Eco-Friendly Fluorescent ELISA Based on Bifunctional Phage for Ultrasensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
2.2. Optimization of GOx-Mediated Fluorescence Quenching of MPA-QDs
2.3. Propagation of M13OTA Bacteriophage
2.4. Preparation of Biotinylated M13OTA Phage
2.5. Preparation of Biotinylated GOx (Biotin-GOx)
2.6. Procedure of M13OTA-FLISA for OTA Detection
2.7. Corn Sample Pretreatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Principle of the Proposed M13OTA-FLISA Method
3.2. GOx-Mediated Fluorescence Quenching of MPA-QDs
3.3. Characterization of Bifunctional M13OTA Phage
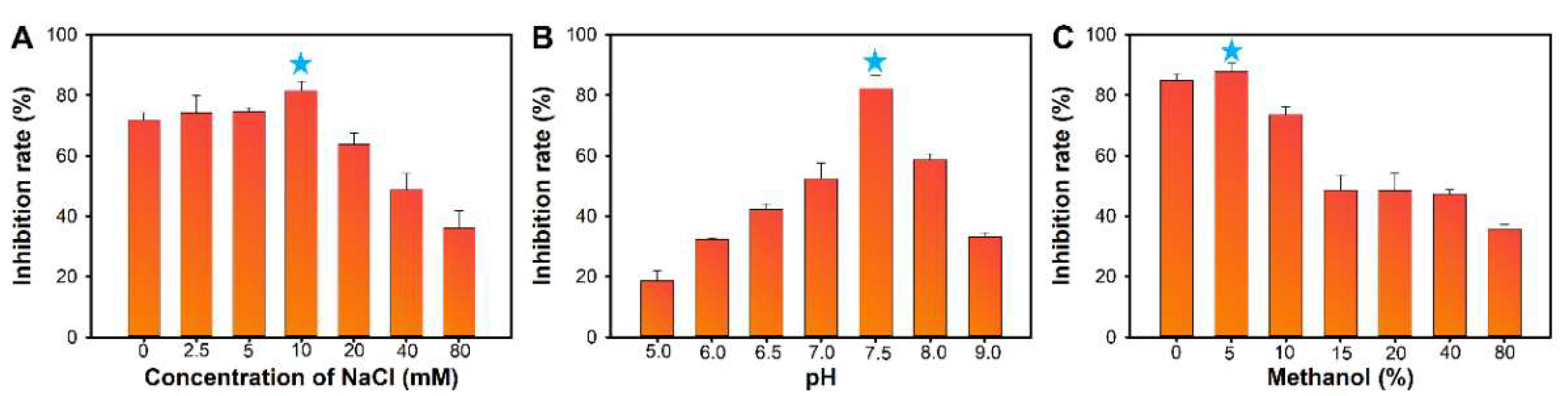
3.4. Development of the M13OTA-FLISA
3.5. Analytical Performance of the M13OTA-FLISA
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van der Merwe, K.; Steyn, P.; Fourie, L.; Scott, D.B.; Theron, J. Ochratoxin a, a toxic metabolite produced by aspergillus ochraceus wilh. Nature 1965, 205, 1112–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink-Gremmels, J.; Jahn, A.; Blom, M.J. Toxicity and metabolism of ochratoxin A. Nat. Toxins 1995, 3, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Placinta, C.; D’Mello, J.F.; Macdonald, A. A review of worldwide contamination of cereal grains and animal feed with fusarium mycotoxins. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1999, 78, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.; Lino, C.; Pena, A. Mycotoxin food and feed regulation and the specific case of ochratoxin a: A review of the worldwide status. Food Addit. Contam. 2010, 27, 1440–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moez, E.; Noel, D.; Brice, S.; Benjamin, G.; Pascaline, A.; Didier, M. Aptamer assisted ultrafiltration cleanup with high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detector for the determination of ota in green coffee. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Taher, F.; Banaszewski, K.; Jackson, L.; Zweigenbaum, J.; Ryu, D.; Cappozzo, J. Rapid method for the determination of multiple mycotoxins in wines and beers by lc-ms/ms using a stable isotope dilution assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2378–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, T.; Cai, X.; Duan, H.; Leng, Y.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. A novel magneto-gold nanohybrid-enhanced lateral flow immunoassay for ultrasensitive and rapid detection of ochratoxin a in grape juice. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, R.; Xu, H.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y. Nanospherical brush as catalase container for enhancing the detection sensitivity of competitive plasmonic elisa. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, L.; González, I.; García, T.; Martín, R. Determination of food authenticity by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (elisa). Food Control 2008, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Ping, G.; Xiong, Y. Plasmonic elisa for naked-eye detection of ochratoxin a based on the tyramine-H2O2 amplification system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Leng, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Emerging strategies to enhance the sensitivity of competitive elisa for detection of chemical contaminants in food samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 126, 115861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, G.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L.; Huang, R.; Chen, X. Application of nano-elisa in food analysis: Recent advances and challenges. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 113, 140–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Chen, C.