Artisanal Household Milk Pasteurization Is Not a Determining Factor in Structuring the Microbial Communities of Labneh Ambaris: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. pH Measruments
2.3. DNA Extraction, Metabarcoding Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analyses
3. Results
3.1. pH
3.2. Bacterial Communities
3.3. Fungal Communities
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mladenović, K.G.; Grujović, M.Ž.; Kiš, M.; Furmeg, S.; Tkalec, V.J.; Stefanović, O.D.; Kocić-Tanackov, S.D. Enterobacteriaceae in Food Safety with an Emphasis on Raw Milk and Meat. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 8615–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashtchi, P.; Bazmi, A.; Noshirvani, N.; Moosavy, M.H. Comparison of the Microbial, Physicochemical, and Sensorial Properties of Raw and Pasteurized Lighvan Cheeses during Ripening Time. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5527–5535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westling, M.; Danielsson-Tham, M.-L.; Jass, J.; Nilsen, A.; Öström, Å.; Tham, W. Contribution of Enterobacteriaceae to Sensory Characteristics in Soft Cheeses Made from Raw Milk. Procedia Food Sci. 2016, 7, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, N.; Ceniti, C.; Santoro, A.; Clausi, M.T.; Casalinuovo, F. Foodborne Pathogen Assessment in Raw Milk Cheeses. Int. J. Food Sci. 2020, 2020, 3616713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales-Barron, U.; Gonçalves-Tenório, A.; Rodrigues, V.; Cadavez, V. Foodborne Pathogens in Raw Milk and Cheese of Sheep and Goat Origin: A Meta-Analysis Approach. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 18, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novella-Rodríguez, S.; Veciana-Nogués, M.T.; Roig-Sagués, A.X.; Trujillo-Mesa, A.J.; Vidal-Carou, M.C. Evaluation of Biogenic Amines and Microbial Counts throughout the Ripening of Goat Cheeses from Pasteurized and Raw Milk. J. Dairy Res. 2004, 71, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.; Lee, S.; Choi, K.-H. Microbial Benefits and Risks of Raw Milk Cheese. Food Control 2016, 63, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.K.; Carstens, C.K.; Ramachandran, P.; Shazer, A.G.; Narula, S.S.; Reed, E.; Ottesen, A.; Schill, K.M. Metagenomics of Pasteurized and Unpasteurized Gouda Cheese Using Targeted 16S RDNA Sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, E.; Javidipour, I.; Tuncturk, Y. Volatile Compounds of Van Herby Cheeses Produced with Raw and Pasteurized Milks from Different Species. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4315–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, M.; Falentin, H.; Parayre, S.; Pawtowski, A.; Maillard, M.-B.; Thierry, A.; Mounier, J.; Coton, M.; Deutsch, S.