Transposed Maxillary Canines: Narrative Review with Clinical Case Report
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Description
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Review Guidelines
2.3. Selection Criteria
- -
- Articles addressing MCT;
- -
- Articles published in English between 2014 and 2024;
- -
- Articles involving human subjects;
- -
- Articles classified as retrospective, case-control, cross-sectional studies, or case reports.
- -
- Encompassed articles involving participants without transposed maxillary canines;
- -
- Articles lacking relevant details on MCT.
2.4. Eligibility Criteria
2.5. Search Strategy
2.6. Selection of Articles and Data Collection
2.7. Clinical Case
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Articles
3.1.1. Quality Assessment
| Risk of Bias Domains | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author and Year of Publication | Bias Due to Confounding | Bias in Selection of Participants into the Study | Bias in Classification of Interventions | Bias due to Deviations from Intended Interventions | Bias due to Missing Data | Bias in Measurement of Outcomes | Bias in Selection of the Reported Result |
| Maspero C. et al. (2016) [8] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Finkelstein T. et al. (2020) [9] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Checklist | Gebert TJ. et al. (2014) [11] | Di Palma E. et al. (2015) [12] | Teresa DM. et al. (2015) [13] | Hsu YL. et al. (2016) [14] | Lorente T. et al. (2016) [15] | Potrubacz MI. et al. (2016) [8] | Nabbout F. et al. (2017) [16] | Lara MS. et al. (2018) [17] | Matsumoto MAN. et al. (2018) [18] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Were patient’s demographic characteristics clearly described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 2. Was the patient’s history clearly described and presented as a timeline? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 3. Was the current clinical condition of the patient on presentation clearly described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 4. Were diagnostic tests or assessment methods and the results clearly described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 5. Was the intervention(s) or treatment procedure(s) clearly described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 6. Was the post-intervention clinical condition clearly described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 7. Were adverse events (harms) or unanticipated events identified and described? | No | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| 8. Does the case report provide takeaway lessons? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Overall appraisal: | Include | Include | Include | Include | Include | Include | Include | Include | Include |
| Checklist | de Souza RM. et al. (2020) [7] | Pedalino A. et al. (2020) [19] | Lorente C. et al. (2020) [6] | Mereani S. et al. (2022) [20] | Paixão MPM. et al. (2023) [21] | QasemAl-Gazzawi AM. et al. (2023) [22] | Pithon MM. et al. (2023) [23] | Andrade EC. et al. (2023) [24] | |
| 1. Were patient’s demographic characteristics clearly described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 2. Was the patient’s history clearly described and presented as a timeline? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 3. Was the current clinical condition of the patient on presentation clearly described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 4. Were diagnostic tests or assessment methods and the results clearly described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 5. Was the intervention(s) or treatment procedure(s) clearly described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 6. Was the post-intervention clinical condition clearly described? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| 7. Were adverse events (harms) or unanticipated events identified and described? | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | Yes | |
| 8. Does the case report provide takeaway lessons? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |
| Overall appraisal: | Include | Include | Include | Include | Include | Include | Include | Include | |
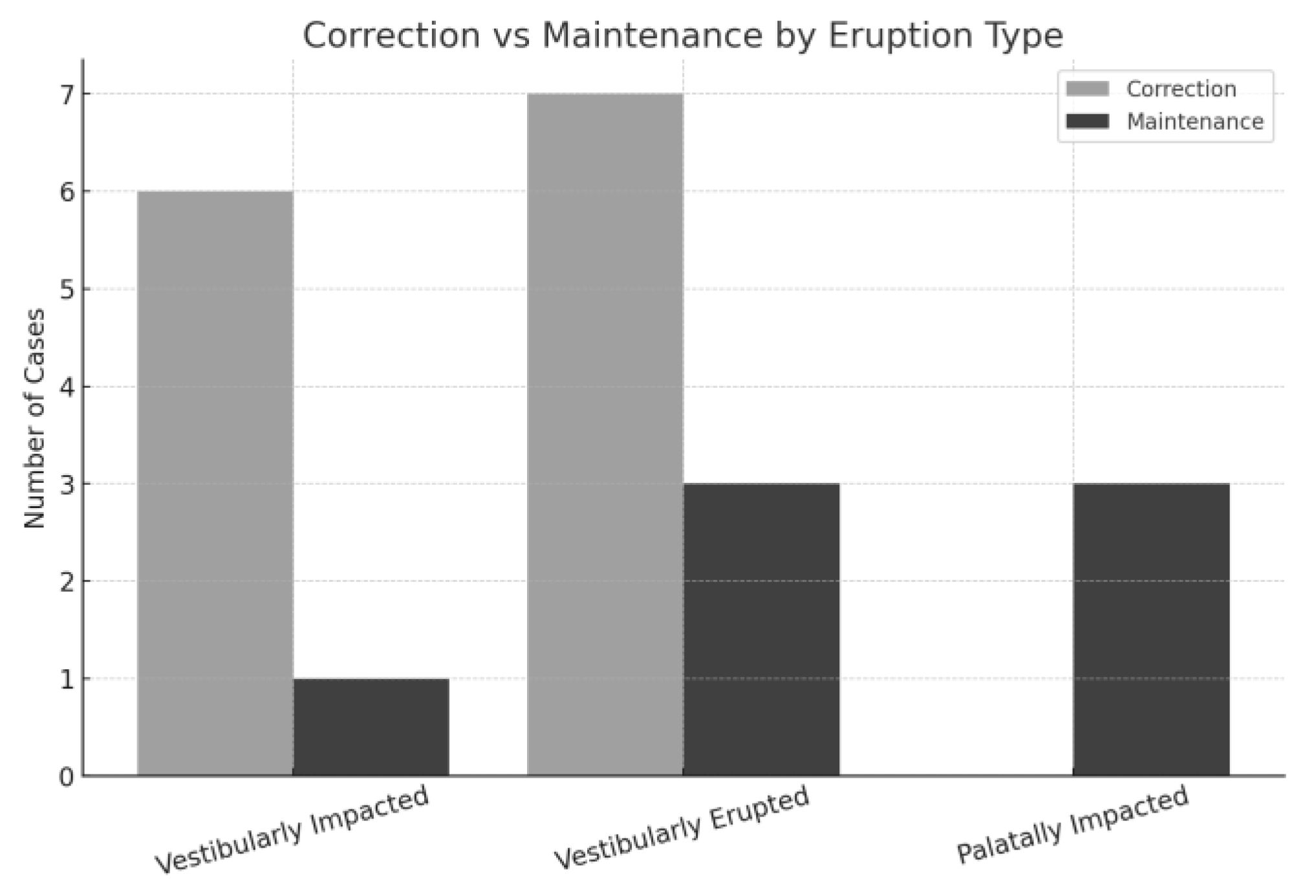
| Authors and Year of Publication | Population | Transposition | Complete or Incomplete | Right, Left, or Bilateral | Vestibular or Palatal | Sagittal | Treatment | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relation | ||||||||
