An Alternative Nutrient Rich Food Index (NRF-ai) Incorporating Prevalence of Inadequate and Excessive Nutrient Intake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development of Weighting Factors
2.2. Application to Selected Foods
2.3. Additional Sustainability Indicators
3. Results
3.1. Model Coefficients
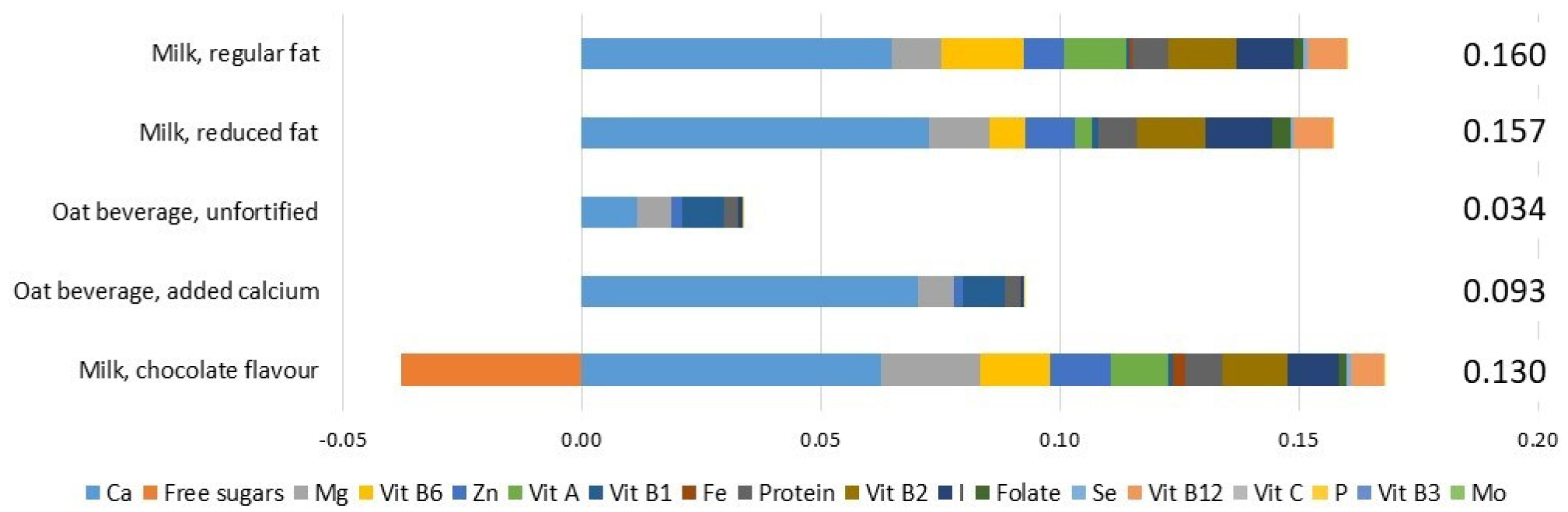
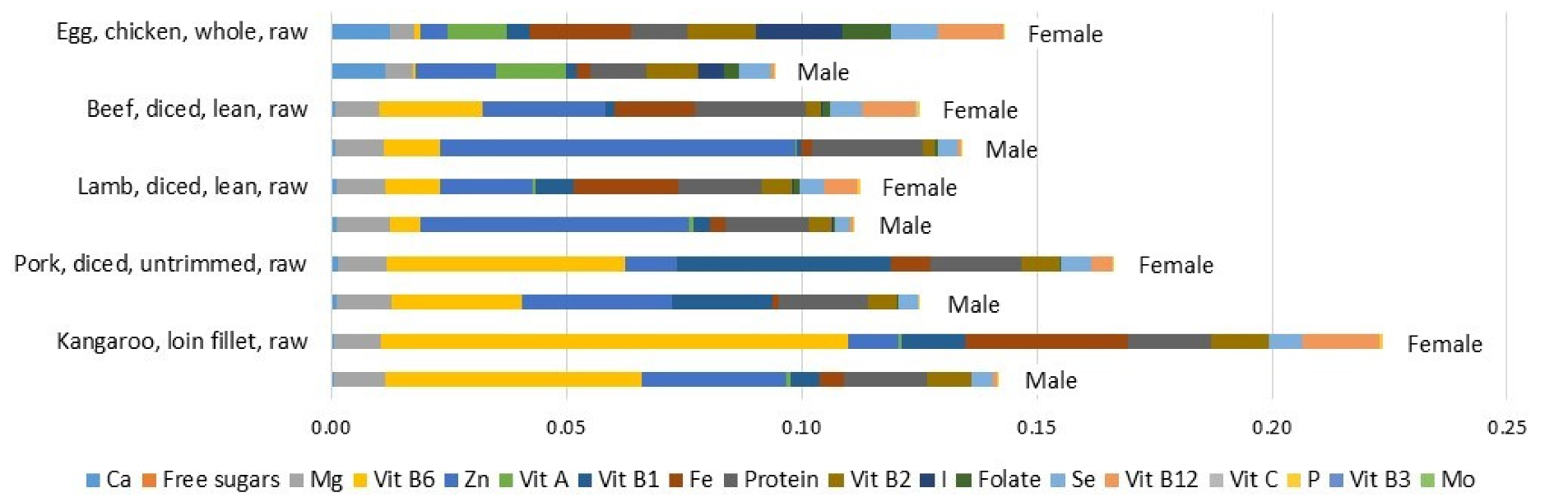
3.2. Nutrient Profiling Scores
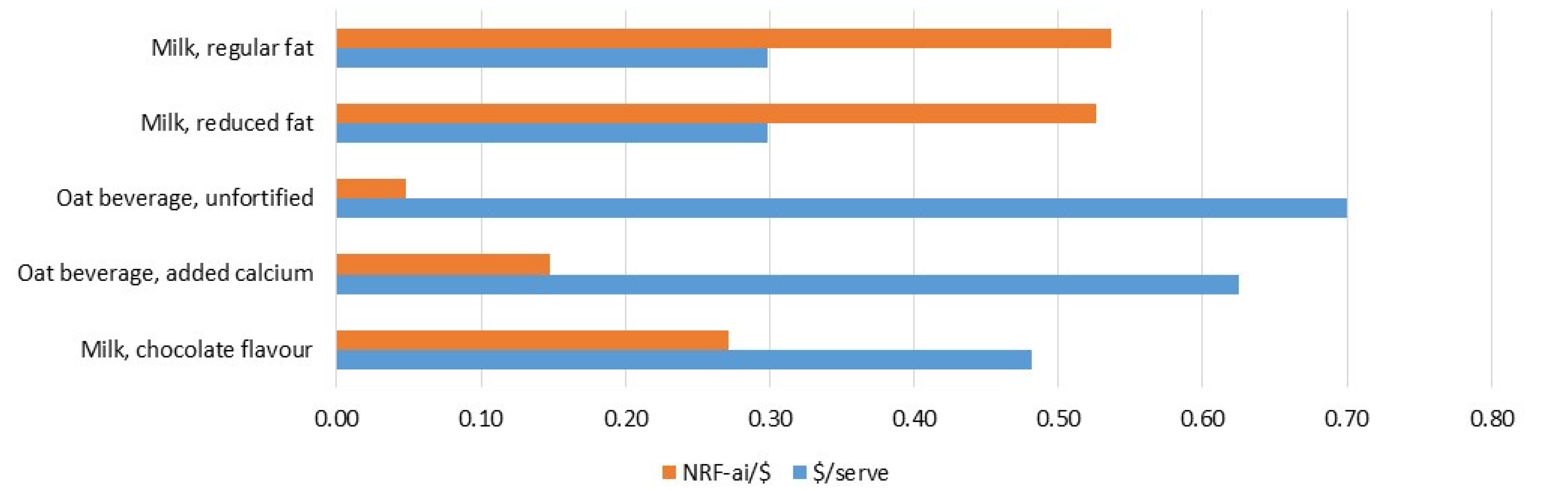
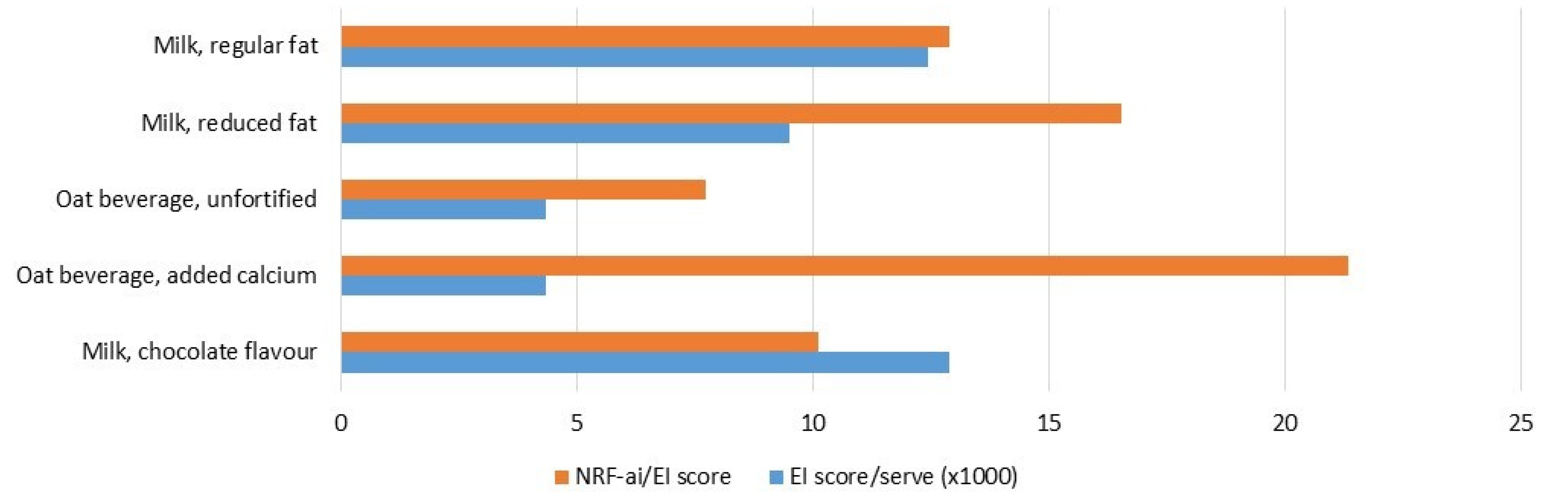
3.3. Affordability and Ecoefficiency
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vermeulen, S.J.; Campbell, B.M.; Ingram, J.S.I. Climate change and food systems. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2012, 37, 195–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willett, W.; Rockström, J.; Loken, B.; Springmann, M.; Lang, T.; Vermeulen, S.; Garnett, T.; Tilman, D.; DeClerck, F.; Wood, A.; et al. Food in the Anthropocene: The EAT-Lancet Commission on healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Lancet 2019, 393, 447–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poore, J.; Nemecek, T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science 2018, 360, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afshin, A.; Sur, P.J.; Fay, K.A.; Cornaby, L.; Ferrara, G.; Salama, J.S.; Mullany, E.C.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abebe, Z.; et al. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; World Health Organization. Sustainable Healthy Diets—Guiding Principles; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Drewnowski, A.; Finley, J.; Hess, J.M.; Ingram, J.; Miller, G.; Peters, C. Towards healthy diets from sustainable food systems. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2020, 4, nzaa083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridoutt, B.G.; Hendrie, G.A.; Noakes, M. Dietary strategies to reduce environmental impact: A critical review of the evidence base. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blackstone, N.T.; El-Abbadi, N.H.; McCabe, M.S.; Griffin, T.S.; Nelson, M.E. Linking sustainability to the healthy eating patterns of the Dietary Guidelines for Americans: A modelling study. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, E344–E352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinhardt, S.L.; Boehm, R.; Blackstone, N.T.; El-Abbadi, N.H.; Brandow, J.S.M.; Taylor, S.F.; DeLonge, M.S. Systematic review of dietary patterns and sustainability in the United States. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 1016–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheelbeek, P.; Green, R.; Papier, K.; Knuppel, A.; Alae-Carew, C.; Balkwill, A.; Key, T.J.; Beral, V.; Dangour, A.D. Health impacts and environmental footprints of diets that meet the Eatwell Guide recommendations: Analyses of multiple UK studies. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e037554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Cottrell, R.; Blanchard, J.L.; Bouwman, L.; Froehlich, H.E.; Gephart, J.A.; Jacobsen, N.S.; Kuempel, C.; McIntyre, P.B.; Metian, M.; et al. Putting all foods on the same table: Achieving sustainable food systems requires full accounting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18152–18156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hendrie, G.A.; Baird, D.; Ridoutt, B.; Hadjikakou, M.; Noakes, M. Overconsumption of energy and excessive discretionary food intake inflates dietary greenhouse gas emissions in Australia. Nutrients 2016, 8, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hallström, E.; Håkansson, N.; Åkesson, A.; Wolk, A.; Sonesson, U. Climate impact of alcohol consumption in Sweden. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 201, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perignon, M.; Sinfort, C.; El Ati, J.; Traissac, P.; Drogué, S.; Darmon, N.; Amiot, M.J.; Achir, N.; Alouane, L.; Bellagha, S.; et al. How to meet nutritional recommendations and reduce diet environmental impact in the Mediterranean region? An optimization study to identify more sustainable diets in Tunisia. Glob. Food Sec. 2019, 23, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridoutt, B.G.; Baird, D.; Hendrie, G.A. Diets within planetary boundaries: What is the potential of dietary change alone. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkos, F.; Tetens, I.; Bügel, S.; Felby, C.; Schacht, S.R.; Hill, J.O.; Ravussin, E.; Astrup, A. A Perspective on the transition to plant-based diets: A diet change may attenuate climate change, but can it also attenuate obesity and chronic disease risk? Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridoutt, B.G.; Baird, D.; Hendrie, G.A. The role of dairy foods in lower greenhouse gas emission and higher diet quality dietary patterns. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Nutrient Profiling: Report of a WHO/IASO Technical Meeting, London, United Kingdom 4–6 October 2010; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Drewnowski, A.; Fulgoni, V., III. Nutrient profiling of foods: Creating a nutrient-rich food index. Nutr. Rev. 2007, 66, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgoni, V.L., III; Keast, D.R.; Drewnowski, A. Development and validation of the Nutrient-Rich Food Index: A tool to measure nutritional quality of foods. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drewnowski, A. The Nutrient Rich Foods Index helps to identify healthy, affordable foods. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1095S–1101S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharrey, M.; Maillot, M.; Azaïs-Braesco, V.; Darmon, N. From the SAIN, LIM system to the SENS algorithm: A review of a French approach of nutrient profiling. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewnowski, A.; Maillot, M.; Darmon, N. Should nutrient profiles be based on 100 g, 100 kcal or serving size? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drewnowski, A. Measures and metrics of sustainable diets with a focus on milk, yogurt, and dairy products. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drewnowski, A.; Burton-Freeman, B. A new category-specific nutrient rich food (NRF9f.3) score adds flavonoids to assess nutrient density of fruit. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnowski, A.; Fulgoni, V.L., III. New nutrient rich food nutrient density models that include nutrients and MyPlate food groups. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Department of Health and Human Services & US Department of Agriculture. Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2005, 6th ed.; US Department of Health and Human Services &US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Food Standards Australia New Zealand. Nutrition Content Claims and Health Claims. Available online: https://www.foodstandards.gov.au/consumer/labelling/nutrition/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Hess, J.; Rao, G.; Slavin, J. The nutrient density of snacks: A comparison of nutrient profiles of popular snack foods using the Nutrient-Rich Food Index. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Astrup, A.; Magkos, F.; Bier, D.M.; Brenna, J.T.; de Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Hill, J.O.; King, J.C.; Mente, A.; Ordovas, J.M.; Volek, J.S.; et al. Saturated fats and health: A reassessment and proposal for food-based recommendations. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darmon, N.; Darmon, M.; Maillot, M.; Drewnowski, A. A nutrient density standard for vegetables and fruits: Nutrients per calorie and nutrients per unit cost. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 4364.0.55.007—Australian Health Survey: Nutrition First Results—Foods and Nutrients, 2011–2012; ABS: Canberra, Australia, 2014.
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 4363.0—National Health Survey: Users’ Guide, 2014–2015; ABS: Canberra, Australia, 2017.
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 43640DO01—20112012 Australian Health Survey: Usual Nutrient Intakes, 2011–2012—Australia; ABS: Canberra, Australia, 2015.
- National Health and Medical Research Council. Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand. Available online: https://www.nrv.gov.au/ (accessed on 15 April 2021).
- Pizzol, M.; Laurent, A.; Sala, S.; Weidema, B.; Verones, F.; Koffler, C. Normalisation and weighting in life cycle assessment: Quo vadis? Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2017, 22, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 31010DO002_201906 Australian Demographic Statistics, June 2019; ABS: Canberra, Australia, 2019.
- Food Standards Australia New Zealand. Australian Food Composition Database. Available online: https://www.foodstandards.gov.au/science/monitoringnutrients/afcd/pages/default.aspx (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- National Health and Medical Research Council. Australian Dietary Guidelines—Summary; NHMRC: Canberra, Australia, 2013.
