Application of Gurma Melon (Citrullus lantus var. colocynthoides) Pulp-Based Gel Fat Replacer in Mayonnaise
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Gurma Melon Pulp (GMP) Preparation
2.2.2. Gurma Melon Pulp Gel (GMPG) Preparation
2.2.3. Chemical Analysis of GMP Powder
2.2.4. GMPG Physical Property Measurement
2.2.5. Mayonnaise Preparation
2.2.6. Mayonnaise Composition Analysis
2.2.7. Caloric Value
2.2.8. Mayonnaise Microstructure
2.2.9. Mayonnaise Physicochemical Analyses
pH and Water Activity (Aw)
Bostwick Consistency Measurement
Particle Size Measurement
Emulsion Stability
Viscosity Measurement
Mayonnaise Color Measurement
Texture Measurement
2.2.10. Sensory Evaluation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Analysis of GMP Powder
3.2. Chemical Composition and Caloric Values
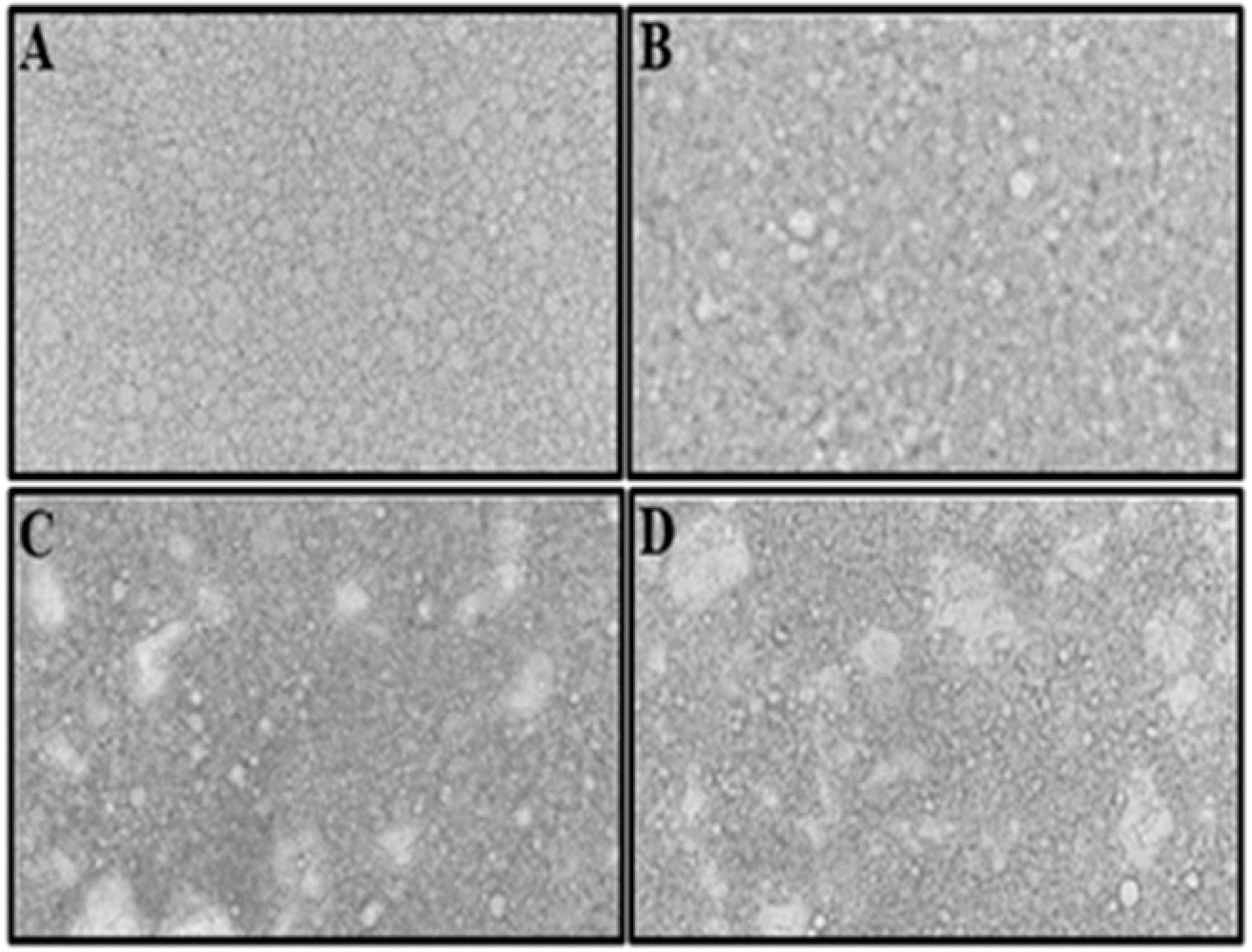
3.3. Mayonnaise Microstructure
3.4. Mayonnaise Physicochemical Properties
3.4.1. Mayonnaise pH and Water Activity (Aw)
3.4.2. Mayonnaise Consistency
3.4.3. Particle Size Analysis
3.4.4. Emulsion Stability
3.4.5. Viscosity Measurement
3.4.6. Mayonnaise Color
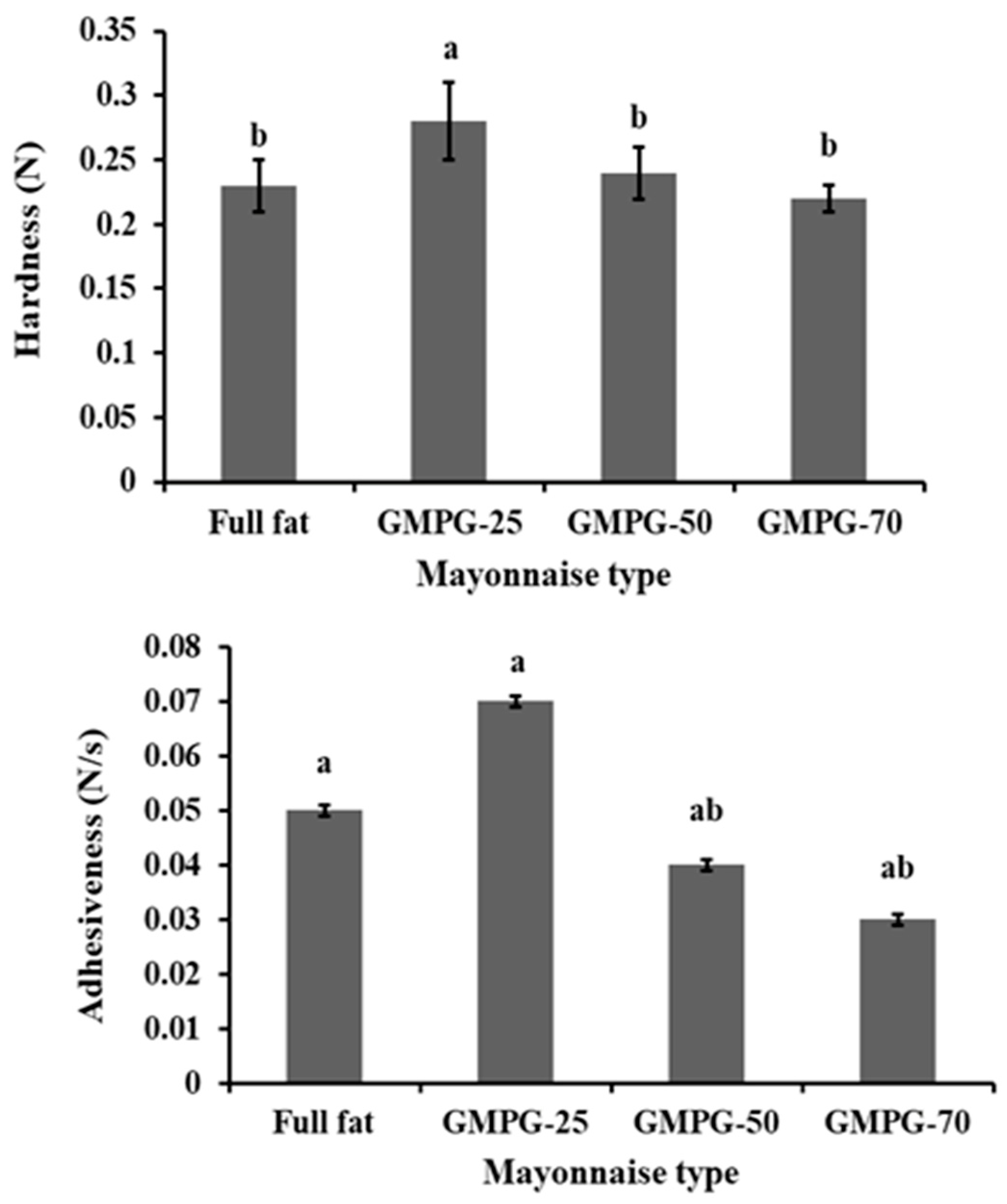
3.4.7. Mayonnaise Texture
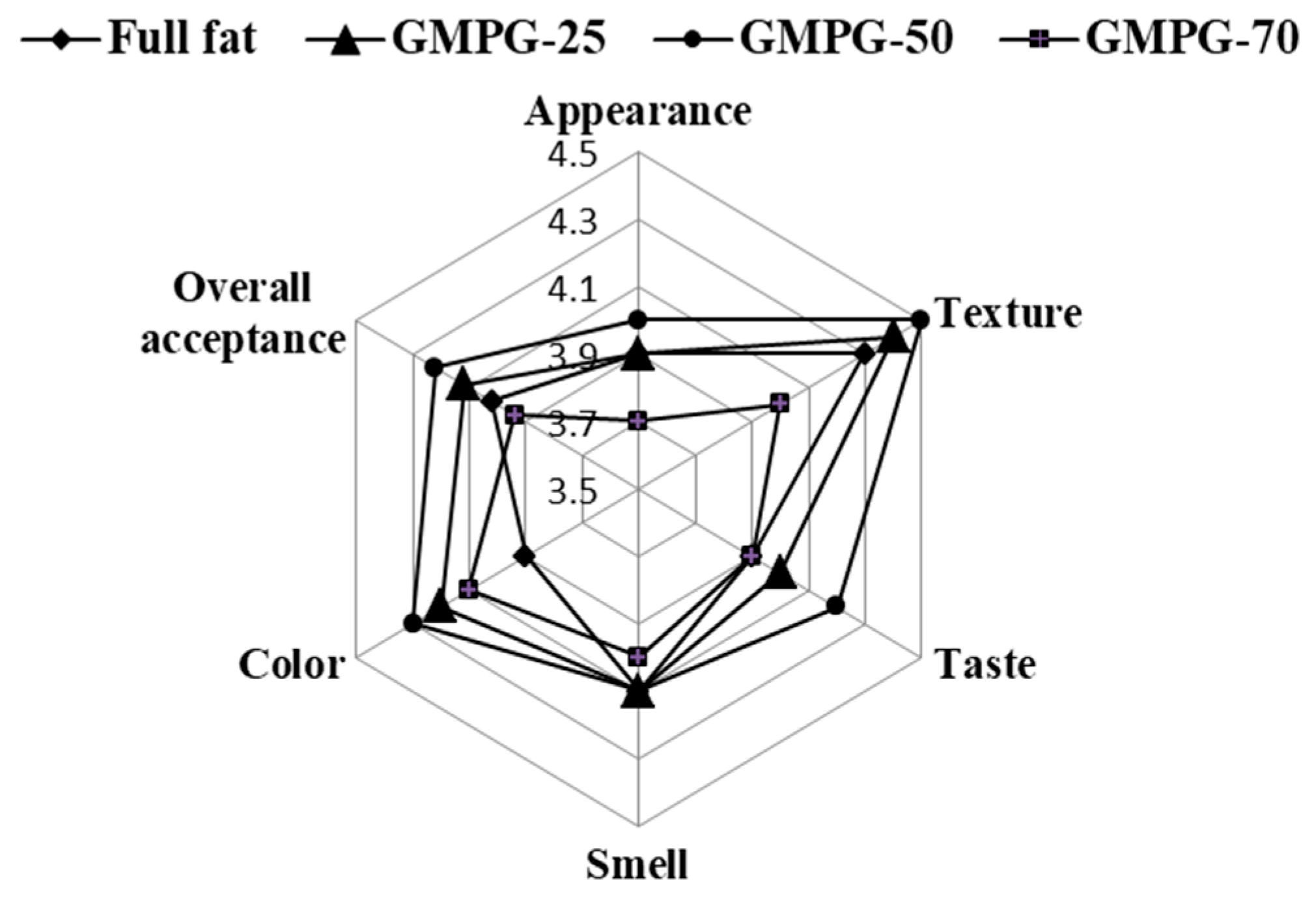
3.5. Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Guo, S.D. Rheological, texture and sensory properties of low-fat mayonnaise with different fat mimetics. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, G.; Rathna, K.; Ken, C.; Bruce, C. Emulsifying functionality of enzyme-modified milk proteins in O/W and mayonnaise-like emulsions. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2010, 4, 16–25. [Google Scholar]
- Honold, P.J.; Jacobsen, C.; Jónsdóttir, R.; Kristinsson, H.G.; Hermund, D.B. Potential seaweed-based food ingredients to inhibit lipid oxidation in fish-oil-enriched mayonnaise. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanuarini, H.; Hastuti, P. Characteristic of low fat mayonnaise containing porang flour as stabilizer. Pak. J. Nutr. 2015, 14, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, T.M.; Waqar, S.; Ali, S.; Mehbsoob, S.; Hasnain, A. Comparison of textural and sensory characteristics of low-fat mayonnaise prepared from octenyl succinic anhydride modified corn and white sorghum starches. Starch-Stärke 2015, 67, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Lee, S.; Lee, N.; Ko, S. Reduced-fat mayonnaise formulated with gelatinized rice starch and xanthan gum. Cereal Chem. 2013, 90, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, N.F.; Mazaheri Tehrani, M.; Daneshvar, K.; Koocheki, A. Influence of selected gums and pregelatinized corn starch on reduced fat mayonnaise: Modeling of properties by central composite design. Food Biophys. 2015, 10, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laneuville, S.I.; Paquin, P.; Turgeon, S.L. Formula optimization of a low-fat food system containing whey protein isolate-xanthan gum complexes as fat replacer. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, s513–s519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyada, A.; Elhussien, S. Physical and ChemicalCharacteristics of Citrullus lanatus Var. Colocynthoide Seed Oil. J. Phys. Sci. 2008, 19, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shabrawy, R.; Hatem, A. Effect of sowing date and plant distribution system on growth and yield of gurma watermelon (Citrullus lanatus var. colocynthoides). J. Plant Prod. 2008, 33, 4397–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhady, M.; Masoud, M.; Elbaz, S. Production of bioethanol from Gurma watermelon wastes. J. Biol. Chem. Environ. Sci 2014, 9, 225–266. [Google Scholar]
- Salama, I.; Abo-Elmaaty, S.; Sulieman, A.; Abdel-Hady, M. Innovation of Jam from Gurma Melon Pulp as Un Traditional Source. Zagazig J. Agric. Res. 2019, 46, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korish, M. Potential utilization of Citrullus lanatus var. Colocynthoides waste as a novel source of pectin. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2401–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belluco, C.Z.; Mendonça, F.J.; Zago, I.C.C.; Di Santis, G.W.; Marchi, D.F.; Soares, A.L. Application of orange albedo fat replacer in chicken mortadella. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 3659–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC (Association of Official Agricultural Chemists); Horwitz, W.; Latimer, G. (Eds.) The Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Worrasinchai, S.; Suphantharika, M.; Pinjai, S.; Jamnong, P. β-Glucan prepared from spent brewer’s yeast as a fat replacer in mayonnaise. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.T. Standard Methods for the Examination of Dairy Products, 16th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Roland, I.; Piel, G.; Delattre, L.; Evrard, B. Systematic characterization of oil-in-water emulsions for formulation design. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 263, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karshenas, M.; Goli, M.; Zamindar, N. The effect of replacing egg yolk with sesame–peanut defatted meal milk on the physicochemical, colorimetry, and rheological properties of low-cholesterol mayonnaise. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, M. Food Texture and Viscosity: Concept and Measurement, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; Elsevier: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nikzade, V.; Tehrani, M.M.; Saadatmand-Tarzjan, M. Optimization of low-cholesterol–low-fat mayonnaise formulation: Effect of using soy milk and some stabilizer by a mixture design approach. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, S.; Parkin, K.L. IQuímica de Alimentos de Fennema, 5th ed.; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Akoh, C.C. Fat replacers. Food Technol. 1998, 52, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Langton, M.; Jordansson, E.; Altskär, A.; Sørensen, C.; Hermansson, A.-M. Microstructure and image analysis of mayonnaises. Food Hydrocoll. 