Luminescent Imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine Cores and Corresponding Zn(II) Complexes: Structural and Optical Tunability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
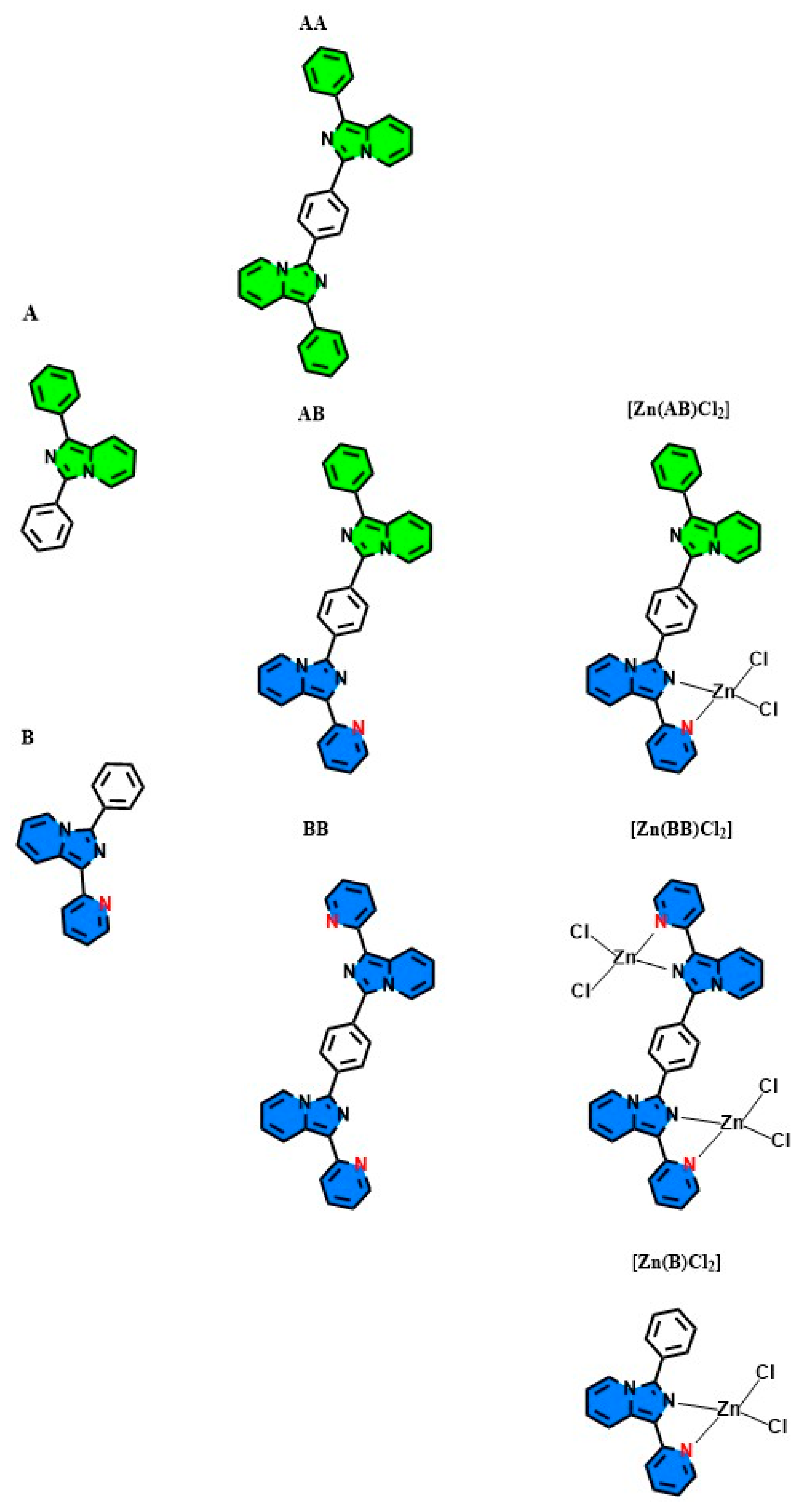
2.1. Synthesis
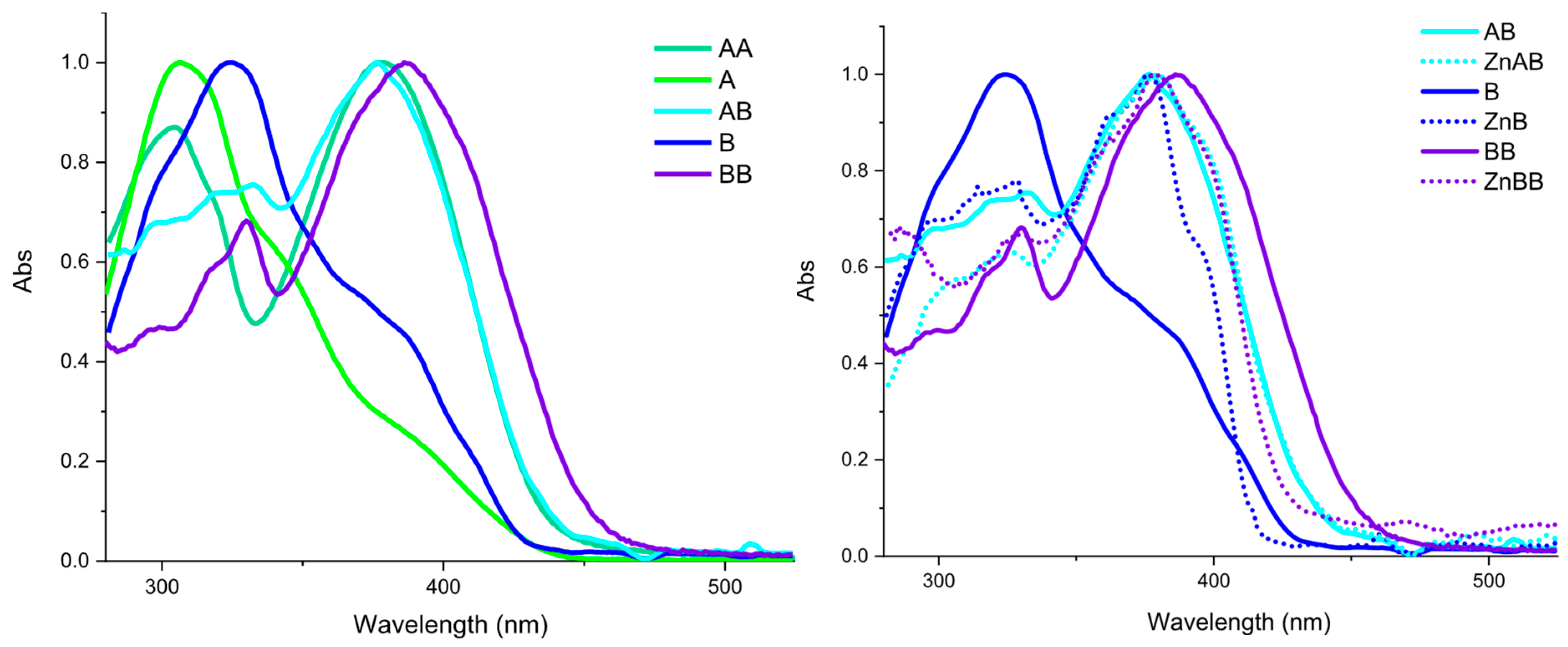
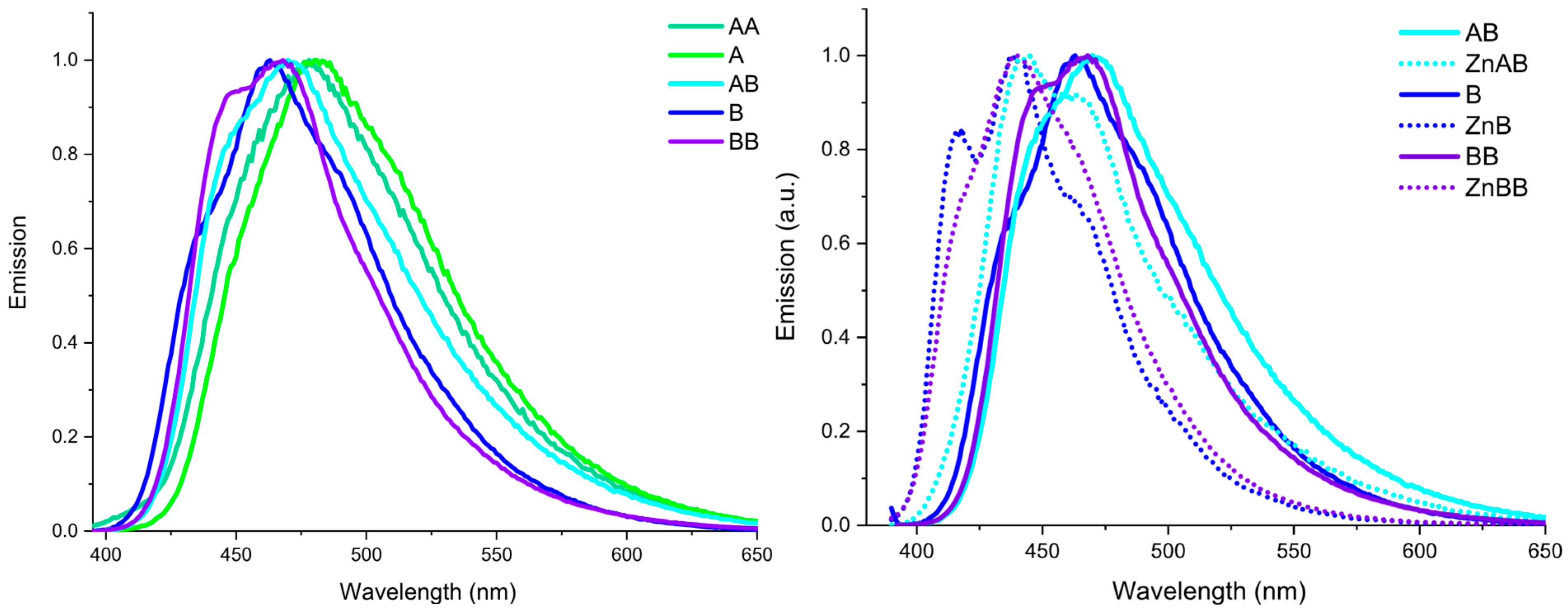
2.2. Optical Characterization
