Na1+yVPO4F1+y (0 ≤ y≤ 0.5) as Cathode Materials for Hybrid Na/Li Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
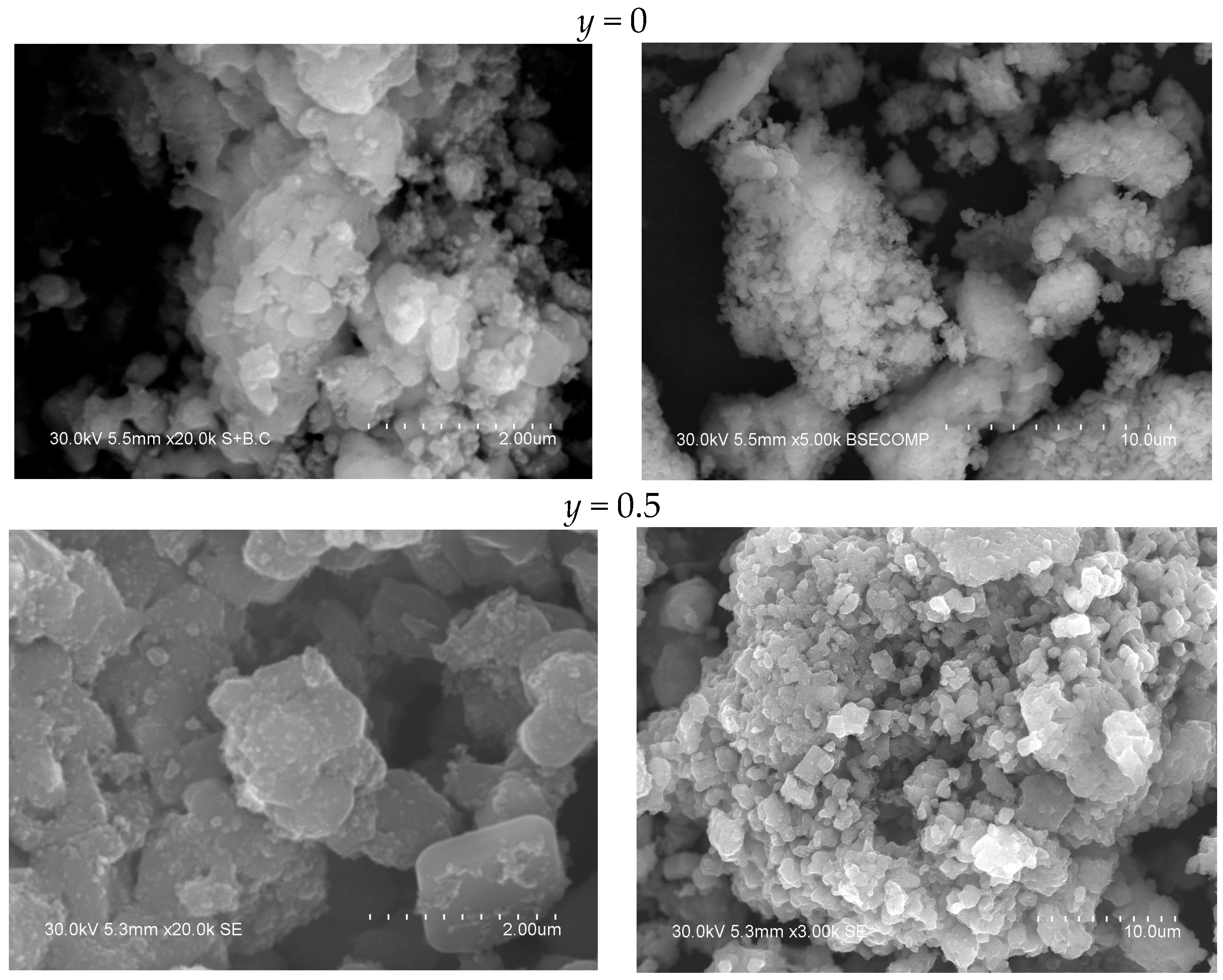
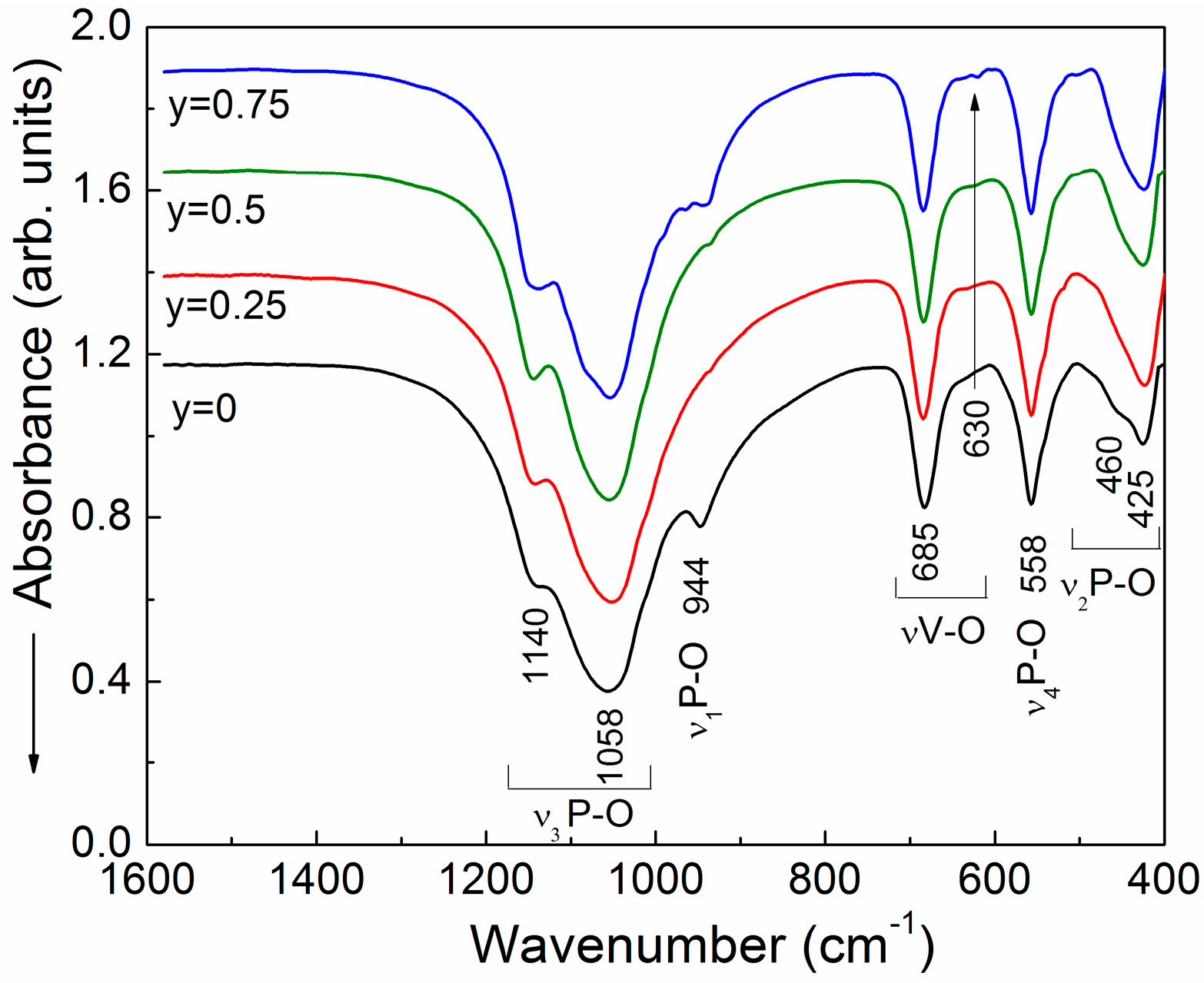
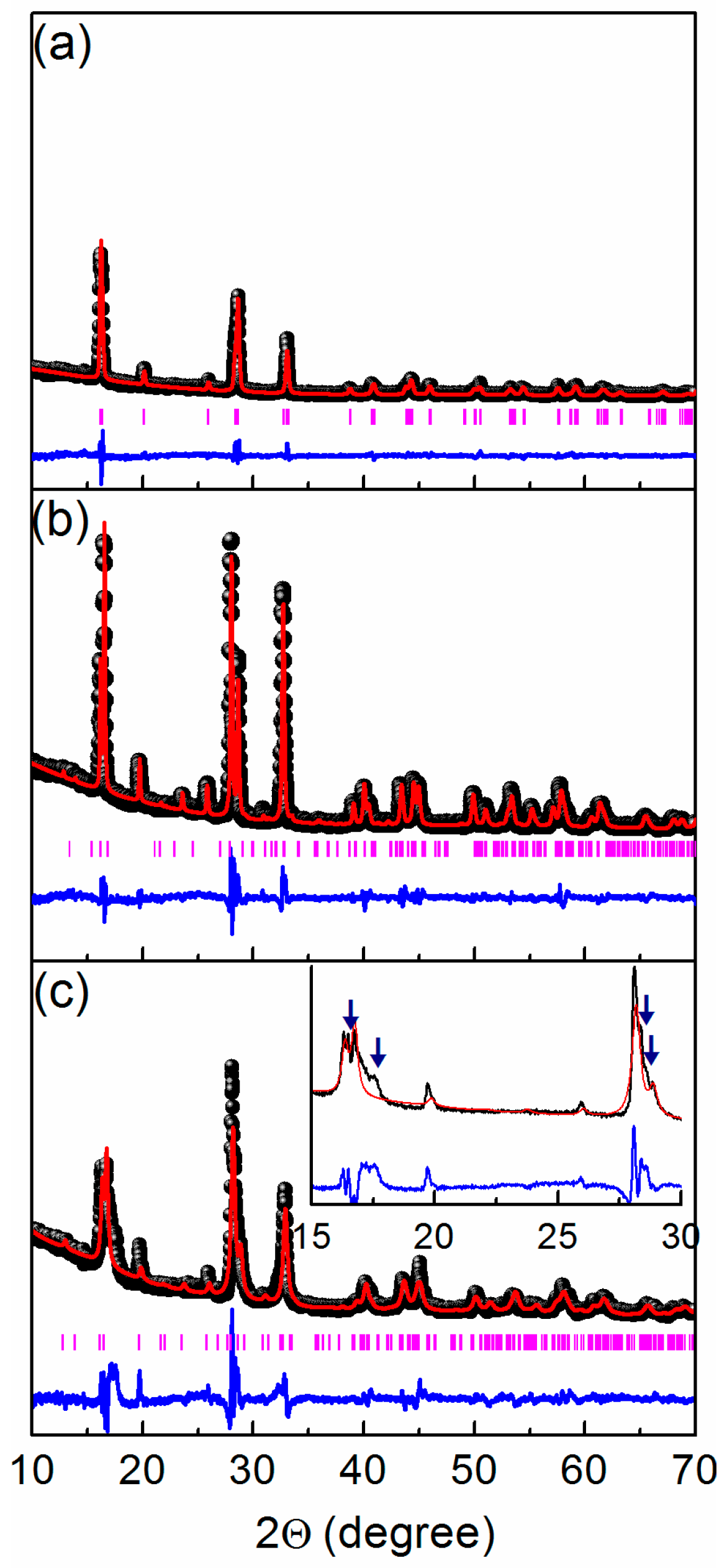
2.1. Crystal Structure and Morphology
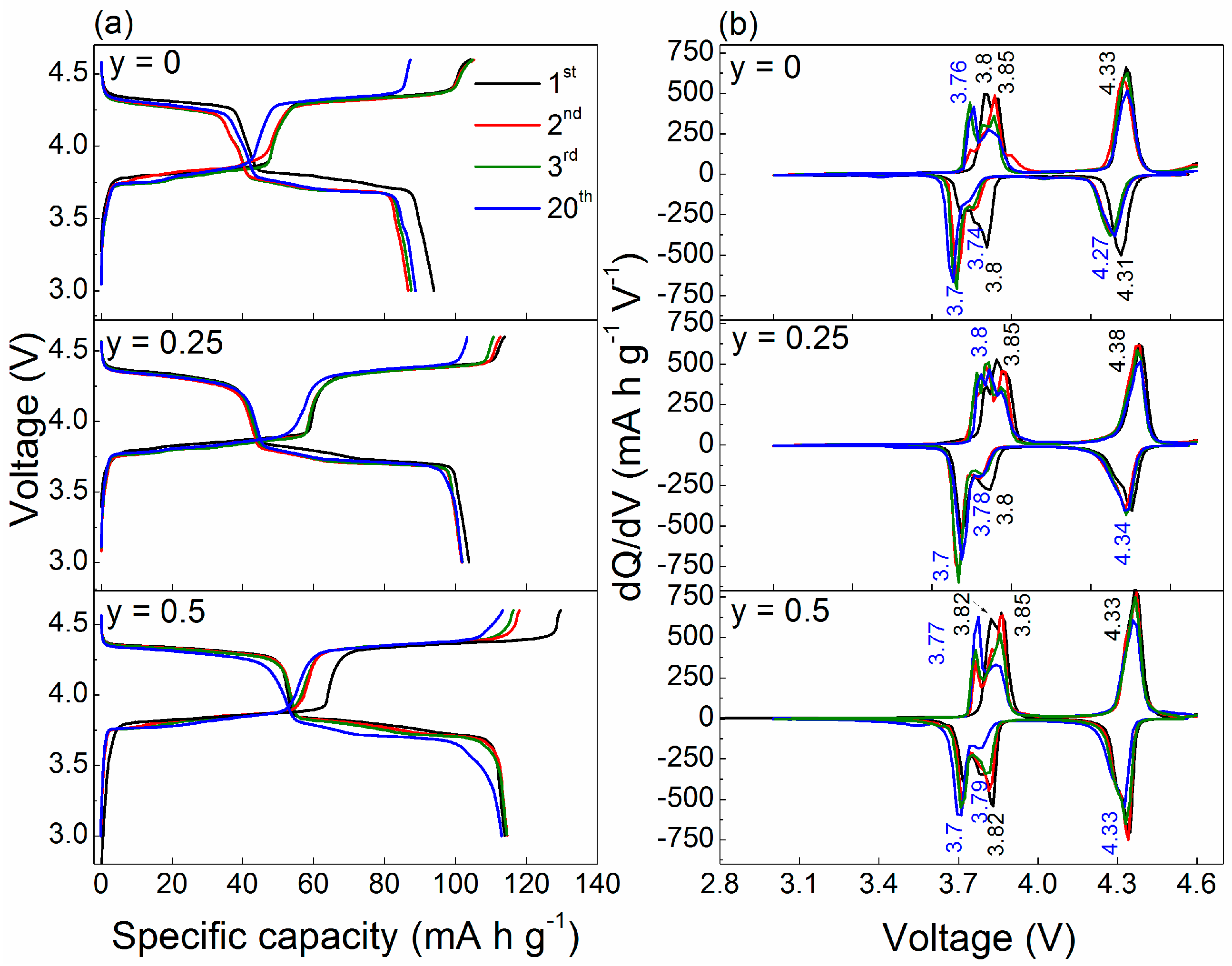
