Overview of Rapid Detection Methods for Salmonella in Foods: Progress and Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Gold Standard Method
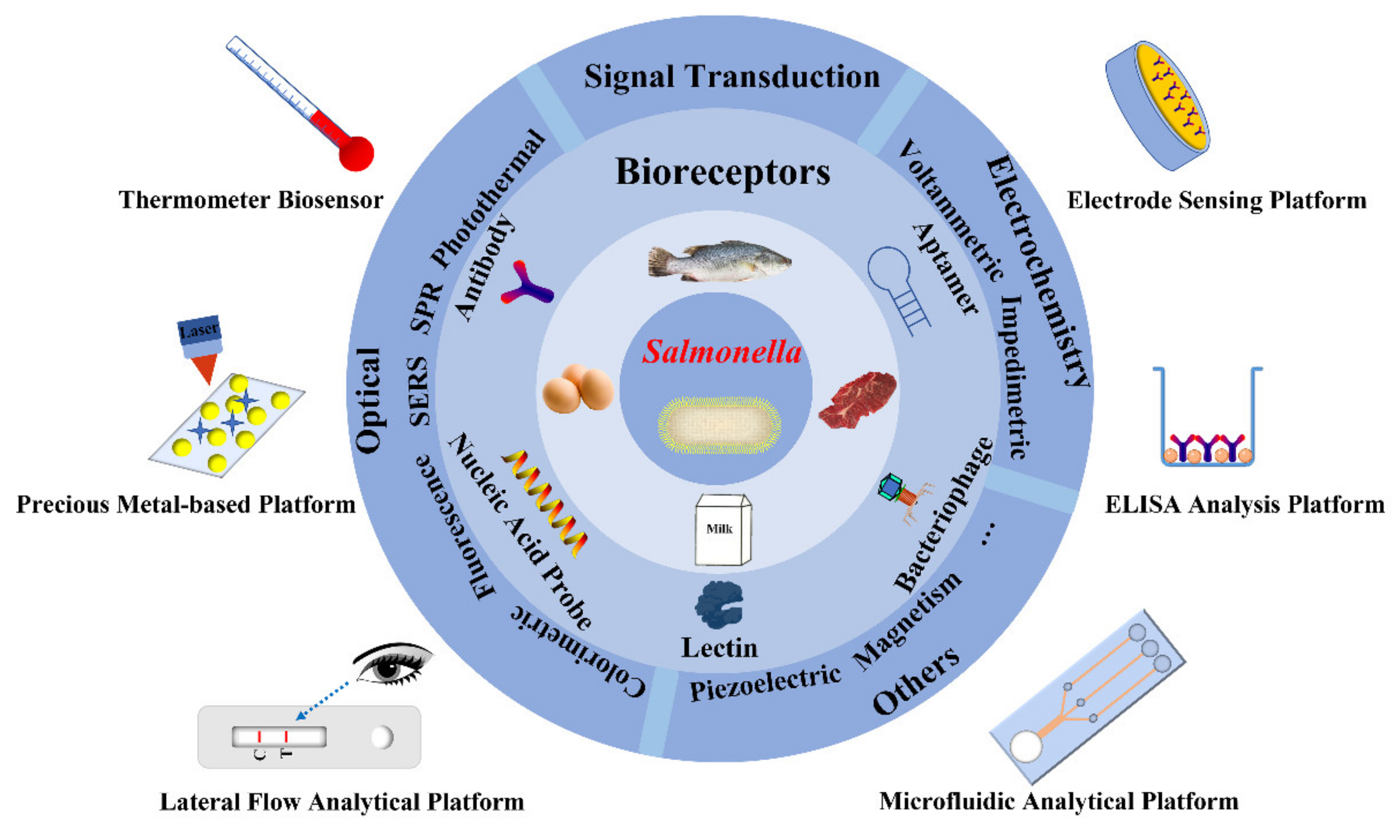
3. Bioreceptors for Salmonella
3.1. Antibody
3.2. Aptamer
3.3. Nucleic Acid Probe
3.4. Bacteriophage
3.5. Lectin
4. Rapid Detection Methods of Salmonella in Foods
4.1. Optical Sensing
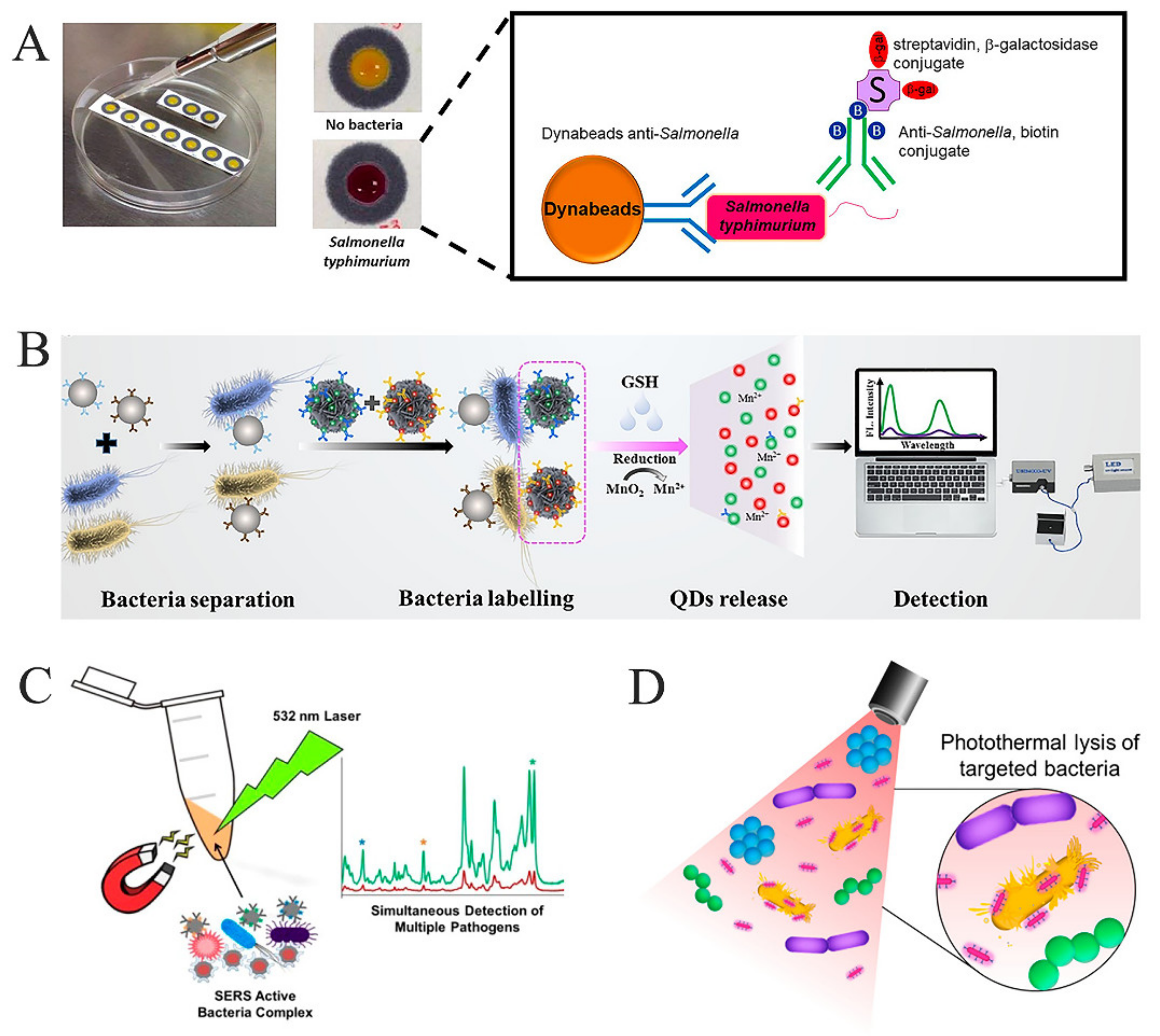
4.1.1. Colorimetry
| Detection Methods | Bioreceptor | Linear Range | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Detection Time | Real Sample Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorimetry | Nucleic acid probe | 100 to 109 CFU/mL | 16 CFU/mL | / | Milk | [57] |
| Antibody | 103 to 108 CFU/mL | 103 CFU/mL | 14 min | Cabbage and drinking water | [58] | |
| Antibody | 1.88 × 104 to 1.88 × 107 CFU/mL | 1.88 × 104 CFU/mL | / | Milk | [59] | |
| Antibody | 0 to 108 CFU/mL | 500 CFU/mL | 60 min | Milk | [60] | |
| Antibody | 0 to 107 CFU/mL | 34 CFU/mL | / | Milk | [61] | |
| Antibody | 100 to 104 CFU/mL | 100 CFU/mL | 90 min | Milk | [62] | |
| Fluorometry | Antibody | 5 × 104 to 107 CFU/mL | 5 × 103 CFU/mL | 12 min | Broth | [9] |
| Antibody | 500 to 5 × 107 CFU/mL | 60 CFU/mL | 60 min | Milk | [63] | |
| Antibody | 40 to 4 × 106 CFU/mL | 40 CFU/mL | 120 min | Chicken | [64] | |
| Aptamer | 10 to 107 CFU/mL | 10 CFU/mL | / | Meat, milk and chicken | [65] | |
| Aptamer | 50 to 106 CFU/mL | 35 CFU/mL | / | Chicken and shrimp | [66] | |
| Aptamer | 12 to 5 × 105 CFU/mL | 11 CFU/mL | / | Milk | [67] | |
| SERS | Aptamer | 10 to 104 CFU/mL | 4 CFU/mL | / | Chicken and milk | [68] |
| Nucleic acid probe | 27 to 2.7 × 106 CFU/mL | 27 CFU/mL | 30 min | Milk, chicken breast and beef | [69] | |
| Aptamer | 100 to 107 CFU/mL | 50 CFU/mL | / | Milk | [70] | |
| Lectin | 10 to 104 CFU/mL | 10 CFU/mL | / | / | [71] | |
| Aptamer | 0 to 107 CFU/mL | 25 CFU/mL | / | Milk, orange juice, and tap water | [72] | |
| SPR | Nucleic acid probe | 0.01 to 100 ng/mL | 10 pg/mL | 60 min | / | [73] |
| Antibody | / | 7.4 × 103 CFU/mL | 80 min | Cucumber and hamburger | [74] | |
| Antibody | 100 to 106 CFU/mL | 103 CFU/mL | 60 min | Powdered milk | [75] | |
| Photothermal | Antibody | 300 to 103 CFU/mL | 300 CFU/mL | 90 min | / | [76] |
| Antibody | 100 to 107 CFU/mL | 100 CFU/mL | 25 min | Milk and grape juice | [77] | |
| Antibody | 104 to 108 CFU/mL | 104 CFU/mL | 20 min | Milk and grape juice | [78] | |
| Antibody | 103 to 109 CFU/mL | 103 CFU/mL | 15 min | Milk and grape juice | [79] | |
| Antibody | 5 to 5 × 103 CFU/mL | 70.7 CFU/mL | 36 min | / | [80] |
4.1.2. Fluorescence Analysis
4.1.3. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection
4.1.4. Surface Plasma Resonance (SPR) Determination
4.1.5. Photothermal Detection
4.2. Electrochemical Detection
4.2.1. Voltammetry
4.2.2. Impedimetry
4.3. Other Signal Transduction Methods
4.3.1. Piezoelectric Biosensors
4.3.2. Magnetic Relaxation Biosensors
5. Challenges and Trends of Rapid Detection Methods
5.1. Sample Pretreatment
5.2. Non-Destructive Testing
5.3. In-Field Application and Stability Problems
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aworh, O.C. Food safety issues in fresh produce supply chain with particular reference to sub-Saharan Africa. Food Control 2021, 123, 107737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zhu, L.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, C.; Zhang, G.; Bi, J.; Yan, S.; Liu, G.; Hou, H. A novel photoelectrochemical aptamer sensor based on rare-earth doped Bi2WO6 and Ag2S for the rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Liu, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, L.; Lu, X.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, H. Detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium based on cell elongation induced by beta-lactam antibiotics. Analyst 2019, 144, 4505–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallan, E.; Hoekstra, R.M.; Angulo, F.J.; Tauxe, R.V.; Widdowson, M.A.; Roy, S.L.; Jones, J.L.; Griffin, P.M. Foodborne illness acquired in the United States-major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, H.-Y. Direct triplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the point-of-care molecular detection of Salmonella genus, subspecies I, and serovar Typhimurium. Food Control 2021, 120, 107504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, Y. Biosensors for rapid detection of Salmonella in food: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 149–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Domesle, K.J.; Ge, B. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Salmonella Detection in Food and Feed: Current Applications and Future Directions. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 309–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Zheng, Q.; Lin, J.; Yuk, H.-G.; Guo, L. Immuno- and nucleic acid-based current technique for Salmonella detection in food. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Tang, F.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Liu, C. Rapid screening and quantitative detection of Salmonella using a quantum dot nanobead-based biosensor. Analyst 2020, 145, 2184–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Gong, J.; Ji, Y.; Tian, P.; Kong, F.; Bai, H.; Gu, N.; Zhang, Y. Lateral flow fluorescent immunoassay based on isothermal amplification for rapid quantitative detection of Salmonella spp. Analyst 2020, 145, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadi, Z.R.; Salehi, T.Z.; Tamai, I.A.; Foroushani, A.R.; Sillanpaa, M.; Dallal, M.M.S. Evaluation of antibiotic resistance and prevalence of common Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from foodborne outbreaks. Microchem. J. 2020, 155, 104660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, C.S.J.; Lau, M.Y.; Chong, C.W.; Ngoi, S.T.; Chua, K.H.; Lee, W.S.; Thong, K.L. One-step differential detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, serovar Paratyphi A and other Salmonella spp. by using a quadruplex real-time PCR assay. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2021, 183, 106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.F.D.; Magalhaes, J.; Freire, C.; Delerue-Matos, C. Electrochemical biosensors for Salmonella: State of the art and challenges in food safety assessment. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 667–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crump, J.A.; Sjolund-Karlsson, M.; Gordon, M.A.; Parry, C.M. Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Laboratory Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Antimicrobial Management of Invasive Salmonella Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 901–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LaRock, D.L.; Chaudhary, A.; Miller, S.I. Salmonellae interactions with host processes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postollec, F.; Falentin, H.; Pavan, S.; Combrisson, J.; Sohier, D. Recent advances in quantitative PCR (qPCR) applications in food microbiology. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-M.; Runyon, M.; Herrman, T.J.; Phillips, R.; Hsieh, J. Review of Salmonella detection and identification methods: Aspects of rapid emergency response and food safety. Food Control 2015, 47, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrac, C.; Eyidogan, F.; Avni Oktem, H. DNA aptamer-based colorimetric detection platform for Salmonella enteritidis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majdinasab, M.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Aptamer-based assays and aptasensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria in food samples. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2018, 107, 60–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Lai, W.; Xiong, Y.; Wei, H.; Xu, H. Novel strategies to enhance lateral flow immunoassay sensitivity for detecting foodborne pathogens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lin, C.W.; Wang, J.; Oh, D.H. Advances in rapid detection methods for foodborne pathogens. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paniel, N.; Noguer, T. Detection of Salmonella in Food Matrices, from Conventional Methods to Recent Aptamer-Sensing Technologies. Foods 2019, 8, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arshad, R.; Pal, K.; Sabir, F.; Rahdar, A.; Bilal, M.; Shahnaz, G.; Kyzas, G.Z. A review of the nanomaterials use for the diagnosis and therapy of Salmonella typhi. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1230, 129928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Aydin, M.; Khatiwara, A.; Dolan, M.C.; Gilmore, D.F.; Bouldin, J.L.; Ahn, S.; Ricke, S.C. Current and emerging technologies for rapid detection and characterization of Salmonella in poultry and poultry products. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Hulme, J.P. Recent Advances in the Detection of Antibiotic and Multi-Drug Resistant Salmonella: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 29921-2021, National Food Safety Standards—Limit of Pathogenic Bacteria in Prepackaged Food; National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- EC No 2160/2003. The Control of Salmonella and Other Specified Food-Borne Zoonotic Agents. Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=celex:32003R2160 (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- GB 4789.4-2016. National Food Safety Standards—Food Microbiology Testing—Salmonella Test. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China. Available online: http://tradechina.dairyaustralia.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/GB-4789.4-2016-Safety-Standard-Food-Microbiological-Examination-Salmonella.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- De Boer, E.; Beumer, R.R. Methodology for detection and typing of foodborne microorganisms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 50, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Miks-Krajnik, M.; Yang, Y.; Lee, S.M.; Lee, S.C.; Yuk, H.G. Evaluation of real-time PCR coupled with immunomagnetic separation or centrifugation for the detection of healthy and sanitizer-injured Salmonella spp. on mung bean sprouts. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 222, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayan, H.; Pu, H.B.; Sun, D.W. Recent development in rapid detection techniques for microorganism activities in food matrices using bio-recognition: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 95, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanegas, D.C.; Gomes, C.L.; Cavallaro, N.D.; Giraldo-Escobar, D.; McLamore, E.S. Emerging Biorecognition and Transduction Schemes for Rapid Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria in Food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 1188–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoyos-Nogues, M.; Gil, F.J.; Mas-Moruno, C. Antimicrobial Peptides: Powerful Biorecognition Elements to Detect Bacteria in Biosensing Technologies. Molecules 2018, 23, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crivianu-Gaita, V.; Thompson, M. Aptamers, antibody scFv, and antibody Fab’ fragments: An overview and comparison of three of the most versatile biosensor biorecognition elements. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, D.R.; Atkins, W.M. Considerations for the Design of Antibody-Based Therapeutics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 74–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schenk, F.; Weber, P.; Vogler, J.; Hecht, L.; Dietzel, A.; Gauglitz, G. Development of a paper-based lateral flow immunoassay for simultaneous detection of lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella serovars. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Park, B. Immunoassay Biosensing of Foodborne Pathogens with Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12927–12939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, S.J.; Wang, K.Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Wei, H.G.; Zhang, W.G.; Liu, W.S.; Wan, J.Y. Ferrocene-functionalized nanocomposites as signal amplification probes for electrochemical immunoassay of Salmonella typhimurium. Mikrochim. Acta 2020, 187, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, H.; Tayyarcan, E.K.; Caglayan, M.G.; Boyaci, I.H.; Saglam, N.; Tamer, U. Replacement of antibodies with bacteriophages in lateral flow assay of Salmonella enteritidis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 189, 113383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, V.J.; McNaughton, B.R. Evaluation of Nanobody Conjugates and Protein Fusions as Bioanalytical Reagents. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 3819–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassanzadeh-Ghassabeh, G.; Devoogdt, N.; De Pauw, P.; Vincke, C.; Muyldermans, S. Nanobodies and their potential applications. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Ren, Y.; Guo, B.; Yang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Development of a specific nanobody and its application in rapid and selective determination of Salmonella Enteritidis in milk. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Lu, L.; Du, S.; Zhang, H. Selection and identification of diethylstilbestrol-specific aptamers based on magnetic-bead SELEX. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukama, O.; Sinumvayo, J.P.; Shamoon, M.; Shoaib, M.; Mushimiyimana, H.; Safdar, W.; Bemena, L.; Rwibasira, P.; Mugisha, S.; Wang, Z. An Update on Aptamer-Based Multiplex System Approaches for the Detection of Common Foodborne Pathogens. Food Anal. Method. 2017, 10, 2549–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Raston, N.H.; Gu, M.B. Aptamer-based nanobiosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chen, F.; Lee, T.Y. Tryptamine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for highly sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Analyst 2021, 146, 2559–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Hwang, A.; Song, Y.; Lee, W.S.; Moon, J.; Jeong, J.; Bae, N.H.; Jung, Y.M.; Jung, J.; Ryu, S.; et al. 3D Hierarchical Nanotopography for On-Site Rapid Capture and Sensitive Detection of Infectious Microbial Pathogens. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 4777–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, W.; Ullah, M.W.; Farooq, U.; Aziz, A.; Wang, S. Bacteriophage-based advanced bacterial detection: Concept, mechanisms, and applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 112973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, E.; Martins, V.C.; Nobrega, C.; Carvalho, C.M.; Cardoso, F.A.; Cardoso, S.; Dias, J.; Deng, D.; Kluskens, L.D.; Freitas, P.P.; et al. A bacteriophage detection tool for viability assessment of Salmonella cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.S.; Choi, E.J.; Jeong, N.N.; Sohn, J.R.; Han, D.W.; Oh, J.W. Research Progress of M13 Bacteriophage-Based Biosensors. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olsson, A.L.; Wargenau, A.; Tufenkji, N. Optimizing Bacteriophage Surface Densities for Bacterial Capture and Sensing in Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 13698–13706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phongtang, W.; Choi, G.P.; Chukeatirote, E.; Ahn, J. Bacteriophage control of Salmonella typhimurium in milk. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, F.; Guan, M.; Hu, C.; Peng, F.; Sun, S.; Wang, X. Application of lectin-based biosensor technology in the detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria: A review. Analyst 2021, 146, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.N.T.; Yoon, J.; Jin, C.E.; Koo, B.; Han, K.; Shin, Y.; Lee, T.Y. Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella based on microfluidic enrichment with a label-free nanobiosensing platform. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 262, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansili, N.; Rattu, G.; Krishna, P.M. Label-free optical biosensors for food and biological sensor applications. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 265, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, C.; Tian, Y.; Fang, S.; Yang, H.; Li, B.; Liu, Q. Colloidal gold immunochromatographic test strips for broad-spectrum detection of Salmonella. Food Control 2021, 126, 108052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Wu, P.; Li, G.; Xiao, W.; Li, L.; He, Y.; He, Y.; Ding, P.; Chen, C. A composite prepared from carboxymethyl chitosan and aptamer-modified gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric determination of Salmonella typhimurium. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Wei, J.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, M.; Zhang, C.; Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Ultrasensitive label-free immunochromatographic strip sensor for Salmonella determination based on salt-induced aggregated gold nanoparticles. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Tang, M.; Wu, L.L.; Xie, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Pang, D.W. Colorimetric-Fluorescent-Magnetic Nanosphere-Based Multimodal Assay Platform for Salmonella Detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, M. A colorimetric and ultrasensitive immunosensor for one-step pathogen detection via the combination of nanoparticle-triggered signal amplification and magnetic separation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 100633–100637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Du, D.; Zhu, M.