Effect of Polishing on Lead and Cadmium Bioavailability in Rice and Its Health Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Rice Polishing
2.2. Determination of the Total Pb, Cd, and Mineral Nutrients in Rice
2.3. Evaluation of the In Vitro Bioaccessibility
2.4. Evaluation of the In Vivo Bioavailability
2.4.1. Mouse Meal Preparation
2.4.2. In Vivo Evaluation of the Pb and Cd Exposure
2.5. Consumption Risk Assessment
2.6. Quality Control and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
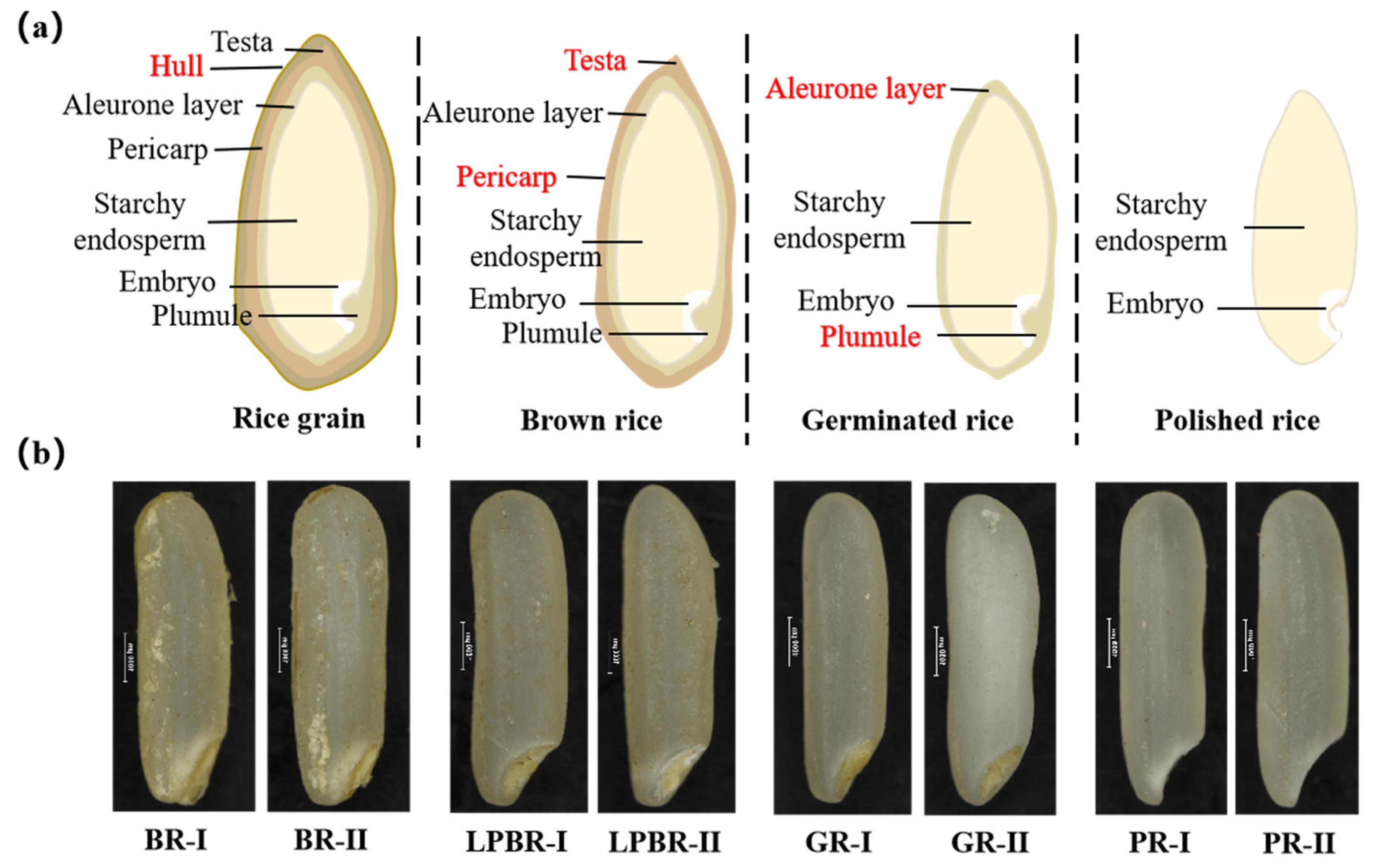
3.1. Effect of the Processing Precision on the Surface Morphology of Rice
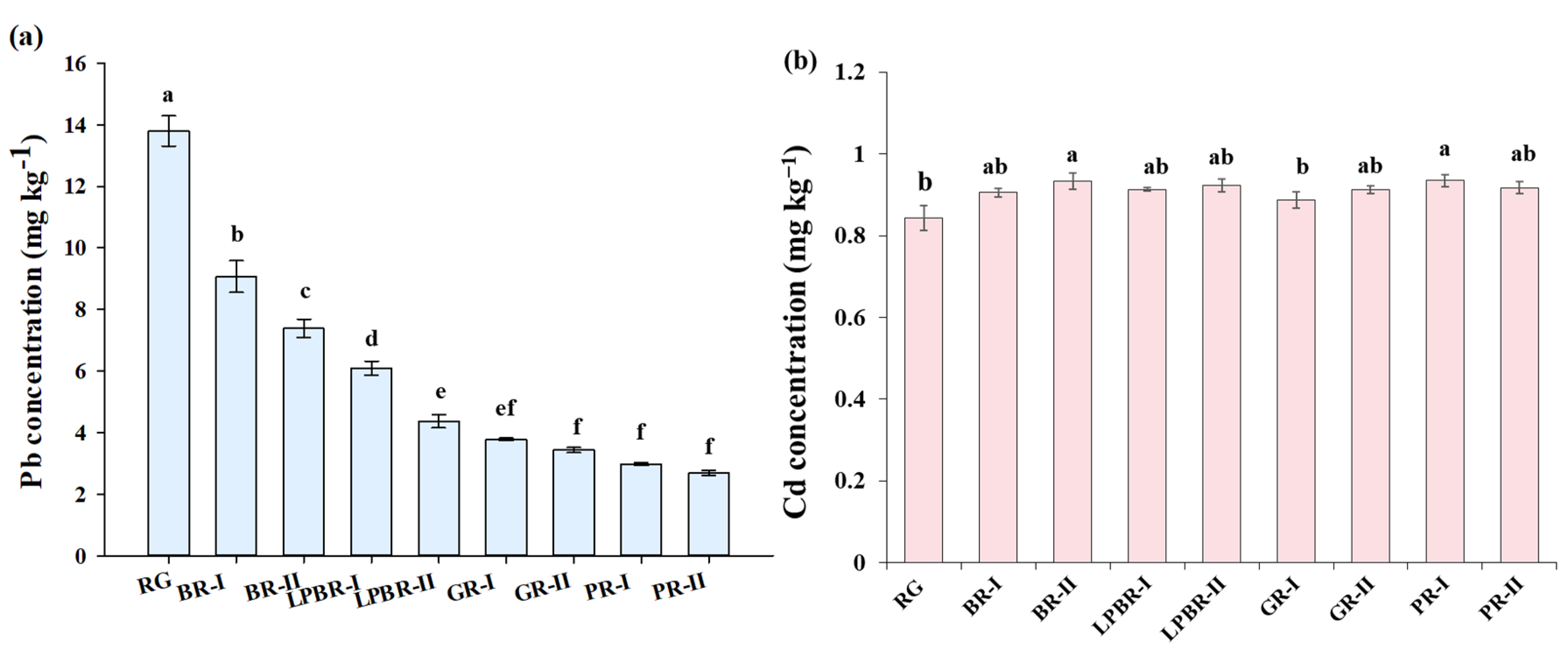
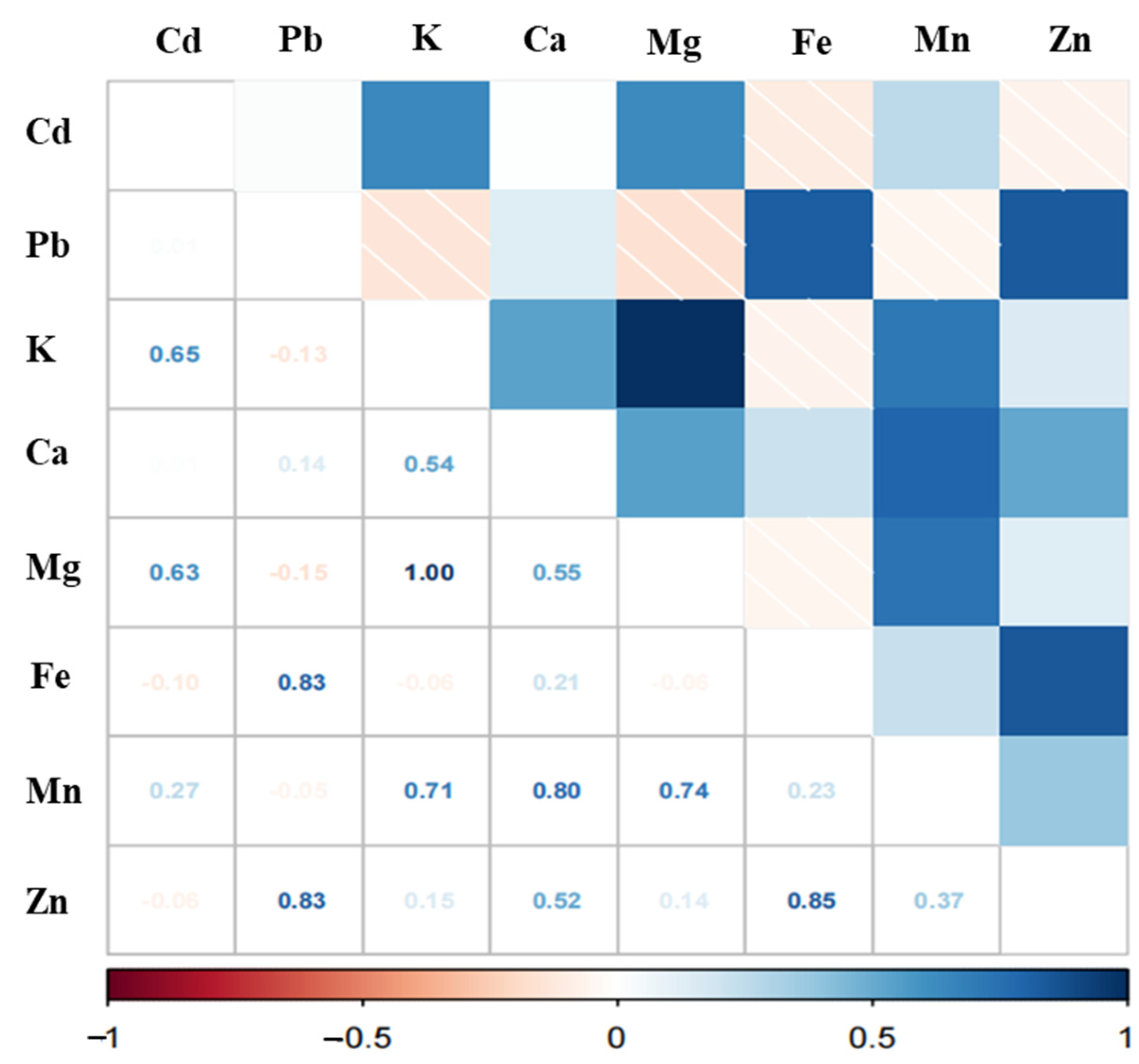
3.2. Total Concentrations of Pb, Cd, and Nutritional Elements in Rice
3.3. Effect of Polishing on the Bioaccessibility of Pb and Cd in Rice
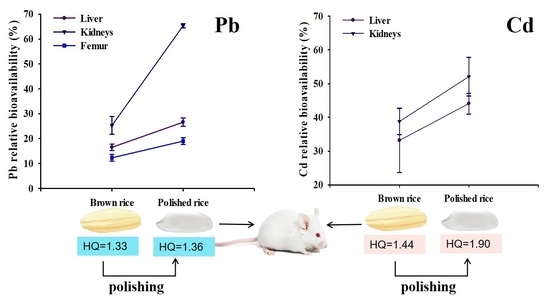
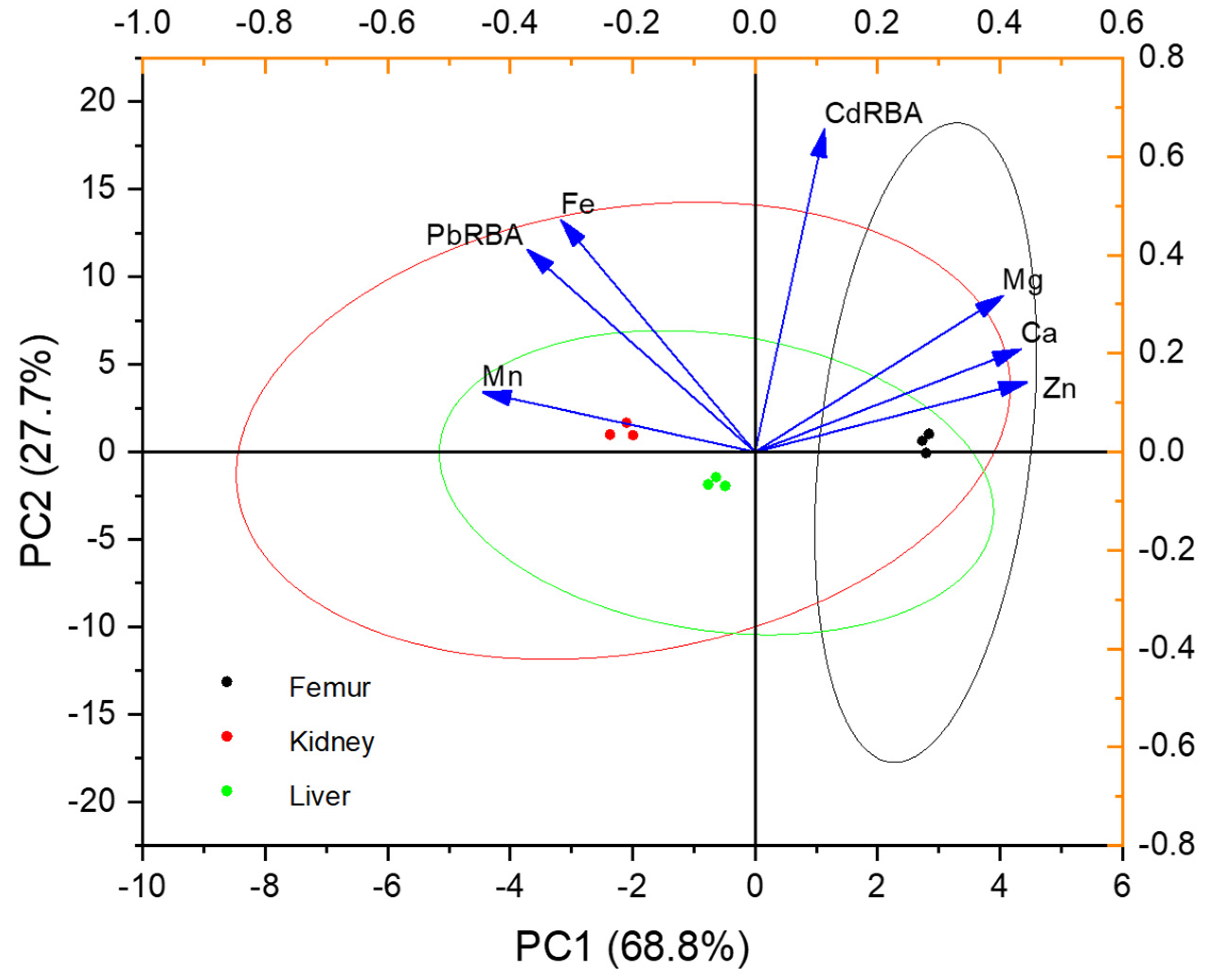
3.4. Effect of Polishing on the Bioavailability of Pb and Cd in Rice
3.5. Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muthayya, S.; Sugimoto, J.D.; Montgomery, S.; Maberly, G.F. An overview of global rice production, supply, trade, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2014, 1324, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.N.; Cheng, H.F.; Tao, S. The Challenges and Solutions for Cadmium-contaminated Rice in China: A Critical Review. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasreddine, L.; Parent-Massin, D. Food contamination by metals and pesticides in the European Union. Should we worry? Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 127, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. CERCLA Priority List of Hazardous Substances. 2019. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/index.html (accessed on 20 June 2022).
