Antibiotics Resistance and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Isolated from Raw Milk from Handmade Dairy Retail Stores in Hefei City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Raw Milk Samples
2.2. Identification and Isolation of S. aureus
2.3. Detection of mecA and Genes Encoding Enterotoxin
2.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
2.5. Biofilm Formation Assay
2.6. spa Typing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of S. aureus
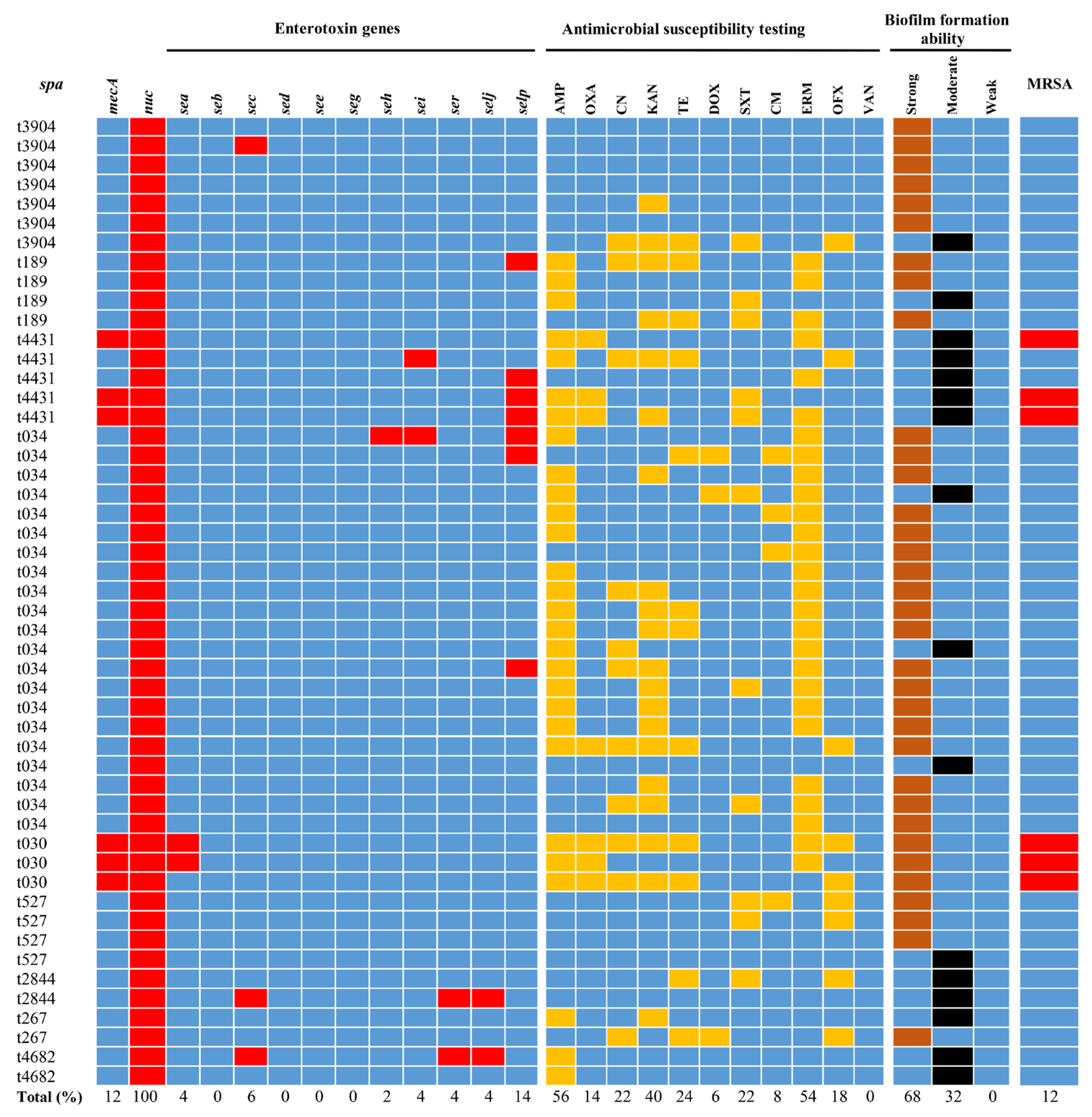
3.2. spa Typing
3.3. Distribution of Enterotoxin Genes
3.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
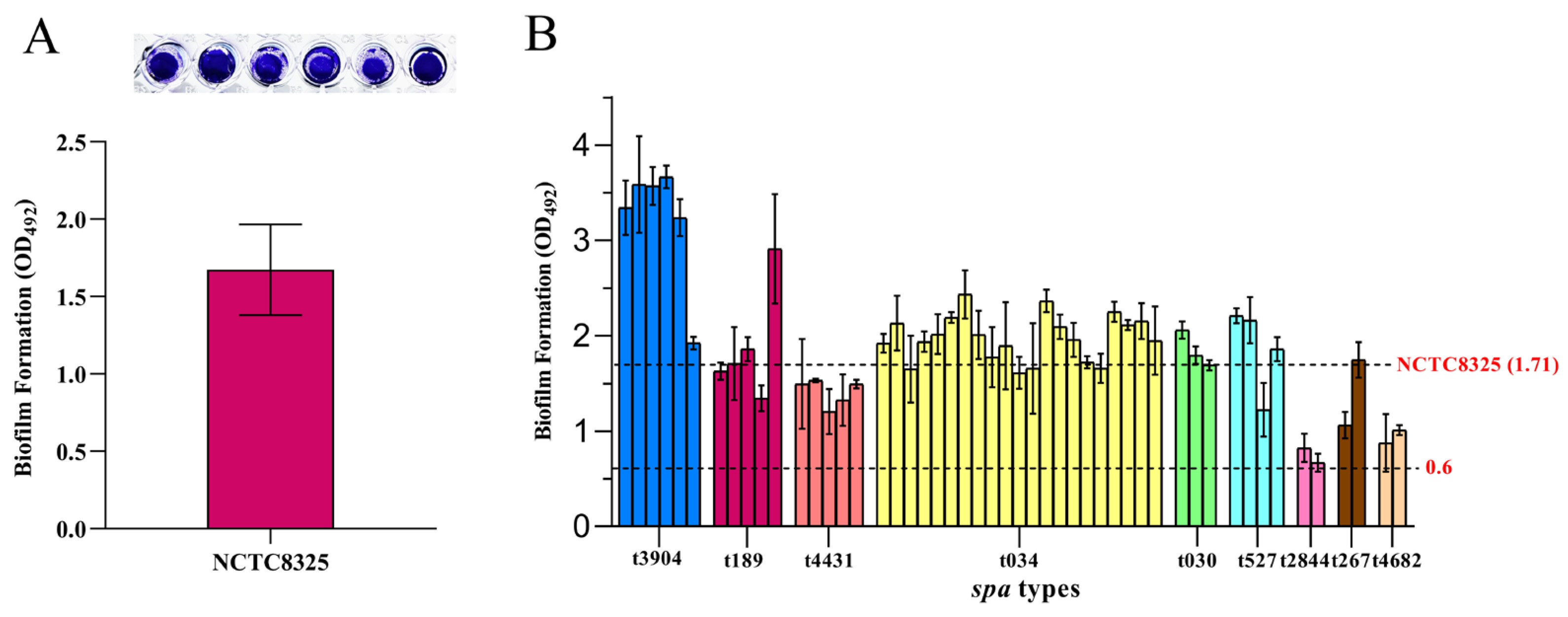
3.5. Detection of the Biofilm Formation Capacity of S. aureus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, K.; Li, C.; Chen, D.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Qu, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xie, S. A review on nanosystems as an effective approach against infections of Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 7333–7347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennekinne, J.-A.; De Buyser, M.-L.; Dragacci, S. Staphylococcus aurieus and its food poisoning toxins: Characterization and outbreak investigation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 815–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Bai, Z.; Li, X.; Rong, Z.; Shen, B.; Wang, S. Magnetic quantum dot based lateral flow assay biosensor for multiplex and sensitive detection of protein toxins in food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 146, 111754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.-A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—Major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Lei, T.; Chen, M.; Ding, Y.; Xue, L. Prevalence and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated From Retail Vegetables in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkerroum, N. Staphylococcal enterotoxins and enterotoxin-like toxins with special reference to dairy products: An overview. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1943–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cong, M.; Peng, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, R.; Liu, B.; Ye, W.; Yue, X. Quantitative proteomic analysis of milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) proteins in human and bovine colostrum and mature milk samples through iTRAQ labeling. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2438–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.; Guo, X.; Wen, F.; Chen, L.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, N.; Cheng, J.; Xue, X.; Wang, J. Aptamer-Based Fluorescence Quenching Approach for Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 653869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Van Dijk, A.D.J.; Hettinga, K. An interactomics overview of the human and bovine milk proteome over lactation. Proteome Sci. 2016, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragão, B.B.; Trajano, S.C.; Silva, J.G.; Silva, B.P.; Oliveira, R.P.; Junior, J.W.P.; Peixoto, R.M.; Mota, R.A. Short communication: High frequency of β-lactam-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in artisanal coalho cheese made from goat milk produced in northeastern Brazil. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 6923–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Chang, Y.; Shen, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y. Prevalence and Characteristics of enterotoxin B-Producing Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Food Sources: A Particular Cluster of ST188 Strains was Identified. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, M715–M718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellio, A.; Chiesa, F.; Gallina, S.; Bianchi, D.M.; Macori, G.; Bossi, D.; Nia, Y.; Mutel, I.; Messio, S.; Hennekinne, J.-A.; et al. Insight Into the Distribution of Staphylococci and Their Enterotoxins in Cheeses Under Natural Conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argudín, M.Á.; Mendoza, M.C.; Rodicio, M.R. Food Poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, E.L.; Otto, M.; Cheung, G.Y.C. Basis of Virulence in Enterotoxin-Mediated Staphylococcal Food Poisoning. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johler, S.; Macori, G.; Bellio, A.; Acutis, P.L.; Gallina, S.; Decastelli, L. Short communication: Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated along the raw milk cheese production process in artisan dairies in Italy. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2915–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyeon, J.-Y.; Chung, G.T.; Bing, S.H.; Kwon, K.S.; Lee, H.H.; Kim, S.J.; Jeon, S.E.; Kang, Y.H.; Kim, J. A Foodborne Outbreak of Staphylococcus aureus associated with Fried chicken in Republic of Korea. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wang, B.; Tao, X.; Hu, Q.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; You, Y.; Shi, X.; Grundmann, H. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Strains associated with food poisoning in Shenzhen, China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6637–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Baloch, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, C.; Peng, Z.; Li, F.; Fanning, S.; Ma, A.; Xu, J. Enterotoxigenicity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Retail Food in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; Molin, S.; Ciofu, O. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Hu, S.; Ye, C.; Li, Y.; Lan, Y.; Shen, J.; et al. In vitro antimicrobial effects and mechanism of air plasma-activated water on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 17, 1900270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoramian, B.; Jabalameli, F.; Niasari-Naslaji, A.; Taherikalani, M.; Emaneini, M. Comparison of virulence factors and biofilm formation among Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from human and bovine infections. Microb. Pathog. 2015, 88, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara, A.; Normanno, G.; Di Ciccio, P.; Pedonese, F.; Nuvoloni, R.; Parisi, A.; Santagada, G.; Colagiorgi, A.; Zanardi, E.; Ghidini, S.; et al. Biofilm Formation and Its Relationship with the Molecular Characteristics of Food-Related Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Nakatsu, C.H.; Bhunia, A.K. Bacterial Biofilms and Their Implications in Pathogenesis and Food Safety. Foods 2021, 10, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, X.; Deng, X.; Tan, M.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, N.; Jiang, R. Effect of resveratrol on the biofilm formation and physiological properties of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Proteom. 