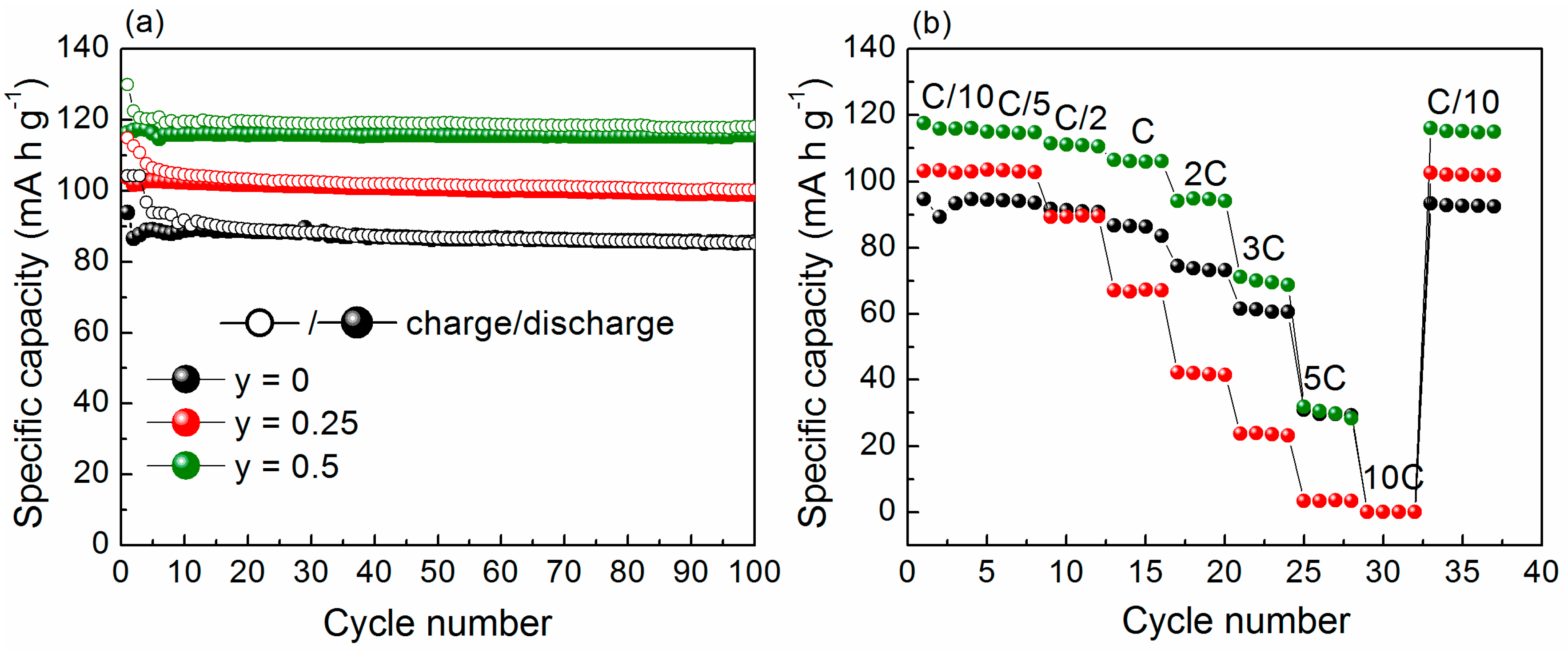
2.2. Electrochemistry
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
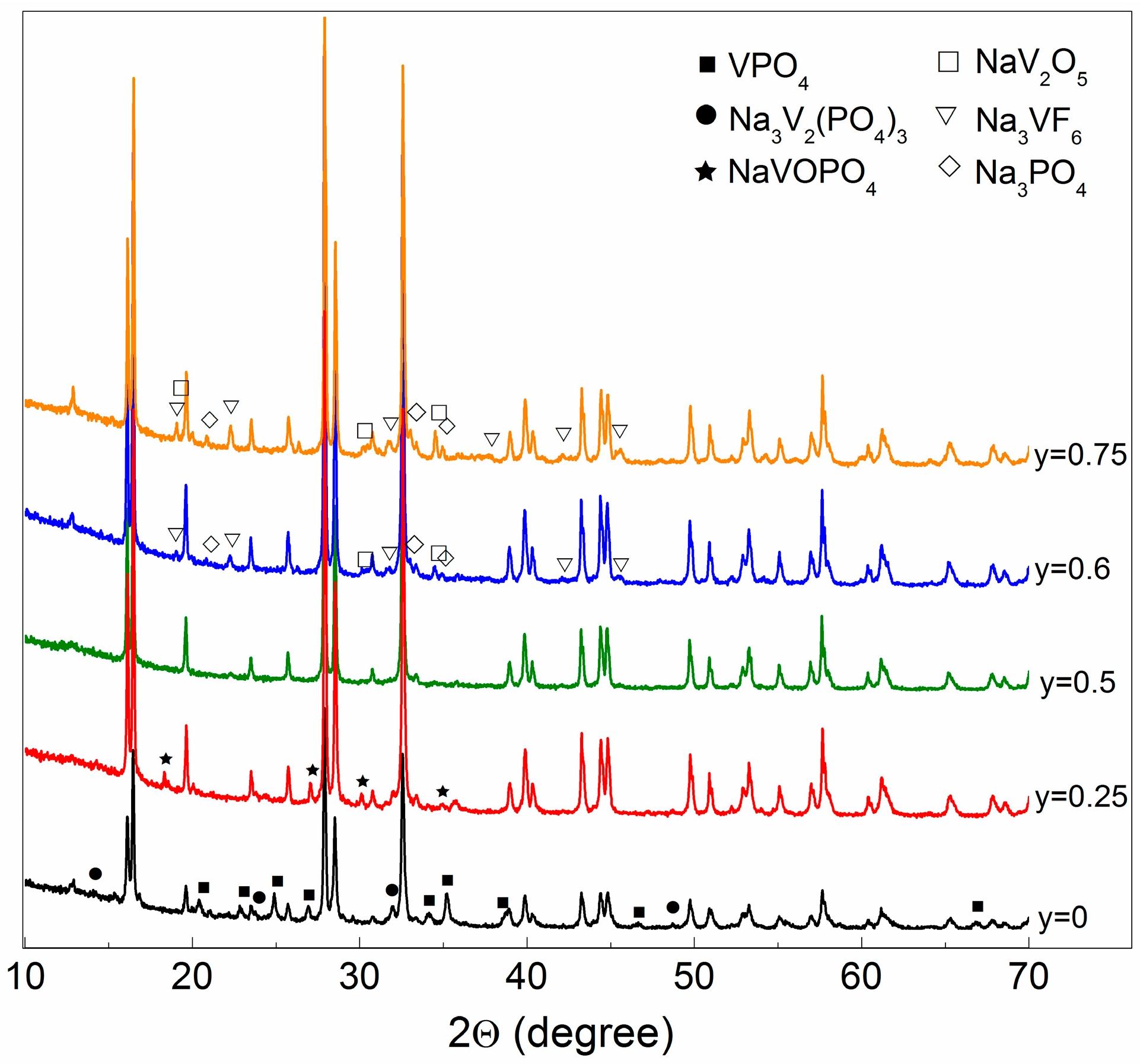
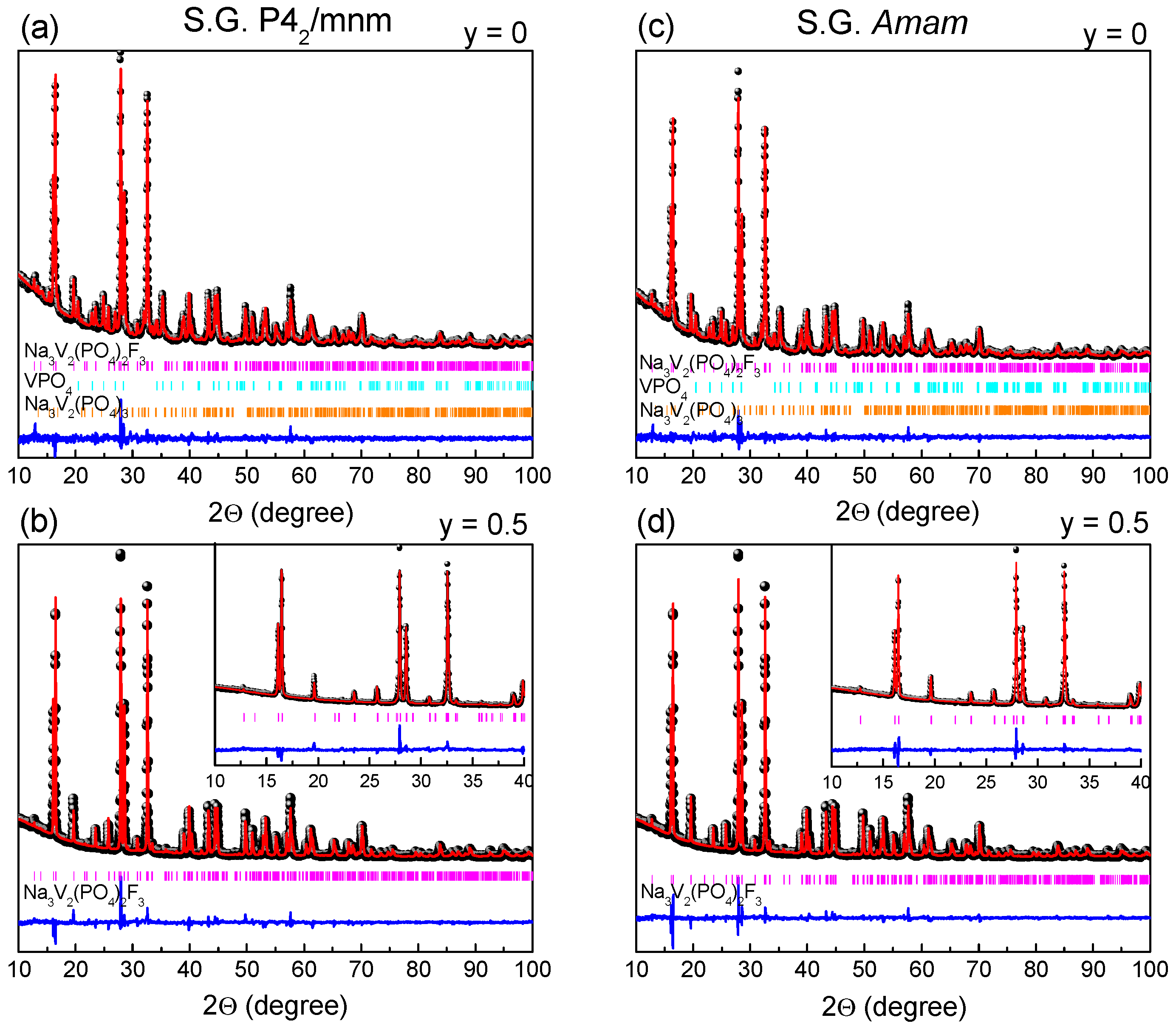
- It has been shown that among sodium vanadium fluorophosphate compositions Na1+yVPO4F1+y (0 ≤ y ≤ 0.75) prepared by the mechanochemically assisted solid-state synthesis, the single-phase material Na1.5VPO4F1.5 or Na3V2(PO4)2F3 with a tetragonal structure (the P42/mnm S.G.) was formed only for y = 0.5. Samples with y < 0.5 and y > 0.5 possess different impurity phases. The compound with the NaVPO4F composition does not exist.
- Sodium vanadium fluorophosphates Na1+yVPO4F1+y can be considered as multifunctional cathode materials for the fabrication of lithium-ion and sodium-ion high-energy batteries. The reversible discharge capacity of 116 mAh·g−1 for y = 0.5, 103 mAh·g−1 for y = 0.25 and 87 mAh·g−1 for y = 0 was achieved. The decrease in the discharge capacity is in accordance with the amount of the electrochemically active phase Na3V2(PO4)2F3 in the samples.
- The ex situ XRD patterns confirm a reversible P42/mnm↔I4/mmm transformation upon charging–discharging in a hybrid-ion cell, similar to the earlier observed transformation in Na-ion cells.
