Abstract
Mono- and binuclear arene–ruthenium(II) complexes with imidazole-containing ligands were prepared by the reaction of the ligands (L1 = bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane; ImH = 1H-Imidazole; BImH = 1H-Benzimidazole) with [(p-cym)Ru(µ-Cl)2]2 dimers. When bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane reacted with [(p-cym)Ru(µ-Cl)2]2 in methanol, a binuclear complex of the type [Ru2(L1)2(p-cym)2Cl2]Cl2 (2) with cyclic structure was synthesized, whereas by using acetonitrile as a solvent under the same reaction conditions, an unexpected C–N bond cleavage was observed, and a complex of formula [Ru(ImH)2(p-cym)Cl]Cl (1) with coordinated imidazole molecules was obtained. Another type of arene–ruthenium complex [Ru(BImH)(p-cym)Cl2] (3) was obtained by the reaction of benzimidazole and [(p-cym)Ru(µ-Cl)2]2. All compounds were characterized by spectral (FT-IR, NMR 1H, 13C) and single-crystal X-ray diffraction methods; their catalytic activity in transfer hydrogenation and the cytotoxicity against MCF-7 and HepG2 cells were evaluated.
1. Introduction
Ruthenium complexes are of interest as catalysts, and they have also emerged as promising nonplatinum antitumor or antimetastatic agents [1,2,3,4,5,6]. A great number of ruthenium complexes with potential antitumor activity have been developed to date. Successful clinical trial candidates NAMI-A [7], KP1019 [8], and TLD1443 [9] as well as many other promising compounds caused ruthenium organometallics to be regarded as a dominant area in nonplatinum antitumor drug research. Among ruthenium organometallics, the arene–ruthenium “piano-stool” complexes show a great promise as anticancer agents. The biological activity of arene–ruthenium complexes is affected by the properties of the ligands coordinated to the metal center and can be tuned by a careful selection of these ligands [10,11]. Poly(pyrazol-1-yl)methanes, a well-known family of scorpionate ligands, are of great interest for fine-tuning the properties of complexes due to their biological relevance and also because of their ability to form different types of complexes. Several reports emerged on the development of arene–ruthenium(II) complexes with tris(pyrazol-1-yl)methane [12] and bis(pyrazol-1-yl)alkanes [13]. It was shown that the arene–ruthenium complex with bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)methane (UNICAM-1) exhibits potent in vivo antitumor effects [14]. Moreover, UNICAM-1 appears promising for the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), one of the most aggressive types of breast cancer [15]. In this regard, arene–ruthenium complexes with bis(azol-1-yl)alkanes look promising for anticancer drug research. Nonetheless, no attempts have been made to synthesize arene–ruthenium(II) complexes with other bis(azol-1-yl)alkanes.
Herein, we report the investigation of the interaction between the p-cymene-ruthenium(II) precursor and some bis(azol-1-yl)alkanes (bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane and bis(benzimidazol-1-yl)methane), together with the characterization of the obtained complexes using single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis and spectral methods.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Coordination Compounds
The interaction between commercially available arene–ruthenium dimer [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 and bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane (L1) in acetonitrile unexpectedly led to an ionic complex [Ru(ImH)2(p-cym)Cl]Cl (1, Scheme 1). Apparently, free imidazole molecules arise from C–N bond breaking in bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane, which then coordinate to the ruthenium center. The same complex 1 could also be obtained as a product of the direct reaction of 1H-imidazole with [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 in acetonitrile (Scheme 1).
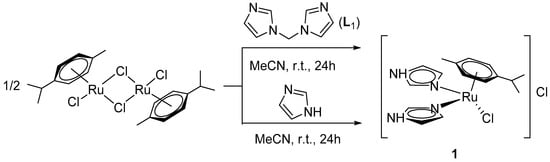
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of complex [Ru(ImH)2(p-cym)Cl]Cl (1).
A similar formation of a complex with neutral pyrazole from bis(pyrazol-1-yl)methane was demonstrated in [13], but in that case, reaction in methanol led to the product with two neutral heterocycles as ligands while the reaction in acetonitrile gave a mononuclear arene–ruthenium complex with bis(pyrazol-1-yl)methane. However, to date, no mechanism was proposed to describe the C–N bond breaking processes. Boron–nitrogen (B–N) bond breaking in complexes containing poly(pyrazol-1-yl)borates was observed previously, but it occurred when at least one coordination site in the ligand is not coordinated, which makes it possible to have an interaction between the solvent molecules and the B and N atoms of an uncoordinated heterocycle [16].
