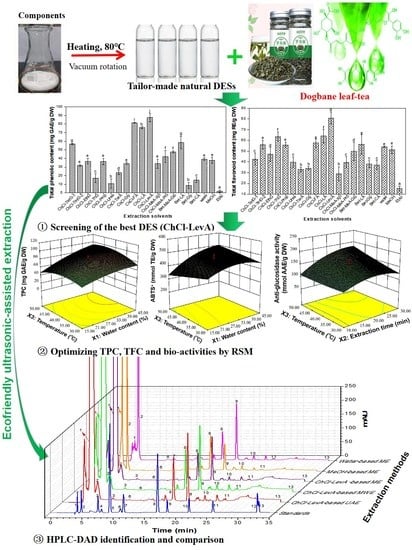
Customized Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Extractants for Ultrasonic-Assisted Enhanced Extraction of Phenolic Antioxidants from Dogbane Leaf-Tea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation and Chemical Characteristics Analysis of DESs
2.3. Total Phenolic Content (TPC) and Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
2.4. Antioxidant Activity In Vitro Assays
2.5. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity (α-GIA) Assay
2.6. Experimental Designs
2.6.1. Full Factorial Design Experiments
2.6.2. Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
2.7. Comparison of ChCl-LevA Based-UAE and Other Methods
2.7.1. Heating Extraction (HE)
2.7.2. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
2.7.3. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE)
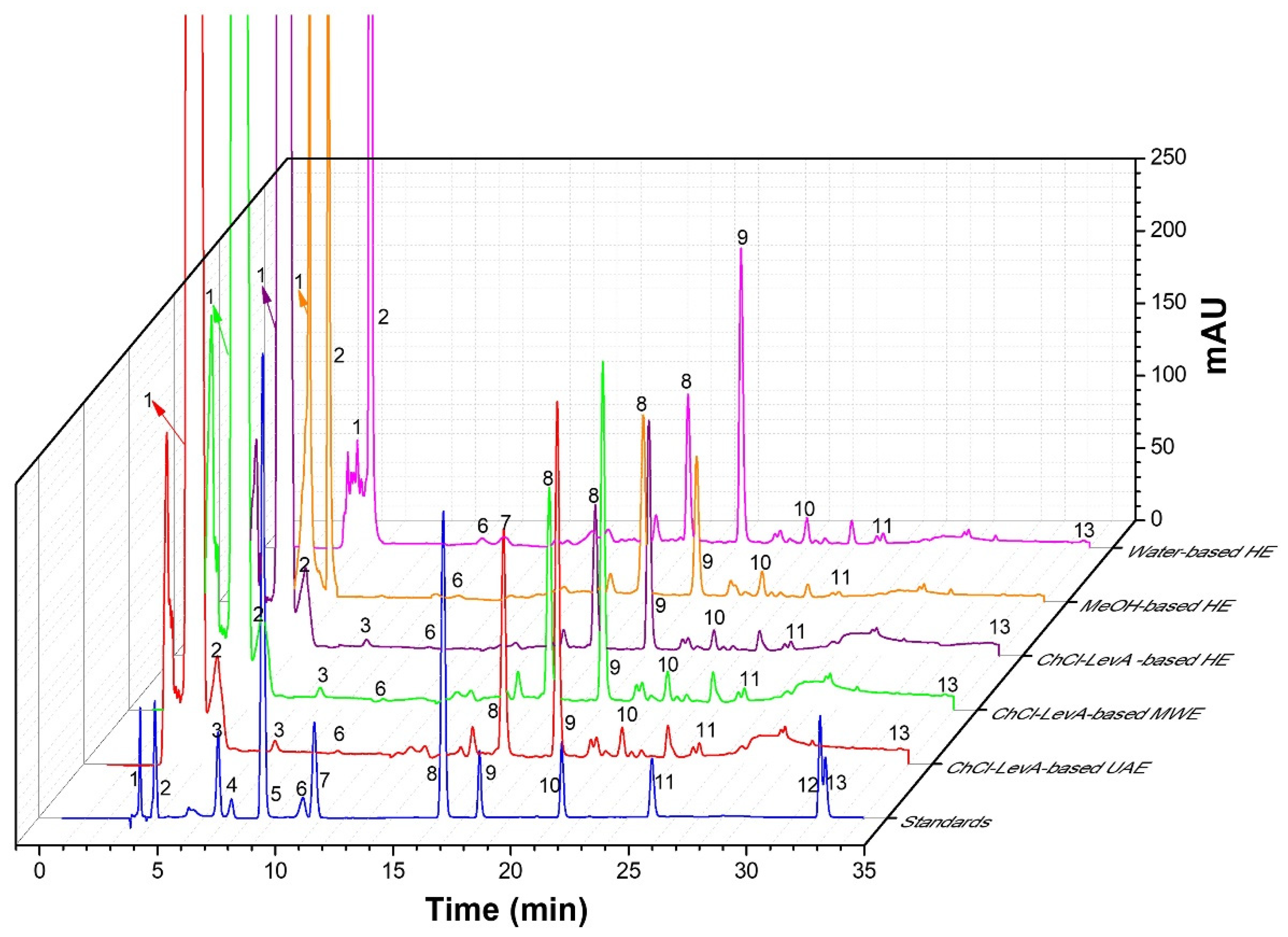
2.8. HPLC-DAD Analysis
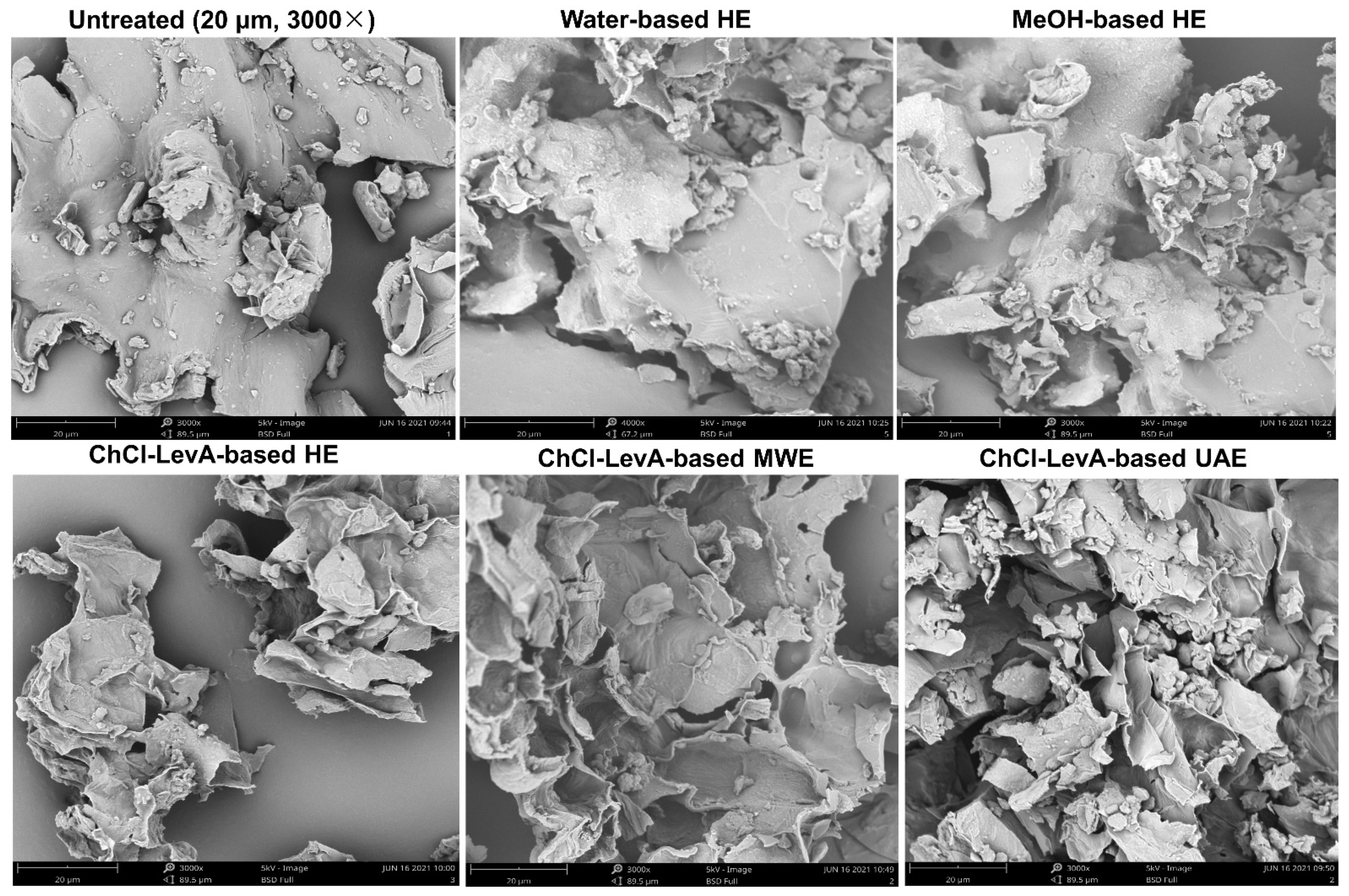
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Screening and Physical-Chemical Properties of DESs
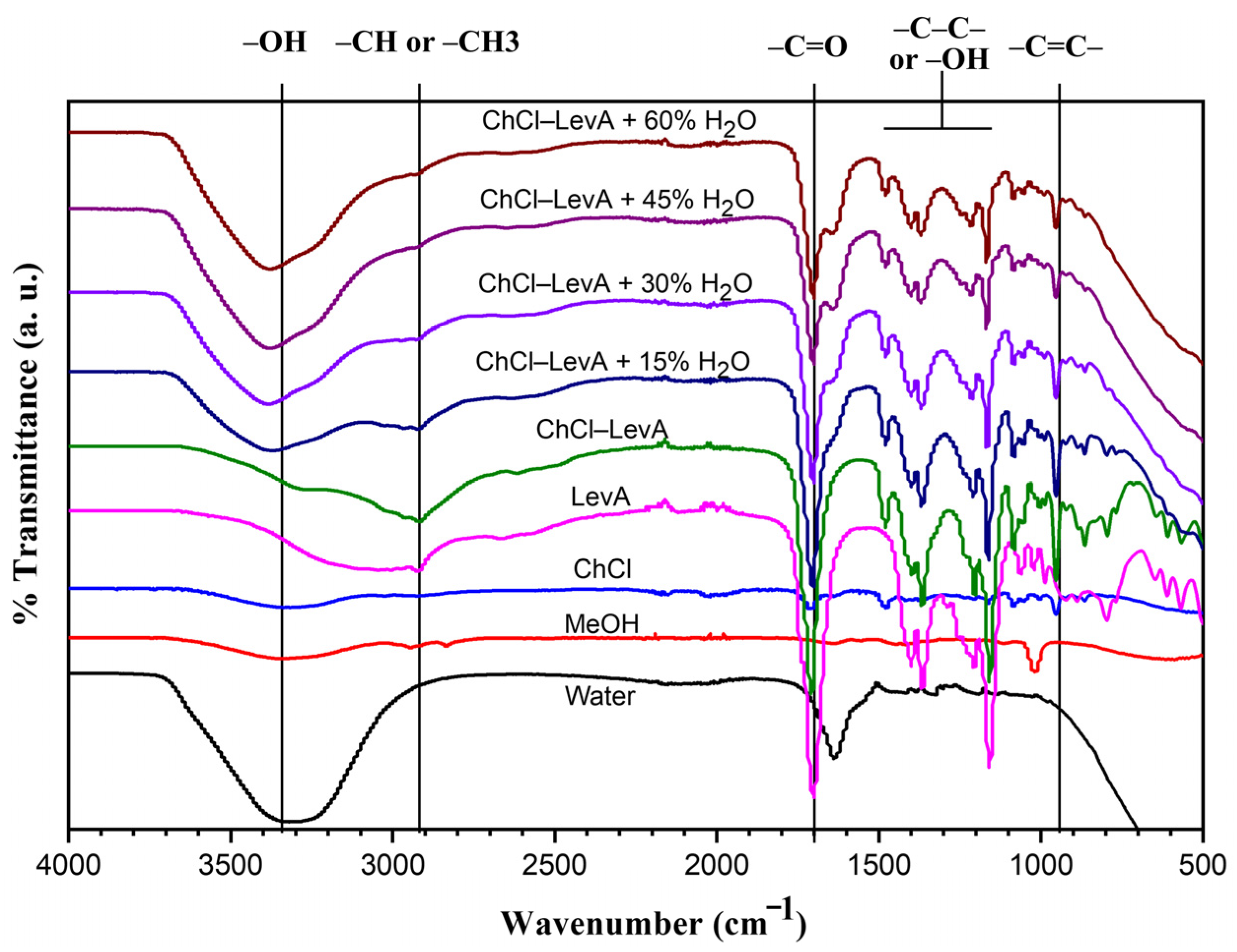
3.2. FT-IR Spectra of Extraction Solvents
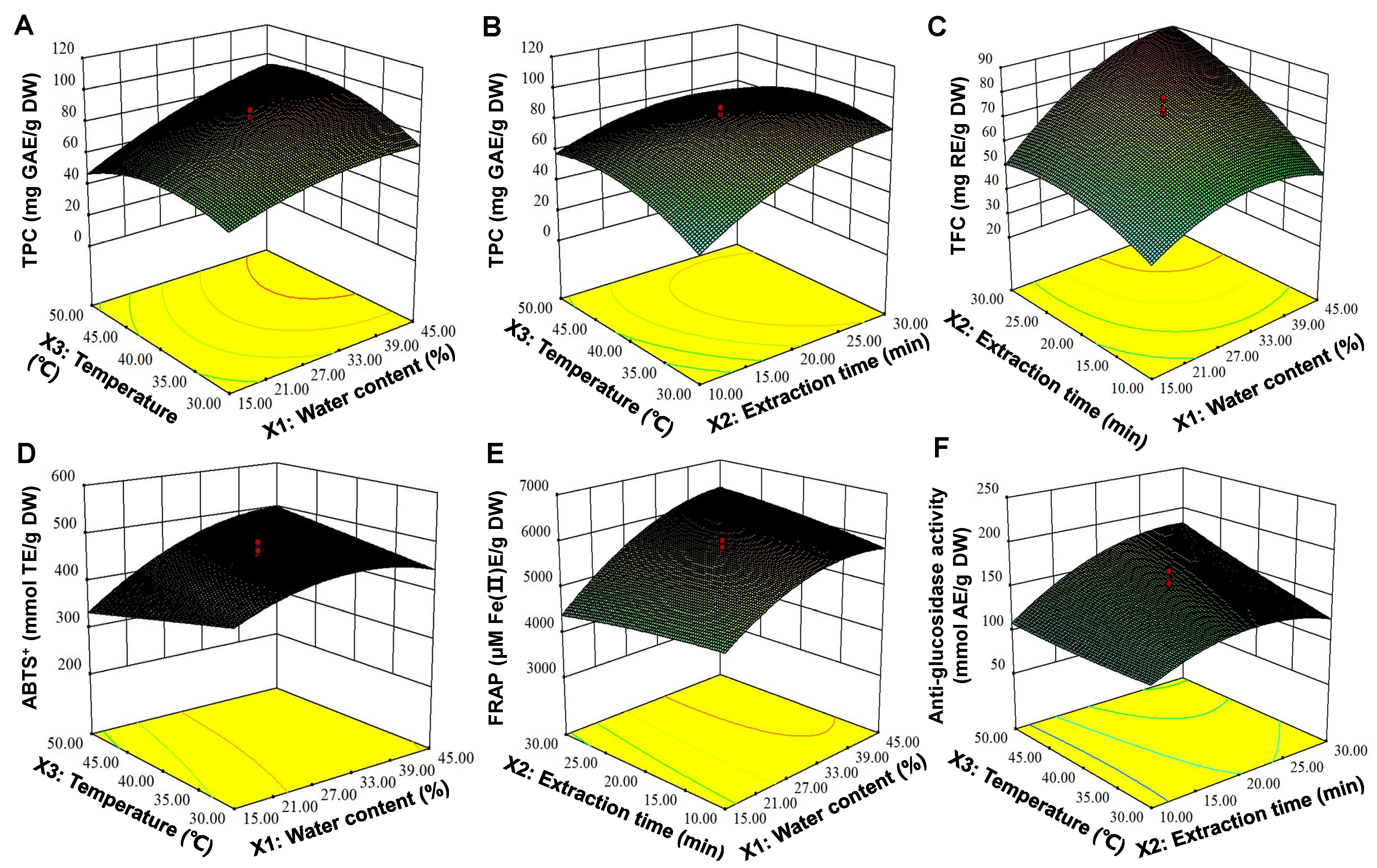
3.3. Modeling of UAE Process Conditions
3.4. Validation of the Optimal UAE Conditions
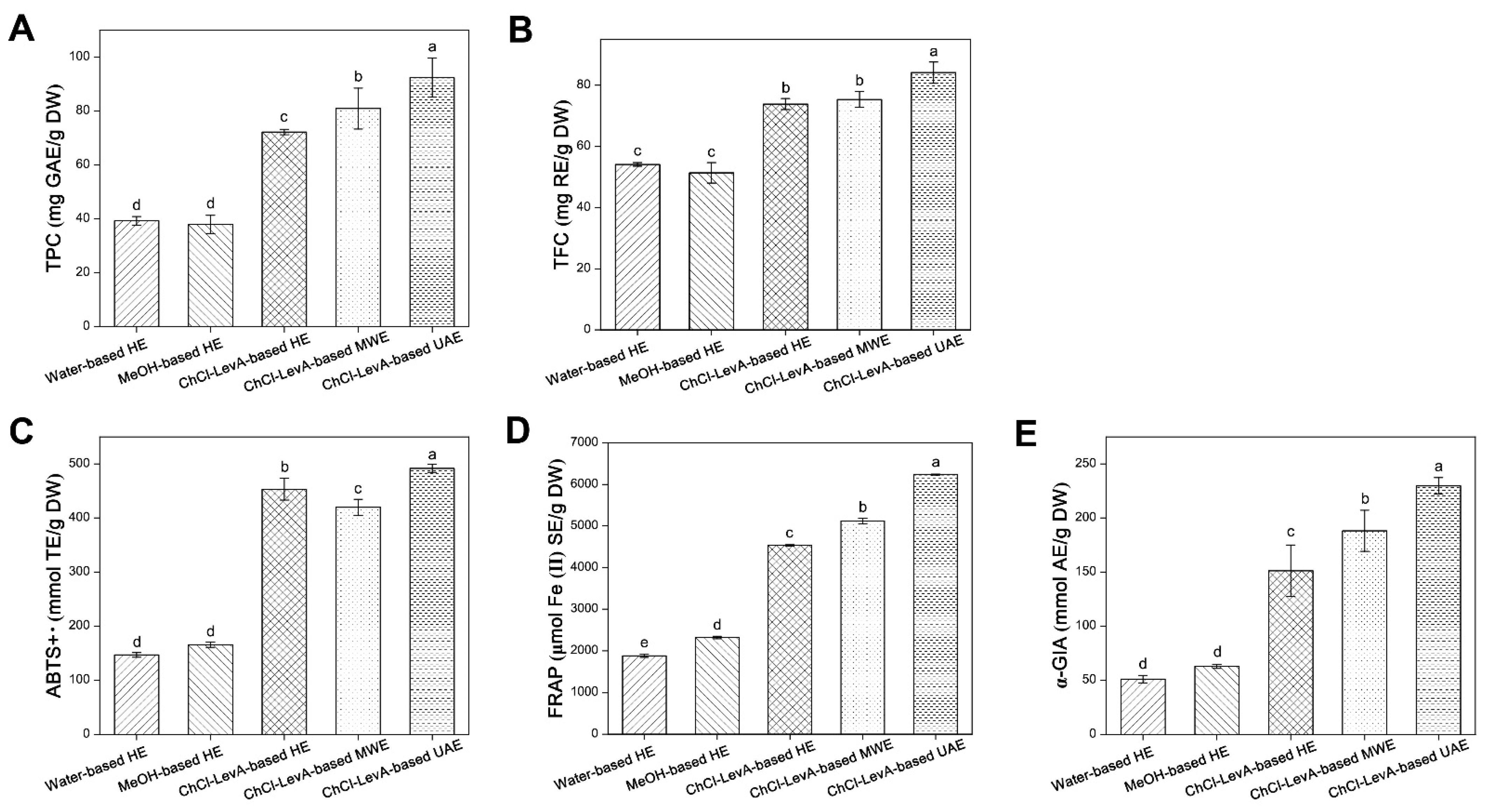
3.5. Comparison of ChCl-LevA-Based UAE and Other Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anand, U.; Nandy, S.; Mundhra, A.; Das, N.; Pandey, D.K.; Dey, A. A review on antimicrobial botanicals, phytochemicals and natural resistancemodifying agents from Apocynaceae family: Possible therapeutic approaches against multidrug resistance in pathogenic microorganisms. Drug Resist. Updates 2020, 51, 100695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Z.; He, M.Y.; Li, G.W.; Wu, W.P.; Qiu, Y.J.; Zeng, H.; Pan, L.Y. UPLC characteristic maps and determination of flavonoids in Apocyni veneti Folium from different producing areas. Modern Chin. Med. 2021, 23, 619–626. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.P.; Xu, H.; Chen, F.; Liu, X.H.; Zhang, F.S.; Hou, Y.; Ma, Y. Analytical studies on flavonoids constituents in Apocynum venetom leaves by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2014, 37, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Deng, J.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Li, S.P. Advanced phytochemical analysis of herbal tea in China. J. Chromatogr. A. 2013, 131, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atawodi, S.E.; Alafiatayo, A.A. Assessment of the phytochemical and antitrypanosomal properties of some extracts of leaves, stem and root bark of Landolphia sp. P. Beauv. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 114, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, E.; Wei, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, X. Phytochemical analysis, cellular antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of various herb plant organs. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 141, 111771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Román, J.; Soliz-Rueda, J.R.; Bravo, F.I.; Aragonès, G.; Muguerza, B. Phenolic compounds and biological rhythms: Who takes the lead? Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 113, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Deng, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, D.; Li, G.L.; Liu, J.W.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, H.M.D. Three novel dietary phenolic compounds from pickled Raphanus sativus L. inhibit lipid accumulation in obese mice by modulating the gut microbiota composition. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2000780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayouni, E.A.; Abedrabba, M.; Bouix, M.; Hamdi, M. The effects of solvents and extraction method on the phenolic contents and biological activities in vitro of Tunisian quercus coccifera L. and Juniperus phoenicea L. fruit extracts. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.L.; Sun, P.; Feng, J.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Shang, Y.F.; Niu, X.L.; Yang, S.H.; Wei, Z.J. Solvent effect on phenolics and antioxidant activity of Huangshan Gongju (Dendranthema morifolium (Ramat) Tzvel. cv. Gongju) extract. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 147, 111875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomicic, C.; Droz, P.O.; Berode, M.; Christinaz, S.; Castella, V.; Danuser, B. Controlled human exposures to organic solvents: Influence of sex on urinary levels of biological indicators. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 19, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhang, M.; Xia, Y.Q.; Bi, W.T.; Chen, D.D.Y. Ecofriendly mechanochemical extraction of bioactive compounds from plants with deep eutectic solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6297–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.F.; Li, L.; Chen, S.J.; Wang, L.; Lin, X. Deep eutectic solvent-based ultrasonic-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from Moringa oleifera L. leaves: Optimization, comparison and antioxidant activity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 117014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansur, A.R.; Song, N.E.; Jang, H.W.; Lim, T.G.; Yoo, M.; Nam, T.G. Optimizing the ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction of flavonoids in common buckwheat sprouts. Food Chem. 2019, 293, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.L.; Yang, J.H.; Wang, E.Z. Well-designed hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents as green and efficient media for the extraction of artemisinin from Artemisia annua leaves. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3270–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.Y.; Lia, F.F.; Liu, L.L.; Tan, Z.J. Deep eutectic solvents used as the green media for the efficient extraction of caffeine from Chinese dark tea. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 227, 115723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Muhammad, G.; Khan, M.N.; Mofijur, M.; Xu, J. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as green extractants for the isolation of phenolic compounds from biomass. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 29, 127445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almusallam, I.A.; Ahmed, I.; Babiker, E.E.; Juhaimi, F.; Alqah, H. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of bioactive properties from date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) spikelets using response surface methodology. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 140, 110816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.M.; He, R.P.; Li, Z.H.; Li, S.J.; Li, C.F.; Wang, L. Tailor-made deep eutectic solvents-based green extraction of natural antioxidants from partridge leaf-tea (Mallotus furetianus L.). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 275, 119159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.C. Eco-friendly and high-efficient extraction of natural antioxidants from Polygonum aviculare leaves using tailor-made deep eutectic solvents as extractants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 262, 118339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, X.; Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, W.M.; Hu, X.; Li, W.; Li, C.F.; Liu, S.X. Extraction methods for the releasing of bound phenolics from Rubus idaeus L. leaves and seeds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 135, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wu, L.F.; Wang, X.; Yao, L.L.; Wang, L. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction for flavonoid compounds content and antioxidant activities of India Moringa oleifera L. leaves: Simultaneous optimization, HPLC characterization and comparison with other methods. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2021, 20, 100284. [Google Scholar]
- Re, R.; Pelegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannaca, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying and improved ABTS radical cátiondescolorization assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.Z.; Wu, L.F.; Lin, X.; Hu, X.P.; Wang, L. Phenolic profiles and screening of potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from Polygonum aviculare L. leaves using ultra-filtration combined with HPLC-ESI-qTOF-MS/MS and molecular docking analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 154, 12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Stavrou, I.J.; Kapnissi-Christodoulou, C.P. Continuous and pulsed ultrasound-assisted extraction of carob’s antioxidants: Processing parameters optimization and identification of polyphenolic composition. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.L.; Zhang, J.C.; Li, C.F.; Liu, S.X.; Wang, L. Morinda citrifolia L. leaves extracts obtained by traditional and eco-friendly extraction solvents: Relation between phenolic compositions and biological properties by multivariate analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 153, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurić, T.; Mićić, N.; Potkonjak, A.; Milanov, D.; Dodić, J.; Trivunović, Z.; Popović, B.M. The evaluation of phenolic content, in vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activity of Mentha piperita extracts obtained by natural deep eutectic solvents. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, Z.N.; Aalim, H.; Limwachiranon, J.; Li, L.; Duan, Z.H.; Ren, G.P.; Luo, Z.S. Green recovery of phenolic compounds from rice byproduct (rice bran) using glycerol based on viscosity, conductivity and density. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2019, 54, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.K.; Dey, S.; Chakraborty, R. Effect of choline chloride-oxalic acid based deep eutectic solvent on the ultrasonic assisted extraction of polyphenols from Aegle marmelos. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 287, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, D.; Belwal, T.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Z. Sonication-synergistic natural deep eutectic solvent as a green and efficient approach for extraction of phenolic compounds from peels of Carya cathayensis Sarg. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, Y.R.; Row, K.H. Examination of 1-methylimidazole series ionic liquids in the extraction of flavonoids from Chamaecyparis obtuse leaves using a response surface methodology. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 933, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Dou, L.L.; Guo, L.; Li, P.; Liu, E.H. Comprehensive evaluation of deep eutectic solvents in extraction of bioactive natural products. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2405–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.C.; Wu, H.W.; Cai, D.X.; Yang, T.J.; Yang, L. Effective extraction of harmine by menthol/anise alcohol-based natural deep eutectic solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 250, 117211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorat, G.M.; Jadhav, H.S.; Roy, A.; Chung, W.J.; Seo, J.G. Dual role of deep eutectic solvent as a solvent and template for the synthesis of octahedral cobalt vanadate for oxygen evolution reaction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16255–16266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, P.V.A.; Shiwaku, I.A.; Maximo, G.J.; Batista, E.A.C. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as potential solvent for extraction of phenolic compounds from olive leaves: Extraction optimization and solvent characterization. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tai, G.L. Optimization of phenolics and flavonoids extraction from the fruit of Empetrum nigrum var. Japonicum from Jeju island in South Korea. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 38, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Qi, X.; Li, T.; Luo, M.; Wang, W.; Zu, Y.; Fu, Y. Application of natural deep eutectic solvents for extraction and determination of phenolics in Cajanus cajan leaves by ultra performance liquid chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 149, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Cao, L.; Chang, Y.H.; Duan, C.J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.L.; Yue, G.L.; Wang, X.Q.; Fu, Y.J. Enhanced extraction performance of iridoids, phenolic acids from Eucommia ulmoides leaves by tailor-made ternary deep eutectic solvent. Microchem. J. 2021, 161, 105788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanioti, S.; Tzia, C. Extraction of phenolic compounds from olive pomace by using natural deep eutectic solvents and innovative extraction techniques. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2018, 48, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, J. Enhanced extraction of hydroxytyrosol, maslinic acid and oleanolic acid from olive pomace: Process parameters, kinetics and thermodynamics, and greenness assessment. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukor, N.F.; Jusoh, R.; Kamarudin, N.S.; Halim, N.; Abdullah, S.B. Synergistic effect of probe sonication and ionic liquid for extraction of phenolic acids from oak galls. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 62, 104876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.S.; Wei, T.J.O.; Nyam, K.L. Effect of various solvents on the pulsed ultrasonic assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from Hibiscus cannabinus L. leaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 140, 111708. [Google Scholar]
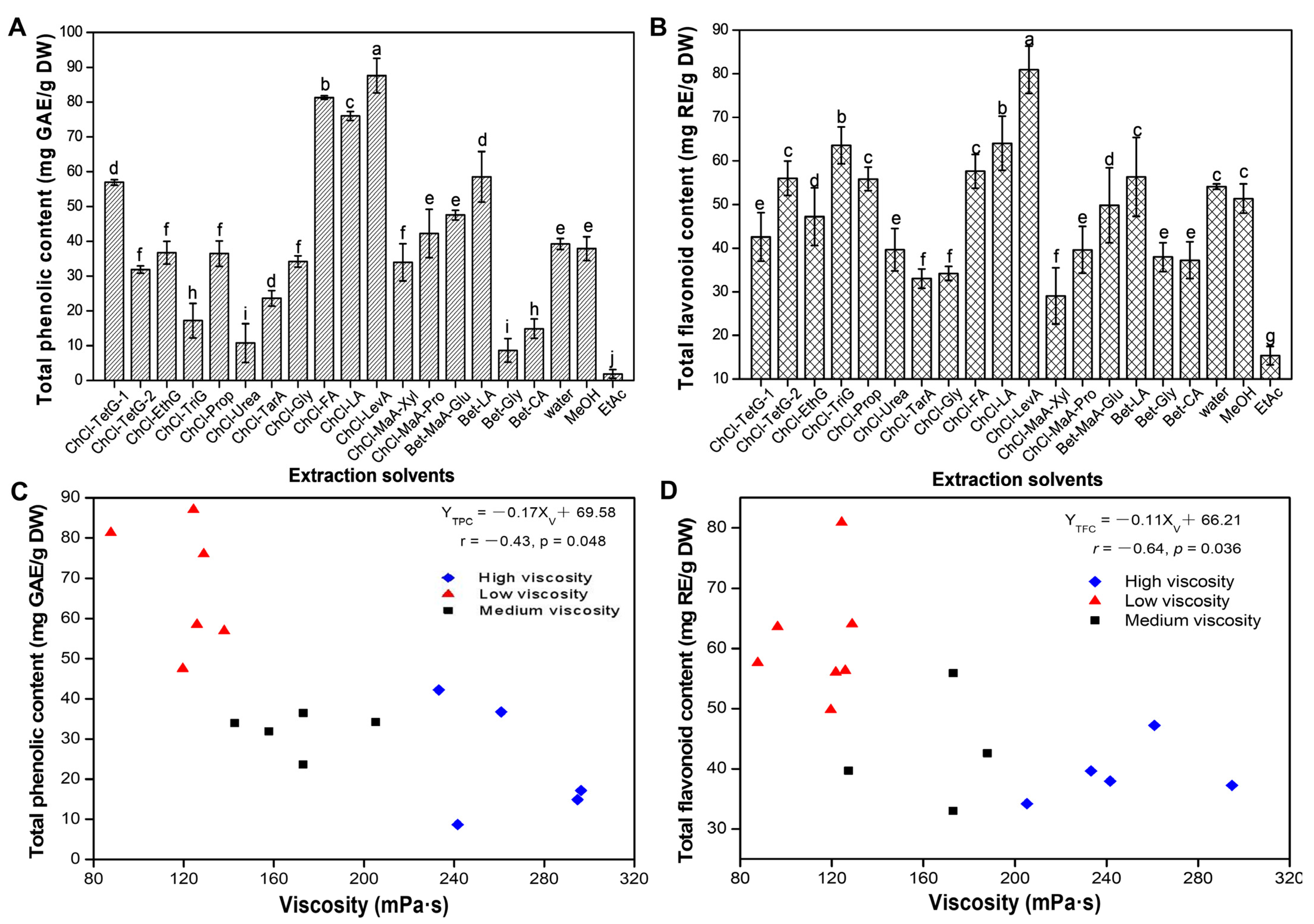
| No. | Component A | Component B | Component C | Abbreviations | Molar Ratio (mol/mol) | pH | Viscosity (mPa·s, 30% Water, 25 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Choline chloride | Tetramethylene glycol | - | ChCl-TetG-1 | 1:1 | 3.15 ± 0.19 | 188 ± 1.38 |
| 2 | Choline chloride | Tetramethylene glycol | - | ChCl-TetG-2 | 1:2 | 2.48 ± 0.09 | 122 ± 3.26 |
| 3 | Choline chloride | Ethylene glycol | - | ChCl-EthG | 1:1 | 4.26 ± 0.13 | 261 ± 6.87 |
| 4 | Choline chloride | Triethylene glycol | - | ChCl-TriG | 1:4 | 3.10 ± 0.08 | 96.35 ± 1.95 |
| 5 | Choline chloride | 1,2-Propanediol | - | ChCl-ProP | 1:2 | 4.58 ± 0.05 | 173 ± 1.77 |
| 6 | Choline chloride | Urea | - | ChCl-Urea | 1:2 | 8.65 ± 0.05 | 127 ± 3.11 |
| 7 | Choline chloride | Tartaric acid | - | ChCl-TarA | 1:2 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 173 ± 6.69 |
