Quality of Set Yogurts Made from Raw Milk and Processed Milk Supplemented with Enriched Milk Fat Globule Membrane in a Two-Stage Homogenization Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
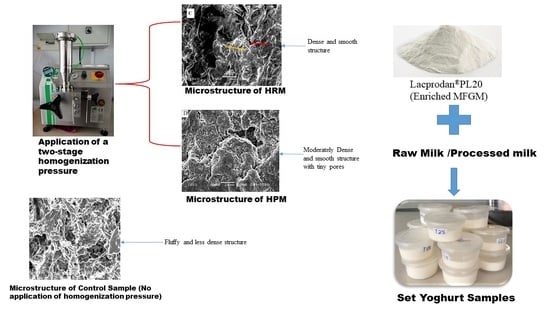
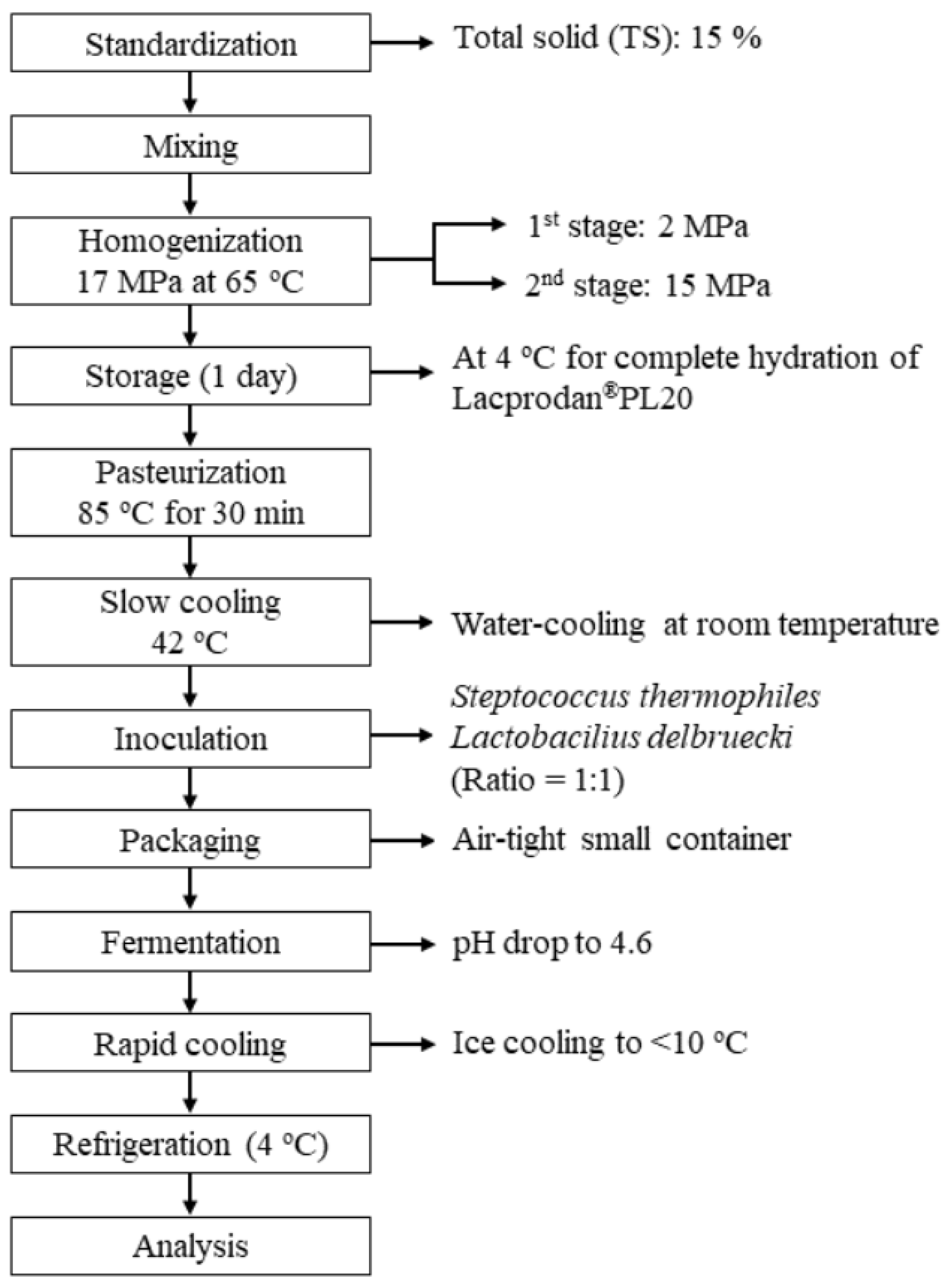
Set Yogurt Preparation
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Physicochemical Analyses
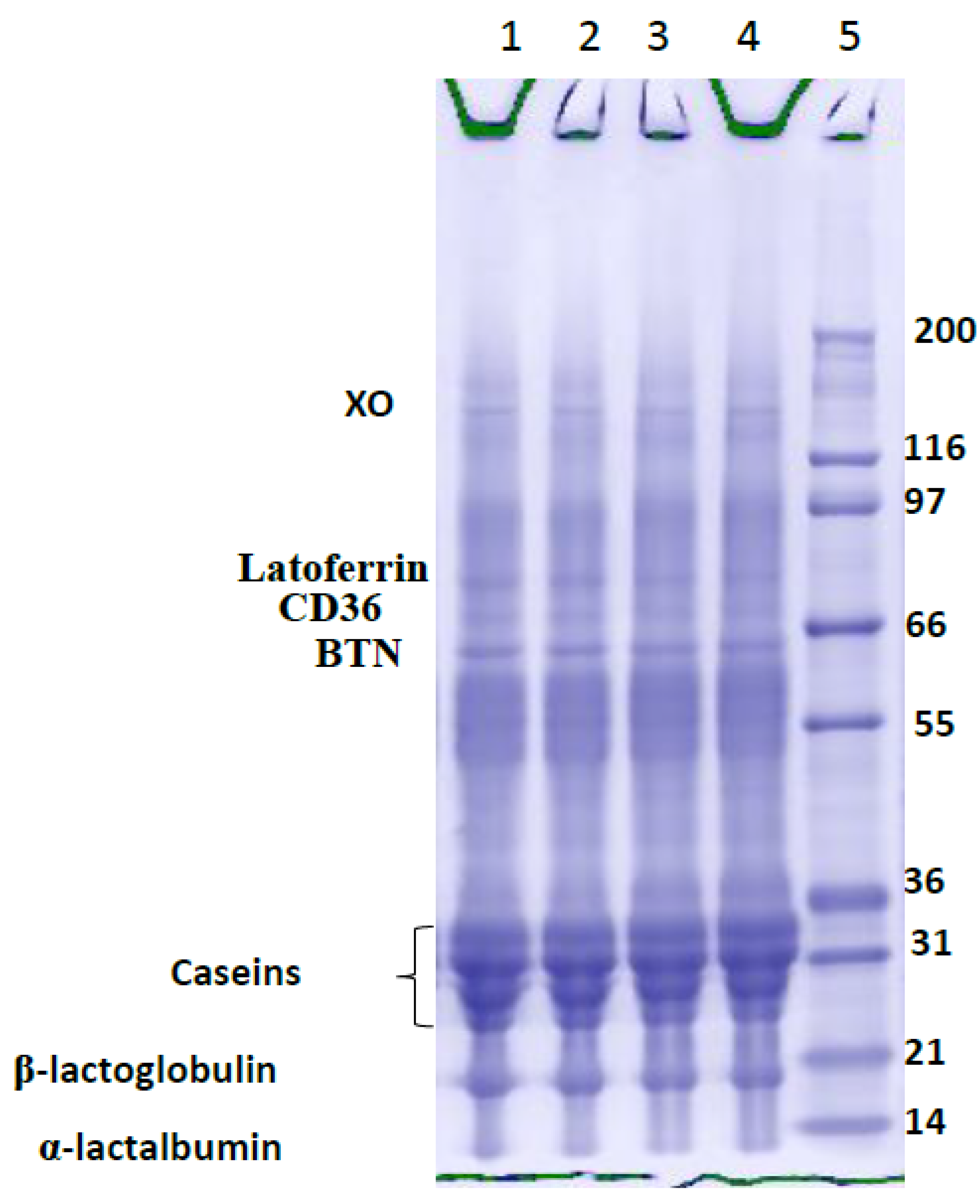
2.2.2. Specific Protein Determination
2.2.3. Firmness
2.2.4. Apparent Viscosity
2.2.5. Determination of Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.2.6. Microstructure Observation
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
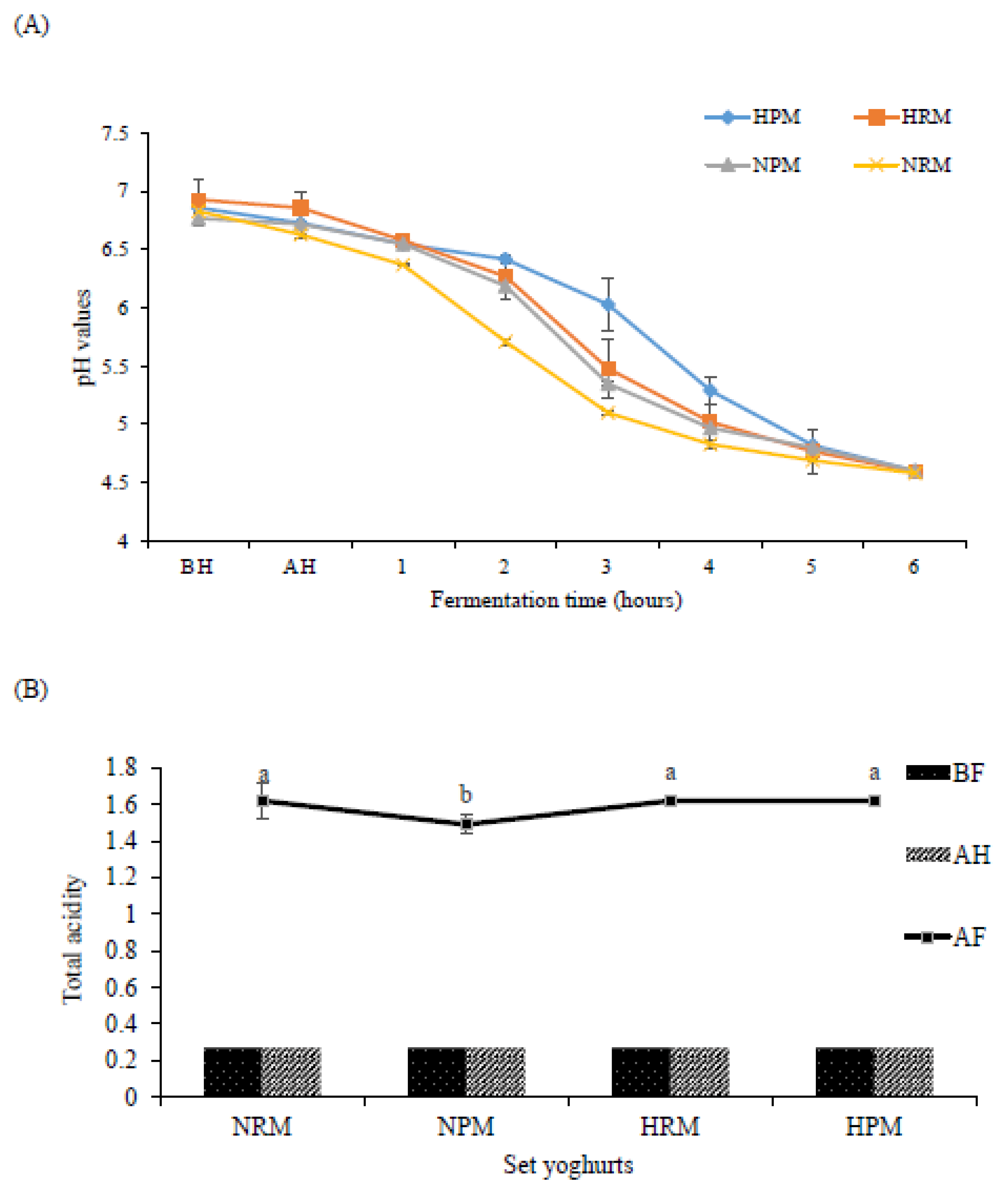
3.1. PH and Total Acidity
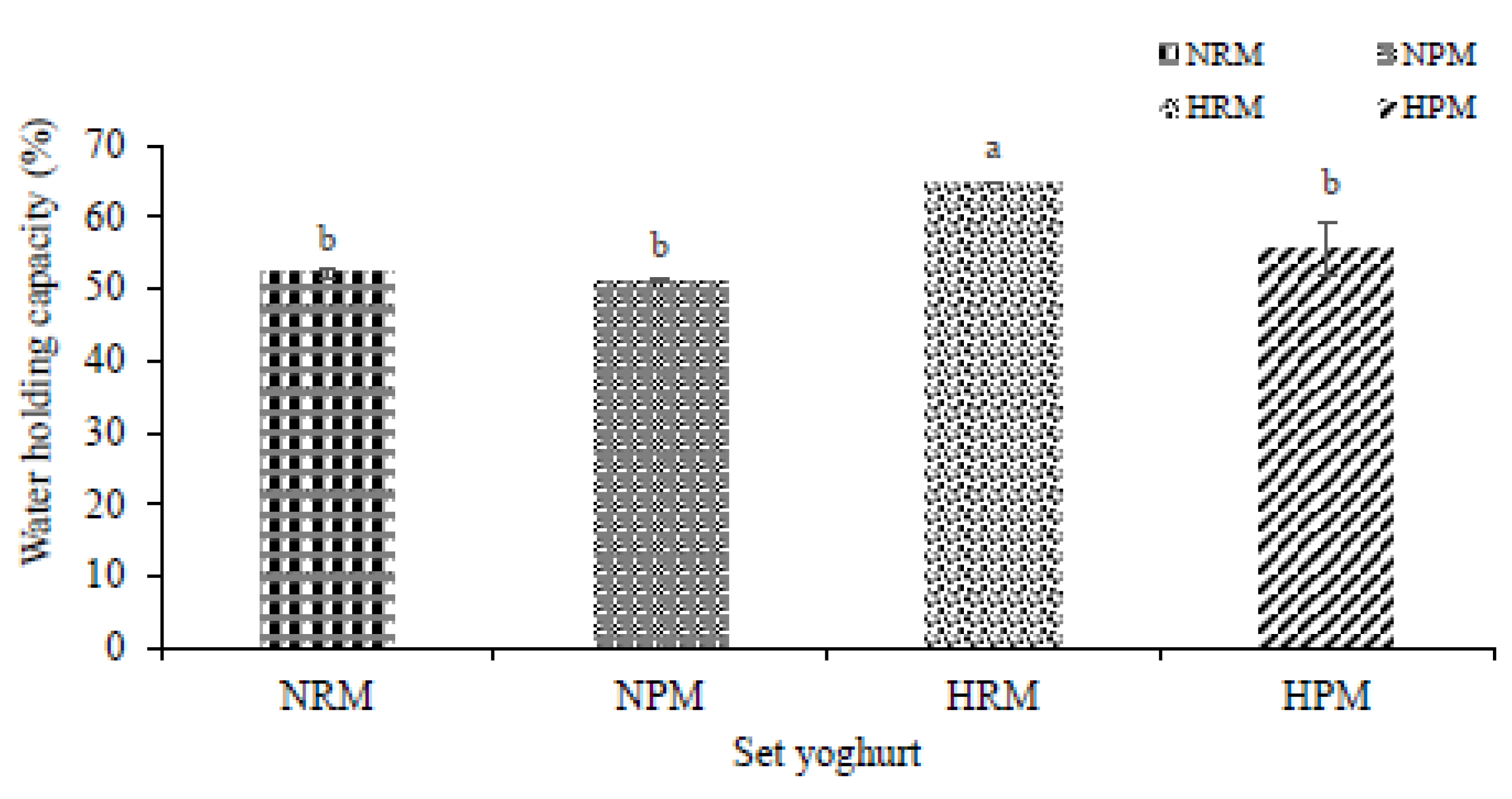
3.2. Water-Holding Capacity
3.3. Firmness of Different Set Yogurts with an Enriched MFGM
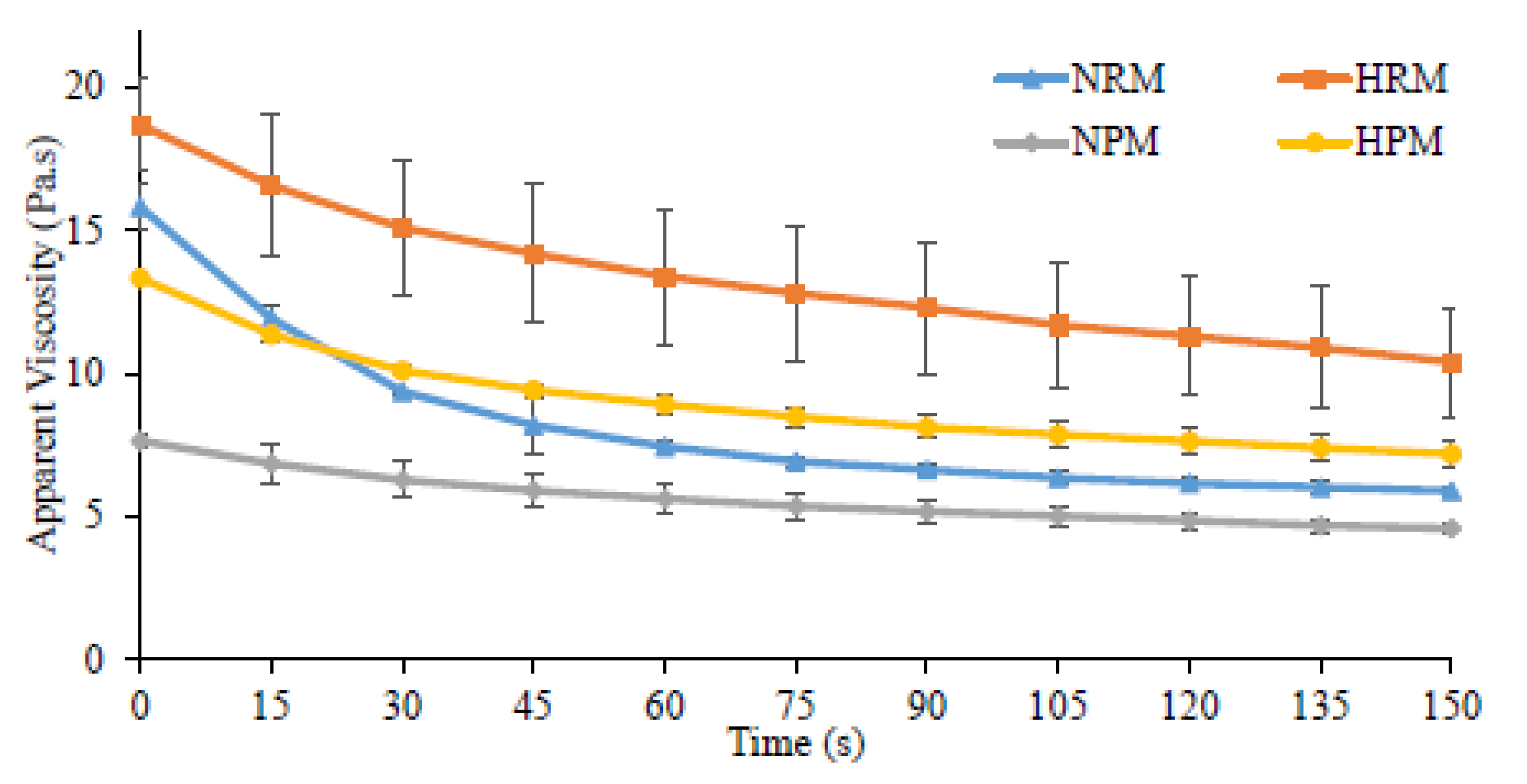