To provide an understanding of the formation of complex 1, NMR monitoring of the reaction between L1 and [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 in acetonitrile-d3 was performed, and the spectra of the reaction mixture were recorded every 2 min after mixing the reagents (Figure 1). Immediately after mixing the reagents, a set of four signals with chemical shifts close to the initial L1 was detected (marked by red circles in Figure 1), and they can be assigned to an intermediate Ru–L1 complex. The concentration of this complex rapidly decreased, and no complex was detected in the reaction mixture after 24 h. The concentration of the initial L1 also decreased (NMR signals marked by green circles), which indicates that L1 was transformed during the reaction. Another set of three signals with increasing intensity appeared synchronously (purple squares in Figure 1); they may be assigned to CH signals of imidazole (protonated or deprotonated form) coordinated to the ruthenium(II) center. After 24 h, a precipitate was visible in the NMR tube, which explains the almost complete disappearance of these signals. No signals of free imidazole (7.07, 7.62, and 10.67 ppm in MeCN-d3 [17]) were detected, which supports the assumption of its coordination to ruthenium after the breaking of the C–N bond in L1. Another signal with increasing intensity is a singlet near 9.94 ppm, which is characteristic for formaldehyde [18]. The relative intensity of this signal increased synchronously with the decrease of the intensity of CH2 singlet in L1 (Figure S1), which leads to the conclusion that the methylene group undergoes ruthenium-catalyzed oxidation by air oxygen, which is known to proceed in polar solvents, such as acetonitrile [19]. It should be noted that the NMR 1H spectrum of the individual complex 1 dissolved in acetonitrile-d3 contains multiple signals, including a signal of the formaldehyde, indicating that the complex is unstable in this solvent and undergoes oxidation.
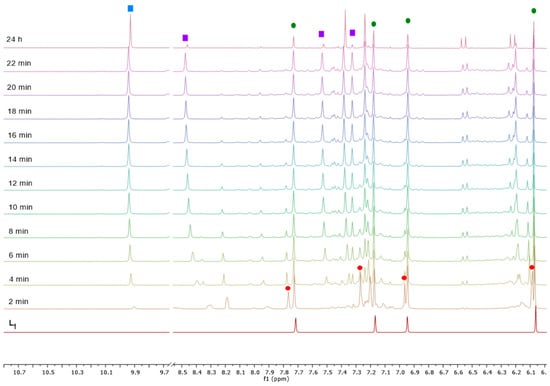
Figure 1.
NMR 1H (500 MHz) monitoring of the reaction between [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 and L1 in MeCN-d3. Signal assignments: L1—red circles; Ru–L1 intermediate complex—green circles; Ru–imidazole complex—purple squares; formaldehyde—blue square.
Changing the solvent from acetonitrile to a less polar methanol in the reaction between [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 and bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane allowed us to isolate a binuclear arene–ruthenium(II) complex [Ru2(L1)2(p-cym)2Cl2]Cl2 (2, Scheme 2).
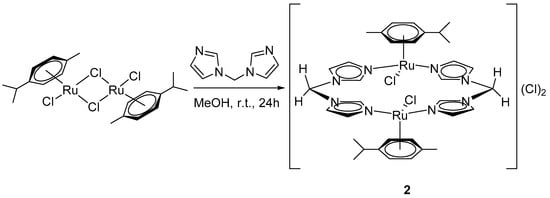
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of complex [Ru2(L1)2(p-cym)2Cl2]Cl2 (2).
The analogous reaction between [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 and bis(benzimidazole-1-yl)methane in methanol or acetonitrile did not lead to any identifiable products. By using free benzimidazole as a ligand in 1:1 or 2:1 Ru:BImH ratio in acetonitrile, a neutral complex [Ru(BImH)(p-cym)Cl2] (3) was prepared (Scheme 3).
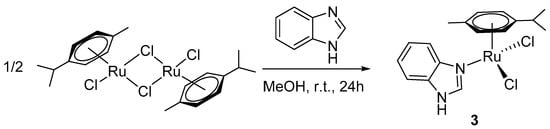
Scheme 3.
Synthesis of complex [Ru(BImH)(p-cym)Cl2] (3).
All complexes are air-stable in the solid state and are soluble in water (except complex 3), acetone, ethanol, chloroform, and DMSO. It should be noted that the synthesis of the complexes 1 and 3 were reported previously [20,21], but in this contribution we were able to determine their crystal structures and study some of their properties.
2.2. Spectroscopic Characterization
The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of 1–3 recorded in DMSO-d6 or CDCl3 displayed all the expected signals of the coordinated p-cymene and nitrogen ligand, in accordance with the existence of only one species in solution (Figures S2–S7). The resonances of the azole protons were shifted upfield with respect to those of uncoordinated ligands, confirming their coordination to the ruthenium(II) center. The 1H NMR spectra of 1–3 exhibit a doublet for the methyl groups in the isopropyl moiety, a singlet for the methyl group in p-cymene moiety, and an AB spin system attributable to the protons of the p-cymene ring in the range of 5.4−6.3 ppm, which is typical of ruthenium–arene systems with a symmetric ruthenium center [22,23]. The 1H NMR spectrum of 1 also exhibits a singlet of NH proton near 13.2 ppm, which indicates the coordination of the imidazole molecules in the protonated form.