| (Before) | ||||||||
| Gebert TJ. et al. 2014 [11] | ♀ 12 YO | Mx.C.I2 | I | L | V (erupted) | R: Cl I L: Cl II | Corrected | - |
| Di Palma E. et al. 2015 [12] | ♀ 7 YO | Mx.C.P1 | C | B | V (erupted) | Cl II div 2 Sk I | Maintained | - |
| Teresa DM. et al. 2015 [13] | ♂ 12 YO | Mx.C.P1 | C | R | V (impacted) | Cl I | Corrected | -Tooth #13 showed slight gingival recession |
| Hsu YL. et al. 2016 [14] | ♀ 12 YO | Mx.C.I2 | C | L | V (erupted) | Cl II div 1 Sk II | Corrected | - |
| Lorente T. et al. 2016 [15] | 1: ♂ 12 YO 2: ♀ 15 YO | 1:Mx.C.I2 2:Mx.C.I2 | 1: I 2: C | 1: B 2: L | 1:V (impacted) 2:V (impacted) | 1: Cl I 2: Cl I | 1: Corrected 2: Corrected | -Teeth #12 and #22 showed root resorption before and after treatment |
| Potrubacz MI. et al. 2016 [8] | ♀ 7 YO | Mx.C.P1 | C | B | V (erupted) | Cl III Sk III | Maintained | - |
| Nabbout F. et al. 2017 [16] | 1: ♀ 13 YO 2: ♀ 11 YO | 1:Mx.C.P1 2:Mx.C.P1 | 1: C 2: C | 1: L 2: R | 1:V (erupted) 2:V (erupted) | 1: Cl II Sk I 2: MSTP Sk I | 1: Corrected 2: Corrected | - |
| Lara MS. et al. 2018 [17] | ♀ 9 YO | Mx.C.I1 | C | L | P (impacted) | Cl I Sk II | Maintained | -Slight root angulation of tooth #13, overall good root parallelism -Diminished root length due to orthodontic treatment before apex closure |
| Matsumoto MAN. et al. 2018 [18] | ♀ 17 YO | Mx.C.I2 | C | R | V (erupted) | Cl Ind Sk II | Corrected | - |
| de Souza RM. et al. 2020 [7] | ♂ 9 YO | Mx.C.P1 | C | R | P (impacted) | Cl II Sk II | Maintained | -Good root parallelism overall, except tooth #14 -Slight apical root resorption observed in maxillary anterior teeth |
| Pedalino A. et al. 2020 [19] | ♀ 12 YO | Mx.C.I2 | C | B | V (impacted) | Cl I Sk I | Corrected | - |
| Lorente C. et al. 2020 [6] | ♂ 12 YO | Mx.C.P1 | R: C L: I | B | V (erupted) | R: Cl II L: Cl I Sk II | Corrected | -Slight gingival recession on tooth #13 |
| Mereani S. et al. 2022 [20] | ♀ 14 YO | Mx.C.P1 | C | B | V (erupted) | Cl I Sk I | Maintained | -Mucogingival issues on teeth #13 and #23 |
| Paixão MPM. et al. 2023 [21] | ♀ 11 YO | Mx.C.I1 | C | R | P (impacted) | Cl I Sk I | Maintained | - |
| QasemAl-Gazzawi AM. et al. 2023 [22] | ♀ 13 YO | Mx.C.I2 | C | B | V (impacted) | Cl II Sk I | Corrected | - |