3.4. Variation in the Apparent Viscosity
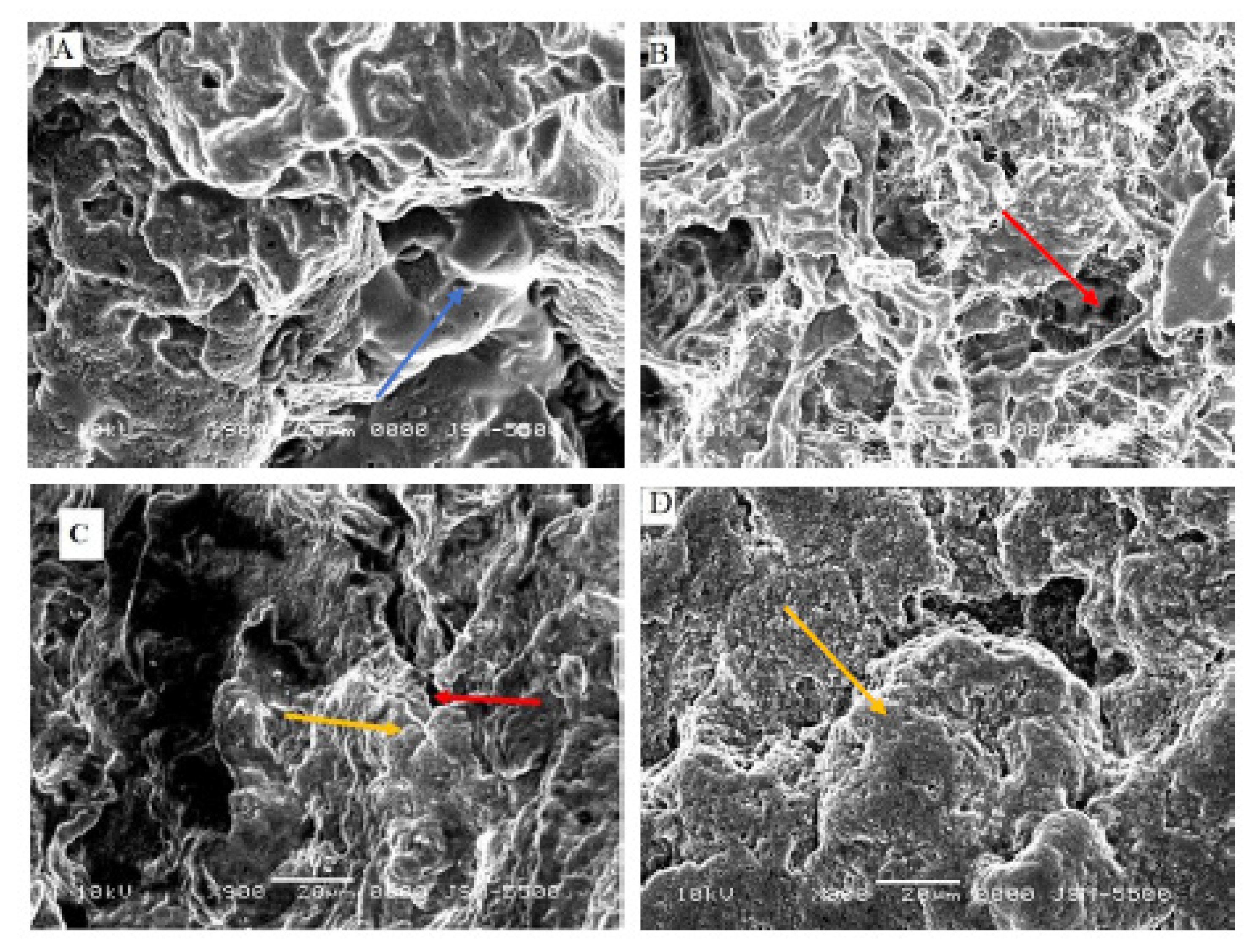
3.5. Microstructure of Set Yogurts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walstra, P.; Wouters, J.T.M.; Geurts, T.J. Dairy Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zou, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, X. Microstructural and lipid composition changes in milk fat globules during milk powder manufacture. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 62638–62646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Argov-Argaman, N.; Anggrek, J.; Boeren, S.; Van Hooijdonk, T.; Vervoort, J.; Hettinga, K.A. The protein and lipid composition of the membrane of milk fat globules depends on their size. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4726–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, P.; Jimenez-flores, R.; Pouliot, Y. Effect of processing on the composition and micro-structure of buttermilk and its milk fat globule membranes. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atehli, D.; Wang, J.; Ali, F. Effects of mono- and diglycerides of fatty acids on the milk fat globule membrane after heat treatment. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2020, 73, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, D.; Giuffrida, M.G.; Cavaletto, M.; Garoffo, L.P.; Dellavalle, G.; Napolitano, L.; Giunta, C.; Fabris, C.; Bertino, E.; Coscia, A.; et al. Structural proteome of human colostral fat globule membrane proteins. Proteomics 2003, 3, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewettinck, K.; Rombaut, R.; Thienpont, N.; Le, T.T.; Messens, K.; Van Camp, J. Nutritional and technological aspects of milk fat globule membrane material. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 436–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.W.; Heid, H.W.; Stadler, J.; Jarasch, E.D.; Franke, W.W. Tight attachment of fatty acids to proteins associated with milk fat globule membrane. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1982, 26, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H. The milk fat globule membrane—A biophysical system for food applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Ruiz, M.; Richter, R. Effect of Homogenization Pressure on the Milk Fat Globule Membrane Proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, J.M. The milkfat globule membrane e methodologies for measuring milkfat globule (membrane) damage. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, P. Changes in milk fat globule membrane proteome after pasteurization in human, bovine and caprine species. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcpherson, A.V.; Kitchen, B.J. Review of the progress of dairy science—The bovine milk fat globule membrane—Its formation, composition, structure and behavior in milk and dairy products. J. Dairy Res. 1983, 50, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Dalgleish, G.D. Interactions between milk serum proteins and synthetic fat globule membrane during heating of homogenized whole milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, D.F.; Butcher, D.W. Milk-fat globule mem- brane in homogenized cream. J. Dairy Res. 1978, 45, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.W.; Moon, T.W.; Dylewski, D.P. Lipid globules retain globule material after homogenization. J. Dairy Sci. 1983, 66, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadian, Z.; Eyres, G.T.; Carne, A.; Everett, D.W.; Bremer, P. Impact of different milk fat globule membrane preparations on protein composition, xanthine oxidase activity, and redox potential. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 64, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, A.; Singh, H.; Taylor, M.W.; Anema, S. Interactions of whey proteins with milk fat globule membrane proteins during heat treatment of whole milk. Le Lait 2004, 84, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlihan, A.V.; Goddard, P.A.; Nottingham, S.M.; Kitchen, B.J.; Masters, C.J. Interactions between the bovine milk fat globule membrane and skim milk components on heating whole milk. J. Dairy Res. 1992, 59, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safety, F.; Authority, S.; Health, M.O.F.; Welfare, F.; Delhi, N.E.W. Manual of Methods of Analysis of Foods. 2012. Available online: www.fssai.gov.in (accessed on 10 April 2019).