1999, 13, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depree, J.; Savage, G. Physical and flavour stability of mayonnaise. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, J.M.; Loessner, M.J.; Golden, D.A. Modern Food Microbiology; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chirife, J.; Vigo, M.S.; Gomez, R.G.; Favetto, G.J. Water activity and chemical composition of mayonnaises. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S.E. Fats: Mayonnaise. In Food Processing: Principles and Applications; Smith, J.S., Hui, Y.H., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; p. 329. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, S.; Kim, Y.-L.; Kang, C.-G.; Park, K.-H.; Shim, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-R. Development of reduced-fat mayonnaise using 4αGTase-modified rice starch and xanthan gum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoj, P.; Fillery-Travis, A.J.; Watson, A.D.; Hibberd, D.J.; Robins, M.M. Characterization of a polydisperse depletion-flocculated emulsion: III. Oscillatory rheological measurements. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 228, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcclements, D.J. Critical review of techniques and methodologies for characterization of emulsion stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 611–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantrapornchai, W.; Clydesdale, F.; McClements, D.J. Influence of droplet characteristics on the optical properties of colored oil-in-water emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 155, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, B.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y. Effect of protein microparticle and pectin on properties of light mayonnaise. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients | Mayonnaise Formulation (% wt) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Fat | GMPG-25 | GMPG-50 | GMPG-70 | |
| soybean oil | 82.20 | 61.65 | 41.10 | 24.67 |
