Retrospective Longitudinal Study on Changes in Atmospheric Pressure as a Predisposing Factor for Odontogenic Abscess Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckert, A.W.; Just, L.; Wilhelms, D.; Schubert, J. Dentogenic infections-part I: The significance of bacterial isolation of dentogenic infections under routineous conditions. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 1946 2012, 162, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, S.H.; Ha-Phuoc, A.-K.; Mohr, C. Treatment of OA: Comparison of Primary and Secondary Removal of the Odontogenic Focus and Antibiotic Therapy. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 24, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mücke, T.; Dujka, N.; Ermer, M.A.; Wolff, K.D.; Kesting, M.; Mitchell, D.A.; Ritschl, L.; Deppe, H. The Value of Early Intraoral Incisions in Patients with Perimandibular Odontogenic Maxillofacial Abscesses. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 220–223. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?q=Mucke%2C+T.%2C+et+al.%2C+The+value+of+early+intraoral+incisions+in+patients+with+perimandibular+odontogenic+maxillofacial+abscesses.+J+Craniomaxillofac+Surg%2C+2015.+43(2)%3A+p.+220-3.&rlz=1C1KNTJ_enHR996HR996&oq=Mucke%2C+T.%2C+et+al.%2C+The+value+of+early+intraoral+incisions+in+patients+with+perimandibular+odontogenic+maxillofacial+abscesses.+J+Craniomaxillofac+Surg%2C+2015.+43(2)%3A+p.+220-3.&aqs=chrome..69i57.1765j0j4&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 (accessed on 6 November 2022). [PubMed]
- Heim, N.; Faron, A.; Wiedemeyer, V.; Reich, R.; Martini, M. Microbiology and Antibiotic Sensitivity of Head and Neck Space Infections of Odontogenic Origin. Differences in Inpatient and Outpatient Management. J. Cranio Maxillo Fac. Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Assoc. 2017, 45, 1731–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttger, S.; Lautenbacher, K.; Domann, E.; Howaldt, H.-P.; Attia, S.; Streckbein, P.; Wilbrand, J.-F. Indication for an Additional Postoperative Antibiotic Treatment after Surgical Incision of Serious OA. J. Cranio Maxillo Fac. Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Assoc. 2020, 48, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashcooli, M.; Salimpour, M.R.; Shirani, E. Heat Transfer Analysis of Skin during Thermal Therapy Using Thermal Wave Equation. J. Therm. Biol. 2017, 64, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlfinger, O.; Graup, B. The effect of weather on OA (author’s transl). MMW Munch. Med. Wochenschr. 1981, 123, 165–168. [Google Scholar]