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, S.; Bayrakci, S. Physicochemical, functional, and sensory properties of yogurts containing persimmon. Turkish J. Agric. For. 2016, 40, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, R.A.; Bradley, R.L., Jr.; Williams, R.R. Chemical and Physical Methods. Standard Methods for the Examination of Dairy Products; Richardson, G.H., Ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1992; pp. 433–531. [Google Scholar]
- Le, T.T.; Van Camp, J.; Rombaut, R.; van Leeckwyck, F.; Dewettinck, K. Effect of washing conditions on the recovery of milk fat globule membrane proteins during the isolation of milk fat globule membrane from milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3592–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, I.H. A Review and Proposed Nomenclature for Major Proteins of the Milk-Fat Globule Membrane. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 203–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.; Van Camp, J.; Pascual, P.A.; Meesen, G.; Thienpont, N.; Messens, K.; Dewettinck, K. Physical properties and microstructure of yoghurt enriched with milk fat globule membrane material. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, L.K.; Haggag, H.; ElKalyoubi, M.; El-Aziz, M.A.; El-Sayed, M.; Sayed, A.F. Physico-chemical properties of yoghurt containing cress seed mucilage or guar gum. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2015, 60, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, P.A.L. Effects of Different Types of Milk Fat Globule Membrane Materials on the Physical and Rheological Characteristics of Set Yoghurts. Int. J. Agric. Innov. Res. 2017, 5, 968–973. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.J.; Sherbon, J.W. Chemical changes in bovine milk fat globule membrane caused by heat treatment and homogenization of whole milk. J. Dairy Res. 2002, 69, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Singh, H.; Taylor, M.W. Composition and Structure of Fat Globule Surface Layers in Recombined Milk. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolling, J.; Duncan, S.E.; Eigel, W.N. Processing effects on physicochemical properties of creams formulated with modified milk fat. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredig, M.; Dalgleish, D.G. Isolates from Industrial Buttermilk: Emulsifying Properties of Materials Derived from the Milk Fat Globule Membrane. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 4595–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, H.J.; Heinegard, D.; Poulsen, J.H. Combined Alcian Blue and Silver Staining of Sub-nanogram Quantities of Proteoglycans and Glycosaminoglycans in Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gels. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 209, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tal, M.; Silberstein, A.; Nusser, E. Why does Coomassie Brilliant Blue R interact differently with different proteins? A partial answer. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 9976–9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Oey, I.; Bremer, P.; Everett, D.W. Reduction of bacterial counts and inactivation of enzymes in bo-vine whole milk using pulsed electric fields. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 39, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claumarchirant, L.; Cilla, A.; Matencio, E.; Sanchez-Siles, L.M.; Castro-Gomez, P.; Fontecha, J.; Alegría, A.; Lagarda, M.J. Addition of milk fat globule membrane as an ingredient of infant formulas for resembling the polar lipids of human milk. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 61, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.T.; Salisbury, V.; Ovejero-Boglione, M.C.; Cherry, R.; Hoare, C.; Eisenthal, R.; Harrison, R. Anti-microbial properties of milk: Dependence on presence of xanthine oxidase and nitrite. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3308–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Martin, H.M.; Hancock, J.T.; Salisbury, V.; Harrison, R. Role of Xanthine Oxidoreductase as an Antimicrobial Agent. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 4933–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitsberg, R.C.; Gorewit, V.L. In vitro phosphorylated bovine milk fat globule membrane proteins. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1997, 8, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guggenmos, J.; Schubart, A.S.; Ogg, S.; Andersson, M.; Olsson, T.; Mather, I.H.; Linington, C. Antibody Cross-Reactivity between Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein and the Milk Protein Butyrophilin in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojdani, A.; Campbell, A.W.; Anyanwu, E.; Kashanian, A.; Bock, K.; Vojdani, E. Antibodies to neuron-specific antigens in children with autism: Possible cross-reaction with encephalitogenic proteins from milk, Chlamydia pneumoniae and Streptococcus group A. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 129, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukkola, A.; Rojas, O.J. Milk fat globules and associated membranes: Colloidal properties and processing effects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 245, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, S.; Guyomarc’H, F.; David-Briand, E.; Gaucheron, F.; Riaublanc, A.; Lopez, C. The phase and charge of milk polar lipid membrane bilayers govern their selective interactions with proteins as demonstrated with casein micelles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 534, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.W.; Dylewski, D.P. Intracellular origin of milk lipid globules and the nature of structure of milk fat globule membrane. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry-Lipids; Fox, P.F., Ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 89–130. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Tang, H.; Yi, H.; Xu, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, R. Properties of emulsions from milk fat globule membrane and its components. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, P.; Britten, M.; Jime’nez-Flores, R.; Pouliot, Y. Microfiltration of buttermilk and washed cream buttermilk for concentration of milk fat globule membrane components. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2132–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.F.