Abstract
Recent progress in the industrial development of dental implants has improved their surface bio-affinity, while clinical implantologists attempt to improve it through coating with various compounds, including platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in clinical settings. However, it is poorly understood how PRP acts on titanium surfaces. To validate this surface modification method and demonstrate how platelet-derived soluble biomolecules released from the activated adherent platelets act on plain, commercially pure-titanium (cp-Ti) plates, we evaluated the distribution of biomolecules by immunofluorescence. PPARγ, PDGF-B, and TGFβ1 were similarly released at immunofluorescence levels from activated adherent platelets, retained in the surrounding extra-platelet spaces for a while, and did not immediately diffuse away to distant spaces. Exogenously added CaCl2 augmented release and retention of those biomolecules along with activation and aggregation. Taken together with our previous data regarding platelet adhesion, these findings suggest that especially when treated with CaCl2, platelets immediately adhere on cp-Ti plates to release their stored biomolecules in the absence of plasma proteins and that these biomolecules do not diffuse away, but stay longer in extra-platelet spaces around the platelets by newly formed, immature fibrin fiber fragments. Consequently, these retained biomolecules are anticipated to cooperatively stabilize implants by stimulating alveolar bone regeneration and integration.
1. Introduction
Among the various materials, titanium has been used as the most favorable material for dental implants [1,2,3]. This is based on the advantages that titanium has, such as relatively higher corrosion resistance and higher bio-inertness and bio-affinity. However, the bio-inertness is hardly anticipated to augment bio-integration between titanium implants and the surrounding soft and bone tissues. In the past two decades, many efforts, mainly on the industrial side, have been made to overcome this possible shortcoming and improve bio-integration, especially osseointegration. For example, the titanium surface has been modified micro-topographically or chemically by etching, blasting, ultraviolet (UV) ray irradiation, atmospheric pressure plasma (APP) treatment, and many other methods [4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Furthermore, hybridization techniques with other materials, such as calcium phosphates, were recently introduced to improve the bio-affinity of implants to bone. The hybrid implants have been increasingly accepted by many clinical implantologists.
On the other hand, the end users of dental implants, clinical implantologists, have also independently attempted to modify the surface property by immersing or coating titanium implants with blood, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18], and therapeutic agents for periodontal regeneration, such as enamel matrix proteins. In such treatments, the titanium surface is commonly anticipated to obtain a higher bio-affinity and ultimately tighter or complete osseointegration by promoting the recruitment and proliferation of stem or progenitor cells involved in alveolar bone regeneration. However, there has been no scientific evidence to strongly support such chairside surface treatment prior to the embedment of dental implants.
To investigate the interaction between the titanium surface and the PRP, especially the platelets, and validate the use of PRP for surface modification, in a previous study [19], we identified the major adhesion molecules involved in human platelet adhesion and activation on commercially pure titanium (cp-Ti) plates. To further investigate these interactions, in this study, we visualized the distribution of the growth factors, PDGF-B and TGFβ1, and the transcription factor, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), which is recently thought to be an anti-inflammatory factor [20,21], and evaluated the biomolecule releasing activity of platelets activated and adhered on cp-Ti plates.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PRP and Platelet Suspension in PBS
As described previously [19], ~9 mL of peripheral blood was collected from non-smoking healthy male volunteers (N = 6; age: 23 to 58 years old) in plain plastic blood-collection tubes (Neotube; NIPRO, Osaka, Japan) containing 1 mL of A formulation of acid-citrate-dextrose (ACD-A; Terumo, Tokyo, Japan) [22,23]. These blood samples were stored in a rotating agitator at ambient temperature until use (~48 h) [24,25]. PRP was prepared by the double-spin method: soft spin (472× g for 10 min) and subsequent hard spin (1065× g for 5 min).
After the initial soft spin using a centrifuge equipped with a swing rotor (KS-5000; Kubota, Tokyo, Japan), the upper plasma fraction was treated with 5 μg/mL of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1; Cayman Chemical Co., Ann Arbor, MI, USA) for 10 min to minimize the platelet aggregation. The samples were subjected to hard spin using a centrifuge equipped with an angle rotor (1–14; Sigma Laborzentrifugen GmbH, Osterode am Harz, Germany). Precipitated platelets were gently resuspended in PBS at appropriate concentrations (2.2–2.8 × 105/µL) using an automated hematology analyzer (pocH 100iV; Sysmex, Kobe, Japan).
The study design and consent forms for all procedures (project identification code: 2297) were approved by the ethics committee for human participants at the Niigata University School of Medicine (Niigata, Japan) and complied with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964, as revised in 2013.
2.2. cp-Ti Plates and APP Treatment
The plain cp-Ti plates (Nilaco, Tokyo, Japan) were used in this study: the cp-Ti plates were cut into square 10 × 10 mm2 pieces, washed serially with acetone, ethanol, and distilled water in an ultrasonic cleaner (Citizen, Tokyo, Japan) and air-dried [19].
A non-thermal APP device (P500-SM; Sakigake-Semiconductor Co., Kyoto, Japan) was used in this study, as described previously [26]. Nitrogen was introduced as a feed gas at a rate of 5 L/min. To maximize the effects of the APP treatment, the cp-Ti plates were placed at a distance of 5 mm or less from the jet-nozzle and treated for 1 min.
