Physicochemical and Functional Modifications of Hemp Protein Concentrate by the Application of Ultrasonication and pH Shifting Treatments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. pH Shifting and Ultrasonication Treatments
2.3. Acoustic Energy Determination
2.4. Hydrodynamic Diameter, Conductivity, Zeta-Potential, and Polydispersity Index
2.5. Optical Characterizations and Turbidity
2.6. Surface Hydrophobicity Determination
2.7. Protein Quantification (Solubility) and Electrophoresis (SDS—PAGE)
2.8. Free Sulfhydryl Group Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
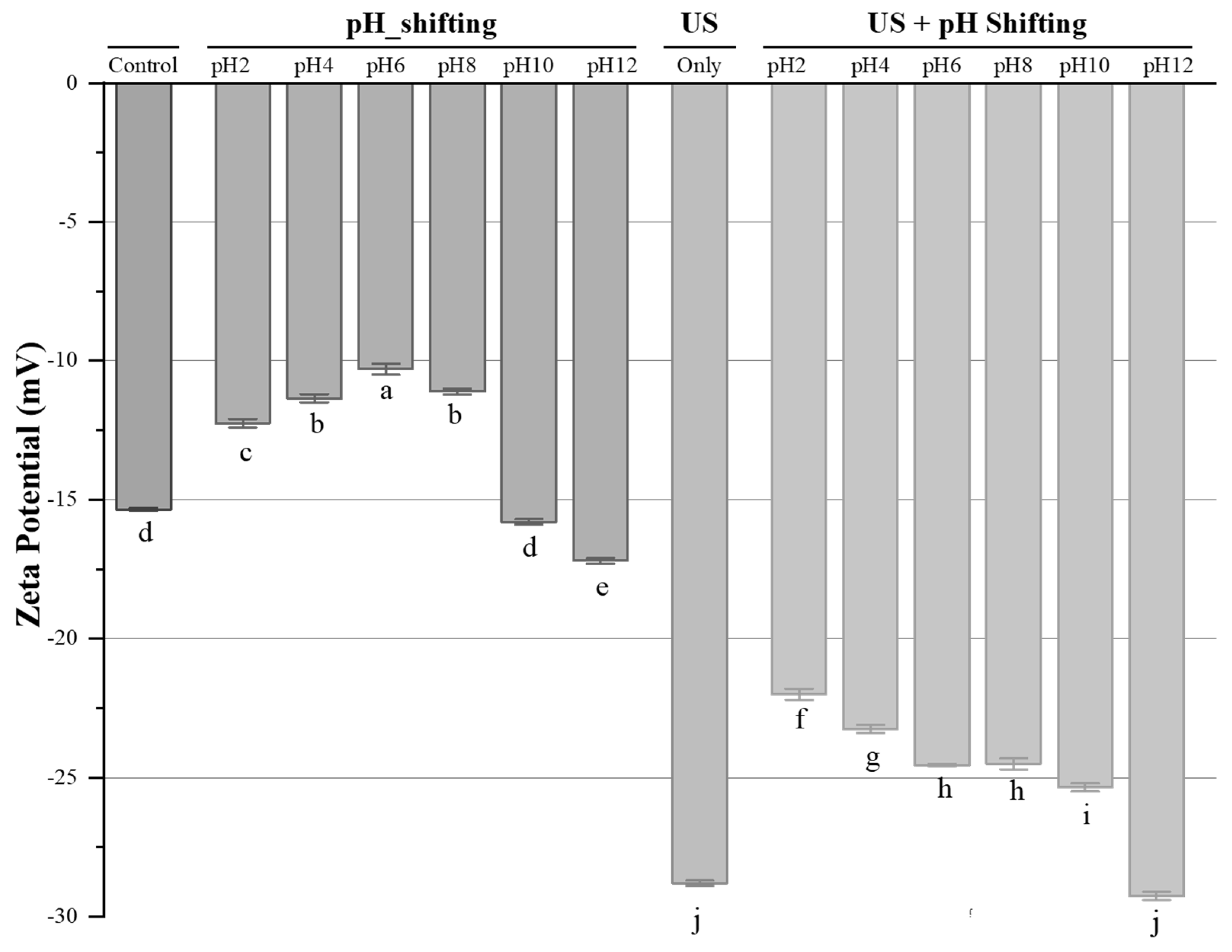
3.1. Hydrodynamic Diameter, Zeta-Potential, Conductivity and Polydispersity Index
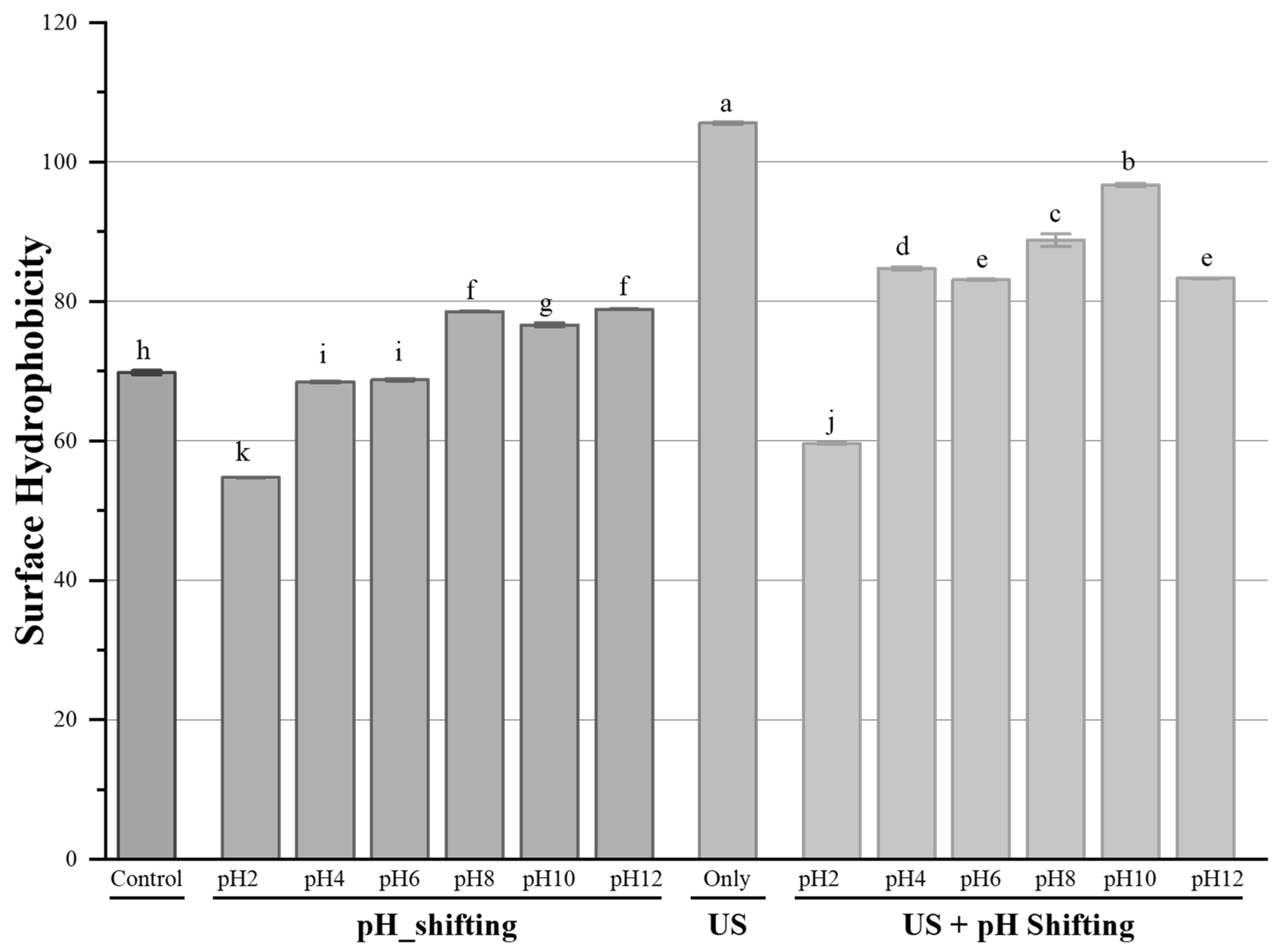
3.2. Surface Hydrophobicity
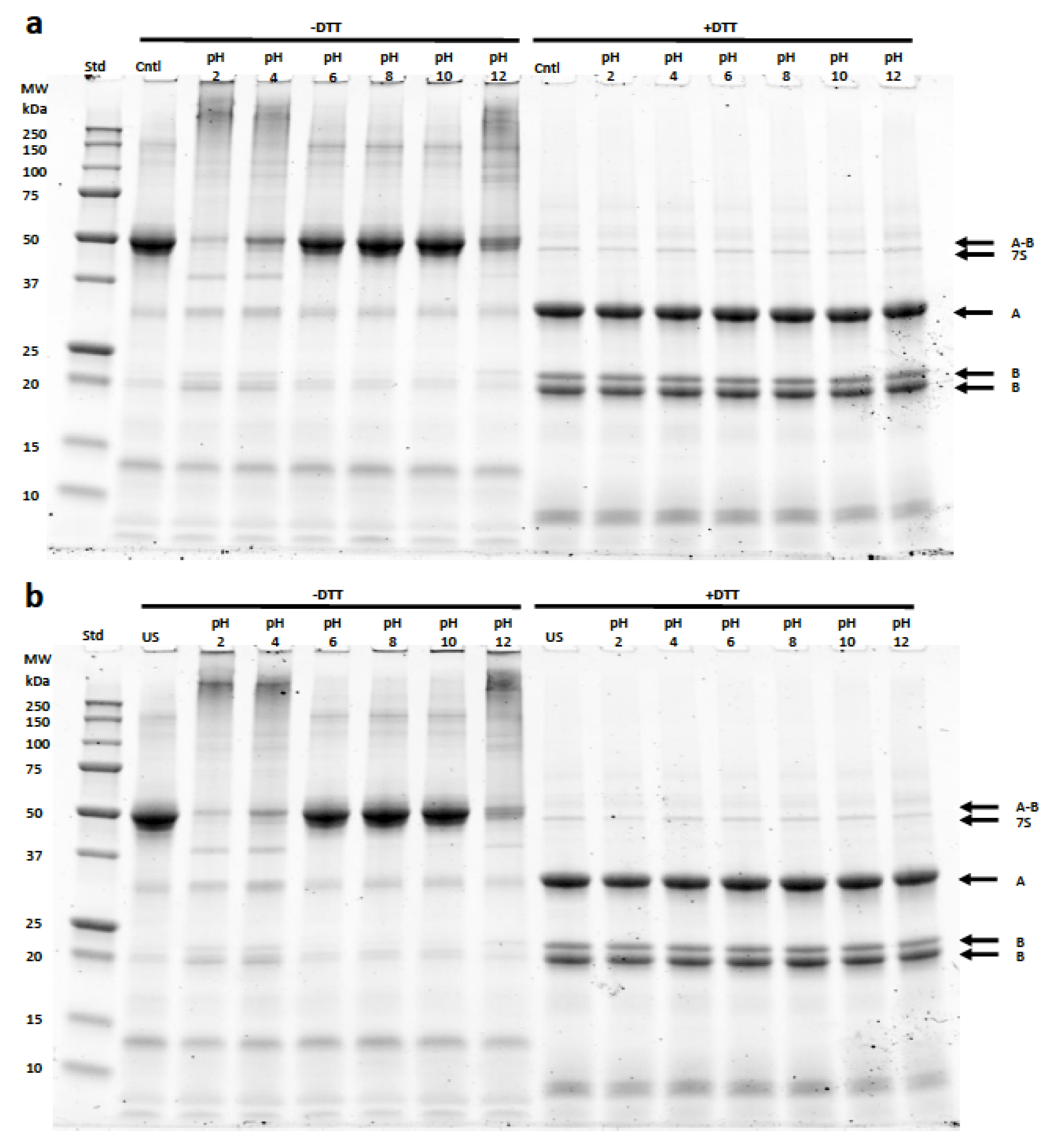
3.3. Protein Quantification (Solubility) and Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
3.4. Free Sulfhydryl Group Analysis
3.5. Optical Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Expert Consultation. Protein and amino acid requirements in human nutrition. In World Health Organization Technical Report Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; Volume 935, pp. 1–265. [Google Scholar]
- Galanakis, C.M. Functionality of food components and emerging technologies. Foods 2021, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World. Available online: www.fao.org.http://www.fao.org/state-of-food-security-nutrition/en/ (accessed on 13 February 2021).
