Consumer Trust in Food and the Food System: A Critical Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
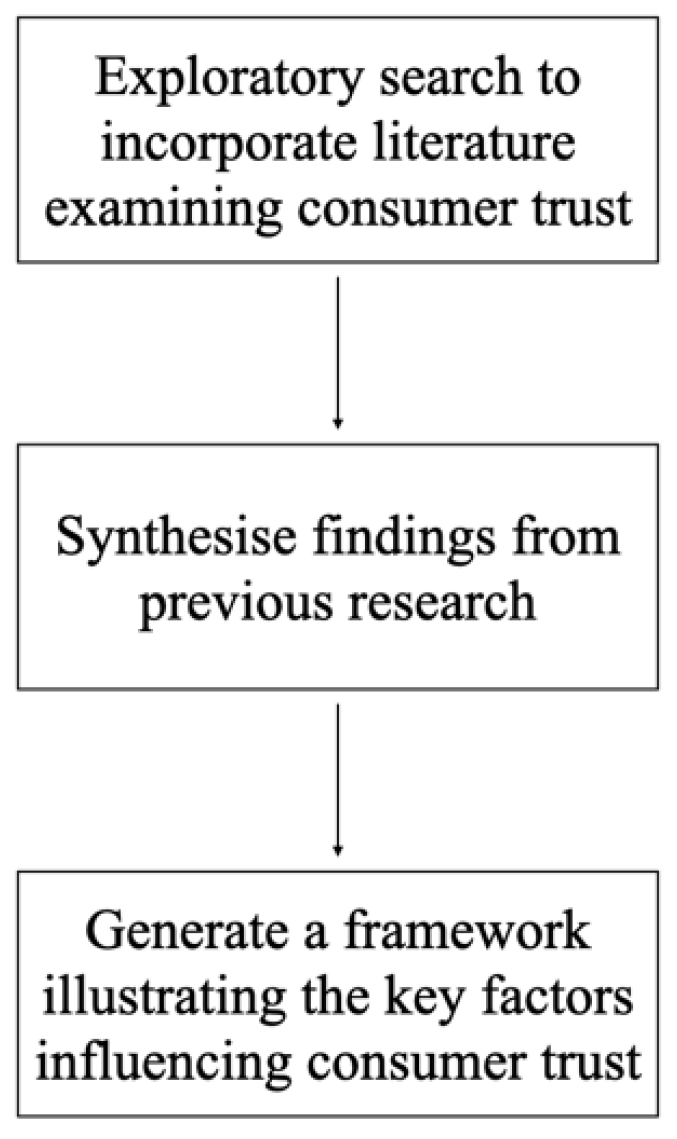
2. Materials and Methods
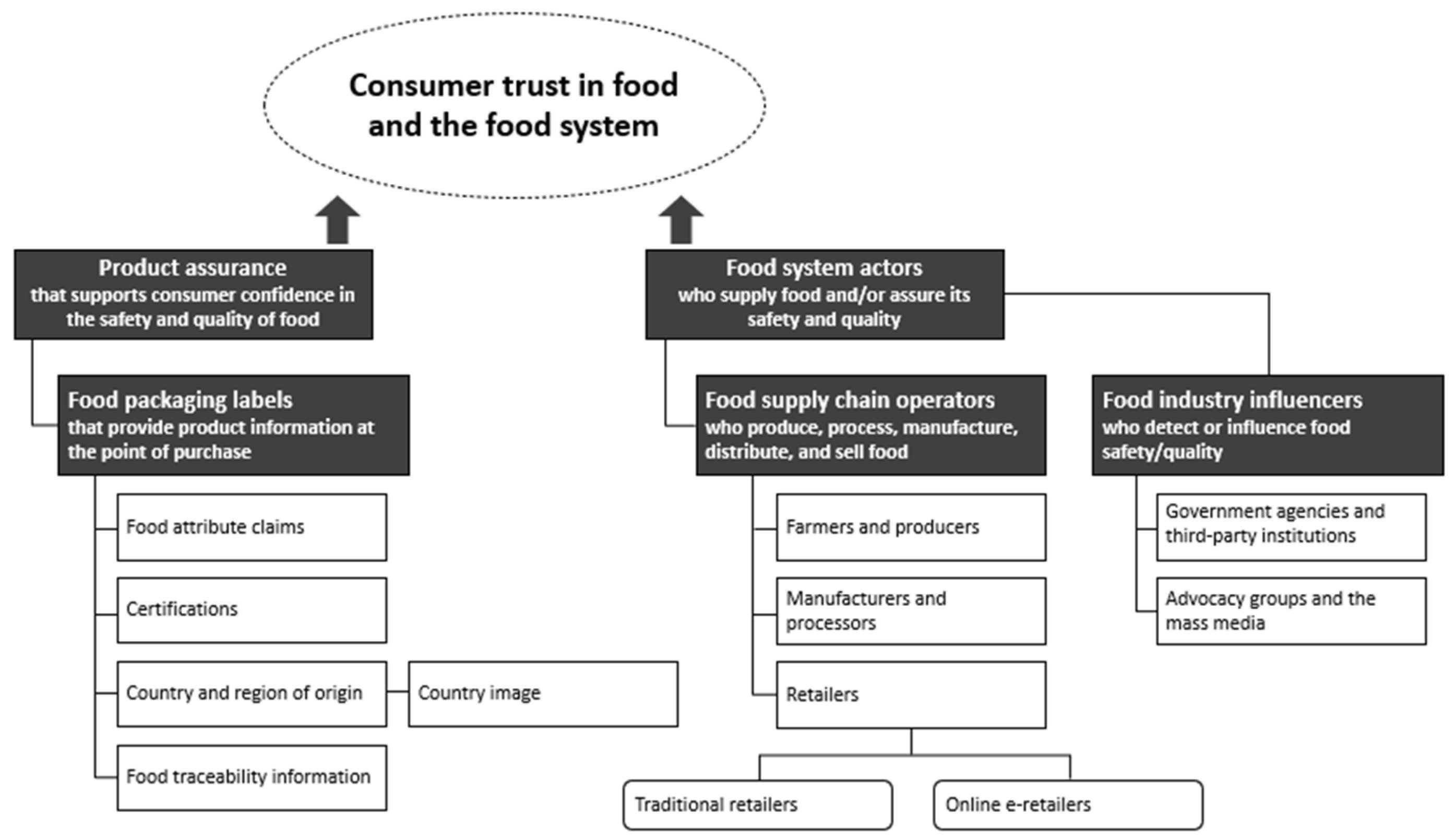
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Product Assurance
Food Packaging Labels
3.2. Food System Actors
3.2.1. Food Supply Chain Operators
3.2.2. Food Industry Influencers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henderson, J.; Ward, P.R.; Coveney, J.; Meyer, S.B. What are the important issues around food safety and nutrition? Findings from a media analysis and qualitative study of consumer trust. Australas. Med. J. 2010, 3, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteki, M.; Regueiro, J.; Simal-Gándara, J. Tackling fraudsters with global strategies to expose fraud in the food chain. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, H.; Clark, B.; Rhymer, C.; Kuznesof, S.; Hajslova, J.; Tomaniova, M.; Brereton, P.; Frewer, L. A systematic review of consumer perceptions of food fraud and authenticity: A European perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 94, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoli, L.; Capitello, R.; De Salvo, M.; Longo, A.; Boeri, M. Food fraud and consumers’ choices in the wake of the horsemeat scandal. Br. Food J. 2016, 118, 1898–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, B.; Poms, R.; Rose, M. Incidents and impacts of unwanted chemicals in food and feeds. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crop. Foods 2012, 4, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachmann, K.; Østby, P. Food, technology, and trust: An introduction. Hist. Technol. 2011, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin, E.; Wilson, A.; Coveney, J.; Henderson, J.; Meyer, S.B.; McCarthy, M.B.; O’Reilly, S.; Calnan, M.; McGloin, A.; Kelly, E.; et al. Food-system actors’ perspectives on trust: An international comparison. Br. Food J. 2019, 121, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamoah, F.; Yawon, D. Assessing supermarket food shopper reaction to horsemeat scandal in the UK. Int. Rev. Manag. Mark. 2014, 4, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- ABC News. Strawberry Needle Contamination Scare: Queensland Woman Charged after Months-long Investigation. 2018. Available online: https://www.abc.net.au/news/2018-11-11/strawberry-needle-scare-woman-arrested-in-queensland/10486418 (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Bozic, B. Consumer trust repair: A critical literature review. Eur. Manag. J. 2017, 35, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Neal, J.A.; Sirsat, S.A. Consumers’ food safety risk perceptions and willingness to pay for fresh-cut produce with lower risk of foodborne illness. Food Control 2018, 86, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttavuthisit, K.; Thøgersen, J. Developing-Economy preferences for imported organic food products. J. Int. Consum. Mark. 2019, 31, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, R.; Ramaswamy, V.; Alden, D.; Steenkamp, J.B.E.M.; Ramachander, S. Effects of brand local and nonlocal origin on consumer attitudes in developing countries. J. Consum. Psychol. 2000, 9, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, L.; Soon, J.M. Food Safety, Food Fraud, and Food Defense: A Fast Evolving Literature. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, R823–R834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhr, A.; Lüddecke, K.; Drusch, S.; Müller, M.J.; Alvensleben, R.V. Food quality and safety––Consumer perception and public health concern. Food Control 2005, 16, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-H.; Menozzi, D.; Török, Á. Eliciting egg consumer preferences for organic labels and omega 3 claims in Italy and Hungary. Foods 2020, 9, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thøgersen, J.; Pedersen, S.; Aschemann-Witzel, J. The impact of organic certification and country of origin on consumer food choice in developed and emerging economies. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 72, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maehle, N.; Iversen, N.; Hem, L.; Otnes, C. Exploring consumer preferences for hedonic and utilitarian food attributes. Br. Food J. 2015, 117, 3039–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijswijk, W.; Frewer, L.J. Consumer perceptions of food quality and safety and their relation to traceability. Br. Food J. 2008, 110, 1034–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Jakku, E. Australian Consumers’ Preferences for Food Attributes: A Latent Profile Analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, M.; Ashman, H.; Torrico, D.; Ha, M.; Warner, R. A Mixed Method Approach for the Investigation of Consumer Responses to Sheepmeat and Beef. Foods 2020, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhu, D.; Hu, W.; Wang, H. Chinese consumers’ preferences and willingness to pay for traceable food quality and safety attributes: The case of pork. China Econ. Rev. 2015, 35, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, Y.; Rahman, Z. Factors Affecting Green Purchase Behaviour and Future Research Directions. Int. Strateg. Manag. Rev. 2015, 3, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.S.; Kim, K.; Nurhidayati, V.A. Satisfaction and purchase intention of imported fresh fruits based on familiarity: A case of Korean pears in Taiwan. Br. Food J. 2020, 122, 2895–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampietri, E.; Verneau, F.; Giudice, T.D.; Carfora, V.; Finco, A. A Theory of Planned behaviour perspective for investigating the role of trust in consumer purchasing decision related to short food supply chains. Food Qual. Prefer. 2018, 64, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærnes, U. Ethics and action: A relational perspective on consumer choice in the European politics of food. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2012, 25, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, H.; Kuznesof, S.; Dean, M.; Chan, M.Y.; Clark, B.; Home, R.; Stolz, H.; Zhong, Q.; Liu, C.; Brereton, P.; et al. Chinese consumer’s attitudes, perceptions and behavioural responses towards food fraud. Food Control 2019, 95, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schjøll, A. Country-of-origin preferences for organic food. Org. Agric. 2017, 7, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, D.L.; Hong, S.J.; Wang, H.H.; Wu, L. Emerging markets for imported beef in China: Results from a consumer choice experiment in Beijing. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirosa, M.; Mangan-Walker, E. Young Chinese and functional foods for mobility health: Perceptions of importance, trust, and willingness to purchase and pay a premium. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2018, 24, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macready, A.L.; Hieke, S.; Klimczuk-Kochańska, M.; Szumial, S.; Vranken, L.; Grunert, K.G. Consumer trust in the food value chain and its impact on consumer confidence: A model for assessing consumer trust and evidence from a 5-country study in Europe. Food Policy 2020, 92, 101880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, J.M.; Liu, X. Chinese consumers’ risk mitigating strategies against food fraud. Food Control 2020, 115, 107298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin, E.; Webb, T.; Coveney, J.; Meyer, S.B.; Wilson, A.M. Consumer trust in the Australian food system–the everyday erosive impact of food labelling. Appetite 2016, 103, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, R.; Imami, D.; Miftari, I.; Ymeri, P.; Grunert, K.; Meixner, O. Consumer Perception of Food Quality and Safety in Western Balkan Countries: Evidence from Albania and Kosovo. Foods 2021, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, A.K.; Tran, B.X.; Nguyen, C.T.; Le, H.T.; Do, H.T.; Nguyen, H.D.; Nguyen, L.H.; Nguyen, H.T.; Mai, H.T.; Tran, T.D.; et al. Consumer preference and attitude regarding online food products in Hanoi, Vietnam. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, C.; Hieke, S.; Taper, C.; Siegrist, M. European consumer healthiness evaluation of ‘Free-from’labelled food products. Food Qual. Prefer. 2018, 68, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Benni, N.; Stolz, H.; Home, R.; Kendall, H.; Kuznesof, S.; Clark, B.; Dean, M.; Brereton, P.; Frewer, L.J.; Chan, M.Y.; et al. Product attributes and consumer attitudes affecting the preferences for infant milk formula in China—A latent class approach. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 71, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, C.D.D.; Fujiyoshi, L.; McGreevy, S.R.; Tayasu, I. Trust me? Consumer trust in expert information on food product labels. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 137, 111170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yin, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, D. Effectiveness of China’s organic food certification policy: Consumer preferences for infant milk formula with different organic certification labels. Can. J. Agric. Econ. 2014, 62, 545–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Chen, M.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y. Chinese consumers’ willingness-to-pay for safety label on tomato: Evidence from choice experiments. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2017, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttavuthisit, K.; Thøgersen, J. The importance of consumer trust for the emergence of a market for green products: The case of organic food. J. Bus. Ethics 2017, 140, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tao, J.; Chu, M. Behind the label: Chinese consumers’ trust in food certification and the effect of perceived quality on purchase intention. Food Control 2020, 108, 106825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moruzzo, R.; Riccioli, F.; Boncinelli, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Y.; Tinacci, L.; Massai, T.; Guidi, A. Urban Consumer Trust and Food Certifications in China. Foods 2020, 9, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gao, Z.; Snell, H.A.; Ma, H. Food safety concerns and consumer preferences for food safety attributes: Evidence from China. Food Control 2020, 112, 107157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezai, G.; Mohamed, Z.; Shamsudin, M.N. Assessment of consumers’ confidence on halal labelled manufactured food in Malaysia. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2012, 20, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Santeramo, F.G.; Lamonaca, E. Evaluation of geographical label in consumers’ decision-making process: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Qin, Z.; Yuan, Q. The impact of eco-label on the young Chinese generation: The mediation role of environmental awareness and product attributes in green purchase. Sustainability 2019, 11, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wezemael, L.; Verbeke, W.; Kügler, J.O.; de Barcellos, M.D.; Grunert, K.G. European consumers and beef safety: Perceptions, expectations and uncertainty reduction strategies. Food Control 2010, 21, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, N.; Zhang, A.; Van Klinken, R.D.; Cui, L. An integrative model to understand consumers’ trust and willingness to buy imported fresh fruit in urban China. Br. Food J. 2021, 123, 2216–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-H.; Chen, C.-I.; Sher, P.J. Investigation on perceived country image of imported food. Food Qual. Prefer. 2010, 21, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andéhn, M.; Nordin, F.; Nilsson, M.E. Facets of country image and brand equity: Revisiting the role of product categories in country-of-origin effect research. J. Consum. Behav. 