Influence of Region on Sensory and Chemical Profiles of Pennsylvania Grüner Veltliner Wines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
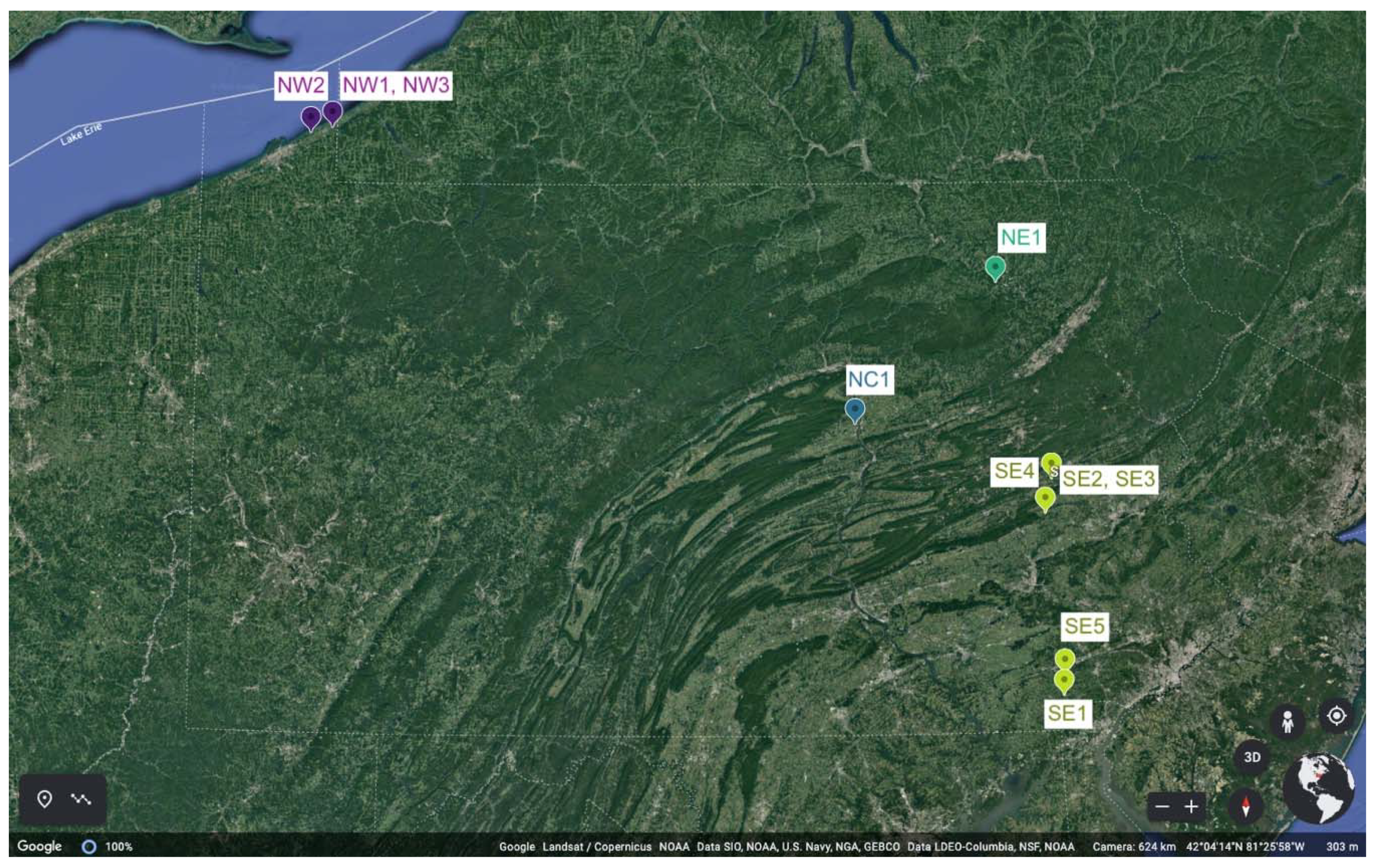
2.1. Site Selection
2.2. Vinification
2.3. Descriptive Analysis
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.4.1. Wine Chemical Analysis
2.4.2. Volatile Wine Analysis
2.4.3. Phenolic Analysis of Wine
2.4.4. Color Analysis of Wines via CIE-Lab Color Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
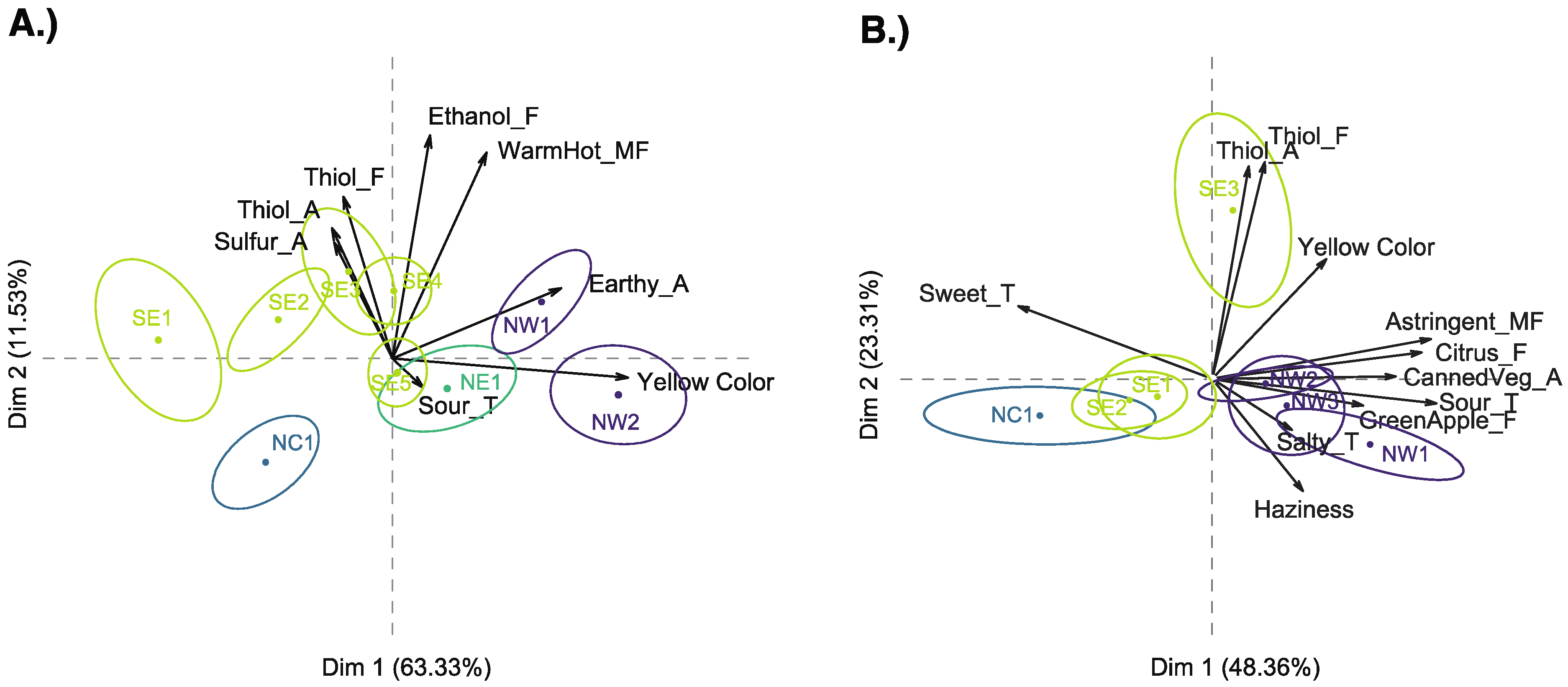
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
3.2. Chemical Analysis
3.2.1. Wine Chemical Analysis
3.2.2. Volatile Aroma Analysis
3.2.3. Phenolic and Color Analysis
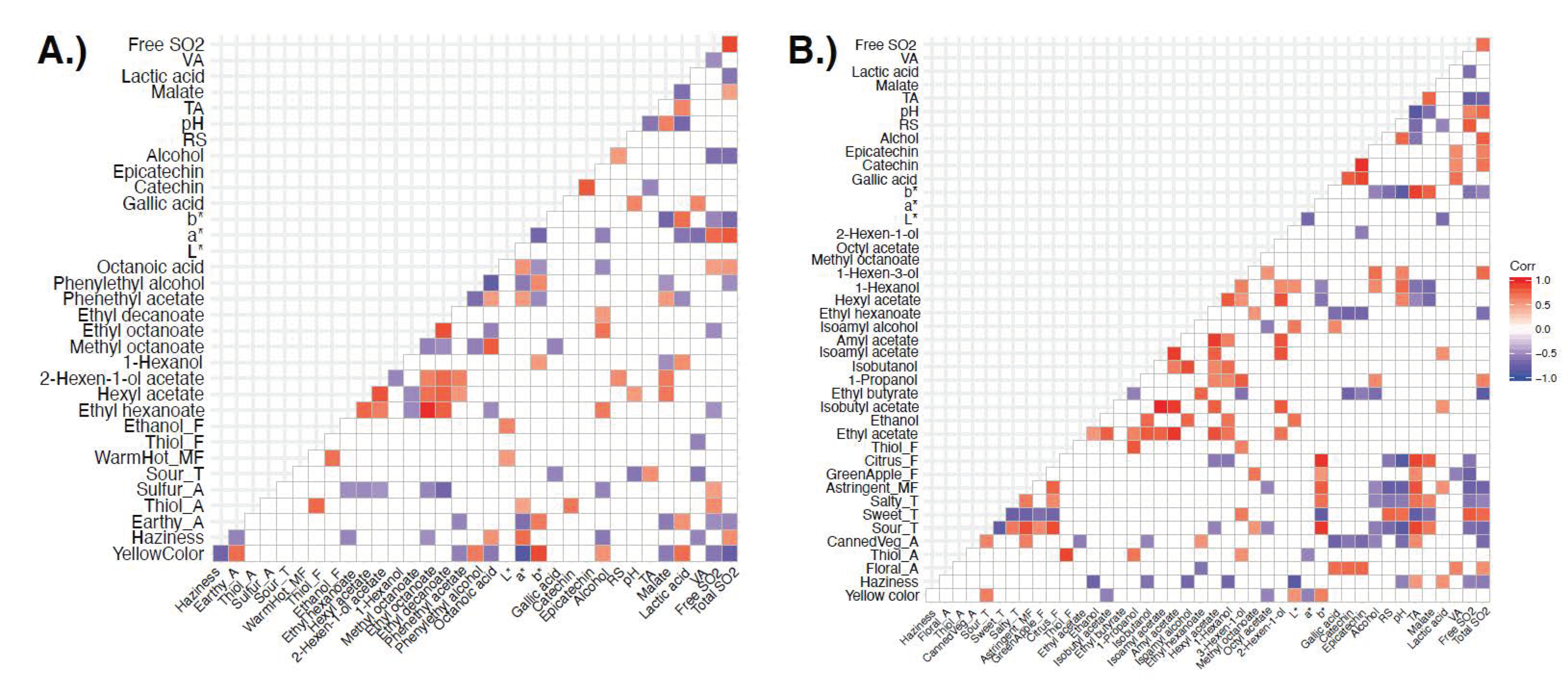
3.3. Relating Sensory and Instrumental Data
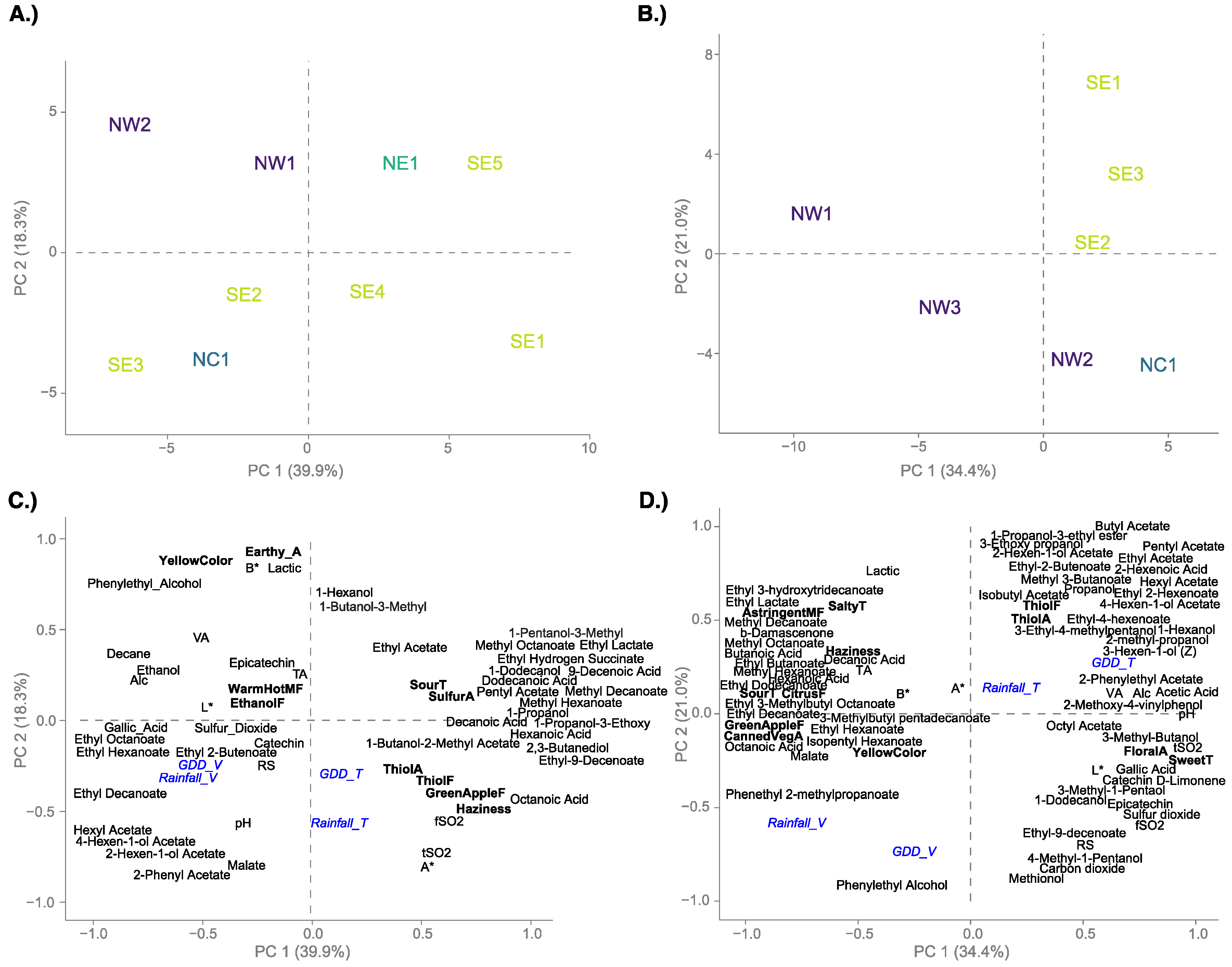
3.4. Relating Wine Data with Weather Conditions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Leeuwen, C. Influence of Climate, Soil, and Cultivar on Terroir. Am. J. Viticult. Enol. 2004, 55, 207–217. [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty, P.H. (Ed.) The Geography of Wine; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 978-94-007-0463-3. [Google Scholar]
- Easingwood, C.; Lockshin, L.; Spawton, A. The Drivers of Wine Regionality. J. Wine Res. 2011, 22, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, E.S.; Stoumen, M.; Buscema, F.; Hjelmeland, A.K.; Ebeler, S.E.; Heymann, H.; Boulton, R.B. Regional sensory and chemical characteristics of Malbec wines from Mendoza and California. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, H.; Robinson, A.L.; Buscema, F.; Stoumen, M.E.; King, E.S.; Hopfer, H.; Boulton, R.B.; Ebeler, S.E. Effect of Region on the Volatile Composition and Sensory Profiles of Malbec and Cabernet Sauvignon Wines. ACS Symp. Ser. 2015, 1203, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, J.; Versini, G.; Van Wyk, C.; Rapp, A. Effect of Region on Free and Bound Monoterpene and C13-N orisoprenoid Concentrations in Weisser Riesling Wines. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2017, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Green, J.; Parr, W.; Breitmeyer, J.; Valentin, D.; Sherlock, R. Sensory and chemical characterisation of Sauvignon blanc wine: Influence of source of origin. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2788–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.L.; Adams, D.O.; Boss, P.K.; Heymann, H.; Solomon, P.S.; Trengove, R.D. Influence of Geographic Origin on the Sensory Characteristics and Wine Composition of Vitis vinifera cv. Cabernet Sauvignon Wines from Australia. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2012, 63, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Úbeda, C.; del Barrio-Galán, R.; Peña-Neira, Á.; Medel-Marabolí, M.; Durán-Guerrero, E. Location Effects on the Aromatic Composition of Monovarietal cv. Carignan Wines. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2017, 68, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D.; Cliff, M.A.; Reynolds, A.G. Canadian terroir. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willwerth, J.J.; Reynolds, A.G.; Lesschaeve, I. Sensory Analysis of Riesling Wines from Different Sub-Appellations in the Niagara Peninsula in Ontario. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2015, 66, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, M. Understanding Regional Sensory Profiles of White Wines in Pennsylvania; The Pennsylvania State University: Twin City, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pompilio, R. Grüner Veltliner Finds a Home. Available online: https://winesvinesanalytics.com/features/article/156978/Gruner-Veltliner-Finds-a-Home (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- Austrian Wine Marketing Board. Austrian Wine Statistics Report 2017. Available online: https://www.austrianwine.com/fileadmin/user_upload/PDF/Doku/Austrian_Wine_Statistics_Report_2017.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2020).
- Flak, W.; Krizan, R.; Kutscher, W.; Tscheik, G.; Wallner, E. Charakterisierung von Weinen Der Sorte Grüner Veltliner Aus Verschiedenen Herkünften Im Weinbaugebiet Weinviertel. Mitteilungen Klosterneuburg 2007, 57, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Flak, W.; Krizan, R.; Passmann, G.; Tscheik, G.; Wallner, E. Charakterisierung von Leitweinen Des