Discriminant Analysis of Brazilian Stingless Bee Honey Reveals an Iron-Based Biogeographical Origin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Honey Samples
2.3. Physicochemical Analysis
2.4. Total Phenolic (TPC) and Total Flavonoid (TFC) Contents
2.5. Antioxidant Capacity Assays
2.6. Mineral Profile Analysis
2.7. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of SBH
3.2. Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Capacity of SBH
3.3. Correlation Analysis of Physicochemical Properties and Antioxidant Activity
3.4. Mineral Profile of SBH
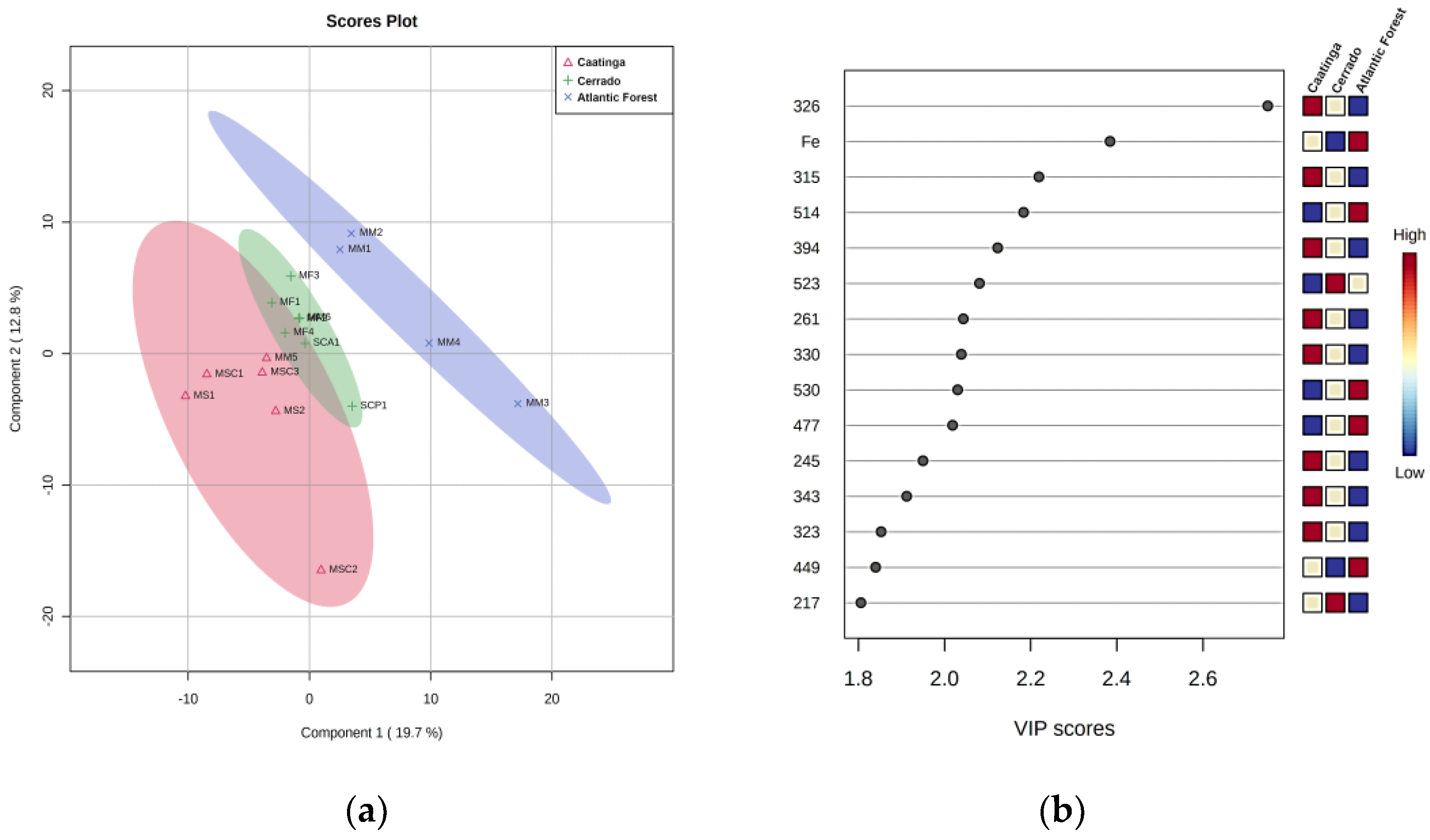
3.5. Discriminant Analysis of SBH
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brazil. Biodiversidade. 2022. Available online: https://www.gov.br/mma/pt-br/assuntos/biodiversidade (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- CBD. Brazil—Biodiversity Facts. 2021. Available online: https://www.cbd.int/countries/profile/?country=br (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Giannini, T.C.; Alves, D.A.; Alves, R.; Cordeiro, G.D.; Campbell, A.J.; Awade, M.; Bento, J.M.S.; Saraiva, A.M.; Imperatriz-Fonseca, V.L. Unveiling the contribution of bee pollinators to Brazilian crops with implications for bee management. Apidologie 2020, 51, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, L.G.A.; Coelho, L.L.; Resende, H.C.; Tavares, M.G.; Campos, L.A.O.; Fernandes-Salomão, T.M. Honey physicochemical properties of three species of the Brazilian Melipona. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2012, 84, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, I.A.; da Silva, T.M.; Camara, C.A.; Queiroz, N.; Magnani, M.; de Novais, J.S.; Soledade, L.E.; de Oliveira Lima, E.; de Souza, A.L.; de Souza, A.G. Phenolic profile, antioxidant activity and palynological analysis of stingless bee honey from Amazonas, Northern Brazil. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3552–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, S.; Hornung, P.S.; Teixeira, G.L.; Malunga, L.N.; Apea-Bah, F.B.; Beux, M.R.; Beta, T.; Ribani, R.H. Bioactive compounds and biological properties of Brazilian stingless bee honey have a strong relationship with the pollen floral origin. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneh, Y.; Ali, F.; Zarei, M.; Akim, A.M.; Hamid, H.A.; Khazaai, H. Malaysian stingless bee and Tualang honeys: A comparative characterization of total antioxidant capacity and phenolic profile using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. LWT 2018, 89, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuttong, B.; Chanbang, Y.; Sringarm, K.; Burgett, M. Physicochemical profiles of stingless bee (Apidae: Meliponini) honey from South East Asia (Thailand). Food Chem. 2016, 192, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC—Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; AOAC: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Aires, E.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Estevinho, L.M. Antioxidant activity of Portuguese honey samples: Different contributions of the entire honey and phenolic extract. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1438–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkmen, N.; Sari, F.; Poyrazoglu, E.S.; Velioglu, Y.S. Effects of prolonged heating on antioxidant activity and colour of honey. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meda, A.; Lamien, C.E.; Romito, M.; Millogo, J.; Nacoulma, O.G. Determination of the total phenolic, flavonoid and proline contents in Burkina Fasan honey, as well as their radical scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2005, 91, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.O.R.; Mársico, E.T.; de Jesus, E.F.O.; Carneiro, C.S.; Júnior, C.A.C.; de Almeida, E.; Filho, V.F.N. Determination of trace elements in honey from different regions in Rio de Janeiro State (Brazil) by total reflection x-ray fluorescence. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, T738–T742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araújo, U.B.; Costa, A.C.M.; Oliveira, D.F.; Jesus, E.F.O.; Anjos, M.J.; Marsico, E.T.; Carneiro, C.S.; Ribeiro, R.O.R.; Lopes, R.T. Analysis of milk trace elements with a home-made portable automated total reflection x-ray fluorescence system. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 156, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlsma, L.; De Bruijn, L.L.M.; Martens, E.P.; Sommeijer, M.J. Water content of stingless bee honeys (Apidae, Meliponini): Interspecific variation and comparison with honey of Apis mellifera. Apidologie 2006, 37, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.; Marchini, L.; Carvalho, C.; Araújo, D.; Olinda, R.; Silveira, T. Physical-chemical parameters of honey of stingless bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Chem. Sci. Int. J. 2015, 7, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kek, S.P.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A.; Tan, S.W.; Chua, L.S. Classification of entomological origin of honey based on its physicochemical and antioxidant properties. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S2723–S2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, S.; Lazzarotto, M.; Hornung, P.S.; Teixeira, G.L.; Ito, V.C.; Bellettini, M.B.; Beux, M.R.; Beta, T.; Ribani, R.H. Influence of stingless bee genus (Scaptotrigona and Melipona) on the mineral content, physicochemical and microbiological properties of honey. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4742–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batiston, T.F.T.P.; Frigo, A.; Stefani, L.M.; Silva, A.S.D.; Araujo, D.N. Physicochemical composition and antimicrobial potential of stingless honey: A food of differentiated quality. Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 10, e709910822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anacleto, D.A.; Souza, B.A.; Marchini, L.C.; Moreti, A.C.C.C. Composição de amostras de mel de abelha Jataí (Tetragonisca angustula latreille, 1811). Cienc. Tecnol. Aliment. 