| Pithon MM. et al. 2023 [23] | ♀ 15 YO | Mx.C.P1 | C | B | V (erupted) | Cl I Sk I | Corrected | - |
| Andrade EC. et al. 2023 [24] | ♂ 9 YO | Mx.C.I2 | C | R | V (impacted) | Cl Ind | Corrected | -Decreased buccal cortical bone on teeth #11, #12, and #13 -Slight external root resorption on tooth #12 -Pulp necrosis, likely due to root movement on tooth #11 |
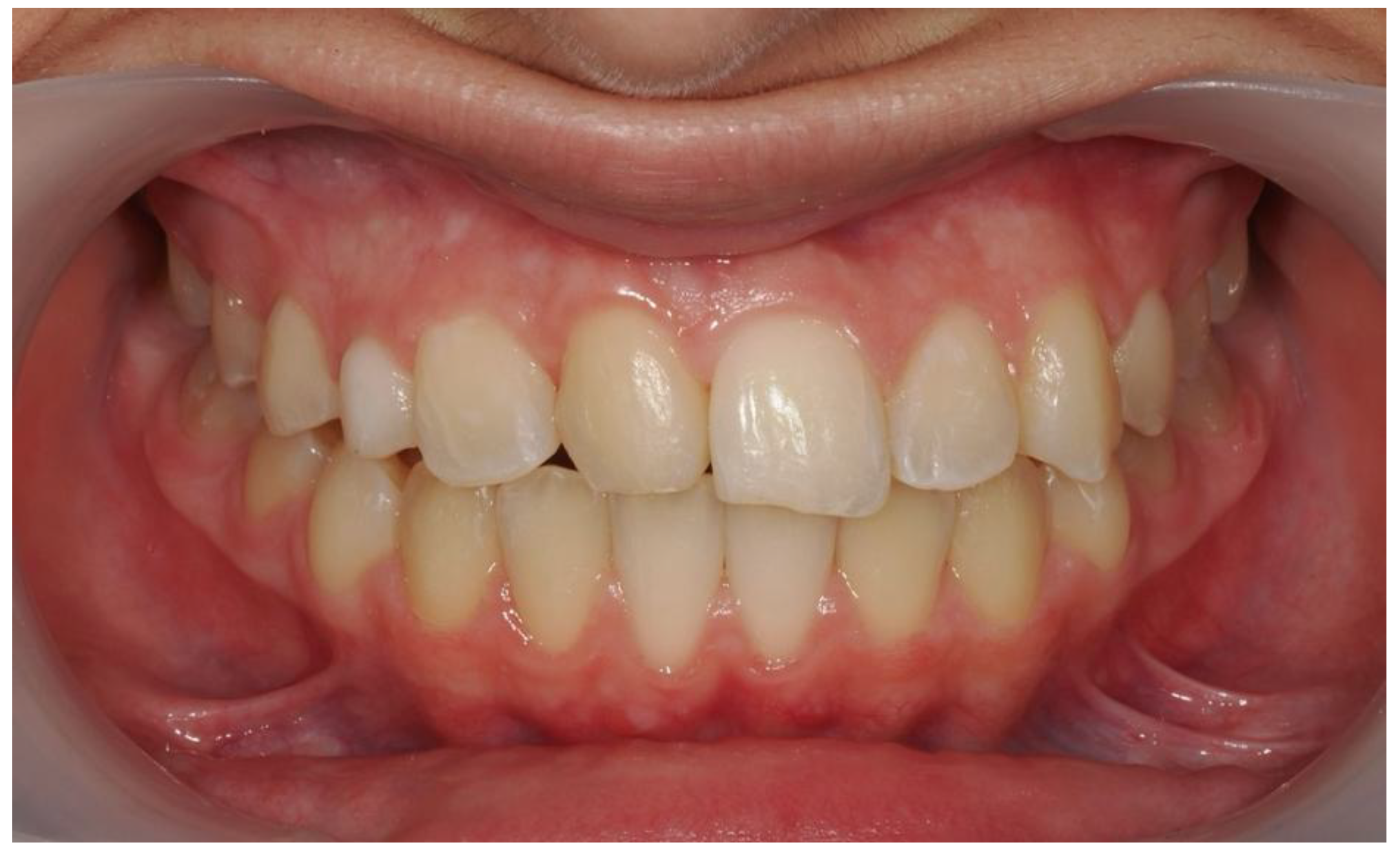
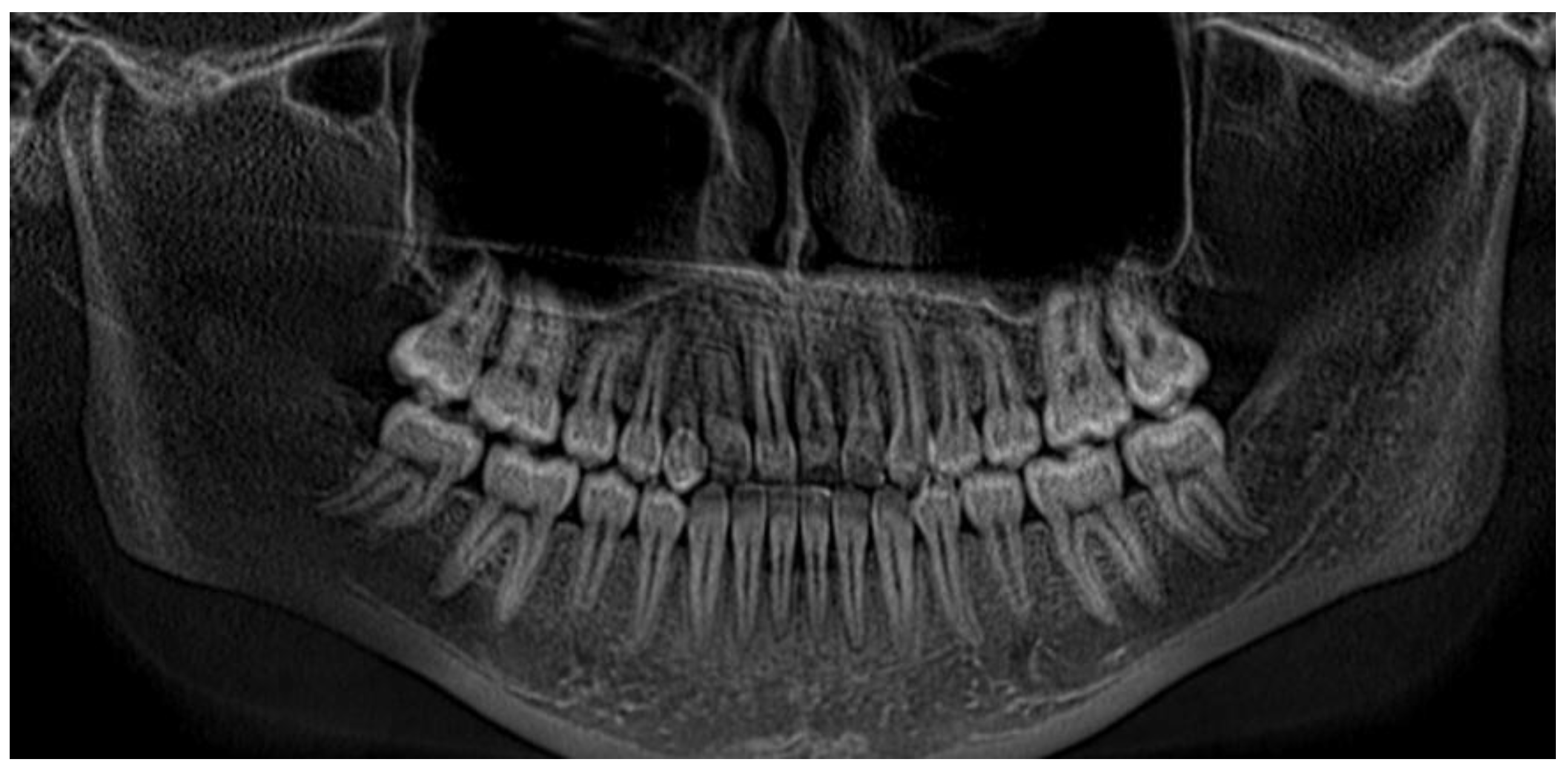
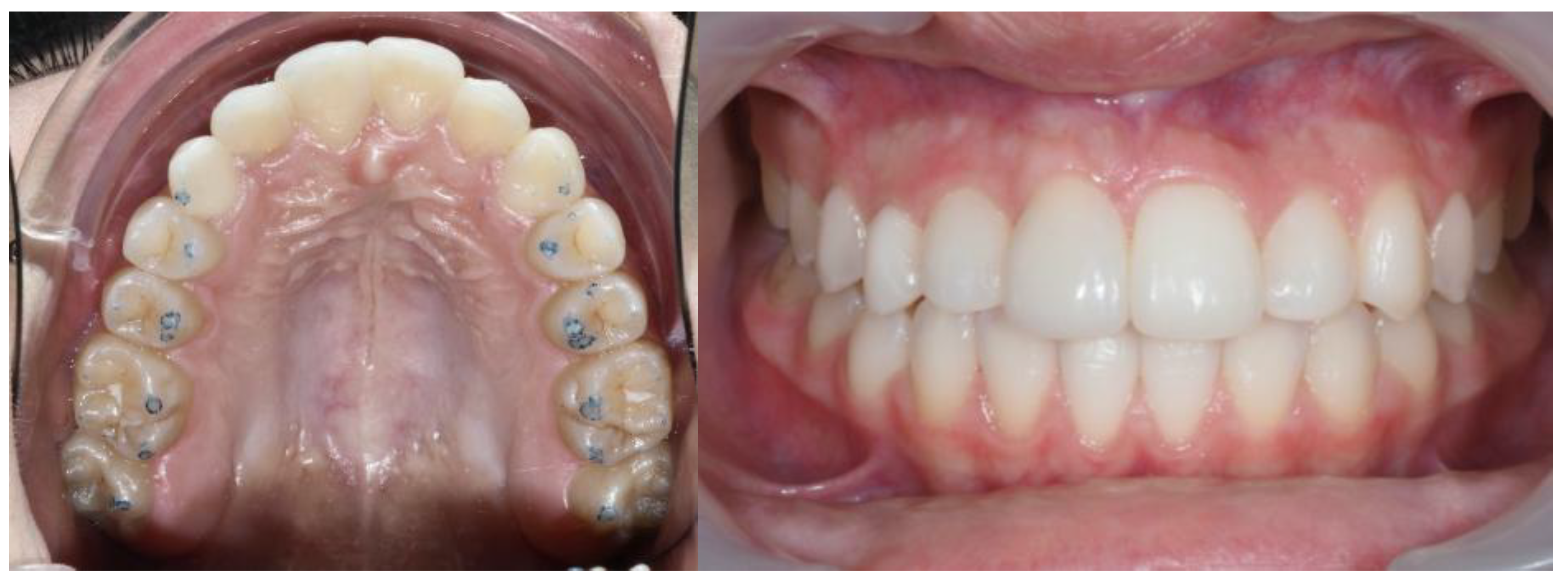
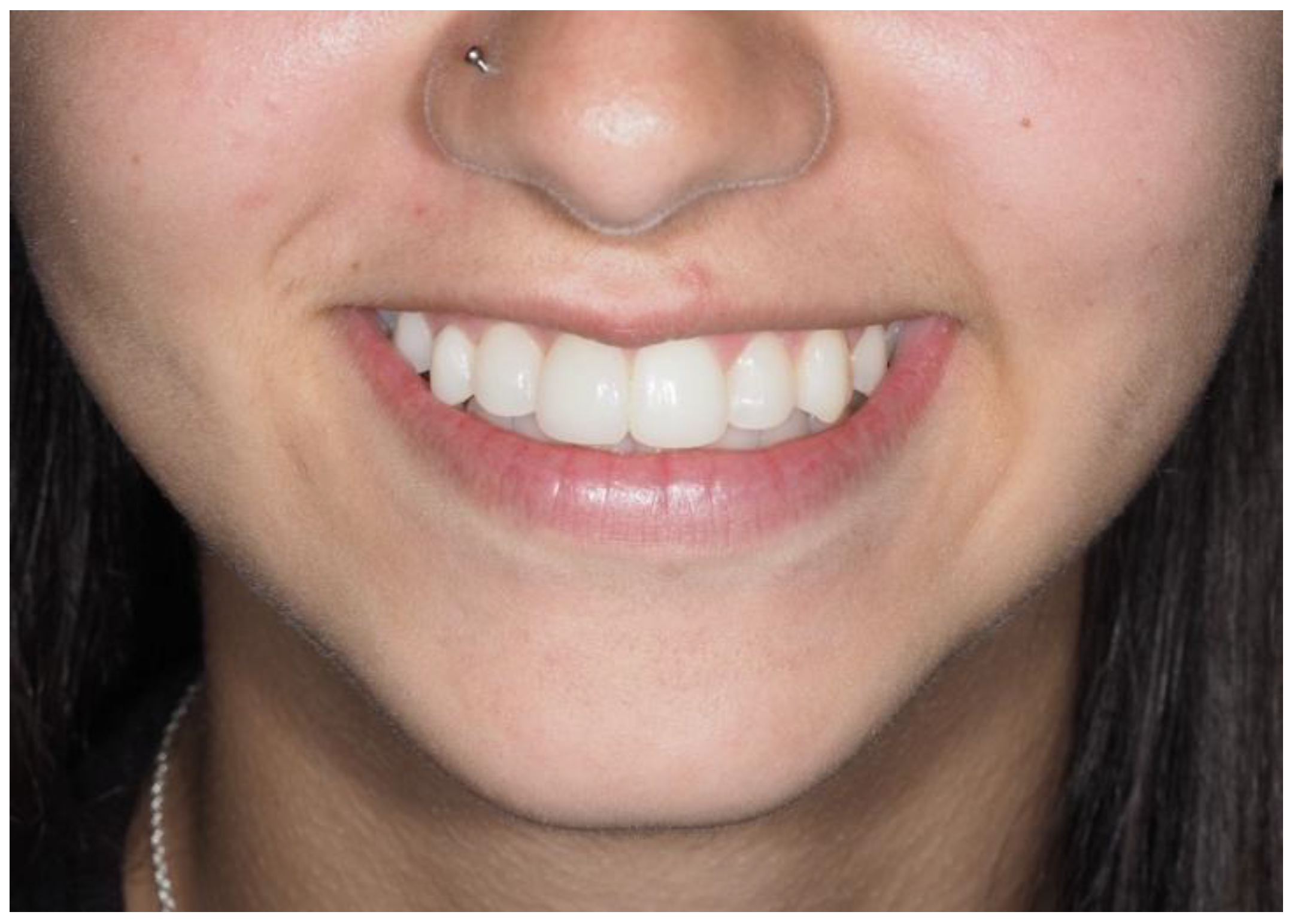
| Pinho T., Amaral R. 2025 | ♀ 13 YO | Mx.C.I1 | C | R | V (impacted) | Cl I | Maintained | -Total root resorption of tooth #11 due to the position of the ectopic canine |
| Authors and Year of Publication | Population | Transposition | Complete or Incomplete | Sagittal Relation (Before) | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maspero C. et al. (2016) [9] | N = 20 between 8 and 12 YO (mean age 10 ± 0.3 YO); | 15 Mx.C.P1 | I | - | 13 were Corrected 2 were Maintained |
| Finkelstein T. et al. (2020) [10] | N = 3.000:1.780 ♀ (59%) and 1.220 ♂ (41%) Ages: between 10 and 40 YO (mean age of 17.3 ± 9.3 YO) | 6 Mx.C.P1 7 Mx.C.I2 | - | All had Cl I | 6 were Maintained 7 were Corrected |
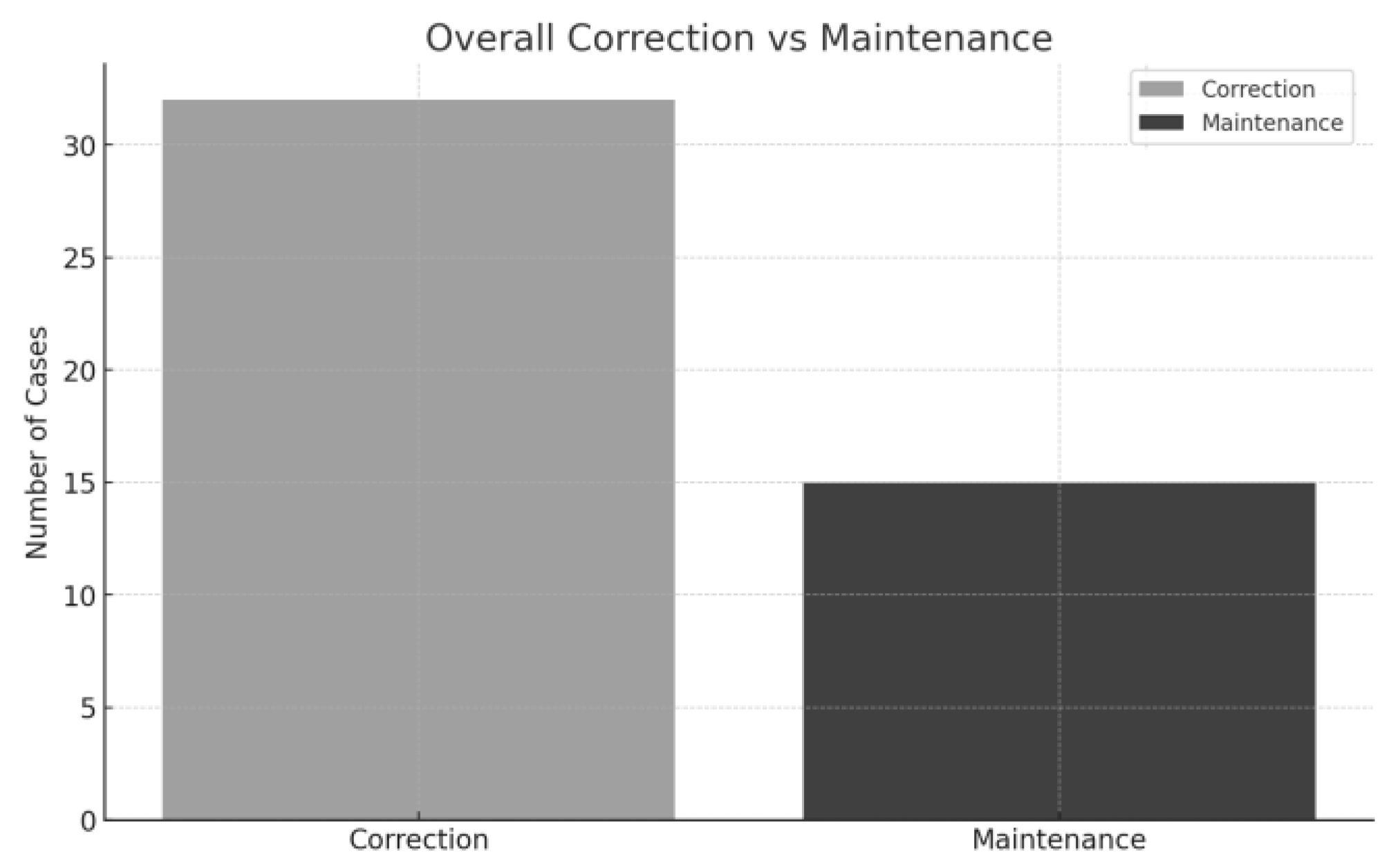
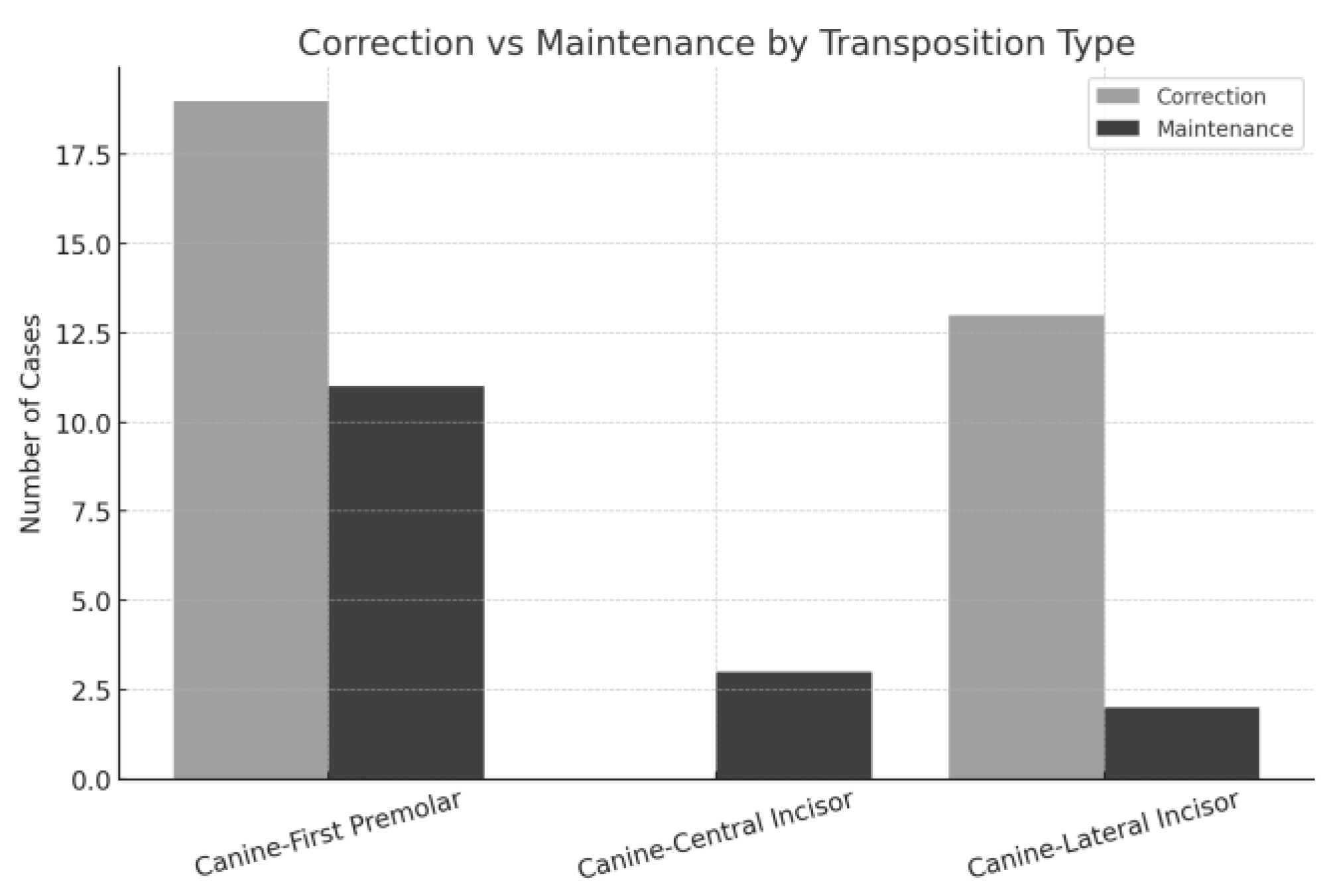
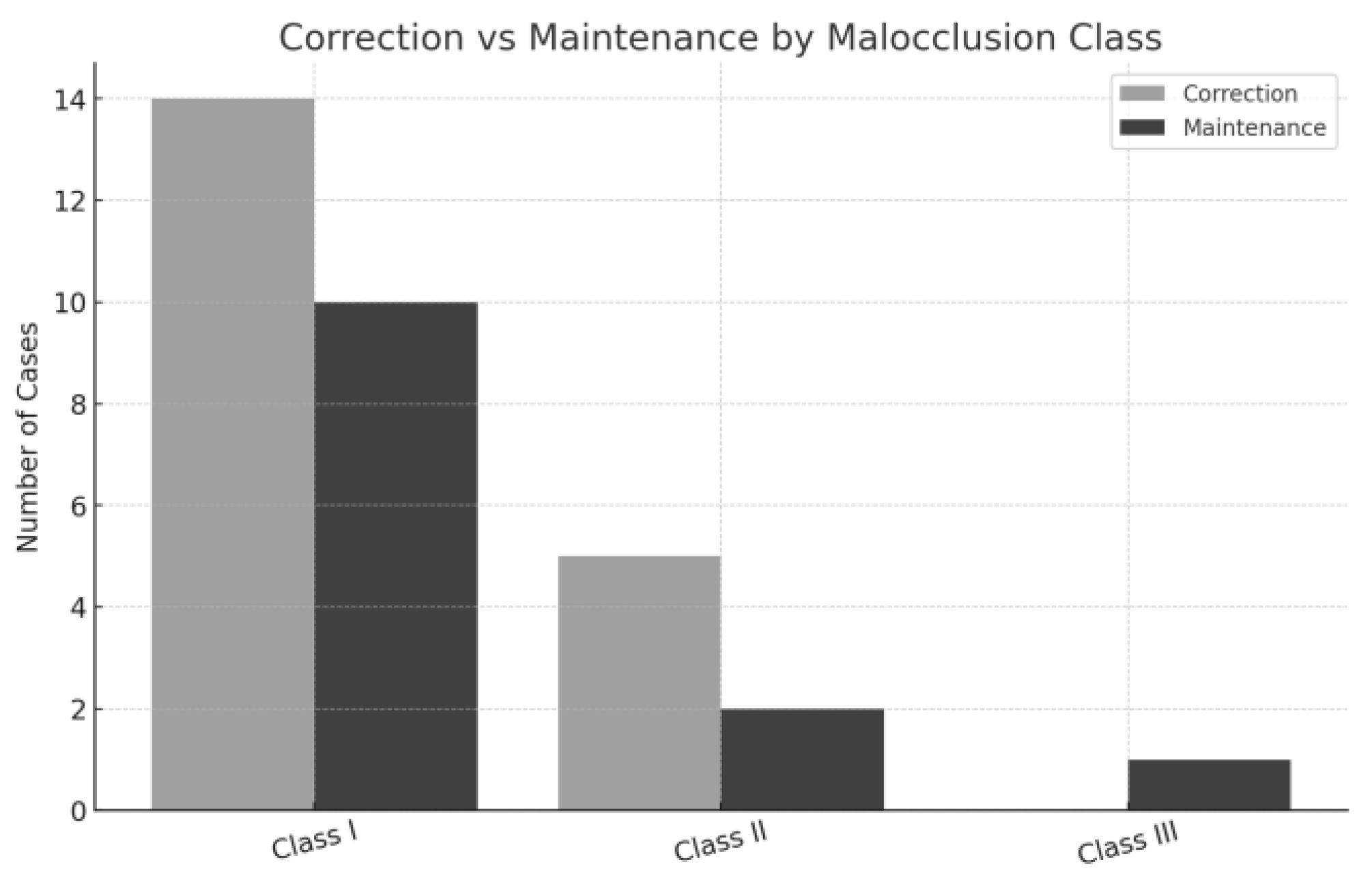
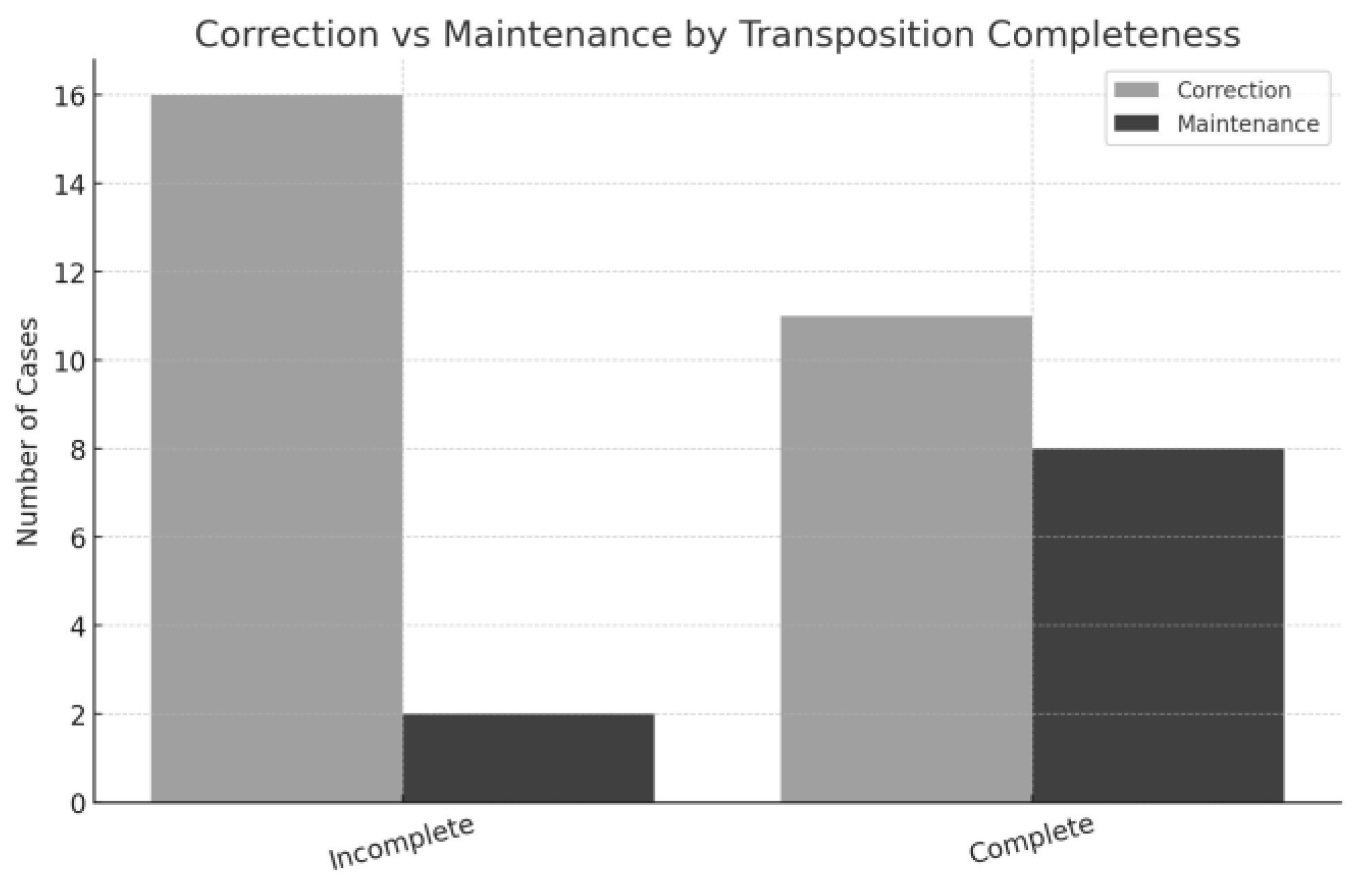
3.1.2. Data Analysis
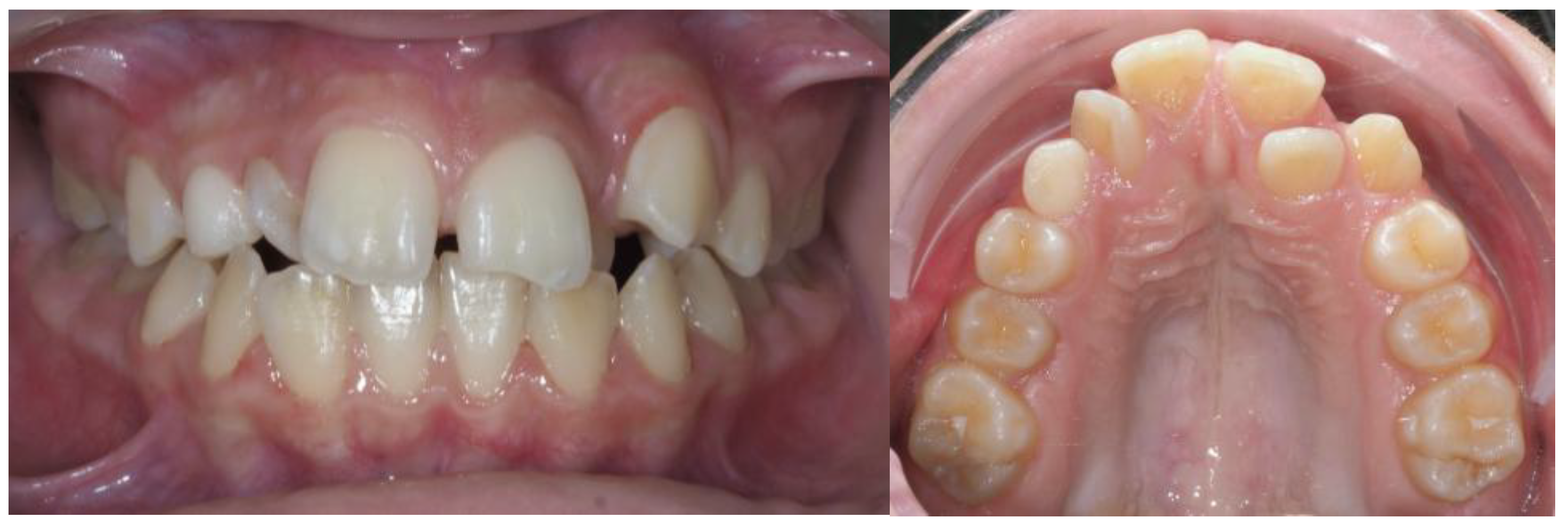
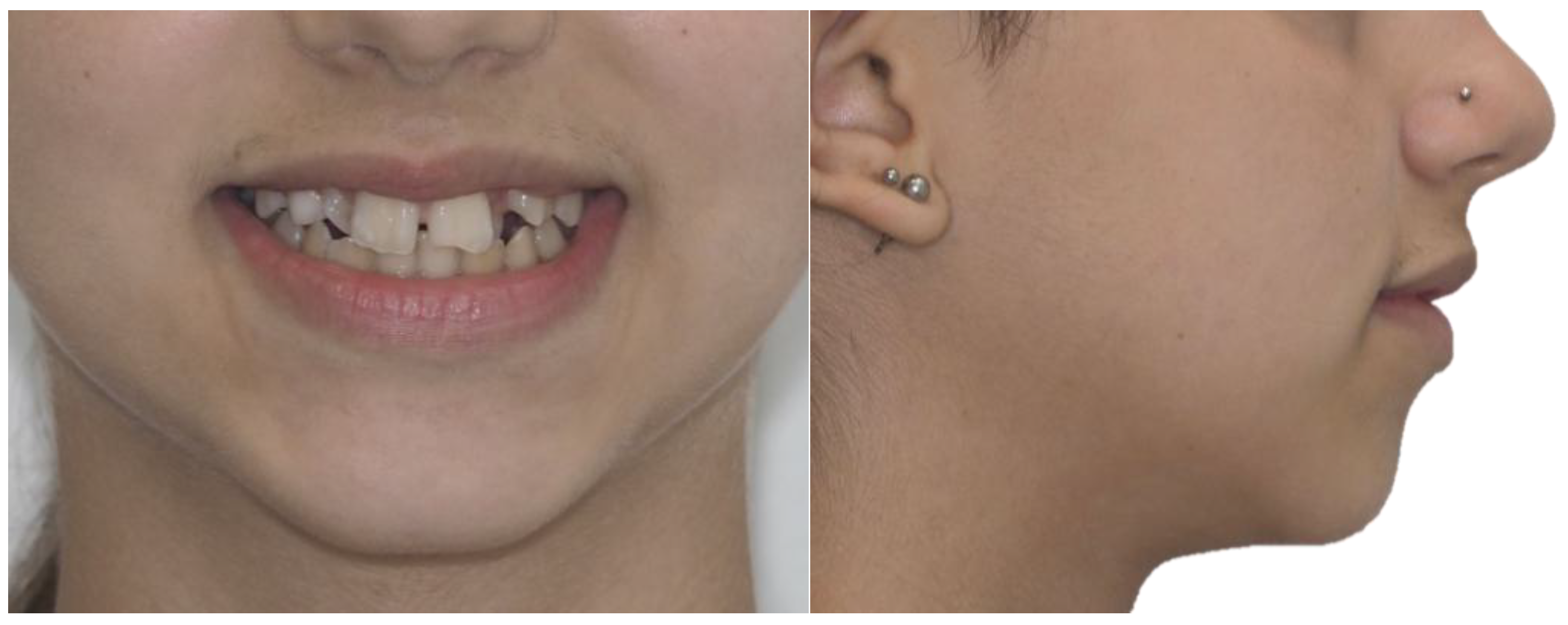
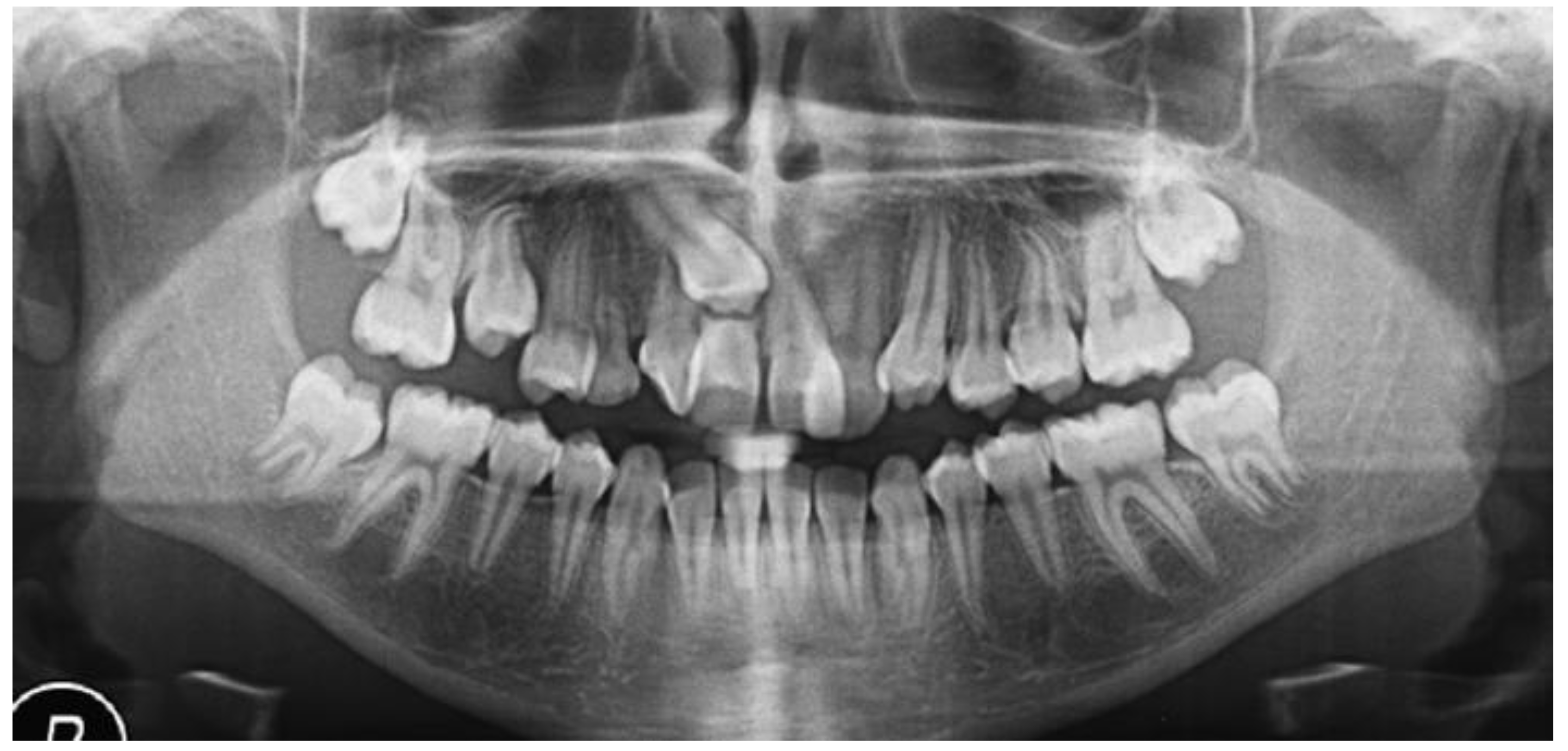
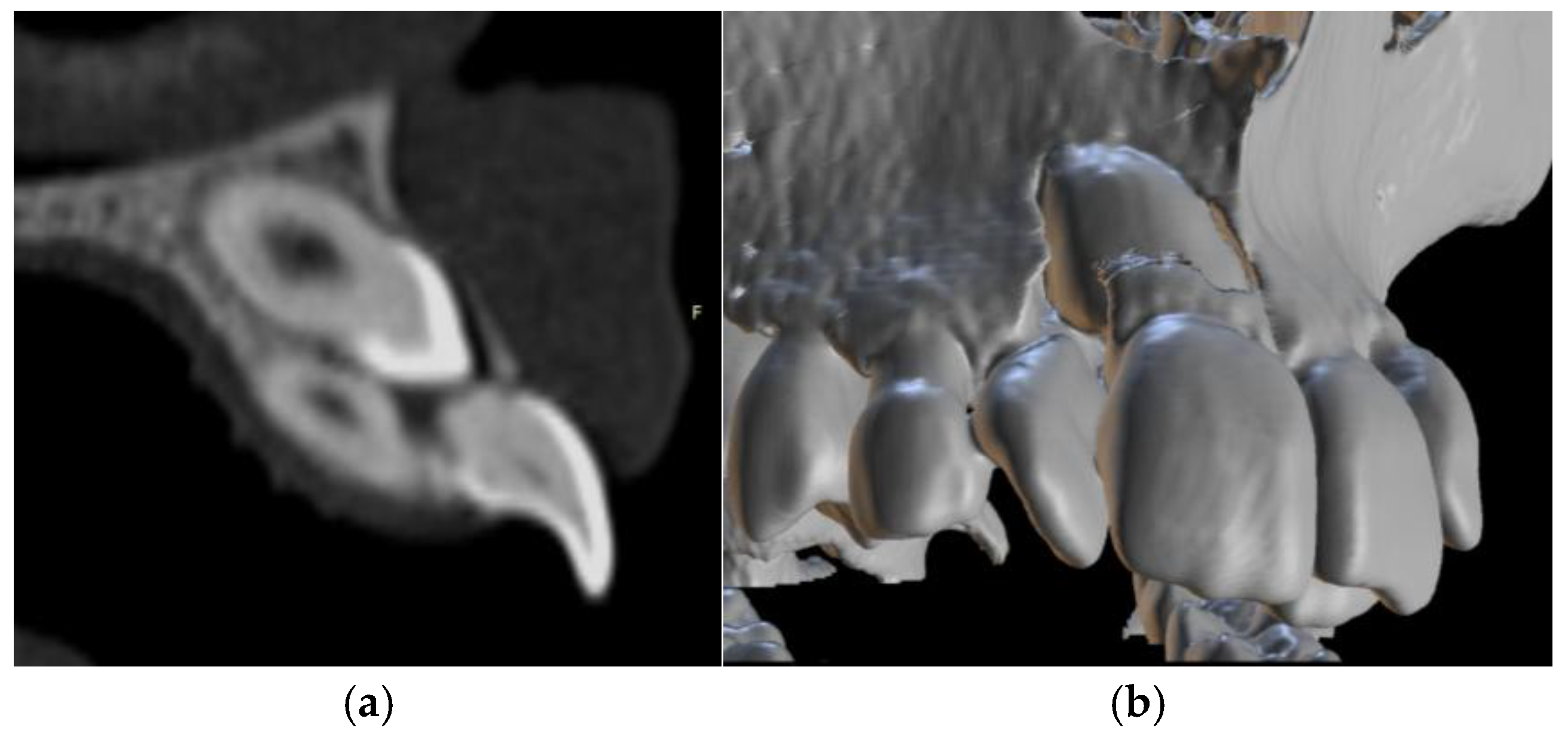
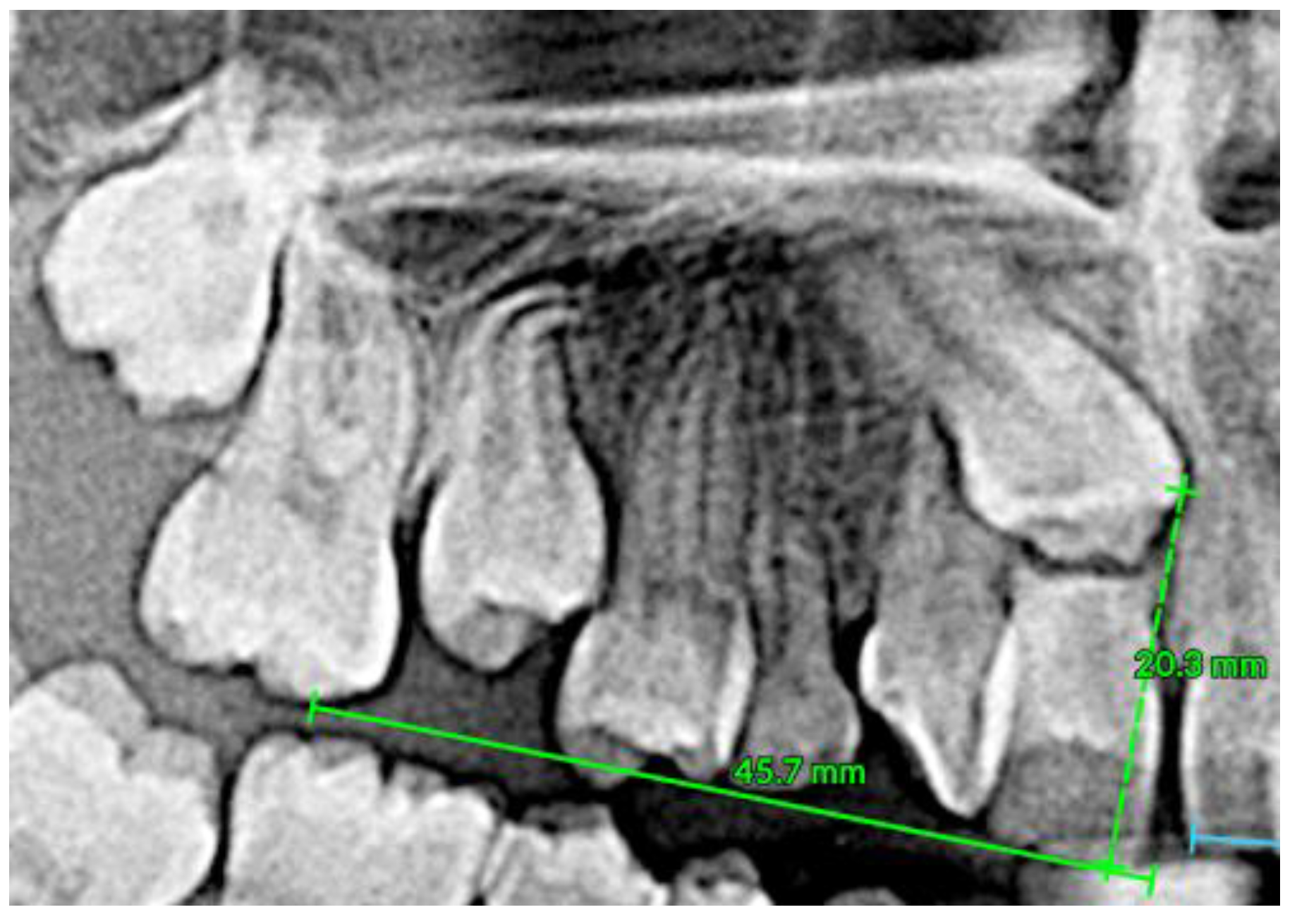
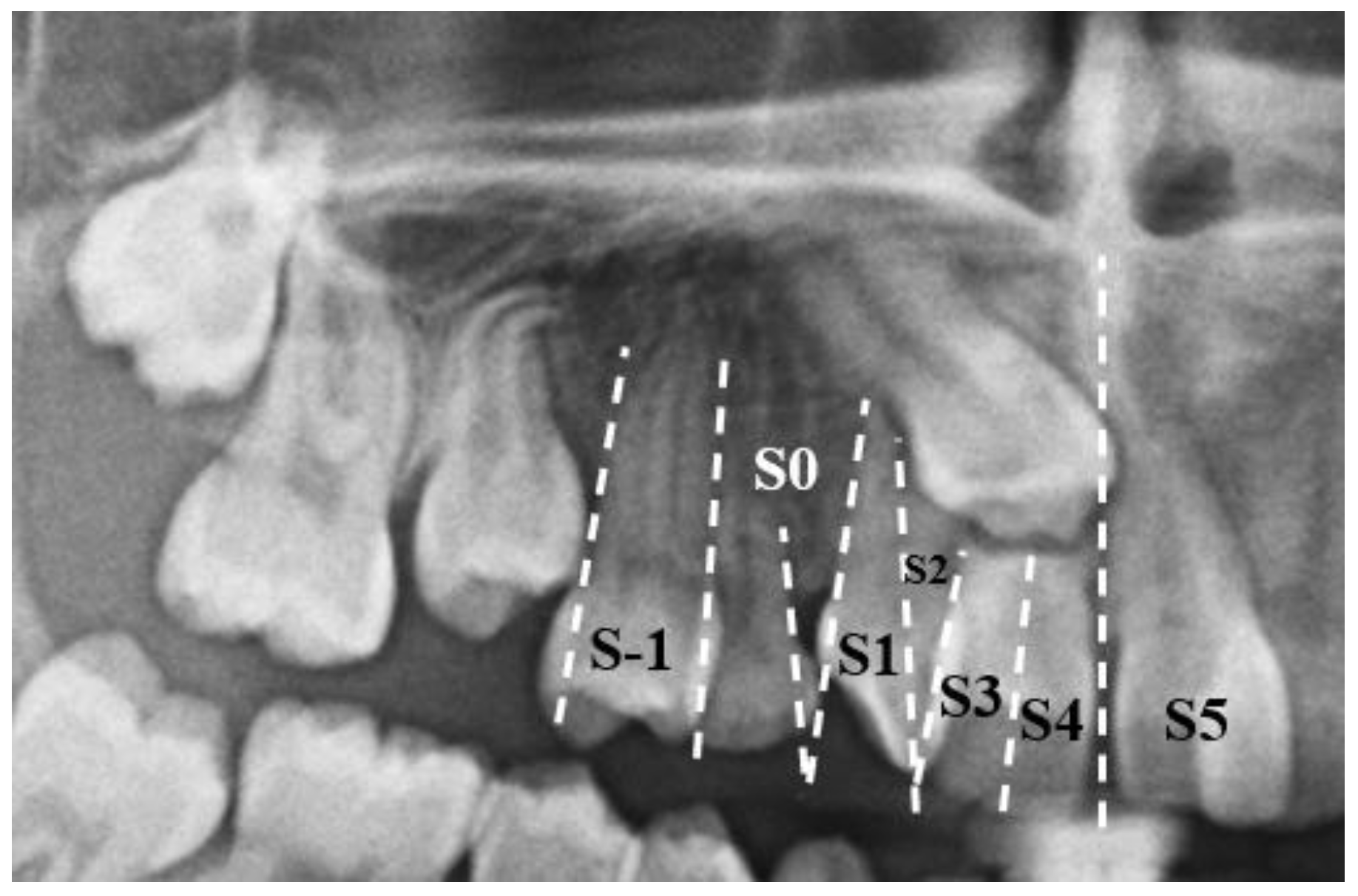
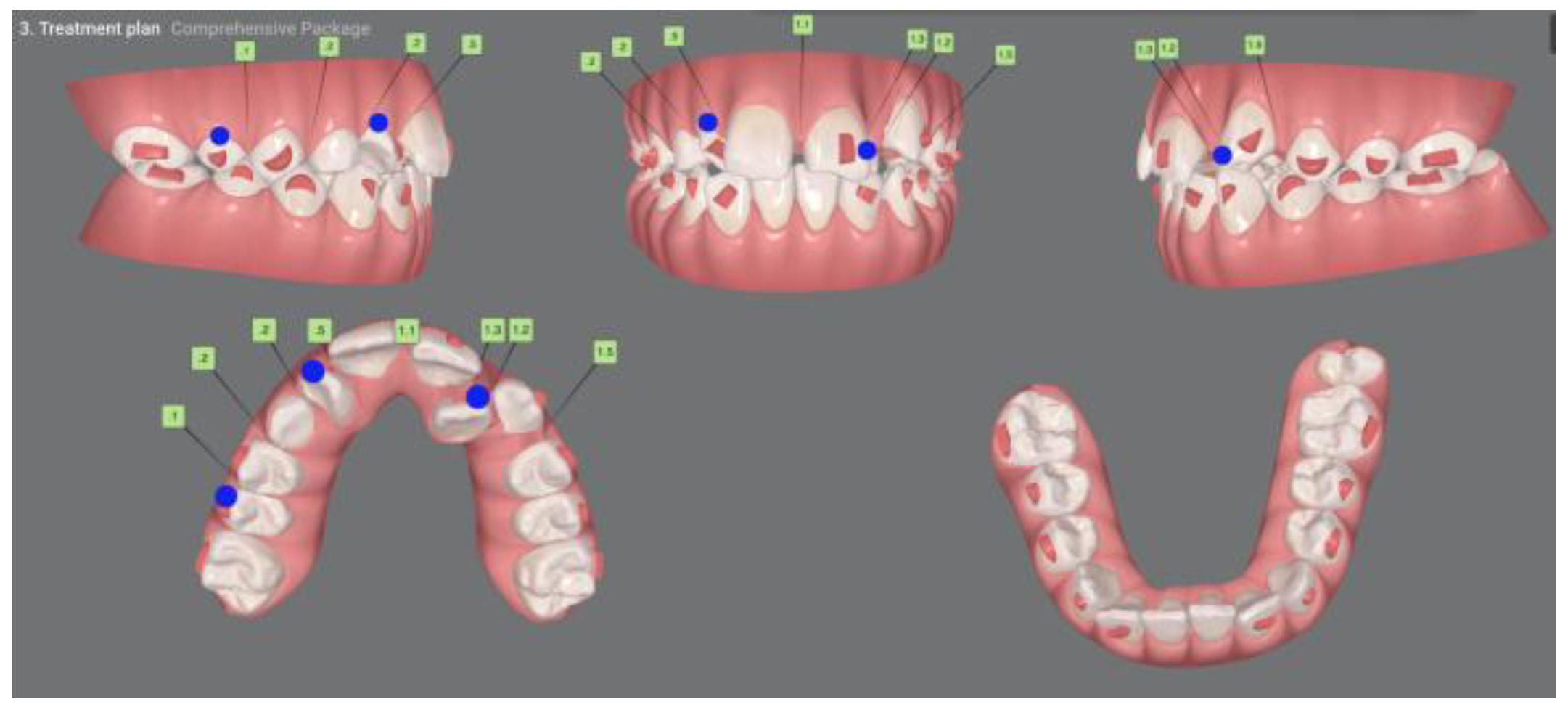
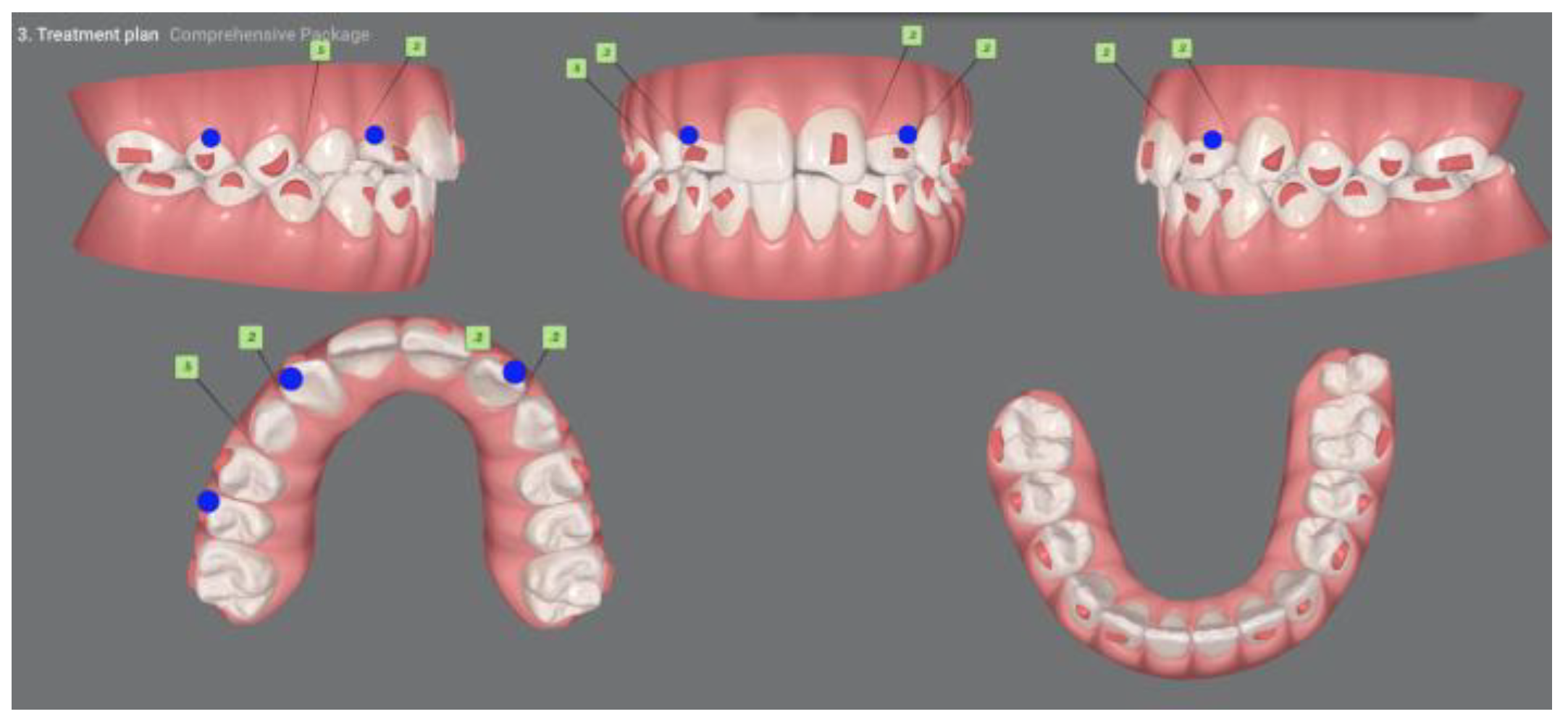
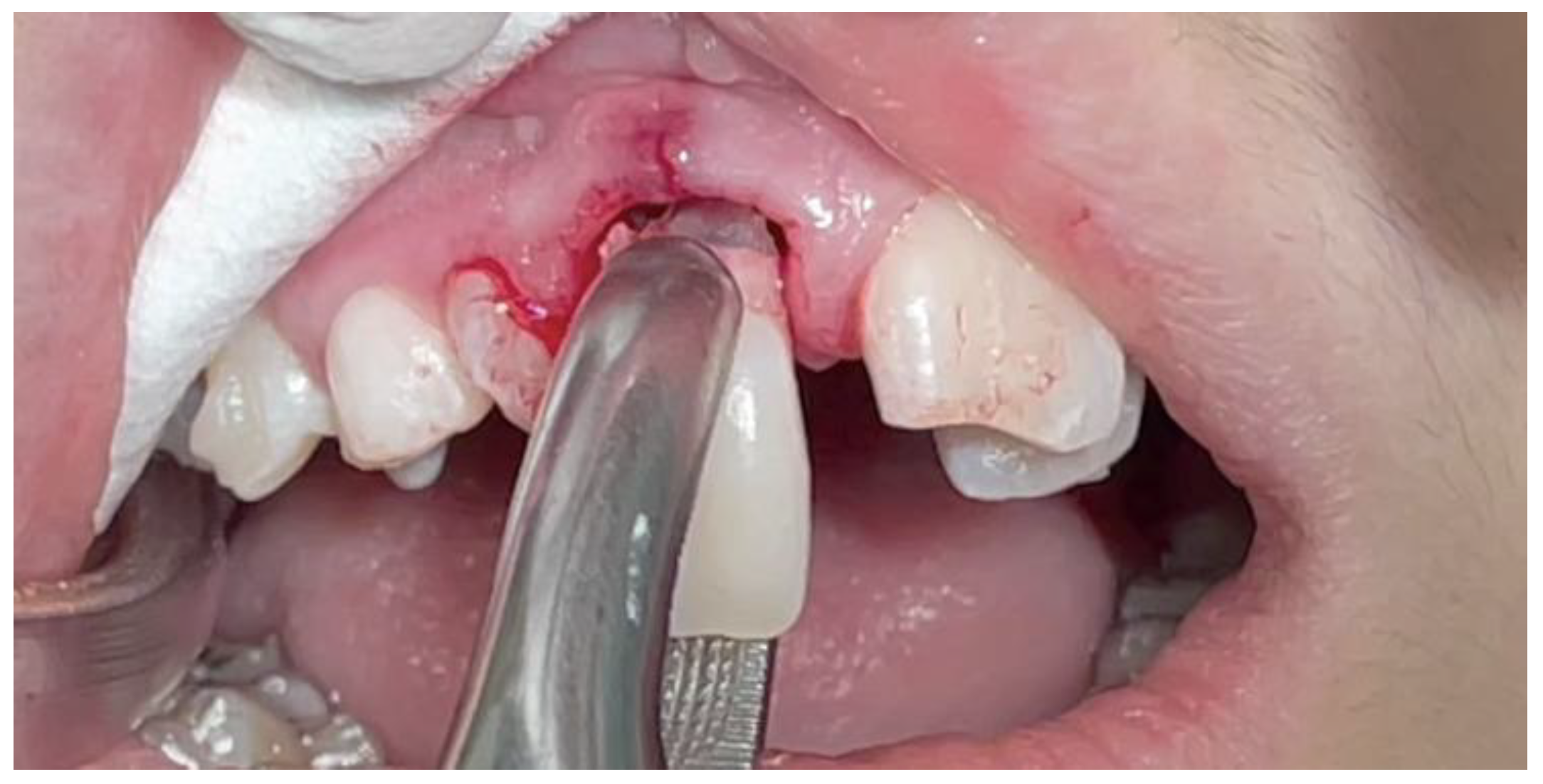
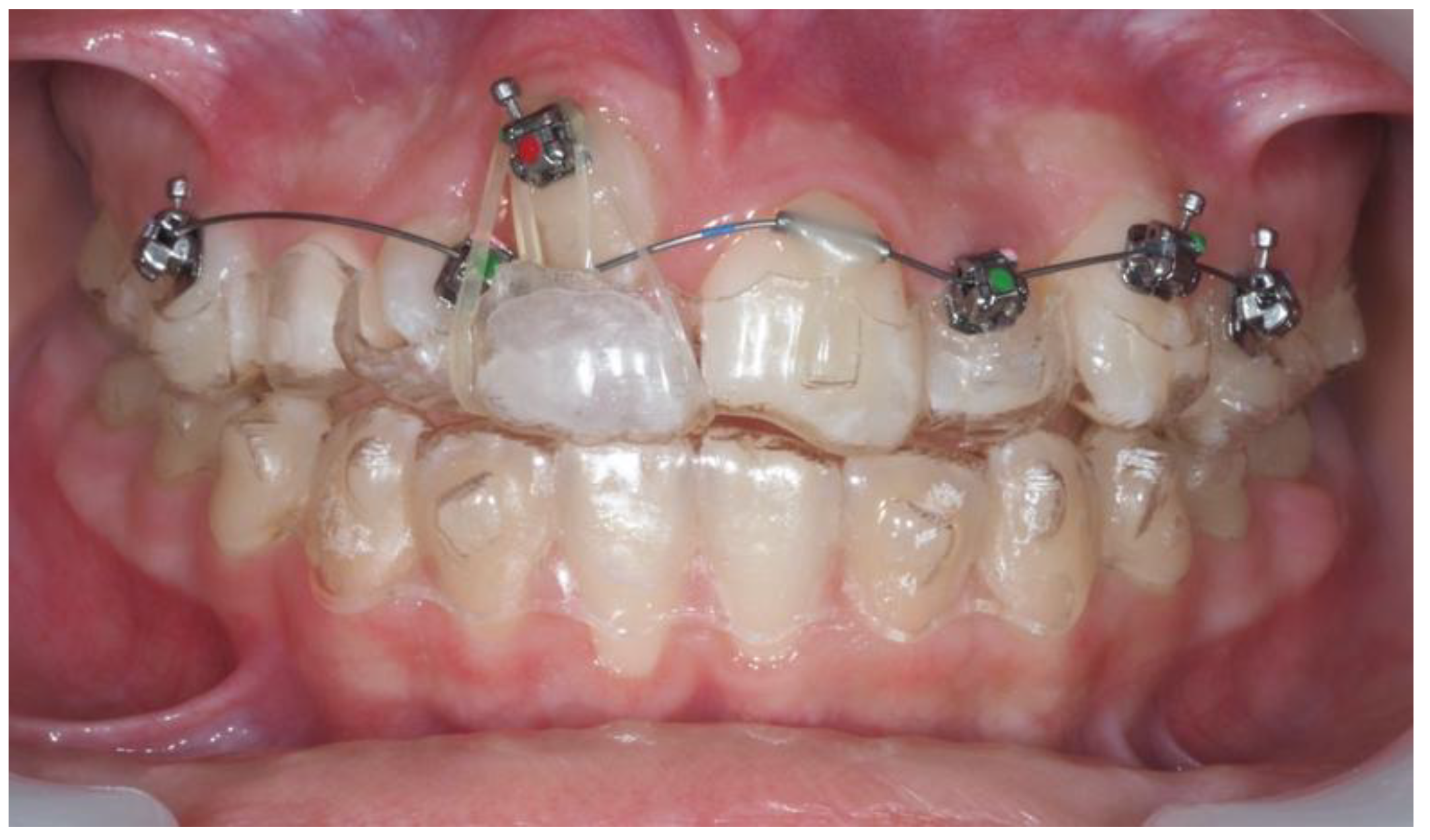
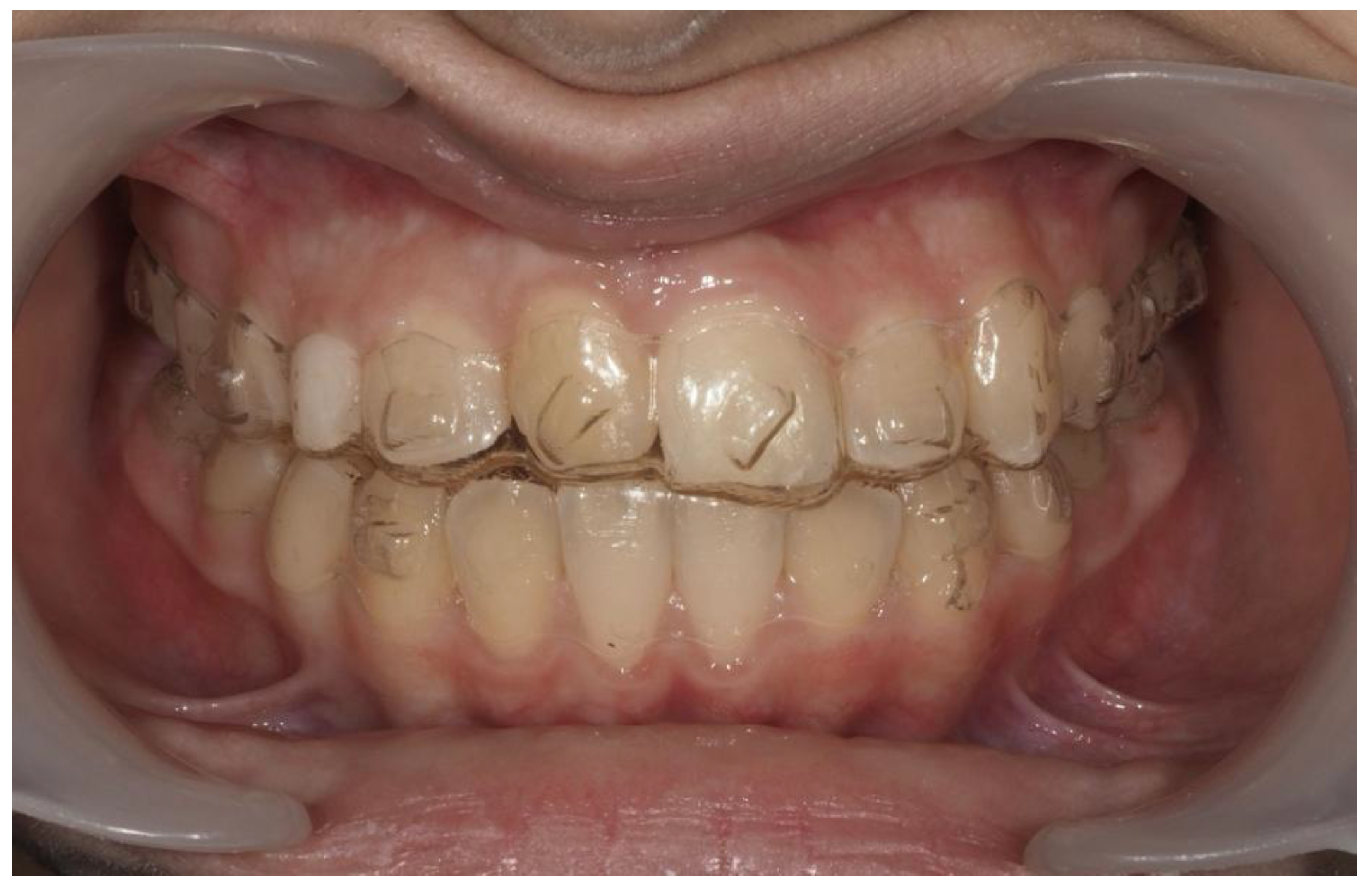
3.2. Clinical Case
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Mx.C.P1 | Maxillary canine–first premolar transposition |
| Mx.C.I2 | Maxillary canine–lateral incisor transposition |
| Mx.C.M1 | Maxillary canine–first molar transposition |
| Mx.I2.I1 | Maxillary central incisor–lateral incisor transposition |