Weinbaugebietes Wagram. Teil 1: Grüner Veltliner. Mitteilungen Klosterneuburg 2009, 59, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Niimi, J.; Boss, P.K.; Bastian, S.E. Sensory profiling and quality assessment of research Cabernet Sauvignon and Chardonnay wines; quality discrimination depends on greater differences in multiple modalities. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineau, B.; Trought, M.; Stronge, K.; Beresford, M.; Wohlers, M.; Jaeger, S. Influence of fruit ripeness and juice chaptalisation on the sensory properties and degree of typicality expressed by Sauvignon Blanc wines from Marlborough, New Zealand. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2011, 17, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, E.S.; Dunn, R.L.; Heymann, H. The influence of alcohol on the sensory perception of red wines. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 28, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.S. Wine Science; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, A.; Cliff, M.; Girard, B.; Kopp, T.G. Influence of Fermentation Temperature on Composition and Sensory Properties of Semillon and Shiraz Wines. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2001, 52, 235–240. [Google Scholar]
- Troxell, S. (Galen Glen Winery, Andreas, PA, USA). Personal Communication, 2019.
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Descriptive Analysis. In Sensory Evaluation of Food; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 227–257. [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer, H.; Ebeler, S.E.; Heymann, H. The Combined Effects of Storage Temperature and Packaging Type on the Sensory and Chemical Properties of Chardonnay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10743–10754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveromo, A. The Impact of Wine Matrix Components on the Static and Temporal Perception of Sensory Attributes in a White, Hybrid Model Wine; The Pennsylvania State University: Twin City, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, M.K.; Elias, R.J. Reaction of Acetaldehyde with Wine Flavonoids in the Presence of Sulfur Dioxide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8615–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bétes-Saura, C.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M. Phenolics in White Free Run Juices and Wines from Penedès by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: Changes during Vinification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 3040–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization of Vine and Wine (OIV). Method OIV-MA-AS2-11: Determination of Chromatic Characteristics According to CIELab. OIV: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lindbloom, B. Spectral Calculator Spreadsheets. Available online: http://brucelindbloom.com/SpectCalcSpreadsheets.html (accessed on 4 January 2020).