2.3. Platelet Inoculation onto cp-Ti Plates
Platelet suspensions were inoculated onto the cp-Ti plates, and the plates were incubated at ambient temperature for up to 30 min. The cp-Ti plates were directly fixed with 10% neutralized formalin solution (Wako, Osaka, Japan) or ThromboFix (Beckman-Coulter, Atlanta GA, USA). Alternatively, the cp-Ti plates were vigorously washed two times with PBS on a shaker (~10 s) prior to fixation.
For activation, platelets in PBS suspensions were treated with 0.1% CaCl2, as described in previous studies [22,23].
2.4. Immunocytochemical Fluorescence Staining
Fixed platelets on the cp-Ti plates were directly subjected to treatment with primary antibodies, such as mouse monoclonal anti-CD62P antibody (1:20 dilution; BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA), rabbit polyclonal anti-PDGF-B (1:200 dilution; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA), anti-TGFβ1 (1:200 dilution; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), rabbit monoclonal anti-PPARγ (1:100 dilution; Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA), and mouse monoclonal anti-fibrin antibodies (1:400 dilution; GeneTex, Inc., Irvine, CA, USA) overnight at 4 °C. In this study, based on our preliminary observations that our routine blocking or washing with Tween-20-containing PBS also visualized intra-platelet binding of the antibodies we used, we did not perform blocking or use such a detergent-containing PBS in the main experiments in this study.
The samples were then probed with the corresponding secondary antibodies or non-immunized rabbit IgG (Life Technologies Corporation, Carlsbad, CA, USA) as an isotype control for 60 min at ambient temperature in the dark. The samples were finally mounted using an antifade mounting medium (Vectashield; Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) and examined under a fluorescence microscope (ECLIPSE 80i; Nikon) connected with a cooled CCD camera (VB-7000; Keyence) [23].
2.5. Observation of Microparticles by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Because of the difficulty of microparticle visualization on cp-Ti plates by SEM, the platelets were suspended in PBS and stimulated with 0.1% CaCl2 in polypropylene sample tubes and immediately transferred onto specific filters (Sem Pore; JOEL, Akishima, Japan). After 10-min incubation, the platelets were fixed with 2.5% neutralized glutaraldehyde, serially dehydrated, and freeze dried.
These samples were examined under a scanning electron microscope (TM-1000; Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan), as described previously [23,27].
2.6. Image Analyses of Immunoflurescence Photomicrographs
We randomly selected original, non-trimmed photomicrographs from representative single experiments (N = 4) and analyzed the images using the Winroof software (Mitani Co., Tokyo, Japan). In brief, the merged images were separated into three independent RGB images. Then, the CD62P+ and biomolecules+ regions in red and green, respectively, were determined as total pixels. The levels of released biomolecules were assessed by the ratio of biomolecules to CD62P.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data are represented in box plots. SigmaPlot (SigmaPlot 13.0; Systat Software, Inc., San Jose, CA, USA) evaluated the image analysis data as parametric by both normality and equal variance testing, and suggested a one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple-comparisons test as the appropriate analysis. The results of this analysis, however, showed significant differences in both PPARγ and PDGF-B and therefore as these data were derived from a limited number of samples (N = 4), a non-parametric analysis was performed. Therefore, we compared the mean values via the Kruskal–Wallis one-way analysis of variance, followed by a Steel-Dwass multiple comparisons test (BellCurve for Excel; Social Survey Research Information Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Differences with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
We obtained whole-blood samples from six volunteers. For practical reasons, we used at least four samples in each experiment; this discrepancy was not because of either opt-out by volunteers or exclusion of outliers.
3. Results
In this study, we chose to visualize not only the representative growth factors, i.e., PDGF-B and TGFβ1, but also a transcription factor, i.e., PPARγ, because the anti-inflammatory effects of PRP are recently thought to be mediated by PPARγ [20,21,28].
3.1. Optimization of Experimental Procedures
Because visualization of platelet-derived biomolecules was preliminarily found to be substantially influenced by experimental procedures, we began with a demonstration of the procedure-dependent differences in visualized platelet-derived biomolecules.
The different effects of the fixatives 10% neutral buffered formalin and ThromboFix on the visualization of PPARγ in control platelets adhered onto cp-Ti plates at 10–30 min are shown in Figure 1. The specimens were double-stained for CD62P and PPARγ and both images were merged to identify the distribution of PPARγ. Although the levels varied with individuals, regardless of fixative types, almost all adherent platelets were visually positive for CD62P. In PPARγ-staining, the cytoplasm of almost all platelets was clearly positive following fixation with formalin, but not after fixation with ThromboFix. Instead, extra-platelet spaces became weakly, but widely, positively stained in a time-dependent manner.
