Occurrence and Estimated Daily Intake of Cortisone and Cortisol in Aquatic Food from China TDS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Zebrafish Culture
2.3. Killing of Zebrafish
2.4. Sample Collection
2.4.1. Samples from Local Market
2.4.2. Aquatic Foods Samples from TDS
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.6. LC-MS/MS Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Validation
3.2. Concentrations of Cortisone and Cortisol in Marine Fish and Freshwater Fish
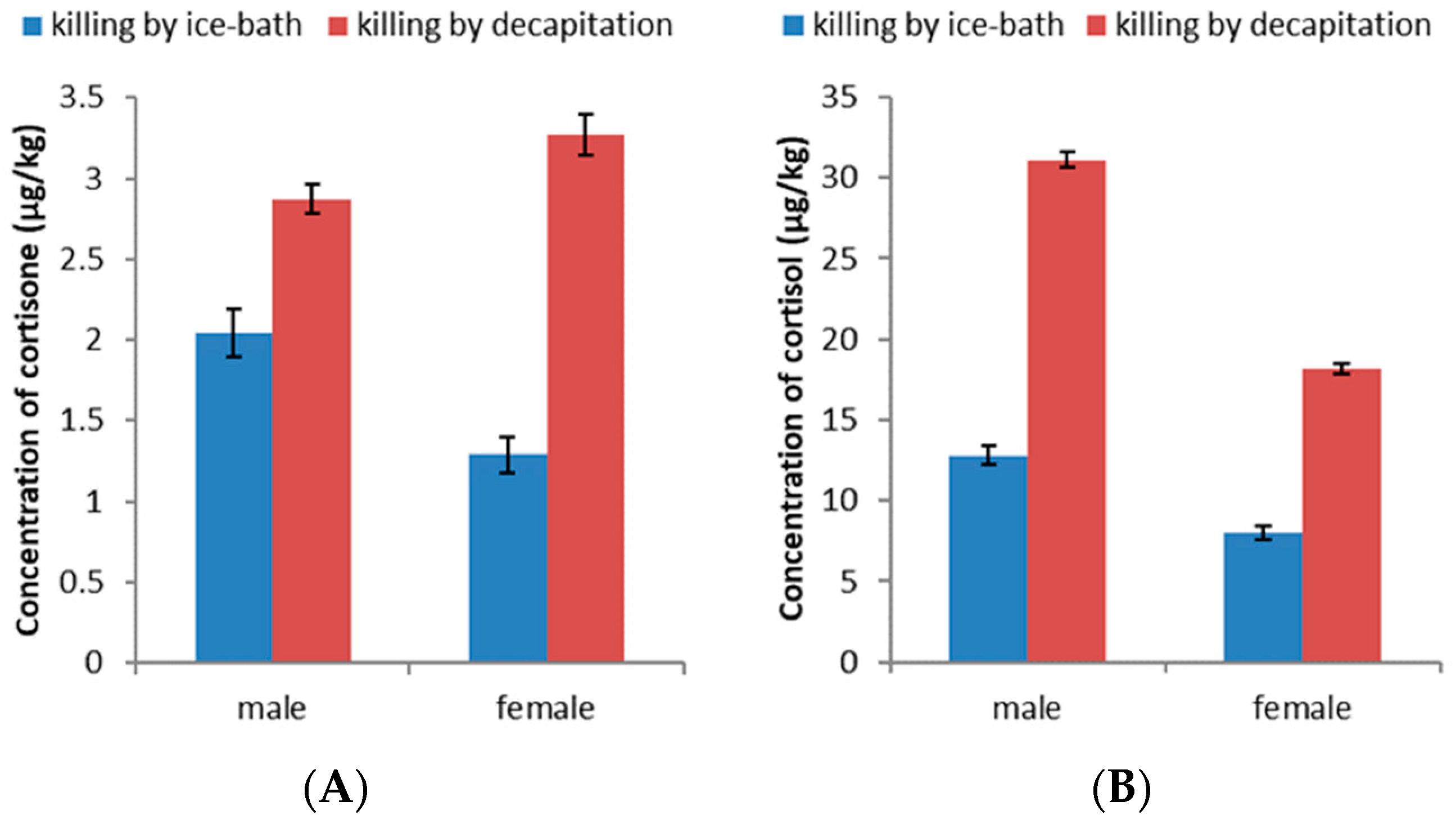
3.3. Effect of Killing Methods on the Levels of Cortisone and Cortisol in Zebrafish
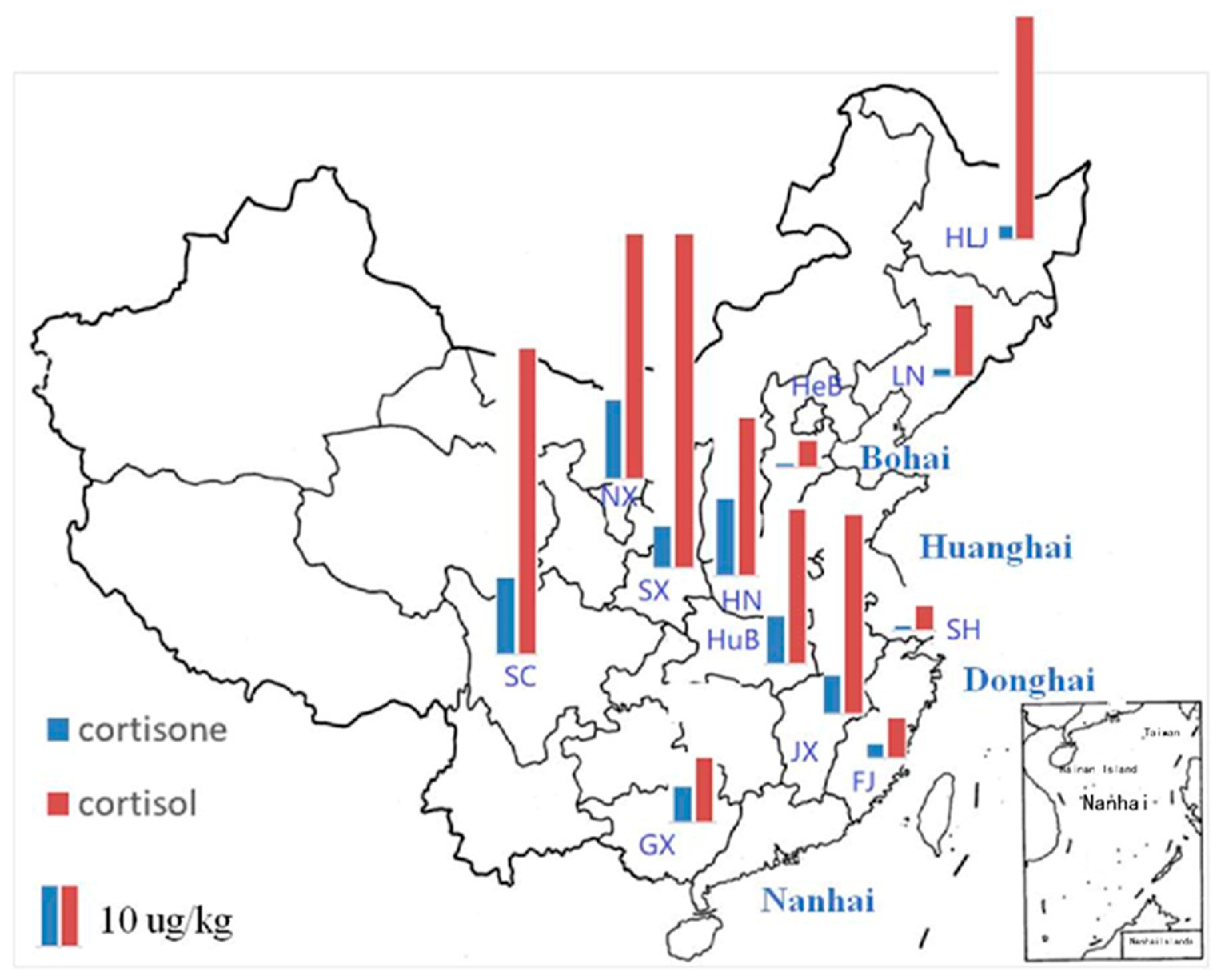
3.4. Occurrence of Cortisone and Cortisol in Aquatic Foods in the TDS
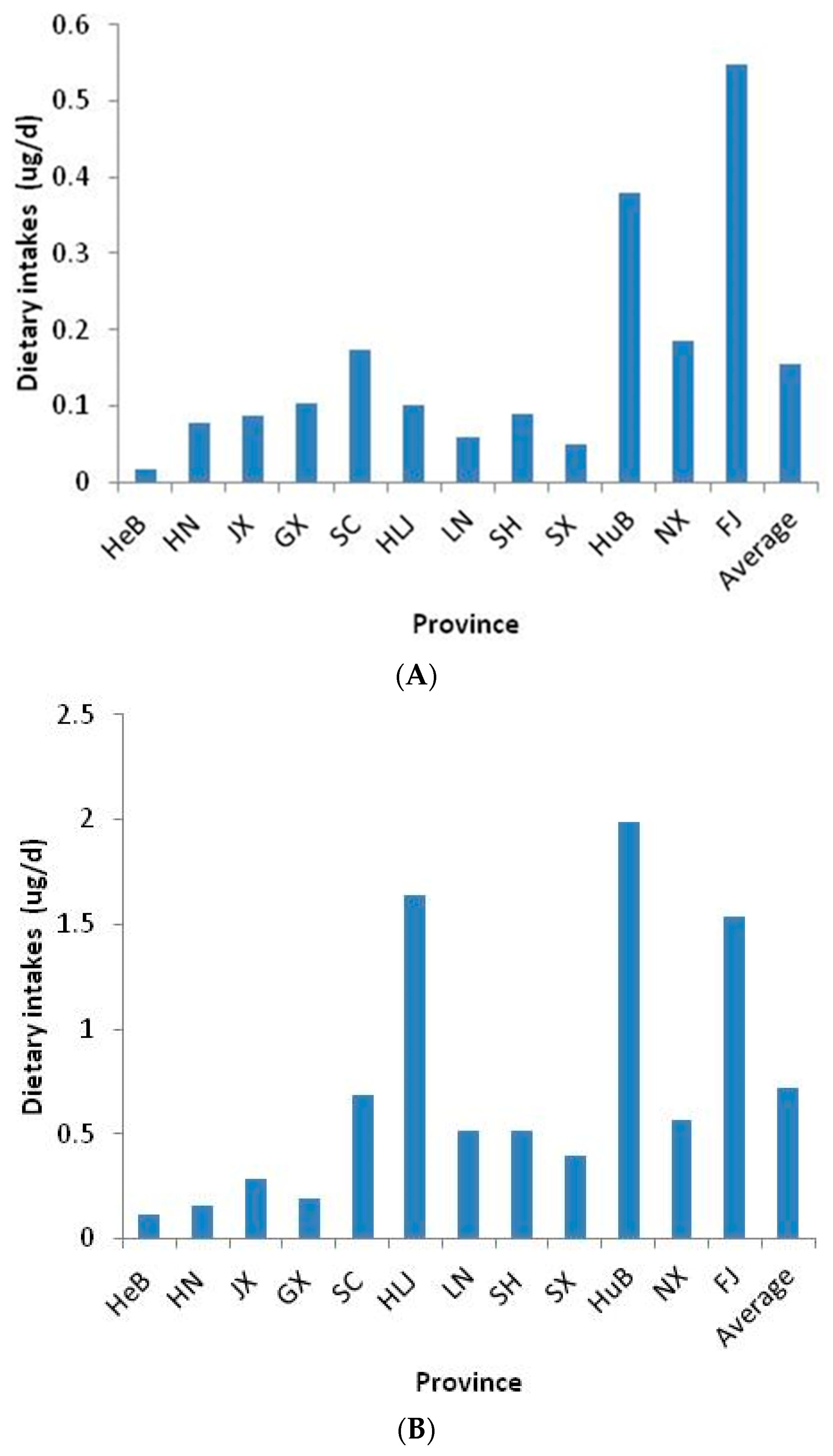
3.5. Dietary Exposure to Cortisone and Cortisol in Chinese Adults through Aquatic Foods
3.6. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andersen, H.R.; Andersson, A.M.; Arnold, S.F.; Autrup, H.; Barfoed, M.; Beresford, N.A.; Bjerregaard, P.; Christiansen, L.B.; Gissel, B.; Hummel, R.; et al. Comparison of short-term estrogenicity tests for identification of hormone-disrupting chemicals. Environ. Health Perspect Suppl. 1999, 107, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, A.; Skakkebaek, N. Exposure to exogenous estrogens in food: Possible impact onhuman development and health. Eur. J. Endoceinol. 1999, 140, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arikan, O.A.; Rice, C.; Codling, E. Occurrence of antibiotics and hormones in a major agricultural watershed. Desalination 2008, 226, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng’ayo, M.O.; Bukusi, E.; Morrow, R.A.; Rowhani-Rahbar, A.; Obare, B.A.; Friedrich, D.; Holmes, K.K. Sexual and demographic determinants for herpes simplex virus type 2 among fishermen along Lake Victoria, Kenya. Sex. Transm Infect. 2008, 84, 140–142. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects ofglucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol. Cell Endocronol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, C.M.; Strehl, C.; van der Goes, M.C.