2009, 29, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jimenez, M.; Beristain, C.I.; Azuara, E.; Mendoza, M.R.; Pascual, L.A. Physicochemical and antioxidant properties of honey from Scaptotrigona mexicana bee. J. Apic. Res. 2016, 55, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISPN. Cerrado—The Heart of Brazil. 2022. Available online: https://ispn.org.br/en/biomes/cerrado/ (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Braga, D.C.; Liberato, M.C.T.C.; Lima, V.L.F.; de Araújo Neto, J.A.M. Analytical study of the physicochemical characteristics from Melipona subnitida d. Honey in adequation to Brazilian law. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, F.H.C.; Menezes, F.N.D.D.; de Sousa, J.M.B.; dos Santos Lima, M.; da Silva Campelo Borges, G.; de Souza, E.L.; Magnani, M. Prebiotic activity of monofloral honeys produced by stingless bees in the semi-arid region of Brazilian Northeastern toward Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-05 and Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12. Food Res. Int. 2020, 128, 108809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, J.M.; de Souza, E.L.; Marques, G.; de Toledo Benassi, M.; Gullón, B.; Pintado, M.M.; Magnani, M. Sugar profile, physicochemical and sensory aspects of monofloral honeys produced by different stingless bee species in Brazilian semi-arid region. LWT 2016, 65, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biluca, F.C.; Braghini, F.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.O.; Fett, R. Physicochemical profiles, minerals and bioactive compounds of stingless bee honey (Meliponinae). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 50, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisquini, M.I.; Lorente, F.L.; Pessenda, L.C.; Junior, A.A.; Mayle, F.E.; Cohen, M.C.; França, M.C.; Bendassolli, J.A.; Giannini, P.C.; Schiavo, J.; et al. Cold and humid Atlantic Rainforest during the last glacial maximum, northern Espírito Santo State, southeastern Brazil. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 244, 106489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacrés-Granda, I.; Coello, D.; Proaño, A.; Ballesteros, I.; Roubik, D.W.; Jijón, G.; Granda-Albuja, G.; Granda-Albuja, S.; Abreu-Naranjo, R.; Maza, F.; et al. Honey quality parameters, chemical composition and antimicrobial activity in twelve Ecuadorian stingless bees (Apidae: Apinae: Meliponini) tested against multiresistant human pathogens. LWT 2021, 140, 110737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juna, C.F.; Cho, Y.H.; Ham, D.; Joung, H. Associations of relative humidity and lifestyles with metabolic syndrome among the Ecuadorian adult population: Ecuador National Health and Nutrition Survey (ENSANUT-ECU) 2012. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2020, 17, 9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’ana, R.S.; de Carvalho, C.A.L.; Oda-Souza, M.; Souza, B.D.A.; Dias, F.D.S. Characterization of honey of stingless bees from the Brazilian semi-arid region. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudin, S.; Selamat, J.; Sanny, M.; Abd Razak, S.B.; Jambari, N.N.; Mian, Z.; Khatib, A. Influence of origins and bee species on physicochemical, antioxidant properties and botanical discrimination of stingless bee honey. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 238–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, A.; Bruni, R.; Maietti, S.; Poli, F.; Rossi, D.; Paganetto, G.; Muzzoli, M.; Scalvenzi, L.; Sacchetti, G. Ecuadorian stingless bee (Meliponinae) honey: A chemical and functional profile of an ancient health product. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1413–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, L.; Kilic, M. Kinetics of hydroxymethylfurfural accumulation and color change in honey during storage in relation to moisture content. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2009, 33, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carina Biluca, F.; Braghini, F.; de Campos Ferreira, G.; Costa dos Santos, A.; Helena Baggio Ribeiro, D.; Valdemiro Gonzaga, L.; Vitali, L.; Amadeu Micke, G.; Carolina Oliveira Costa, A.; Fett, R. Physicochemical parameters, bioactive compounds, and antibacterial potential of stingless bee honey. J. Food Process Preserv. 2021, 45, e15127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biluca, F.C.; da Silva, B.; Caon, T.; Mohr, E.T.B.; Vieira, G.N.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Vitali, L.; Micke, G.; Fett, R.; Dalmarco, E.M.; et al. Investigation of phenolic compounds, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities in stingless bee honey (Meliponinae). Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, M.; Ellulu, M.S.; Abu Bakar, M.F. Melissopalynological study, phenolic compounds, and antioxidant properties of Heterotrigona itama honey from Johor, Malaysia. Scientifica 2020, 2020, 2529592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Khalil, M.I.; Gan, S.H. Evaluation of physicochemical and antioxidant properties of sourwood and other Malaysian honeys: A comparison with manuka honey. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucholobek, G.; de Andrade, C.K.; Rigobello, E.S.; Wielewski, P.; de Toledo, V.D.; Quináia, S.P. Determination of the Ca, Mn, Mg and Fe in honey from multiple species of stingless bee produced in Brazil. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Nascimento, A.S.; Chambó, E.D.; de Jesus Oliveira, D.; Andrade, B.R.; Bonsucesso, J.S.; de Carvalho, C.A.L. Honey from stingless bee as indicator of contamination with metals. Sociobiology 2018, 65, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basari, N.; Ramli, S.N.; Abdul-Mutalid, N.A.; Shaipulah, N.F.; Hashim, N.A. Flowers morphology and nectar concentration determine the preferred food source of stingless bee, Heterotrigona itama. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2021, 24, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, L. Biomas brasileiros, 1st ed.; Oficina de Textos: São Paulo, Brazil, 2016; Available online: https://books.google.com.br/books?hl=pt-BR&lr=&id=KlLdDgAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PT4&dq=coutinho+and+biomas+brasileiros&ots=sj7bwkppna&sig=9s_q-KFYGslNzq2aASMv9sAAcY0#v=onepage&q=coutinho%20and%20biomas%20brasileiros&f=false (accessed on 14 November 2022).
