Clinical Performance of Subperiosteal Implants in the Full-Arch Rehabilitation of Severely Resorbed Edentulous Jaws: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- Population (P): Edentulous patients with severe atrophy of the jaws restored with subperiosteal implants.
- -
- Intervention (I): SPIs supporting full-arch rehabilitations placed in a single surgery.
- -
- Comparison (C): SPIs placed in two surgical procedures.
- -
- Outcome (O): Clinical performance in terms of survival and complications.
- -
- Study design (s): Clinical studies with a minimum sample size of four patients.
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
- Randomized controlled clinical trials, cohort studies, case-control studies, cross-sectional studies.
- Case series.
- SPI placement in one or two surgical phases.
- Follow-up continuing until (at least) the time of prosthetic restoration.
- Articles published up to and including 28 February 2025.
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Case reports.
- Animal studies.
- In vitro studies.
- Insufficient information about SPI placement.
2.2. Type of Intervention and Comparison
2.3. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.4. Selection Process and Screening Methods
2.5. Data Collection and Data Items
2.6. Study Risk of Bias Assessment, Reporting Bias Assessment and Certainty Assessment
2.7. Effect Measures and Synthesis Methods
3. Results
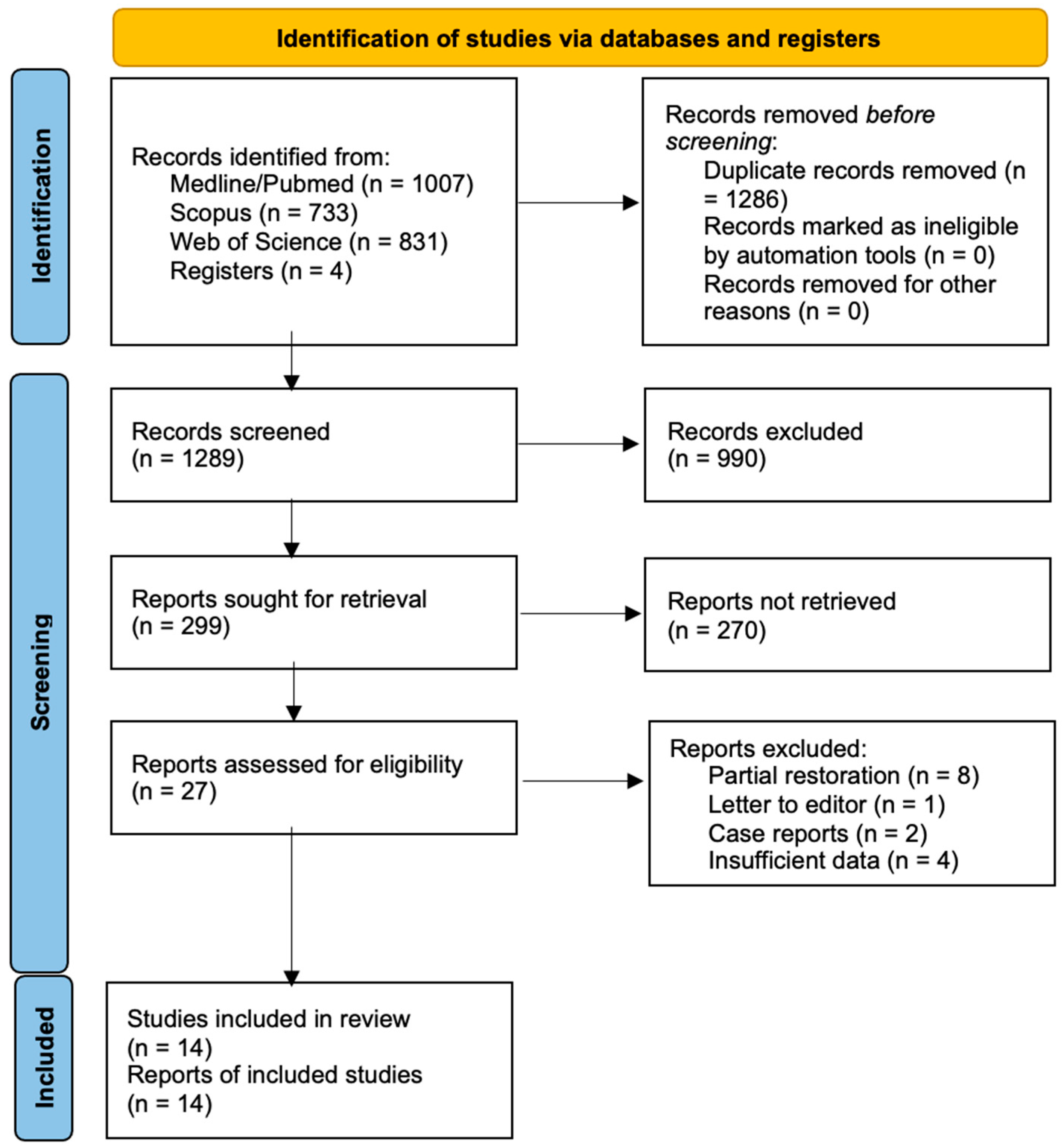
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Inter-Investigator Agreement
3.3. Study Characteristics
3.4. Synthesis of Results
3.4.1. Patient Characteristics
3.4.2. Subperiosteal Implant Survival Rate
3.4.3. Complications
3.4.4. Quality Assessment of Individual Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- -
- SPIs would appear a good option for full-arch rehabilitation of severely resorbed edentulous jaws. The studies included in this SR obtained high survival rates and a low rate of complications, especially for those SPIs placed in a single surgery.