- Seemann, R.; Svabik, O.; Orlik, A.; Figl, M.; Fischer, M.B.; Schicho, K.; Wutzl, A.; Forster, J.; Jesch, P.; Perisanidis, C.; et al. The Frequency of Dental Abscesses Increases in Periods of Low Barometric Pressure. J. Cranio Maxillo Fac. Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Assoc. 2015, 43, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.O.; Feifel, H.; Bucher, K.; Reineke, T.; Riediger, D. Correlation of odontogenic soft tissue infection and thermal effects with special reference to temperature sense. Statistical analysis of 2111 patients. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschirurgie MKG 1998, 2, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meningaud, J.P.; Roudot-Thoraval, F.; Bertrand, J.C.; Guilbert, F. Do Temperature and Atmospheric Pressure Affect the Incidence of Serious Odontogenic Infection? Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 1998, 85, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalthoff, S.; Jehn, P.; Treptow, K.; Zimmerer, R.; Korn, P.; Tavassol, F.; Gellrich, N.-C.; Dittmann, J. Dependence of OA on Meteorological Parameters: Truth or Myth? Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 3619–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Dental Association. Tooth Eruption: The Permanent Teeth. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2006, 137, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamai-Homata, E.; Koletsi-Kounari, H.; Margaritis, V. Gender Differences in Oral Health Status and Behavior of Greek Dental Students: A Meta-Analysis of 1981, 2000, and 2010 Data. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2016, 6, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krmek, S.J.; Marić, R.; Ivanišević, A.M.; Matijević, J. The Oral Status of Adult Population in the Croatian Town of Knin: A Cross Sectional Study. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2015, 49, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, G.; Schmidseder, R. Effect of weather on OA. Dtsch. Zahnarztl. Z. 1978, 33, 794–795. [Google Scholar]
- Zadik, Y. Barodontalgia. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadik, Y. Barodontalgia: What Have We Learned in the Past Decade? Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2010, 109, e65–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakubo, M.; Sato, J.; Obata, K.; Mizumura, K. The Rate and Magnitude of Atmospheric Pressure Change That Aggravate Pain-Related Behavior of Nerve Injured Rats. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2011, 55, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Laskar, N.; Kadouri, D.E. Evaluating the Effect of Oxygen Concentrations on Antibiotic Sensitivity, Growth, and Biofilm Formation of Human Pathogens. Microbiol. Insights 2016, 9, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdamowicz, N.H.; Hull, R.C.; Foster, S.J.; Condliffe, A.M. The Impact of Hypoxia on the Host-Pathogen Interaction between Neutrophils and Staphylococcus Aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, E5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, K.G.; Merten, H.A.; Wiltfang, J.; Luhr, H.G. Clinical studies on the pathophysiology of OA. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschirurgie MKG 1999, 3, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, A. Factors Influencing the Seasonal Patterns of Infectious Diseases. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Trakht, I.; Srinivasan, V.; Spence, D.W.; Maestroni, G.J.M.; Zisapel, N.; Cardinali, D.P. Physiological Effects of Melatonin: Role of Melatonin Receptors and Signal Transduction Pathways. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 85, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, V.; Spence, D.W.; Trakht, I.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Cardinali, D.P.; Maestroni, G.J. Immunomodulation by Melatonin: Its Significance for Seasonally Occurring Diseases. Neuroimmunomodulation 2008, 15, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.; Carl, F.; Neumann, K.; Voss, J.O.; Hartwig, S.; Waluga, R.; Heiland, M.; Raguse, J.-D. OA-Related Emergency Hospital Admissions: A Retrospective Data Analysis of 120 Children and Young People Requiring Surgical Drainage. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3504727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.; Smith, A.J. The Microbiology of the Acute Dental Abscess. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Jackson, M.S.; Bagg, J. The Ecology of Staphylococcus Species in the Oral Cavity. J. Med. Microbiol. 2001, 50, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coticchia, J.M.; Getnick, G.S.; Yun, R.D.; Arnold, J.E. Age-, Site-, and Time-Specific Differences in Pediatric Deep Neck Abscesses. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, I.; Frazier, E.H.; Gher, M.E. Aerobic and Anaerobic Microbiology of Periapical Abscess. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1991, 6, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.E.; Salmasian, H.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Zachariah, P.; Wright, J.D.; Freedberg, D.E. Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis and Risk for Postoperative Antibiotic-Resistant Infections. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2017, 225, 631–638.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemaleelakul, S.; Baumgartner, J.C.; Pruksakorn, S. Identification of Bacteria in Acute Endodontic Infections and Their Antimicrobial Susceptibility. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2002, 94, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, D.; Camerer, C.; Camerer, D.-M.; Raguse, J.-D.; Menneking, H.; Hoffmeister, B.; Adolphs, N. Incidence and Management of Severe Odontogenic Infections-a Retrospective Analysis from 2004 to 2011. J. Cranio Maxillo Fac. Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Assoc. 2015, 43, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnke, P.H.; Becker, S.T.; Springer, I.N.G.; Haerle, F.; Ullmann, U.; Russo, P.A.J.; Wiltfang, J.; Fickenscher, H.; Schubert, S. Penicillin Compared with Other Advanced Broad Spectrum Antibiotics Regarding Antibacterial Activity against Oral Pathogens Isolated from OA. J. Cranio Maxillo Fac. Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Assoc. 2008, 36, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F.; Rôças, I.N. Microbiology and Treatment of Acute Apical Abscesses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.A.; Carmichael, F.; MacFarlane, T.W.; Milligan, S.G. A Randomised Trial of Co-Amoxiclav (Augmentin) versus Penicillin V in the Treatment of Acute Dentoalveolar Abscess. Br. Dent. J. 1993, 175, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, Y.; Yoshimori, R.N. In-Vitro Activity of Spiramycin and Metronidazole Alone or in Combination against Clinical Isolates from OA. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1997, 40, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, T.; Karasawa, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Saiki, Y.; Yamamoto, E.; Nakamura, S. Bacteriologic Features and Antimicrobial Susceptibility in Isolates from Orofacial Odontogenic Infections. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2000, 90, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakya, N.; Sharma, D.; Newaskar, V.; Agrawal, D.; Shrivastava, S.; Yadav, R. Epidemiology, Microbiology and Antibiotic Sensitivity of Odontogenic Space Infections in Central India. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2018, 17, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smieja, M. Current Indications for the Use of Clindamycin: A Critical Review. Can. J. Infect. Dis. J. Can. Mal. Infect. 1998, 9, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, M.; Mahmood, S.; Fagiry, R.; Mohamed Ahmed, M.; Rajaram, K.; Baker, A.; Avery, C. Comparative Analysis of Paediatric and Adult Surgically Drained Dental Infections at a University Teaching Hospital. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 58, e307–e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, T.R.; Shanti, R.M.; Levi, M.H.; Adamo, A.K.; Kraut, R.A.; Trieger, N. Severe Odontogenic Infections, Part 1: Prospective Report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.