- Da Silva, J.M.C.; Lacher, T.E. Caatinga—South America. Reference module in earth systems and environmental sciences. In Encyclopedia of the World’s Biomes; Goldstein, M.I., DellaSala, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biogeographical Zones | Bee Species | Popular Name | Year (Season) | Sample Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atlantic Forest | Melipona mondury | Uruçu Amarela | 2017 (autumn) | MM1 |
| Melipona mondury | Uruçu Amarela | 2017 (autumn) | MM2 | |
| Melipona mondury | Uruçu Amarela | 2017 (autumn) | MM3 | |
| Melipona mondury | Uruçu Amarela | 2018 (summer) | MM4 | |
| Melipona quadrifasciata | Mandaçaia | 2018 (spring) | MQ1 | |
| Caatinga | Melipona subnitida | Jandaíra | 2018 (autumn) | MS1 |
| Melipona subnitida | Jandaira | 2018 (winter) | MS2 | |
| Melipona scutellaris | Uruçu Nordestina | 2018 (winter) | MSC1 | |
| Melipona scutellaris | Uruçu Nordestina | 2018 (summer) | MSC2 | |
| Melipona scutellaris | Uruçu Nordestina | 2018 (summer) | MSC3 | |
| Melipona mondury | Uruçu Amarela | 2018 (summer) | MM5 (6) | |
| Scaptotrigona aff. postica | Tubi | 2018 (winter) | SCA1 | |
| Cerrado | Melipona fasciculata | Tiúba | 2018 (winter) | MF1 |
| Melipona fasciculata | Tiúba | 2018 (winter) | MF2 | |
| Melipona fasciculata | Tiúba | 2018 (winter) | MF3 | |
| Melipona fasciculata | Tiúba | 2018 (spring) | MF4 | |
| Scaptotrigona polysticta | Benjoi | 2018 (winter) | SCP1 | |
| Melipona mondury | Uruçu Amarela | 2018 (summer) | MM6 (5) |
| Biogeogr. Zone | Samples | Aw | Moisture (%) | TSS (°Brix) | pH | Total Acidity (meq/Kg) | Free Acidity (meq/Kg) | Brown Pigment | HMF (mg/Kg) | Pfund (mm) | Color Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atlantic Forest | MM1 | 0.75 ± 0.00 c,d | 30.43 ± 0.37 c,d | 67.65 ± 0.35 g | 3.24 ± 0.10 f | 71.04 ± 0.55 k | 59.74 ± 0.99 f | 0.05 ± 0.00 d | 0.38 ± 0.08 d | 23.82 ± 0.00 d | White |
| MM2 | 0.75 ± 0.00 c | 36.31 ± 0.09 a | 61.33 ± 0.13 i | 3.57 ± 0.02 b | 81.79 ± 1.65 j | 67.11 ± 1.87 e | 0.12 ± 0.00 a | 5.16 ± 1.17 b | 46.72 ± 0.00 a | Extra light amber | |
| MM3 | 0.73 ± 0.00 f,g | 28.55 ± 0.70 e,f | 69.33 ± 0.45 e,f | 3.26 ± 0.03 e,f | 143.86 ± 2.77 i | 83.80 ± 1.86 c | 0.12 ± 0.00 a | nd | 28.77 ± 0.00 c | White | |
| MM4 | 0.74 ± 0.01 d,e | 30.79 ± 0.65 c | 69.05 ± 1.13 e,f,g | 3.40 ± 0.00 c,d | 240.67 ± 0.00 c | 75.26 ± 0.00 d | 0.07 ± 0.00 b,c,d | nd | ≤8.00 | Water white | |
| MQ1 | 0.81 ± 0.00 a | 35.79 ± 0.10 a | 61.92 ± 0.13 i | - | - | - | 0.07 ± 0.01 b,c,d | nd | 0.00 | Water white | |
| Caatinga | MS1 | 0.72 ± 0.00 g,h | 27.96 ± 0.10 e,f,g | 70.08 ± 0.13 e | 3.37 ± 0.00 c,d,e | 204.91 ± 0.00 g | 50.80 ± 0.00 h | 0.07 ± 0.02 b,c,d | nd | ≤8.00 | Water white |
| MS2 | 0.73 ± 0.00 e,f | 28.83 ± 0.00 d,e,f | 69.25 ± 0.00 e,f | 3.26 ± 0.05 e,f | 211.09 ± 0.00 f | 42.50 ± 0.00 i | 0.06 ± 0.02 c,d | 1.05 ± 0.00 d | ≤8.00 | Water white | |