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Buttgereit, F. Glucocorticoids. Best Pract. Res. 2011, 25, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varas-Lorenzo, C.; Rodriguez, L.A.G.; Maguire, A.; Castellsague, J.; Perez-Gutthann, S. Use of oral corticosteroids and the risk of acute myocardial infarction. Atherosclerosis 2007, 192, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, S.J.; Couto, L.; Cohen, V.; Lalazar, Y.; Makotkine, I.; Williams, N.; Yehuda, R. Goldstein RZ and Geer EB, Glucocorticoid Regulation of Food-Choice Behavior in Humans: Evidence from Cushing’s Syndrome. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.E.; Thurston, L.M.; Fowkes, R.C. Hormonal Regulation of Glucocorticoid Inactivation and Reactivation in αT3-1 and LβT2 Gonadotroph Cells. Biology 2019, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, J.C.; O Halloran, A.M.; Kenny, R.A. The Association Between Hair Cortisol, Hair Cortisone, and Cognitive Function in a Population-Based Cohort of Older Adults: Results from The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Lacorn, M.; Steinhart, H. Natural occurrence of steroid hormones in food. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyon, A.; Cai, J.Z.; Kraehenbuehl, K.; Hartmann, C.; Shao, B.; Mottier, P. Determination of steroid hormones in bovine milk by LC-MS/MS and their levels in Swiss Holstein cow milk. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2016, 33, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shao, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Duan, H. Determination of the residues of 50 anabolic hormones in muscle, milk and liver by very-high-pressure liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Qi, Z.H.; Chen, H.; Hao, Q.W.; Hu, Y.X.; Zhao, J.L.; Ying, G.G. Steroid bioaccumulation profiles in typical freshwater aquaculture environments of South China and their human health risks via fish consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Duan, H.; Wu, Y.; Shao, B. Bisphenol A and nonylphenol in foodstuffs: Chinese dietary exposure from the 2007 total diet study and