Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Gelsemium Alkaloids in Honey
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Standard Solutions
2.3. Sample Preparation Step
2.4. D-LC Analysis
2.5. Method Validation Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
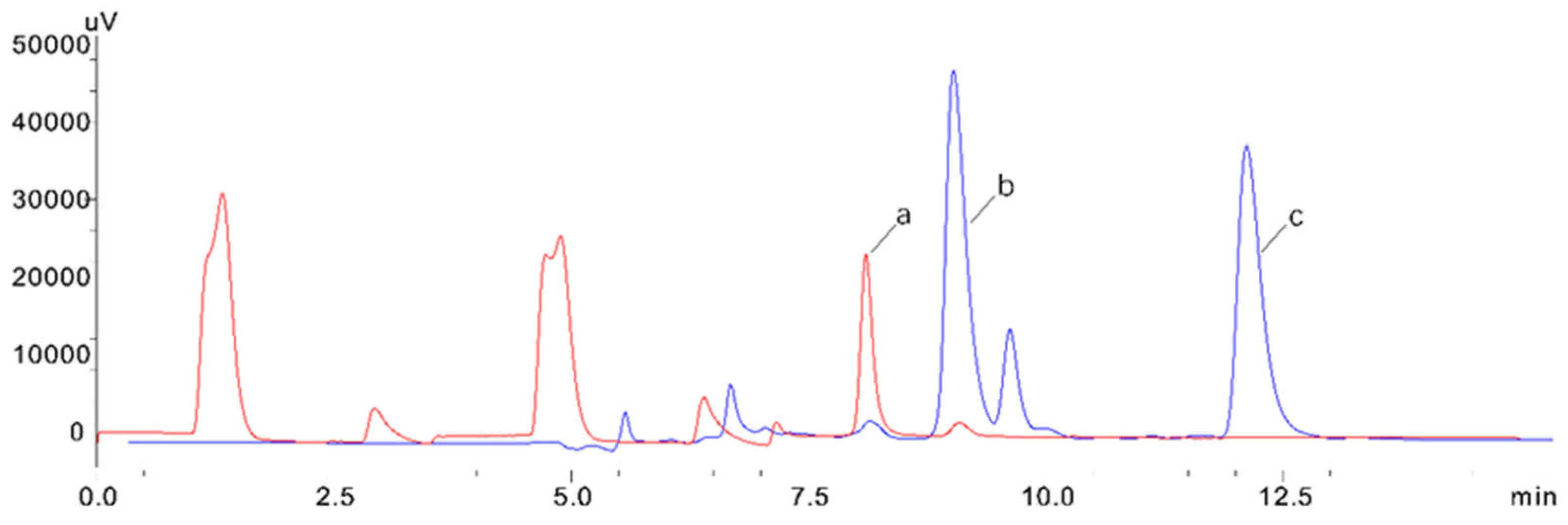
3.1. Optimization of Chromatographic Separation
3.2. SPE Column Selection
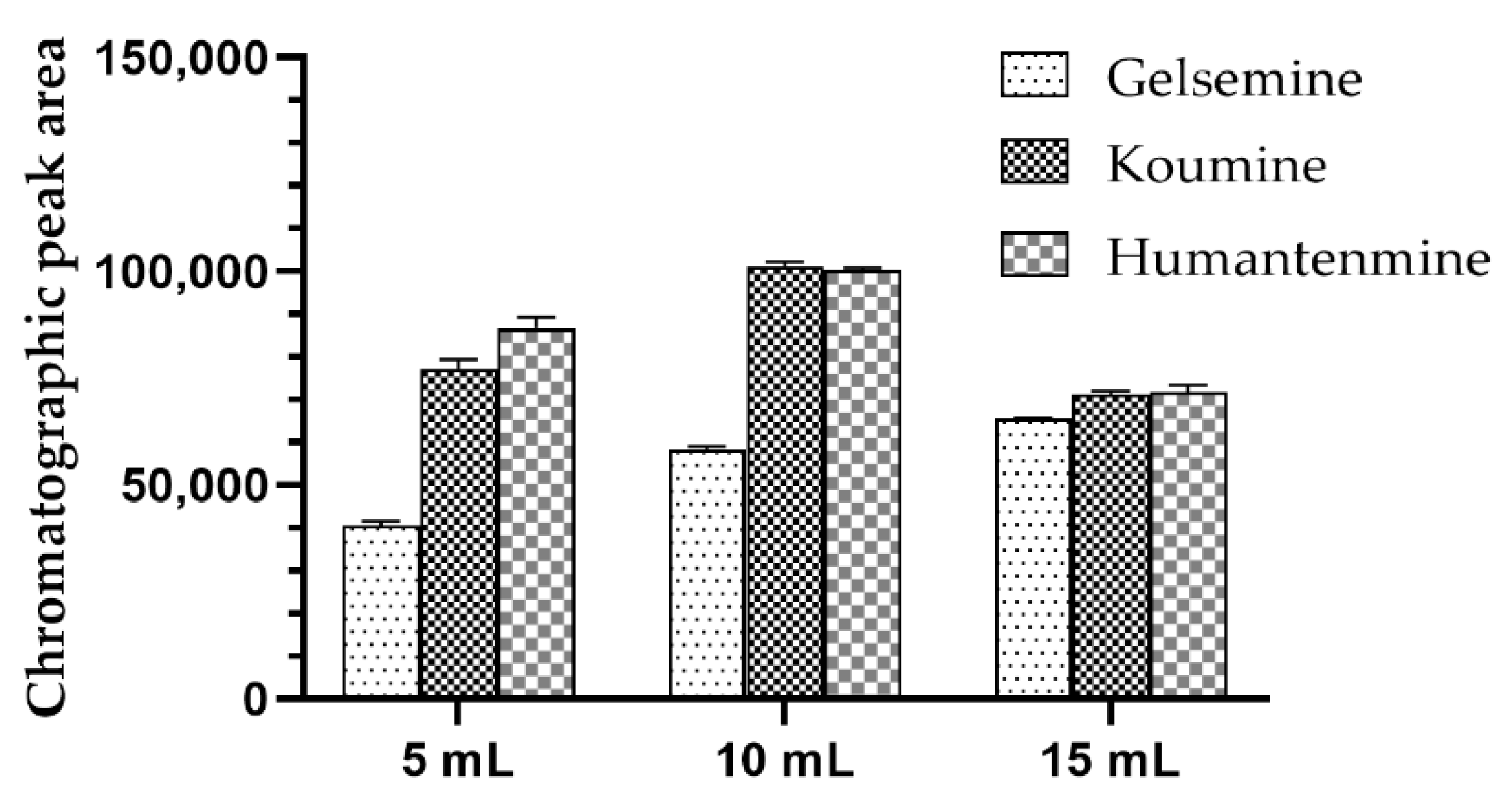
3.3. Optimization Flush Solvent
3.4. Optimization Elution Solvent
3.5. Method Validation Results
3.6. Analysis of Actual Honey Samples
3.7. Methods to Compare
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GB 14963-2011; National food safety standard Honey. Ministry of Health P. R. China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Ajibola, A.; Chamunorwa, J.; Erlwanger, K. Nutraceutical values of natural honey and its contribution to human health and wealth. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezmirean, G.I.; Mărghitaş, L.A.; Dezmirean, D.S. Honey Like Component of Functional Food. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 44, 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Stefan, B.; Tomislav, J.; Robert, S.; Peter, G. Honey for nutrition and health: A review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2008, 27, 677–689. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, M.U.; Majid, S. Therapeutic Applications of Honey and Its Phytochemicals. Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Statistical Information—FAO Statistical Database [EB/OL]. Available online: http://www.fao.org/statistics/zh (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- National Bureau of Statistics. National Data [EB/OL]. Available online: https://data.stats.gov.cn (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- Xiang, H.; Zhou, Y.J.; Huang, P.L.; Yu, C.N.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.Y.; He, P. Lethal poisoning with Gelsemium elegans in Guizhou, China. Public Health 2016, 136, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliferis, K.A.; Tarantilis, P.A.; Harizanis, P.C.; Alissandrakis, E. Botanical discrimination and classification of honey samples applying gas chromatography/mass spectrometry fingerprinting of headspace volatile compounds. Food Chem. 2009, 121, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, A.; Turedi, S.; Uzun, H.; Topbas, M. Mad honey poisoning. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2006, 24, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biberoğlu, S.; Biberoğlu, K.; Komsuoğlu, B. Mad honey. JAMA 1988, 259, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Ruan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Su, W.; Peng, M.; Wan, Q.; Zhao, J. Analysis of wild honey poisoning events from 2010 to 2019 in Yunnan Province. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2020, 11, 9063–9067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wan, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. The analysis of main toxic alkaloids in honey from distribution areas of toxic nectariferous plant in Yunnan. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 18, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lin, L.; Wei, X. Investigation on the source plants of toxic honey powder and honey poisoning in Guizhou Province. Apic. China 2017, 68, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Guo, Y.H.; Nicolson, S.W.; Radloff, S.E.; Song, Q.S.; Hepburn, H.R. Honeybee (Apis cerana) foraging responses to the toxic honey of Tripterygium hypoglaucum (Celastraceae): Changing threshold of nectar acceptability. J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 2209–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, J.A.; Roeder, E.; Molyneux, R.J. Honey from plants containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids: A potential threat to health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 2719–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.; Su, Y.; Liu, M.; Xu, Y.; Yang, J.; Liao, K.; Yu, C. Medicinal plants of the genus Gelsemium (Gelsemiaceae, Gentianales)--a review of their phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and traditional use. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shen, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, C. Gelsenicine from Gelsemium elegans attenuates neuropathic and inflammatory pain in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1877–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Lei, L.; Fang, F.; Yang, S.; Wang, J. Inhibitory effect of koumine on splenocyte proliferation and humoral immune response in mice. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater. Med. 1999, 15, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, J.; Zhong, W. Advances in chemical constituents and pharmacology of Gelsemium elegans. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2003, 26, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Long, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Z. Development and in-house validation of a sensitive LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of gelsemine, koumine and humantenmine in porcine plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1076, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.-J.; Liu, W. Simultaneous determination of Koumine Gelsemine, and Gelsenicine in biological samples by LC-MS/MS. J. Forensic Med. 2017, 33, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Zhao, N.; Meng, F. Simultaneous determination of three alkaloids in extracts from gelsemium elegans benth. by HPLC. Chin. J. Pharmacovigil. 2017, 14, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T.; Tao, S.; Ruan, S.; Li, X.; Lin, D. Emergency detection of a food poisoning by gelsemine GC-MS technology. Mod. Food 2021, 6, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S. Determination of Phytotoxins in Biological Samples by Quechers-HPLC-MS/MS Method. Master’s Thesis, People’s Public Security University of China, Beijin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawski, M.W.; Namieśnik, J. Challenges in preparing honey samples for chromatographic determination of contaminants and trace residues. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.Q.