-M. Linking Pélardon Artisanal Goat Cheese Microbial Communities to Aroma Compounds during Cheese-Making and Ripening. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 345, 109130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeluri, J.B.R.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; Sheehan, J.J.; Cotter, P.D. Sequencing of the Cheese Microbiome and Its Relevance to Industry. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zago, M.; Bardelli, T.; Rossetti, L.; Nazzicari, N.; Carminati, D.; Galli, A.; Giraffa, G. Evaluation of Bacterial Communities of Grana Padano Cheese by DNA Metabarcoding and DNA Fingerprinting Analysis. Food Microbiol. 2021, 93, 103613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida Brasiel, P.G.; Dutra Medeiros, J.; Barbosa Ferreira Machado, A.; Schuchter Ferreira, M.; Gouveia Peluzio, M.D.C.; Potente Dutra Luquetti, S.C. Microbial Community Dynamics of Fermented Kefir Beverages Changes over Time. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2021, 74, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenenboom, A.E.; Shindano, J.; Cheepa, N.; Smid, E.J.; Schoustra, S.E. Microbial Population Dynamics during Traditional Production of Mabisi, a Spontaneous Fermented Milk Product from Zambia: A Field Trial. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazou, M.; Grafakou, A.; Tsakalidou, E.; Georgalaki, M. Zooming Into the Microbiota of Home-Made and Industrial Kefir Produced in Greece Using Classical Microbiological and Amplicon-Based Metagenomics Analyses. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 621069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsak, N.; Taminiau, B.; Leclercq, M.; Nezer, C.; Crevecoeur, S.; Ferauche, C.; Detry, E.; Delcenserie, V.; Daube, G. Short Communication: Evaluation of the Microbiota of Kefir Samples Using Metagenetic Analysis Targeting the 16S and 26S Ribosomal DNA Fragments. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 3684–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi Khalil, R.; Yvon, S.; Couderc, C.; Belahcen, L.; Jard, G.; Sicard, D.; Bigey, F.; El Rammouz, R.; Abi Nakhoul, P.; Eutamène, H.; et al. Microbial Communities and Main Features of Labneh Ambaris, a Traditional Lebanese Fermented Goat’s Milk Product. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub, M.-J.; Bechara, P.; Habchi, M.; Hosri, R.; Akl, M.; Haj Hassan, S.; Abi Nakhoul, P. Raw Goat’s Milk Fermented Anbaris from Lebanon: Insights into the Microbial Dynamics and Chemical Changes Occurring during Artisanal Production, with a Focus on Yeasts. J. Dairy Res. 2022, 89, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Gastrow, L.; Madec, M.