- Gay, C. Invitation to comment. Food Qual. Pref. 1998, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R. Emmeans Estimated Marginal Means, Aka Least-Squares Means. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/emmeans (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Le, S.; Husson, F. Sensominer: A Package for Sensory Data Analysis. J. Sens. Stud. 2008, 23, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mendiburu, F. Agricolae: Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=agricolae (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Johnsen, L.G.; Skou, P.B.; Khakimov, B.; Bro, R. Gas chromatography—Mass spectrometry data processing made easy. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1503, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Míguez, M.J.; Gómez-Míguez, M.; Vicario, I.M.; Heredia, F.J. Assessment of colour and aroma in white wines vinifications: Effects of grape maturity and soil type. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadras, V.; Moran, M.; Bonada, M. Effects of elevated temperature in grapevine. I Berry sensory traits. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2012, 19, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawless, H.T.; Heymann, H. Physiological and Psychological Foundations of Sensory Function. In Sensory Evaluation of Food; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 28–82. [Google Scholar]
- Sherman, E.; Greenwood, D.R.; Villas-Boâs, S.G.; Heymann, H.; Harbertson, J.F. Impact of Grape Maturity and Ethanol Concentration on Sensory Properties of Washington State Merlot Wines. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2017, 68, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casassa, L.F.; Beaver, C.W.; Mireles, M.; Larsen, R.C.; Hopfer, H.; Heymann, H.; Harbertson, J.F. Influence of Fruit Maturity, Maceration Length, and Ethanol Amount on Chemical and Sensory Properties of Merlot Wines. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2013, 64, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, A.; Gambuti, A.; Piombino, P.; Moio, L. Sensory properties and aroma compounds of sweet Fiano wine. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T.; Boyer, J.D. Vineyard Site Selection. Available online: https://pubs.ext.vt.edu/content/dam/pubs_ext_vt_edu/463/463-020/463-020_pdf.pdf (accessed on 19 March 2020).
- Grifoni, D.; Carreras, G.; Zipoli, G.; Sabatini, F.; Marta, A.D.; Orlandini, S. Row orientation effect on UV-B, UV-A and PAR solar irradiation components in vineyards at Tuscany, Italy. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2008, 52, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.L.; Sacks, G.L.; Jeffery, D.W. Understanding Wine Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781118627808. [Google Scholar]
- Kliewer, W.M.; Weaver, R.J. Effect of Crop Level and Leaf Area on Growth, Composition, and Coloration of ‘Tokay’ Grapes. Am. J. Viticult. Enol. 1971, 22, 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Guidoni, S.; Allara, P.; Schubert, A. Effect of Cluster Thinning on Berry Skin Anthocyanin Composition of Vitis Vinifera Cv. Nebbiolo. Am. J. Viticult. Enol. 2002, 53, 224–226. [Google Scholar]
- Rutan, T.E.; Herbst-Johnstone, M.; Kilmartin, P.A. Effect of Cluster ThinningVitis viniferacv. Pinot Noir on Wine Volatile and Phenolic Composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10053–10066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawel, R.; Day, M.; Van Sluyter, S.C.; Holt, H.; Waters, E.J.; Smith, P.A. White Wine Taste and Mouthfeel as Affected by Juice Extraction and Processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10008–10014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saucier, C.T.; Waterhouse, A.L. Synergetic activity of catechin and other antioxidants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4491–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, M.A.; Elsey, G.M.; Capone, D.L.; Perkins, M.V.; Sefton, M.A. Fate of Damascenone in Wine: The Role of SO2. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 8127–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garde-Cerdán, T.; Ancín-Azpilicueta, C. Effect of SO2 on the formation and evolution of volatile compounds in wines. Food Control 2007, 18, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, J.L.; Noble, A.C. Astringency and bitterness of selected phenolics in wine. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1990, 53, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harner, A.D.; Heuvel, J.E.V.; Marini, R.P.; Elias, R.J.; Centinari, M. Modeling the Impacts of Weather and Cultural Factors on Rotundone Concentration in Cool-Climate Noiret Wine Grapes. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Attribute | Reference Standard |
|---|---|
| Yellow Color | Rated on line scale with anchors “No Yellow” to “Very Yellow” |
| Haziness | Rated on line scale with anchors “No Haze” to “Very Hazy” |
| Green Apple | 10.0 g fresh granny smith apple (Wegmans, State College, PA, USA) in 20 mL wine |
| Pear | 25.0 g fresh Bartlett pear (Wegmans) in 25 mL wine |
| Other Fruit | 10.0 g fresh nectarine + 10.0 g fresh peach (Wegmans) in 40 mL wine |
| 10 mL canned Fruit Cocktail juice (Wegmans) in 20 mL wine | |
| Grape | 3 halved fresh green grapes (Wegmans) in 20 mL wine |
| Citrus | 3 × 2 cm fresh lemon peel (Wegmans) in 20 mL wine |
| 3 × 2 cm each fresh orange peel + grapefruit peel (Wegmans) in 40 mL wine | |
| Floral | 4 drops of Floral stock in 20 mL wine (Floral stock: 1 drop lavender essential oil (Aura Cacia, Norway, IA, USA) in 25 mL wine) |
| Earthy | 1.0 g soil (Indoor Potting Mix, Miracle Gro Lawn Products Inc., Marysville, OH, USA) in 20 mL wine |
| Thiol | 0.075 mL of 30 µM 4-methyl-4-mercaptopentan-2-one in 50 mL RO water |
| Canned Vegetable | 2.5 mL canned pea juice + 2.5 mL canned green bean juice (Wegmans) in 20 mL wine |
| Rotten Egg | 0.4 g hardboiled egg yolk in 20 mL wine |
| Sulfur | 2 pinches potassium metabisulfite (Presque Isle Wine Cellars) in 25 mL RO water |
| Yeasty | 2 pinches baker’s yeast (Fleischman’s ActiveDry Yeast, ACH Food Companies, Memphis, TN, USA) in 5 mL RO water |
| Oxidized | 5 mL dry sherry (Taylor Wine Company, Canandaigua, NY, USA) in 20 mL wine |
| Chemical/Solvent | 1 drop ethyl acetate (VWR International, Radnor, PA, USA) in 50 mL wine |
| Ethanol | 10% (v/v) ethanol (Decon Labs, Inc., King of Prussia, PA, USA) solution |
| Sour | 1.5 g/L tartaric acid (≥99.7%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) in RO water 2.0 g/L malic acid (≥99%, Sigma-Aldrich) in RO water |
| Sweet | 20.0 g/L sucrose (Domino Foods, Inc., Yonkers, NY, USA) in RO water |
| Salty | 2.0 g/L salt (Morton Salt, Chicago, IL, USA) in RO water |
| Bitter | 0.8 g/L caffeine (Sigma-Aldrich) in RO water |
| Umami | 5.0 g/L monosodium glutamate (B&G Foods, Inc., Parsippany-Troy Hills, NJ, USA) in RO water |
| Viscous/Thick | 1.0 g/L carboxymethyl cellulose (Tic Gums, Belcamp, MD, USA) in RO water |
| Astringent | 0.8 g/L alum (McCormick, Hunt Valley, MD, USA) in RO water |
| Warm/Hot | 6% (v/v) ethanol (Decon Labs, Inc., King of Prussia, PA, USA) solution |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keller, S.T.; Harner, A.D.; Centinari, M.; Elias, R.J.; Hopfer, H. Influence of Region on Sensory and Chemical Profiles of Pennsylvania Grüner Veltliner Wines. Foods 2021, 10, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040825
Keller ST, Harner AD, Centinari M, Elias RJ, Hopfer H. Influence of Region on Sensory and Chemical Profiles of Pennsylvania Grüner Veltliner Wines. Foods. 2021; 10(4):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040825
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeller, Stephanie T., Andrew D. Harner, Michela Centinari, Ryan J. Elias, and Helene Hopfer. 2021. "Influence of Region on Sensory and Chemical Profiles of Pennsylvania Grüner Veltliner Wines" Foods 10, no. 4: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040825
APA StyleKeller, S. T., Harner, A. D., Centinari, M., Elias, R. J., & Hopfer, H. (2021). Influence of Region on Sensory and Chemical Profiles of Pennsylvania Grüner Veltliner Wines. Foods, 10(4), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10040825