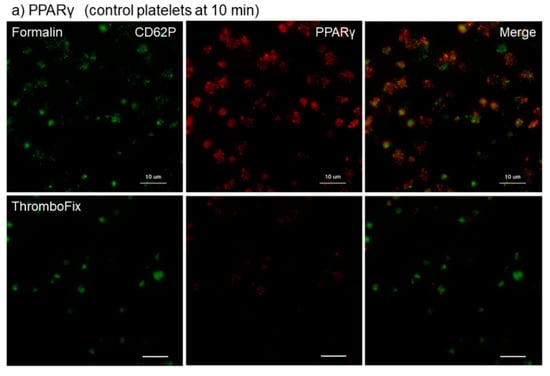
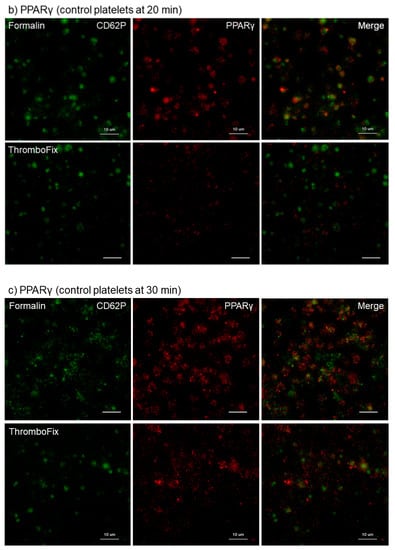
Figure 1.
Different effects of fixatives on visualization of PPARγ in control platelets adhered onto cp-Ti plates. Platelets suspended in PBS were incubated on cp-Ti plates for (a) 10 min, (b) 20 min, or (c) 30 min and fixed with 10% neutral buffered formalin or ThromboFix without intensive washing. Activated platelets (CD62P; green) and PPARγ (red) were visualized by immunofluorescence and their distribution were compared between formalin and ThromboFix. Similar findings were obtained from the samples prepared from the other three donor samples, which were kept separate and tested individually. Bar = 10 µm.
This finding was confirmed for growth factors in Ca2+-activated platelets. The different effects of fixatives on visualization of PPARγ and PDGF-B in Ca2+-activated platelets aggregated and adhered onto cp-Ti plates at 30 min are shown in Figure 2. Essentially as shown in Figure 1, both PPARγ and PDGF-B were found at higher levels in the cytoplasm of platelets fixed with formalin than with ThromboFix. In ThromboFix-fixed platelets, extra-platelet spaces were widely positive.
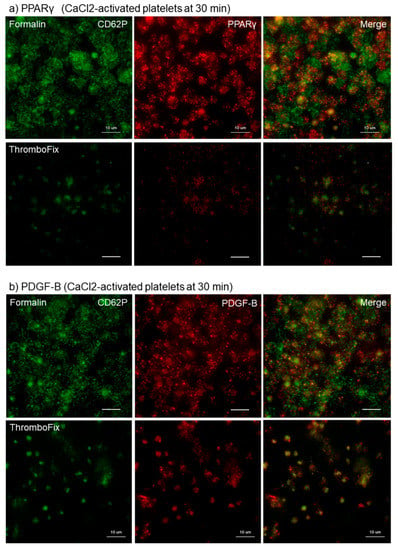
Figure 2.
Different effects of fixatives on visualization of PPARγ and PDGF-B in Ca2+-activated platelets aggregated and adhered onto cp-Ti plates. Platelets were treated with 0.1% CaCl2 in PBS, incubated on cp-Ti plates for 30 min and fixed with 10% neutral buffered formalin or ThromboFix without intensive washing. (a,b) Activated platelets (CD62P; green), (a) PPARγ (red), and (b) PDGF-B (red) were visualized by immunofluorescence. Similar findings were obtained from the samples prepared from the other three donors. Bar = 10 µm.
The effects of intensive washing on the distribution of PPARγ, PDGF-B, and TGFβ1 in Ca2+-activated platelets at 15 min of fixation with ThromboFix are shown in Figure 3. Regardless of platelet-derived biomolecule types, the intensive washing totally reduced those biomolecules by partially excluding fibrin fiber fragments and probably also weakly adherent platelets without apparently influencing CD62P expression in strongly adherent platelets.
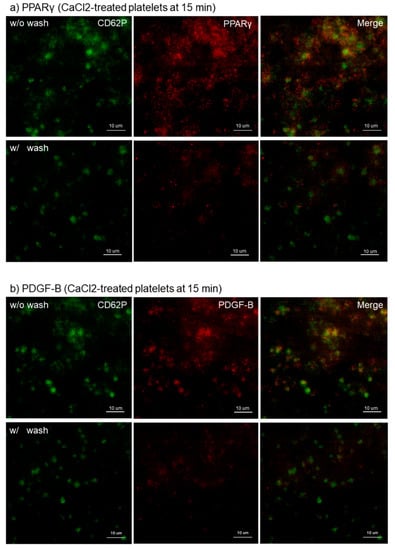
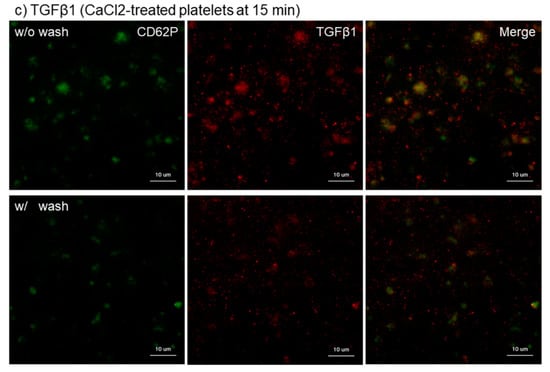
Figure 3.