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Xiong, Y. Phage-free peptide elisa for ochratoxin a detection based on biotinylated mimotope as a competing antigen. Talanta 2016, 146, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Mari, G.M.; Yu, X.; Ke, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, W.; Wen, K. Development of a fluorescence immunoassay for highly sensitive detection of amantadine using the nanoassembly of carbon dots and mno2 nanosheets as the signal probe. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2019, 286, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Hu, T.; Xu, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, X. A fluorescent elisa based on the enzyme-triggered synthesis of poly (thymine)-templated copper nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16846–16850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Zhan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, X.; Leng, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, Y. Fluorescence elisa based on cat-regulated fluorescence quenching of cdte qds for sensitive detection of fb 1. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5797–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yu, C.; Pan, D.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Yan, M.; Segura, T.; Lu, Y. Quantum-dot-decorated robust transductable bioluminescent nanocapsules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12780–12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akshath, U.S.; Shubha, L.R.; Bhatt, P.; Thakur, M.S. Quantum dots as optical labels for ultrasensitive detection of polyphenols. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 57, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhan, S.; Xu, H.; Meng, X.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, X. Ultrasensitive fluorescence immunoassay for detection of ochratoxin a using catalase-mediated fluorescence quenching of cdte qds. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 9390–9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, X.; Yu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, Y. Fluorescence elisa for sensitive detection of ochratoxin a based on glucose oxidase-mediated fluorescence quenching of cdte qds. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Wei, J.; Ren, X.; Ren, J.; Tang, F. A simple and sensitive fluorescence biosensor for detection of organophosphorus pesticides using h2o2-sensitive quantum dots/bi-enzyme. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molek, P.; Bratkovic, Ť. Bacteriophages as scaffolds for bipartite display: Designing swiss army knives on a nanoscale. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminga, M.A.; Vos, W.L.; Nazarov, P.V.; Koehorst, R.B.; Wolfs, C.J.; Spruijt, R.B.; Stopar, D. Viruses: Incredible nanomachines. New advances with filamentous phages. Eur. Biophys. J. 2010, 39, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, J.-S.; Kim, W.-G.; Shin, D.-M.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, C.; Lee, Y.; Han, J.; Kim, K.; Yoo, S.Y.; Oh, J.-W. Bioinspired m-13 bacteriophage-based photonic nose for differential cell recognition. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.S.; Chen, P.H.C.; Hampton, J.T.; Tharp, J.M.; Reed, C.A.; Das, S.K.; Wang, D.S.; Hayatshahi, H.S.; Shen, Y.; Liu, J. A genetically encoded, phage-displayed cyclic-peptide library. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 16051–16056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaik, R.A.; Lan, E.; Huang, Y.; Dunn, B. Gold-coated m13 bacteriophage as a template for glucose oxidase biofuel cells with direct electron transfer. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Moon, J.-S.; Oh, J.-W. Recent advances in m13 bacteriophage-based optical sensing applications. Nano Converg. 