- -
- It would appear that applying CAD-CAM technology to the design of these structures, and so reducing the procedure to a single surgery, improves outcomes and minimizes complications.
- -
- Nevertheless, we should interpret the results of this SR with some caution; well-conceived clinical trials—ideally randomized clinical trials with adequate sample sizes and longer follow-up periods—are needed to confirm our findings.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GBR | Guided bone regeneration |
| SPIs | Subperiosteal implants |
| SR | Systematic review |
Appendix A
| Studies | Reason for Exclusion |
|---|---|
| Paris et al., 1978; Linkow et al., 1999 Aras et al., 2005; Claffey et al., 2015 | Insufficient data |
| Sirvu et al., 2003; Nguyen et al., 2018 | Case report |
| Knott et al., 2010 | Letter to editor |
| Kay et al., 1987; Minichetti et al., 2003 Gellrich et al., 2017; Cerea et al., 2018; Mittal et al., 2019; Mangano et al., 2020; Onică N et al., 2024; Zielinski R et al., 2025 | Partial restoration |
References
- Cerea, M.; Dolcini, G.A. Custom-made direct metal laser sintering titanium subperiosteal implants: A retrospective clinical study on 70 patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 5420391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellrich, N.C.; Rahlf, B.; Zimmerer, R.; Pott, P.C.; Rana, M. A new concept for implant-borne dental rehabilitation; how to overcome the biological weak-spot of conventional dental implants? Head Face Med. 2017, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Martínez, P.; Quispe-Lopez, N.; Montesdeoca-García, N.; Esparza-Gómez, G.; Cebrián-Carretero, J.L. Maxillary reconstruction with subperiosteal implants in a cancer patient: A one-year follow-up. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2022, 14, e293–e297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, I.A.; Monje, A. Guided bone regeneration in alveolar bone reconstruction. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 31, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starch-Jensen, T.; Becktor, J.P. Maxillary alveolar ridge expansion with split-crest technique compared with lateral ridge augmentation with autogenous bone block graft: A systematic review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, A.; Green, J. Sinus lift procedures: An overview of current techniques. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 56, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano-Serrabona, J.; Sánchez-Garcés, M.A.; Sánchez-Torres, A.; Gay-Escoda, C. Alveolar distraction osteogenesis for dental implant treatments of the vertical bone atrophy: A systematic review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2019, 24, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; De Neef, B.; Loomans, N.A.; Mommaerts, M.Y. Guidelines for the use of resection guides for subperiosteal maxillary implants in cases of terminal dentition—A novel approach. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 10, 467–471. [Google Scholar]
- Gellrich, N.C.; Zimmerer, R.M.; Spalthoff, S.; Jehn, P.; Pott, P.C.; Rana, M.; Rahlf, A. A customised digitally engineered solution for fixed dental rehabilitation in severe bone defifiency: A new innovative line extensión in implant dentistry. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrián Carretero, J.L.; Del Castillo Pardo de Vera, N.; Montesdeoca García, P.; Garrido Martínez, M.M.; Pampín Martínez, I.; Aragón Niño, I.; Navarro Cuéllar, C.; Navarro Cuéllar, I. Virtual surgical planning and customized subperiosteal titanium maxillary implant (CSTMI) for three-dimensional reconstruction and dental implants of maxillary defects after oncological resection: Case series. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro-Pons, M.; Arias-Gallo, J.; Margarit-Pérez, L.; Demaría Martínez, G.; Cidad Vicario, A. Implantes subperiósticos personalizados para la rehabilitación complete del maxilar superior atrófico. Revisión de una serie clínica de 8 casos. Rev. Esp. Cir. Oral Maxilofac. 2021, 43, 140–148. [Google Scholar]
- Claffey, N.; Bashara, H.; O’Reilly, P.; Polyzois, I. Evaluation of new bone formation and osseointegration around subperiosteal titanium implants with histometry and nanoindentation. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2015, 30, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillo, G.; Carnicero, A.; Perera, R. Submodelling approach to screw-to-bone interaction in additively manufactured subperiosteal implant structures. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 39, e3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Zheng, L.; Ji, P.; Wan, H.; Zhou, N.; Liu, R.; Wang, C. Additively manufactured lattice-like subperiosteal implants for rehabilitation of the severely atrophic ridge. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnicero, A.; Peláez, A.; Restoy-Lozano, A.; Jacquott, I.; Perera, R. Improvement of an additively manufactured subperiosteal implant structure design by finite elements based topological optimization. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehn, P.; Spalthoff, S.; Korn, P.; Stoetzer, M.; Gercken, M.; Gellrich, N.C.; Rahlf, B. Oral health-related quality of life in tumour patients treated with patient-specific dental implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 49, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Petterson, J. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 25 June 2023).
