Rice Quality-Related Metabolites and the Regulatory Roles of Key Metabolites in Metabolic Pathways of High-Quality Semi-Glutinous japonica Rice Varieties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Growth Conditions of Plants
2.2. Detection of Rice Quality Traits
2.3. Sample Metabolite Obtaining
2.4. LC–MS/MS Analysis
2.5. Differential Metabolite Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rice Quality Traits of Three Semi-Glutinous japonica Rice Varieties
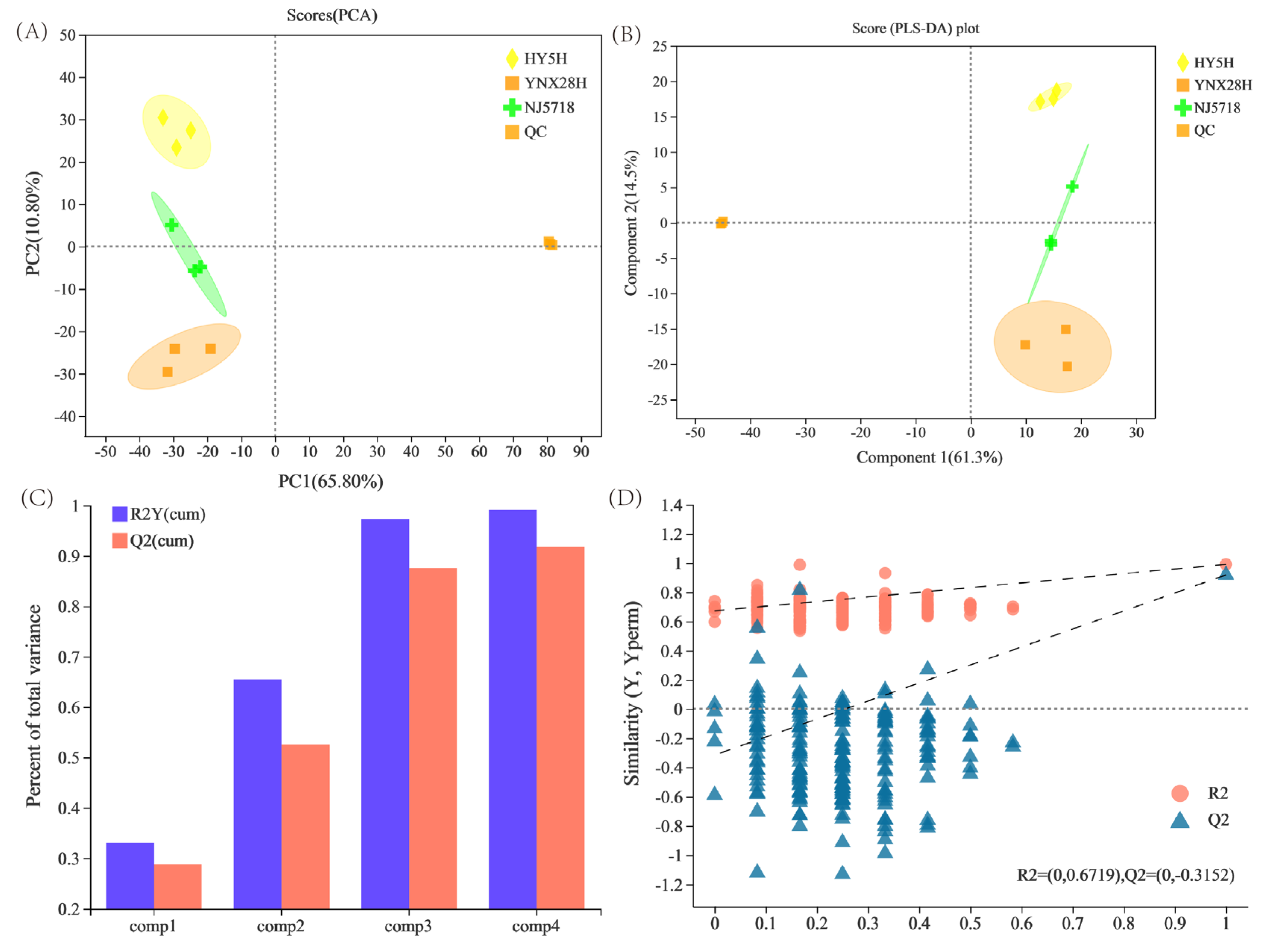
3.2. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
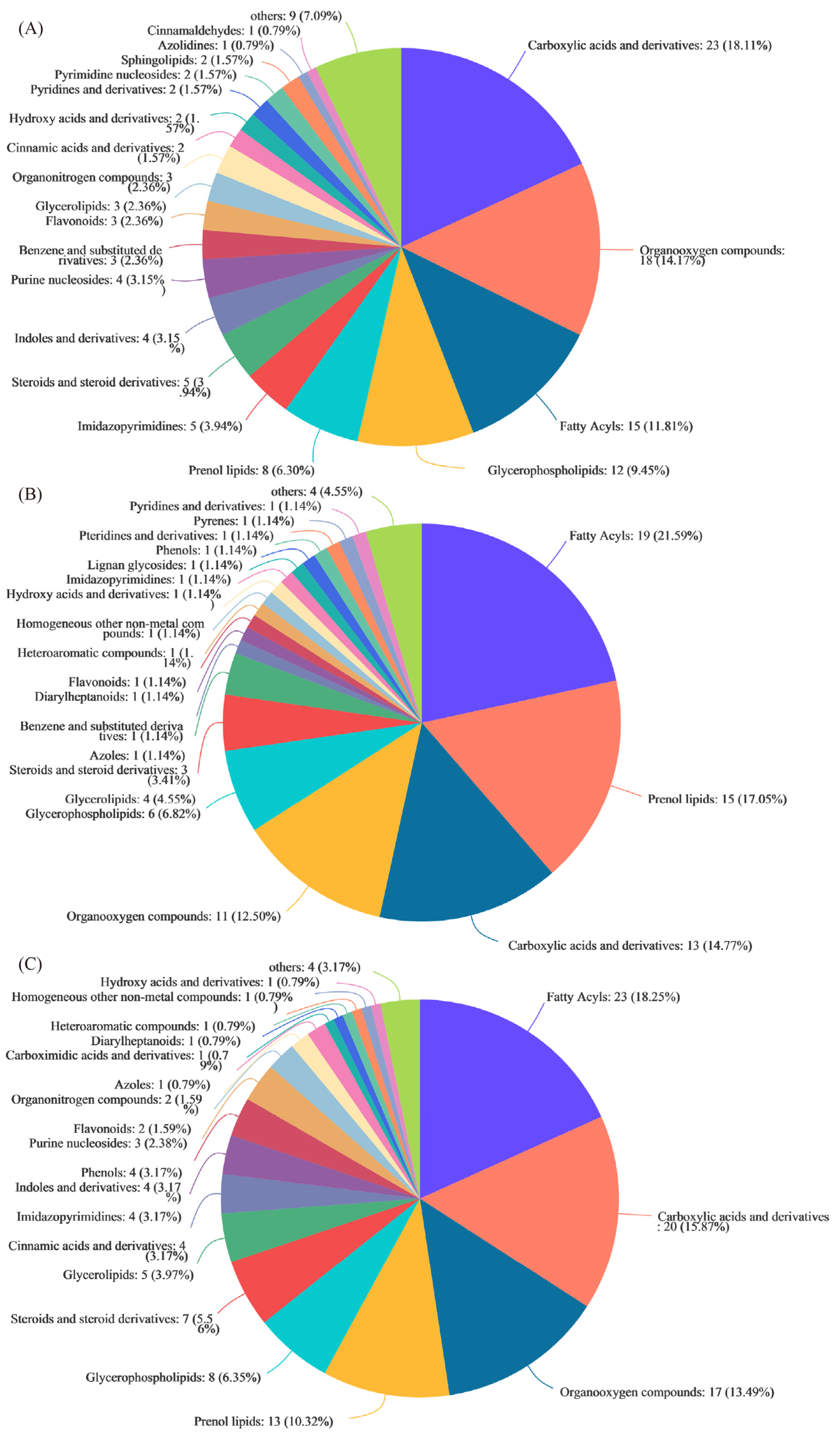
3.3. Metabolic Profiling
3.4. KEGG Pathways
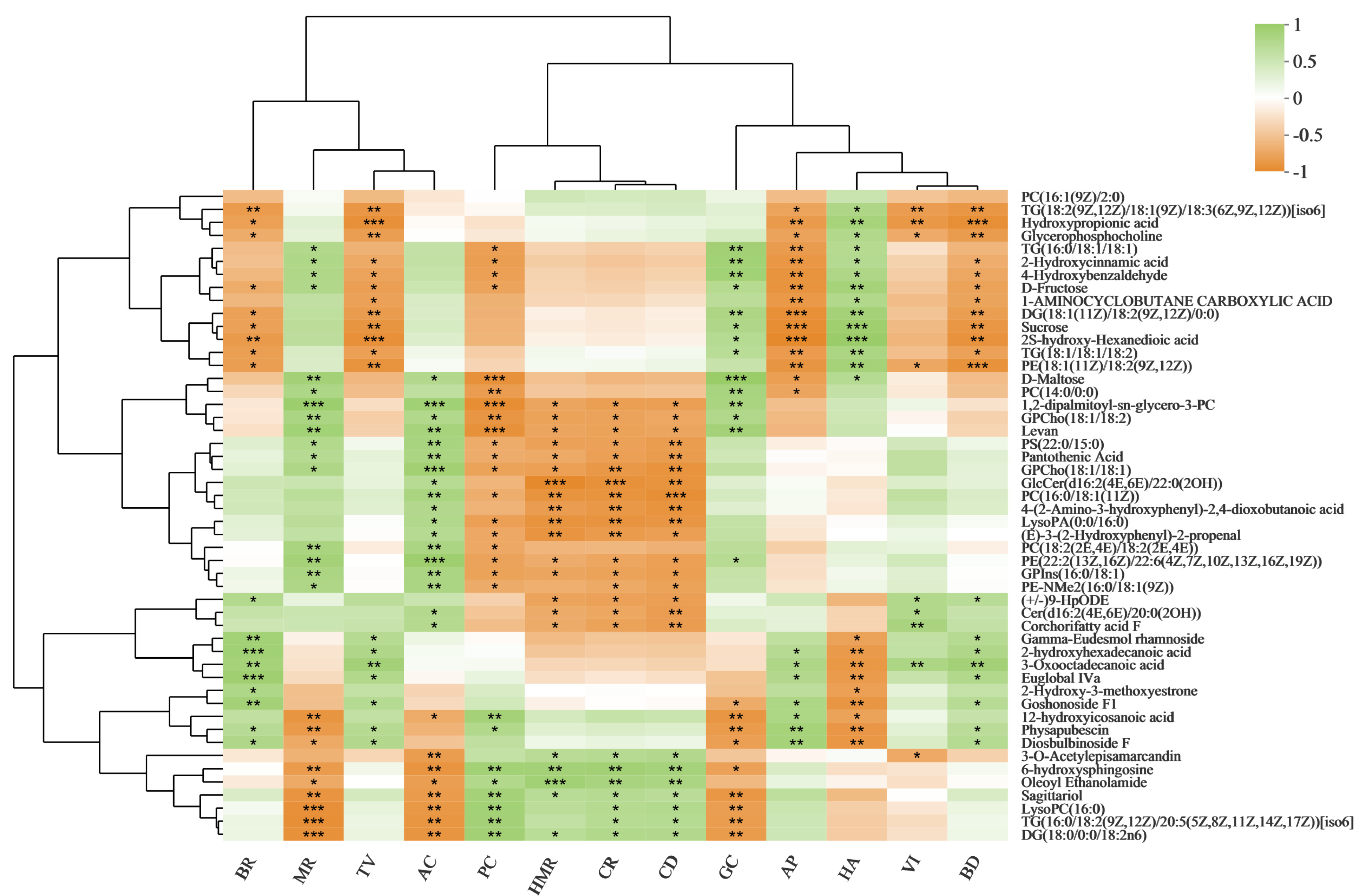
3.5. Correlation Analysis between Rice Quality Traits and Metabolite Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wei, X.; Chen, T.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, L.; Yao, S.; Zhou, L.; et al. Development and application of quality standard for semi-glutinous japonica rice with good taste. Jiangsu J. Agr. Sci. 2022, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, N.; Zhang, J.; Fang, S.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H. Effects of temperature and solar radiation on yield of good eating-quality rice in the lower reaches of the Huai River Basin, China. J. Integr. Agr. 2021, 20, 1762–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Xu, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, J.; Zhang, H. Recent research advances in the development of chalkiness and transparency in rice. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Yao, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, L.; Wei, X.; et al. Rapid breeding of new Semi-glutinous japonica rice varieties with good eating quality by crossing between sister lines. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2021, 35, 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, D.; Chen, X.; Ma, Z.; Ma, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H. Quality characteristics of semi-glutinous japonica rice cultivated in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 3712–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Yeon, S.; Daliri, E.B.M.; Chen, X.; Chelliah, R.; Oh, D.H. Untargeted metabolomics of Korean fermented brown rice using UHPLC Q-TOF MS/MS reveal an abundance of potential dietary antioxidative and stress-reducing compounds. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Huang, D.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, L.; Pan, Y.; Gong, R.; Zhou, S. Comparisons of metabolic profiles for carbohydrates, amino acids, lipids, fragrance and flavones during grain development in Indica rice cultivars. Rice Sci. 2022, 29, 155–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kusano, M.; Yang, Z.; Okazaki, Y.; Nakabayashi, R.; Fukushima, A.; Saito, K. Using metabolomic approaches to explore chemical diversity in rice. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uawisetwathana, U.; Karoonuthaisiri, N. Metabolomics for rice quality and traceability: Feasibility and future aspects. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 28, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Peng, M.; Gong, L.; Gao, Y.; Wan, J.; Wang, S.; Shi, L.; Zhou, B.; Li, Z.; et al. Comparative and parallel genome-wide association studies for metabolic and agronomic traits in cereals. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Khan, A.; Li, P.; Cao, C. Metabolomic analysis reveals metabolites and pathways involved in grain quality traits of high-quality rice cultivars under a dry cultivation system. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, F.C.; Broeckling, C.D. Metabolomics for rice grain quality. In The Future of Rice Demand: Quality Beyond Productivity; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 495–531. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhan, L.; Yan, Y.; Cao, L.; Niu, F.; Zhu, J.; Hu, J.; Wu, S. Identification of a new giant emrbryo allele, and integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis of giant embryo development in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 697889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Shang, B.; Yang, W.; Duan, X.; Sun, H. Metabolomic analysis reveals insights into deterioration of rice quality during storage. Foods 2022, 11, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Xie, M.; Hu, C.; Shi, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, J. Identification of the biochemical characteristics of developing giant embryo rice grains using non-targeted metabolomics. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 85, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Sun, C.; Shi, H.; Cai, S.; Xie, H.; Liu, F.; Zhu, J. Analysis of related metabolites affecting taste values in rice under different nitrogen fertilizer amounts and planting densities. Foods 2022, 11, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Sun, C.; Li, A.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhou, N.; Wei, H.; Liu, B.; et al. Metabolomics and biochemical analyses revealed metabolites important for the antioxidant properties of purple glutinous rice. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 133080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, A.; Lu, W.; Hu, J.; Zhou, N.; Wei, H.; et al. The key metabolites associated with nutritional components in purple glutinous rice. Food Res. Int. 2022, 160, 111686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, Q. Genetic control of grain appearance quality in rice. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 60, 108014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Fang, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhen, X.; Shao, Y. Characteristics of high-quality rice varieties and taste sensory evaluation values in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2022, 55, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, D.; Bal, S. Cooking quality and instrumental textural attributes of cooked rice for different milling fractions. J. Food Eng. 2006, 73, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Qian, Q.; Liu, Q.; Yan, M.; Liu, X.; Yan, C.; Liu, G.; Gao, Z.; Tang, S.; Zeng, D.; et al. Allelic diversities in rice starch biosynthesis lead to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21760–21765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Gilbert, R.G. Starch molecular structure: The basis for an improved understanding of cooked rice texture. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 195, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Reyes, I.; Diebold, L.P.; Kong, H.; Schieber, M.; Huang, H.; Hensley, C.T.; Mehta, M.M.; Wang, T.; Santos, J.H.; Woychik, R.; et al. TCA cycle and mitochondrial membrane potential are necessary for diverse biological functions. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Beard, K.F.; Swart, C.; Bergmann, S.; Krahnert, I.; Nikoloski, Z.; Graf, A.; Ratcliffe, R.G.; Sweetlove, L.J.; Fernie, A.R.; et al. Protein-protein interactions and metabolite channelling in the plant tricarboxylic acid cycle. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Varieties | BR | MR | HMR | CR | CD | GC | AP | HA | VI | BD | TV | AC | PC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HY5H | 84.88% b | 71.43% a | 43.49% c | 22.07 c | 5.97 c | 86.67 a | 6.23 b | 6.67 a | 6.23 a | 6.17 b | 67.17 b | 13.78% a | 7.93% b |