| 8 | Choline chloride | Glycerol | - | ChCl-Gly | 1:1 | 5.15 ± 0.12 | 205 ± 5.59 |
| 9 | Choline chloride | Formic acid | - | ChCl-FA | 1:1 | 0.85 ± 0.10 | 87.63 ± 2.18 |
| 10 | Choline chloride | Lactic acid | - | ChCl-LA | 1:1 | 0.81 ± 0.14 | 129 ± 4.95 |
| 11 | Choline chloride | Levulinic acid | - | ChCl-LevA | 1:2 | 1.36 ± 0.07 | 124 ± 2.16 |
| 12 | Choline chloride | Malic acid | Xylitol | ChCl-MaA-Xyl | 1:1:1 | 0.73 ± 0.04 | 143 ± 2.32 |
| 13 | Choline chloride | Malic acid | Proline | ChCl-MaA-Pro | 1:1:1 | 2.77 ± 0.17 | 233 ± 8.87 |
| 14 | Betaine | Malic acid | Glucose | Bet-MaA-Glu | 1:1:1 | 2.67 ± 0.13 | 120 ± 8.90 |
| 15 | Betaine | Lactic acid | - | Bet-LA | 1:2 | 3.09 ± 0.18 | 126 ± 3.18 |
| 16 | Betaine | Glycerol | - | Bet-Gly | 1:1 | 6.44 ± 0.18 | 242 ± 2.33 |
| 17 | Betaine | Citric acid | - | Bet-CA | 1:1 | 2.72 ± 0.14 | 295 ± 2.98 |
| Run | Independent Variables | Responses | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1: Water Content (WC) (%) | B: t (min) | C: T (°C) | TPC (mg GAE/g DW) | TFC (mg RE/g DW) | ABTS+ (mmol TE/g DW) | FRAP (μmol Fe(II)E/g DW) | α-GIA (mmol AE/g DW) | ||||||
| Experimental Value (Exp.) | Predictive Value (Pred.) | Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | Exp. | Pred. | ||||
| 1 | 30.00 (0) | 3.18 (−1.68) | 40.00 (0) | 18.93 ± 2.10 | 31.03 | 26.41 ± 2.95 | 35.84 | 293 ± 6.94 | 350 | 5600 ± 145 | 5648 | 59.83 ± 2.29 | 53.67 |
| 2 | 30.00 (0) | 20.00 (0) | 40.00 (0) | 91.34 ± 5.22 | 83.23 | 73.08 ± 3.42 | 72.79 | 484 ± 9.04 | 463 | 6038 ± 257 | 5842 | 173 ± 0.72 | 151 |
| 3 | 15.00 (−1) | 10.00 (−1) | 30.00 (−1) | 37.09 ± 1.96 | 27.90 | 30.55 ± 1.89 | 26.92 | 420 ± 7.16 | 372 | 4691 ± 213 | 4568 | 61.50 ± 5.09 | 62.80 |
| 4 | 30.00 (0) | 20.00 (0) | 23.18 (−1.68) | 36.98 ± 2.63 | 47.47 | 41.21 ± 1.13 | 41.52 | 437 ± 7.98 | 472 | 4570 ± 139 | 4959 | 143 ± 4.68 | 136 |
| 5 | 30.00 (0) | 20.00 | 40.00 (0) | 83.18 ± 2.02 | 83.23 | 65.61 ± 1.40 | 72.79 | 474 ± 6.43 | 463 | 5664 ± 31.91 | 5843 | 117 ± 2.06 | 151 |
| 6 | 15.00 (−1) | 30.00 (+1) | 30.00 (−1) | 66.29 ± 3.69 | 61.64 | 40.15 ± 4.28 | 45.75 | 411 ± 1.29 | 401 | 4373 ± 77 | 4090 | 88.22 ± 0.70 | 84.46 |
| 7 | 15.00 (−1) | 10.00 (−1) | 50.00 (+1) | 39.74 ± 1.55 | 33.75 | 42.28 ± 3.59 | 40.21 | 351 ± 16.28 | 323 | 4711± 154 | 4714 | 67.44 ± 6.82 | 62.69 |
| 8 | 45.00 (+1) | 10.00 (−1) | 30.00 (−1) | 45.48 ± 2.97 | 37.15 | 32.28 ± 2.60 | 28.27 | 376 ± 12.01 | 352 | 5588 ± 129 | 5342 | 144 ± 5.24 | 154 |
| 9 | 30.00 (0) | 20.00 (0) | 40.00 (0) | 82.84 ± 3.17 | 83.23 | 74.95 ± 1.62 | 72.79 | 491 ± 10.09 | 463 | 5865 ± 121 | 5843 | 157 ± 3.05 | 151 |
| 10 | 45.00 (+1) | 30.00 (+1) | 30.00 (−1) | 91.00 ± 3.10 | 89.22 | 77.75 ± 0.28 | 76.96 | 488 ± 19.59 | 489 | 5817 ± 192 | 5823 | 151 ± 0.03 | 158 |
| 11 | 30.00 (0) | 36.82 (+1.68) | 40.00 (0) | 81.92 ± 3.56 | 80.81 | 83.21 ± 0.40 | 77.82 | 461 ± 11.44 | 442 | 5773 ± 235 | 5712 | 124 ± 4.50 | 127 |
