Antibacterial Additives in Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Focused Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review
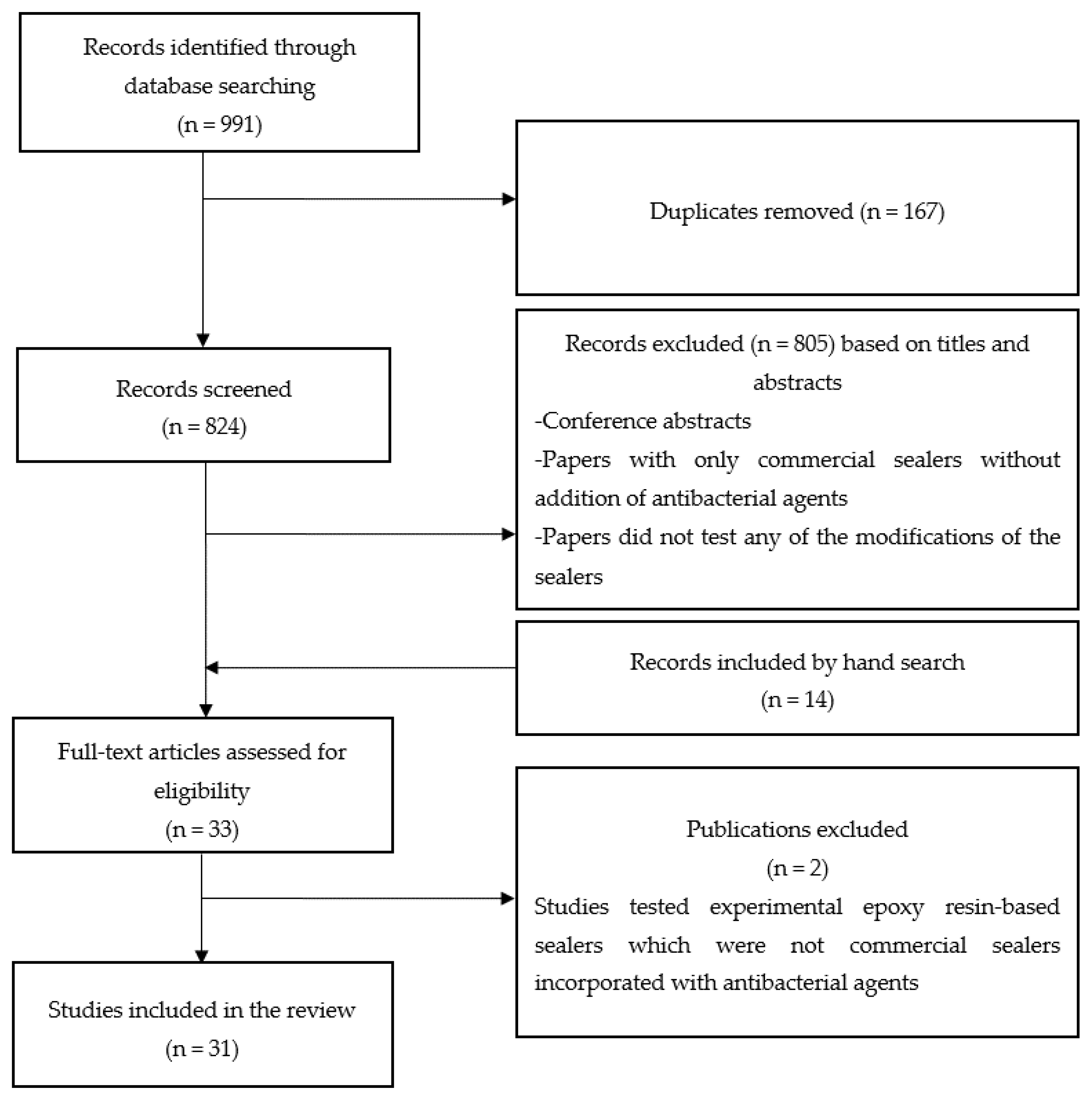
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Results
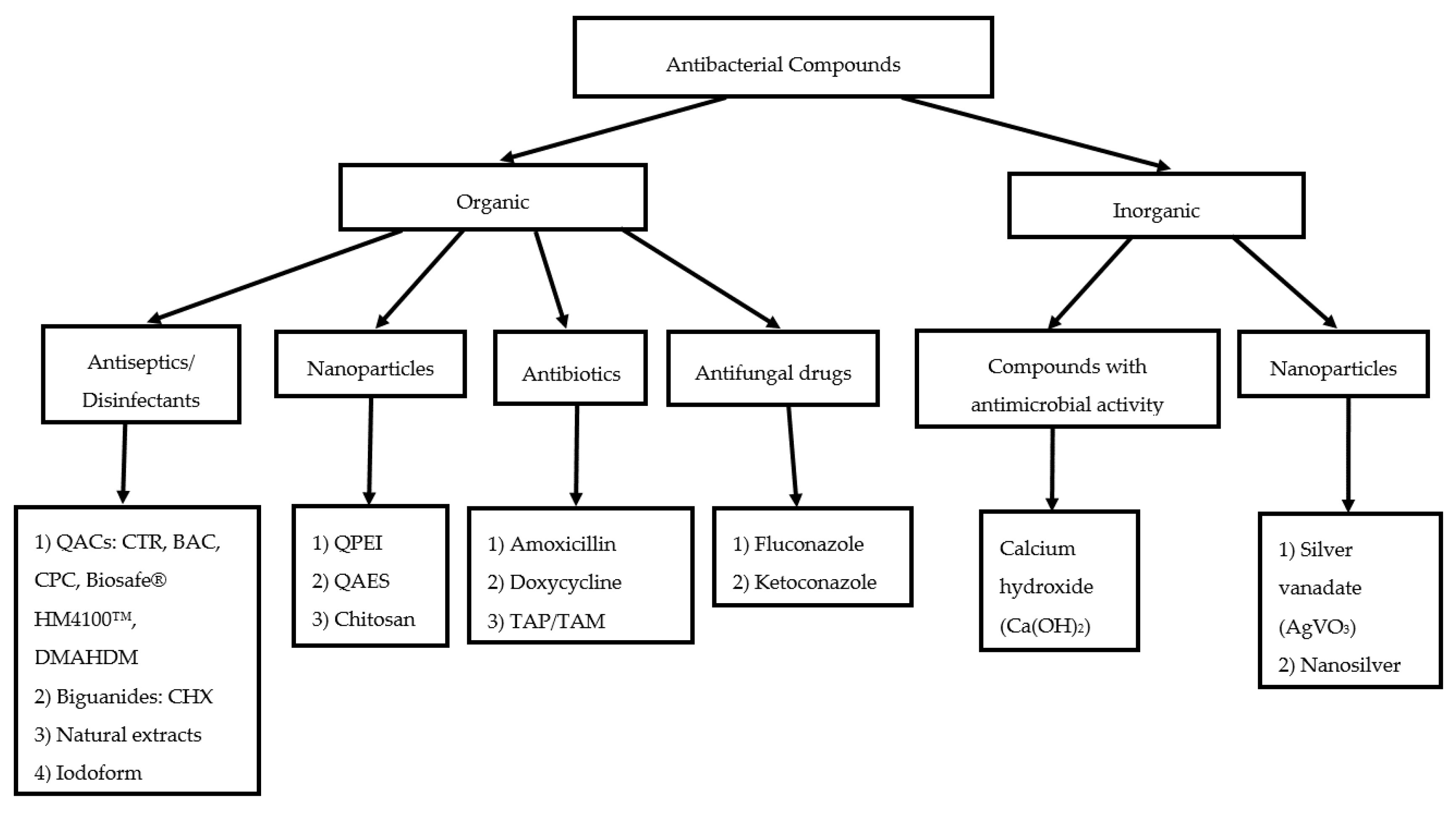
3. Review of Antimicrobial Effects
3.1. Antiseptics/Disinfectants and Compounds with Antimicrobial Activity
3.1.1. Quaternary Ammonium Compounds (QACs)
3.1.2. Natural Agents
3.1.3. Iodoform
3.1.4. Calcium Hydroxide
3.2. Antibiotics
3.3. Antifungal Drugs
3.4. Nanoparticulate Drugs and Nanoparticle-Based Delivery Systems
3.4.1. Chitosan
3.4.2. Silver Vanadate
3.4.3. Quaternary Ammonium Epoxy Silicate (QAES)
3.4.4. Quaternary Ammonium Polyethylenimine (QPEI) Nanoparticles
4. Effect of Antimicrobial Additives on Physicochemical Properties of Epoxy Resin Sealers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Du, J.; Peng, Z. Correlation between Enterococcus faecalis and Persistent Intraradicular Infection Compared with Primary Intraradicular Infection: A Systematic Review. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelakantan, P.; Romero, M.; Vera, J.; Daood, U.; Khan, A.U.; Yan, A.; Cheung, G.S.P. Biofilms in endodontics—Current status and future directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Rôças, I.N. Clinical implications and microbiology of bacterial persistence after treatment procedures. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 1291.e3–1301.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, R.M. Enterococcus faecalis—A mechanism for its role in endodontic failure. Int. Endod. J. 2001, 34, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trope, M.; Debelian, G. Endodontic Treatment of Apical Periodontitis. In Essential Endodontology: Prevention and Treatment of Apical Periodontitis, 2nd ed.; Ørstavik, D., Pitt Ford, T., Eds.; Blackwell Munksgaard: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 347–380. ISBN 978-14051-4976-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder, M. Root canal irrigants. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.A.A.; Neelakantan, P. Light Activated Disinfection in Root Canal Treatment—A Focused Review. Dent. J. 2018, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricucci, D.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Biofilms and apical periodontitis: Study of prevalence and association with clinical and histopathologic findings. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1277–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez de Paz, L.E. Redefining the persistent infection in root canals: Possible role of biofilm communities. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Rôças, I.N. Community as the unit of pathogenicity: An emerging concept as to the microbial pathogenesis of apical periodontitis. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2009, 107, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensäter, G.; Bergenholtz, G. Biofilms in endodontic infections. Endod. Top. 2004, 9, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShwaimi, E.; Bogari, D.; Ajaj, R.; Al-Shahrani, S.; Almas, K.; Majeed, A. In Vitro Antimicrobial Effectiveness of Root Canal Sealers Against Enterococcus faecalis: A Systematic Review. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayaoglu, G.; Erten, H.; Alacam, T.; Ørstavik, D. Short-term antibacterial activity of root canal sealers towards Enterococcus faecalis. Int. Endod. J. 2005, 38, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzo, G.; Giammanco, G.M.; Cumbo, E.; Nicolosi, G.; Gallina, G. In vitro antibacterial activity of endodontic sealers. J. Dent. 2006, 34, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Ruse, N.D.; Haapasalo, M. Antibacterial activity of endodontic sealers by modified direct contact test against Enterococcus faecalis. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, E.; Bering, N.; Bürklein, S. Selected physicochemical properties of AH Plus, EndoREZ and RealSeal SE root canal sealers. Odontology 2015, 103, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.V.; Silveira, F.F.; Horta, M.C.R.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Cavenago, B.C.; Morais, I.G.; Nunes, E. Filling Effectiveness and Dentinal Penetration of Endodontic Sealers: A Stereo and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Study. Braz. Dent. J. 2015, 26, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.J.; Accorsi-Mendonca, T.; Pedrosa, A.C.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Zaia, A.A. Long-Term Cytotoxicity, pH and Dissolution Rate of AH Plus and MTA Fillapex. Braz. Dent. J. 2016, 27, 419–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miletić, I.; Jukić, S.; Anić, I.; Zeljezić, D.; Garaj-Vrhovac, V.; Osmak, M. Examination of cytotoxicity and mutagenicity of AH26 and AH Plus sealers. Int. Endod. J. 2003, 36, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakantan, P.; Sharma, S.; Shemesh, H.; Wesselink, P.R. Influence of Irrigation Sequence on the Adhesion of Root Canal Sealers to Dentin: A Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Push-out Bond Strength Analysis. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Carpio-Perochena, A.; Kishen, A.; Shrestha, A.; Bramante, C.M. Antibacterial Properties Associated with Chitosan Nanoparticle Treatment on Root Dentin and 2 Types of Endodontic Sealers. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DaSilva, L.; Finer, Y.; Friedman, S.; Basrani, B.; Kishen, A. Biofilm formation within the interface of bovine root dentin treated with conjugated chitosan and sealer containing chitosan nanoparticles. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andolfatto, C.; Bonetti-Filho, I.; Carlos, I.Z.; Guerreiro-Tanomaru, J.M.; Kuga, M.C.; Tormin, F.B.C.; Faria, G. Cytocompatibility, physical properties, and antibiofilm activity of endodontic sealers with amoxicillin. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2017, 80, 1036–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangarlou, A.; Neshandar, R.; Matini, N.; Dianat, O. Antibacterial efficacy of AH Plus and AH26 sealers mixed with amoxicillin, triple antibiotic paste and nanosilver. J. Dent. Res. Dent. Clin. Dent. Prospects 2016, 10, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanapatla, A.; Vemisetty, H.; Punna, R.; Veeramachineni, C.; Venkata, R.P.; Muppala, J.N.; Dandolu, R. Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Effect of Three Endodontic Sealers with and Without Antibiotics—An In-vitro Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, ZC69–ZC72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Grover, R.; Pinnameneni, P.S.; Dey, S.; Raju, P.R. Evaluation of efficacy of combinations of five endodontic sealers with five antibiotics against Enterococcus Faecalis—An in-vitro study. J. Int. Oral. Health 2014, 6, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Binoy, D.; Sajjan, G.S.; Peddireddi, S.; Kumar, M.S.; Bhavana, V.; Raju, S.R. A Comparitive Evaluation of Sealing Ability, pH and Rheological Properties of Zinc Oxide Eugenol Sealer Combined with Different Antibiotics: An In Vitro Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, ZC05–ZC08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmi, H.; Ashofteh Yazdi, K.; Jabalameli, F.; Parvizi, S. Antimicrobial Effects of AH26 Sealer/Antibiotic Combinations Against Enterococcus Faecalis. Iran. Endod. J. 2008, 3, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hoelscher, A.A.; Bahcall, J.K.; Maki, J.S. In vitro evaluation of the antimicrobial effects of a root canal sealer-antibiotic combination against Enterococcus faecalis. J. Endod. 2006, 32, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collares, F.M.; Leitune, V.C.B.; Portella, F.F.; Santos, P.D.; Balbinot, G.S.; Dos Santos, L.A.; Parolo, C.C.F.; Samuel, S.M.W. Methacrylate-based root canal sealer containing chlorexidine and α-tricalcium phosphate. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 106, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailon-Sanchez, M.E.; Baca, P.; Ruiz-Linares, M.; Ferrer-Luque, C.M. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activity of AH Plus with chlorhexidine and cetrimide. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Linares, M.; Bailon-Sanchez, M.E.; Baca, P.; Valderrama, M.; Ferrer-Luque, C.M. Physical properties of AH Plus with chlorhexidine and cetrimide. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 1611–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraishi, N.; Yiu, C.K.; King, N.M.; Tay, F.R. Antibacterial effect of experimental chlorhexidine-releasing polymethyl methacrylate-based root canal sealers. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 1255–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, F.; Xiao, Y. Quaternary ammonium compounds in dental restorative materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2018, 37, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomonov, M.; Ben Itzhak, J. Evaluating the physical properties of one novel and two well-established epoxy resin-based root canal sealers. ENDO (Lond. Engl.) 2017, 11, 285–290. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, T.; Sterer, N.; Greenstein, R.B.-N.; Toledano, T.; Solomonov, M. Antibiofilm activity of epoxy sealer incorporated with quaternary ammonium macromolecule. EBEJ 2019, 4, 1:1–1:6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjorgievska, E.S.; Nicholson, J.W.; Coleman, N.J.; Booth, S.; Dimkov, A.; Hurt, A. Component Release and Mechanical Properties of Endodontic Sealers following Incorporation of Antimicrobial Agents. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2129807:1–2129807:6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjorgievska, E.; Apostolska, S.; Dimkov, A.; Nicholson, J.W.; Kaftandzieva, A. Incorporation of antimicrobial agents can be used to enhance the antibacterial effect of endodontic sealers. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, e29–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Moliz, M.T.; Ruiz-Linares, M.; Cassar, G.; Ferrer-Luque, C.M.; Baca, P.; Ordinola-Zapata, R.; Camilleri, J. The effect of benzalkonium chloride additions to AH Plus sealer. Antimicrobial, physical and chemical properties. J. Dent. 2015, 43, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, J.; Weir, M.D.; Melo, M.A.S.; Romberg, E.; Nosrat, A.; Xu, H.H.K.; Tordik, P.A. A Modified Resin Sealer: Physical and Antibacterial Properties. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 1553–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.H.; Lin, D.J.; Chang, K.W.; Hsia, S.M.; Ko, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Hsue, S.S.; Wang, T.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Shieh, T.M. Evaluation physical characteristics and comparison antimicrobial and anti-inflammation potentials of dental root canal sealers containing hinokitiol in vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94941:1–e94941:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Dhinsa, G.; Ghoshal, U.; Afzal Hussain, A.; Nag, S.; Garg, A. Influence of plant extracts mixed with endodontic sealers on the growth of oral pathogens in root canal: An in vitro study. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2019, 37, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuga, M.C.; Faria, G.; So, M.V.; Keine, K.C.; Santos, A.D.; Duarte, M.A.; Kopper, P.M. The impact of the addition of iodoform on the physicochemical properties of an epoxy-based endodontic sealer. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2014, 22, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.A.; de O. Demarchi, A.C.C.; de Moraes, I.G. Determination of pH and calcium ion release provided by pure and calcium hydroxide-containing AHPlus. Int. Endod. J. 2004, 37, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.A.; Ordinola-Zapata, R.; Bernardes, R.A.; Bramante, C.M.; Bernardineli, N.; Garcia, R.B.; de Moraes, I.G. Influence of calcium hydroxide association on the physical properties of AH Plus. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, J.; Maki, J.S. In vitro evaluation of the antimicrobial effect of three endodontic sealers mixed with amoxicillin. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1170–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckwerth, P.H.; Lima, F.L.; Greatti, V.R.; Duarte, M.A.; Vivan, R.R. Effects of the association of antifungal drugs on the antimicrobial action of endodontic sealers. Braz. Oral. Res. 2015, 29, S1806-83242015000100269:1–S1806-83242015000100269:7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.Q.; Huang, Z.B.; Shi, W.; Ma, B.; Tay, F.R.; Zhou, B. In vitro evaluation of antibacterial effect of ah plus incorporated with quaternary ammonium epoxy silicate against enterococcus faecalis. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.B.V.; Vidal, C.L.; de Castro, D.T.; de Oliveira-Santos, C.; Schiavon, M.A.; dos Reis, A.C. Incorporating Antimicrobial Nanomaterial and its Effect on the Antimicrobial Activity, Flow and Radiopacity of Endodontic Sealers. Eur. Endod. J. 2017, 2, 16:1–16:8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela Teixeira, A.B.; Vidal, C.L.; de Castro, D.T.; da Costa Valente, M.L.; Oliveira-Santos, C.; Alves, O.L.; dos Reis, A.C. Effect of incorporation of a new antimicrobial nanomaterial on the physical-chemical properties of endodontic sealers. J. Conserv. Dent. 2017, 20, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela Teixeira, A.B.; Vidal, C.L.; Albiasetti, T.; de Castro, D.T.; dos Reis, A.C. Influence of Adding Nanoparticles of Silver Vanadate on Antibacterial Effect and Physicochemical Properties of Endodontic Sealers. Iran. Endod. J. 2019, 14, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesler Shvero, D.; Abramovitz, I.; Zaltsman, N.; Perez Davidi, M.; Weiss, E.I.; Beyth, N. Towards antibacterial endodontic sealers using quaternary ammonium nanoparticles. Int. Endod. J. 2013, 46, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesler Shvero, D.; Zaltsman, N.; Weiss, E.I.; Polak, D.; Hazan, R.; Beyth, N. Lethal bacterial trap: Cationic surface for endodontic sealing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2016, 104, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyth, N.; Kesler Shvero, D.; Zaltsman, N.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Abramovitz, I.; Davidi, M.P.; Weiss, E.I. Rapid kill-novel endodontic sealer and Enterococcus faecalis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78586:1–e78586:10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.; Silva, M.G.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Alves, F.R.; Lopes, M.A.; Pina-Vaz, I.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Antibacterial, physicochemical and mechanical properties of endodontic sealers containing quaternary ammonium polyethylenimine nanoparticles. Int. Endod. J. 2014, 47, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaltsman, N.; Kesler-Shvero, D.; Weiss, E.I.; Beyth, N. Synthesis variants of quaternary ammonium polyethyleneimine nanoparticles and their antibacterial efficacy in dental materials. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2016, 14, e205–e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramovitz, I.; Wisblech, D.; Zaltsman, N.; Weiss, E.I.; Beyth, N. Intratubular Antibacterial Effect of Polyethyleneimine Nanoparticles: An Ex Vivo Study in Human Teeth. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 980529:1–980529:5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.; Silva, M.G.; Rocas, I.N.; Goncalves, L.S.; Alves, F.F.; Lopes, M.A.; Pina-Vaz, I.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Antibiofilm effects of endodontic sealers containing quaternary ammonium polyethylenimine nanoparticles. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, P.; Jamaledin, R.; Jabbari, M.; Nikfarjam, N.; Borzacchiello, A. Antibacterial quaternary ammonium compounds in dental materials: A systematic review. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Niu, L.N.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Tay, F.R.; Chen, J.H. Quaternary ammonium-based biomedical materials: State-of-the-art, toxicological aspects and antimicrobial resistance. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 71, 53–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, P.; Esposito Corcione, C.; Paladini, F.; Gallo, A.L.; Montagna, F.; Jamaledin, R.; Pollini, M.; Maffezzoli, A. Antimicrobial modified hydroxyapatite composite dental bite by stereolithography. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Editorial Board of the Journal of Endodontics. Wanted: A base of evidence. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 1401–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Godoy, F. Evaluation of an iodoform paste in root canal therapy in infected primary teeth. ASDC J. Dent. Child. 1987, 54, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, L.A.; Leonardo, M.R.; Oliveira, D.S.; Silva, R.A.; Queiroz, A.M.; Hernandez, P.G.; Nelson-Filho, P. Histopathological evaluation of root canal filling materials for primary teeth. Braz. Dent. J. 2010, 21, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sarigol, C.G.; Cogulu, D.; Oncag, O.; Deliloglu, I.G. Cytotoxic effects of primary tooth root canal filling materials on L929 cell line. J. Dent. Child. (Chic.) 2010, 77, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Petel, R.; Moskovitz, M.; Tickotsky, N.; Halabi, A.; Goldstein, J.; Houri-Haddad, Y. Cytotoxicity and proliferative effects of Iodoform-containing root canal-filling material on RAW 264.7 macrophage and RKO epithelial cell lines. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungaro Duarte, M.A.; de Oliveira El Kadre, G.D.; Vivan, R.R.; Guerreiro Tanomaru, J.M.; Tanomaru Filho, M.; de Moraes, I.G. Radiopacity of portland cement associated with different radiopacifying agents. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, D.F.; Mello-Moura, A.C.; Santos, E.M.; Guedes-Pinto, A.C. Cytotoxicity, histopathological, microbiological and clinical aspects of an endodontic iodoform-based paste used in pediatric dentistry: A review. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2008, 32, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Lopes, H.P. Mechanisms of antimicrobial activity of calcium hydroxide: A critical review. Int. Endod. J. 1999, 32, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, S.C. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference, 37th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK; Chicago, IL, USA, 2011; pp. 325–1788. ISBN 978-0853699330. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, B.I.; Pagnillo, M.K.; Musikant, B.L.; Deutsch, A.S. Formaldehyde evaluation from endodontic materials. Oral Health 1998, 88, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Athanassiadis, B.; George, G.A.; Abbott, P.V.; Wash, L.J. A review of the effects of formaldehyde release from endodontic materials. Int. Endod. J. 2015, 48, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restani, P.; Galli, C.L. Oral toxicity of formaldehyde and its derivatives. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1991, 21, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman-McKeeman, L. Paracelsus and formaldehyde 2010: The dose to the target organ makes the poison. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 116, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, R. Identifying an indoor air exposure limit for formaldehyde considering both irritation and cancer hazards. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2011, 41, 672–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checkoway, H.; Boffetta, P.; Mundt, D.J.; Mundt, K.A. Critical review and synthesis of the epidemiologic evidence on formaldehyde exposure and risk of leukemia and other lymphohematopoietic malignancies. Cancer Causes Control 2012, 23, 1747–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicher, G.; Peters, J. Microbial resistance to formaldehyde. I. Comparative quantitative studies in some selected species of vegetative bacteria, bacterial spores, fungi, bacteriophages and viruses. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Orig. B 1976, 163, 486–508. [Google Scholar]