2.3. Crystal Structures of the Complexes
Mononuclear ionic complex 1 crystallized in a monoclinic P21/n space group. The molecular structure of the compound is shown in Figure 2. The ruthenium center is in a six-coordinated environment, and the structure of the cation complex adopted a half-sandwich “piano-stool” type of geometry with angles around the ruthenium atom of 83.41(5) (N(5)–Ru–N(4)), 87.57(4) (N(4)–Ru–Cl(2)), 87.29(4) (N(5)–Ru–Cl(2)). The p-cymene ring is planar, and the Ru–C average bond length of 2.1902(16) Å (range 2.1676(17)–2.2142(16) Å) was observed. The Ru–Cl(2) bond length of 2.4203(4) Å is of the same order as reported in cationic arene–ruthenium(II) complexes [24]. The imidazole–ruthenium Ru–N(4) and Ru–N(5) distances are almost identical, i.e., 2.1118(3) Å and 2.1106(14) Å, respectively. Hydrogen bond linking of the chlorine anion and imidazole rings N(6)–H(6)···Cl(3) (distance 3.116; N(6)–H(6)–Cl(3) angle 172.01) and N(7)–H(7)···Cl(3) (distance 3.107; N(7)–H(7)–Cl(3) angle 164.34) was observed. Short contacts between the chlorine anion (Cl(3)) and –CH– in the imidazole ring (distance 2.850) and between the chlorine atom (Cl(2)) and –CH– in the imidazole ring (distance 2.763) were also observed. (Figure 3).
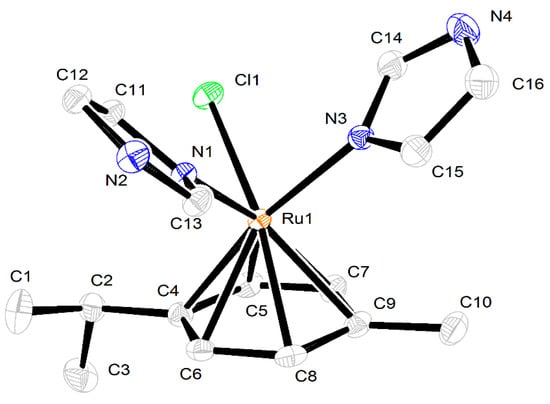
Figure 2.
X-ray molecular structure of complex 1. Thermal ellipsoids are drawn at a 50% probability level. Hydrogen atoms and Cl− anions are omitted for clarity.
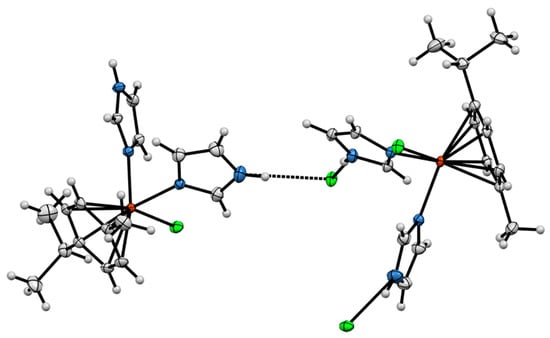
Figure 3.
Intermolecular N–H···Cl interactions in the crystal structure of complex 1.
Complex 2 crystallized in a centrosymmetric monoclinic space group P21/c. The asymmetric unit contained half of molecule 2 and one molecule of methanol. In binuclear complex 2, the coordination environment of the metal centers retained the sandwich geometry in which the p-cymene ligands occupied half of the coordination sphere in η6-coordination mode. The chlorine atom and two nitrogen atoms of the bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane completed the second half of the coordination sphere. Bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane ligands were coordinated in a bridging bidentate fashion, forming a cyclic binuclear structure (Figure 4). Despite there being a few structurally characterized arene–ruthenium complexes involving bis(pyrazol-1-yl)methanes that exhibit coordination in bidentate chelating mode [13,25,26], compound 2 is the first example of ruthenium complexes in which the bis(azol-1-yl)alkane ligand acts as a bridging component. The interatomic Ru–N distances are 2.0933(18) (Ru–N(2)) and 2.1099(17) (Ru–N(4)) Å. The interatomic Ru–Cl distance is 2.4059(6) Å, while Ru–C distances are in the range 2.170(2)–2.197(2) Å and are close to those typically found in arene–ruthenium complexes.
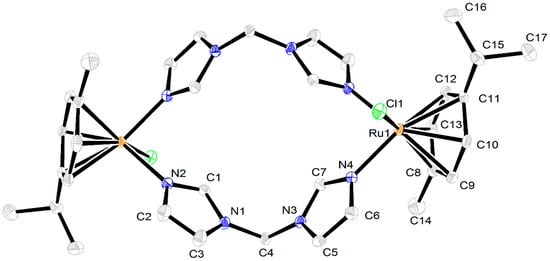
Figure 4.