| 12 | 45.00 (+1) | 10.00 (−1) | 50.00 (+1) | 73.87 ± 1.38 | 70.75 | 65.08 ± 3.42 | 56.63 | 453 ± 3.81 | 436 | 5632 ± 217 | 5924 | 141 ± 9.06 | 148 |
| 13 | 15.00 (−1) | 30.00 (+1) | 50.00 (+1) | 40.31 ± 2.41 | 40.88 | 40.28 ± 3.46 | 41.44 | 298 ± 6.93 | 295 | 4056 ± 147 | 4310 | 152 ± 2.59 | 145 |
| 14 | 30.00 (0) | 20.00 (0) | 56.82 (+1.68) | 57.78 ± 1.39 | 58.27 | 58.01 ± 3.21 | 61.74 | 450 ± 4.61 | 453 | 6034 ± 39.80 | 5633 | 177 ± 1.16 | 181 |
| 15 | 55.23 (+1.68) | 20.00 (0) | 40.00 (0) | 91.11 ± 2.09 | 94.39 | 60.81 ± 3.72 | 66.86 | 432 ± 5.60 | 431 | 5954 ± 225 | 5848 | 220 ± 8.48 | 207 |
| 16 | 30.00 (0) | 20.00 (0) | 40.00 (0) | 76.29 ± 1.50 | 83.23 | 79.61 ± 0.92 | 72.79 | 461 ± 11.14 | 463 | 6010 ± 121 | 5843 | 162 ± 0.34 | 151 |
| 17 | 30.00 (0) | 20.00 (0) | 40.00 (0) | 86.75 ± 1.90 | 83.23 | 78.81 ± 2.87 | 72.79 | 413 ± 4.02 | 463 | 5921 ± 267 | 5843 | 137 ± 5.41 | 151 |
| 18 | 45.00 (+1) | 30.00 (+1) | 50.00 (+1) | 94.79 ± 2.24 | 96.22 | 86.95 ± 3.40 | 87.72 | 495 ± 4.61 | 516 | 6348 ± 101 | 6479 | 211 ± 2.22 | 213 |
| 19 | 30.00 (0) | 20.00 (0) | 40.00 (0) | 80.86 ± 0.49 | 83.23 | 65.35 ± 3.67 | 72.79 | 465 ± 9.22 | 463 | 5555 ± 36.18 | 5843 | 159 ± 0.92 | 151 |
| 20 | 4.77 (−1.68) | 20.00 (0) | 40.00 (0) | 32.38 ± 2.61 | 40.09 | 28.81 ± 0.92 | 26.80 | 222 ± 3.89 | 262 | 32800 ± 6.96 | 3373 | 64.02 ± 0.19 | 73.74 |
| Term | Df | F Values (p Values) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC | TFC | ABTS+• | FRAP | α-GIA | ||
| Mode | 9 | 17.06 (<0.0001) *** | 16.18 (<0.0001) *** | 6.91 (0.0028) ** | 30.10 (<0.0001) *** | 16.21 (<0.0001) *** |
| X1 | 1 | 51.83 (<0.0001) *** | 38.28 (<0.0001) *** | 23.26 (<0.0001) *** | 114.36 (<0.0001) *** | 79.44 (<0.0001) *** |
| X2 | 1 | 43.55 (<0.0001) *** | 42.06 (<0.0001) *** | 6.95 (0.0249) * | 0.48 (0.5151) ns | 23.67 (<0.0001) *** |
| X3 | 1 | 2.05 (0.1823) ns | 9.76 (0.0108) * | 0.28 (0.6067) ns | 34.26 (0.0011) * | 9.24 (0.0125) ** |
| X1 × 2 | 1 | 2.45 (0.1489) ns | 8.82 (0.0141) * | 3.88 (0.0773) ns | 14.71 (0.0086) ** | 0.55 (0.4761) ns |
| X1 × 3 | 1 | 5.61 (0.0394) * | 2.24 (0.1650) ns | 5.95 (0.0349) * | 3.04 (0.1316) ns | 0.071 (0.7950) ns |
| X2 × 3 | 1 | 5.15 (0.0466) * | 3.06 (0.1107) ns | 1.09 (0.3201) ns | 0.089 (0.7761) ns | 6.77 (0.0264) * |
| X12 | 1 | 6.70 (0.0270) * | 23.99 (0.0006) *** | 16.59 (0.0022) ** | 87.50 (< 0.0001) *** | 0.74 (0.4087) ns |
| X22 | 1 | 19.56 (0.0013) ** | 9.07 (0.0131) * | 5.57 (0.0400) * | 1.52 (0.2631) ns | 24.71 (0.0006) *** |
| X32 | 1 | 24.17 (0.0006) *** | 15.94 (0.0025) ** | 1.12 (0.9786) ns | 17.22 (0.0061) ** | 0.37 (0.5573) ns |
| Residual | 10 | 686.94 | 505.88 | 14811.05 | 847400.00 | 2709.45 |
| Lack of fit (F-value) | 5 | 4.22 | 1.60 | 2.85 | 3.53 | 0.32 |
| Lack of fit (p-value) | 5 | 0.0798 | 0.3088 | 0.1372 | 0.0964 | 0.8819 |
| R2 | 0.9389 | 0.9701 | 0.9296 | 0.9849 | 0.9507 | |