- Ordinola-Zapata, R.; Bramante, C.M.; Minotti, P.G.; Cavenago, B.C.; Garcia, R.B.; Bernardineli, N.; Jaramillo, D.E.; Hungaro Duarte, M.A. Antimicrobial activity of triantibiotic paste, 2% chlorhexidine gel, and calcium hydroxide on an intraoral-infected dentin biofilm model. J. Endod. 2013, 39, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Shin, S.J.; Park, J.W.; Jung, I.Y. Tooth discoloration of immature permanent incisor associated with triple antibiotic therapy: A case report. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheek, C.C.; Heymann, H.O. Dental and oral discolorations associated with minocycline and other tetracycline analogs. J. Esthet. Dent. 1999, 11, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmad, A.; Ameen, H.; Pelz, K.; Karygianni, L.; Wittmer, A.; Anderson, A.C.; Spitzmuller, B.; Hellwig, E. Antibiotic resistance and capacity for biofilm formation of different bacteria isolated from endodontic infections associated with root-filled teeth. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netuschil, L.; Auschill, T.M.; Sculean, A.; Arweiler, N.B. Confusion over live/dead stainings for the detection of vital microorganisms in oral biofilms—which stain is suitable? BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 2:1–2:12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiefel, P.; Schmidt-Emrich, S.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Ren, Q. Critical aspects of using bacterial cell viability assays with the fluorophores SYTO9 and propidium iodide. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 36:1–36:9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tronstad, L.; Barnett, F.; Flax, M. Solubility and biocompatibility of calcium hydroxide-containing root canal sealers. Dent. Traumatol. 1988, 4, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.; Chandler, N. Calcium hydroxide–based root canal sealers: A review. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeniz, A.; Mustafa, K.; Ørstavik, D.; Dahl, J. Cytotoxicity of new resin-, calcium hydroxide-and silicone-based root canal sealers on fibroblasts derived from human gingiva and L929 cell lines. Int. Endod. J. 2007, 40, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.M.; Du, T.F.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Zheng, Y.F.; Haapasalo, M. In vitro cytotoxicity of calcium silicate–containing endodontic sealers. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Sielker, S.; Hanisch, M.R.; Libricht, V.; Schäfer, E.; Dammaschke, T. Cytotoxic effects of four different root canal sealers on human osteoblasts. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194467:1–e0194467:14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Libricht, V.; Sielker, S.; Hanisch, M.R.; Schäfer, E.; Dammaschke, T. Evaluation of the biocompatibility of root canal sealers on human periodontal ligament cells ex vivo. Odontology 2019, 107, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Search Builder | Search Words | Results |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | “epoxy resin” OR epoxy-based OR amine-epoxy OR amine epoxy OR epoxy OR epoxide | 41,898 |
| #2 | Sealer * OR sealing OR sealant * OR filling * OR cement * | 150,150 |
| #3 | antibacterial OR antimicrobial OR antibiofilm OR anti-biofilm OR biofilm * OR fungus OR fungi OR fungal OR antifungal OR anti-fungal OR bactericidal OR infection OR antiinfective OR anti-infective OR microbial OR bacterial OR nanoparticle * OR antibiotic * | 4,663,057 |
| #1 AND #2 AND #3 | 656 | |
| Advanced Search Field in Scopus with Key Words | Results |
