Mycoprotein Production by Submerged Fermentation of the Edible Mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus in a Batch Stirred Tank Bioreactor Using Agro-Industrial Hydrolysate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Microorganism
2.3. Media and Growth Conditions
2.4. Study of the Effect of Xylose Concentration
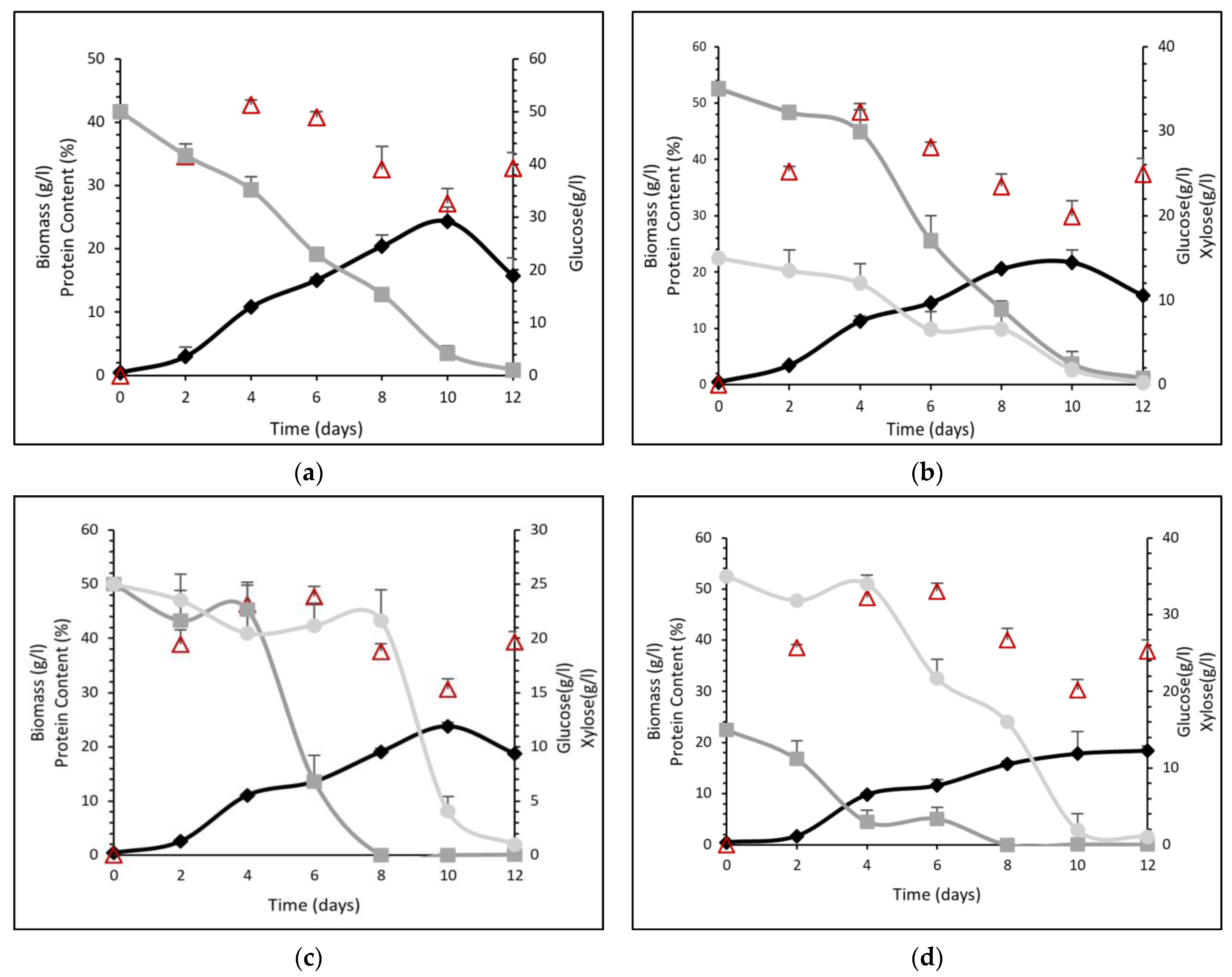
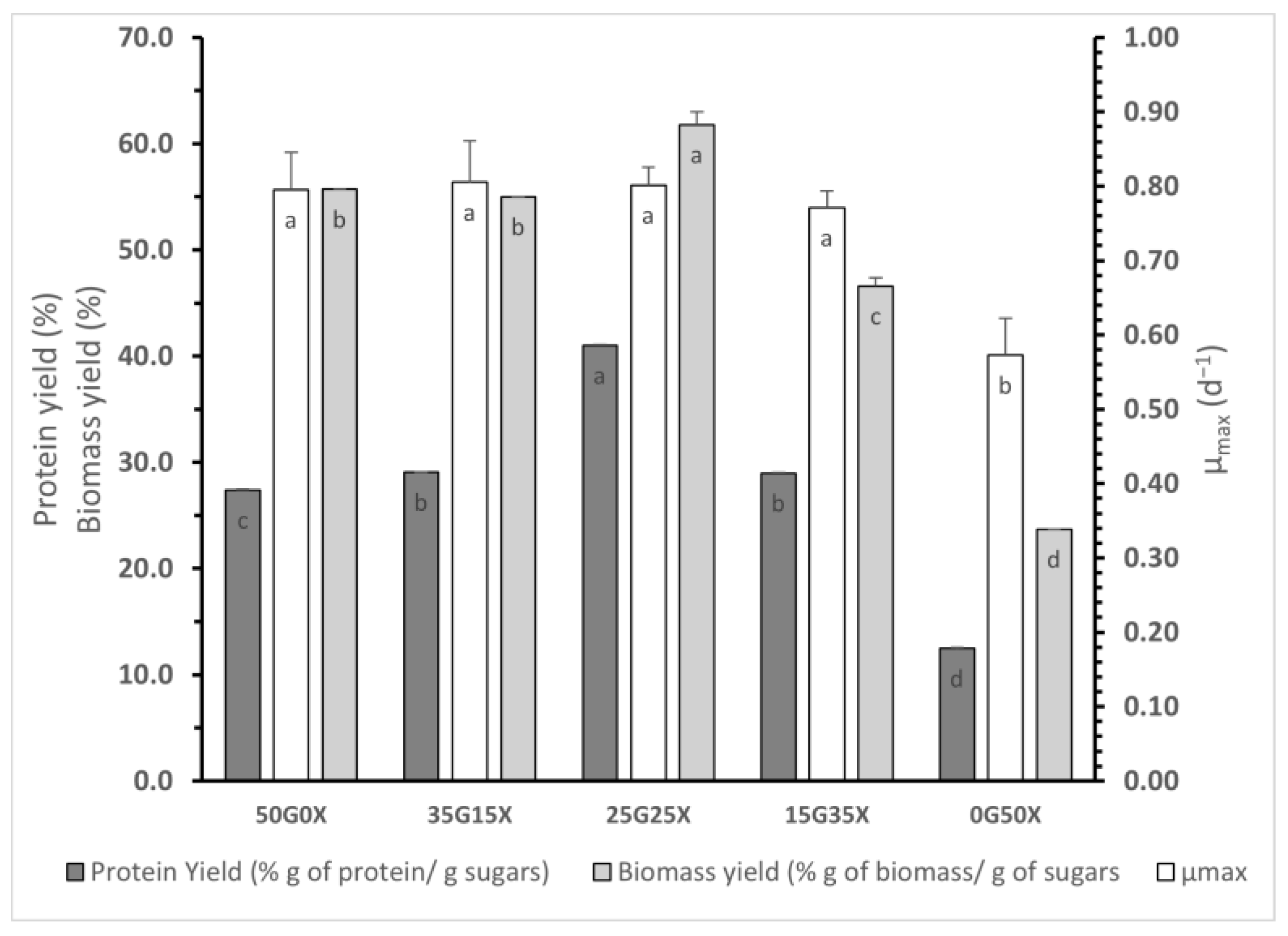
2.5. Study on the Effect of Glucose/Xylose Mixtures
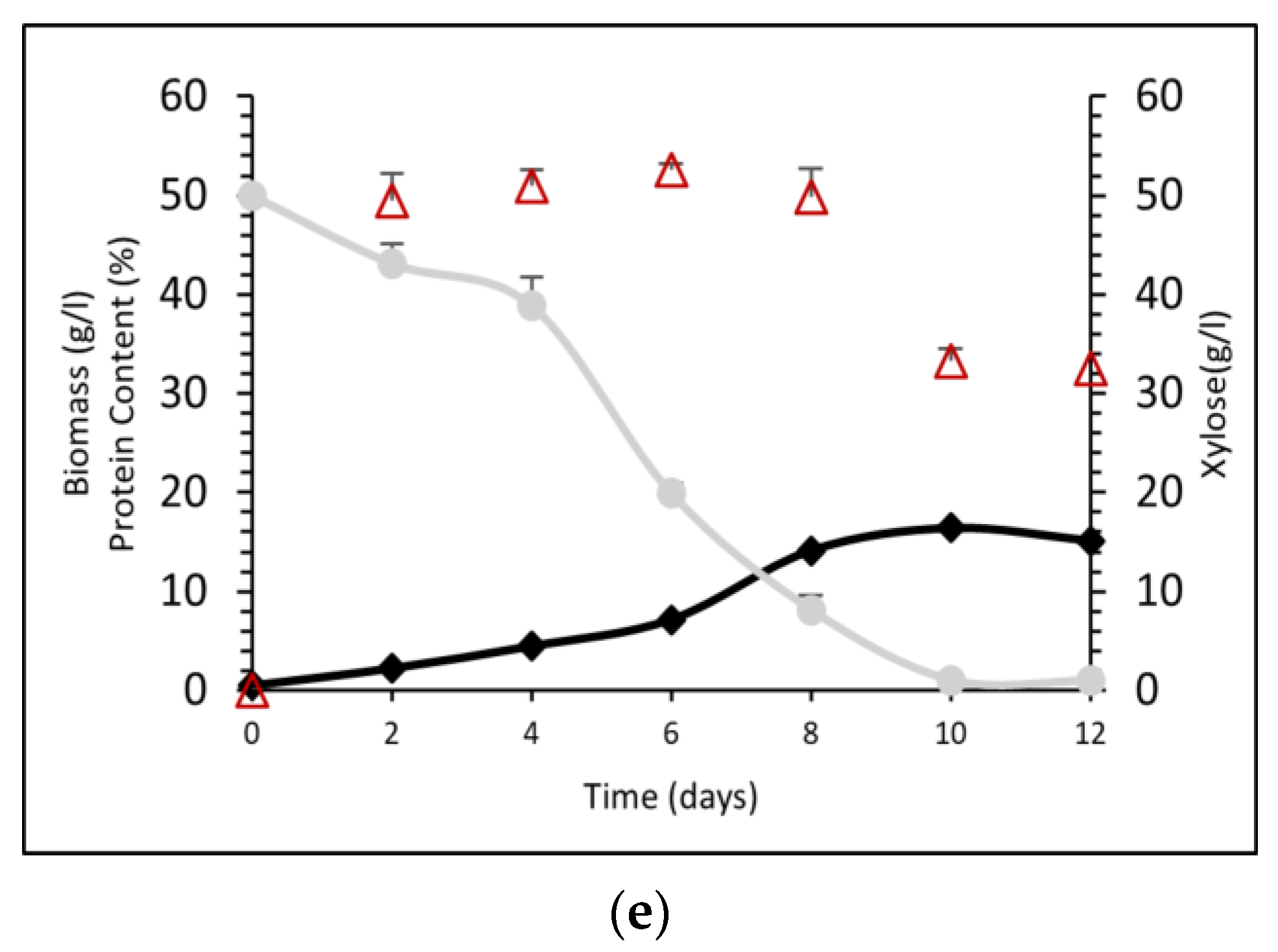
2.6. Cultivation on Aspen Hydrolysate
2.7. Biomass and Reducing Sugars Determination
2.8. Protein Estimation
2.9. Amino Acid Analysis
2.10. Aspen Hydrolysate Analysis
2.11. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Xylose Concentration
3.2. Effect of Glucose/Xylose Mixtures
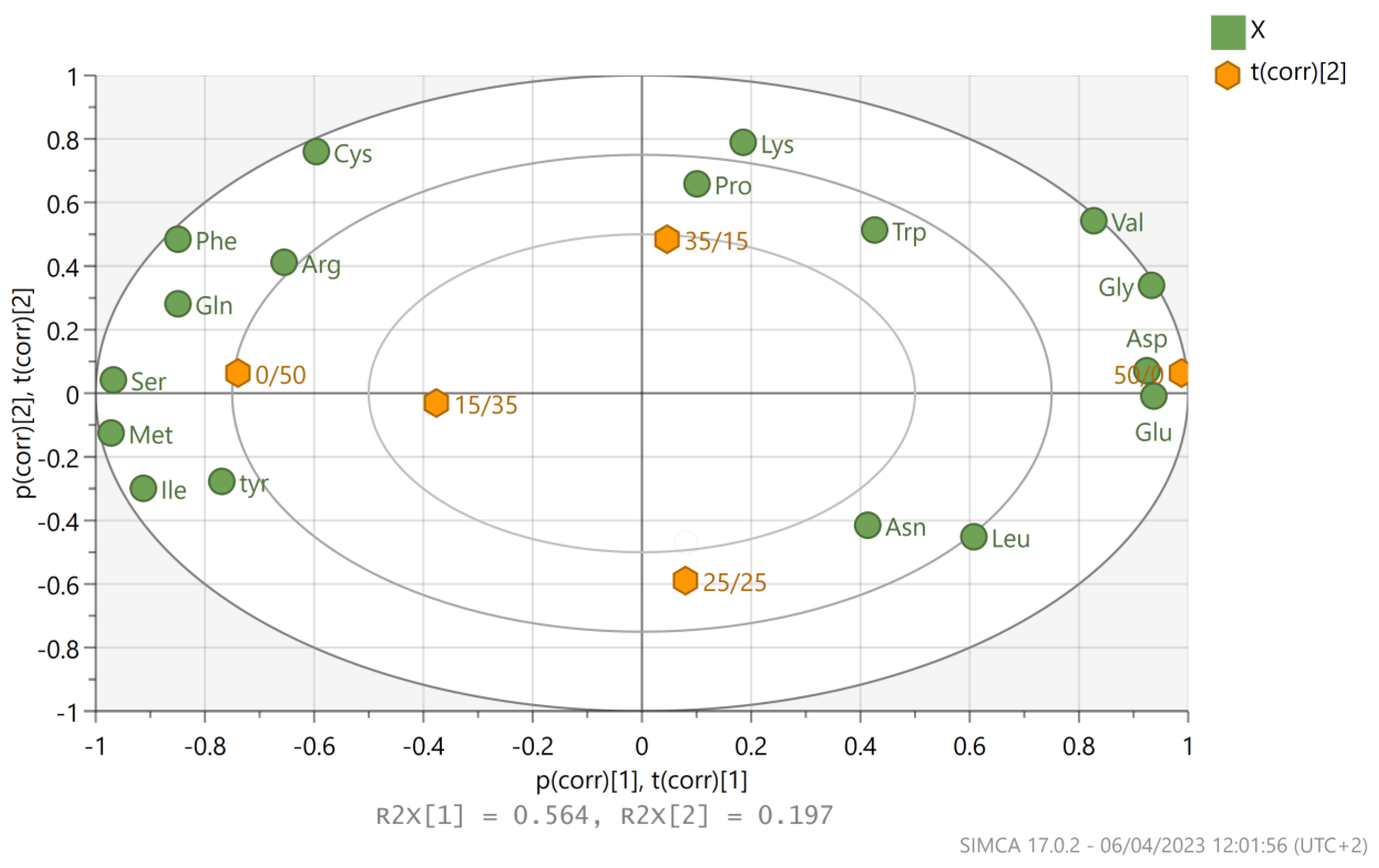
3.3. Amino Acids Analysis for P. ostreatus LGAM 1123 Cultivation on Different Glucose/Xylose Mixtures
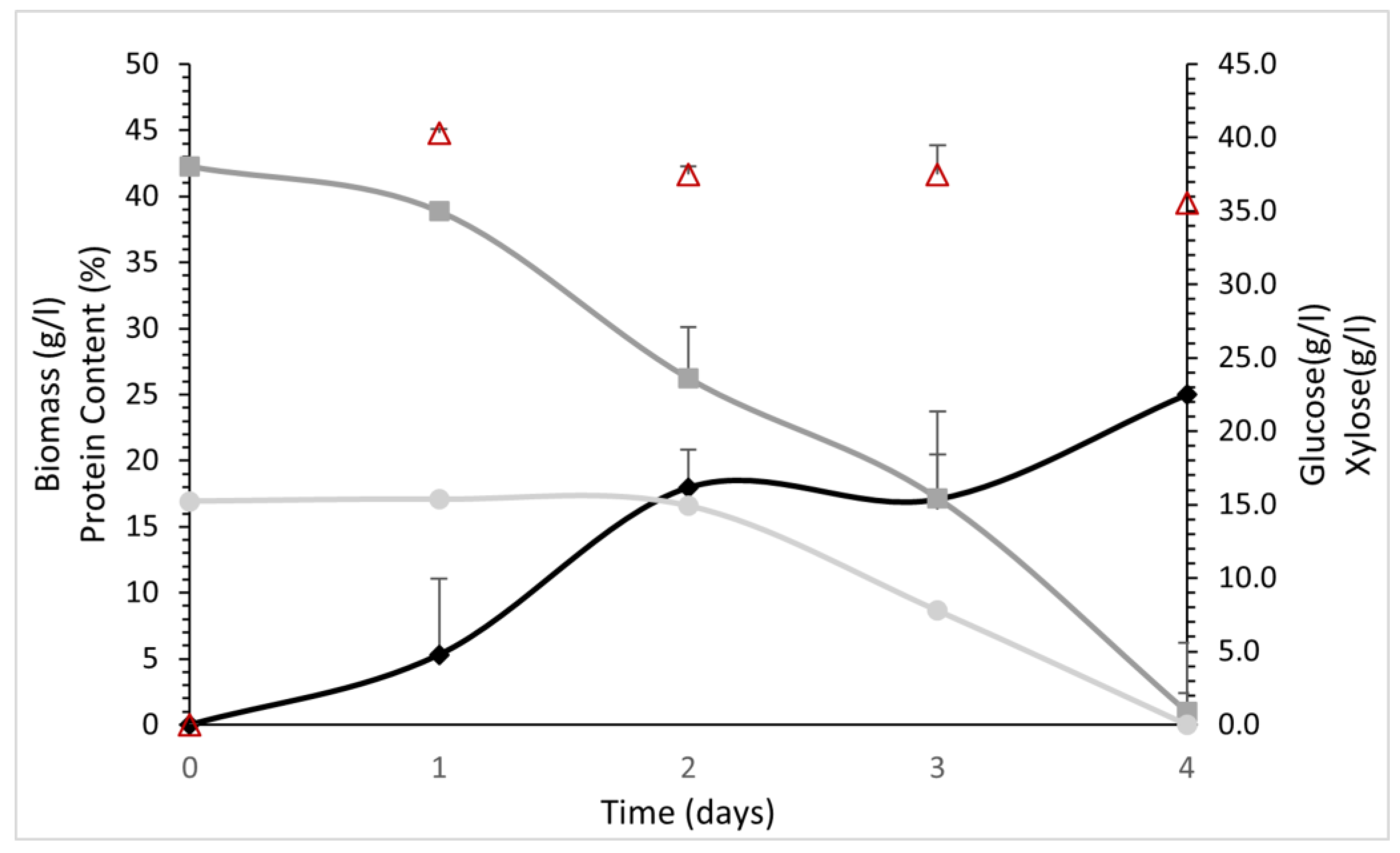
3.4. Protein Production by P. ostreatus LGAM 1123 in a 4 L Stirred-Tank Bioreactor Using Aspen Hydrolysate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, M.I.; Farooq, S.; Alhamoud, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, H. A Review on Mycoprotein: History, Nutritional Composition, Production Methods, and Health Benefits. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 121, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiviya, P.; Gamage, A.; Kapilan, R.; Merah, O.; Madhujith, T. Single Cell Protein Production Using Different Fruit Waste: A Review. Separations 2022, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Nanda, P.K.; Dandapat, P.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Gullón, P.; Sivaraman, G.K.; McClements, D.J.; Gullón, B.; Lorenzo, J.M. Edible Mushrooms as Functional Ingredients for Development of Healthier and More Sustainable Muscle Foods: A Flexitarian Approach. Molecules 2021, 26, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derbyshire, E.J.; Delange, J. Fungal Protein—What Is It and What Is the Health Evidence? A Systematic Review Focusing on Mycoprotein. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 581682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlborn, J.; Stephan, A.; Meckel, T.; Maheshwari, G.; Rühl, M.; Zorn, H. Upcycling of Food Industry Side Streams by Basidiomycetes for Production of a Vegan Protein Source. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Choi, B.; Lee, I.; Lee, H.; Kwon, S.; Oh, K.; Kim, A.Y. Bioproduction of Mushroom Mycelium of Agaricus Bisporus by Commercial Submerged Fermentation for the Production of Meat Analogue. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakratsas, G.; Polydera, A.; Katapodis, P.; Stamatis, H. Recent Trends in Submerged Cultivation of Mushrooms and Their Application as a Source of Nutraceuticals and Food Additives. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisashvili, V. Submerged Cultivation of Medicinal Mushrooms: Bioprocesses and Products. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2012, 14, 211–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaspyridi, L.M.; Aligiannis, N.; Topakas, E.; Christakopoulos, P.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Fokialakis, N. Submerged Fermentation of the Edible Mushroom Pleurotus Ostreatus in a Batch Stirred Tank Bioreactor as a Promising Alternative for the Effective Production of Bioactive Metabolites. Molecules 2012, 17, 2714–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudekula, U.T.; Doriya, K.; Devarai, S.K. A Critical Review on Submerged Production of Mushroom and Their Bioactive Metabolites. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakratsas, G.; Polydera, A.; Nilson, O.; Κossatz, L.; Xiros, C.; Katapodis, P.; Stamatis, H. Single-Cell Protein Production by Pleurotus Ostreatus in Submerged Fermentation. Sustain. Food Technol. 2023, 1, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydor, M.; Cofta, G.; Doczekalska, B.; Bonenberg, A. Fungi in Mycelium-Based Composites: Usage and Recommendations. Materials 2022, 15, 6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza Filho, P.F.; Nair, R.B.; Andersson, D.; Lennartsson, P.R.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Vegan-Mycoprotein Concentrate from Pea-Processing Industry Byproduct Using Edible Filamentous Fungi. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2018, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zikou, E.; Chatzifragkou, A.; Koutinas, A.A.; Papanikolaou, S. Evaluating Glucose and Xylose as Cosubstrates for Lipid Accumulation and γ-Linolenic Acid Biosynthesis of Thamnidium Elegans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardeli, C.; Athenaki, M.; Xenopoulos, E.; Mallouchos, A.; Koutinas, A.A.; Aggelis, G.; Papanikolaou, S. Lipid Production and Characterization by Mortierella (Umbelopsis) Isabellina Cultivated on Lignocellulosic Sugars. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 1461–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jach, M.E.; Serefko, A.; Ziaja, M.; Kieliszek, M. Yeast Protein as an Easily Accessible Food Source. Metabolites 2022, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hwang, S.; Lee, S.M. Metabolic Engineering for the Utilization of Carbohydrate Portions of Lignocellulosic Biomass. Metab. Eng. 2022, 71, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppram, R.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; Xiros, C.; Olsson, L. Lignocellulosic Ethanol Production at High-Gravity: Challenges and Perspectives. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlbach, D.J.; Kuo, A.; Sato, T.K.; Potts, K.M.; Salamov, A.A.; LaButti, K.M.; Sun, H.; Clum, A.; Pangilinan, J.L.; Lindquist, E.A.; et al. Comparative Genomics of Xylose-Fermenting Fungi for Enhanced Biofuel Production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13212–13217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xian, M.; Liu, M.; Zhao, G. Biochemical Routes for Uptake and Conversion of Xylose by Microorganisms. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Ma, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, X. Differential Proteomic Profiles of Pleurotus Ostreatus in Response to Lignocellulosic Components Provide Insights into Divergent Adaptive Mechanisms. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, S.S.; Dhiman, S.S.; Kim, T.S.; Li, J.; Lee, J.K.; Kang, Y.C. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Aspen Biomass into Fermentable Sugars by Using Lignocellulases from Armillaria Gemina. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 133, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.; Cohen, J.; Asatiani, M.D.; Varshney, V.K.; Yu, H.T.; Yang, Y.C.; Li, Y.H.; Mau, J.L.; Wasser, S.P. Chemical Composition and Nutritional and Medicinal Value of Fruit Bodies and Submerged Cultured Mycelia of Culinary-Medicinal Higher Basidiomycetes Mushrooms. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2014, 16, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiderle, F.R.; Olsen, L.M.; Ruthes, A.C.; Czelusniak, P.A.; Santana-Filho, A.P.; Sassaki, G.L.; Gorin, P.A.J.; Iacomini, M. Exopolysaccharides, Proteins and Lipids in Pleurotus Pulmonarius Submerged Culture Using Different Carbon Sources. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, B.; Andrade, P.B.; Silva, B.M.; Baptista, P.; Seabra, R.M.; Valentão, P. Comparative Study on Free Amino Acid Composition of Wild Edible Mushroom Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10973–10979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauria, A.; Ippolito, M.; Almerico, A.M. Principal Component Analysis on Molecular Descriptors as an Alternative Point of View in the Search of New Hsp90 Inhibitors. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2009, 33, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consultation, F.A.O.E. Dietary Protein Quality Evaluation in Human Nutrition; Report of an FAO Expert Consultation; Office of Knowledge Exchange, Research and Extension, FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 92, ISBN 9789251074176. [Google Scholar]
- Papaspyridi, L.M.; Katapodis, P.; Gonou-Zagou, Z.; Kapsanaki-Gotsi, E.; Christakopoulos, P. Optimization of Biomass Production with Enhanced Glucan and Dietary Fibres Content by Pleurotus Ostreatus ATHUM 4438 under Submerged Culture. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 50, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songulashvili, G.G.; Elisashvili, V.; Wasser, S.P.; Hadar, Y.; Nevo, E. Effect of the Carbon Source and Inoculum Preparation Method on Laccase and Manganese Peroxidase Production in Submerged Cultivation by the Medicinal Mushroom Ganoderma Lucidum (W. Curt.: Fr.) P. Karst. (Aphyllophoromycetideae). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2008, 10, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduyn, C.; Stouthamer, A.H.; Scheffers, W.A.; van Dijken, J.P. A Theoretical Evaluation of Growth Yields of Yeasts. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 1991, 59, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, D.S. Production of Protein-Rich Mycelial Biomass of a Mushroom, Pleurotus Sajor-Caju, on Corn Stover. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1989, 68, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gern, R.M.M.; Wisbeck, E.; Rampinelli, J.R.; Ninow, J.L.; Furlan, S.A. Alternative Medium for Production of Pleurotus Ostreatus Biomass and Potential Antitumor Polysaccharides. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wordofa, G.G.; Kristensen, M. Tolerance and Metabolic Response of Pseudomonas Taiwanensis VLB120 towards Biomass Hydrolysate-Derived Inhibitors. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanmarcke, G.; Demeke, M.M.; Foulquié-Moreno, M.R.; Thevelein, J.M. Identification of the Major Fermentation Inhibitors of Recombinant 2G Yeasts in Diverse Lignocellulose Hydrolysates. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiros, C.; Vafiadi, C.; Paschos, T.; Christakopoulos, P. Toxicity Tolerance of Fusarium Oxysporum towards Inhibitory Compounds Formed during Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Materials. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2011, 86, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food, E.; Authority, S. Scientific Opinion on the Safety and Efficacy of Formic Acid When Used as a Technological Additive for All Animal Species. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCOEL/SUM/98 Recommendation from the Scientific Committee on Occupational Exposure Limits for Acetic Acid. Employment, Social Affairs and Inclusion. 2012, Volume 12. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/social/BlobServlet?docId=7877&langId=en (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, P.; Luo, P.; Wu, P. Occurrence of Furfural and Its Derivatives in Coffee Products in China and Estimation of Dietary Intake. Foods 2023, 12, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aids, P. Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Food Additives, Flavourings, Processing Aids and Materials in Contact with Food (AFC) on a Request from the Commission Related to Tertiary-Butylhydroquinone (TBHQ). EFSA J. 2004, 2, 1–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upcraft, T.; Tu, W.C.; Johnson, R.; Finnigan, T.; Van Hung, N.; Hallett, J.; Guo, M. Protein from Renewable Resources: Mycoprotein Production from Agricultural Residues. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 5150–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritala, A.; Häkkinen, S.T.; Toivari, M.; Wiebe, M.G. Single Cell Protein-State-of-the-Art, Industrial Landscape and Patents 2001-2016. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Suo, F.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Shen, Y.; Bao, X. Fine-Tuning of NADH Oxidase Decreases Byproduct Accumulation in Respiration Deficient Xylose Metabolic Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, W.; Yao, Y.; Tian, C. The Weimberg Pathway: An Alternative for Myceliophthora Thermophila to Utilize d-Xylose. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2023, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J. Metabolic Response of Pleurotus Ostreatus to Continuous Heat Stress. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Optimization of Liquid Fermentation Conditions and Protein Nutrition Evaluation of Mycelium from the Caterpillar Medicinal Mushroom, Cordyceps Militaris (Ascomycetes). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2016, 18, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.M.; Blasi, F.; Angelini, P.; Ianni, F.; Alabed, H.B.R.; Emiliani, C.; Venanzoni, R.; Cossignani, L. LC/MS Q-TOF Metabolomic Investigation of Amino Acids and Dipeptides in Pleurotus Ostreatus Grown on Different Substrates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 10371–10382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
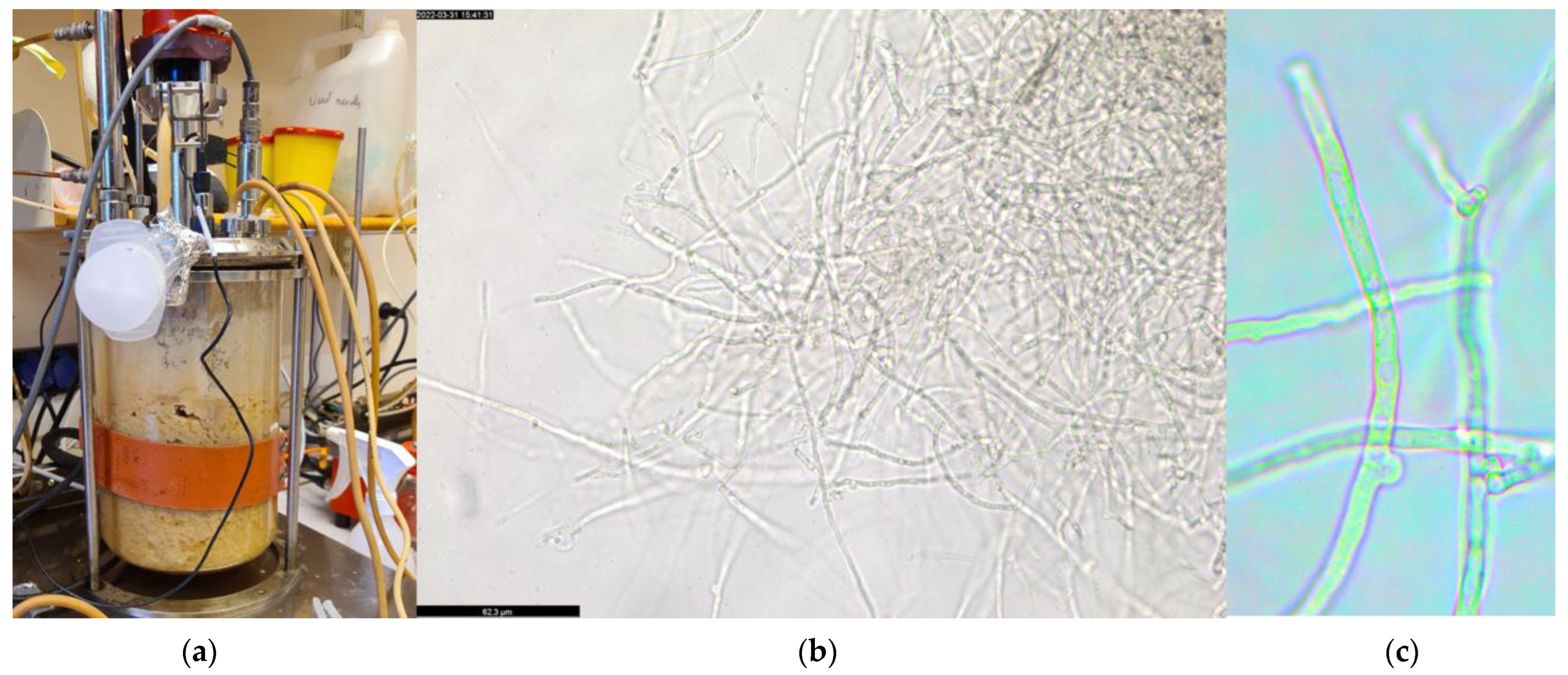