| Adj R2 | 0.8838 | 0.9054 | 0.8778 | 0.9522 | 0.9438 | |
| Pre R2 | 0.8087 | 0.9763 | 0.8014 | 0.9716 | 0.8119 | |
| Adequacy precision | 11.657 | 10.900 | 9.321 | 20.811 | 10.304 | |
| Validation of the optimal UAE conditions | ||||||
| Predicted results | 96.21 | 86.58 | 481 | 6473 | 218 | |
| Experimental results | 91.38 ± 7.20 | 84.12 ± 3.47 | 492 ± 7.33 | 6235 ± 121 | 230 ± 7.59 | |
| Error (%) | 5.02 | 2.84 | 2.12 | 3.68 | 5.47 | |
| p value (Predicted vs. Experimental) | 0.78 | 1.02 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 1.07 | |
| Individual Phenolic Content (μg/g DW) | Water-Based HE | MeOH-Based HE | ChCl-LevA-Based HE | ChCl-LevA-Based MWE | ChCl-LevA-Based UAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 463 ± 5.74 e | 596 ± 3.43 d | 1009± 18.41 a | 924 ± 50.14 b | 829 ± 15.63 c |
| (-)-Epigallocatechin | 2781 ± 19.57 d | 1503 ± 33.26 e | 3003 ± 39.77 c | 4050 ± 19.13 b | 4272 ± 84.86 a |
| Catechin | 0.00 | 0.00 | 4338 ± 28.75 c | 5025 ± 106 b | 5268 ± 24.53 a |
| Protocatechuic acid | 15.06 ± 1.92 e | 284 ± 7.96 d | 418 ± 32.22 c | 575 ± 4.36 b | 644 ± 1.65 a |
| Vanillic acid | 565 ± 6.42 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Rutin | 128 ± 8.62 c | 119 ± 2.33 c | 169 ± 1.62 b | 255 ± 5.10 a | 239 ± 26.88 a |
| Isoquercitrin | 2126 ± 10.32 a | 2900 ± 63.22 b | 2031 ± 24.12 a | 3411 ± 12.93 c | 3500 ± 86.07 d |
| Kaempferol 3-O-rutinoside | 2994 ± 71.44 c | 1550 ± 38.72 e | 2026 ± 29.01 d | 3669 ± 25.42 b | 3717 ± 97.71 a |
| Myricetin | 791 ± 11.37 a | 584 ± 10.00 c | 530 ± 33.49 c | 711 ± 2.16 b | 716 ± 11.85 b |
| Phloretin | 24.65 ± 3.45 b | 0.00 | 18.85 ± 0.39 c | 29.57 ± 0.29 a | 31.33 ± 0.51 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; He, R.; Li, W.; Wang, L. Customized Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Extractants for Ultrasonic-Assisted Enhanced Extraction of Phenolic Antioxidants from Dogbane Leaf-Tea. Foods 2021, 10, 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112527
Wang R, Zhang W, He R, Li W, Wang L. Customized Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Extractants for Ultrasonic-Assisted Enhanced Extraction of Phenolic Antioxidants from Dogbane Leaf-Tea. Foods. 2021; 10(11):2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112527
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruimin, Weimin Zhang, Ruiping He, Wu Li, and Lu Wang. 2021. "Customized Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Extractants for Ultrasonic-Assisted Enhanced Extraction of Phenolic Antioxidants from Dogbane Leaf-Tea" Foods 10, no. 11: 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112527
APA StyleWang, R., Zhang, W., He, R., Li, W., & Wang, L. (2021). Customized Deep Eutectic Solvents as Green Extractants for Ultrasonic-Assisted Enhanced Extraction of Phenolic Antioxidants from Dogbane Leaf-Tea. Foods, 10(11), 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112527