2016, 3, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.; Qi, J.; deQuilettes, D.W.; Huang, M.; Lin, C.W.; Bardhan, N.M.; Dang, X.; Bulović, V.; Belcher, A.M. M13 virus-based framework for high fluorescence enhancement. Small 2019, 15, 1901233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Xu, P.F.; Domaille, D.W.; Choi, C.; Jin, S.; Cha, J.N. M13 bacteriophage as materials for amplified surface enhanced raman scattering protein sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2079–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Zhan, S.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Guo, Q.; Guo, Y.; He, Q.; Xiong, Y. Chemical modification of m13 bacteriophage as nanozyme container for dramatically enhanced sensitivity of colorimetric immunosensor. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2021, 346, 130368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiong, S.; Zou, X.; Chen, C.; Shao, H.; Chen, X. Mimic epitope of ochratoxin a and its application in phage enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 856–861. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, K.; Xiong, Y.; Xu, B.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Xiong, Y. Colorimetric elisa for ochratoxin a detection based on the urease-induced metallization of gold nanoflowers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 262, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Spiked-OTA (μg/kg) | Intra-Assay (n = 3) | Inter-Assay (n = 3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTA Recovered (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | CV (%) | OTA Recovered (μg/kg) | Recovery (%) | CV (%) | |
| 2 | 2.06 ± 0.32 | 116.45 | 13.86 | 2.13 ± 0.19 | 106.74 | 8.83 |
| 8 | 8.11 ± 0.62 | 101.32 | 7.71 | 7.36 ± 0.96 | 92.02 | 13.06 |
| 40 | 41.12 ± 4.78 | 102.79 | 11.62 | 38.64 ± 4.03 | 96.59 | 10.44 |
| 80 | 84.76 ± 6.96 | 105.95 | 8.21 | 80.89 ± 6.47 | 101.12 | 8.04 |
| 120 | 108.2 ± 16.02 | 90.16 | 14.81 | 115.51 ± 11.32 | 96.26 | 9.80 |
| 160 | 159.93 ± 19.67 | 99.96 | 12.30 | 155.41 ± 14.92 | 97.13 | 9.60 |
| Incurred Samples | M13OTA-FLISA | UPLC-FLD |
|---|---|---|
| OTA Recovered (μg/kg) | OTA Recovered (μg/kg) | |
| 1 | 103.26 ± 3.12 | 119.91 |
| 2 | 42.60 ± 5.41 | 33.79 |
| 3 | 25.41 ± 3.86 | 21.49 |
| 4 | 40.53 ± 3.49 | 52.60 |
| 5 | 159.74 ± 21.31 | 163.76 |
| 6 | 57.48 ± 0.63 | 76.06 |
| 7 | 28.75 ± 1.29 | 31.07 |
| 8 | 183.68 ± 9.38 | 208.76 |
| 9 | 94.56 ± 1.53 | 88.76 |
| 10 | 21.72 ± 1.6 | 19.14 |
| 11 | 16.79 ± 0.84 | 16.83 |
| 12 | 53.18 ± 0.71 | 61.83 |
| 13 | 132.76 ± 9.33 | 144.91 |
| 14 | 26.07 ± 0.81 | 25.80 |
| 15 | 37.21 ± 2.84 | 34.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, W.; Fang, H.; Xiong, H.; Wei, D.; Leng, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Eco-Friendly Fluorescent ELISA Based on Bifunctional Phage for Ultrasensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn. Foods 2021, 10, 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102429
Tong W, Fang H, Xiong H, Wei D, Leng Y, Hu X, Huang X, Xiong Y. Eco-Friendly Fluorescent ELISA Based on Bifunctional Phage for Ultrasensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102429
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Weipeng, Hao Fang, Hanpeng Xiong, Daixian Wei, Yuankui Leng, Xinyu Hu, Xiaolin Huang, and Yonghua Xiong. 2021. "Eco-Friendly Fluorescent ELISA Based on Bifunctional Phage for Ultrasensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn" Foods 10, no. 10: 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102429
APA StyleTong, W., Fang, H., Xiong, H., Wei, D., Leng, Y., Hu, X., Huang, X., & Xiong, Y. (2021). Eco-Friendly Fluorescent ELISA Based on Bifunctional Phage for Ultrasensitive Detection of Ochratoxin A in Corn. Foods, 10(10), 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102429