-J.; Luo, Y.; Xu, W.; Lin, Y. Nanozyme Enhanced Colorimetric Immunoassay for Naked-Eye Detection of Salmonella Enteritidis. J. Anal. Test. 2018, 3, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srisa-Art, M.; Boehle, K.E.; Geiss, B.J.; Henry, C.S. Highly Sensitive Detection of Salmonella typhimurium Using a Colorimetric Paper-Based Analytical Device Coupled with Immunomagnetic Separation. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, B.F.; Wang, Y.; Dong, M.L.; Wu, J.; Ran, B.; Xie, M.X.; Joo, S.W.; Chen, Y.P. One-step multiplexed detection of foodborne pathogens: Combining a quantum dot-mediated reverse assaying strategy and magnetic separation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, L.; Huang, F.C.; Hao, L.; Cai, G.Z.; Zheng, L.Y.; Li, Y.B.; Lin, J.H. A sensitive immunoassay for simultaneous detection of foodborne pathogens using MnO2 nanoflowers-assisted loading and release of quantum dots. Food Chem. 2020, 322, 126719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renuka, R.M.; Maroli, N.; Achuth, J.; Ponmalai, K.; Kadirvelu, K. Highly adaptable and sensitive FRET-based aptamer assay for the detection of Salmonella paratyphi A. Spectrochim. Acta A 2020, 243, 118662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, N.; Wu, S.J.; Dai, S.L.; Miao, T.T.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.P. Simultaneous detection of pathogenic bacteria using an aptamer based biosensor and dual fluorescence resonance energy transfer from quantum dots to carbon nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.Y.; Zhang, J.G.; Zhang, L.P.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.Q. Aptamer biosensor for Salmonella typhimurium detection based on luminescence energy transfer from Mn2+-doped NaYF4:Yb, Tm upconverting nanoparticles to gold nanorods. Spectrochim. Acta A 2017, 171, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Li, D.; Yin, P.; Xie, Q.; Li, Y.; Lin, Q.; Duan, Y. A novel surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) strategy for ultrasensitive detection of bacteria based on three-dimensional (3D) DNA walker. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.B.; Du, X.J.; Zang, Y.X.; Li, P.; Wang, S. SERS-Based Lateral Flow Strip Biosensor for Simultaneous Detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella enterica Serotype Enteritidis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10290–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Lin, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z. Fabrication of gold/silver nanodimer SERS probes for the simultaneous detection of Salmonella typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, H.; Goodacre, R.; Jamieson, L.E.; Graham, D.; Faulds, K. SERS Detection of Multiple Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens Using Nanosensors. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12666–12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Xiao, R.; Cheng, S.; Wang, S.; Shi, L.; Wang, C.; Qi, K.; Wang, S. A universal SERS-label immunoassay for pathogen bacteria detection based on Fe3O4@Au-aptamer separation and antibody-protein A orientation recognition. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1160, 338421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melaine, F.; Saad, M.; Faucher, S.; Tabrizian, M. Selective and High Dynamic Range Assay Format for Multiplex Detection of Pathogenic Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhimurium, and Legionella pneumophila RNAs Using Surface Plasmon Resonance Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7802–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisocherova-Lisalova, H.; Visova, I.; Ermini, M.L.; Springer, T.; Song, X.C.; Mrazek, J.; Lamacova, J.; Scott Lynn, N., Jr.; Sedivak, P.; Homola, J. Low-fouling surface plasmon resonance biosensor for multi-step detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens in complex food samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farka, Z.; Jurik, T.; Pastucha, M.; Skladal, P. Enzymatic Precipitation Enhanced Surface Plasmon Resonance Immunosensor for the Detection of Salmonella in Powdered Milk. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11830–11836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Han, L.; Du, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H. Rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium based on the photothermal effect of magnetic nanomaterials. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 268, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ge, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Du, S. Rapid and sensitive multimode detection of Salmonella typhimurium based on the photothermal effect and peroxidase-like activity of MoS2@Au nanocomposite. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2021, 326, 128807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Su, S.; Du, S.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H. Rapid Detection for Salmonella typhimurium by Conventional Resistive Temperature Sensor Based on Photothermal Effect of Carboxylated Graphene Oxide. Food Anal. Method. 2020, 13, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H. A portable immune-thermometer assay based on the photothermal effect of graphene oxides for the rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 144, 111670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.U.; Jo, E.J.; Noh, Y.; Mun, H.; Ahn, Y.D.; Kim, M.G. Adenosine Triphosphate Bioluminescence-Based Bacteria Detection Using Targeted Photothermal Lysis by Gold Nanorods. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 10171–10178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Song, L.; Zhou, N.