X-ray molecular structure of complex 2. Thermal ellipsoids are drawn at a 50% probability level. Hydrogen atoms, solvate methanol molecules, and Cl− anions are omitted for clarity.
Compound 3 crystallized in the orthorhombic space group Pna21 with one molecule in the asymmetric unit (Figure 5). The Ru atom adopted a η6-coordination mode to the p-cymene ring, with Ru–C distances in the range from 2.145(3) to 2.204(3) Å (average 2.175(3) Å); Ru–Cl bond lengths are close to those in related compounds, i.e., 2.4319(8) Å for Ru(1)–Cl(1) and 2.4193(8) Å for Ru(1)–Cl(2). The BImH ligand displays a Ru–N distance of 2.144(3) Å. The molecules of 3 are linked via intermolecular weak N–H···Cl hydrogen bonds (distance 3.229 Å, angel N(2)–H(2)–Cl(1) 163.73) (Figure 6).
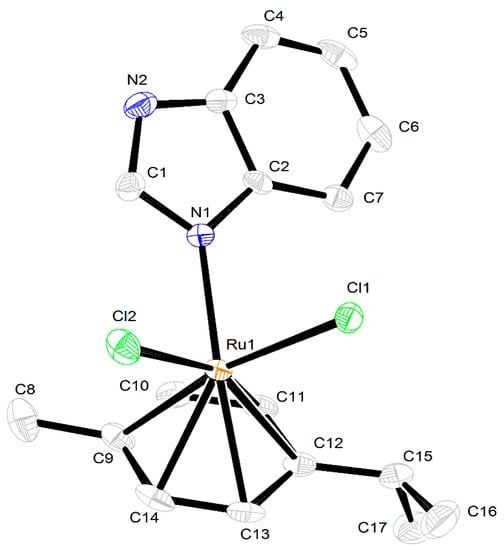
Figure 5.
X-ray molecular structure of complex 3. Thermal ellipsoids are drawn at a 50% probability level. Hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity.
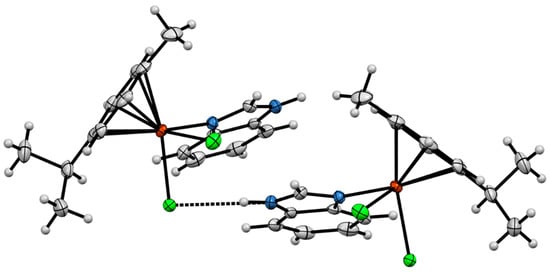
Figure 6.
Intermolecular N–H···Cl interactions in the crystal structure of complex 3.
The phase purity of bulk products of complexes 1–3 was confirmed by powder X-ray diffraction analysis; the experimental and calculated patterns and shown in Figures S8–S10.
2.4. Cytoxicity Evaluation
The cytotoxic activity of complexes 1–3 against HepG2 and MCF-7 cells was examined in the presence of different concentrations of the tested compounds dissolved in ethanol. The cytotoxicity study was carried out using dual staining with Hoechst 33342/propidium iodide (PI) with the differentiation of cells into live and apoptotic ones. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was defined as the drug concentration that reduces the number of living cells by 50%. Among the tested compounds, complex 1 showed no cytotoxicity in the 5–100 μM concentration range. Due to the limited solubility of the complexes 2 and 3 in ethanol, 1–50 μM concentration range was used. In the case of complexes 2 and 3, no cell death or apoptosis were observed, but cell count decreased by more than a half at 50 μM concentration, which clearly indicates a cytostatic effect (Figure S11). The MCF-7 cell line was used to evaluate the cytotoxicity of complex 3, which showed the highest cytostatic effect on HepG2 cells. As one can see from Figure S11, treatment of MCF-7 cells for 48 h with complex 3 initiated apoptosis (39%) and cell death (17%) after incubation with the highest tested compound concentration. The IC50 value of complex 3 is 47.3 ± 0.8 μM, which is comparable to the IC50 of cisplatin against this cell line (33.7 ± 1.8 μM) [27].
2.5. Catalytic Activity of Complexes 1–3 in Transfer Hydrogenation
Compounds 1–3 were investigated as catalysts in transfer hydrogenation using acetophenone as a model substrate (Scheme 4). All reactions were run with 5 mol % of Ru catalyst, NaOH as the base, and isopropyl alcohol as a hydrogen source.
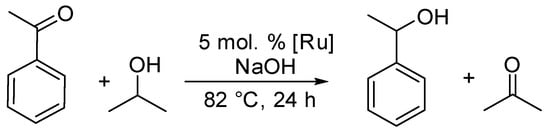
Scheme 4.
Transfer hydrogenation of acetophenone catalyzed by complexes 1–3.
