242 | 0.2 | |
| CH | - | 14.29 ± 0.0 | 0.0 | - | - |
| 0.5 | 15.66 ± 0.084 | 0.5 | 105.9 ± 0.569 | 0.5 | |
| 1.5 | 16.88 ± 0.127 | 0.7 | 106.9 ± 0.802 | 0.7 | |
| 5.0 | 19.15 ± 0.127 | 0.7 | 99.3 ± 0.656 | 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Semeniuc, C.A.; Ranga, F.; Podar, A.S.; Ionescu, S.R.; Socaciu, M.-I.; Fogarasi, M.; Fărcaș, A.C.; Vodnar, D.C.; Socaci, S.A. Determination of Coenzyme Q10 Content in Food By-Products and Waste by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Diode Array Detection. Foods 2023, 12, 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122296
Semeniuc CA, Ranga F, Podar AS, Ionescu SR, Socaciu M-I, Fogarasi M, Fărcaș AC, Vodnar DC, Socaci SA. Determination of Coenzyme Q10 Content in Food By-Products and Waste by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Diode Array Detection. Foods. 2023; 12(12):2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122296
Chicago/Turabian StyleSemeniuc, Cristina Anamaria, Floricuța Ranga, Andersina Simina Podar, Simona Raluca Ionescu, Maria-Ioana Socaciu, Melinda Fogarasi, Anca Corina Fărcaș, Dan Cristian Vodnar, and Sonia Ancuța Socaci. 2023. "Determination of Coenzyme Q10 Content in Food By-Products and Waste by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Diode Array Detection" Foods 12, no. 12: 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122296
APA StyleSemeniuc, C. A., Ranga, F., Podar, A. S., Ionescu, S. R., Socaciu, M.-I., Fogarasi, M., Fărcaș, A. C., Vodnar, D. C., & Socaci, S. A. (2023). Determination of Coenzyme Q10 Content in Food By-Products and Waste by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Diode Array Detection. Foods, 12(12), 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122296