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Z. A novel aptasensor for the colorimetric detection of S. typhimurium based on gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 245, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Zhuang, J.; Nie, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, N.; Wang, T.; Feng, J.; Yang, D.; Perrett, S.; et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Song, D.; Zhuo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, A.; Long, F. Simultaneous and sensitive determination of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium using evanescent wave dual-color fluorescence aptasensor based on micro/nano size effect. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 185, 113288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Xue, L.; Huang, F.; Cai, G.; Qi, W.; Zhang, M.; Han, Q.; Wang, Z.; Lin, J. A Microfluidic Biosensor Based on Magnetic Nanoparticle Separation, Quantum Dots Labeling and MnO2 Nanoflower Amplification for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Micromachines 2020, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamal, Z.; Ghobadi, M.Z.; Mohseni, S.M.; Ghourchian, H. High-performance porphyrin-like graphene quantum dots for immuno-sensing of Salmonella typhi. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 188, 113334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt, H.; Yuce, M.; Hussain, B.; Budak, H. Dual-excitation upconverting nanoparticle and quantum dot aptasensor for multiplexed food pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 81, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Romero-Lozano, A.; Hwang, D.S.; Yoon, J.Y. A guanidinium-rich polymer as a new universal bioreceptor for multiplex detection of bacteria from environmental samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.B.A.; Chan, E.W.C.; Chen, S.; Zeng, Z.L. Development of a Novel Quantum Dots and Graphene Oxide Based FRET Assay for Rapid Detection of invA Gene of Salmonella. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.R.; Armstrong, R.L.; Smith, G.B. Detection of Salmonella using Surfaced Enhanced Raman Scattering. Chem. Biol. Sens. IV 2003, 5085, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Park, B.; Huang, Y.W.; Zhao, Y.P.; Kwon, Y. Label-free SERS detection of Salmonella Typhimurium on DNA aptamer modified AgNR substrates. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Y.; Tsai, K.T.; Wang, H.H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Chao, Y.C.; Chang, H.H.; Lin, C.H.; Wang, J.K.; Wang, Y.L. Functionalized arrays of Raman-enhancing nanoparticles for capture and culture-free analysis of bacteria in human blood. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Park, B. Label-free screening of foodborne Salmonella using surface plasmon resonance imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5455–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Verma, H.N.; Arora, K. Surface plasmon resonance based label-free detection of Salmonella using DNA self assembly. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 1330–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, D.; Chen, F.C.; Bridgman, R.C. Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in Romaine Lettuce Using a Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor. Biosensors 2019, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Hu, K.; Kwee, S.; Tang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xia, J.; Li, X. Gold Nanoparticle Aggregation-Induced Quantitative Photothermal Biosensing Using a Thermometer: A Simple and Universal Biosensing Platform. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Chen, J.; Yu, Z.; Tang, D. Self-Powered Temperature Sensor with Seebeck Effect Transduction for Photothermal-Thermoelectric Coupled Immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 2809–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Tao, Y.; Pang, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, Y. Nanoparticle-based photothermal and photodynamic immunotherapy for tumor treatment. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 3050–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jia, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. An immunofiltration strip method based on the photothermal effect of gold nanoparticles for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Analyst 2019, 144, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, Q.; Tang, B. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Cancer Cells Based on the Photothermal Effect of Graphene Functionalized Magnetic Microbeads. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2016, 8, 29933–29938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H. Establishment of an immunofiltration strip for the detection of 17beta-estradiol based on the photothermal effect of black phosphorescence. Analyst 2019, 144, 6647–6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Lu, Z.; Gao, L.; Ge, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H. Salmonella typhimurium detector based on the intrinsic peroxidase-like activity and photothermal effect of MoS2. Mikrochim. Acta 2020, 187, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Fu, G.; Li, X. Detector-Free Photothermal Bar-Chart Microfluidic Chips (PT-Chips) for Visual Quantitative Detection of Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7754–7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Chan, W.C.; Boulware, D.R.; Akkin, T.; Butler, E.K.; Bischof, J.C. Significantly improved analytical sensitivity of lateral flow immunoassays by using thermal contrast. Angew. Chem. 2012, 51, 4358–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Du, S.; Su, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Rapid detection method and portable device based on the photothermal effect of gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 123, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Luo, F.; Lin, Y.; Dong, N.; Li, C.; Lin, Z. Quantitative gold nanorods based photothermal biosensor for glucose using a thermometer as readout. Talanta 2021, 230, 122364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Xue, L.; Cai, G.; Qi, W.