Compounds 1–3 were active in transfer hydrogenation with conversion 33%, 93%, and 94%, respectively. Neutral complex 3 was the most effective, resulting in the highest acetophenone conversion.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of the Complexes
The dimer [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 was purchased from Alfa Aesar. Bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane was synthesized analogously to a previously reported procedure [28]. All other materials were obtained from commercial sources and were used as received.
[Ru(ImH)2(p-cym)Cl]Cl·0.5CH3CN (1). Imidazole (14 mg, 0.2 mmol) was dissolved in MeCN (1 mL). [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 (31 mg, 0.05 mmol) was dissolved in MeCN (3 mL), and the resulting solution was added to the initial one. The orange needle crystals formed in 12 h at room temperature and were filtered off, washed twice with MeCN, and dried in air. Yield was 36 mg (89%). Found, %: C 44.1, H 5.2, N 14.0. C16H22Cl2N4Ru·0.5CH3CN. Calculated, %: C 44.1, H 5.1, N 13.6. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 1.11 (d, 6H, (CH3)2CH, J 6.8 Hz), 1.74 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.44 (m, 1H, (CH3)2CH), 5.59 (AB spin system, 4H, J 5.9 Hz, p-cym), 6.92 (s, 2H, 5-H-Im), 7.35 (s, 2H, 4-H-Im), 8.33 (s, 2H, 2-H-Im), 13.16 (s, 2H, NH-ImH) ppm. 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 17.8 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 22.4 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 30.7 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 81.2, 86.5, 100.5, 102.0 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 117.9 (5-C-Im), 130.1 (4-C-Im), 139.2 (2-C-Im) ppm. FT-IR (cm−1): 3439 (s), 3098 (s), 3032 (s), 2960 (s), 2938 (s), 2860 (s), 2726 (w), 2631 (w), 2253 (w), 1629 (m), 1546 (m), 1500 (m), 1474 (w), 1446 (m), 1389 (w), 1326 (w), 1268 (w), 1200 (w), 1180 (w), 1142 (m), 1114 (m), 1099 (m), 1071 (s), 1031 (m), 919 (w), 876 (w), 865 (w), 830 (m), 802 (m), 767 (s), 673 (m), 656 (m), 624 (m), 449 (w), 435 (w).
[Ru2(L1)2(p-cym)2Cl2]Cl2·3CH3OH (2). Bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane (74 mg, 0.5 mmol) was dissolved in MeOH (5 mL). [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 (153 mg, 0.25 mmol) was dissolved in MeOH (10 mL), and the resulting solution was added to the initial one. Slow evaporation afforded a yellow solid, which was washed with MeOH and dried in air. Yield was 94 mg (41%). Found, %: C 44.1, H 5.7, N 11.2. C34H44Cl4N8Ru2·3CH3OH. Calculated, %: C 44.2, H 5.6, N 11.1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ = 1.10 (d, 12H, (CH3)2CH, J 6.8 Hz), 1.81 (s, 6H, CH3), 2.54 (m, 2H, (CH3)2CH), 5.74 (AB spin system, 8H, J 6.1 Hz, p-cym), 7.61 (d, 8H, 4,5-Im, J 7.9 Hz), 7.82 (s, 4H, 2-H-Im) ppm. 13C NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6): 18.0 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 22.3 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 30.6 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 56.2 (CH2), 82.3, 85.3, 99.6, 103.3 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 121.1 (5-C-Im), 133.3 (4-C-Im), 140.6 (2-C-Im) ppm. FT-IR (cm-1): 3410 (s), 3301 (m), 3250 (m), 3112 (s), 3089 (m), 3052 (m), 3003 (w), 2963 (m), 2926 (m), 2869 (m), 2820 (m), 2583 (w), 1626 (m), 1509 (s), 1469 (m), 1443 (m), 1400 (s), 1354 (m), 1326 (w), 1300 (s), 1234 (vs), 1205 (m), 1162 (w), 1102 (vs), 1062 (m), 1039 (s), 999 (w), 950 (w), 876 (m), 796 (m), 764 (s), 716 (s), 653 (m), 618 (m), 521 (w), 464 (w), 449 (w), 421 (w).