infant health risk from formulas. Food Chem. 2015, 67, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X. The Fourth China Total Diet Study; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, T.; Fu, H.; Huang, D. Rapid Screening of 16 Hormone Residues in Aquatic Products by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 337–343. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Luo, H.; Lai, G.; Huang, X.; Wu, H. Screening of Drug Residues of Aquatic Products in Guangzhou. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2015, 4, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.A.; DuRant, S.E.; Beck, M.L.; Ray, W.K.; Helm, R.F.; Romero, L.M. Cortisol is the predominant glucocorticoid in the giant paedomorphic hellbender salamander (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis). Gen. Comp. Endocr. 2020, 285, 113267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Abbate, J.M.; Iaria, C.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; D’Amico, R.; Fusco, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Environmental Risk Assessment of Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate and Tocilizumab Mixture in Zebrafish Early Life Stage (Danio rerio). Toxics 2022, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paola, D.; Natale, S.; Iaria, C.; Crupi, R.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Spanò, N.; Gugliandolo, E.; Peritore, A.F. Environmental Co-Exposure to Potassium Perchlorate and Cd Caused Toxicity and Thyroid Endocrine Disruption in Zebrafish Embryos and Larvae (Danio rerio). Toxics 2022, 10, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, G.; Park, E.; Ryu, J.H.; Jung, J.W.; Park, S.J.; Kim, G.; Lee, S. Hydrangeae Dulcis Folium Attenuates Physical Stress by Supressing ACTH-Induced Cortisol in Zebrafish. Chin. J. Integr Med. 2020, 26, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijanowski, L.; Jurecka, P.; Irnazarow, I.; Kepka, M.; Szwejser, E.; Verburg-van, K.; Chadzinska, M. Activity of the hypothalamus–pituitary–interrenal axis (HPI axis) and immune response in carp lines with different susceptibility to disease. Fish. Physiol Biochem. 