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J. Fe-MIL-88NH2 Metal–Organic Framework Nanocubes Decorated with Pt Nanoparticles for the Detection of Salmonella. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 5115–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Volpe, G.; Piermarini, S.; Delibato, E.; Palleschi, G. Electrochemical Biosensors for Rapid Detection of Foodborne Salmonella: A Critical Overview. Sensors 2017, 17, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.F.D.; Magalhaes, J.; Barroso, M.F.; Oliva-Teles, T.; Freire, C.; Delerue-Matos, C. In situ formation of gold nanoparticles in polymer inclusion membrane: Application as platform in a label-free potentiometric immunosensor for Salmonella typhimurium detection. Talanta 2019, 194, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, C.; Ali, M.A.; Reddy, V.; Singh, D.; Kim, C.G.; Sumana, G.; Malhotra, B.D. Biofunctionalized graphene oxide wrapped carbon nanotubes enabled microfluidic immunochip for bacterial cells detection. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 255, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, J.; Dou, W.; Zhao, G. A sandwich electrochemical immunosensor for Salmonella pullorum and Salmonella gallinarum based on a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with an ionic liquid and electrodeposited gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2267–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.; Rani, C.; Ho, J.A. Electrochemical immunosensor for multiplexed detection of food-borne pathogens using nanocrystal bioconjugates and MWCNT screen-printed electrode. Talanta 2012, 94, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freitas, M.; Viswanathan, S.; Nouws, H.P.; Oliveira, M.B.; Delerue-Matos, C. Iron oxide/gold core/shell nanomagnetic probes and CdS biolabels for amplified electrochemical immunosensing of Salmonella typhimurium. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 51, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagheryan, Z.; Raoof, J.B.; Golabi, M.; Turner, A.P.F.; Beni, V. Diazonium-based impedimetric aptasensor for the rapid label-free detection of Salmonella typhimurium in food sample. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ranjbar, S.; Shahrokhian, S.; Nurmohammadi, F. Nanoporous gold as a suitable substrate for preparation of a new sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Sens. Actuat. B Chem 2018, 255, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, R.R.A.; Hjort, R.G.; Pola, C.C.; Parate, K.; Reis, E.L.; Soares, N.F.F.; McLamore, E.S.; Claussen, J.C.; Gomes, C.L. Laser-Induced Graphene Electrochemical Immunosensors for Rapid and Label-Free Monitoring of Salmonella enterica in Chicken Broth. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 1900–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, C.; Ali, M.A.; Kumar, V.; Ahmad, R.; Sumana, G. Functionalized MoS2 nanosheets assembled microfluidic immunosensor for highly sensitive detection of food pathogen. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2018, 259, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Guo, R.; Huang, F.; Qi, W.; Liu, Y.; Cai, G.; Lin, J. An impedance biosensor based on magnetic nanobead net and MnO2 nanoflowers for rapid and sensitive detection of foodborne bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 173, 112800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peng, T.; Meng, Q.; Zhu, X.; Guo, L.; Yao, K.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, P.; Ren, Z.; He, Z.; et al. Rapid and ultrasensitive detection of Salmonella typhimurium using a novel impedance biosensor based on SiO2@MnO2 nanocomposites and interdigitated array microelectrodes. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2020, 324, 128654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riu, J.; Giussani, B. Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of pathogenic bacteria in food. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2020, 126, 115863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Q.; Song, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Leng, X.; Cui, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J. A facile signal-on electrochemical DNA sensing platform for ultrasensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria based on Exo III-assisted autonomous multiple-cycle amplification. Analyst 2019, 144, 3023–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyet, N.T.; Yen, L.T.H.; Doan, V.Y.; Hoang, N.L.; Van Thu, V.; Lan, H.; Trung, T.; Pham, V.H.; Tam, P.D. A label-free and highly sensitive DNA biosensor based on the core-shell structured CeO2-NR@Ppy nanocomposite for Salmonella detection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 96, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniandy, S.; Dinshaw, I.J.; Teh, S.J.; Lai, C.W.; Ibrahim, F.; Thong, K.L.; Leo, B.F. Graphene-based label-free electrochemical aptasensor for rapid and sensitive detection of foodborne pathogen. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 6893–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinshaw, I.J.; Muniandy, S.; Teh, S.J.; Ibrahim, F.; Leo, B.F.; Thong, K.L. Development of an aptasensor using reduced graphene oxide chitosan complex to detect Salmonella. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 806, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Tellez, J.; Sanchez-Ortega, I.; Hornung-Leoni, C.T.; Santos, E.M.; Miranda, J.M.; Rodriguez, J.A. Impedimetric Biosensor Based on a Hechtia argentea Lectin for the Detection of Salmonella spp. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M. Overview of Piezoelectric Biosensors, Immunosensors and DNA Sensors and Their Applications. Materials 2018, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Jin, L.; Feng, K.; Yang, T.; Yue, X.; Wu, B.; Ding, S.; Liang, X.; Huang, G.; Zhang, J. A novel low-field NMR biosensor based on dendritic superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the rapid detection of Salmonella in milk. LWT 2020, 133, 110149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhneva, E.; Farka, Z.; Skládal, P.; Zajíčková, L. Cyclopropylamine plasma polymer surfaces for label-free SPR and QCM immunosensing of Salmonella. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 276, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulgione, A.; Cimafonte, M.; Della Ventura, B.; Iannaccone, M.; Ambrosino, C.; Capuano, F.; Proroga, Y.T.R.; Velotta, R.; Capparelli, R. QCM-based immunosensor for rapid detection of Salmonella Typhimurium in food. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xianyu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Huang, R.; Chen, Y. Broad-Range Magnetic Relaxation Switching Bioassays Using Click Chemistry-Mediated Assembly of Polystyrene Beads and Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Li, T.; Yang, T.; Liang, X.; Wu, B.; Zou, D.; Hu, L.; Huang, G.; Zhang, J. NMR rapid detection of Salmonella in milk based on ultra-small iron oxide nanobiosensor. Int. Dairy J. 2020, 110, 104807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xianyu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, A.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y. Background Signal-Free Magnetic Bioassay for Food-Borne Pathogen and Residue of Veterinary Drug via Mn(VII)/Mn(II) Interconversion. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2771–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Wang, Z.; Feng, C.; Xianyu, Y.; Chen, Y. Direct Transverse Relaxation Time Biosensing Strategy for Detecting Foodborne Pathogens through Enzyme-Mediated Sol-Gel Transition of Hydrogels. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6613–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoszowski, A.; Fraser, A.D.; Brooks, B.W.; Riche, E.M. Rapid detection and enumeration of Salmonella in chicken carcass rinses using filtration, enrichment and colony blot immunoassay. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 28, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cai, R.; Gao, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Immunomagnetic separation: An effective pretreatment technology for isolation and enrichment in food microorganisms detection. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3802–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Nguyen, H.V.; Bui, K.H.; Seo, T.S. Smart phone-powered capillary electrophoresis on a chip for foodborne bacteria detection. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2019, 301, 127108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srbova, J.; Krulisova, P.; Holubova, L.; Pereiro, I.; Bendali, A.; Hamiot, A.; Podzemna, V.; Macak, J.; Dupuy, B.; Descroix, S.; et al. Advanced immunocapture of milk-borne Salmonella by microfluidic magnetically stabilized fluidized bed. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.E.; Tieu, M.V.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, M.H. Magnetic Particles: Their Applications from Sample Preparations to Biosensing Platforms. Micromachines 2020, 11, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wu, J. Recent advances in biosensor-integrated enrichment methods for preconcentrating and detecting the low-abundant analytes in agriculture and food samples. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2020, 128, 115914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, D.; Muñoz, R.; Marty, J.L. Fluorescence analyzer based on smartphone camera and wireless for detection of Ochratoxin A. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2016, 232, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budagovskaya, O.N.; Budagovsky, A.V. Nondestructive laser testing of fruit. Russ. J. Nondestruct. Test. 2015, 51, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Chen, J. A Review of Hyperspectral Imaging for Chicken Meat Safety and Quality Evaluation: Application, Hardware, and Software. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, C.; Huan, H.; Zhao, B.; Yan, L. Photoacoustic Spectroscopy as a Non-destructive Tool for Quantification of Pesticide Residue in Apple Cuticle. Int. J. Thermophys. 2014, 36, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidane, F.; Lanteri, J.; Marot, J.; Brochier, L.; Joachimowicz, N.; Roussel, H.; Migliaccio, C. Nondestructive Control of Fruit Quality via Millimeter Waves and Classification Techniques: Investigations in the Automated Health Monitoring of Fruits. IEEE Antenn. Propag. M. 2020, 62, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.G.; Zhang, Z.N.; Tian, S.Q. Nondestructive Testing for Wheat Quality with Sensor Technology Based on Big Data. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 8851509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, A.; Hammerl, J.A.; Boone, I.; Jansen, W.; Fohler, S.; Klein, G.; Dieckmann, R.; Al Dahouk, S. Overview of validated alternative methods for the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2017, 62, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, S.; Vahed, S.Z.; Ahmadian, E.; Dizaj, S.M.; Eftekhari, A.; Khalilov, R.; Ahmadi, M.; Hamidi-Asl, E.; Labib, M. Detection of pathogenic bacteria via nanomaterials-modified aptasensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 150, 111933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, L.; Huang, Q.; Tong, T.