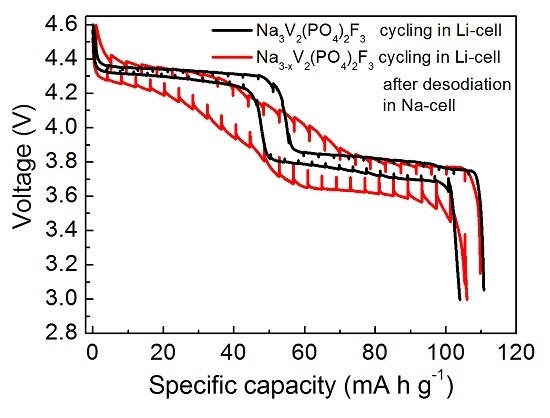
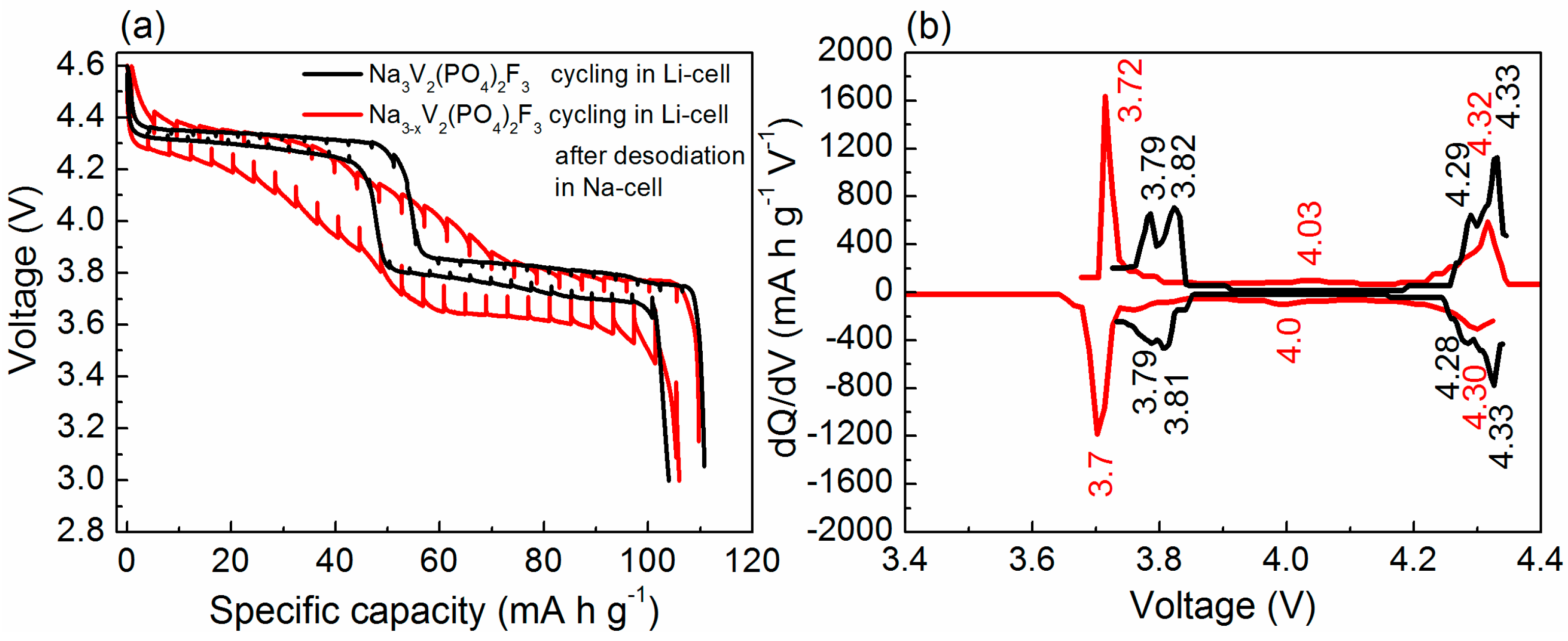
- The structural study of charged and discharged samples and the analysis of the differential capacity curves indicated a negligible Na/Li electrochemical exchange (~16%) and a predominantly sodium-based cathode reaction in the hybrid-ion cell. This is significantly lower than the ~50% exchange observed for other Na-based cathodes, such as Na2FePO4F [32] and Na2FeP2O7 [33] when cycled in hybrid-ion cells, showing that the properties of hybrid-ion batteries can be varied based on the alkali-ion selectivity of electrode materials. To increase the degree of the Na/Li electrochemical exchange in Na3V2(PO4)2F3, it first needs to be desodiated in a Na cell, and then cycled in a Li cell with the electrolyte enriched with Li ions.
- After cycling in hybrid-ion cells, Na3V2(PO4)2F3 showed nice cycleability and high-rate performance, presumably due to operating in the mixed Na/Li electrolyte. Thus, the hybrid-ion approach may open possibilities for many new active materials and material combinations with enhanced electrochemical performance. This approach provides an opportunity for sodium cathode materials to be used without the requirement for ion Na/Li exchange prior to cell fabrication. Since in hybrid-ion systems all anodic charge carriers originate from the electrolyte, this may limit their use in high-energy applications, where relatively thick electrodes are used in combination with thin electrolytes. However, in high power applications, this may not represent a major drawback, since thinner electrodes and thicker electrolytes are commonly used.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yabuuchi, N.; Kubota, K.; Dahbi, M.; Komaba, S. Research development on sodium-ion batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masquelier, C.; Croguennec, L. Polyanionic (phosphates, silicates, sulfates) frameworks as electrode materials for rechargeable Li (or Na) batteries. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 6552–6591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, J.; Saidi, M.Y.; Swoyer, J.L. A sodium-ion cell based on the fluorophosphate compound NaVPO4F. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2003, 6, A1–A4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; He, J.; Ding, X.; Zhou, J.; Ma, Y.; Wu, S.; Huang, R. A novel sol–gel synthesis route to NaVPO4F as cathode material for hybrid lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 6854–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Meins, J.-M.; Crosnier-Lopez, M.-P.; Hemon-Ribaud, A.; Courbion, G. Phase transitions in the Na3M2(PO4)2F3 family (M = Al3+, V3+, Cr3+, Fe3+, Ga3+): Synthesis, thermal, structural, and magnetic studies. J. Solid State Chem. 1999, 148, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, F.; Quarez, E.; Tarascon, J.M.; Baudrin, E. Crystal structure and electrochemical properties vs. Na+ of the sodium fluorophosphate Na1.5VOPO4F0.5. Solid State Sci. 2006, 8, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirlin, A.A.; Nath, R.; Abakumov, A.M.; Furukawa, Y.; Johnston, D.C.; Hemmida, M.; Krug von Nidda, H.-A.; Loidl, A.; Geibel, C.; Rosner, H. Phase separation and frustrated square lattice magnetism of Na1.5VOPO4F0.5. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 014429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.U.; Seo, D.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, B.; Kang, K. A family of high-performance cathode materials for Na-ion batteries, Na3(VO1−xPO4)2F1+2x(0 ≤ x ≤ 1): Combined first-principles and experimental study. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4603–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broux, T.; Bamine, T.; Fauth, F.; Simonelli, L.; Olszewski, W.; Marini, C.; Menetrier, M.; Carlier, D.; Masquelier, C. Strong impact of the oxygen content in Na3V2(PO4)2F3−yOy (0 ≤ y ≤ 0.5) on its structural and electrochemical properties. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 7683–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serras, P.; Palomares, V.; Goni, A.; Kubiak, P.; Rojo, T. Electrochemical performance of mixed valence Na3V2O2x(PO4)2F3−2x/C as cathode for sodium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 241, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serras, P.; Palomares, V.; Goni, A.; Gil de Muro, I.; Kubiak, P.; Lezama, L.; Rojo, T. High voltage cathode materials for Na-ion batteries of general formula Na3V2O2x(PO4)2F3−2x. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 22301–22308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gover, R.K.B.; Bryan, A.; Burns, P.; Barker, J. The electrochemical insertion properties of sodium vanadium fluorophosphate, Na3V2(PO4)2F3. Solid State Ion. 2006, 177, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, M.; Brisset, N.; Fauth, F.; Weill, F.; Elkaim, E.; Suard, E.; Masquelier, C.; Croguennec, L. Na3V2(PO4)2F3 revisited: A high-resolution diffraction study. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4238–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, A.; Liu, Z.; Gamboa, S.; Sebastian, P.J. The preparation of NaV1−xCrxPO4F cathode materials for sodium-ion battery. J. Power Sources 2006, 160, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Xue, L.; Xu, G.; Zhang, X. Preparation and characterization of carbon-coated NaVPO4F as cathode material for rechargeable sodium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 247, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, R.A.; Seo, D.-H.; Kim, H.; Park, Y.-U.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.-W.; Gwon, H.; Lee, S.; Kang, K. A combined first principles and experimental study on Na3V2(PO4)2F3 for rechargeable Na batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20535–20541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihara, K.; Kitajou, A.; Gocheva, I.D.; Okada, S.; Yamaki, J. Cathode properties of Na3M2(PO4)2F3 [M = Ti, Fe, V] for sodium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 227, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Cao, X.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, H.; Lan, Q.; Ji, X. Investigation of the sodium ion pathway and cathode behavior in Na3V2(PO4)2F3 combined via a first principles calculation. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12438–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Dunstan, M.T.; Huo, H.; Hao, X.; Zou, H.; Zhong, G.; Yang, Y.; Grey, C.P. Local structure and dynamics in the Na ion battery positive electrode material Na3V2(PO4)2F3. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2513–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Chen, G.; Li, A.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. Sol–gel preparation and electrochemical properties of Na3V2(PO4)2F3/C composite cathode material for lithium ion batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 478, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghi, N.; Caes, S.; Mahmoud, A.; Cloots, R.; Vertruyen, B.; Boschini, F. Sodium vanadium (III) fluorophosphate/carbon nanotubes composite (NVPF/CNT) prepared by spray-drying: Good electrochemical performance thanks to well-dispersed CNT network within NVPF particles. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 228, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosova, N. Mechanochemical reactions and processing of nanostructured electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.; Gover, R.K.B.; Burns, P.; Bryan, A.J. Hybrid-ion. A lithium-ion cell based on a sodium insertion material. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2006, 9, A190–A192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Liu, S. A sodium vanadium three-fluorophosphate cathode for rechargeable batteries synthesized by carbothermal reduction. Solid State Sci. 2013, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.; Cover, R.; Burns, P.; Bryan, A.J. Li4/3Ti5/3O4||Na3V2(PO4)2F3: An example of a hybrid-ion cell using a non-graphitic anode. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, A882–A887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-U.; Seo, D.-H.; Kim, B.; Hong, K.-P.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.; Shakoor, R.A.; Miyasaka, K.; Tarascon, J.-M.; Kang, K. Tailoring a fluorophosphate as a novel 4 V cathode for lithium-ion batteries. Sci. Rep. 2012, 704, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait Salah, A.; Jozwiak, P.; Garbarczyk, J.; Benkhouja, K.; Zaghib, K.; Gendron, F.; Julien, C.M. Local structure and redox energies of lithium phosphates with olivine- and Nasicon-like structures. J. Power Sources 2005, 140, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosova, N.V.; Devyatkina, E.T.; Slobodyuk, A.B.; Gutakovskii, A.K. LiVPO4F/Li3V2(PO4)3 nanostructured composite cathode materials prepared via mechanochemical way. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2014, 18, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kera, Y. Infrared study of alkali tri- and hexavanadates as formed from their melts. J. Solid State Chem. 1984, 51, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, M.; Fauth, F.; Brisset, N.; Weill, F.; Suard, E.; Masquelier, C.; Croguennec, L. A comprehensive investigation of the Na3V2(PO4)2F3–NaV2(PO4)2F3 system by operando high resolution synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 3009–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheary, R.W.; Coelho, A.A. A fundamental parameters approach to X-ray line-profile fitting. J. Appl. Cryst. 