Thaumatin-Like Protein (Pru av 2) Is a Cherry Allergen That Triggers Percutaneous Sensitization in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Cherry Extract and Protein Estimation
2.3. Animal Studies
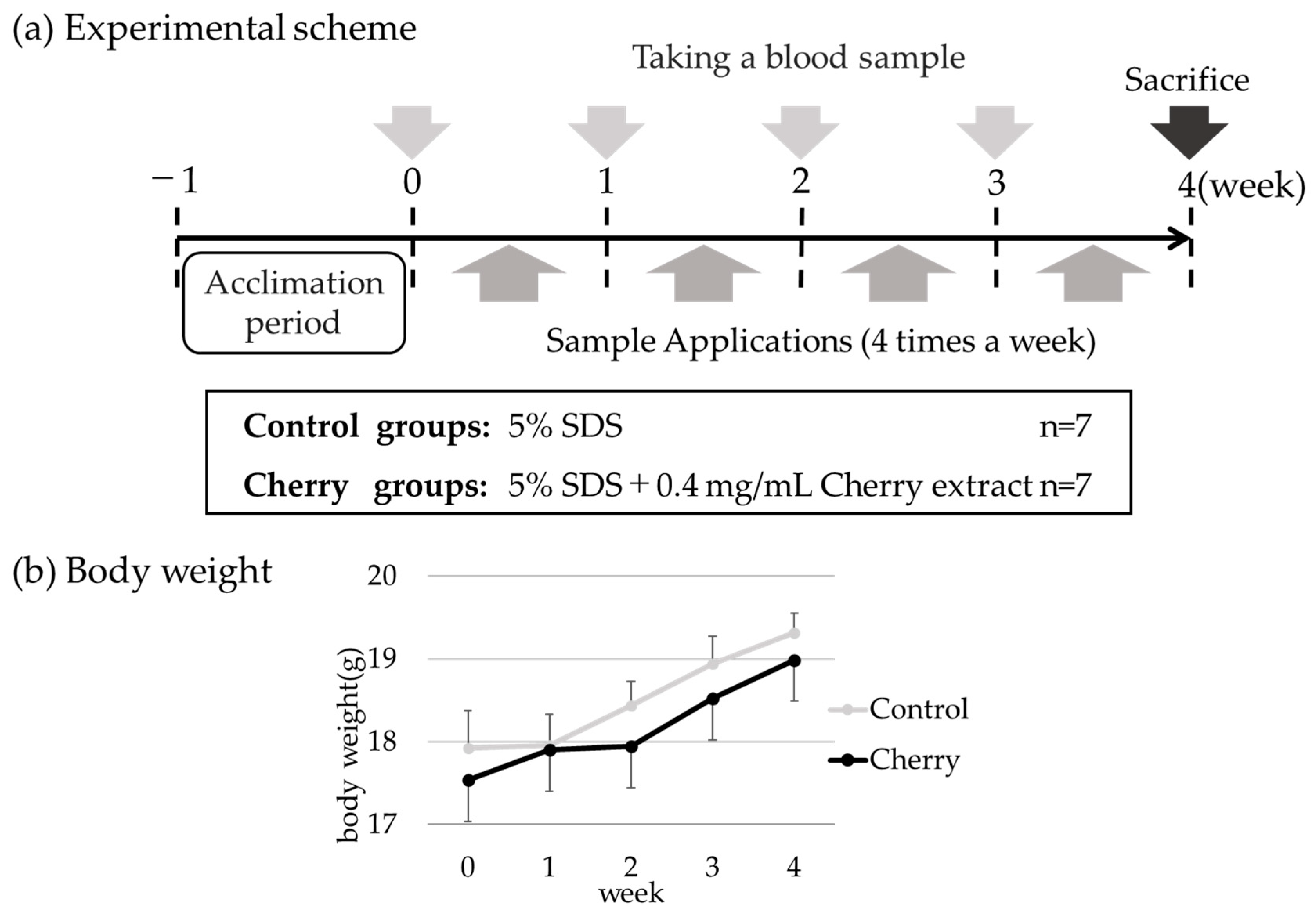
2.4. Induction of Percutaneous Sensitization
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Electrophoresis and Immunoblotting
2.7. Purification and Identification of IgG1-Reactive Major Cherry Proteins
2.7.1. Ammonium Sulfate Precipitation
2.7.2. Ion-Exchange Chromatography
2.7.3. Gel-Filtration Chromatography
2.8. N-Terminal Amino Acid Sequence Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Percutaneous Sensitization with Cherry Extract Did Not Affect Mouse Growth
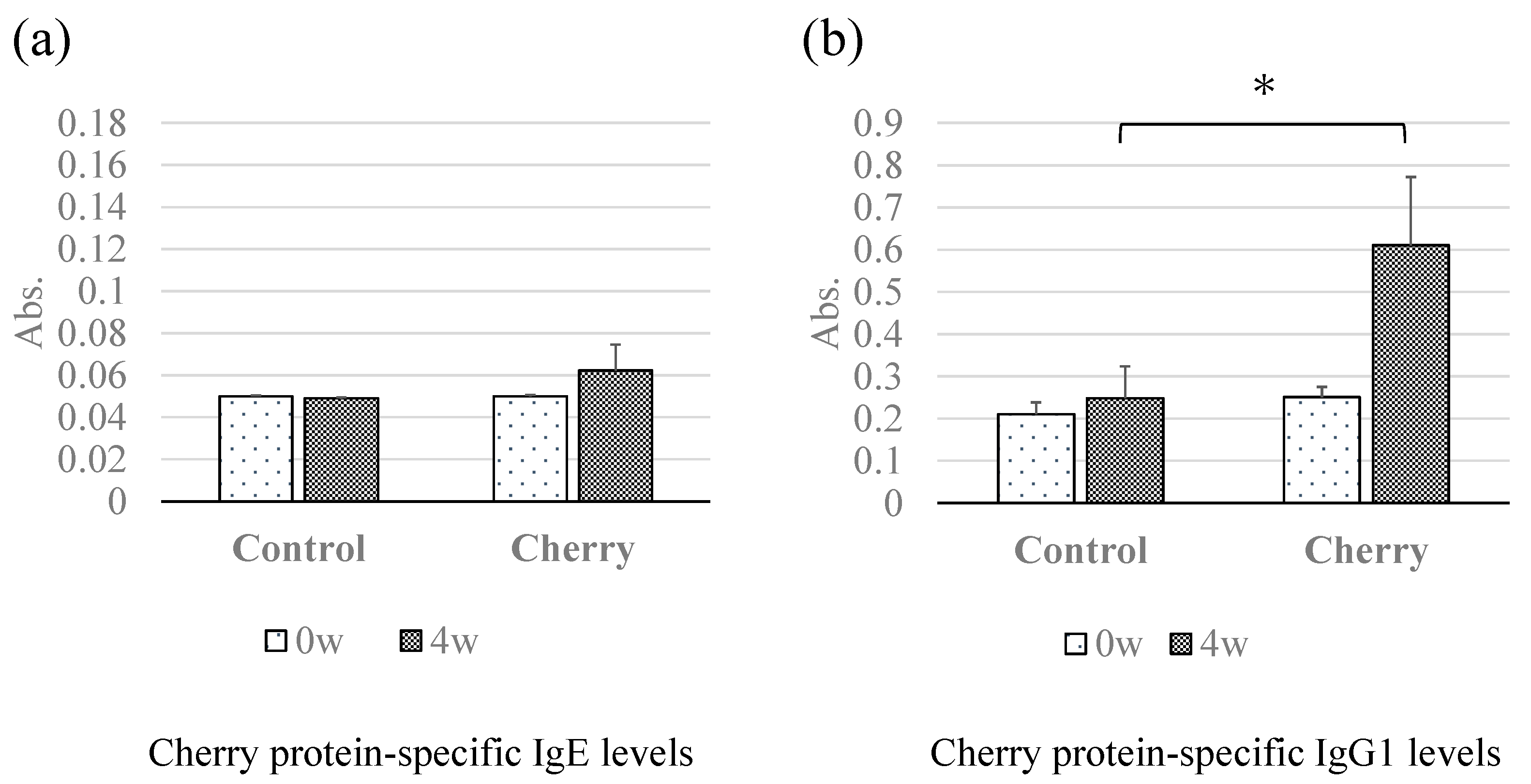
3.2. Changes in Cherry-Specific IgE and IgG1 Antibodies Determined Using ELISA
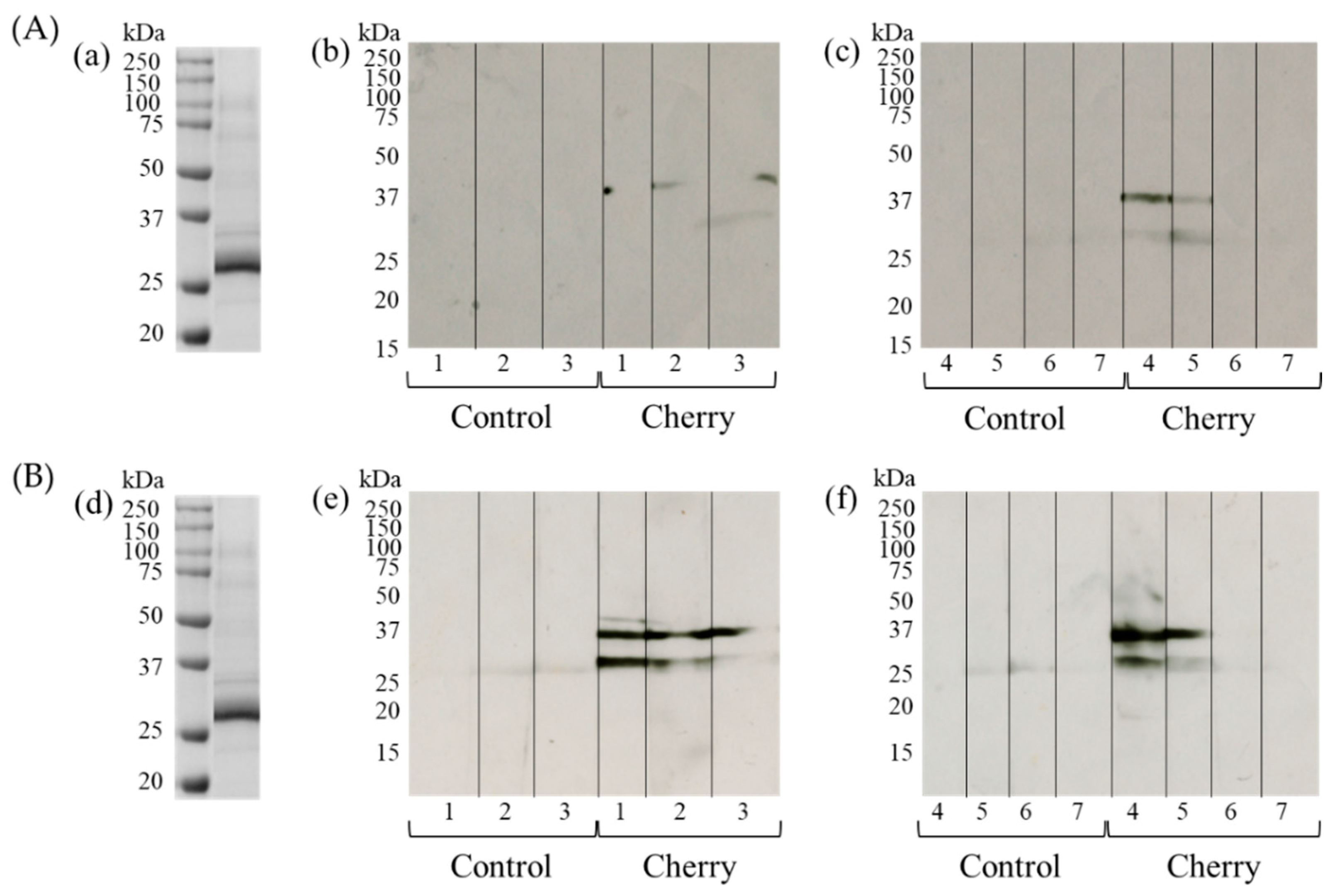
3.3. Detection of IgE- and IgG1-Binding Cherry Proteins Using Immunoblotting
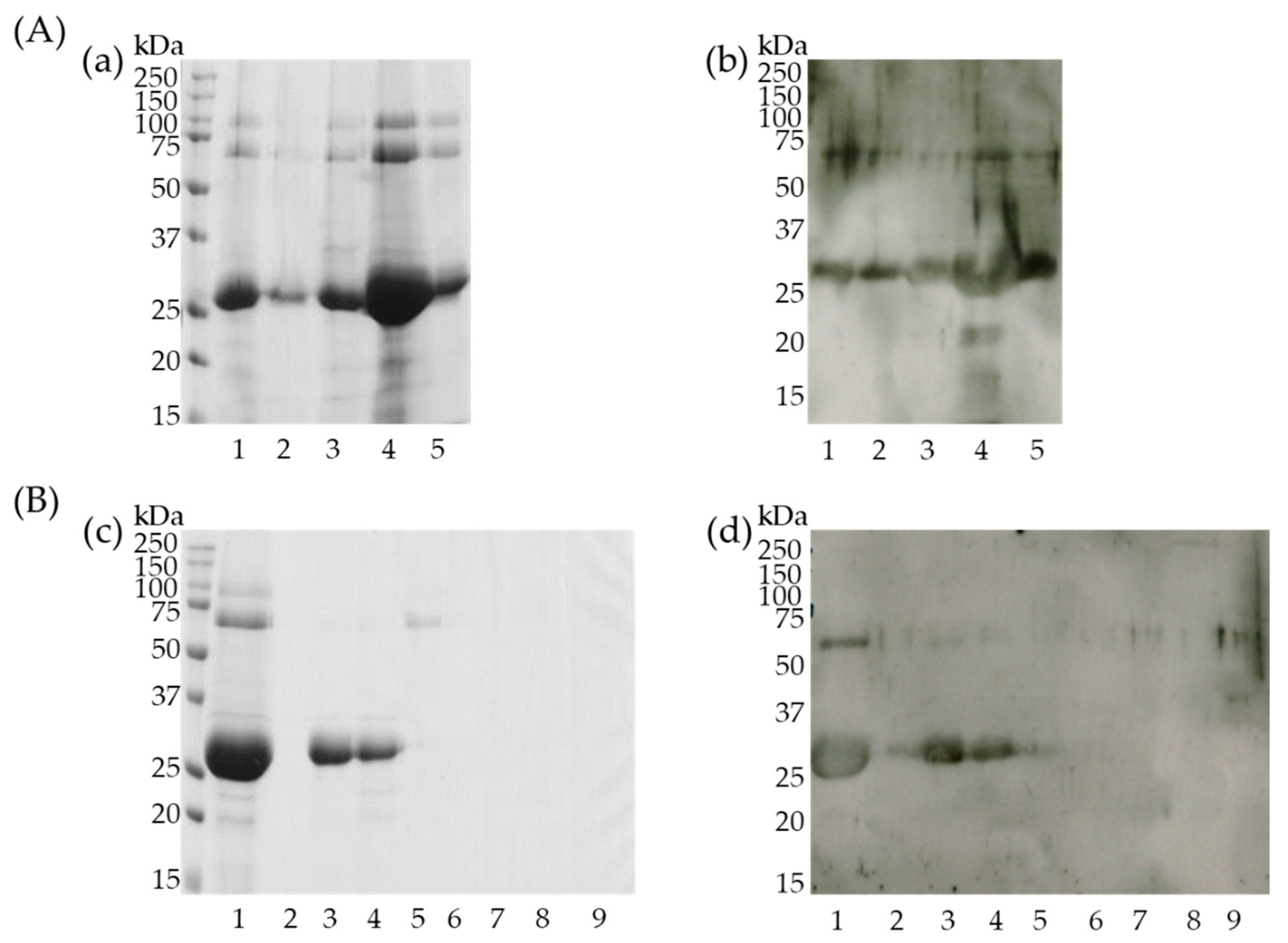
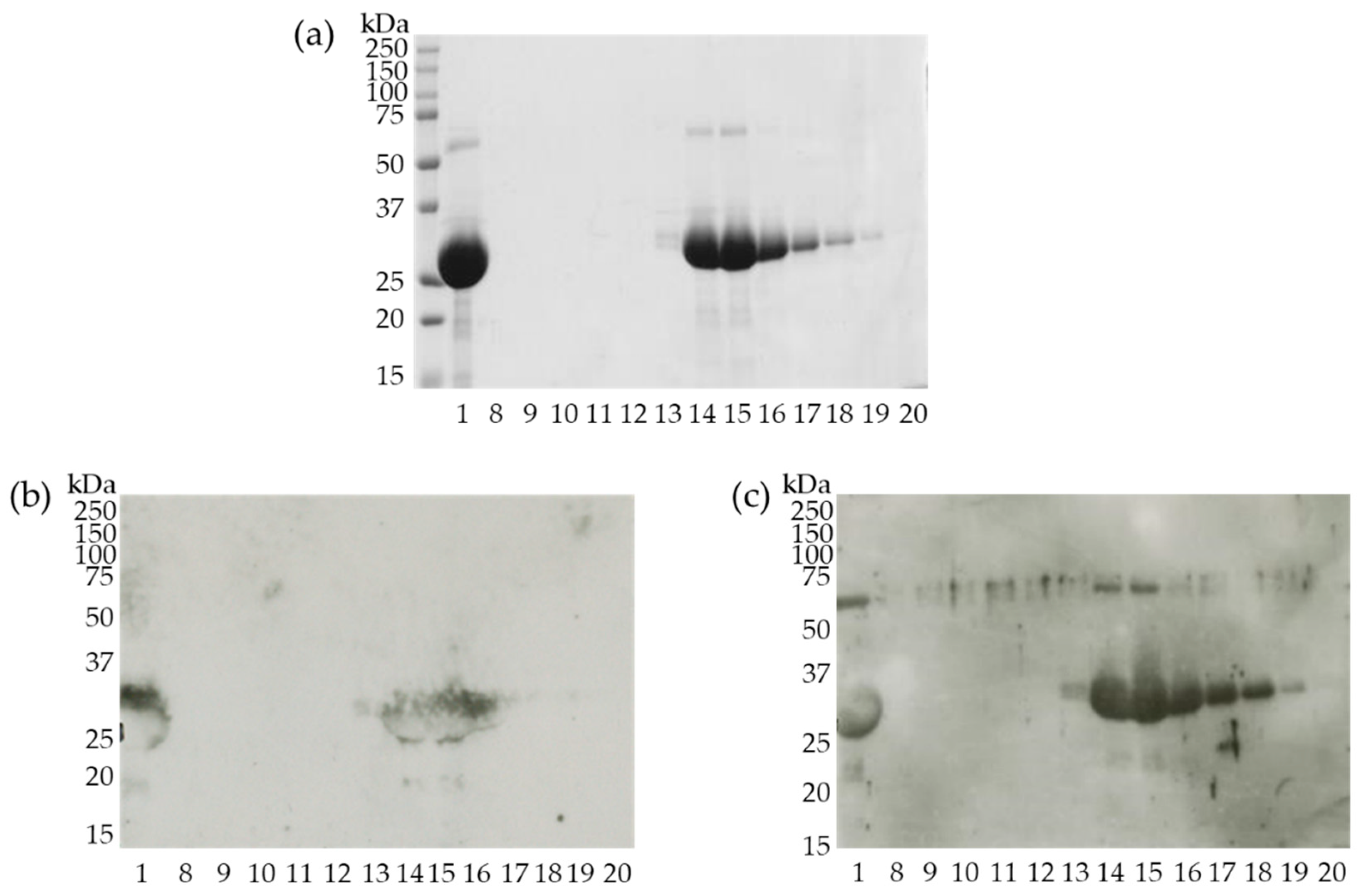