- McPheeters, M.L.; Kripalani, S.; Kripalani, N.B. Closing the quality gap: Revisiting the state of the science (vol. 3: Quality improvement interventions to address health disparities). Evid. Rep. Technol. Assess. 2012, 208, 1–475. [Google Scholar]
- Munn, Z.; Barker, T.H.; Moola, S.; Tufanaru, C.; Stern, C.; McArthur, A.; Stephenson, M.; Aromataris, E. Methodological quality of case series studies: An introduction to the JBI critical appraisal tool. JBI Evid. Synth. 2020, 18, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Borre, C.; Rinaldi, M.; De Neef, B.; Loomans, N.A.J.; Nout, E.; Van Doorne, L. Patient-and clinician-reported outcomes for the additively manufactures sub-periosteal jaw implant (AMSJI) in the maxilla: A prospective multicentre one-year follow-up study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 51, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, R.T.; Linkow, R.L.; Tom, J.F. The mandibular subperiosteal implant denture: A prospective survival study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1994, 71, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomquist, D.S. Long-term results of subperiosteal implants combined with cancellous bone grafts. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1982, 40, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.J.; Hansen, P.A. A descriptive 18-year retrospective review of subperiosteal implants for patients with severely atrophied edentulous mandibles. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 94, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.; Michel, J.D.; Moore, D.J. A twenty-year evaluation of subperiosteal implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 49, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodine, R.L.; Yanase, R.T.; Bodine, A. Forty years of experience with subperiosteal implant dentures in 41 edentulous patients. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1996, 75, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, J.H.; Yanase, R.T.; Bodine, R.L. The mandibular subperiosteal implant denture: A fourteen-year study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1988, 60, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkow, L.I.; Ghalili, R. Critical design errors in maxillary subperiosteal implants. J. Oral Implantol. 1998, 24, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkow, L.I.; Wagner, J.R.; Chanavaz, M. Tripodal mandibular subperiosteal implant: Basic sciences, operational procedures, and clinical data. J. Oral Implantol. 1998, 24, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rams, T.E.; Balkin, B.E.; Roberts, T.W.; Molzan, A. Microbiological aspects of human mandibular subperiosteal dental implants. J. Oral Implantol. 2013, 34, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawy, S.M.; Elgamal, E.M.; Ahmed, W.M.; El-Daker, M.A.; Hegazy, S.A. Polyetheretherketone subperiosteal implant retaining a maxillary fixed prosthesis: A case series. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2024, 132, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viera, A.J.; Garrett, J.M. Understanding interobserver agreement: The kappa statistic. Fam. Med. 2005, 37, 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, R.; Henningsen, A.; Jung, O.; Heiland, M.; Hammächer, C.; Stein, J.M. Definition, etiology, prevention and treatment of peri-implantitis—A review. Head. Face Med. 2014, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, M.S.; Keys, W.; Richards, D. Long-term (10-year) dental implant survival: A systematic review and sensitivity meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2019, 84, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misch, C.E.; Perel, M.L.; Wang, H.L.; Sammartino, G.; Galindo-Moreno, P.; Trisi, P.L. Implant success, survival, and failure: The International Congress of Oral Implantologists (ICOI) Pisa Consensus Conference. Implant. Dent. 2008, 17, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bäumer, D.; Ozga, A.K.; Körner, G.; Bäumer, A. Patient satisfaction and oral health-related quality of life 10 years after implant placement. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáez-Alcaide, L.M.; Cortés-Bretón-Brinkmann, J.; Sánchez-Labrador, L.; Pérez-González, F.; Forteza-López, A.; Molinero-Mourelle, P.; López-Quiles, J. Patient-reported outcomes in patients with severe maxillary bone atrophy restored with zygomatic implant-supported complete dental prostheses: A systematic review. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2022, 80, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, E.M.; Padovan, L.E.; De Mattias Sartori, I.A.; Ribeiro, P.D., Jr.; Gomes de Souza Carvalho, A.C.; Goiato, M.C. Evaluation of satisfaction of patients rehabilitated with zygomatic fixtures. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Muñoz, D.; Obrador-Aldover, C.; Zubizarreta-Macho, A.; González Menéndez, H.; Lorrio Castro, J.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D. Survival rate and prosthetic and sinus complications of zygomatic dental implants for the rehabilitation of the atrophic edentulous maxilla: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biology 2021, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, K.; Wang, F.; Huang, W.; Davó, R.; Wu, Y. Quad zygomatic implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis on survival and complications. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2021, 36, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herce-López, J.; Del Canto Pingarrón, M.; Tofé-Povedano, A. Customized subperiosteal implants for the rehabilitation of atrophic jaws: A consensus report and literature review. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, R.; Okulski, J.; Piechaczek, M. Five-year comparative study of zygomatic and subperiosteal implants: Clinical outcomes, complications, and treatment strategies for Ssvere maxillary atrophy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surovas, A. A digital workflow for modeling of custom dental implants. 3D Print. Med. 2019, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, G.; Khare, G.; Garg, R.; Rathi, A.; Sharma, S.; Raghaw, D. Efficacy of hybrid implants in oral and maxillofacial surgery: A clinical prospective study. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 10, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onică, N.; Budală, D.G.; Baciu, E.R. Long-term clinical outcomes of 3D-printed subperiosteal Tttanium implants: A 6-year follow-up. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, L.; Angelis, F.; Orefici, A.; Cielo, A. Metals used in maxillofacial surgery. Oral Implantol. 2017, 9, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Eguia, A.; Staudigl, C.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Clinical performance of additively manufactured subperiosteal implants: A systematic review. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2024, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author Year Journal | Study | Patient | Follow-Up | Implant Number Position | Nº of Interventions | Time and Type of Prosthesis Loading | Survival Rate | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Van der Borre et al. [20] 2022 Int. J. Oral Maxillofac | Prospective | 15 (8 ♂ 7 ♀) | 12 months | 30 implants (2 per maxilla) 15 maxillae | 1 | Immediate loading Definitive prothesis/2 months | 100% | No complications |
| Rinaldi et al. [8] 2020 Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. | Prospective | 15 (7 ♂ 8 ♀) (mean age 61 years) | 8–19 months | 15 maxillae | 1 | - | 100% | 2 implant exposures |
| Chamorro-Pons et al. [11] 2021 Rev. Esp. Cir. Oral Maxilofac | Case series | 8 (2 ♂ 6 ♀) (59–82 years) | 4–36 months | 8 maxillae | 1 | Immediate loading Definitive prothesis/1.5–2 months | 100% | 1 gingival inflammation |
| Cebrian-Carretero et al. [10] 2022 J. Clin. Med. | Case series Retrospective | 4 (3 ♂ 1 ♀) (66.2 years) | 9–38 months (medium 18 months) | 4 maxillae | 1 | Early loading/14 days Definitive prothesis/1.5 months | 100% | No complications |