1992, 25, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosova, N.V.; Podugolnikov, V.R.; Devyatkina, E.T.; Slobodyuk, A.B. Structure and electrochemictry of NaFePO4 and Na2FePO4F cathode materials prepared via mechanochemical route. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 60, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosova, N.V.; Rezepova, D.O.; Petrov, S.A.; Slobodyuk, A.B. Elelctrochemical and chemical Na+/Li+ ion exchange in Na-based cathode materials: Na1.56Fe1.22P2O7 and Na3V2(PO4)2F3. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A6192–A6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Synthetic Method | Treatment Temperature | Treatment Time | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid-state synthesis, CTR * | 600–800 °C | 8 h | Gover et al. [12] |
| Solid-state synthesis, CTR, MA ** | 750 °C | 1.5 h | Shakoor et al. [16] |
| Solid-state synthesis, CTR, MA | 800 °C | 1 h | Bianchini et al. [13] |
| Solution-based solid-state synthesis | 650 °C | 8 h | Song et al. [18] |
| Hydrothermal reaction | 180 °C | 64 h | Le Meins et al. [5] |
| Sol–gel preparation | 650 °C | 8 h | Jiang et al. [20] |
| Spray drying | 600 °C | 2 h | Eshraghi et al. [21] |
| Solid-state synthesis, CTR, MA | 650 °C | 1 h | This work |
| Sample (y) | Main Phase Na3V2(PO4)2F3 | Impurities | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80.6 | Na3V2(PO4)3—4.6 | VPO4—14.8 | - |
| 0.25 | 92.5 | - | - | NaVOPO4—7.5 |
| 0.5 | 100 | - | - | - |
| 0.6 | 86.6 | Na3VF6—2.9 | NaV2O5—4.0 | Na3PO4—6.5 |
| 0.75 | 78.9 | Na3VF6—6.6 | NaV2O5—4.8 | Na3PO4—9.7 |
| Composition | S.G. | a = b, Å | c, Å | Volume, Å3 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaVPO4F | I4/mmm | 6.387(2) | 10.734(3) | 438.1 | [3] |
| I4/mmm | 6.38 | 10.72 | 436.4 | [4] | |
| Na3V2(PO4)2F3 | P42/mnm | 9.047(2) | 10.705(2) | 876.2(3) | [5] |
| P42/mnm | 9.0378(3) | 10.7482(4) | 877.94(6) | [12] | |
| P42/mnm | 9.0358(2) | 10.7403(4) | 876.90(4) | [13] | |
| P42/mnm | 9.04 | 10.74 | 877.69 | [17] | |
| P42/mnm | 9.05 | 10.74 | 876.9 | [18] | |
| P42/mnm | 9.04 | 10.73 | 877.0 | [19] | |
| Na3V2(PO4)2F3 | Amam | a = 9.0288(6) | 10.7402(5) | 876.88(9) | [13] |
| b = 9.0426(6) | |||||
| Na1.5VOPO4F0.5 | I4/mmm | 6.37028(8) | 10.6365(2) | 431.63(1) | [6] |
| Na3V2O2x(PO4)2F3−2x | P42/mnm | 9.02548–9.04499 | 10.63184–0.62113 | 866.1–869.0 | [11] |
| Na1.5VO0.8PO4F0.7 | P42/mnm | 9.0332(1) | 10.6297(2) | 867.37(2) | [26] |
| Na1.5VOPO4F0.5 | P42/mnm | 9.03051(2) | 10.62002(3) | 866.064 | [7] |
| y | S.G. | a = b, Å | c, Å | V, Å3 | GOF */Rwp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | P42/mnm | 9.0376(2) | 10.7588(3) | 878.77(5) | 1.69/7.28 |
| 0.25 | P42/mnm | 9.0372(1) | 10.7545(2) | 878.32(3) | 1.77/7.08 |
| 0.5 | P42/mnm | 9.0393(1) | 10.7520(2) | 878.54(2) | 1.71/6.75 |
| 0.0 | Amam | 9.0298(5)/9.0465(5) | 10.7595(3) | 878.92(7) | 1.64/6.61 |
| 0.25 | Amam | 9.0296(2)/9.0450(2) | 10.7448(2) | 878.37(4) | 1.58/6.37 |
| 0.5 | Amam | 9.0323(2)/9.0467(2) | 10.7523(1) | 878.60(2) | 1.44/5.73 |
| Sample | Stage | S.G. | a = b, Å | c, Å | V, Å3 | Na+/f.u. | GOF/Rwp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y = 0.5 | charge | I4/mmm | 6.2496(2) | 10.9568(7) | 427.94(4) | 0.54(2) | 1.67/10.78 |
| y = 0.5 (sample A) | discharge | P42/mnm | 9.0251(3) | 10.7524(6) | 875.82(8) | 1.30(2) | 2.09/7.89 |
| y = 0.5 (sample B) | discharge | P42/mnm | 9.0175(12) | 10.7000(19) | 870.07(27) | 0.82(6) | 2.43/12.65 |
| Na1.3(VPO4)2F3 [30] | charge | I4/mmm | 6.2481(1) | 10.9222(2) | 426.39(1) | 0.65 | 1.31(6) |
| Na1.8(VPO4)2F3 [30] | charge | I4/mmm | 6.2800(1) | 10.8493(3) | 427.88(1) | 0.9 | 1.85(7) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosova, N.V.; Rezepova, D.O. Na1+yVPO4F1+y (0 ≤ y≤ 0.5) as Cathode Materials for Hybrid Na/Li Batteries. Inorganics 2017, 5, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5020019
Kosova NV, Rezepova DO. Na1+yVPO4F1+y (0 ≤ y≤ 0.5) as Cathode Materials for Hybrid Na/Li Batteries. Inorganics. 2017; 5(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosova, Nina V., and Daria O. Rezepova. 2017. "Na1+yVPO4F1+y (0 ≤ y≤ 0.5) as Cathode Materials for Hybrid Na/Li Batteries" Inorganics 5, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5020019
APA StyleKosova, N. V., & Rezepova, D. O. (2017). Na1+yVPO4F1+y (0 ≤ y≤ 0.5) as Cathode Materials for Hybrid Na/Li Batteries. Inorganics, 5(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5020019