|---|---|
| (TITLE-ABS-KEY (“epoxy resin” OR epoxy-based OR amine-epoxy OR “amine epoxy” OR epoxy OR epoxide ) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (sealer * OR sealing OR sealant * OR filling * OR cement *) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (antibacterial OR antimicrobial OR antibiofilm OR anti-biofilm OR biofilm * OR fungus OR fungi OR fungal OR antifungal OR anti-fungal OR bactericidal OR infection OR antiinfective OR anti-infective OR microbial OR bacterial OR nanoparticle * OR antibiotic *)) | 335 |
| Publication | Epoxy Resin Sealer Tested | Antimicrobial Additive(s) | Methods of Studying the Antimicrobial Activity | Physicochemical Properties Tested | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bailon-Sanchez et al. [31] | AH Plus™ | Chlorhexidine digluconate (CHX) liquid 1%, 2% and cetrimide (CTR) 0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3%, 0.4%, 0.5%, and a mixture of both | DCT; Biofilm test: Calgary Biofilm Device (MBEC-high throughput [HTP]; Innovotech, Edmonton, AB, Canada). | Not tested |
|
| Ruiz-Linares et al. [32] | AH Plus™ | Chlorhexidine digluconate (CHX) liquid 1%, 2% and cetrimide (CTR) 0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3%, 0.5%, and mixture of both | Not tested | Setting time, flow, solubility, radiopacity |
|
| Solomonov et al. [36] | BJM Root Canal Sealer™, AH Plus™, MM-Seal™ | Biosafe® HM4100™ (3-(Trihydroxysilyl) propyldimethyl-octadecyl ammonium chloride) as an additive into BJM Root Canal Sealer™. | Not tested | Flow, working time, solubility, dimensional change |
|
| Becker et al. [37] | BJM Root Canal Sealer™ | Biosafe® HM4100™ (3-(Trihydroxysilyl) propyldimethyl-octadecyl ammonium chloride) at 0%, 0.4%, 0.8%, 1.6%, 3.3% w/v | Crystal violet staining, Optical density (spectrophotometer). Fluorescence microscopy | Not tested |
|
| Gjorgievska et al. [38] | AH Plus™ | Benzalkonium Chloride (BAC), Cetylpyridinium Chloride (CPC) at 2% w/w | Not tested | Release of BAC and CPC after week 1 and week 4. Compressive strength. |
|
| Gjorgievska et al. [39] | AH Plus™ | Benzalkonium Chloride (BAC), Cetylpyridinium Chloride (CPC) at 2% w/w | ADT | Not tested |
|
| Arias-Moliz et al. [40] | AH Plus™ | Benzalkonium chloride (BAC) at 1%, 2%, and 3% w/w | DCT; Antibiofilm test: MBEC-high-throughput (HTP) device; CLSM | Setting time, flow, solubility, microhardness, contact angle measurement |
|
| Seung et al. [41] | AH Plus™ | Dimethylaminododecyl methacrylate (DMAHDM) at 2.5%, 5%, 10% w/w; Nanosilver (NAg) 0.05%, 0.10%, 0.15% w/w; Combination of DMAHDM 2.5% w/w and NAg 0.15% w/w | DCT (modified DCT) CFU counts | Setting time, flow, solubility, dimensional change. |
|
| Shih et al. [42] | AH Plus™ | Hinokitiol at 0.2%, 0.5%, 1%, and 2% w/w 0.2% used for physical, biological and antimicrobial tests | ADT; DCT | Setting time, working time, flowability, film thickness, solubility, cytotoxicity. |
|
| Saha et al. [43] | AH Plus™ | Herbal extracts: Glycyrrhiza glabra (Licorice); Tinospora cordifolia (Guduchi); Mimusops elengi (Bakul) | ADT | Not tested |
|
| Kuga et al. [44] | Sealer 26™ | Iodoform at 0.275 g: 2.1 g; 0.55 g: 2.1 g; 1.1 g: 2.1 g (to the sealer) | Not tested | Setting time, flow, solubility, pH, calcium release. |
|
| Duarte et al. [45] | AH Plus™ | Calcium hydroxide (CH) at 5% w/w and 10% w/w | Not tested | pH, calcium release (Ca2+) |
|
| Duarte et al. [46] | AH Plus™ | Calcium hydroxide (CH) at 5% w/w and 10% w/w | Not tested | Setting time, flow, film thickness, solubility, dimensional changes, radiopacity |
|
| Andolfatto et al. [23] | AH Plus™ | Amoxicillin added at 0.25% w/w, 0.5%, 1%, 2.5%, 5.5%, 7.5%, 10% w/w into the sealer | CFU counts | Flow, setting time, cytocompatibility |
|
| Kangarlou et al. [24] | AH Plus™, AH 26™ | Amoxicillin; triple antibiotic paste (TAP); nanosilveradded at 10% w/w into sealers. | ADT | Not tested |
|