| Elsawy et al. [30] 2022 J. Prosthet. Dent. | Case series | 4 (2 ♂ 2 ♀) (65–75 years) | 12 months | 4 maxillae | 1 | Early loading/After healing and remodeling of the soft tissue Definitive prothesis/12 months | 100% | 1 implant exposure |
| Author Year Journal | Study | Patient | Follow-Up | Implant Number Position | Number of Interventions | Time and Type of Prosthesis Loading | Survival Rate | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moore et al. [23] 2004 J. Prosthet. Dent. | Retrospective | 40 (7 ♂ 33 ♀) | 18 years | 40 mandibles | 2 | - | 97.5% | No complications |
| Young et al. [24] 1983 J. Prosthet. Dent. | Retrospective | 25 (-) | 20 years | 25 mandibles | 2 | - | 72.7% | 3 new prostheses |
| Yanase et al. [21] 1994 J. Prosthet. Dent. | Prospective | 81 (18 ♂ 63 ♀) (39–77 years) 53 years | 21 years | 81 mandibles | 2 | - | 60% | - |
| Bloomquist et al. [22] 1982 J. Oral Maxillofac Surg. | Prospective | 23 (-) | 4.5 years | 23 mandibles | 2 | - | 84.2% | - |
| Bodine et al. [25] 1996 J. Prosthet. Dent. | Retrospective | 41 (19 ♂ 22 ♀) | 20 years | 41 mandibles | 2 | - | 66% | 10 exposures 3 epuli 5 sequestration of bone screw 13 gingival inflammation |
| Bailey et al. [26] 1988 J. Prosthet. Dent. | Retrospective | 74 (17 ♂ 57 ♀) (53 years) | 14 years | 74 mandibles | 2 | - | 86% | 38 paresthesias 24 exposures |
| Linkow et al. [27] 1998 J. Oral Implantol. | Case series | 317 (-) | 3 years | 317 mandibles | 2 | - | 98.7% | 7 paresthesias |
| Linkow et al. [28] 1998 J. Oral Implantol. | Case series | 300 (-) | 12 years | 300 maxillae | 2 | - | 93% | - |
| Rams et al. [29] 2013 J. Oral Implantol. | Case series | 11 (2 ♂ 9 ♀) (64–83 years) | 10–13 years (3 subjects) 9–22 years (8 subjects) | 11 mandibles | 2 | - | 100% | 3 patients with periimplantitis |
| Selection | Comparability | Outcome | Number of Stars (Out of 8) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | C1 | C2 | E1 | E2 | E3 | |
| Van der Borre et al. [20] | ★ | 0 | ★ | ★ | ★ | 0 | 0 | 0 | ★ | 5 |
| Rinaldi et al. [8] | ★ | 0 | ★ | ★ | ★ | 0 | 0 | 0 | ★ | 5 |
| Moore et al. [23] | ★ | 0 | ★ | ★ | ★ | 0 | 0 | ★ | ★ | 6 |
| Young et al. [24] | ★ | 0 | 0 | ★ | ★ | 0 | 0 | ★ | 0 | 4 |
| Yanase et al. [21] | ★ | 0 | ★ | ★ | ★ | 0 | 0 | ★ | ★ | 6 |
| Bloomquist et al. [22] | 0 | 0 | 0 | ★ | ★ | 0 | 0 | ★ | ★ | 4 |
| Bodine et al. [25] | ★ | 0 | ★ | ★ | ★ | 0 | 0 | ★ | ★ | 6 |
| Bailey et al. [26] | 0 | 0 | ★ | ★ | ★ | 0 | 0 | ★ | ★ | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez-Labrador, L.; Bazal-Bonelli, S.; Pérez-González, F.; Beca-Campoy, T.; Cobo-Vázquez, C.M.; Cortés-Bretón Brinkmann, J.; Martínez-González, J.M. Clinical Performance of Subperiosteal Implants in the Full-Arch Rehabilitation of Severely Resorbed Edentulous Jaws: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060240
Sánchez-Labrador L, Bazal-Bonelli S, Pérez-González F, Beca-Campoy T, Cobo-Vázquez CM, Cortés-Bretón Brinkmann J, Martínez-González JM. Clinical Performance of Subperiosteal Implants in the Full-Arch Rehabilitation of Severely Resorbed Edentulous Jaws: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis. Dentistry Journal. 2025; 13(6):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060240
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez-Labrador, Luis, Santiago Bazal-Bonelli, Fabián Pérez-González, Tomás Beca-Campoy, Carlos Manuel Cobo-Vázquez, Jorge Cortés-Bretón Brinkmann, and José María Martínez-González. 2025. "Clinical Performance of Subperiosteal Implants in the Full-Arch Rehabilitation of Severely Resorbed Edentulous Jaws: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis" Dentistry Journal 13, no. 6: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060240
APA StyleSánchez-Labrador, L., Bazal-Bonelli, S., Pérez-González, F., Beca-Campoy, T., Cobo-Vázquez, C. M., Cortés-Bretón Brinkmann, J., & Martínez-González, J. M. (2025). Clinical Performance of Subperiosteal Implants in the Full-Arch Rehabilitation of Severely Resorbed Edentulous Jaws: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis. Dentistry Journal, 13(6), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj13060240