- Clark, M.A.; Domingo, N.G.; Colgan, K.; Thakrar, S.K.; Tilman, D.; Lynch, J.; Azevedo, I.L.; Hill, J.D. Global food system emissions could preclude achieving the 1.5° and 2° C climate change targets. Science 2020, 370, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.; Gao, Z.; Fang, B.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Ferreting out the secrets of industrial hemp protein as emerging functional food ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Ten, Z.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, X.Q. Physicochemical and functional properties of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8945–8950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Meinninger, C.J. Regulation of nitric oxide synthesis by dietary factors. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 61–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the healthy brain. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 799–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- House, J.D.; Neufeld, J.; Leson, G. Evaluating the quality of protein from hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) products through the use of the protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11801–11807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Gao, Z.; Xu, M.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Physicochemical and structural properties of proteins extracted from dehulled industrial hempseeds: Role of defatting process and precipitation pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Tang, C.H.; Li, B.S.; Li, L.; Yang, X.Q.; Ma, C.Y. Effects of high pressure treatment on some physicochemical and functional properties of soy protein isolates. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, X.Q.; Lin, L. Formation of soluble aggregates from insoluble commercial soy protein isolate by means of ultrasonic treatment and their gelling properties. J. Food Eng. 2009, 92, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Fu, H.; Subbiah, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Effects of radio frequency heating treatment on structure changes of soy protein isolate for protein modification. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, O.; Lee, H.; Zhang, W.; Feng, H. Manothermosonication (MTS) treatment of apple-carrot juice blend for inactivation of Escherichia coli 0157:47. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambrak, A.R.; Mason, T.J.; Lelas, V.; Herceg, Z.; Herceg, L.J.I. Effect of ultrasound treatment on solubility and foaming properties of whey protein suspensions. J. Food Eng. 2008, 86, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Sharma, H.K.; Saini, C.S. High intensity ultrasound treatment of protein isolate extracted from dephenolized sunflower meal: Effect on physicochemical and functional properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Lu, J.; Liu, L.; Ulukoa, H.; Su, Y.; Cui, W.; Ge, W.; et al. Effect of power ultrasound pre-treatment on the physical and functional properties of reconstituted milk protein concentrate. J. Food Eng. 2014, 124, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Fang, T.; Gao, F.; Guo, M. Effects of ultrasound treatment on physicochemical and emulsifying properties of whey proteins pre- and post-treatment aggregation. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Sharifian, P.; Soltanizades, N. Application of ultrasound treatment for improving the physicochemical, functional and rheological properties of myofibtillar proteins. International J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Bai, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, W. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on physicochemical, interfacial and gel properties of chickpea protein isolate. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 129, 109563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Irfan, S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Shafique, B.; Kanwal, R.; Pateiro, M.; Arshad, R.N.; Wang, L.; Nayik, G.A.; Roobab, U.; et al. Sonication, a potential technique for extraction of phytoconstituents: A systematic review. Processes 2021, 9, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, Y.L. A pH shift approach to the improvement of interfacial properties of plant seed proteins. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 19, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, F.; Cheng, Y. Improving the solubility and digestibility of potato protein with an online ultrasound-assisted pH shifting treatment at medium temperature. Foods 2020, 9, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Yildiz, G.; Dos Santos, L.C.; Jiang, S.; Andrade, J.E.; Engeseth, N.J.; Feng, H. Soy protein nano-aggregates with improved functional properties prepared by sequential pH treatment and ultrasonication. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 55, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pan, Z.; Shen, K.; Cai, X.; Zheng, B.; Miao, S. Influence of ultrasound-assisted alkali treatment on the structural properties and functionalities of rice protein. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Ding, J.; Andrade, J.; Rababah, T.M.; Almajwal, A.; Abulmeaty, M.M. Modifying the physicochemical properties of pea protein by pH-shifting and ultrasound combined treatments. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, B.H.; Arroyo, C.; Condón, S.; Pagán, R.; Bayindirli, A.; Alpas, H. Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli by ultrasonic waves under pressure at nonlethal (manosonication) and lethal temperatures (manothermosonication) in acidic fruit juices. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2014, 7, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misono, T.; Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS); Abe, M. (Eds.) Measurement Techniques and Practices of Colloid and Interface Phenomena; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Pathare, B.; Opara, U.L.; Al-Said, F.A.-J. Colour Measurement and Analysis in Fresh and Processed Foods: A Review. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2013, 6, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Nakai, S. Hydrophobicity determined by a fluorescence probe method and its correlation with surface properties of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. 1980, 624, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, T.; Toma, S.J.; Nakai, S. Determination of SH- and SS- groups in some food proteins using Ellman’s reagent. J. Food Sci. 1974, 39, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M.; Jiang, H.; He, R.; Ma, H. Modification of rapeseed protein by ultrasound-assisted pH shift treatment: Ultrasonic mode and frequency screening, changes in protein solubility and structural characteristics. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 69, 105240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Ren, X.; Qu, W.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, H. The impact of ultrasound duration on the structure of β-lactoglobulin. J. Food Eng. 2021, 292, 110365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P.; Yang, Y.L. Effects of high intensity ultrasound modification on physicochemical property and water in myofibrillar protein gel. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhu, W.; Yi, J.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.; Lu, J.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Effects of sonication on the physicochemical and functional properties of walnut protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, J.; Yao, H.; Zhou, J.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H. Advances in renewable plant-derived protein source: The structure, physicochemical properties affected by ultrasonication. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 53, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jambrak, A.R.; Lelas, V.; Mason, T.J.; Kresic, G.; Badanjak, M. Physical properties of ultrasound treated soy proteins. J. Food Eng. 2009, 93, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, I.A.; Arreola, W.T.; Jimenez, G.M.S.; Suarez, J.C.R.; Onofre, J.E.J.; Felix, F.R.; Rios, E.M. Effect of ultrasound on physicochemical and foaming properties of protein concentrate from giant squid (Dosidicus gigas) mantle. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 121, 108954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Liu, X.; Ren, X.E.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhang, K. Swirling cavitation improves the emulsifying properties of commercial soy protein isolate. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 42, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Xiong, W.; Ge, M.; Xia, J.; Li, B.; Chen, Y. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on structure and foaming properties of pea protein isolate. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, L. Roles of four enzyme crosslinks on structural, thermal and gel properties of potato proteins. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 123, 109116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, H. The aggregation, structures and emulsifying properties of soybean protein isolate induced by ultrasound and acid. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Helikh, A.; Duan, Z. Determining the effect of ph-shifting treatment on the solubility of pumpkin seed protein isolate. East. -Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2021, 5, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, R.; Chena, Y.; Ma, W.; Qi, B.; Zhang, M. Effects of ultrasound on the structure and physical properties of black bean protein isolates. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, M.Y. Isolation and characterization of edestin from Cheungsam hempseed. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2011, 54, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.J.; Xiong, Y.L. Heating-aided pH shifting modifies hemp seed protein structure, cross-linking, and emulsifying properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10827–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, F.; Pan, S. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on physicochemical and functional properties of soybean glycinin at different ionic strengths. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 34, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.; Smith, B. The functional modification of legume proteins by ultrasonication: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.J.; Dong, M.; Tang, C.B.; Han, M.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Glycation-induced structural modification of myofibrillar protein and its relation to emulsifying properties. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 117, 108664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xu, J.; Gao, H.; Yu, Z.; Liang, J.; Mu, D.; Li, X.; Zhong, X.; Luo, S.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Effects of combined high hydrostatic pressure and pH-shifting pretreatment on the structure and emulsifying properties of soy protein isolates. J. Food Eng. 2021, 306, 110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Qin, L.; Wu, C.; Du, M. Ultrasound treatment improved the physicochemical characteristics of cod protein and enhanced the stability of oil-in-water emulsion. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraza, O.A.H.; Arreola, W.T.; Brauer, J.M.E.; Moroyoqui, F.J.C.; Figueroa, J.C.R.; Rios, E.M. Effect of pulsed ultrasound on the physicochemical characteristics and emulsifying properties of squid (Dosidicus gigas) mantle proteins. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hydrodynamic Diameter (µm) | Polydispersity Index (%) | Conductivity (mS/cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.048 ± 0.05 a | 55.90 ± 1.2 a | 0.958 ± 0.004 k |