-N.; Chuat, V.; Lubac, S.; Morinière, C.; Lé, S.; Santoni, S.; Sicard, D.; Valence, F. Microbial Diversity Associated with Gwell, a Traditional French Mesophilic Fermented Milk Inoculated with a Natural Starter. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meola, M.; Rifa, E.; Shani, N.; Delbès, C.; Berthoud, H.; Chassard, C. DAIRYdb: A Manually Curated Reference Database for Improved Taxonomy Annotation of 16S RRNA Gene Sequences from Dairy Products. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.-H.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Jeppesen, T.S.; Schigel, D.; Kennedy, P.; Picard, K.; Glöckner, F.O.; Tedersoo, L.; et al. The UNITE Database for Molecular Identification of Fungi: Handling Dark Taxa and Parallel Taxonomic Classifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D259–D264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudié, F.; Auer, L.; Bernard, M.; Mariadassou, M.; Cauquil, L.; Vidal, K.; Maman, S.; Hernandez-Raquet, G.; Combes, S.; Pascal, G. FROGS: Find, Rapidly, OTUs with Galaxy Solution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariadassou, M. AffiliationExplorer 2021. Available online: https://shiny.migale.inrae.fr/app/affiliationexplorer (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Paës, C.; Gidenne, T.; Bébin, K.; Duperray, J.; Gohier, C.; Guené-Grand, E.; Rebours, G.; Bouchez, O.; Barilly, C.; Aymard, P.; et al. Early Introduction of Solid Feeds: Ingestion Level Matters More Than Prebiotic Supplementation for Shaping Gut Microbiota. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, A.; Alirezalu, K.; Damirchi, S.A.; Hesari, J.; Papademas, P.; Domínguez, R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Yaghoubi, M. Effect of Pasteurization and Ripening Temperature on Chemical and Sensory Characteristics of Traditional Motal Cheese. Fermentation 2020, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grappin, R.; Beuvier, E. Possible Implications of Milk Pasteurization on the Manufacture and Sensory Quality of Ripened Cheese. Int. Dairy J. 1997, 7, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, L.; Valence, F.; Mounier, J. Diversity and Control of Spoilage Fungi in Dairy Products: An Update. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcenserie, V.; Taminiau, B.; Delhalle, L.; Nezer, C.; Doyen, P.; Crevecoeur, S.; Roussey, D.; Korsak, N.; Daube, G. Microbiota Characterization of a Belgian Protected Designation of Origin Cheese, Herve Cheese, Using Metagenomic Analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6046–6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, M.G.; Häni, J.P.; Gruskovnjak, J.; Schaeren, W.; Wechsler, D. Characterisation of the Non-Starter Lactic Acid Bacteria (NSLAB) of Gruyère PDO Cheese. Le Lait 2006, 86, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S. Microbiological Considerations: Pasteurized Milk. Int. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 10, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, A.J.; Yap, M.; Crispie, F.; Feehily, C.; Hill, C.; Cotter, P.D. Microbiome-Based Environmental Monitoring of a Dairy Processing Facility Highlights the Challenges Associated with Low Microbial-Load Samples. Npj. Sci. Food 2021, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidou, S.; Pavlou, E.; Pasentsis, K.; Rhoades, J.; Likotrafiti, E.; Argiriou, A. Microbial Profiles of Greek PDO Cheeses Assessed with Amplicon Metabarcoding. Food Microbiol. 2021, 99, 103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, Á.R.; Seseña, S.; Garzón, A.; Arias, R. Factors Affecting Levels of Airborne Bacteria in Dairy Farms: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich-Wyder, M.-T.; Arias-Roth, E.; Jakob, E. Cheese Yeasts. Yeast 2019, 36, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, C.D.; Sheehan, J.J.; Wilkinson, M.G.; Auty, M.A.E. Growth and Location of Bacterial Colonies within Dairy Foods Using Microscopy Techniques: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, V.P.P.; Kabuki, D.Y. Formation and Dispersal of Biofilms in Dairy Substrates. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2019, 72, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Singh, D.; Avadhanula, M.; Marka, S. Development and Control of Bacterial Biofilms on Dairy Processing Membranes. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Jara, M.J.; Ilabaca, A.; Vega, M.; García, A. Biofilm Forming Lactobacillus: New Challenges for the Development of Probiotics. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korcz, E.; Varga, L. Exopolysaccharides from Lactic Acid Bacteria: Techno-Functional Application in the Food Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prete, R.; Alam, M.K.; Perpetuini, G.; Perla, C.; Pittia, P.; Corsetti, A. Lactic Acid Bacteria Exopolysaccharides Producers: A Sustainable Tool for Functional Foods. Foods 2021, 10, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciata, M.; Gaglio, R.; Scatassa, M.L.; Sala, G.; Cardamone, C.; Palmeri, M.; Moschetti, G.; La Mantia, T.; Settanni, L. Formation and Characterization of Early Bacterial Biofilms on Different Wood Typologies Applied in Dairy Production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02107-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montel, M.-C.; Buchin, S.; Mallet, A.; Delbes-Paus, C.; Vuitton, D.A.; Desmasures, N.; Berthier, F. Traditional Cheeses: Rich and Diverse Microbiota with Associated Benefits. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 177, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psoni, L.; Tzanetakis, N.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E. Characteristics of Batzos Cheese Made from Raw, Pasteurized and/or Pasteurized Standardized Goat Milk and a Native Culture. Food Control 2006, 17, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