2021, 249, 104357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.C.; Crisóstomo, I.; Santos-Sanches, I.; Major, P.; Alves, C.R.; Aires-De-Sousa, M.; Thege, M.K.; de Lencastre, H. Comparison of DNA Sequencing of the protein A Gene polymorphic region with other molecular typing techniques for typing Two epidemiologically diverse collections of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmsen, D.; Claus, H.; Witte, W.; Rothgäger, J.; Claus, H.; Turnwald, D.; Vogel, U. Typing of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a University hospital setting by using novel software for spa repeat determination and database management. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5442–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Liao, G.; Wu, Z.; Lv, J.; Chen, W. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from subclinical bovine mastitis in southern Xinjiang, China. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3368–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, W.; Meng, H.; Huang, Q.; He, L.; Gao, Q.; Lv, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Decreasing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections is attributable to the disappearance of predominant MRSA ST239 clones, Shanghai, 2008–2017. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, Q.; Dai, Y.; Shang, J.; Li, M. Molecular Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Bovine Mastitis between 2014 and 2015. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.N.; Yuan, X.M.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, X.X.; Wang, W.B.; Liu, Y.Q. Prevalence and charac-terization of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bulk tank milk in Shandong dairy farms. Food Control 2021, 50, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brakstad, O.G.; Aasbakk, K.; Maeland, J.A. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, S.J.; Paterson, G.K. Mechanisms of Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 577–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiba, Y.; Katayama, Y.; Hishinuma, T.; Murakami-Kuroda, H.; Cui, L.; Hiramatsu, K. Mutation of RNA Polymerase beta-subunit Gene promotes heterogeneous-to-homogeneous conversion of beta-Lactam resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4861–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Zhao, L.; Xue, T.; Sun, B. Staphylococcus aureus autoinducer-2 quorum sensing decreases biofilm formation in an icaR-dependent manner. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Chen, X.; Shang, F. Short communication: Effects of lactose and milk on the expression of biofilm-associated genes in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from a dairy cow with mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 6129–6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, X.; Jiang, T.; Peng, Z.; Xu, J.; Yi, L.; Li, F.; Fanning, S.; Baloch, Z. Prevalence and Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Cultured From Raw Milk Taken From Dairy Cows With Mastitis in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-García, M.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Influence of serotype on the growth kinetics and the ability to form biofilms of Salmonella isolates from poultry. Food Microbiol. 2012, 31, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiran, E.; Di Ciccio, P.A.; Graber, H.U.; Zanardi, E.; Ianieri, A.; Hummerjohann, J. Biofilm formation of Staphylococcus aureus dairy isolates representing different genotypes. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.-H.; Maharik, N.M.S.; Valero, A.; Kamal, S.M. Incidence of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus in milk and Egyptian artisanal dairy products. Food Control 2019, 104, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetsch, A.; Contzen, M.; Hartelt, K.; Kleiser, A.; Maassen, S.; Rau, J.; Kraushaar, B.; Layer, F.; Strommenger, B. Staphylococcus aureus food-poisoning outbreak associated with the consumption of ice-cream. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 187, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Tang, C.; Chen, J.; Du, Y.; Yang, X.N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yue, H. Phenotypic Characterization and prevalence of enterotoxin genes in Staphylococcus aureus Isolates from outbreaks of illness in Chengdu City. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, M.C.D.; Campos, M.R.H.; Borges, L.J.; Kipnis, A.; Pimenta, F.C.; Serafini, Á.B. Comparison of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from food handlers, raw bovine milk and Minas Frescal cheese by antibiogram and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis following SmaI digestion. Food Control 2008, 19, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johler, S.; Weder, D.; Bridy, C.; Huguenin, M.-C.; Robert, L.; Hummerjohann, J.; Stephan, R. Outbreak of staphylococcal food poisoning among children and staff at a Swiss boarding school due to soft cheese made from raw milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2944–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, S.; Meng, L.; Dong, L.; Zhao, S.; Lan, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility, and molecular characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from dairy herds in northern China. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8796–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Rong, D. Multilocus Sequence Typing and Virulence-Associated Gene Profile Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates From Retail Ready-to-Eat Food in China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entorf, M.; Feßler, A.T.; Kaspar, H.; Kadlec, K.; Peters, T.; Schwarz, S. Comparative erythromycin and tylosin susceptibility testing of streptococci from bovine mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 194, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslantaş, Ö.; Demir, C. Investigation of the antibiotic resistance and biofilm-forming ability of Staphylococcus aureus from subclinical bovine mastitis cases. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 8607–8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tang, T.; Stegger, M.; Dalsgaard, A.; Liu, T.; Leisner, J.J. Characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from retail foods in Beijing, China. Food Microbiol. 2021, 93, 103603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Yu, Z.; Ho, H.; Wang, J.; Wu, W.; Xing, M.; Wang, Y.; Rahman, S.M.E.; Han, R. Occurrence, Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns, and Genetic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Raw Milk in the Dairy Farms over Two Seasons in China. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haran, K.P.; Godden, S.M.; Boxrud, D.; Jawahir, S.; Bender, J.B.; Sreevatsan, S. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus, Including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Isolated from bulk tank milk from Minnesota Dairy farms. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.; Paydar, M.; Radmehr, B.; Ismail, S.; Dadrasnia, A. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from raw milk and dairy products. Food Control 2015, 54, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilloniz, C.; Dominedò, C.; Gabarrús, A.; Garcia-Vidal, C.; Becerril, J.; Tovar, D.; Moreno, E.; Pericás, J.M.; Vargas, C.R.; Torres, A. Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in community-acquired pneumonia: Risk factors and outcomes. J. Infect. 2020, 82, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhou, L.; Wang, L.; Xue, H.; Zhao, X. Characterization of Methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcal isolates from Bovine milk in northwestern china. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.; Xia, X.; Yang, B.; Xi, M.; Meng, J. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in retail foods in Shaanxi, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, K.; Zhang, Y. Multidrug-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococci in food animals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Bai, L.; Li, W.; Han, H.; Fu, P.; Ma, X.; Bi, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhen, S.; et al. Trends of foodborne diseases in China: Lessons from laboratory-based surveillance since 2011. Front. Med. 2018, 12, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrynowicz-Paciorek, M.; Kochman, M.; Piekarska, K.; Grochowska, A.; Windyga, B. The distribution of enterotoxin and enterotoxin-like genes in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from nasal carriers and food samples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J.; Reyes, V.E. Staphylococcal enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 2177–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Ge, W.; Wu, C. Prevalence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from goat milk powder processing plants. Food Control 2016, 59, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Kou, X.; Ji, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S.; Li, B.; Dong, J.; Wang, Q.; et al. Prevalence and characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Kazak cheese in Xinjiang, China. Food Control 2020, 123, 107759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, G.; Bao, G.; Cao, Y.; Yan, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Y. Prevalence and diversity of enterotoxin genes with genetic background of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from different origins in China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 211, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yan, W.; Niu, X.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. The Distribution of 18 Enterotoxin and Enterotoxin-Like Genes in Staphylococcus aureus Strains from Different Sources in East China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Sánchez, D.; López-Cabo, M.; Saá-Ibusquiza, P.; Rodríguez-Herrera, J.J. Incidence and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus in fishery products marketed in Galicia (Northwest Spain). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 157, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Wang, J.; Mei, L.; Wang, Z.; Qi, K.; Yang, B. Recognition and enrichment specificity of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles surface modified by chitosan and Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins A antiserum. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 103, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Mandell, J.B.; Donegan, N.P.; Cheung, A.L.; Ma, W.; Rothenberger, S.; Shanks, R.M.Q.; Richardson, A.R.; Urish, K.L. The Toxin-Antitoxin MazEF Drives Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation, Antibiotic Tolerance, and Chronic Infection. mBio 2019, 10, e01658-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Liu, D. A systematic characterization of the distribution, biofilm-forming potential and the resistance of the biofilms to the CIP processes of the bacteria in a milk powder processing factory. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Mangolin, B.L.; Goncalves, J.L.; Neeff, D.V.; Silva, M.P.; Cruz, A.G.; Oliveira, C.A. Biofilm-producing ability of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from Brazilian dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 1812–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, N.; Toledo-Arana, A.; Vergara-Irigaray, M.; Valle, J.; Solano, C.; Calvo, E.; Lopez, J.A.; Foster, T.J.; Penadés, J.R.; Lasa, I. Protein A-Mediated Multicellular Behavior in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, C.; Haslinger-Löffler, B.; Westh, H.; Boye, K.; Peters, G.; Neumann, C.; Kahl, B.C. Non-spa-typeable clinical Staphylococcus aureus Strains are naturally occurring protein A mutants. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 3624–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Shang, W.; Hu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, J.; Hu, Q.; Peng, H.; Cai, X.; Tan, L.; Li, S.; et al. A novel SigB(Q225P) mutation in Staphylococcus aureus retains virulence but promotes biofilm formation. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Primer | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Product Size (bp) | Reference or Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16S | 27-F | AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG | 1510 | This study |
| 1492-R | TACCTTGTTACGACTT | |||
| nuc | SAnuc-F | AGTATATAGTGCAACTTCAAC | 448 | This study |
| SAnuc-R | ATCAGCGTTGTCTTCGCTCCAA | |||
| mecA | mecA-F | GTTGTAGTTGTCGGGTTT | 445 | This study |
| mecA-R | CCACATTGTTTCGGTCTA | |||
| spa | spa-1113F spa-1514R | TAAAGACGATCCTTCGGTGAGC CAGCAGTAGTGCCGTTTGCTT | variable | Ridom |
| sea | GSEAR-1 | GGTTATCAATGTGCGGGTGG | 102 | [15] |
| GSEAR-2 | CGGCACTTTTTTCTCTTCGG | |||
| seb | GSEBR-1 | GTATGGTGGTGTAACTGAGC | 164 | [15] |
| GSEBR-2 | CCAAATAGTGACGAGTTAGG | |||
| sec | GSECR-1 | AGATGAAGTAGTTGATGTGTATGG | 451 | [15] |
| GSECR-2 | CACACTTTTAGAATCAACCG | |||
| sed | GSEDR-1 | CCAATAATAGGAGAAAATAAAAG | 278 | [15] |
| GSEDR-2 | ATTGGTATTTTTTTTCGTTC | |||
| see | SA-U | TGTATGTATGGAGGTGTAAC | 213 | [15] |
| SA-E rev | GCCAAAGCTGTCTGAG | |||
| seg | SEG-F | GTTAGAGGAGGTTTTATG | 198 | [15] |
| SEG-R | TTCCTTCAACAGGTGGAGA | |||
| seh | SEH-F | CAACTGCTGATTTAGCTCAG | 173 | [15] |
| SEH-R | CCCAAACATTAGCACCA | |||
| sei | SEI-F | GGCCACTTTATCAGGACA | 328 | [15] |
| SEI-R | AACTTACAGGCAGTCCA | |||
| ser | SER 1 | AGATGTGTTTGGAATACCCTAT | 123 | [15] |
| SER 2 | CTATCAGCTGTGGAGTGCAT | |||
| selj | SEJ-F | GTTCTGGTGGTAAACCA | 131 | [15] |
| SEJ-R | GCGGAACAACAGTTCTGA | |||
| selp | SEP-F | TCAAAAGACACCGCCAA | 396 | [15] |
| SEP-R | ATTGTCCTTGAGCACCA |