| MSC1 | 0.77 ± 0.00 b | 32.90 ± 0.20 b | 65.00 ± 0.23 | 3.26 ± 0.11 e,f | 299.42 ± 0.00 a | 130.79 ± 0.00 a | 0.12 ± 0.00 a | 0.15 ± 0.00 d | 15.39 ± 0.00 e | Extra white | |
| MSC2 | 0.74 ± 0.00 e,f | 28.13 ± 0.18 e,f,g | 70.08 ± 0.13 e | 3.47 ± 0.00 b,c | 201.97 ± 0.00 g | 33.35 ± 0.00 j | 0.09 ± 0.01 a,b,c,d | nd | 15.27 ± 0.00 f | Extra white | |
| MSC3 | 0.73 ± 0.00 e,f | 29.16 ± 1.36 c,d,e,f | 67.67 ± 1.32 g | 4.78 ± 0.00 a | 179.11 ± 0.00 h | 17.26 ± 0.00 k | 0.09 ± 0.01 a,b,c,d | 1.03 ± 0.00 d | ≤8.00 | Water white | |
| MM5 (6) | 0.75 ± 0.00 c | 29.52 ± 0.95 c,d,e | 67.92 ± 0.13 f,g | 3.54 ± 0.00 b | 220.17 ± 0.00 e | 58.13 ± 0.00 f | 0.10 ± 0.03 a,b,c | 3.56 ± 0.00 c | ≤8.00 h | Water white | |
| SCA1 | 0.71 ± 0.00 i | 25.92 ± 0.00 h | 72.25 ± 0.00 c | 3.06 ± 0.00 g | 288.71 ± 0.00 b | 120.52 ± 0.00 b | 0.12 ± 0.02 a | 3.43 ± 0.00 c | 40.78 ± 0.00 b | Extra light amber | |
| Cerrado | MF1 | 0.68 ± 0.00 j | 23.87 ± 0.10 i | 74.17 ± 0.13 b | 3.46 ± 0.00 b,c | 227.45 ± 0.00 d | 53.51 ± 0.00 g | 0.07 ± 0.01 b,c,d | nd | ≤8.00 | Water white |
| MF2 | 0.65 ± 0.00 k | 19.47 ± 0.63 j | 75.75 ± 0.22 a | 3.30 ± 0.00 d,e,f | 218.32 ± 0.00 e | 51.69 ± 0.00 g,h | 0.07 ± 0.00 b,c,d | nd | ≤8.00 | Water white | |
| MF3 | 0.67 ± 0.00 j | 23.13 ± 0.21 i | 75.08 ± 0.13 a,b | - | - | - | 0.07 ± 0.01 b,c,d | nd | ≤8.00 | Water white | |
| MF4 | 0.67 ± 0.00 j | 23.40 ± 0.00 i | 74.92 ± 0.13 a,b | - | - | - | 0.07 ± 0.01 b,c,d | nd | ≤8.00 | Water white | |
| SCP1 | 0.71 ± 0.00 i | 26.61 ± 0.10 g,h | 71.75 ± 0.23 c,d | - | - | - | 0.11 ± 0.01 a,b | 12.64 ± 0.00 a | 13.11 ± 0.00 g | Extra White | |
| MM6 (5) | 0.72 ± 0.00 h | 27.72 ± 0.00 f,g | 70.50 ± 0.00 d,e | - | - | - | 0.08 ± 0.03 a,b,c,d | 0.45 ± 0.00 d | ≤8.00 | Water white |
| Biogeographical Zone | Samples | TPC (mg GAE/100 g FW) | TFC (mg QE/100 g FW) | Antioxidant Activity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FRAP (µmol Fe2+/100 g FW) | ABTS (%) | ||||
| Atlantic Forest | MM1 | 47.11 ± 1.39 a,b,c | 16.70 ± 0.32 b | 110.85 ± 4,42 b,c | 38.22 ± 1.47 b,c |
| MM2 | 44.46 ± 1.16 a,b,c,d | 15.02 ± 0.18 b,c | 114.49 ± 9.38 b,c | 40.08 ± 2.07 b,c | |
| MM3 | 35.69 ± 2.45 b,c,d,e | 13.53 ± 0.04 c,d | 84.87 ± 8.53 c | 51.61 ± 8.24 a,b | |
| MM4 | 46.74 ± 5.75 a,b,c | 9.93 ± 0.38 f,g | 212.16 ± 8.84 a | 39.82 ± 1.70 b,c | |
| MQ1 | 29.80 ± 4.50 c,d,e,f | 9.04 ± 0.38 f,g,h,i | - | - | |
| MS1 | 32.99 ± 9.44 b,c,d,e,f | 6.99 ± 0.63 j,k | 108.95 ± 1.18 b,c | 39.82 ± 2.20 b,c | |
| MS2 | 16.30 ± 4.26 f | 5.39 ± 1.07 k | - | - | |
| MSC1 | 25.26 ± 1.66 d,e,f | 8.89 ± 1.22 f,g,h,i | - | 39.20 ± 3.42 b,c | |
| MSC2 | 22.24 ± 18.18 e,f | 10.55 ± 0.21 e,f | 118.71 ± 23.28 b,c | 48.74 ± 6.30 a,b,c | |
| MSC3 | 39.29 ± 7.23 b,c,d,e | 8.33 ± 0.21 g,h,i,j | 215.07 ± 7.27 a | 54.95 ± 11.88 a | |
| MM5(6) | 36.03 ± 6.17 b,c,d,e | 7.91 ± 0.04 h,i,j | 143.96 ± 15.80 b | 43.71 ± 4.79 a,b,c | |
| SCA1 | 62.33 ± 4.33 a | 27.22 ± 3.04 a | - | - | |
| Cerrado | MF1 | 39.86 ± 6.88 b,c,d,e | 9.26 ± 0.07 f,g,h | 88.70 ± 0.19 c | 44.20 ± 5.49 a,b,c |
| MF2 | 37.98 ± 6.00 b,c,d,e | 7.66 ± 0.10 h,i,j | 84.53 ± 2.55 c | 37.84 ± 3.24 c | |