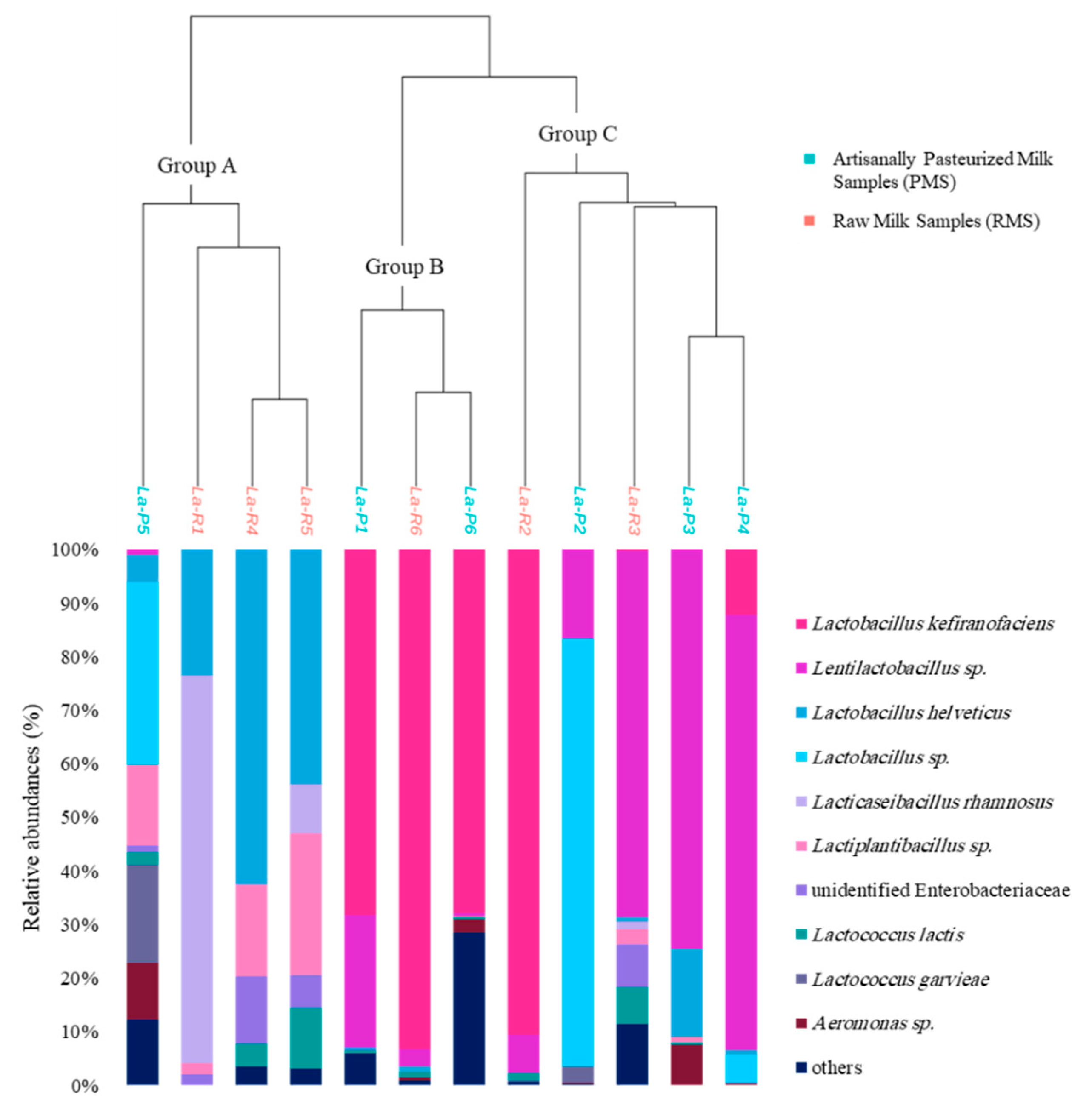
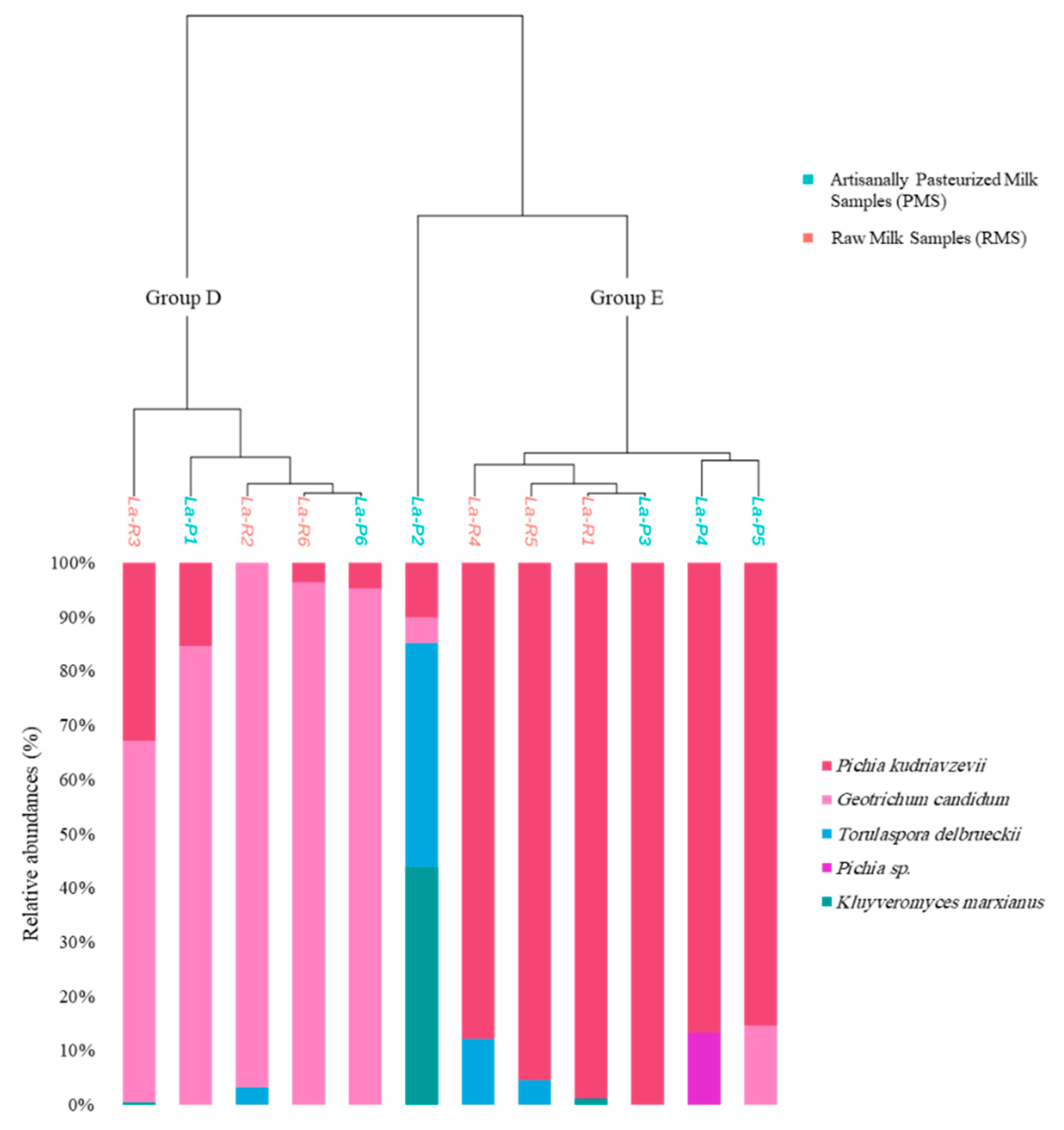
| Sample Code | Milk Type | pH Values | Bacterial Richness Indices | Bacterial Shannon Indices | Fungal Richness Indices | Fungal Shannon Indices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La-R1 | RMS | 3.50 ± 0.02 | 6 | 1.03 | 3 | 0.07 |
| La-R2 | RMS | 3.01 ± 0.02 | 12 | 0.41 | 2 | 0.15 |
| La-R3 | RMS | 3.99 ± 0.02 | 13 | 1.51 | 3 | 0.66 |
| La-R4 | RMS | 3.53 ± 0.03 | 10 | 1.16 | 3 | 0.37 |
| La-R5 | RMS | 3.58 ± 0.01 | 10 | 1.49 | 3 | 0.18 |
| La-R6 | RMS | 3.33 ± 0.02 | 11 | 0.38 | 2 | 0.16 |
| La-P1 | PMS | 3.54 ± 0.01 | 13 | 1.31 | 2 | 0.44 |
| La-P2 | PMS | 3.73 ± 0.01 | 13 | 0.74 | 4 | 1.09 |
| La-P3 | PMS | 3.66 ± 0.01 | 11 | 1.4 | 1 | 0.00 |
| La-P4 | PMS | 3.46 ± 0.01 | 13 | 0.84 | 2 | 0.39 |
| La-P5 | PMS | 3.66 ± 0.01 | 12 | 1.97 | 2 | 0.41 |
| La-P6 | PMS | 3.43 ± 0.01 | 7 | 0.78 | 3 | 0.20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abi Khalil, R.; Couderc, C.; Yvon, S.; Jard, G.; Sicard, D.; Bigey, F.; El Rammouz, R.; Abi Nakhoul, P.; Eutamène, H.; Tormo, H.; et al. Artisanal Household Milk Pasteurization Is Not a Determining Factor in Structuring the Microbial Communities of Labneh Ambaris: A Pilot Study. Foods 2022, 11, 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233874
Abi Khalil R, Couderc C, Yvon S, Jard G, Sicard D, Bigey F, El Rammouz R, Abi Nakhoul P, Eutamène H, Tormo H, et al. Artisanal Household Milk Pasteurization Is Not a Determining Factor in Structuring the Microbial Communities of Labneh Ambaris: A Pilot Study. Foods. 2022; 11(23):3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233874
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbi Khalil, Reine, Christel Couderc, Sophie Yvon, Gwenaelle Jard, Delphine Sicard, Frédéric Bigey, Rabih El Rammouz, Pierre Abi Nakhoul, Hélène Eutamène, Hélène Tormo, and et al. 2022. "Artisanal Household Milk Pasteurization Is Not a Determining Factor in Structuring the Microbial Communities of Labneh Ambaris: A Pilot Study" Foods 11, no. 23: 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233874
APA StyleAbi Khalil, R., Couderc, C., Yvon, S., Jard, G., Sicard, D., Bigey, F., El Rammouz, R., Abi Nakhoul, P., Eutamène, H., Tormo, H., & Ayoub, M.-J. (2022). Artisanal Household Milk Pasteurization Is Not a Determining Factor in Structuring the Microbial Communities of Labneh Ambaris: A Pilot Study. Foods, 11(23), 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233874