| Vanapatla et al. [25] | AH Plus™ | Triple antibiotic mixture (TAM) added at 10% w/w together with a gutta-percha point | CFU counts | Not tested |
|
| Razmi et al. [28] | AH 26™ | Amoxicillin; doxycycline added at 1%, 5%, 10%, 25%, 50% w/w into the sealer | ADT; CFU counts (In vitro human root inoculation method) | Not tested |
|
| Baer and Maki [47] | AH Plus™ | Amoxicillin at 10% w/w | DCT Optical density (spectrophotometer) | Not tested |
|
| Weckwerth et al. [48] | AH Plus™, Sealer 26™ | Ketoconazole; Fluconazole at 0.5% w/w | ADT | Setting time, flowability |
|
| Del Carpio-Perochena et al. [21] | ThermaSeal Plus™ | Chitosan nanoparticles (CNps) | CFU calculation (log CFU/mL); Direct contact and membrane-restricted antibacterial experiments; CLSM, Sealer–dentine interface after pretreatment of dentine with CMCS (carboxymethyl-chitosan) or CMCS+RB (rose bengal) | Not tested |
|
| Vilela Teixeira et al. [50] | AH Plus™, Sealer 26™ | Nanostructured silver vanadate (AgVO3) decorated with silver nanoparticles at 0% w/w, 2.5% w/w, 5% w/w, 10% w/w | MIC (for AgVO3) by the visual assessment of turbidity; ADT | Flow, radiopacity |
|
| Vilela Teixeira et al. [51] | AH Plus™, Sealer 26™ | Nanostructured silver vanadate (AgVO3) decorated with silver nanoparticles at 0%, 2.5%, 5%, 10% w/w | Not tested | Radiopacity, colour change |
|
| Vilela Teixeira et al. [52] | AH Plus™, Sealer 26™ | Nanostructured silver vanadate (AgVO3) decorated with silver nanoparticles at 0%, 2.5%, 5%, 10% w/w | DCT CFU counts; Epifluorescence microscopy | pH, solubility |
|
| Gong et al. [49] | AH Plus™ | QAES (quaternary ammonium epoxy silicate) particles at 2%, 4%, 8% w/w | DCT; Optical density (spectrophotometer); Viability analysis of biofilm: CLSM | Not tested |
|
| Kesler Shvero et al. [53] | AH Plus™ | QPEI nanoparticles at 0.5%, 1%, 2% w/w | DCT Optical density (spectrophotometer); ADT; SEM | Not tested |
|
| Kesler Shvero et al. [54] | AH Plus™ | QPEI Nanoparticles at 2% w/w | Optical density (spectrophotometer); CLSM; Flow cytometry | Not tested |
|
| Beyth et al. [55] | RCS (BJM)™ | QPEI Nanoparticles at 1.5% w/w | DCT; Optical density (spectrophotometer), CFU counts ADT; SEM | Solubility, flow, cytotoxicity |
|
| Barros et al. [56] | AH Plus™ | QPEI nanoparticles at 1% or 2% w/w | DCT, CFU counts | Setting time, flow, solubility, apparent porosity, dimensional change, wettability, zeta potential, compressive strength |
|
| Zaltsman et al. [57] | AH Plus™ | QPEI nanoparticles variants | DCT, Optical density (spectrophotometer) MIC SEM | Not tested |
|
| Abramovitz et al. [58] | AH Plus™ | QPEI nanoparticles at 1% w/w | CLSM | Not tested |
|
| Barros et al. [59] | AH Plus™ | QPEI nanoparticles at 2% w/w | DCT, CFU counts; membrane-restricted test; Crystal-violet microtiter-plate assay CLSM (data not shown in the paper) | Not tested |
|
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brezhnev, A.; Neelakantan, P.; Tanaka, R.; Brezhnev, S.; Fokas, G.; Matinlinna, J.P. Antibacterial Additives in Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Focused Review. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj7030072
Brezhnev A, Neelakantan P, Tanaka R, Brezhnev S, Fokas G, Matinlinna JP. Antibacterial Additives in Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Focused Review. Dentistry Journal. 2019; 7(3):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj7030072
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrezhnev, Alexander, Prasanna Neelakantan, Ray Tanaka, Sergey Brezhnev, George Fokas, and Jukka P. Matinlinna. 2019. "Antibacterial Additives in Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Focused Review" Dentistry Journal 7, no. 3: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj7030072
APA StyleBrezhnev, A., Neelakantan, P., Tanaka, R., Brezhnev, S., Fokas, G., & Matinlinna, J. P. (2019). Antibacterial Additives in Epoxy Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Focused Review. Dentistry Journal, 7(3), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj7030072