- Itoh, H.; Iwasaki, M.; Sawada, N.; Takachi, R.; Kasuga, Y.; Yokoyama, S.; Onuma, H.; Nishimura, H.; Kusama, R.; Yokoyama, K.; et al. Dietary cadmium intake and breast cancer risk in Japanese women: A case-control study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, P.; McBride, M.B.; Xia, H.; Li, N.; Lia, Z. Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruby, M.V.; Davis, A.; Schoof, R.; Eberle, S.; Sellstone, C.M. Estimation of lead and arsenic bioavailability using a physiologically based extraction test. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1996, 30, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oomen, A.G.; Hack, A.; Minekus, M.; Zeijdner, E.; Cornelis, C.; Schoeters, G.; Verstraete, W.; Van de Wiele, T.; Wragg, J.; Rompelberg, C.J.M.; et al. Comparison of five in vitro digestion models to study the bioaccessibility of soil contaminants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3326–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casteel, S.W.; Weis, C.P.; Henningsen, G.M.; Brattin, W.J. Estimation of relative bioavailability of lead in soil and soil-like materials using young swine. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhasz, A.L.; Gancarz, D.; Herde, C.; McClure, S.; Scheckel, K.G.; Smith, E. In situ formation of pyromorphite is not required for the reduction of in vivo Pb relative bioavailability in contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7002–7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.W.; Sun, H.J.; Wang, G.; Cui, X.Y.; Juhasz, A.L.; Li, H.B.; Ma, L.Q. Lead relative bioavailability in soils based on different endpoints of a mouse model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 326, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, R.Y.; Xiang, P.; Juhasz, A.L.; Huang, L.; Luo, J.; Li, H.B.; Ma, L.Q. Applying cadmium relative bioavailability to assess dietary intake from rice to predict cadmium urinary excretion in nonsmokers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6756–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.B.; Zhao, D.; Li, J.; Li, S.W.; Wang, N.; Juhasz, A.L.; Zhu, Y.G.; Ma, L.Q. Using the SBRC assay to predict lead relative bioavailability in urban soils: Contaminant source and correlation model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4989–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, G. High levels of heavy metals in rice (Oryza sativa L.) from a typical E-waste recycling area in southeast China and its potential risk to human health. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.R.; Fan, Y.Y.; Hu, B.L.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Chen, D.Z.; Zhuang, J.Y. Assessment and genetic analysis of heavy metal content in rice grain using an Oryza sativa x O-rufipogon backcross inbred line population. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, T.; Shindoh, K.; Taguchi, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Yasui, A.; Joh, T. Changes in the cadmium content of rice during the milling process. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 44, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yadav, B.K.; Jindal, V.K. Monitoring milling quality of rice by image analysis. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2001, 33, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.; Zhang, C.S.; Li, Y.W.; Zou, B.; Mo, H.; Wu, K.J.; Wu, J.T.; Li, Z.A. Assessment of influences of cooking on cadmium and arsenic bioaccessibility in rice, using an in vitro physiologically-based extraction test. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; Shang, Y.e.; Sun, B. Health risk assessment of cadmium via dietary intake by adults in China. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 373–380. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JECFA (Joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additive). In Proceedings of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additive 79th Meeting, Geneva, Switzerland, 17–26 June 2014.