3.4. Identification of Cherry Antigens That Trigger Percutaneous Sensitization
3.5. Semi-Purified 27 kDa Protein Binds IgE
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A. Food allergy: A review and update on epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabst, O.; Mowat, A.M. Oral tolerance to food protein. Mucosal. Immunol. 2012, 5, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, S.J.; Tsai, M. IgE and mast cells in allergic disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinuki, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Sakieda, K.; Murata, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Morita, E. Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis Sensitized with Hydrolyzed Wheat Protein in Soap. Allergol. Int. 2012, 61, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukutomi, Y.; Itagaki, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Saito, A.; Yasueda, H.; Nakazawa, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Nakamura, H.; Akiyama, K. Rhinoconjunctival sensitization to hydrolyzed wheat protein in facial soap can induce wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 127, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinuki, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Dekio, I.; Kaneko, S.; Tokuda, R.; Nagao, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Morita, E. Higher allergenicity of high molecular weight hydrolysed wheat protein in cosmetics for percutaneous sensitization. Contact Dermat. 2013, 68, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagami, A.; Suzuki, K.; Nakamura, M.; Sano, A.; Iwata, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Suzuki, M.; Hara, K.; Teshima, R.; Matsunaga, K. Case of anaphylactic reaction to soy following percutaneous sensitization by soy-based ingredients in cosmetic products. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 917–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lack, G. Epidemiologic risks for food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Saito, H. Epicutaneous