Effects of intensive washing on distribution of PPARγ, PDGF-B, and TBGβ1 in Ca2+-activated platelets on cp-Ti plates. Platelets were treated with 0.1% CaCl2 in PBS, incubated on cp-Ti plates for 15 min and fixed with ThromboFix with or without intensive washing. (a–c) Activated platelets (CD62P; green), (a) PPARγ (red), (b) PDGF-B (red), and (c) TGFβ1 (red) were visualized by immunofluorescence. Similar findings were obtained from the samples prepared from the other three donors. Bar = 10 µm.
To support this finding, the distribution of microparticles and fibrin fiber fragments need to be examined. Effects of activation with CaCl2 on microparticle release and effects of intensive washing on the levels of fibrin formed on and around platelets are shown in Figure 4. Because microparticles, if any, are embedded with plasma proteins after preparation for SEM examination, the presence of microparticles was examined on the specific filter after activation with 0.1% CaCl2. In Ca2+-activated platelets, many microparticles were released 10 min after activation (Figure 4a). Intensive washing totally reduced the apparent amounts of fibrin fiber fragments and simultaneously those of PPARγ and TGFβ1 in Ca2+-activated platelets at 30 min (Figure 4b,c).

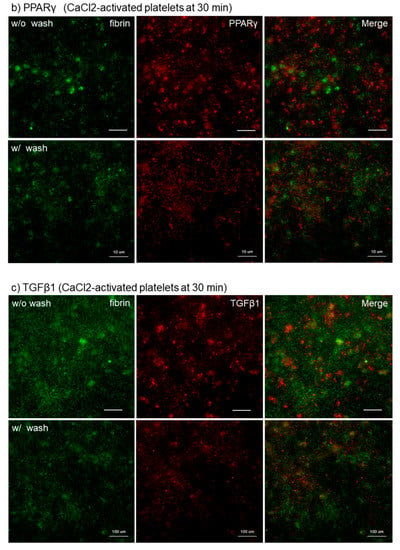
Figure 4.
(a) Effects of activation with CaCl2 on microparticle release and (b,c) effects of intensive washing on the levels of fibrin formed on and around platelets. (a) Platelets suspended in PBS were activated by 0.1% CaCl2, incubated on the filter for 10 min, fixed with glutaraldehyde, and subjected to SEM examination. (b,c) As described in the legend of Figure 3, activated platelets were fixed with or without intensive washing and (b,c) Activated platelets (CD62P; green), (b) PPARγ (red), and (c) TGFβ1 (red) were visualized by immunofluorescence. Similar findings were obtained from the samples prepared from the other three donors. Bar = 10 µm.
3.2. Effects of APP and CaCl2 on Platelet-Derived Factor Release
According to the results obtained by the optimization of experimental procedures, we adjusted the preparation protocol so that platelets adhered on cp-Ti plates are fixed with ThromboFix without receiving intensive washing in the following experiments. In addition to the treatment of platelets with 0.1% CaCl2, cp-Ti plates were treated with non-thermal APP immediately prior to the inoculation of platelets. This was based on our working hypothesis that APP-treatment facilitates platelet adhesion and activation and thereby augments the release of platelet-derived biomolecules.
The effects of CaCl2 and APP treatments on PPARγ distribution on cp-Ti plates at 30 min are shown in Figure 5. Again, CaCl2 substantially increased PPARγ release and/or retention in extra-platelet spaces, while APP significantly reduced the basal and CaCl2-induced increases in PPARγ release and/or retention. These merged photomicrographs were image-analyzed and the quantified results are shown in Figure S1a. However, no statistical differences were observed among these groups according to non-parametric analyses.
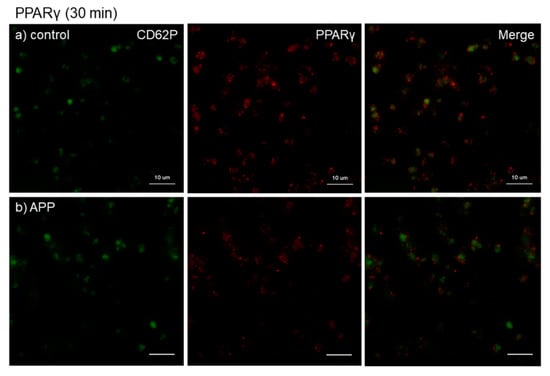
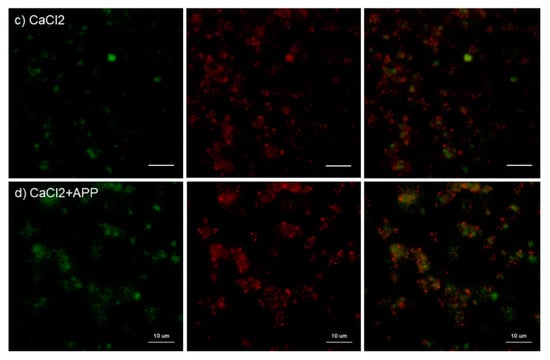
Figure 5.
Effects of CaCl2 and atmospheric pressure plasma (APP) treatments on PPARγ distribution on cp-Ti plates at 30 min. Platelets were prepared, treated, and fixed for visualization (green: CD62P, red: PPARγ) as described in the legend of Figure 4. (a) Control platelets on non-treated cp-Ti plates, (b) control platelets on APP-treated cp-Ti plates, (c) CaCl2-stimulated platelets on non-treated cp-Ti plates, (d) CaCl2-stimulated platelets on APP-treated cp-Ti plates. Similar findings were obtained from the samples prepared from the other three donors. Bar = 10 µm.