2015, 41, 1261–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA; FAO; WHO. Towards a harmonised total diet study approach: A guidance document. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2450–2516. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y. The 30 years’ evolution of China total diet study. Chin. J. Food Hyg. 2019, 31, 403–406. [Google Scholar]
| Sample | Fish | Cortisone | Cortisol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine fish | Detection rate | 25/26 | 26/26 |
| Maximum (μg/kg) | 3.32 | 13.55 | |
| Mean (μg/kg) | 0.76 | 3.32 | |
| Median (μg/kg) | 0.53 | 2.19 | |
| Freshwater fish | Detection rate | 29/29 | 29/29 |
| Maximum (μg/kg) | 33.01 | 123.50 | |
| Mean (μg/kg) | 14.59 | 69.15 | |
| Median (μg/kg) | 11.34 | 62.10 | |
| Total | Mean (μg/kg) | 8.05 | 38.03 |
| Compound | Province | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeB | HN | JX | GX | SC | HLJ | LN | SH | SX | HuB | NX | FJ | |
| cortisone | 0.72 | 15.22 | 9.44 | 7.04 | 15.22 | 2.68 | 1.62 | 0.86 | 8.23 | 7.50 | 15.75 | 2.80 |
| cortisol | 5.34 | 31.14 | 30.68 | 12.8 | 60.38 | 44.02 | 14.25 | 4.90 | 66.13 | 39.38 | 48.56 | 7.84 |
| PLADs | Food Name | Consumption a (g) | Consumption of MF b (g) | Consumption of FF c (g) | Percent of FF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeB | Ribbon fish | 16.97 | 16.97 | 2.12 | 9.7 |
| Prawn | 2.74 | ||||
| Carp | 2.12 | ||||
| Subtotal | 21.82 | ||||
| HN | Crucian carp | 4.42 | 0.39 | 4.42 | 87.5 |
| Ribbon fish | 0.39 | ||||
| Small shrimp soup | 0.24 | ||||
| Subtotal | 5.05 | ||||
| JX | Braised catfish | 1.49 | 0 | 7.66 | 83.1 |
| Brsised carp | 5.37 | ||||
| Braised fish fillet | 1.56 | ||||
| Braised yellow fillet | 0.80 | ||||
| subtotal | 9.22 | ||||
| GX | Grass carp | 8.05 | 4.46 | 10.20 | 69.6 |
| Rice field eel | 2.15 | ||||
| Ribbon fish | 4.46 | ||||
| Subtotal | 14.65 | ||||
| SC | Crucian carp | 9.63 | 0 | 11.38 | 100 |
| Grass carp | 1.75 | ||||
| subtotal | 11.38 | ||||
| HLJ | Carp | 35.14 | 2.18 | 35.14 | 94.2 |
| Ribbon fish | 2.18 | ||||
| Subtotal | 37.32 | ||||