immunity and onset of allergic diseases—per-“eczema”tous sensitization drives the allergy march. Allergol. Int. 2013, 62, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, N.; Nagashima, M.; Hakuta, A.; Aihara, M. Food allergy preceded by contact urticaria due to the same food: Involvement of epicutaneous sensitization in food allergy. Allergol. Int. 2015, 64, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toit, G.D.; Katz, Y.; Sasieni, P.; Mesher, D.; Maleki, S.J.; Fisher, H.R.; Fox, A.T.; Turcanu, V.; Amir, T.; Zadik-Mnuhin, G.; et al. Early consumption of peanuts in infancy is associated with a low prevalence of peanut allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, C.N.A.; Irvine, A.D.; Terron-Kwiatkowski, A.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, H.; Lee, S.P.; Goudie, D.R.; Sandilands, A.; Campbell, L.E.; Smith, F.J.D.; et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.J.; Sporik, R.; Thorburn, J.; Hosking, C.S. The association of atopic dermatitis in infancy with immunoglobulin E food sensitization. J. Pediatr. 2000, 137, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, T.; Fukuoka, A.; Kabashima, K.; Ziegler, S.F.; Nakanishi, K.; Matsushita, K.; Yoshimoto, T. The role of basophils and proallergic cytokines, TSLP and IL-33, in cutaneously sensitized food allergy. Int. Immunol. 2014, 26, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noti, M.; Kim, B.S.; Siracusa, M.C.; Rak, G.D.; Kubo, M.; Moghaddam, A.E.; Sattentau, Q.A.; Comeau, M.R.; Spergel, J.M.; Artis, D. Exposure to food allergens through inflamed skin promotes intestinal food allergy through the thymic stromal lymphopoietin–basophil axis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Ogawa, T.; Takafuta, A.; Yano, E.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T. Identification of the 7S and 11S globulins as percutaneously sensitizing soybean allergens as demonstrated through epidermal application of crude soybean extract. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Ogawa, T.; Takafuta, A.; Yano, E.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T. Percutaneous sensitization to soybean proteins is attenuated by oral tolerance. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2018, 64, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheurer, S.; Pastorello, E.A.; Wangorsch, A.; Kästnera, M.; Haustein, D.; Vieths, S. Recombinant allergens Pru av1 and Pru av 4 and a newly identified lipid transfer protein in the in vitro diagnosis of cherry allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartz, C.; Lauer, I.; Moncin, M.M.S.M.; Cistero-Bahima, A.; Foetisch, K.; Lidholm, J.; Vieths, S.; Scheurer, S. Comparison of IgE-binding capacity, cross-reactivity and biological potency of allergenic non-specific lipid transfer proteins from peach, cherry and hazelnut. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 153, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Home Page. Available online: http://www.allergen.org/search.php?allergensource=Prunus+avium&searchsource=Search (accessed on 27 November 2020).