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, Q.H.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.J. Antibiotic residues in honey: A review on analytical methods by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 110, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.; Namieśnik, J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 50, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud-Vernich, P.; Calatayud, F.; Simo, E.; Pico, Y. Efficiency of QuEChERS approach for determining 52 pesticide residues in honey and honey bees. MethodsX 2016, 3, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalong, L.; Hua, W.; Chaojie, C.; Jialiang, Z.; Yongcheng, Y. Determination of Gelsemine and Koumine in Honey by liquid Chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Ind. 2020, 41, 297–300. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.S.; Yang, K.; Sun, Z.L.; Zheng, X.; Bai, X.; Liu, Z.Y. A novel two-dimensional liquid chromatography system for the simultaneous determination of three monoterpene indole alkaloids in biological matrices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 3857–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. Codex Guidelines for the Establishment of a Regulatory Programme for Control of Veterinary Drug Residues in Foods. Part III Attributes of Analytical Methods for Residue of Veterinary Drugs in Foods16; Codex Alimentarius Commission, CAC: Rome, Italy, 1993; Volume 16, p. 41. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Chao, R. Determination of Five Aminoalcohol-diterpenoid Alkaloids in the Lateral Root of Aconitum carmichaeli by HPLC-ELSD with SPE. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 55, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brian, K. Determination of Ephedra Alkaloids and Synephrine in Dietary Supplements via Strong Cation-Exchange SPE and LC-MS/MS Detection. LC GC Eur. 2017, 30, 696. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Dan, W.; Shuang, Z.; Jiangling, Z.; Yunfeng, Z. Determination of five pyrrolizidine alkaloids in honey by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Environ. Chem. 2014, 33, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar]
- Mudge, E.M.; Jones, A.M.P.; Brown, P.N. Quantification of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in North American plants and honey by LC-MS: Single laboratory validation. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2015, 32, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Li-Li, D.; Xiu-ling, W.; Zhang-Ji, H.; Min, L.; Jun-chun, W. Determination of caffeine in honey by HPLC coupled with Ultrasound-assisted dispersive Liquid-Liquid microextraction. Phys. Test. Chem. Anal. (Part B Chem. Anal.) 2015, 51, 897–901. [Google Scholar]


| t/min | Time Program Setting | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00–1.20 | 1.20–3.20 | 3.21–3.8 | 3.81–4.7 | 4.70–17.0 | |
| Column connection | The 1D column is disconnected from the MC column | The 1D column is disconnected from the MC column | The 1D column is connected to the MC column | The MC column is connected to the 2D column | The MC column is disconnected from the 2D column |