| LN | Sea crab | 8.1 | 15.5 | 3.8 | 10.6 |
| Squid | 6.3 | ||||
| Ribbon fish | 5.7 | ||||
| Prawn | 5.4 | ||||
| Carp | 3.8 | ||||
| Scomber | 3.5 | ||||
| Salted fish | 3.1 | ||||
| Subtotal | 35.88 | ||||
| SH | Boiled shrimp with salt | 16.63 | 29.91 | 12.81 | 12.2 |
| Braised flat fish | 29.91 | ||||
| Braised shredded eel | 12.81 | ||||
| Steamed prawn | 23.41 | ||||
| Braised ribbon fish | 15.8 | ||||
| Srir-fried spiral shell | 5.79 | ||||
| Subtotal | 104.35 | ||||
| SX | Crap | 4.93 | 0 | 6.02 | 100 |
| Grass carp | 1.10 | ||||
| Subtotal | 6.02 | ||||
| HuB | Silver carp | 27.69 | 0 | 36.99 | 73.1 |
| Bream fish | 9.3 | ||||
| Lobster | 13.60 | ||||
| Subtotal | 50.58 | ||||
| NX | Carp | 9.69 | 0 | 11.70 | 100 |
| Crucian carp | 2.01 | ||||
| Subtotal | 11.70 | ||||
| FJ | Razor clam | 80.03 | 187.28 | 8.64 | 4.4 |
| Long surf clam | 13.48 | ||||
| Ribbon fish | 15.92 | ||||
| Little yellow croaker | 34.45 | ||||
| cuttlefish | 13.96 | ||||
| Sea pomfret | 14.10 | ||||
| Sea shrimp | 15.33 | ||||
| Grass carp | 8.64 | ||||
| Subtotal | 195.92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; Yin, J.; Yang, Y.; Shao, B.; Zhang, J. Occurrence and Estimated Daily Intake of Cortisone and Cortisol in Aquatic Food from China TDS. Foods 2022, 11, 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213481
Yang Y, Shi J, Yin J, Yang Y, Shao B, Zhang J. Occurrence and Estimated Daily Intake of Cortisone and Cortisol in Aquatic Food from China TDS. Foods. 2022; 11(21):3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213481
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yi, Jiachen Shi, Jie Yin, Yunjia Yang, Bing Shao, and Jing Zhang. 2022. "Occurrence and Estimated Daily Intake of Cortisone and Cortisol in Aquatic Food from China TDS" Foods 11, no. 21: 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213481
APA StyleYang, Y., Shi, J., Yin, J., Yang, Y., Shao, B., & Zhang, J. (2022). Occurrence and Estimated Daily Intake of Cortisone and Cortisol in Aquatic Food from China TDS. Foods, 11(21), 3481. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213481