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. J. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyhse-Andersen, J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: A simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polycrylamide to nitrocellulose. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1984, 10, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edman, P.; Hogfeldt, E.; Sillen, L.G.; Kinell, P.-O. Method for determination of the amino acid sequence in peptides. Acta Chem. Scand. 1950, 4, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wel, H.; Loeve, K. Isolation and Characterization of Thaumatin I and II, the Sweet-Tasting Proteins from Thaumatococcus daniellii Benth. Eur. J. Biochem. 1972, 31, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sturrock, R.; Ekramoddoullah, A.K.M. The superfamily of thaumatin-like proteins: Its origin, evolution, and expression towards biological function. Plant. Cell Rep. 2010, 29, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiteneder, H.; Radauer, C. A classification of plant food allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 113, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inschlag, C.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; O’Riordain, G.; Ahorn, H.; Ebner, C.; Scheiner, O.; Breiteneder, H. Biochemical characterization of Pru a 2, a 23-kD thaumatin-like protein representing a potential major allergen in cherry (Prunus avium). Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1998, 116, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrović-Jankulović, M.; Ćirković, T.; Vučković, O.; Atanasković-Marković, M.; Petersen, A.; Gojgić, G.; Burazer, L.; Jankov, R.M. Isolation and biochemical characterization of a thaumatin-like kiwi allergen. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebitz, M.; Wagner, B.; Ferreira, F.; Peterbauer, C.; Campillo, N.; Witty, M.; Kolarich, D.; Steinkellner, H.; Scheiner, O.; Breiteneder, H. Plant-based heterologous expression of Mal d 2, a thaumatin-like protein and allergen of apple (Malus domestica), and its characterization as an antifungal protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 329, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, P.; Menu-Bouaouiche, L.; Peumans, W.J.; Payan, F.; Barre, A.; Roussel, A.; Damme, E.J.M.V.; Rougé, P. Resolution of the structure of the allergenic and antifungal banana fruit thaumatin-like protein at 1.7-Å. Biochimie 2006, 88, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.B.; Cho, B.H.; Næsby, M.; Gregersen, P.L.; Brandt, J.; Madriz-Ordeñana, K.; Collinge, D.B.; Thordal-Christensen, H. The molecular characterization of two barley proteins establishes the novel PR-17 family of pathogenesis-related proteins. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2002, 3, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loon, L.C.; Rep, M.; Pieterse, C.M.J. Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev. Phytopathol. 2006, 44, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trudel, J.; Grenier, J.; Potvin, C.; Asselin, A. Several thaumatinlike proteins bind to 1, 3-glucans. Plant. Physiol. 1998, 118, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, J.; Potvin, C.; Trudel, J.; Asselin, A. Some thaumatin-like proteins hydrolyse polymeric b-1, 3-glucans. Plant. J. 1999, 19, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, J.; Potvin, C.; Asselin, A. Some fungi express b-1, 3- glucanases similar to thaumatin-like proteins. Mycologia 2000, 92, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierens, E.; Gebruers, K.; Voet, A.R.D.; Maeyer, M.D.; Courtin, C.M.; Delcour, J.A. Biochemical and structural characterization of TLXI, the Triticum aestivum L. thaumatin-like xylanase inhibitor. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smole, U.; Bublin, M.; Radauer, C.; Ebner, C.; Breiteneder, H. Mal d 2, the thaumatin-like allergen from apple, is highly resistant to gastrointestinal digestion and thermal processing. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2008, 147, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midoro-Horiuti, T.; Goldblum, R.M.; Kurosky, A.; Wood, T.G.; Brooks, E.G. Variable expression of pathogenesis-related protein allergen in mountain cedar (Juniperus ashei) pollen. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 188–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, T.; Futamura, N.; Midoro-Horiuti, T.; Togawa, A.; Goldblum, R.M.; Yasueda, H.; Saito, A.; Shinohara, K.; Masuda, K.; Kurata, K.; et al. Isolation and characterization of native Cry j 3 from Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) pollen. Allergy 2007, 62, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacín, A.; Rivas, L.A.; Gómez-Casado, C.; Aguirre, J.; Tordesillas, L.; Bartra, J.; Blanco, C.; Carrillo, T.; Cuesta-Herranz, J.; Bonny, J.A.; et al. The involvement of thaumatin-like proteins in plant food cross-reactivity: A multicenter study using a specific protein microarray. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cycles | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asp | 1.10 | 5.01 | 11.94 | 20.52 | 24.42 | 33.92 | 50.18 | 56.75 |
| Glu | 1.32 | 5.37 | 7.45 | 19.44 | 27.47 | 33.45 | 33.73 | 34.11 |
| Asn | 1.21 | 2.51 | 4.28 | 6.44 | 8.85 | 22.27 | 258.58 | 346.43 |
| Gln | 6.31 | 6.35 | 11.15 | 33.78 | 30.37 | 36.25 | 41.57 | 45.86 |
| Ser | 1.30 | 2.48 | 6.02 | 142.57 | 49.54 | 23.91 | 19.28 | 20.20 |
| Thr | 2.92 | 279.90 | 59.23 | 26.13 | 28.82 | 34.38 | 34.00 | 37.62 |
| His | 0.25 | 14.61 | 5.10 | 2.59 | 2.60 | 3.39 | 4.12 | 4.25 |
| Gly | 16.28 | 10.38 | 21.03 | 31.10 | 29.91 | 35.57 | 39.70 | 46.69 |
| Ala | 526.88 | 91.78 | 27.39 | 42.33 | 43.13 | 52.08 | 57.41 | 68.76 |
| Tyr | 4.70 | 5.72 | 5.05 | 7.92 | 13.42 | 17.06 | 18.24 | 20.99 |
| Arg | 1.44 | 2.27 | 2.58 | 23.59 | 8.40 | 6.50 | 6.89 | 6.45 |
| Met | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.57 | 0.80 | 2.77 | 3.28 | 3.69 |
| Val | 1.76 | 3.03 | 11.25 | 22.41 | 28.31 | 38.54 | 42.67 | 45.15 |
| Pro | 1.18 | 9.73 | 29.07 | 46.34 | 56.17 | 69.89 | 77.27 | 86.14 |
| Trp | 1.23 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.48 | 2.00 | 1.07 | 2.55 | 2.17 |
| Phe | 0.36 | 4.26 | 14.78 | 22.84 | 392.79 | 182.05 | 85.35 | 66.37 |
| Lys | 0.05 | 0.93 | 1.73 | 3.29 | 8.57 | 353.62 | 151.10 | 70.93 |
| Ile | 1.85 | 6.72 | 491.51 | 118.35 | 22.74 | 12.88 | 9.12 | 14.75 |
| Leu | 0.50 | 5.85 | 19.65 | 21.70 | 21.72 | 32.54 | 32.84 | 38.84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Izumi, E.; Hidaka, S.; Hiroi, A.; Kinugasa, S.; Yano, E.; Zaima, N.; Moriyama, T. Thaumatin-Like Protein (Pru av 2) Is a Cherry Allergen That Triggers Percutaneous Sensitization in Mice. Foods 2021, 10, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010134
Izumi E, Hidaka S, Hiroi A, Kinugasa S, Yano E, Zaima N, Moriyama T. Thaumatin-Like Protein (Pru av 2) Is a Cherry Allergen That Triggers Percutaneous Sensitization in Mice. Foods. 2021; 10(1):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010134
Chicago/Turabian StyleIzumi, Eri, Shota Hidaka, Ayako Hiroi, Serina Kinugasa, Erika Yano, Nobuhiro Zaima, and Tatsuya Moriyama. 2021. "Thaumatin-Like Protein (Pru av 2) Is a Cherry Allergen That Triggers Percutaneous Sensitization in Mice" Foods 10, no. 1: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010134
APA StyleIzumi, E., Hidaka, S., Hiroi, A., Kinugasa, S., Yano, E., Zaima, N., & Moriyama, T. (2021). Thaumatin-Like Protein (Pru av 2) Is a Cherry Allergen That Triggers Percutaneous Sensitization in Mice. Foods, 10(1), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10010134