-T.; Liu, T.-C.; Chen, P.-R.; Tseng, F.-Y.; Yeh, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-S. Deep Neck Infection: Analysis of 185 Cases. Head Neck 2004, 26, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.K.; Wen, Y.S.; Chang, C.C.; Huang, M.T.; Hsiao, H.C. Predisposing Factors of Life-Threatening Deep Neck Infection: Logistic Regression Analysis of 214 Cases. J. Otolaryngol. 1998, 27, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haug, R.H.; Hoffman, M.J.; Indresano, A.T. An Epidemiologic and Anatomic Survey of Odontogenic Infections. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1991, 49, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowe, C.M.; O’Neill, M.A.; O’Connell, J.E.; Kearns, G.J. The Surgical Management of Severe Dentofacial Infections (DFI)-a Prospective Study. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 188, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ScienceDirect. Risk Factors Affecting Hospital Length of Stay in Patients with Odontogenic Maxillofacial Infections. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0278239196902499 (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Bègue, L.; Schlund, M.; Raoul, G.; Ferri, J.; Lauwers, L.; Nicot, R. Biological Factors Predicting the Length of Hospital Stay in Odontogenic Cellulitis. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 123, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylijoki, S.; Suuronen, R.; Jousimies-Somer, H.; Meurman, J.H.; Lindqvist, C. Differences between Patients with or without the Need for Intensive Care Due to Severe Odontogenic Infections. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 59, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgen, O.; Atici, T.; Durak, K.; Karaeminoğullari; Bilgen, M.S. C-Reactive Protein Values and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rates after Total Hip and Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Int. Med. Res. 2001, 29, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H.; Smith, P.N.; Rao, N.; Donaldson, W.F. Serum C-Reactive Protein Levels Correlate with Clinical Response in Patients Treated with Antibiotics for Wound Infections after Spinal Surgery. Spine J. Off. J. North Am. Spine Soc. 2006, 6, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jundt, J.S.; Gutta, R. Characteristics and Cost Impact of Severe Odontogenic Infections. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012, 114, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry. Wiley Online Library. Management of Facial Cellulitis of Odontogenic Origin in a Paediatric Hospital—Ritwik. 2020. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/ipd.12613 (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Lin, Y.