| Mx.C.I1 | Maxillary canine–central incisor transposition |
| CBCT | Cone beam computed tomography |
| IMC | Impacted maxillary canines |
| MCT | Maxillary canine transposition |
| PICOS | Population/Patient/Problem; Intervention; Comparation; Outcomes; Study design |
References
- Thilander, B.; Bjerklin, K.; Bondemark, L. Essential Orthodontics, 1st ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, P.E. Functional Occlusion: From TMJ to Smile Design, 1st ed.; Mosby: Chantilly, VA, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-323-03371-8. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, A.H.; Pedro, F.L.M.; Bandéca, M.C.; Volpato, L.E.R.; Marques, A.T.C.; Borba, A.M.; De Musis, C.R. Prevalence of Impacted Teeth in a Brazilian Subpopulation. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2014, 15, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, S.; Peck, L. Classification of Maxillary Tooth Transpositions. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 1995, 107, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-Y.; Park, J.; Jung, J.-G.; Chae, J.-M. Forced Eruption of a Palatally Impacted and Transposed Canine with a Temporary Skeletal Anchorage Device. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2017, 151, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, C.; Lorente, P.; Perez-Vela, M.; Esquinas, C.; Lorente, T. Orthodontic Management of a Complete and an Incomplete Maxillary Canine-First Premolar Transposition. Angle Orthod. 2020, 90, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.M.D.; Oliveira, H.T.D.; Farret, M.M. Orthodontic Treatment of Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Associated with Maxillary Canine/Premolar Transposition: Case Report. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2020, 25, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potrubacz, M.I.; Tepedino, M.; Chimenti, C. Maxillary Canine–First Premolar Bilateral Transposition in a Class III Patient: A Case Report. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maspero, C.; Giannini, L.; Galbiati, G.; Feresini, M.; Farronato, G. Effect of Rapid Palatal Expansion in Early Tratment and Spontaneous Correction of Maxillary Canine-First Premolar Transposition. Minerva Stomatol. 