[Ru(BImH)(p-cym)Cl2] (3). Benzimidazole (12 mg, 0.1 mmol) was dissolved in MeOH (1 mL). [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 (31 mg, 0.05 mmol) was dissolved in MeOH (3 mL), and the resulting solution was added to the initial one. The red block crystals formed in 24 h at room temperature and were filtered off, washed twice with MeOH, and dried in air. Yield was 26 mg (61%). Found, %: C 48.1, H 4.8, N 6.5. C17H20Cl2N2Ru. Calculated, %: C 48.1, H 4.7, N 6.6. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 1.31 (d, 6H, (CH3)2CH, J 6.9 Hz), 2.07 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.92 (m, 1H, (CH3)2CH), 5.46 (AB spin system, 4H, J 5.7 Hz, p-cym), 6.72 (t, 1H, 6-H-BIm, J 7.3 Hz), 6.80 (t, 1H, 7-H-BIm, J 7.7 Hz), 7.03 (t, 1H, 5-H-BIm, J 8.1 Hz), 7.69 (d, 1H, 8-H-BIm, J 8.2 Hz), 8.21 (s, 1H, 2-H-BIm), 10.90 (s, 1H, NH-BIm) ppm. 13C (125 MHz, DMSO-d6): 18.4 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 22.3 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 30.7 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 80.9, 82.8, 97.4, 102.8 (CH3-C6H4-CH(CH3)2), 112.7 (6-C-BIm), 118.7 (7-C-BIm), 121.9 (5-C-BIm), 123.3 (8-C-BIm), 132.3 (4-C-BIm), 140.2 (9-C-BIm), 144,8 (2-C-BIm) ppm. FT-IR (cm-1): 3442 (m), 3158 (s), 2969 (s), 2920 (m), 2866 (m), 1623 (m), 1595 (w), 1492 (s), 1474 (m), 1454 (s), 1414 (s), 1386 (s), 1326 (w), 1303 (w), 1271 (m), 1248 (s), 1194 (w), 1157 (w), 1145 (w), 1134 (w), 1108 (m), 1085 (w), 1059 (m), 1011 (m), 979 (w), 965 (w), 928 (w), 893 (m), 870 (s), 804 (w), 779 (w), 741 (vs), 698 (w), 670 (w), 638 (w), 615 (m), 570 (w), 550 (w), 461 (w), 447 (m), 432 (m), 421 (m), 406 (w).
3.2. Spectral Methods and Elemental Analysis
Elemental analyses were performed on a Vario MicroCube CHN(S) analyzer (Elementar Analysensysteme GmbH, Langenselbold, Germany). IR spectra for compounds 1–3 were recorded from 4000 to 400 cm−1 on a Scimitar FTS 2000 Spectrometer (Digilab LLC, Randolph, MA, USA). IR spectra of the complexes 1–3 are shown in Figures S12–S14. 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Ascend 500 instrument (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) operating at room temperature (500 MHz for 1H and 125 MHz for 13C); solvent residual peaks were used as internal standards.
3.3. X-ray Crystal Structure Determination
The diffraction data of 1 and 2–3 were measured at 300 K and 140 R, respectively, on an automated Agilent Xcalibur four-circle diffractometer equipped with an area AtlasS2 detector. Graphite-monochromated Mo Kα radiation (λ = 0.71073 Å) was used in all cases. Absorption corrections were applied with the use of the SADABS program [29]. The crystal structures were solved and refined by means of the SHELXT [30] and SHELXL [31] programs using OLEX2 GUI [32]. Atomic thermal displacement parameters for nonhydrogen atoms—except some solvate molecules—were refined anisotropically. The positions of hydrogen atoms were calculated, corresponding to their geometrical conditions, and refined using the riding model. The crystallographic data and details of the structure refinement are summarized in Table 1. CCDC 2074083–2074085 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data can be obtained free of charge from the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Center at http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/data_request/cif.

Table 1.
Crystallographic data of the compounds 1–3.
The powder X-ray diffraction data were obtained on Shimadzu XRD 7000S powder diffractometer (Cu Kα irradiation).
3.4. Cytotoxicity Study
Cell viability was evaluated by Hoechst/PI staining by the standard method as previously described [27]. Human breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) and human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell lines were seeded on 96-well plates at 6 × 103 cells per well and cultured in Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium (IMDM, pH = 7.4) supplemented with a 10% fetal bovine serum under a humidified atmosphere (5% CO2 and 95% air) at 37 °C. After 24 h, cells were treated with complexes 1–3. Complexes were dissolved in ethanol, then serial dilutions were prepared in IMDM medium in the concentration range of 5–100 μM (complex 1) and 1–50 μM (complexes 2 and 3). In the case of complexes 2 and 3, lower concentrations were used due to the limited solubility of the complexes in ethanol and the need to limit the final percentage of the solvent (<1%). For the identification of live, apoptotic, and dead cells, treated cells and control cells were stained after 48 h with a mixture of fluorescent dyes Hoechst 33342 (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) and propidium iodide (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) for 30 min at 37 °C. An IN Cell Analyzer 2200 (GE Healthcare, Chalfont Saint Giles, UK) was used to perform the automatic imaging of four fields per well under 200× magnification, in bright-field and fluorescence channels. IN Cell Investigator image analysis software (GE Healthcare, Chalfont Saint Giles, UK) was used to determine the live, apoptotic, and dead cells among the whole population. All data shown are the mean of three wells. The quantitative data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was defined as the drug concentration that reduces the number of living cells by 50% and calculated from curves constructed by plotting cell survival (%) versus drug concentration (µM).