-T.J.; Lu, P.-W. Retrospective Study of Pediatric Facial Cellulitis of Odontogenic Origin. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2006, 25, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thikkurissy, S.; Rawlins, J.T.; Kumar, A.; Evans, E.; Casamassimo, P.S. Rapid Treatment Reduces Hospitalization for Pediatric Patients with Odontogenic-Based Cellulitis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 28, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, J.A.; Hibbert, S.A. Presentation and Management of Facial Swellings of Odontogenic Origin in Children. Eur. Arch. Paediatr. Dent. Off. J. Eur. Acad. Paediatr. Dent. 2014, 15, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
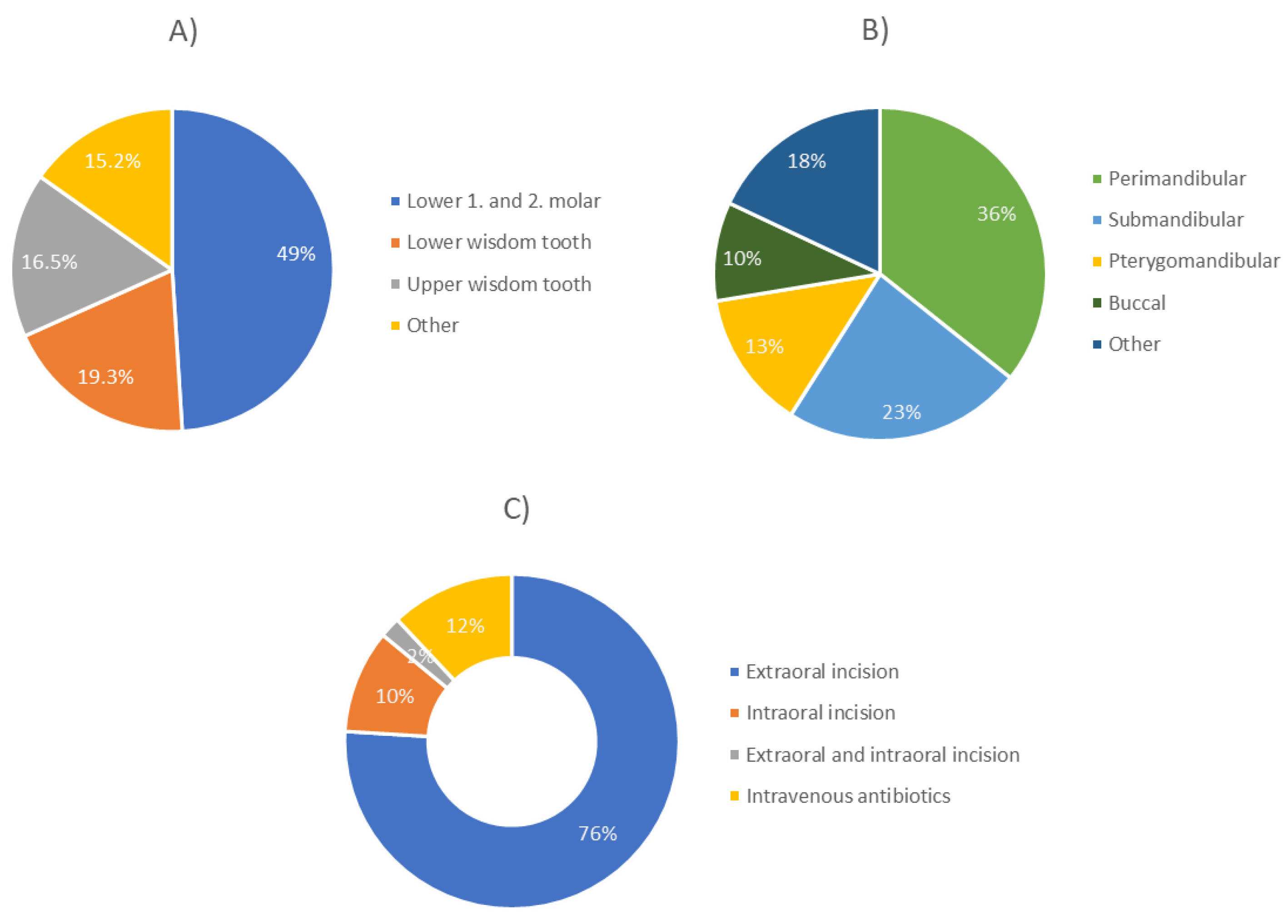

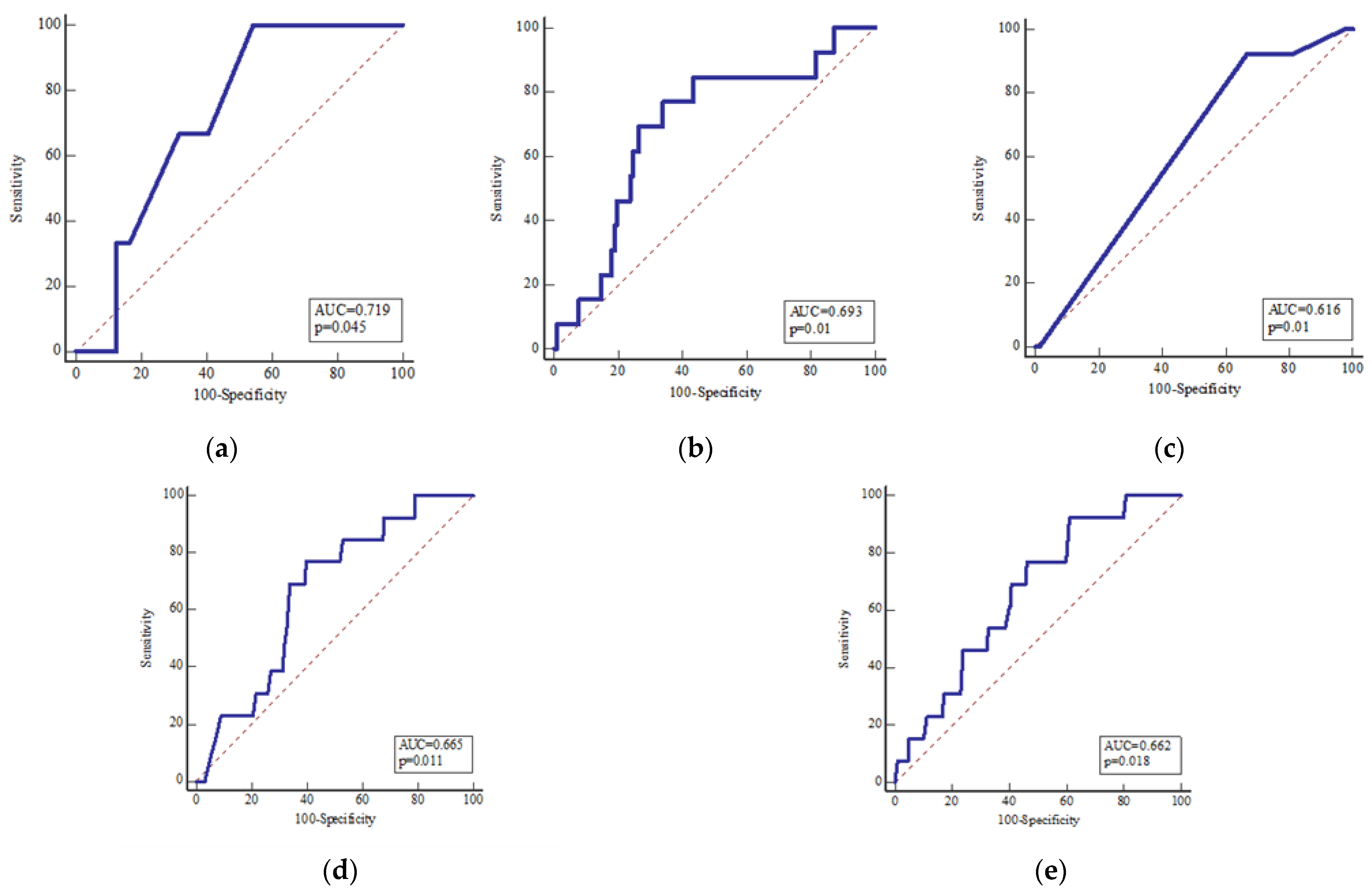
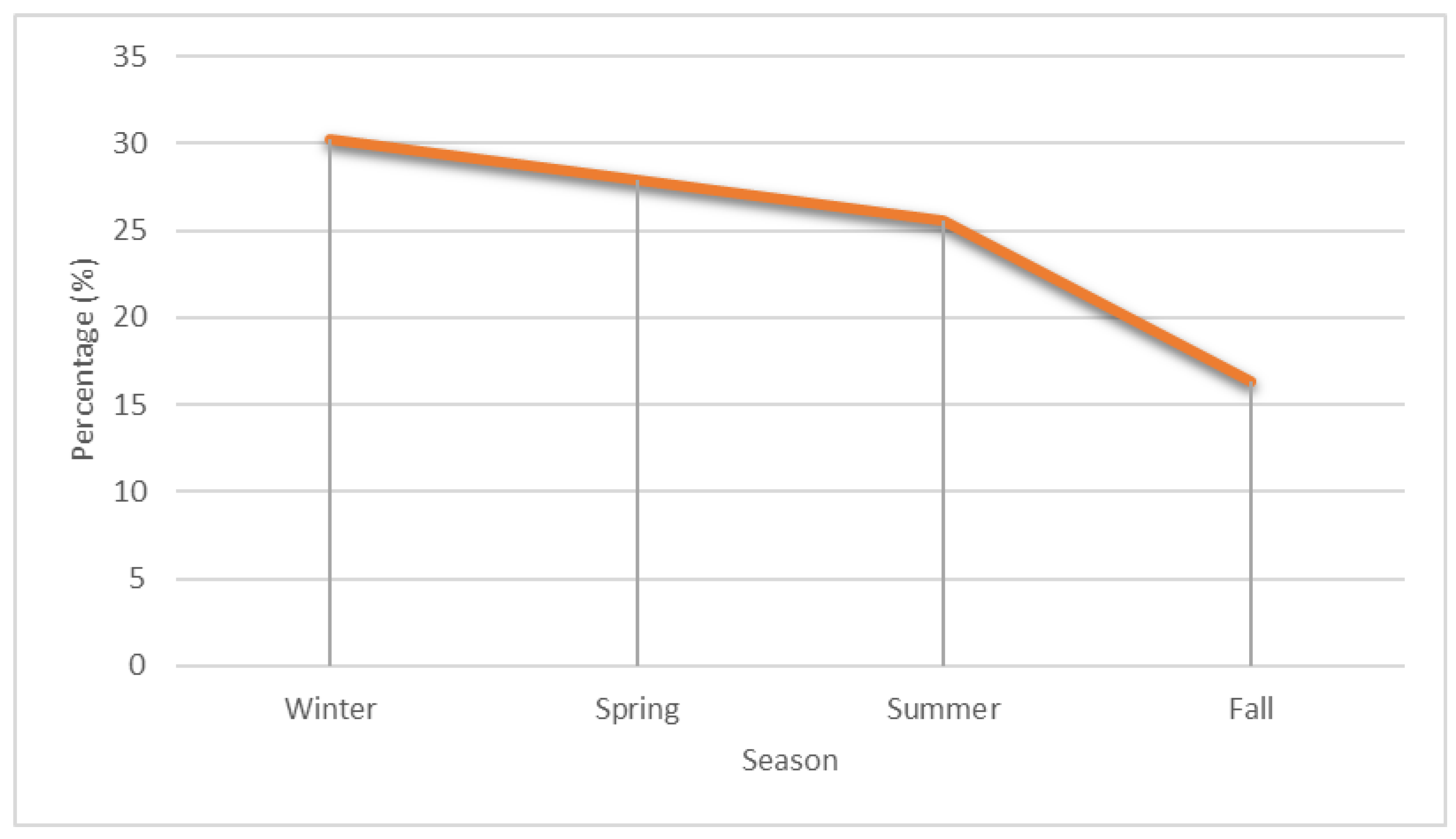


| Meteorological Parameters | Hospital Admission | Two Days Prior to Hospitalization | Five Days Prior to Hospitalization | Seven Days Prior to Hospitalization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δ mean temperature | r = 0.03, p = 0.58 | r = 0.12, p = 0.78 | r = 0.01, p = 0.86 | r = 0.00, p = 0.88 |
| Δ relative humidity | r = 0.17, p = 0.24 | r = 0.01, p = 0.97 | r = 0.01, p = 0.90 | r = 0.01, p = 0.14 |
| Δ atmospheric pressure | r = 0.23, p = 0.07 | r = 0.24, p = 0.07 | r = 0.48, p = 0.05 | r = 0.19, p = 0.11 |
| Δ precipitation | r = 0.01, p = 0.98 | r = 0.11, p = 0.39 | r = 0.02, p = 0.62 | r = 0.02, p = 0.44 |
| Tooth | Intervention | Location | Prophylaxis | Complications | Hospital Days | Leukocyte | CRP | Antibiotics | Comorbidities | Type of Intervention | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tooth | p = 0.823, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p < 0.0001, r = 0.23, R2= 0.053 | p = 0.47, r = 0.04 R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.989, r = 0.001, R2 = 0.0001 | p < 0.0001, r = 0.41, R2= 0.167 | p = 0.765, r = 0.02, R2 = 0.0003 | p = 0.072, r = 0.11, R2 = 0.01 | p = 0.490, r = 0.04, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.233, r = 0.07, R2 = 0.004 | p = 0.886, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | |
| intervention | p = 0.823, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.317, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.003 | p < 0.0001, r = 0.39, R2= 0.152 | p = 0.916, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.473, r = 0.04, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.337, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.003 | p = 0.408, r = 0.05, R2 = 0.002 | p = 0.272, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.004 | p = 0.297, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.003 | p < 0.0001, r = 0.81, R2= 0.657 | |