| YNX28H | 85.51% a | 69.00% b | 50.56% b | 38.77 b | 13.73 b | 64.00 b | 7.53 a | 6.07 b | 6.47 a | 6.97 a | 72.47 a | 11.50% b | 8.47% a |
| NJ5718 | 84.59% b | 69.26% b | 60.81% a | 57.32 a | 23.18 a | 70.33 b | 6.43 b | 6.67 a | 5.70 a | 5.93 b | 66.07 b | 10.74% b | 8.47% a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Li, A.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, N.; Xiong, Q. Rice Quality-Related Metabolites and the Regulatory Roles of Key Metabolites in Metabolic Pathways of High-Quality Semi-Glutinous japonica Rice Varieties. Foods 2022, 11, 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223676
Zhu J, Li A, Sun C, Zhang J, Hu J, Wang S, Zhou N, Xiong Q. Rice Quality-Related Metabolites and the Regulatory Roles of Key Metabolites in Metabolic Pathways of High-Quality Semi-Glutinous japonica Rice Varieties. Foods. 2022; 11(22):3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223676
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jinyan, Ao Li, Changhui Sun, Jiao Zhang, Jinlong Hu, Shuai Wang, Nianbing Zhou, and Qiangqiang Xiong. 2022. "Rice Quality-Related Metabolites and the Regulatory Roles of Key Metabolites in Metabolic Pathways of High-Quality Semi-Glutinous japonica Rice Varieties" Foods 11, no. 22: 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223676
APA StyleZhu, J., Li, A., Sun, C., Zhang, J., Hu, J., Wang, S., Zhou, N., & Xiong, Q. (2022). Rice Quality-Related Metabolites and the Regulatory Roles of Key Metabolites in Metabolic Pathways of High-Quality Semi-Glutinous japonica Rice Varieties. Foods, 11(22), 3676. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223676