| Xylose Concentration (g L−1) | Biomass (g L−1) | Xylose Consumption (%) | Total Protein Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 2.5 ± 0.2 g | 100 ± 0.0 a | 10.7 ± 1.5 g |
| 10 | 6.4 ± 0.4 f | 100 ± 0.0 a | 42.9 ± 0.8 a |
| 20 | 9.7 ± 0.0 e | 100 ± 0.0 a | 42.6 ± 0.4 ab |
| 30 | 13.3 ± 0.6 d | 100 ± 0.0 a | 39.3 ± 2.1 ab |
| 40 | 16.2 ± 1.5 c | 100 ± 0.0 a | 32.2 ± 1.8 cdef |
| 50 | 19.4 ± 0.4 ab | 100 ± 0.0 a | 33.6 ± 1.2 cde |
| 60 | 20.4 ± 0.3 a | 93.7 ± 0.4 b | 30.7 ± 2.1 ef |
| 80 | 20.4 ± 2.9 ab | 71.2 ± 6.7 c | 37.5 ± 7.8 abcd |
| 50G0X | 35G15X | 25G25X | 15G35X | 0G50X | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg/g Protein | mg/g Protein | mg/g Protein | mg/g Protein | mg/g Protein | |
| Asp 1 | 49.0 ± 2.3 | 33.8 ± 10.7 | 33.7 ± 3.5 | 23.7 ± 4.4 | 28.4 ± 11.6 |
| Glu 2 | 42.8 ± 3.1 | 29.7 ± 4.2 | 31.1 ± 1.6 | 29.1 ± 4.5 | 27.6 ± 3.2 |
| Asn 3 | 3.6 ± 0.8 | 6.3 ± 0.6 | 10.4 ± 2.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Gln 4 | 37.7 ± 0.9 | 43.4 ± 4.9 | 37.7 ± 2.1 | 52.9 ± 6.3 | 53.5 ± 6.4 |
| Ser 5 | 10.2 ± 1.5 | 15.2 ± 3.8 | 14.8 ± 1.1 | 15.9 ± 2.6 | 20.2 ± 2.9 |
| Gly 6 | 282.2 ± 4.2 | 264.6 ± 1.2 | 252.2 ± 6.7 | 248.2 ± 18.5 | 246.5 ± 3.5 |
| Val 7 | 82.4 ± 2.6 | 77.3 ± 3.0 | 68.9 ± 0.8 | 71.9 ± 2.3 | 69.3 ± 0.2 |
| Pro 8 | 143.5 ± 5.1 | 154.5 ± 30.8 | 143.8 ± 18.3 | 143.9 ± 2.8 | 142.2 ± 9.6 |
| Arg 9 | 59.9 ± 10.2 | 71.6 ± 0.2 | 61.6 ± 0.1 | 78.3 ± 1.1 | 68.7 ± 2.8 |
| Met 10 | 2.5 ± 0.5 | 10.9 ± 1.2 | 12.2 ± 0.6 | 12.6 ± 2.0 | 16.1 ± 3.5 |
| Ile 11 | 47.1 ± 2.3 | 51.1 ± 0.3 | 53.2 ± 0.4 | 54.9 ± 2.5 | 54.0 ± 1.9 |
| Leu 12 | 103.5 ± 3.5 | 89.1 ± 1.9 | 97.3 ± 2.9 | 99.2 ± 3.5 | 91.7 ± 1.9 |
| Trp 13 | 46.5 ± 1.5 | 49.7 ± 1.9 | 45.4 ± 3.0 | 46.6 ± 0.9 | 42.8 ± 6.6 |
| Phe 14 | 66.7 ± 0.1 | 84.2 ± 18.4 | 69.5 ± 2.3 | 81.0 ± 6.3 | 93.7 ± 7.7 |
| Cys 15 | 5.7 ± 0.7 | 7.8 ± 1.5 | 4.4 ± 0.1 | 6.8 ± 2.2 | 8.6 ± 5.6 |
| Lys 16 | 2.9 ± 0.3 | 2.8 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.4 | 2.9 ± 1.0 |
| Tyr 17 | 3.4 ± 2.1 | 5.0 ± 1.6 | 9.5 ± 5.1 | 6.4 ± 0.1 | 15.8 ± 0.6 |
| AAA (Phe + Tyr) 18 | 70.1 ± 2.3 | 89.2 ± 20.0 | 79.0 ± 7.4 | 87.4 ± 6.1 | 109.5 ± 8.3 |