2016, 65, 134–143. [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein, T.; Shapira, Y.; Pavlidi, A.M.; Davidovitch, M.; Blumer, S.; Schonberger, S.; Shpack, N. Canine Transposition—Prevalence, Distribution and Treatment Considerations among Orthodontic Patients. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2020, 44, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, T.J.; Palma, V.C.; Borges, A.H.; Volpato, L.E.R. Dental Transposition of Canine and Lateral Incisor and Impacted Central Incisor Treatment: A Case Report. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2014, 19, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, E.D.; Giuseppe, B.D.; Tepedino, M.; Chimenti, C. Orthodontic Management of Bilateral Maxillary Canine-First Premolar Transposition and Bilateral Agenesis of Maxillary Lateral Incisors: A Case Report. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2015, 20, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teresa, D.M.; Stefano, M.; Annalisa, M.; Enrico, M.; Vincenzo, C.; Giuseppe, M. Orthodontic Treatment of the Transposition of a Maxillary Canine and a First Premolar: A Case Report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2015, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Chang, C.H.; Roberts, W.E. Canine-Lateral Incisor Transposition: Controlling Root Resorption with a Bone-Anchored T-Loop Retraction. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 150, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, T.; Lorente, C.; Murray, P.G.; Lorente, P. Surgical and Orthodontic Management of Maxillary Canine-Lateral Incisor Transpositions. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 150, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabbout, F.; Skaf, Z.; Hlayhel, J. Maxillary Tooth Transposition: A Report of Two Cases. Int. Orthod. 2017, 15, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, M.S.; Rodríguez, R.B.; Perea, M.B.; Mendoza, B.S. Canine Transposition as an Alternative to Trauma of the Maxillary Incisors: Case Report. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2018, 23, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.A.N.; Stuani, M.B.S. Tooth Transposition: A Multidisciplinary Approach. Dent. Press J. Orthod. 