The effects of CaCl2 and APP treatments on PDGF-B distribution on cp-Ti plates at 30 min are shown in Figure 6. CaCl2 appeared to increase PDGF-B release and/or retention in extra-platelet spaces, whereas APP to some extent reduced the CaCl2-induced increases in PDGF-B release and/or retention. These merged photomicrographs were image-analyzed and the quantified results are shown in Figure S1b. Again, no statistical differences were observed among these groups according to non-parametric analyses.
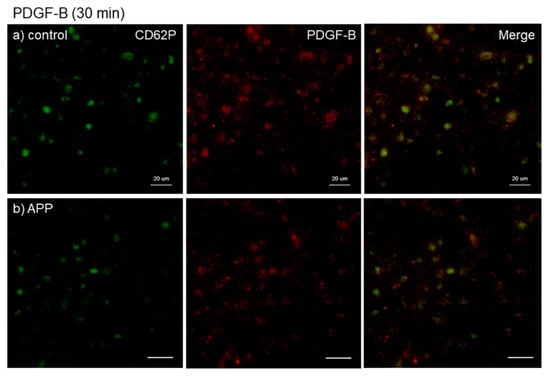
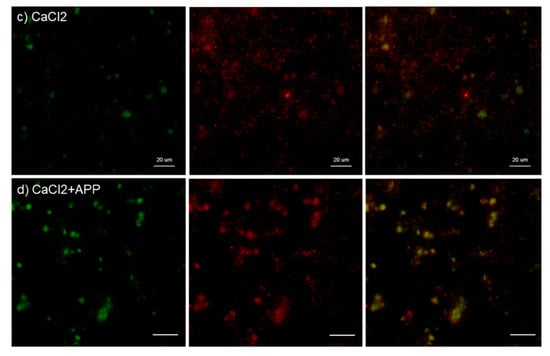
Figure 6.
Effects of CaCl2 and APP treatments on PDGF-B distribution on cp-Ti plates at 30 min. Platelets were prepared, treated, and fixed for visualization (green: CD62P, red: PDGF-B) as described in the legend of Figure 4. (a) Control platelets on non-treated cp-Ti plates, (b) control platelets on APP-treated cp-Ti plates, (c) CaCl2-stimulated platelets on non-treated cp-Ti plates, (d) CaCl2-stimulated platelets on APP-treated cp-Ti plates. Similar findings were obtained from the samples prepared from the other three donors. Bar = 10 µm.
The effects of CaCl2 and APP treatments on TGFβ1 distribution on cp-Ti plates at 30 min are shown in Figure 7. CaCl2 slightly increased TGFβ1 release and/or retention in extra-platelet spaces. APP to some extent reduced the CaCl2-induced TGFβ1 release and/or retention. These merged photomicrographs were image-analyzed and the quantified results are shown in Figure S1c. Again, no statistical differences were observed among these groups according to non-parametric analyses.
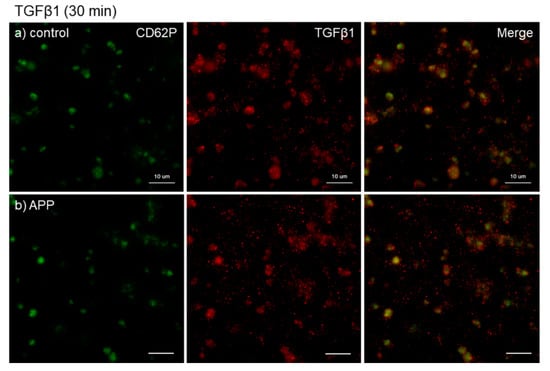
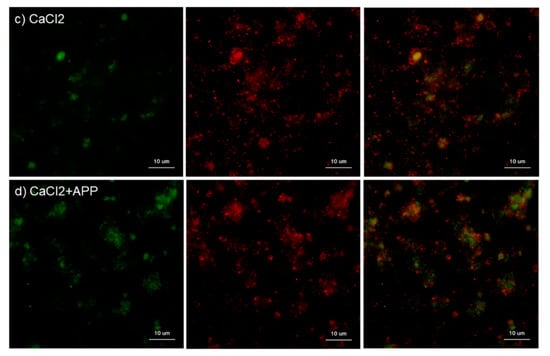
Figure 7.
Effects of CaCl2, and APP treatments on TGFβ1 distribution on cp-Ti plates at 30 min. Platelets were prepared, treated, and fixed for visualization (green: CD62P, red: TGFβ1) as described in the legend of Figure 4. (a) Control platelets on non-treated cp-Ti plates, (b) control platelets on APP-treated cp-Ti plates, (c) CaCl2-stimulated platelets on non-treated cp-Ti plates, (d) CaCl2-stimulated platelets on APP-treated cp-Ti plates. Similar findings were obtained from the samples prepared from the other three donors. Bar = 10 µm.
4. Discussion
It is generally accepted that in the process of wound-healing, platelets gather and aggregate at injury sites and release growth factors and other soluble biomolecules from α-granules to extra-platelet spaces occupied mainly by fibrin fibers, a complex which is called a blood clot [29,30]. Thus, growth factors released from platelets do not immediately diffuse away but can stay there for a while to induce blood capillaries and stem and progenitor cells involved in tissue repair and regeneration. In addition, anti-inflammatory factors, including PPARγ, simultaneously released from activated platelets [31], are expected to suppress inflammation and indirectly facilitate tissue repair and regeneration in cooperation with growth factors such as PDGF and TGFβ [32].