| fat replacer | - | 20.55 | 41.10 | 57.53 |
| egg yolk | 7.27 | 7.27 | 7.27 | 7.27 |
| vinegar (5%) | 8.72 | 8.72 | 8.72 | 8.72 |
| salt | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.73 |
| mustard | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| sugar | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| ground white pepper | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.36 |
| Parameters | GMP Powder |
|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 13.46 ± 0.32 |
| Fat (%) | 2.14 ± 0.09 |
| Proteins (%) | 11.38 ± 0.55 |
| Ash (%) | 3.85 ± 0.19 |
| Total Carbohydrates (%) | 69.17 ± 0.71 |
| L* | 90.73 ± 2.07 |
| a* | −1.34 ± 0.19 |
| b* | 22.61 ± 0.40 |
| Hue angle | 93.39 ± 1.13 |
| Chroma | 22.65 ± 0.52 |
| GMPG | |
| L* | 92.85 ± 2.88 |
| a* | −1.59 ± 0.12 |
| b* | 18.37 ± 1.03 |
| Hue angle | 94.95 ± 1.39 |
| Chroma | 18.44 ± 0.63 |
| pH | 3.49 ± 0.01 |
| water activity (Aw) | 0.94 ± 0.002 |
| Parameters | Mayonnaise Formulation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Fat | GMPG-25 | GMPG-50 | GMPG-70 | |
| Moisture (%) | 12.30 ± 0.09 d | 33.27 ± 0.49 c | 51.36 ± 0.26 b | 66.25 ± 0.17 a |
| Fat (%) | 85.02 ± 0.48 a | 62.86 ± 1.21 b | 43.66 ± 1.60 c | 27.94 ± 0.12 d |
| Proteins (%) | 1.25 ± 0.06 a | 1.43 ± 0.10 a | 1.60 ± 0.08 a | 1.73 ± 0.10 a |
| Ash (%) | 0.85 ± 0.02 a | 0.89 ± 0.02 a | 0.94 ± 0.01 a | 0.97 ± 0.02 a |
| Total Carbohydrates (%) | 0.58 ± 0.01 c | 1.55 ± 0.23 b | 2.44 ± 0.38 ab | 3.11 ± 0.45 a |
| Caloric values (kcal/100 g) | 772.50 ± 2.10 a | 577.66 ± 4.65 b | 409.1 ± 5.82 c | 270.82 ± 1.94 d |
| Parameters | Mayonnaise Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Fat | GMPG-25 | GMPG-50 | GMPG-70 | |
| pH | 3.96 ± 0.09 a | 3.85 ± 0.10 a | 3.81 ± 0.06 a | 3.78 ± 0.09 a |
| Water activity (Aw) | 0.948 ± 0.004 a | 0.979 ± 0.003 a | 0.985 ± 0.002 a | 0.988 ± 0.003 a |
| Running distance (cm) | 0.2 ± 0.1 b | 0.1 ± 0.00 b | 0.3 ± 0.1 b | 0.5 ± 0.1 a |
| Particle size (µm) | 9.38 ± 0.12 a | 4.21 ± 0.05 b | 2.37 ± 0.05 c | 1.95 ± 0.07 d |