2018, 23, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedalino, A.; Matias, M.; Gaziri, D.; Vieira, B.; Alves, L.; Ursi, W. Treatment of Maxillary Canine Transposition. Angle Orthod. 2020, 90, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mereani, S.; Alotaibi, A.; Bokhari, A. Orthodontic Management of a Rare Incidence Bilateral Maxillary Canine-First Premolar Transposition Using Fixed Appliance. Case Rep. Dent. 2022, 2022, 9973333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixão, M.P.M.; Moreira, K.M.S.; Navarro, R.S.; De Oliveira, S.C.M.; Imparato, J.C.P.; Reis, J.B. Root Resorption of the Permanent Central Incisor through Ectopic Eruption of the Maxillary Canine. Case Rep. Dent. 2023, 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gazzawi, A.M.Q.; Venugopal, A.; Al-Murtadha, R.H.; Adel, S.M.; Vaid, N.R. Orthodontic Management of Bilateral Ectopic and Transposed Canines Using Mini-Implant Assisted Rapid Palatal Expander and an Implant-Borne Distalizer. AJO-Clin. Companion 2023, 3, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pithon, M.M.; De Freitas, L.M.A.; De Souza, R.A.; Vargas, E.O.A.; Gasparello, G.G.; Tanaka, O.M. Treatment of Bilateral Maxillary Canine Transposition with the Use of Temporary Skeletal Anchorage Devices. AJO-Clin. Companion 2023, 3, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, E.; Neves, L.; Gontijo, S. Orthodontic Correction of Maxillary Canine-Lateral Incisor Transposition and Traction of the Impacted Central Incisor: A Case Report. AJO-Clin. Companion 2023, 3, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, M. JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Systematic Reviews and Research Syntheses (Product Review). J. Can. Health Libr. Assoc. J. Assoc. Bibl. Santé Can. 2024, 45, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Non-Randomised Studies of Interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericson, S.; Kurol, J. Early Treatment of Palatally Erupting Maxillary Canines by Extraction of the Primary Canines. Eur. J. Orthod. 1988, 10, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, A.E.; Alkhalidi, E.F.; Saeed, M.A. Shear Bond Strength between Conventional Composite Resin and Alkasite-Based Restoration Used in Sandwich Technique: An in Vitro Study. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2024, 14, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| P | Patients with at least one transposed maxillary canine |