On the basis of these physiological functions of platelets, PRP and its derivatives have been developed and applied in regenerative therapy. In the case of its application in pretreatment of dental implants, PRP is expected to stimulate the growth and adhesion of the surrounding osteoblastic and other cell types in connective tissues and ultimately improve the stability and osseointegration of embedded implants. PDGF, TGFβ, and PPARγ have been often demonstrated to have potential positive effects. PDGF enhances bone formation and bone-to-implant contact through direct activation of osteoblasts, in addition to recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells through vascularization [33], and consequently accelerates the process of osseointegration [34,35,36]. Although being unable to directly induce osteogenesis in stem cells, TGFβ1 increases the pool of osteoprogenitors by inducing chemotaxis and proliferation [37]. These actions may eventually contribute to early implant stability. In addition, it is generally thought that inflammation exerts negative effects on osseointegration of Ti-based implants [38]. Lee et al. [39] have recently demonstrated in the diabetes mellitus-induced rat model that PPARγ released from the corresponding cDNA introduced on titanium implant surfaces enhances osseointegration and implant longevity. However, there are limited data that supports such an application of PRP.
In the previous study [19], we demonstrated the time-dependent adhesion of platelets onto the cp-Ti platelets and the adhesion molecules mainly involved in this initial adhesion. To add new findings to the previous data, this study was performed to visualize the release of growth factors and a transcription factor. Although not determining those soluble biomolecules in a quantitative manner, this immunofluorescence method has a merit to semi-quantitatively demonstrate those distribution and level on a small scale of sample without procedure-dependent loss of soluble biomolecules. In a previous study regarding PRF matrix [32], we successfully demonstrated distribution of growth factors by the immunohistochemical method. The main finding of this study is, as illustrated in Figure 8, that in the absence of plasma proteins such as fibrinogen and albumin that disturb platelet adhesion, platelets immediately adhere to cp-Ti plates and become mildly activated to release PDGF-B, TGFβ1, and PPARγ to extra-platelet spaces. Additional stimuli such as exogenously added Ca2+ to facilitate platelet adhesion and activate further release of growth factors [23]. These biomolecules are then retained by newly formed fibrin fragments adjacent to activated platelets on cp-Ti plates. The other possible, but minor, mechanism is that growth factors may be captured by their specific receptors expressed on the membrane surface of the platelets [40].
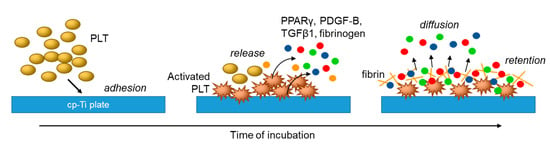
Figure 8.
Proposed mechanisms of platelet adhesion and activation and subsequent growth factor release and retention on cp-Ti plates.
Our data for optimization of experimental procedures suggest that the routine fixation method using 10% formalin is not suitable to visualize only platelet-derived biomolecules distributed in extra-platelet spaces. According to the manufacturer’s document, formalin solution we used contains 5–10% methanol as a stabilizer. Thus, “10% neutralized formalin solution” is calculated to contain 0.5–1.0% methanol. This amount of methanol is sufficient to perforate the plasma membrane of the platelets and platelet-derived biomolecules stored in α-granules could be visualized even without treatment with specific detergents. The formula of the fixative we chose, ThromboFix, is not disclosed by the manufacturer; however, considering its formula is optimized for evaluation of platelet CD62P by flow-cytometry, we speculate that this fixative stabilizes platelets without chemically damaging the integrity of the membrane of the platelets and thereby that the intra-platelet growth and transcription factors could be masked from immunofluorescence detection.
Because platelets contain and release fibrinogen and thrombin upon activation, it was theoretically difficult to exclude the possible involvement of fibrin formation in retention of platelet-derived biomolecules. However, we preliminarily found that intensive washing with tapping reduced the amount of immature fibrin formed around the platelets and applied this procedure to test the possible retention of growth factors by the fibrin matrix. Although not completely excluding fibrin, this washing process apparently reduced the platelet-derived biomolecules distributed around the adherent platelets. Therefore, these findings support the hypothesis that platelet-derived biomolecules released are trapped and retained in the surrounding extra-platelet spaces occupied mainly with immature fibrin fragments. However, it is also possible that those biomolecules are to some extent adsorbed onto the cp-Ti surface and platelet membrane receptors.
Regarding the effects of APP treatment, it is known that APP treatment enhances adhesive quality, fibrin polymerization capacity, and surface coating efficiency [41]. Therefore, this technology has been applied in the modification of dental implant surfaces. In this study, we confirmed that APP treatment markedly increased the surface wettability [26]. Thus, we initially raised a working hypothesis that APP treatment makes platelet adhesion on cp-Ti plates more rapid and tighter, as shown previously in osteoblastic progenitor cells [26]. Contrary to our expectation, however, APP treatment showed no positive effects on platelet adhesion and fibrin polymerization in this study. Exceptionally, APP treatment significantly reduced the distribution of all the platelet-derived biomolecules in Ca2+-activated platelets. The most likely explanation for this phenomenon is that platelet-derived biomolecules diffuse away rapidly. However, it cannot be ruled out that platelet-derived biomolecules could not be visualized clearly in a single focal plane because of the thicker polymerized fibrin in the APP-treated cp-Ti plates than in the control plates. This is a limitation of a regular fluorescent microscope. The possible effects of APP treatment on fibrin polymerization on cp-Ti plates should be further investigated with a confocal microscope or other powerful modern modalities for 3D visualization.