| Stability | 99.8 ± 0.43 b | 99.8 ± 0.72 b | 100 ± 0.54 a | 99.7 ± 0.39 b |
| Viscosity (cP) | 17.42 ± 1.1 b | 21.13 ± 0.97 a | 16.60 ± 0.85 b | 15.89 ± 0.94 bc |
| Parameters | Mayonnaise Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Fat | GMPG-25 | GMPG-50 | GMPG-70 | |
| L* | 82.35 ± 0.87 c | 85.27 ± 0.82 b | 87.62 ± 0.94 a | 88.26 ± 0.93 a |
| a* | −3.19 ± 0.28 c | −3.42 ± 0.26 ab | −3.62 ± 0.30 a | −3.39 ± 0.22 b |
| b* | 23.36 ± 0.94 ab | 22.90 ± 1.02 b | 21.86 ± 0.95 bc | 22.88 ± 0.97 b |
| Hue angle | 97.78 | 98.49 | 99.40 | 98.43 |
| Chroma | 23.58 | 23.15 | 22.16 | 23.13 |
| ΔE | 0 | 2.96 | 5.50 | 5.93 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elsebaie, E.M.; Mousa, M.M.; Abulmeaty, S.A.; Shaat, H.A.Y.; Elmeslamy, S.A.-E.; Elgendy, M.S.A.; Saleh, F.M.; Essa, R.Y. Application of Gurma Melon (Citrullus lantus var. colocynthoides) Pulp-Based Gel Fat Replacer in Mayonnaise. Foods 2022, 11, 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182731
Elsebaie EM, Mousa MM, Abulmeaty SA, Shaat HAY, Elmeslamy SA-E, Elgendy MSA, Saleh FM, Essa RY. Application of Gurma Melon (Citrullus lantus var. colocynthoides) Pulp-Based Gel Fat Replacer in Mayonnaise. Foods. 2022; 11(18):2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182731
Chicago/Turabian StyleElsebaie, Essam Mohamed, Mona Metwally Mousa, Samah Amin Abulmeaty, Heba Ali Yousef Shaat, Soher Abd-Elfttah Elmeslamy, Manal Salah Abbas Elgendy, Fatma M. Saleh, and Rowida Younis Essa. 2022. "Application of Gurma Melon (Citrullus lantus var. colocynthoides) Pulp-Based Gel Fat Replacer in Mayonnaise" Foods 11, no. 18: 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182731
APA StyleElsebaie, E. M., Mousa, M. M., Abulmeaty, S. A., Shaat, H. A. Y., Elmeslamy, S. A.-E., Elgendy, M. S. A., Saleh, F. M., & Essa, R. Y. (2022). Application of Gurma Melon (Citrullus lantus var. colocynthoides) Pulp-Based Gel Fat Replacer in Mayonnaise. Foods, 11(18), 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182731