- Coles. Coles Online. Available online: https://shop.coles.com.au/a/national/home (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Woolworths. Woolworths Online. Available online: https://www.woolworths.com.au/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO14045, Environmental Management—Eco-Efficiency Assessment of Product Systems—Principles, Requirements and Guidelines; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ridoutt, B.; Baird, D.; Hendrie, G.A. Diets within environmental limits: The climate impact of current and recommended Australian diets. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridoutt, B.G.; Baird, D.; Anastasiou, K.; Hendrie, G.A. Diet quality and water scarcity: Evidence from a large population health survey. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ridoutt, B.; Anastasiou, K.; Baird, D.; Navarro Garcia, J.; Hendrie, G. Cropland footprints of Australian dietary choices. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ling, M.; Inglis, S.C.; Hickman, L.; Parker, D. Eating and healthy ageing: A longitudinal study on the association between food consumption, memory loss and its comorbidities. Int. J. Public Health 2020, 65, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, E.; Kellett, J.; Bacon, R.; Naumovski, N. Food habits of older Australians living alone in the Australian Capital Territory. Geriatrics 2020, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwynn, J.; Sim, K.; Searle, T.; Senior, A.; Lee, A.; Brimblecombe, J. Effect of nutrition interventions on diet-related and health outcomes of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schouten, K.; Lindeman, M.A.; Reid, J.B. Nutrition and older Indigenous Australians: Service delivery implications in remote communities. A narrative review. Australas. J. Ageing 2013, 32, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsenault, J.E.; Fulgoni, V.L., III; Hersey, J.C.; Muth, M.K. A novel approach to selecting and weighting nutrients for nutrient profiling of foods and diets. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 1968–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health and Medical Research Council. A Modelling System to Inform the Revision of the Australian Guide to Healthy Eating; NHMRC: Canberra, Australia, 2011.
- Riley, M.D.; Baird, D.L.; Hendrie, G.A. Dairy food at the first occasion of eating is important for total dairy food intake for Australian children. Nutrients 2014, 6, 3878–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, A.; Nemecek, T.; Chaudhary, A.; Mathys, A. Assessing nutritional, health, and environmental sustainability dimensions of agri-food production. Glob. Food Sec. 2020, 26, 100406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.; Nemecek, T.; Smetana, S.; Mathys, A. Reconciling regionally-explicit nutritional needs with environmental protection by means of nutritional life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craddock, J.C.; Genoni, A.; Strutt, E.F.; Goldman, D.M. Limitations with the digestible indispensable amino acid score (DIAAS) with special attention to plant-based diets: A review. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2021, 10, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreman, L.; Nommensen, P.; Pennings, B.; Laus, M.C. Comprehensive overview of the quality of plant- and animal-sourced proteins based on the digestible indispensable amino acid score. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5379–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinangeli, C.P.F.; House, J.D. Potential impact of the digestible indispensable amino acid score as a measure of protein quality on dietary regulations and health. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakaloudi, D.R.; Halloran, A.; Rippin, H.L.; Oikonomidou, A.C.; Dardavesis, T.I.; Williams, J.; Wickramasinghe, K.; Breda, J.; Chourdakis, M. Intake and adequacy of the vegan diet. A systematic review of the evidence. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3503–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barré, T.; Perignon, M.; Gazan, R.; Vieux, F.; Micard, V.; Amiot, M.J.; Darmon, N. Integrating nutrient bioavailability and co-production links when identifying sustainable diets: How low should we reduce meat consumption? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phan, M.A.T.; Paterson, J.; Bucknall, M.; Arcot, J. Interactions between phytochemicals from fruits and vegetables: Effects on bioactivities and bioavailability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 1310–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Stockmann, R.; Ng, K.; Ajlouni, S. Revisiting phylate-element interactions: Implications for iron, zinc and calcium bioavailability, with emphasis on legumes. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Nutrient | Population Subgroup | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19–30 y | 31–50 y | 51–70 y | 70+ y | Females 19+ y | Males 19+ y | Adults 19+ y | |
| Calcium | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.22 |
| Free sugars | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.15 |
| Magnesium | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.13 |
| Vitamin B6 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.12 |
| Zinc | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.09 |
| Vitamin A | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.05 |
| Vitamin B1 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| Iron | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.04 |
| Protein | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
| Vitamin B2 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Iodine | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Folate | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Selenium | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| Vitamin C | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Phosphorus | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Vitamin B3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Molybdenum | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ridoutt, B. An Alternative Nutrient Rich Food Index (NRF-ai) Incorporating Prevalence of Inadequate and Excessive Nutrient Intake. Foods 2021, 10, 3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123156
Ridoutt B. An Alternative Nutrient Rich Food Index (NRF-ai) Incorporating Prevalence of Inadequate and Excessive Nutrient Intake. Foods. 2021; 10(12):3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123156
Chicago/Turabian StyleRidoutt, Bradley. 2021. "An Alternative Nutrient Rich Food Index (NRF-ai) Incorporating Prevalence of Inadequate and Excessive Nutrient Intake" Foods 10, no. 12: 3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123156
APA StyleRidoutt, B. (2021). An Alternative Nutrient Rich Food Index (NRF-ai) Incorporating Prevalence of Inadequate and Excessive Nutrient Intake. Foods, 10(12), 3156. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10123156