5. Conclusions
The present findings suggest that within the limitation of the study that the pretreatment of dental implants with plasma-free platelet suspension increases the abundance of platelets, growth factors, and the anti-inflammatory factor PPARγ, which could contribute to the improved initial stability and osseointegration of titanium dental implants.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2304-6767/7/4/109/s1, Figure S1: Analyses of immunofluorescence photomicrograph images of CD62P and other biomolecules (a: PPARγ, b: PDGF-B, c: TGFβ1). Each photograph was separated into three RGB files and the individual regions or particles positive for CD62P or the biomolecules were expressed as total pixels. The ratio of each biomolecule to CD62P is expressed as a box plot. N = 4.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.T., A.T., and T.K.; methodology, T.T. and T.K.; validation, A.T., and T.K.; formal analysis, T.W.; investigation, T.T., A.T., T.W., K.I., Y.K., and T.K.; resources, T.K.; data curation, K.O. and K.N.; writing—original draft preparation, T.T. and T.K.; writing—review and editing, T.T., K.N., and T.K.; visualization, A.T.; supervision, T.W. and K.N.; project administration, T.K.; funding acquisition, K.O. and T.K.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial supports by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Grant Number 17K11799, 18K09595).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| PDGF-B | platelet-derived growth factor-B |
| TGFβ1 | transforming growth factor β1 |
| PPARγ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| PRP | platelet-rich plasma |
| cp-Ti | commercially pure-titanium |
| APP | atmospheric pressure plasma |
| UV | ultraviolet |
| PGE1 | prostaglandin E1 |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline |
| IgG | immunoglobulin |
References
- Black, J. Biological performance of tantalum. Clin. Mater. 1994, 16, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohler, O.E. Unalloyed titanium for implants in bone surgery. Injury 2000, 31 (Suppl. S4), 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, T. Surface treatment of titanium in deical applications. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 2005, 55, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annunziata, M.; Guida, L. The Effect of Titanium Surface Modifications on Dental Implant Osseointegration. Front. Oral Biol. 2015, 17, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barfeie, A.; Wilson, J.; Rees, J. Implant surface characteristics and their effect on osseointegration. Br. Dent. J. 2015, 218, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiati, L.; Eales, M.G.; Nobbs, A.H.; Su, B.; Tsimbouri, P.M.; Salmeron-Sanchez, M.; Dalby, M.J. Impact of surface topography and coating on osteogenesis and bacterial attachment on titanium implants. J. Tissue Eng. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindy, A.; Farahmand, F.; Tabatabaei, F.S. In vitro biological outcome of laser application for modification or processing of titanium dental implants. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T. Ultraviolet photofunctionalization of titanium implants. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, e95–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachauri, P.; Bathala, L.R.; Sangur, R. Techniques for dental implant nanosurface modifications. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2014, 6, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, M.; Jefferies, S.R.; Xia, W.; Engqvist, H.; Suzuki, J.B. Classification and Effects of Implant Surface Modification on the Bone: Human Cell-Based In Vitro Studies. J. Oral Implantol. 2017, 43, 58–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Orive, G.; Pla, R.; Roman, P.; Serrano, V.; Andia, I. The effects of PRGF on bone regeneration and on titanium implant osseointegration in goats: A histologic and histomorphometric study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2009, 91, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, G.; Egilmez, F.; Cekic-Nagas, I.; Karaca, İ.R.; Bozkaya, S. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on the outcome of early loaded Dental implants: A 3-year follow-up study. J. Oral Implantol. 2013, 39, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.G.; Chung, C.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, J.C.; Lim, S.C. Use of particulate dentin-plaster of Paris combination with/without platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of bone defects around implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2002, 17, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Kundu, R.; Rathee, M. Effect of Platelet-Rich-Plasma (PRP) and Implant Surface Topography on Implant Stability and Bone. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monov, G.; Fuerst, G.; Tepper, G.; Watzak, G.; Zechner, W.; Watzek, G. The effect of platelet-rich plasma upon implant stability measured by resonance frequency analysis in the lower anterior mandibles. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2005, 16, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streckbein, P.; Kleis, W.; Buch, R.S.; Hansen, T.; Weibrich, G. Bone healing with or without platelet-rich plasma around four different dental implant surfaces in beagle dogs. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechner, W.; Tangl, S.; Tepper, G.; Furst, G.; Bernhart, T.; Haas, R.; Mailath, G.; Watzek, G. Influence of platelet-rich plasma on osseous healing of dental implants: A histologic and histomorphometric study in minipigs. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2003, 18, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, R.V.; Gabrielli, M.A.C.; Hochuli-Vieira, E.; Spolidorio, L.C.; Filho, J.G.P.; Neto, F.A.D.; Cardoso, L.A.G.D.; Shibli, J.A. Effect of Platelet-Rich Plasma on Peri-Implant Bone Repair: A Histologic Study in Dogs. J. Oral Implantol. 2010, 36, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Takahashi, S.; Tsujino, T.; Isobe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Nakata, K.; Kawase, T. Platelet adhesion on commercially pure titanium plates in vitro I: Effects of plasma components and involvement of the von Willebrand factor and fibronectin. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2019, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannan, K.L.; Sahler, J.; Kim, N.; Spinelli, S.L.; Maggirwar, S.B.; Garraud, O.; Cognasse, F.; Blumberg, N.; Phipps, R.P. Breaking the mold: Transcription factors in the anucleate platelet and platelet-derived microparticles. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.M.; Spinelli, S.L.; Pollock, S.J.; Murant, T.I.; O’Brien, J.J.; Blumberg, N.; Francis, C.W.; Taubman, M.B.; Phipps, R.P. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and retinoid X receptor transcription factors are released from activated human platelets and shed in microparticles. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 99, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, Y.; Isobe, K.; Kawabata, H.; Tsujino, T.; Watanabe, T.; Nakamura, M.; Toyoda, T.; Okudera, H.; Okuda, K.; Nakata, K.; et al. Quantitative evaluation of morphological changes in activated platelets in vitro using digital holographic microscopy. Micron 2018, 113, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, T.; Isobe, K.; Tsujino, T.; Koyata, Y.; Ohyagi, F.; Watanabe, T.; Nakamura, M.; Kitamura, Y.; Okudera, H.; Nakata, K.; et al. Direct activation of platelets by addition of CaCl2 leads coagulation of platelet-rich plasma. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, K.; Suzuki, M.; Watanabe, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kawabata, H.; Nakamura, M.; Okudera, T.; Okudera, H.; Uematsu, K.; et al. Platelet-rich fibrin prepared from stored whole-blood samples. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2017, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, H.; Isobe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Okudera, T.; Nakamura, M.; Suzuki, M.; Ryu, J.; Kitamura, Y.; Okudera, H.; Okuda, K.; et al. Quality Assessment of Platelet-Rich Fibrin-Like Matrix Prepared from Whole Blood Samples after Extended Storage. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawase, T.; Tanaka, T.; Minbu, H.; Kamiya, M.; Oda, M.; Hara, T. An atmospheric-pressure plasma-treated titanium surface potentially supports initial cell adhesion, growth, and differentiation of cultured human prenatal-derived osteoblastic cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isobe, K.; Watanebe, T.; Kawabata, H.; Kitamura, Y.; Okudera, T.; Okudera, H.; Uematsu, K.; Okuda, K.; Nakata, K.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Mechanical and degradation properties of advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), concentrated growth factors (CGF), and platelet-poor plasma-derived fibrin (PPTF). Int. J. Implant Dent. 2017, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahler, J.; Woeller, C.; Spinelli, S.; Blumberg, N.; Phipps, R. A novel method for overexpression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in megakaryocyte and platelet microparticles achieves transcellular signaling. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 2563–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mackie, I.J.; Bull, H.A. Normal haemostasis and its regulation. Blood Rev. 1989, 3, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.J.; Clark, R.A. Cutaneous wound healing. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbiyik, F.; Ray, D.M.; Gettings, K.F.; Blumberg, N.; Francis, C.W.; Phipps, R.P. Human bone marrow megakaryocytes and platelets express PPARgamma, and PPARgamma agonists blunt platelet release of CD40 ligand and thromboxanes. Blood 2004, 104, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Tsujino, T.; Yamaguchi, S.; Isobe, K.; Watanabe, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Okuda, K.; Nakata, K.; Kawase, T. Distrubution of platelets, transforming growth factor-β1, platelet-derived growth factor-BB, vascular endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloprotease-9 in advanced platelet-rich fibrin and concentrated growth factor matrices. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yu, W.; Niibe, K.; Zhang, W.; Egusa, H.; Tang, T.; Jiang, X. The Effects of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor-BB on Bone Marrow Stromal Cell-Mediated Vascularized Bone Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 3272098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hezaimi, K.; Nevins, M.; Kim, S.W.; Fateh, A.; Kim, D.M. Efficacy of growth factor in promoting early osseointegration. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 40, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Leonidou, A.; Lester, M.; Heliotis, M.; Mantalaris, A.; Tsiridis, E. Investigating the role of PDGF as a potential drug therapy in bone formation and fracture healing. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 1633–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerer, P.W.; Schiegnitz, E.; Palarie, V.; Dau, M.; Frerich, B.; Al-Nawas, B. Influence of platelet-derived growth factor on osseous remodeling properties of a variable-thread tapered dental implant in vivo. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.-P. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast, skeletal development, and bone formation, homeostasis and disease. Bone Res. 2016, 4, 16009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, G.; Lee, Y.H.; Yi, H.K. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma loaded dental implant improves osteogenesis of rat mandible. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.E.; Lee, M.H.; Jeon, J.G.; Park, I.S.; Yi, H.K. Nanoparticle mediated PPARgamma gene delivery on dental implants improves osseointegration via mitochondrial biogenesis in diabetes mellitus rat model. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demoulin, J.B.; Montano-Almendras, C.P. Platelet-derived growth factors and their receptors in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Am. J. Blood Res. 2012, 2, 44–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, S.; Park, Y.S. Plasma in dentistry. Clin. Plasma Med. 2014, 2, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).