| MF3 | 50.95 ± 4.59 a,b | 7.39 ± 0.07 i,j | 79.53 ± 2.55 c | 40.08 ± 3.21 b,c | |
| MF4 | 26.68 ± 2.19 d,e,f | 6.67 ± 0.60 j,k | 88.56 ± 5.91 c | 38.22 ± 1.30 b,c | |
| SCP1 | 34.30 ± 11.23 b,c,d,e,f | 12.13 ± 0.07 d,e | 140.03 ± 3.34 b | 45.09 ± 6.68 a,b,c | |
| MM6 (5) | 36.41 ± 9.89 b,c,d,e | 7.91 ± 0.18 h,i,j | - | - | |
| Mineral | Atlantic Forest | Caatinga | Cerrado |
|---|---|---|---|
| P | 3.54 ± 0.56 | 49.20 ± 29.81 | 20.19 ± 14.36 |
| (3.01–4.06) a | (4.60–100.19) b | (2.59–40.75) b | |
| Cl | 1.71 ± 1.69 | 4.20 ±1.46 | nd |
| (0.69–0.16) a | (2.54–6.41) a | ||
| K | 411.58 ± 107.74 | 234.22 ± 109.23 | 127.03 ± 44.57 |
| (249.01–679.50) a | (79.73–419.23) a | (67.35–177.99) b | |
| Ca | 91.65 ± 48.98 | 39.18 ± 15.72 | 31.84 ± 6.20 |
| (44.28–165.00) a | (21–47–57.28) b | (24.45–39.75) b | |
| Cr | 0.27 ± 0.22 | 0.26 ± 0.13 | 0.19 ± 0.01 |
| (0.04–0.55) a | (0.15–0.48) a | (0.18–0.19) a | |
| Mn | 1.24 ± 0.91 | 0.90 ± 0.48 | 0.56 ± 0.16 |
| (0.47–2.66) a | (0.37–1.75) a | (0.36–0.77) a | |
| Fe | 8.71 ± 4.41 | 1.32 ± 0.47 | 0.84 ± 0.10 |
| (1.68–12.92) a | (0.96–2.32) b | (0.73–0.97) c | |
| Ni | 0.61 ± 0.45 | 0.22 ± 0.08 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| (0.01–0.99) a | (0.13–0.30) a | (0.20–0.21) a | |
| Cu | 3.76 ± 3.80 | 3.86 ± 1.73 | 2.31 ± 0.67 |
| (0.34–9.82) a | (1.70–6.72) a | (1.66–3.33) a | |
| Zn | 0.87 ± 0.38 | 0.36 ± 0.22 | 0.88 ± 0.29 |
| (0.44–1.36) a | (0.10–0.73) b | (0.49–1.23) a | |
| Rb | 1.22 ± 0.41 | 0.54 ± 0.36 | 0.52 ± 0.01 |
| (0.85–1.59) a | (0.20–1.08) a,b | (0.51–0.52) b | |
| Sr | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.26 | 0.26 ± 0.08 |
| (0.08–0.11) a | (0.15–0.81) b | (0.19–0.33) b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lavinas, F.C.; Gomes, B.A.; Silva, M.V.T.; Nunes, R.M.; Leitão, S.G.; Moura, M.R.L.; Simas, R.C.; Carneiro, C.S.; Rodrigues, I.A. Discriminant Analysis of Brazilian Stingless Bee Honey Reveals an Iron-Based Biogeographical Origin. Foods 2023, 12, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010180
Lavinas FC, Gomes BA, Silva MVT, Nunes RM, Leitão SG, Moura MRL, Simas RC, Carneiro CS, Rodrigues IA. Discriminant Analysis of Brazilian Stingless Bee Honey Reveals an Iron-Based Biogeographical Origin. Foods. 2023; 12(1):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010180
Chicago/Turabian StyleLavinas, Flavia C., Brendo A. Gomes, Marcos V. T. Silva, Renata M. Nunes, Suzana G. Leitão, Mirian R. L. Moura, Rosineide C. Simas, Carla S. Carneiro, and Igor A. Rodrigues. 2023. "Discriminant Analysis of Brazilian Stingless Bee Honey Reveals an Iron-Based Biogeographical Origin" Foods 12, no. 1: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010180
APA StyleLavinas, F. C., Gomes, B. A., Silva, M. V. T., Nunes, R. M., Leitão, S. G., Moura, M. R. L., Simas, R. C., Carneiro, C. S., & Rodrigues, I. A. (2023). Discriminant Analysis of Brazilian Stingless Bee Honey Reveals an Iron-Based Biogeographical Origin. Foods, 12(1), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12010180