| location | p < 0.0001, r = 0.23, R2= 0.053 | p = 0.317, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.003 | p = 0.852, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.331, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.003 | p = 0.01, r = 0.25, R2 = 0.063 | p = 0.887, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.00007 | p = 0.014, r = 0.14, R2 = 0.02 | p = 0.151, r = 0.08, R2 = 0.007 | p = 0.441, r = 0.05, R2 = 0.002 | p = 0.554, r = 0.05, R2 = 0.002 | |
| prophylaxis | p = 0.47, r = 0.04 R2 = 0.001 | p < 0.0001, r = 0.39, R2= 0.152 | p = 0.852, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.575, r = 0.03, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.529, r = 0.04, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.500, r = 0.04, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.940, r = 0.00, R2 = 0.00001 | p < 0.001, r = 0.21, R2 = 0.004 | p = 0.597, r = 0.03, R2 = 0.0009 | p = 0.004, r = 0.22, R2 = 0.051 | |
| complications | p = 0.989, r = 0.001, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.916, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.331, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.003 | p = 0.575, r = 0.03, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.83, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.62, r = 0.03, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.05, r = 0.12, R2 = 0.015 | p = 0.314, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.003 | p = 0.154, r = 0.08, R2 = 0.007 | p = 0.230, r = 0.10, R2 = 0.009 | |
| hospital days | p < 0.0001, r = 0.41, R2= 0.167 | p = 0.473, r = 0.04, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.01, r = 0.25, R2 = 0.063 | p = 0.529, r = 0.04, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.83, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.85, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.01, r = 0.25, R2 = 0.063 | p = 0.071, r = 0.11, R2 = 0.011 | p = 0.488, r = 0.04, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.389, r = 0.07, R2 = 0.004 | |
| leukocyte | p = 0.765, r = 0.02, R2 = 0.0003 | p = 0.337, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.003 | p = 0.887, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.00007 | p = 0.500, r = 0.04, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.62, r = 0.03, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.85, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p = 0.041, r = 0.12, R2 = 0.01 | p = 0.249, r = 0.07, R2 = 0.004 | p = 0.650, r = 0.03, R2 = 0.0007 | p = 0.764, r = 0.02, R2 = 0.0005 | |