| SAA (Met + Cys) 19 | 8.3 ± 1.1 | 18.7 ± 0.3 | 16.5 ± 0.5 | 19.4 ± 4.2 | 24.8 ± 9.1 |
| Total | 989.9 ± 0.0 | 989.9 ± 9.3 | 989.9 ± 9.3 | 989.9 ± 9.3 | 989.9 ± 9.3 |
| Aspen Hydrolysate | C (g/L) |
|---|---|
| Glucose | 67.7 ± 0.41 |
| Xylose | 41.31 ± 0.18 |
| Mannose | 4.18 ± 0.21 |
| Cellobiose | 1.89 ± 0.09 |
| Arabinose | 1.86 ± 0.09 |
| Galactose | 1.77 ± 0.09 |
| Levulinic acid | 0.05 ± 0.004 |
| HMF | 0.10 ± 0.01 |
| Furfural | 0.73 ± 0.17 |
| Acetic acid | 6.01 ± 0.005 |
| Formic acid | 3.98 ± 0.06 |
| Ethanol | 11.63 ± 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bakratsas, G.; Polydera, A.; Nilson, O.; Chatzikonstantinou, A.V.; Xiros, C.; Katapodis, P.; Stamatis, H. Mycoprotein Production by Submerged Fermentation of the Edible Mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus in a Batch Stirred Tank Bioreactor Using Agro-Industrial Hydrolysate. Foods 2023, 12, 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122295
Bakratsas G, Polydera A, Nilson O, Chatzikonstantinou AV, Xiros C, Katapodis P, Stamatis H. Mycoprotein Production by Submerged Fermentation of the Edible Mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus in a Batch Stirred Tank Bioreactor Using Agro-Industrial Hydrolysate. Foods. 2023; 12(12):2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122295
Chicago/Turabian StyleBakratsas, Georgios, Angeliki Polydera, Oskar Nilson, Alexandra V. Chatzikonstantinou, Charilaos Xiros, Petros Katapodis, and Haralambos Stamatis. 2023. "Mycoprotein Production by Submerged Fermentation of the Edible Mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus in a Batch Stirred Tank Bioreactor Using Agro-Industrial Hydrolysate" Foods 12, no. 12: 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122295
APA StyleBakratsas, G., Polydera, A., Nilson, O., Chatzikonstantinou, A. V., Xiros, C., Katapodis, P., & Stamatis, H. (2023). Mycoprotein Production by Submerged Fermentation of the Edible Mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus in a Batch Stirred Tank Bioreactor Using Agro-Industrial Hydrolysate. Foods, 12(12), 2295. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12122295






_Stamatis.png)