| Major function | Complete sample on-line enrichment | Perform the first-dimension chromatography separation | The target component is transferred to the MC column | The target component is transferred to 2D column | The further two-dimensional separation of target components |
| Alkaloid | Added Concentration (ng/g) | Linear Range (ng/g) | Linearity (r2) | LOD (ng/g) | LOQ (ng/g) | Recovery (%) | Intraday RSD (%) | Interday RSD (%) | Short-Term RSD (%) | Freeze–Thaw RSD (%) | Long-Term RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelsemine | QCLL | 5–1000 | 0.9998 | 2 | 5 | 87.1 | 3.4 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 8.6 |
| QCL | 94.2 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 4.5 | 3.1 | |||||
| QCM | 82.2 | 5.0 | 3.2 | 3.8 | 2.1 | 1.5 | |||||
| QCH | 83 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 4 | |||||
| Koumine | QCLL | 5–1000 | 0.9985 | 2 | 5 | 92.9 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 2.9 | 1.2 | 4.3 |
| QCL | 88.0 | 1.1 | 2.5 | 1.2 | 4.3 | 8.1 | |||||
| QCM | 89.4 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 10.2 | |||||
| QCH | 81 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 3.2 | |||||
| Humantenmine | QCLL | 20–1000 | 0.9999 | 2 | 20 | 81.5 | 3.9 | 3.0 | 3.7 | 7.1 | 7.4 |
| QCL | 82.8 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 1.1 | 2.1 | 5.5 | |||||
| QCM | 83.4 | 3.1 | 1.9 | 6.1 | 4.4 | 2.3 | |||||
| QCH | 81.3 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| Alkaloid | Added Concentration (ng/g) | 0 d RSD (%) | 7 d RSD (%) | 30 d RSD (%) | 60 d RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gelsemine | 20 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 1.0 |
| 900 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.3 | |
| Koumine | 20 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 2.3 |
| 900 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 1.7 | |
| Humantenmine | 50 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| 900 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 2.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Zuo, M.-T.; Qi, X.-J.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Liu, Z.-Y. Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Gelsemium Alkaloids in Honey. Foods 2022, 11, 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182891
Ma X, Zuo M-T, Qi X-J, Wang Z-Y, Liu Z-Y. Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Gelsemium Alkaloids in Honey. Foods. 2022; 11(18):2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182891
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiao, Meng-Ting Zuo, Xue-Jia Qi, Zi-Yuan Wang, and Zhao-Ying Liu. 2022. "Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Gelsemium Alkaloids in Honey" Foods 11, no. 18: 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182891
APA StyleMa, X., Zuo, M.-T., Qi, X.-J., Wang, Z.-Y., & Liu, Z.-Y. (2022). Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Method for the Determination of Gelsemium Alkaloids in Honey. Foods, 11(18), 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182891