| I | Analyze multiple treatments of maxillary canine transposition |
| C | Compare maxillary canine transposition cases |
| O | Conclude when the maxillary canine transposition should be corrected or maintained |
| S | Retrospective studies and case reports |
| Data Bases | Advanced Research | Articles |
|---|---|---|
| PubMed | (cuspid [MeSH Terms] OR (cuspid) OR (cuspids) AND (maxilla[MeSH Terms]) AND (tooth eruption, ectopic [MeSH Terms]) OR (ectopic tooth eruption) OR (tooth eruptions, ectopic) OR (ectopic tooth eruptions) | 134 |
| ScienceDirect | (ectopic tooth eruption AND maxilla AND tooth eruption, ectopic AND orthodontics) | 112 |
| Cochrane Library | (ectopic tooth eruption AND maxilla AND tooth eruption, ectopic AND orthodontics) | 15 |
| EBSCO | (cuspid) AND (maxilla) AND (tooth eruption, ectopic) OR (ectopic tooth eruption) OR (tooth eruptions, ectopic) OR (ectopic tooth eruptions) AND (orthodontics) | 170 |
| Scopus | (ectopic tooth eruption AND maxilla AND tooth eruption, ectopic AND orthodontics) | 22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pinho, T.; Amaral, R. Transposed Maxillary Canines: Narrative Review with Clinical Case Report. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060251
Pinho T, Amaral R. Transposed Maxillary Canines: Narrative Review with Clinical Case Report. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(6):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060251
Chicago/Turabian StylePinho, Teresa, and Rui Amaral. 2025. "Transposed Maxillary Canines: Narrative Review with Clinical Case Report" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 6: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060251
APA StylePinho, T., & Amaral, R. (2025). Transposed Maxillary Canines: Narrative Review with Clinical Case Report. Dentistry Journal, 13(6), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060251