- Bhattacharya, K.R. Rice Quality: A guide to Rice Properties and Analysis; Woodhead Publishing Limited: New Delhi, India, 2011; pp. 100–114. [Google Scholar]
- Juliano, B.O. Rice in Human Nutrition; International Rice Research Institute: Rome, Italy, 1993; pp. 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.X.; Lin, Q.L.; Chen, X. Contents and distributions of cadmium and lead in rice from main rice cultivation areas in China. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2013, 29, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.; Ding, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, J.; He, R. Response surface prediction of As, Cd and Pb residue distribution in milled rice. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2017, 32, 159–164. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Qian, M.; Cai, G.; Yang, J.C.; Zhu, Q. Uptake and translocation of Cd in different rice cultivars and the relation with Cd accumulation in rice grain. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 143, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Guo, B.L.; Peng, L.X.; Jiang, T.; Li, M.; Wei, Y.M. Cadmium distribution and characteristics of cadmium-binding proteins in rice (Oryza sativa L.) kernel. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2017, 23, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.H.; Lombi, E.; Fitzgerald, M.; Laursen, K.H.; Frydenvang, J.; Husted, S.; Boualaphanh, C.; Resurreccion, A.; Howard, D.L.; de Jonge, M.D.; et al. Losses of essential mineral nutrients by polishing of rice differ among genotypes due to contrasting grain hardness and mineral distribution. J. Cereal Sci. 2012, 56, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, G.; Todorov, T.I. Distribution of nutrient and toxic elements in brown and polished rice. Food Chem. 2019, 289, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.L.; Wu, J.G.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.E.; Shi, C.H. Correlation analysis of mineral element contents and quality traits in milled rice (Oryza stavia L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9608–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; He, M. Distribution of heavy metals in polluted crops seeds and the effect of heavy metals in the food processing. Environ. Sci. 2000, 21, 52–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Ding, W.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xiong, Y.L. Effect of degree of milling on the cadmium in vitro bioaccessibility in cooked rice. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 3756–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; He, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Fu, J. 24 h absorption and excretion profiles of cadmium from contaminated cooked brown rice and white rice in female rats. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 102, 103300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesey, D.A. Transport pathways for cadmium in the intestine and kidney proximal tubule: Focus on the interaction with essential metals. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 198, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahter, M.; Berglund, M.; Nermell, B.; Akesson, A. Bioavailability of cadmium from shellfish and mixed diet in women. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1996, 136, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, A.; Morgan, E.H. Interactions between tissue uptake of lead and iron in normal and iron-deficient rats during development. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1996, 52, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, A.; Thielecke, F. Dietary intakes of whole grains, health benefits but do contaminants pose a major risk? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, E436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, H.; Ohba, K. Involvement of metal transporters in the intestinal uptake of cadmium. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 45, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Zhuang, P. In vitro and in vivo testing to determine Cd bioaccessibility and bioavailability in contaminated rice in relation to mouse chow. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Liu, N.Q.; Zhao, B.L.; Chai, Z.F. Effects of lead on the contents of Zn, Cu, Fe and Mn in rats. J. Nucl. Radiochem. 2004, 26, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Vanessa, A.; Fitsanakis, N.; Zhang, J.G.; Anderson, K.M. Measuring Brain Manganese and Iron Accumulation in Rats following 14 Weeks of Low-Dose Manganese Treatment Using Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 103, 116–124. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, M.L.; Montaña, F.P.; Miranda, M.; Castillo, C.; Hernandez, J.; Benedito, J.L. Interactions between toxic (As, Cd, Hg and Pb) and nutritional essential (Ca, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, Se, Zn) elements in the tissues of cattle from NW Spain. Biometals 2004, 17, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Jones, O.A.H.; Dorne, J.L.C.M.; Svendsen, C.; Swain, S.; Stuerzenbaum, S.R. Systems toxicology approaches for understanding the joint effects of environmental chemical mixtures. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3725–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrick, M.D.; Singleton, S.T.; Vargas, F.; Kuo, H.C.; Zhao, L.; Knopfel, M.; Davidson, T.; Costa, M.; Paradkar, P.; Roth, J.A.; et al. DMTI: Which metals does it transport? Biol. Res. 2006, 39, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollson, C.J.; Smith, E.; Herde, P.; Juhasz, A.L. Influence of sample matrix on the bioavailability of arsenic, cadmium and lead during co-contaminant exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.D.; Cherrington, N.J.; Klaassen, C.D. Intestinal absorption of cadmium is associated with divalent metal transporter 1 in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 68, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Cui, X.Y.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Juhasz, A.L.; Ma, L.Q. Assessment of in vitro lead bioaccessibility in house dust and its relationship to in Vivo Lead Relative Bioavailability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8548–8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.C.; Juhasz, A.; Smith, E.; Naidu, R. Assessing the bioavailability and bioaccessibility of metals and metalloids. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8802–8825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannon, D.I.; Portnoy, M.E.; Olivi, L.; Lees, P.S.J.; Culotta, V.C.; Bressler, J.P. Uptake of lead and iron by divalent metal transporter 1 in yeast and mammalian cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 295, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Polishing Precision | Nutritional Elements | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K | Ca | Mg | Fe | Mn | Zn | |
| BR-Ⅰ | 2501 ± 12.8 d | 125 ± 5.1 a | 856 ± 4.3 d | 366 ± 20.6 a | 25 ± 0.3 b | 48 ± 1.4 a |
| BR-Ⅱ | 2451 ± 31.7 d | 103 ± 2.2 b | 843 ± 16.9 d | 255 ± 22.2 c | 23 ± 0.6 d | 39 ± 1.1 c |
| LPBR-Ⅰ | 2449 ± 9.6 d | 104 ± 0.5 b | 844 ± 3.4 d | 324 ± 12.8 a | 23 ± 0.1 cd | 42 ± 0.6 b |
| LPBR-Ⅱ | 2735 ± 20.5 a | 119 ± 1.4 a | 976 ± 6.7 a | 309 ± 33.1 b | 26 ± 0.4 a | 41 ± 0.1 bc |
| GR-Ⅰ | 1914 ± 11.4 e | 104 ± 10.0 b | 616 ± 6.4 e | 191 ± 2.2 d | 22 ± 0.2 d | 36 ± 0.4 d |
| GR-Ⅱ | 2658 ± 18.3 b | 115 ± 1.3 ab | 943 ±7.0 b | 187 ± 4.9 d | 24 ± 0.1 c | 38 ± 0.1 cd |
| PR-Ⅰ | 2770 ± 34.9 a | 120 ± 0.3 a | 988 ± 5.8 a | 120 ± 0.5 e | 25 ± 0.1 b | 38 ± 0.2 cd |
| PR-Ⅱ | 2587 ± 25.4 c | 107 ± 1.6 b | 884 ± 7.8 c | 109 ± 0.1 e | 23 ± 0.3 cd | 36 ± 0.5 d |
| Polishing Degrees | Pb RBA | HQ a | Cd RBA | HQ a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liver | Kidneys | Femur | Liver | Kidneys | |||
| Brown rice | 16.5 ± 1.29b | 25.3 ± 3.56b | 12.3 ± 1.33b | 1.33 | 33.2 ± 9.55b | 38.8 ± 3.86b | 1.44 |
| Polished rice | 26.6 ± 1.68a | 65.3 ± 0.83a | 19.0 ± 1.39a | 1.36 | 44.1 ± 3.09a | 52.1 ± 5.76a | 1.90 |
| Processing Precision | Pb | Cd | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDItotal | EDIBAC | EDItotal | EDIBAC | |
| BR-Ⅰ | 49.38 | 21.32 | 4.95 | 3.11 |
| BR-Ⅱ | 40.23 | 16.27 | 5.06 | 3.04 |
| LPBR-Ⅰ | 33.21 | 17.40 | 4.95 | 3.11 |
| LPBR-Ⅱ | 23.79 | 10.07 | 5.01 | 2.89 |
| GR-Ⅰ | 20.58 | 10.96 | 4.85 | 3.23 |
| GR-Ⅱ | 18.67 | 8.87 | 4.95 | 3.20 |
| PR-Ⅰ | 16.22 | 7.77 | 5.12 | 3.05 |
| PR-Ⅱ | 14.64 | 7.06 | 5.01 | 3.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Chen, F.; Sun, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Mo, H.; Li, Z.; Zhuang, P. Effect of Polishing on Lead and Cadmium Bioavailability in Rice and Its Health Implications. Foods 2022, 11, 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172718
Chen X, Chen F, Sun S, Li Y, Li Y, Mo H, Li Z, Zhuang P. Effect of Polishing on Lead and Cadmium Bioavailability in Rice and Its Health Implications. Foods. 2022; 11(17):2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172718
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xianghua, Fangman Chen, Shuo Sun, Yingwen Li, Yongxing Li, Hui Mo, Zhian Li, and Ping Zhuang. 2022. "Effect of Polishing on Lead and Cadmium Bioavailability in Rice and Its Health Implications" Foods 11, no. 17: 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172718
APA StyleChen, X., Chen, F., Sun, S., Li, Y., Li, Y., Mo, H., Li, Z., & Zhuang, P. (2022). Effect of Polishing on Lead and Cadmium Bioavailability in Rice and Its Health Implications. Foods, 11(17), 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172718