| CRP | p = 0.072, r = 0.11, R2 = 0.01 | p = 0.408, r = 0.05, R2 = 0.002 | p = 0.014, r = 0.14, R2 = 0.02 | p = 0.940, r = 0.00, R2 = 0.00001 | p = 0.05, r = 0.12, R2 = 0.015 | p = 0.01, r = 0.25, R2 = 0.063 | p = 0.041, r = 0.12, R2 = 0.01 | p = 0.879, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.00008 | p = 0.642, r = 0.03, R2 = 0.0007 | p = 0.966, r = 0.00, R2 = 0.00001 | |
| antibiotics | p = 0.490, r = 0.04, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.272, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.004 | p = 0.151, r = 0.08, R2 = 0.007 | p < 0.001, r = 0.21, R2 = 0.004 | p = 0.314, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.003 | p = 0.071, r = 0.11, R2 = 0.011 | p = 0.249, r = 0.07, R2 = 0.004 | p = 0.879, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.00008 | p = 0.002, r = 0.18, R2= 0.003 | p = 0.168, r = 0.11, R2 = 0.012 | |
| comorbidities | p = 0.233, r = 0.07, R2 = 0.004 | p = 0.297, r = 0.06, R2 = 0.003 | p = 0.441, r = 0.05, R2 = 0.002 | p = 0.597, r = 0.03, R2 = 0.0009 | p = 0.154, r = 0.08, R2 = 0.007 | p = 0.488, r = 0.04, R2 = 0.001 | p = 0.650, r = 0.03, R2 = 0.0007 | p = 0.642, r = 0.03, R2 = 0.0007 | p = 0.002, r = 0.18, R2 = 0.003 | p = 0.013, r = 0.20, R2 = 0.03 | |
| type of intervention | p = 0.886, r = 0.01, R2 = 0.0001 | p < 0.0001, r = 0.81, R2= 0.657 | p = 0.554, r = 0.05, R2 = 0.002 | p = 0.004, r = 0.22, R2 = 0.051 | p = 0.230, r = 0.10, R2 = 0.009 | p = 0.389, r = 0.07, R2 = 0.004 | p = 0.764, r = 0.02, R2 = 0.0005 | p = 0.966, r = 0.00, R2 = 0.00001 | p = 0.168, r = 0.11, R2 = 0.012 | p = 0.013, r = 0.20, R2 = 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarle, M.; Zubović, A.; Kos, B.; Raguž, M.; Lukšić, I. Retrospective Longitudinal Study on Changes in Atmospheric Pressure as a Predisposing Factor for Odontogenic Abscess Formation. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11020042
Tarle M, Zubović A, Kos B, Raguž M, Lukšić I. Retrospective Longitudinal Study on Changes in Atmospheric Pressure as a Predisposing Factor for Odontogenic Abscess Formation. Dentistry Journal. 2023; 11(2):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11020042
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarle, Marko, Arijan Zubović, Boris Kos, Marina Raguž, and Ivica Lukšić. 2023. "Retrospective Longitudinal Study on Changes in Atmospheric Pressure as a Predisposing Factor for Odontogenic Abscess Formation" Dentistry Journal 11, no. 2: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11020042
APA StyleTarle, M., Zubović, A., Kos, B., Raguž, M., & Lukšić, I. (2023). Retrospective Longitudinal Study on Changes in Atmospheric Pressure as a Predisposing Factor for Odontogenic Abscess Formation. Dentistry Journal, 11(2), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj11020042