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; Lynch, C.M. Lynch Significance of non-starter lactic acid bacteria in Cheddar cheese. Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 1998, 53, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Moe, K.; Porcellato, D.; Skeie, S. Metabolism of milk fat globule membrane components by nonstarter lactic acid bacteria isolated from cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, I.A.; Trout, G.M. The effect of homogenization on some of the characteristics of milk fat. J. Agric. Res. 1936, 52, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Goudédranche, H.; Fauquant, J.; Maubois, J.L. Fractionation of globular milk fat by membrane microfiltration. Le Lait 2000, 80, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Chang, Q.; Liu, X.; Meng, G. Improvement of crossflow microfiltration per-formances for treatment of phosphorus-containing wastewater. Desalination 2006, 194, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, S.; Guyomarc’h, F.; Francius, G.; Guillemin, H.; Wu, X.; Pezennec, S.; Famelart, M.-H.; Cauty, C.; Gaucheron, F.; Lopez, C. The surface properties of milk fat globules govern their interactions with the caseins: Role of homogenization and pH probed by AFM force spectroscopy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2019, 182, 110363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgleish, D.G. Denaturation and aggregation of serum proteins and caseins in heated milk. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1995–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, H. The milk fat globule: Emulsion science as applied to milk products and com-parable foods. Cent. Agric. Publ. Doc. Wagening. Netherl. 1974, 4, 163–192. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, O.; Blanchot, V.; Vuillemard, J.C.; Paquin, P. Microfluidization of dairy model emulsions. I. Preparation of emulsions and influence of processing and formulation on the size distribu-tion of milk fat globules. Le Lait 1992, 72, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britten, M.; Lamothe, S.; Robitaille, G. Effect of cream treatment on phospholipids and protein recovery in butter-making process. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 43, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Jiménez-Flores, R.; Everett, D.W. Lateral lipid organization of the bovine milk fat globule membrane is revealed by washing processes. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 5964–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzmüller, W.; Kulozik, U. Technical difficulties and future challenges in isolating membrane material from milk fat globules in industrial settings—A critical review. Int. Dairy J. 2016, 61, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, I.H.; Keenan, T.W. Studies on the structure of milk fat globule membrane. J. Membr. Biol. 1975, 21, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.; Golding, M. Influence of calcium ions on creaming and rheology of emulsions containing sodium caseinate. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1998, 144, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredig, M.; Dalgleish, D.G. The mechanisms of the heat-induced interaction of whey proteins with casein micelles in milk. Int. Dairy J. 1999, 9, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.P.; Kinsella, J.E. Effect of heat denaturation on the absorption of beta- lactoglobulin at the oil-water interface and on coalescence stability of emulsions. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1990, 139, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Kamiya, T.; Yamauchi, K. The adsorption of whey proteins on the surface of emulsified fat. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1981, 45, 2491–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Camier, B.; Gassi, J.Y. Development of the milk fat microstructure during the manufacture and ripening of Emmental cheese observed by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Set Yogurts | TS | TS Non-Fat | Protein | Fat | Ash | Lactose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRM | 18.62 ± 0.18 AB | 14.37 ± 0.38 A | 37.17 ± 0.19 A | 22.84 ± 1.39 B | 7.09 ± 0.30 AB | 32.90 ± 1.59 B |
| NPM | 17.49 ± 0.22 B | 13.01 ± 0.38 B | 36.03 ± 0.71 A | 25.64 ± 1.34 AB | 7.19 ± 0.18 A | 31.14 ± 1.82 B |
| HRM | 19.48 ± 1.05 A | 14.06 ± 1.11 AB | 33.90 ± 2.88 AB | 27.91 ± 2.41 A | 6.67 ± 0.26 B | 31.52 ± 4.70 B |
| HPM | 18.51 ± 0.04 AB | 14.23 ± 0.17 AB | 30.48 ± 1.33 B | 23.11 ± 1.01 B | 6.78 ± 0.24 AB | 39.64 ± 1.10 A |
| Set Yogurts | Firmness (g) |
|---|---|
| NRM | 28.00 ± 1.41 AB |
| NPM | 18.50 ± 2.12 B |
| HRM | 38.50 ± 2.12 A |
| HPM | 23.50 ± 3.54 B |
| Apparent Viscosity vs. Time (Pa.s) at 0.5 s−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Set Yogurts | Initial Viscosity | Final Viscosity | Loss of Structure (%) |
| NRM | 15.83 ± 0.83 AB | 5.89 ± 0.16 B | 62.72 ± 2.95 A |
| HRM | 18.70 ± 1.61 A | 10.49 ± 1.91 A | 44.12 ± 5.40 B |
| NPM | 7.64 ± 0.26 C | 4.58 ± 0.20 B | 42.52 ± 8.18 B |
| HPM | 13.34 ± 0.14 B | 7.18 ± 0.48 AB | 46.20 ± 3.03 B |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibitoye, J.O.; Ly-Nguyen, B.; Le, D.N.; Dewettinck, K.; Trzcinski, A.P.; Phan, T.T.Q. Quality of Set Yogurts Made from Raw Milk and Processed Milk Supplemented with Enriched Milk Fat Globule Membrane in a Two-Stage Homogenization Process. Foods 2021, 10, 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071534
Ibitoye JO, Ly-Nguyen B, Le DN, Dewettinck K, Trzcinski AP, Phan TTQ. Quality of Set Yogurts Made from Raw Milk and Processed Milk Supplemented with Enriched Milk Fat Globule Membrane in a Two-Stage Homogenization Process. Foods. 2021; 10(7):1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071534
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbitoye, Joshua Oladapo, Binh Ly-Nguyen, Duy Nghia Le, Koen Dewettinck, Antoine P. Trzcinski, and Thi Thanh Que Phan. 2021. "Quality of Set Yogurts Made from Raw Milk and Processed Milk Supplemented with Enriched Milk Fat Globule Membrane in a Two-Stage Homogenization Process" Foods 10, no. 7: 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071534
APA StyleIbitoye, J. O., Ly-Nguyen, B., Le, D. N., Dewettinck, K., Trzcinski, A. P., & Phan, T. T. Q. (2021). Quality of Set Yogurts Made from Raw Milk and Processed Milk Supplemented with Enriched Milk Fat Globule Membrane in a Two-Stage Homogenization Process. Foods, 10(7), 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071534