| Monitoring Period (Month) | No. of Samples | No. of MRSA 1 Isolates | No. of Non-MRSA Isolates | No. and Proportion of Positive Samples of S. aureus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 69 | 6 | 44 | 50 (72.5%) |
| spa Type | spa Repeat Succession | No. and Proportion of Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| t3904 | 07-23-12-21-17-34-34-34-34 | 7 (14%) |
| t189 | 07-23-12-21-17-34 | 4 (8%) |
| t4431 | 07-12-21-17-13-34-33-13 | 5 (10%) |
| t034 | 08-16-02-25-02-25-34-24-25 | 21 (42%) |
| t030 | 15-12-16-02-24-24 | 3 (6%) |
| t527 | 07-23-12-21-17-34-34-34-34-34-33-34 | 4 (8%) |
| t2844 | 07-16-34-33-34 | 2 (4%) |
| t267 | 07-23-12-21-17-34-34-34-33-34 | 2 (4%) |
| t4682 | 26-34-34-34-33-34 | 2 (4%) |
| Enterotoxin Genes | Isolate Code No. | Detection Rate |
|---|---|---|
| sea | 49, 50 | 4% |
| seb | / | 0 |
| sec | 2, 46, 47 | 6% |
| sed | / | 0 |
| see | / | 0 |
| seg | / | 0 |
| sei | 7, 26 | 4% |
| seh | 7 | 2% |
| ser | 46, 47 | 4% |
| selj | 46, 47 | 4% |
| selp | 7, 8, 9, 19, 34, 35, 42 | 14% |
| Antibiotic Class | Antimicrobial | No. and Proportion of Resistant Isolates |
|---|---|---|
| β-Lactams | Ampicillin | 28 (56%) |
| Oxacillin | 7 (14%) | |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamicin | 11 (22%) |
| Kanamycin | 20 (40%) | |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline | 12 (24%) |
| Doxycycline | 3 (6%) | |
| Sulfonamides | Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim | 11 (22%) |
| Chloramphenicol | Chloramphenicol | 4 (8%) |
| Glycopeptides | Vancomycin | 0 (0%) |
| Macrolides | Erythromycin | 27 (54%) |
| Quinolones | Ofloxacin | 9 (18%) |
| No resistance to an antimicrobial agent | 8 (16%) | |
| Resistant to 1 antimicrobial agent | 5 (10%) | |
| Resistant to 2 antimicrobial agents | 8 (16%) | |
| Multi-drug resistant | 29 (58%) |
| spa Type (No) | No. of Isolates | No. and Proportion of Positive Samples of MRSA |
|---|---|---|
| t3904 | 7 | 0 (0%) |
| t189 | 4 | 0 (0%) |
| t4431 | 5 | 3 (60%) |
| t034 | 21 | 0 (0%) |
| t030 | 3 | 3 (100%) |
| t527 | 4 | 0 (0%) |
| t2844 | 2 | 0 (0%) |
| t267 | 2 | 0 (0%) |
| t4682 | 2 | 0 (0%) |
| Total | 50 | 6 (12%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Zhu, C.; Ma, K.; Fang, M.; Li, B.; Wang, W.; Xue, T. Antibiotics Resistance and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Isolated from Raw Milk from Handmade Dairy Retail Stores in Hefei City, China. Foods 2022, 11, 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152185
Wang H, Shen J, Zhu C, Ma K, Fang M, Li B, Wang W, Xue T. Antibiotics Resistance and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Isolated from Raw Milk from Handmade Dairy Retail Stores in Hefei City, China. Foods. 2022; 11(15):2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152185
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hui, Jiawei Shen, Chengfeng Zhu, Kai Ma, Mengcheng Fang, Bingbing Li, Wenhui Wang, and Ting Xue. 2022. "Antibiotics Resistance and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Isolated from Raw Milk from Handmade Dairy Retail Stores in Hefei City, China" Foods 11, no. 15: 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152185
APA StyleWang, H., Shen, J., Zhu, C., Ma, K., Fang, M., Li, B., Wang, W., & Xue, T. (2022). Antibiotics Resistance and Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Isolated from Raw Milk from Handmade Dairy Retail Stores in Hefei City, China. Foods, 11(15), 2185. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152185