2016, 15, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.; Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Thøgersen, J. Consumers’ evaluation of imported organic food products: The role of geographical distance. Appetite 2018, 130, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorostidi-Martinez, H.; Xu, W.; Zhao, X. A review of Spanish consumers’ product-country image of China. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkias, G.; Davvetas, V.; Diamantopoulos, A. The interplay between country stereotypes and perceived brand globalness/localness as drivers of brand preference. J. Bus. Res. 2016, 69, 3621–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Mathur, P.; Maheswaran, D. The effects of country-related affect on product evaluations. J. Consum. Res. 2014, 41, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Carneiro, J.; Goldszmidt, R. A contingent approach to country-of-origin effects on foreign products evaluation: Interaction of facets of country image with product classes. Int. Bus. Rev. 2016, 25, 1066–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekhili, S.; Achabou, M.A. Towards greater understanding of ecolabel effects: The role of country of origin. J. Appl. Bus. Res. 2014, 30, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, C.; McFadden, B.R. The interaction between country of origin and genetically modified orange juice in urban China. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 71, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, B.L. Trends in organic and green food consumption in China: Opportunities and challenges for regional Australian exporters. J. Econ. Soc. Policy 2015, 17, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zander, K.; Feucht, Y. Consumers’ willingness to pay for sustainable seafood made in Europe. J. Int. Food Agribus. Mark. 2018, 30, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denver, S.; Jensen, J.D.; Olsen, S.B.; Christensen, T. Consumer preferences for ‘Localness’ and organic food production. J. Food Prod. Mark. 2019, 25, 668–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerding, S.G.; Trajer, N.; Lehberger, M. What is local food? The case of consumer preferences for local food labeling of tomatoes in Germany. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyawardana, A.; Ganegodage, K.; Mortlock, M.Y. Consumers’ trust in vegetable supply chain members and their behavioural responses: A study based in Queensland, Australia. Food Control 2017, 73, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfnes, F.; Sharma, A. Locally produced food in restaurants: Are the customers willing to pay a premium and why? Int. J. Revenue Manag. 2010, 4, 238–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, K.; Janssen, M. Boundary conditions for traceability in food supply chains using blockchain technology. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, M.K.; Trigui, I.T. Smart Packaging: Consumer’s Perception and Diagnostic of Traceability Information. In International Conference on Digital Economy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Powell, W.; Foth, M.; Natanelov, V.; Miller, T.; Dulleck, U. Strengthening consumer trust in beef supply chain traceability with a blockchain-based human-machine reconcile mechanism. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meat and Livestock Australia. Commercial Application of Supply Chain Integrity and Shelf Life Systems; Meat and Livestock Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sander, F.; Semeijn, J.; Mahr, D. The acceptance of blockchain technology in meat traceability and transparency. Br. Food J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumblauskas, D.; Mann, A.; Dugan, B.; Rittmer, J. A blockchain use case in food distribution: Do you know where your food has been? Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, T.; Benson, T.; Lavelle, F.; Spence, M.; Elliott, C.T.; Dean, M. The development and validation of a toolkit to measure consumer trust in food. Food Control 2020, 110, 106988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gao, Z.; Nayga Jr., R.M.; Snell, H.A.; Ma, H. Consumers’ valuation for food traceability in China: Does trust matter? Food Policy 2019, 88, 101768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menozzi, D.; Halawany-Darson, R.; Mora, C.; Giraud, G. Motives towards traceable food choice: A comparison between French and Italian consumers. Food Control 2015, 49, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhu, D.; Hu, W.; Wang, S. Chinese consumers’ willingness to pay for pork traceability information—The case of Wuxi. Agric. Econ. 2016, 47, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzembacher, D.E.; Stangherlin, I.D.C.; Slongo, L.A.; Cataldi, R. An integration of traceability elements and their impact in consumer’s trust. Food Control 2018, 92, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regan, Á.; Raats, M.; Shan, L.C.; Wall, P.G.; McConnon, Á. Risk communication and social media during food safety crises: A study of stakeholders’ opinions in Ireland. J. Risk Res. 2016, 19, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnot, C. Perspective-Building Consumer Trust in the Food System. Food Technol. 2011, 65, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, W.A. The future relationship between the media, the food industry and the consumer. Br. Med. Bull. 2000, 56, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tonkin, E.; Wilson, A.M.; Coveney, J.; Meyer, S.B.; Henderson, J.; McCullum, D.; Webb, T.; Ward, P.R. Consumers respond to a model for (re) building consumer trust in the food system. Food Control 2019, 101, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.K. BSE in the UK: Why the risk communication strategy failed. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2004, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C.J.; Lok, C.; Morley, K.; Powell, D.A. Government management of two media-facilitated crises involving dioxin contamination of food. Public Underst. Sci. 2011, 20, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.M.; Withall, E.; Coveney, J.; Meyer, S.B.; Henderson, J.; McCullum, D.; Webb, T.; Ward, P.R. A model for (re) building consumer trust in the food system. Health Promot. Int. 2017, 32, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkheimer, J.; Heide, M. Trust and brand recovery campaigns in crisis: Findus Nordic and the horsemeat scandal. Int. J. Strateg. Commun. 2015, 9, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Wu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, D.; Ying, R.; Tsai, F.S. Consumers’ Willingness to Pay for Foods with Traceability Information: Ex-Ante Quality Assurance or Ex-Post Traceability? Sustainability 2019, 11, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Amount of information and the willingness of consumers to pay for food traceability in China. Food Control 2017, 77, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Steele, W.; Fang, X. A study on Chinese consumer preferences for food traceability information using best-worst scaling. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, L. Consumer preference and demand for traceable food attributes. Br. Food J. 2016, 118, 2140–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Sargeant, J.M.; Majowicz, S.E.; Sheldrick, B.; McKeen, C.; Wilson, J.; Dewey, C.E. Enhancing public trust in the food safety regulatory system. Health Policy 2012, 107, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.Z.; Alam, M. What determines the purchase intention of liquid milk during a food security crisis? The role of perceived trust, knowledge, and risk. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bai, J.; Wahl, T.I. Consumers’ willingness to pay for traceable pork, milk, and cooking oil in Nanjing, China. Food Control 2012, 27, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y. Consumer preference and willingness to pay for the traceability information attribute of infant milk formula: Evidence from a choice experiment in China. Br. Food J. 2017, 119, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Gong, X.; Qin, S.; Chen, X.; Zhu, D.; Hu, W.; Li, Q. Consumer preferences for pork attributes related to traceability, information certification, and origin labeling: Based on China’s Jiangsu Province. Agribusiness 2017, 33, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, H.; Naughton, P.; Kuznesof, S.; Raley, M.; Dean, M.; Clark, B.; Stolz, H.; Home, R.; Chan, M.Y.; Zhong, Q.; et al. Food fraud and the perceived integrity of European food imports into China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- My, N.H.D.; Demont, M.; Van Loo, E.J.; De Guia, A.; Rutsaert, P.; Tuan, T.H.; Verbeke, W. What is the value of sustainably-produced rice? Consumer evidence from experimental auctions in Vietnam. Food Policy 2018, 79, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, N.M.; Basri, H.N.; Kamarulzaman, N.H.; Shamsudin, M.N. Factors influencing consumers’ preferences towards meat and meat products with traceability systems in Malaysia. Int. Food Res. J. 2018, S157–S164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, A.; Mankad, A.; Ariyawardana, A. Establishing confidence in food safety: Is traceability a solution in consumers’ eyes? J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2020, 15, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Wang, S.; Yu, X. The impact of food traceability system on consumer perceived value and purchase intention in China. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2020, 120, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.; Coveney, J.; Ward, P.R.; Taylor, A.W. Farmers are the most trusted part of the Australian food chain: Results from a national survey of consumers. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2011, 35, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonkin, E.; Henderson, J.; Meyer, S.B.; Coveney, J.; Ward, P.R.; McCullum, D.; Webb, T.; Wilson, A.M. Expectations and everyday opportunities for building trust in the food system. Br. Food J. 2020, 123, 702–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, C.; Lawrence, G.; Burch, D. Supermarkets and agro-industrial foods: The strategic manufacturing of consumer trust. Food Cult. Soc. 2011, 14, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.; Ward, P.; Coveney, J.; Meyer, S. Trust in the Australian food supply: Innocent until proven guilty. Health Risk Soc. 2012, 14, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupton, D.A. Lay discourses and beliefs related to food risks: An Australian perspective. Sociol. Health Illn. 2005, 27, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carfora, V.; Cavallo, C.; Caso, D.; Giudice, T.D.; Devitiis, B.D.; Viscecchia, R.; Nardone, G.; Cicia, G. Explaining consumer purchase behavior for organic milk: Including trust and green self-identity within the theory of planned behavior. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 76, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y.; Oosterveer, P.; Mol, A.P.J. Consumer trust in different food provisioning schemes: Evidence from Beijing, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 134, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sijtsema, S.J.; Kornelis, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, S. Consumer confidence in the safety of milk and infant milk formula in China. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 8807–8818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Kowatthanakul, S.; Satanasavapak, P. Generation Y consumer online repurchase intention in Bangkok: Based on Stimulus-Organism-Response (SOR) model. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasquet, M.; Descals, A.M.; Ruiz-Molina, M.E. Understanding loyalty in multichannel retailing: The role of brand trust and brand attachment. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2017, 45, 608–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, H.; D’Acunto, D.; Johns, N. Home and away: Why do consumers shy away from reporting negative experiences in the peer-to-peer realms? Psychol. Mark. 2019, 36, 1162–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Hofacker, C.F.; Peloza, J.; Allen, A. How online trust evolves over time: The role of social perception. Psychol. Mark. 2020, 37, 1539–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhllima, E.; Imami, D.; Canavari, M. Consumer perceptions of food safety risk: Evidence from a segmentation study in Albania. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Pieniak, Z.; Verbeke, W. Food-related hazards in China: Consumers’ perceptions of risk and trust in information sources. Food Control 2014, 46, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, A.; Bachmann, R. Online consumer trust: Trends in research. J. Technol. Manag. Innov. 2017, 12, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Liu, Y.; Wei, X. Influence of online product presentation on consumers’ trust in organic food. Br. Food J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopdar, P.K.; Balakrishnan, J. Consumers response towards mobile commerce applications: SOR approach. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 53, 102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doorn, J.; Mende, M.; Noble, S.M.; Hulland, J.; Ostrom, A.L.; Grewal, D.; Petersen, J.A. Domo arigato Mr. Roboto: Emergence of automated social presence in organizational frontlines and customers’ service experiences. J. Serv. Res. 2017, 20, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Fan, W.; Zhou, M. Social presence, trust, and social commerce purchase intention: An empirical research. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 56, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, X.; Hajli, N. Building e-commerce satisfaction and boosting sales: The role of social commerce trust and its antecedents. Int. J. Electron. Commer. 2019, 23, 328–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Li, M.; Sivakumar, K. Online review characteristics and trust: A cross-country examination. Decis. Sci. 2019, 50, 537–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F. Consumer trust in food safety—A multidisciplinary approach and empirical evidence from Taiwan. Risk Anal. Int. J. 2008, 28, 1553–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddle, E.A.; Bray, H.J. How farm animal welfare issues are framed in the Australian media. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2019, 32, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, H.J.; Ankeny, R.A. Happy chickens lay tastier eggs: Motivations for buying free-range eggs in Australia. Anthrozoös 2017, 30, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, W.; Zhang, A.; van Klinken, R.D.; Schrobback, P.; Muller, J.M. Consumer Trust in Food and the Food System: A Critical Review. Foods 2021, 10, 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102490
Wu W, Zhang A, van Klinken RD, Schrobback P, Muller JM. Consumer Trust in Food and the Food System: A Critical Review. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102490
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Wen, Airong Zhang, Rieks Dekker van Klinken, Peggy Schrobback, and Jane Marie Muller. 2021. "Consumer Trust in Food and the Food System: A Critical Review" Foods 10, no. 10: 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102490
APA StyleWu, W., Zhang, A., van Klinken, R. D., Schrobback, P., & Muller, J. M. (2021). Consumer Trust in Food and the Food System: A Critical Review. Foods, 10(10), 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102490