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Bai, Q.; Liang, H.; Chen, L. Recent advances on aptamer-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourakbari, R.; Shadjou, N.; Yousefi, H.; Isildak, I.; Yousefi, M.; Rashidi, M.R.; Khalilzadeh, B. Recent progress in nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors for pathogenic bacteria. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Belwal, T.; Li, L.; Lin, X.; Xu, Y.; Luo, Z. Nanomaterial-based biosensors for sensing key foodborne pathogens: Advances from recent decades. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1465–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, M.H.; Wiwasuku, T.; Day, A.S.; Youngme, S.; Hwang, D.S.; Yoon, J.Y. Human sensor-inspired supervised machine learning of smartphone-based paper microfluidic analysis for bacterial species classification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 188, 113335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyvazi, S.; Baradaran, B.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Guardia, M.d.l. Recent advances on development of portable biosensors for monitoring of biological contaminants in foods. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 114, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Yu, Z.; Tong, P.; Tang, D. Ti3C2 MXene quantum dot-encapsulated liposomes for photothermal immunoassays using a portable near-infrared imaging camera on a smartphone. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 15659–15667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, L.; Dou, L.; Zhao, B.; Li, T.; Zhang, D. New Functional Tracer-Two-Dimensional Nanosheet-Based Immunochromatographic Assay for Salmonella Enteritidis Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6642–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, T.; Yao, X.; Huang, L.; Dou, L.; Zhao, B.; Yang, B.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D. Dual recognition strategy and magnetic enrichment based lateral flow assay toward Salmonella Enteritidis detection. Talanta 2020, 206, 120204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wu, H.; He, L.; Tan, L.; Jia, Z.; Gan, N. The universal dual-mode aptasensor for simultaneous determination of different bacteria based on naked eyes and microfluidic-chip together with magnetic DNA encoded probes. Talanta 2021, 225, 122062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Microfluidic-Based Approaches for Foodborne Pathogen Detection. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puiu, M.; Bala, C. Microfluidics-integrated biosensing platforms as emergency tools for on-site field detection of foodborne pathogens. TrAC Trends in Anal. Chem. 2020, 125, 115831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Bioreceptors | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antibody | Specific recognition proteins produced by immune cells stimulated by antigens | High affinity and specificity | Time-consuming and low output; poor resistant to high temperature and acid and alkali |
| Aptamer | A single stranded nucleic acid | Simple synthesis, strong anti-interference and high affinity | Special 3-dimensional structure is required to identify the target |
| Nucleic acid probe | Nucleotide sequences complementary to bacterial genes | Simple synthesis and high affinity | Special immobilization |
| Bacteriophage | A virus that can infect and replicate in bacteria | Identification of living and dead bacteria | Lysis of bacteria |
| Lectin | A class of non-enzyme and non-antibody proteins that can recognize carbohydrate chemicals | High stability and low cost | Limited selectivity, less practical types |
| Detection Methods | Bioreceptor | Linear Range | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Detection Time | Real Sample Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltammetry | Antibody | 13 to1.3 × 106 cells/mL | 6 cells/mL | 60 min | Apple juice | [108] |
| Antibody | 10 to 107 CFU/mL | 0.37 CFU/mL | / | / | [109] | |
| Antibody | 104 to 109 CFU/mL | 3.0 × 103 CFU/mL | / | Egg, chicken and meat | [110] | |
| Antibody | 103 to 5 × 105 cells/mL | 400 cells/mL | / | Milk | [111] | |
| Antibody | 10 to 106 cells/mL | 13 cells/mL | 60 min | Milk | [112] | |
| Impedimetry | Aptamer | 10 to 108 CFU/mL | 6 CFU/mL | / | Apple juice | [113] |
| Aptamer | 650 to 6.5 × 108 CFU/mL | 65 CFU/mL | / | Egg | [114] | |
| Antibody | 10 to 105 CFU/mL | 13 CFU/mL | 22 min | Chicken broth | [115] | |
| Antibody | 10 to 107 CFU/mL | 10 CFU/mL | / | / | [116] | |
| Antibody | 30 to 3.0 × 106 CFU/mL | 19 CFU/mL | 90 min | Chicken | [117] | |
| Antibody | 20 to 2.0 × 105 CFU/mL | 21 CFU/mL | / | Milk | [118] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, F.; Liu, X.; Du, S.; Ren, G. Overview of Rapid Detection Methods for Salmonella in Foods: Progress and Challenges. Foods 2021, 10, 2402. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102402
Wang M, Zhang Y, Tian F, Liu X, Du S, Ren G. Overview of Rapid Detection Methods for Salmonella in Foods: Progress and Challenges. Foods. 2021; 10(10):2402. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102402
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Minglu, Yilun Zhang, Fangyuan Tian, Xiaoyu Liu, Shuyuan Du, and Guocheng Ren. 2021. "Overview of Rapid Detection Methods for Salmonella in Foods: Progress and Challenges" Foods 10, no. 10: 2402. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102402
APA StyleWang, M., Zhang, Y., Tian, F., Liu, X., Du, S., & Ren, G. (2021). Overview of Rapid Detection Methods for Salmonella in Foods: Progress and Challenges. Foods, 10(10), 2402. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102402