3.5. General Procedure for Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation
The catalyst (0.0005 mmol) and NaOH (0.02 mmol) were dissolved in 2-propanol (0.4 mL). Acetophenone (0.1 mmol) was then added, and the reaction mixture was stirred at 82 °C for 24 h. The solvent was evaporated, and the residue was dissolved in CDCl3 and analyzed by NMR. The NMR spectra of products obtained with compounds 1–3 as catalysts are shown in the Supplementary Materials.
4. Conclusions
The reaction of bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane and [Ru(p-cym)Cl2]2 was investigated for the first time. It was found that the solvent strongly influenced the type of ruthenium complexes formed. Unusual C–N bond breaking in bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane was observed in acetonitrile, leading to the formation of the complex with imidazole. In methanol, a binuclear complex with two bridging bis(imidazol-1-yl)methane ligands was obtained; this complex is the first example of a ruthenium coordination compound with bis(imidazole-1-yl)methane.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/inorganics9050034/s1, Figure S1: Change in relative intensities of methylene signals of L1 (CH2) and formaldehyde (CH2=O); Figures S2–S7: NMR 1H and 13C spectra of complexes 1–3; Figures S8–S10: Experimental and calculated powder X-ray diffraction patterns of complexes 1–3; Figure S11: Effect of complexes 1–3 on the viability of HepG2 and MCF-7 cells determined by dual staining with Hoechst 33342/propidium iodide; Figures S12–S14: FT-IR spectra of complexes 1–3; Crystallographic information files (CIF) and checkCIF report files for complexes 1–3.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S.P.; methodology, A.S.P.; resources, V.P.B. and S.V.B.; investigation, V.V.M., D.I.P., D.G.S., E.A.E. and L.S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, V.V.M.; writing—review and editing, A.S.P.; visualization, D.I.P.; supervision, A.S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The cytotoxicity study was performed at the Proteomic Analysis Center of the Institute of Molecular Biology and Biophysics of Federal State Budget Scientific Institution “Federal Research Centre of Fundamental and Translational Medicine” (IMBB FRC FTM), Novosibirsk, Russia. The authors thank Irina Mirzaeva for assistance with NMR reaction monitoring.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Štarha, P. Multinuclear biologically active Ru, Rh, Os and Ir arene complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 431, 213690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Li, Y.; Li, P. Design of Ru-arene Complexes for Antitumor Drugs. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilak Simović, A.; Masnikosa, R.; Bratsos, I.; Alessio, E. Chemistry and reactivity of ruthenium(II) complexes: DNA/protein binding mode and anticancer activity are related to the complex structure. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 398, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, C.Y.; Nam, T.-G. Ruthenium Complexes as Anticancer Agents: A Brief History and Perspectives. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 5375–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, B.; Roy, N.; Pete, S.; Moharana, P.; Paira, P. Ruthenium and iridium based mononuclear and multinuclear complexes: A Breakthrough of Next-Generation anticancer metallopharmaceuticals. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2020, 512, 119858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharana, P.; Ghosh, D.; Paira, P. Drive to organoruthenium and organoiridium complexes from organoplatinum: Next-generation anticancer metallotherapeutics. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 124, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademaker-Lakhai, J.M.; Van Den Bongard, D.; Pluim, D.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M. A phase I and pharmacological study with imidazolium-trans-DMSO-imidazole-tetrachlororuthenate, a novel ruthenium anticancer agent. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3717–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartinger, C.G.; Jakupec, M.A.; Zorbas-Seifried, S.; Groessl, M.; Egger, A.; Berger, W.; Zorbas, H.; Dyson, P.J.; Keppler, B.K. KP1019, A New Redox-Active Anticancer Agent—Preclinical Development and Results of a Clinical Phase I Study in Tumor Patients. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 2140–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monro, S.; Colón, K.L.; Yin, H.; Roque, J.; Konda, P.; Gujar, S.; Thummel, R.P.; Lilge, L.; Cameron, C.G.; McFarland, S.A. Transition Metal Complexes and Photodynamic Therapy from a Tumor-Centered Approach: Challenges, Opportunities, and Highlights from the Development of TLD1433. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 797–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, L.; Gupta, P.; Chen, Y.; Wang, E.; Ji, L.; Chao, H.; Chen, Z.-S. The development of anticancer ruthenium(II) complexes: From single molecule compounds to nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 5771–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Menches, S.M.; Gerner, C.; Berger, W.; Hartinger, C.G.; Keppler, B.K. Structure-activity relationships for ruthenium and osmium anticancer agents-towards clinical development. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 909–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhambri, S.; Tocher, D.A. Synthesis and characterisation of ruthenium(II) arene complexes containing κ3- and κ2-poly(pyrazolyl)borates and methanes. J. Chem. Soc. Dalt. Trans. 1997, 18, 3367–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, F.; Pettinari, C.; Pettinari, R.; Cerquetella, A.; Di Nicola, C.; Macchioni, A.; Zuccaccia, D.; Monari, M.; Piccinelli, F. Synthesis and Intramolecular and Interionic Structural Characterization of Half-Sandwich (Arene)Ruthenium(II) Derivatives of Bis(Pyrazolyl)Alkanes. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 11593–11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montani, M.; Pazmay, G.V.B.; Hysi, A.; Lupidi, G.; Pettinari, R.; Gambini, V.; Tilio, M.; Marchetti, F.; Pettinari, C.; Ferraro, S.; et al. The water soluble ruthenium(II) organometallic compound [Ru(p-cymene)(bis(3,5-dimethylpyrazol-1-yl)methane)Cl]Cl suppresses triple negative breast cancer growth by inhibiting tumor infiltration of regulatory T cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 107, 202–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, T.O.; Hsu, F.D.; Jensen, K.; Cheang, M.; Karaca, G.; Hu, Z.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; Livasy, C.; Cowan, D.; Dressler, L.; et al. Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5367–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellachioma, G.; Cardaci, G.; Gramlich, V.; Macchioni, A.; Pieroni, F.; Venanzi, L.M. Synthesis and characterisation of bis- and tris-(pyrazol-1-yl)borate acetyl complexes of FeII and RuII and isolation of an intermediate of B–N bond hydrolysis. J. Chem. Soc. Dalt. Trans. 1998, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Castro, F.; Torres, L.A. Understanding the solvation process and solute-solvent interactions of imidazole compounds in three different solvents through solution calorimetry and 1H NMR. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 284, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, B.L.; Kopchik, R.M.; Ebersole, S.J. Proton NMR Studies of CHDO and CH2O. J. Chem. Phys. 1963, 39, 3154–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Malollari, K.G.; Uliana, A.; Hartwig, J.F. Ruthenium-Catalyzed, Chemoselective and Regioselective Oxidation of Polyisobutene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4531–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vock, C.A.; Scolaro, C.; Phillips, A.D.; Scopelliti, R.; Sava, G.; Dyson, P.J. Synthesis, Characterization, and in Vitro Evaluation of Novel Ruthenium(II) η6-Arene Imidazole Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5552–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertin, G.; Antoniutti, S.; Castro, J.; García-Fontán, S. Preparation of Pyrazole–Pyrazolate Half-Sandwich Complexes of Ruthenium and Osmium. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2011, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Melchart, M.; Habtemariam, A.; Parsons, S.; Sadler, P.J. Use of Chelating Ligands to Tune the Reactive Site of Half-Sandwich Ruthenium(II)–Arene Anticancer Complexes. Chem. A Eur. J. 2004, 10, 5173–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peacock, A.F.A.; Melchart, M.; Deeth, R.J.; Habtemariam, A.; Parsons, S.; Sadler, P.J. Osmium(II) and Ruthenium(II) Arene Maltolato Complexes: Rapid Hydrolysis and Nucleobase Binding. Chem. A Eur. J. 2007, 13, 2601–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Małecki, J.G.; Dziȩgielewski, J.O.; Jaworska, M.; Kruszynski, R.; Bartczak, T.J. Synthesis, molecular, crystal and electronic structures of [(C6H6)RuCl(HPz)2]Cl and [(C6H6)RuCl2(Me2HPz)]. Polyhedron 2004, 23, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, L.D.; Messerle, B.A.; Soler, L.; Buys, I.E.; Hambley, T.W. Polypyrazolylmethane complexes of ruthenium. J. Chem. Soc. Dalt. Trans. 2001, 1959–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, M.H.V.; Lasker, J.M.; Wetzler, M.; Mort, B.; Szczepura, L.F.; Witham, L.M.; Cintron, J.M.; Marschilok, A.C.; Ackerman, L.J.; Castellano, R.K.; et al. Remarkable spectator ligand effect on the rate constant of ligand substitution of (Aqua)ruthenium(II) complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8780–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremina, J.A.; Lider, E.V.; Kuratieva, N.V.; Samsonenko, D.G.; Klyushova, L.S.; Sheven’, D.G.; Trifonov, R.E.; Ostrovskii, V.A. Synthesis and crystal structures of cytotoxic mixed-ligand copper(II) complexes with alkyl tetrazole and polypyridine derivatives. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2021, 516, 120169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semitut, E.; Sukhikh, T.; Filatov, E.; Ryadun, A.; Potapov, A. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Luminescent Properties of 2D Zinc Coordination Polymers Based on Bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methane and 1,3-Bis(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propane. Crystals 2017, 7, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APEX2 (Version 2.0), SAINT (Version 8.18c), and SADABS (Version 2.11), Bruker Advanced X-ray Solutions; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2012.
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT-Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. IUCr Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).