| pH2 | 0.945 ± 0.021 b | 46.20 ± 0.14 b | 1.143 ± 0.010 i |
| pH4 | 0.920 ± 0.028 b | 42.90 ± 0.14 d | 1.302 ± 0.025 f |
| pH6 | 0.925 ± 0.007 b | 46.80 ± 0.42 b | 1.210 ± 0.006 h |
| pH8 | 0.905 ± 0.007 b | 42.30 ± 0.28 d | 1.025 ± 0.001 j |
| pH10 | 0.915 ± 0.007 b | 40.80 ± 0.42 e | 1.272 ± 0.026 fg |
| pH12 | 0.925 ± 0.007 b | 45.00 ± 0.28 c | 1.221 ± 0.016 gh |
| US_Only | 0.370 ± 0.014 def | 13.40 ± 0.14 g | 2.906 ± 0.021 b |
| US + pH2 | 0.340 ± 0.014 ef | 16.35 ± 0.21 f | 2.186 ± 0.006 e |
| US + pH4 | 0.33 ± 0.02 f | 12.10 ± 0.02 h | 2.275 ± 0.005 d |
| US + pH6 | 0.400 ± 0.014 d | 16.30 ± 0.28 f | 2.329 ± 0.005 c |
| US + pH8 | 0.380 ± 0.014 de | 14.30 ± 0.28 g | 2.962 ± 0.010 a |
| US + pH10 | 0.425 ± 0.021 d | 16.95 ± 0.21 f | 2.203 ± 0.003 e |
| US + pH12 | 0.510 ± 0.014 c | 17.30 ± 0.14 f | 2.169 ± 0.004 e |
| Free S-S (umol/g) | Solubility (ug/mL) | Turbidity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 32.8 ± 0.212 f | 1442.75 ± 0.35 f | 0.222 ± 0.001 e |
| pH2 | 24.45 ± 0.212 j | 1040.65 ± 0.21 n | 0.040 ± 0.001 k |
| pH4 | 20.80 ± 0.424 k | 1312.65 ± 0.35 l | 0.052 ± 0.001 j |
| pH6 | 27.70 ± 0.141 h | 1378.25 ± 0.35 h | 0.074 ± 0.000 i |
| pH8 | 36.65 ± 0.212 e | 1462.10 ± 0.28 d | 0.146 ± 0.001 h |
| pH10 | 42.35 ± 0.212 c | 1451.40 ± 0.14 a | 0.144 ± 0.001 h |
| pH12 | 13.55 ± 0.071 l | 1069.35 ± 0.07 m | 0.196 ± 0.001 f |
| US_Only | 40.68 ± 0.042 d | 1432.90 ± 0.14 g | 0.321 ± 0.001 b |
| US + pH2 | 28.65 ± 0.071 g | 1341.25 ± 0.35 k | 0.315 ± 0.001 b |
| US + pH4 | 25.50 ± 0.141 i | 1544.15 ± 0.35 h | 0.227 ± 0.003 e |
| US + pH6 | 41.61 ± 0.354 c | 1349.35 ± 0.35 j | 0.283 ± 0.002 d |
| US + pH8 | 58.72 ± 0.028 a | 1617.70 ± 0.14 b | 0.301 ± 0.001 c |
| US + pH10 | 46.54 ± 0.049 b | 1718.20 ± 0.28 e | 0.342 ± 0.001 a |
| US + pH12 | 11.25 ± 0.354 m | 1372.30 ± 0.28 i | 0.176 ± 0.002 g |
| L* | a* | b* | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 89.350 ± 0.78 e | −0.060 ± 0.01 bc | 4.110 ± 0.01 a |
| pH2 | 94.855 ± 0.01 b | −0.275 ± 0.04 ef | 1.450 ± 0.06 g |
| pH4 | 95.845 ± 0.05 a | −0.245 ± 0.02 e | 0.920 ± 0.01 h |
| pH6 | 93.130 ± 0.04 c | −0.320 ± 0.01 fg | 2.405 ± 0.04 c |
| pH8 | 93.655 ± 0.05 c | −0.160 ± 0.01 d | 1.635 ± 0.04 f |
| pH10 | 92.895 ± 0.02 c | −0.020 ± 0.00 b | 3.135 ± 0.02 b |
| pH12 | 92.015 ± 0.02 d | −0.105 ± 0.01 cd | 3.160 ± 0.03 b |
| US_Only | 83.140 ± 0.06 h | 0.295 ± 0.02 a | 3.075 ± 0.04 b |
| US + pH2 | 87.880 ± 0.04 f | −0.440 ± 0.01 h | 1.770 ± 0.03 e |
| US + pH4 | 88.385 ± 0.05 f | −0.360 ± 0.01 g | 1.370 ± 0.03 gh |
| US + pH6 | 86.120 ± 0.03 g | −0.475 ± 0.01 h | 1.460 ± 0.03 g |
| US + pH8 | 89.910 ± 0.04 e | −0.675 ± 0.02 i | 1.280 ± 0.01 h |
| US + pH10 | 82.740 ± 0.06 h | −0.690 ± 0.01 i | 2.020 ± 0.01 d |
| US + pH12 | 90.165 ± 0.09 e | −0.160 ± 0.03 d | 1.265 ± 0.02 h |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kahraman, O.; Petersen, G.E.; Fields, C. Physicochemical and Functional Modifications of Hemp Protein Concentrate by the Application of Ultrasonication and pH Shifting Treatments. Foods 2022, 11, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040587
Kahraman O, Petersen GE, Fields C. Physicochemical and Functional Modifications of Hemp Protein Concentrate by the Application of Ultrasonication and pH Shifting Treatments. Foods. 2022; 11(4):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040587
Chicago/Turabian StyleKahraman, Ozan, Greg E. Petersen, and Christine Fields. 2022. "Physicochemical and Functional Modifications of Hemp Protein Concentrate by the Application of Ultrasonication and pH Shifting Treatments" Foods 11, no. 4: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040587
APA StyleKahraman, O., Petersen, G. E., & Fields, C. (2022). Physicochemical and Functional Modifications of Hemp Protein Concentrate by the Application of Ultrasonication and pH Shifting Treatments. Foods, 11(4), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040587