| Compound | Absorption (nm) | Excitation (nm) | Emission (nm) | Stokes Shift [cm−1 (nm)] | Quantum Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 306 342 sh 385 sh | 385 | 484 | 5313 (178) | 22 |
| AA | 303 378 | 377 | 480 | 5692 (102) | 10 |
| AB | 331 379 | 379 | 449 sh 468 | 5018 (89) | 18 |
| [Zn(AB)Cl2] | 326 379 | 379 | 444 466 sh | 3863 (65) | 35 |
| B | 325 380 sh | 380 | 435 sh 462 | 4671 (137) | 19 |
| [Zn(B)Cl2] | 325 362 sh 376 394 sh | 376 | 416 sh 440 462 sh | 3868 (64) | 32 |
| BB | 330 387 | 380 | 447 sh 466 | 4856 (79) | 25 |
| [Zn2(BB)Cl4] | 330 378 | 380 | 440 466 sh | 3588 (62) | 37 |
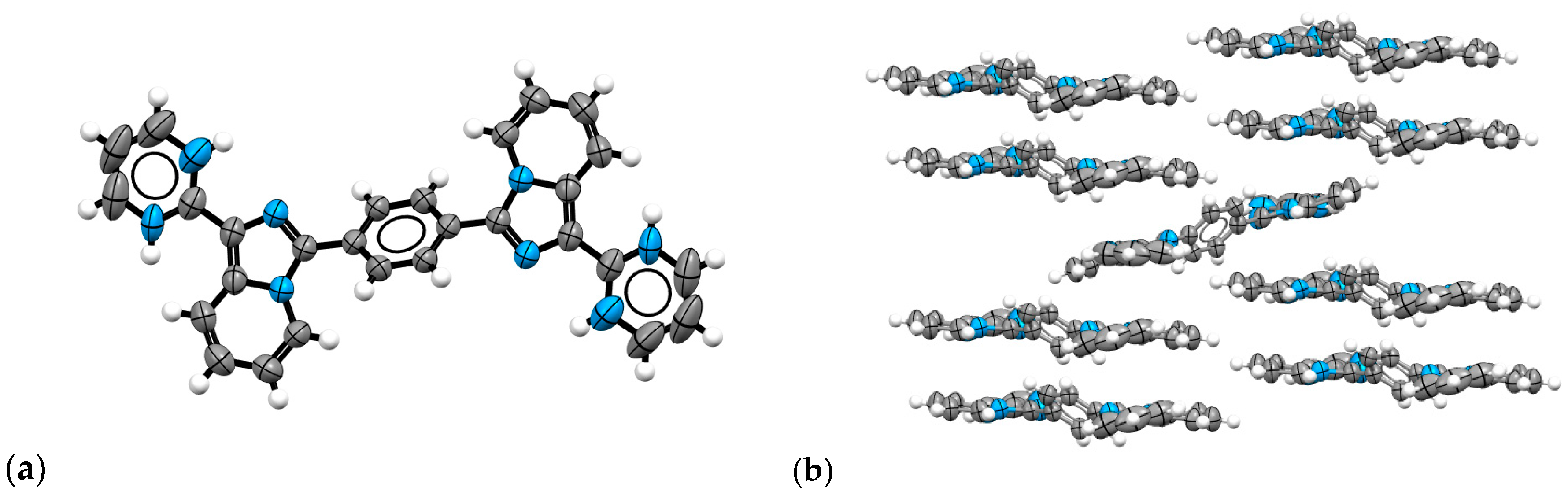
2.3. Structural Characterization
2.4. Vibrational Characterization
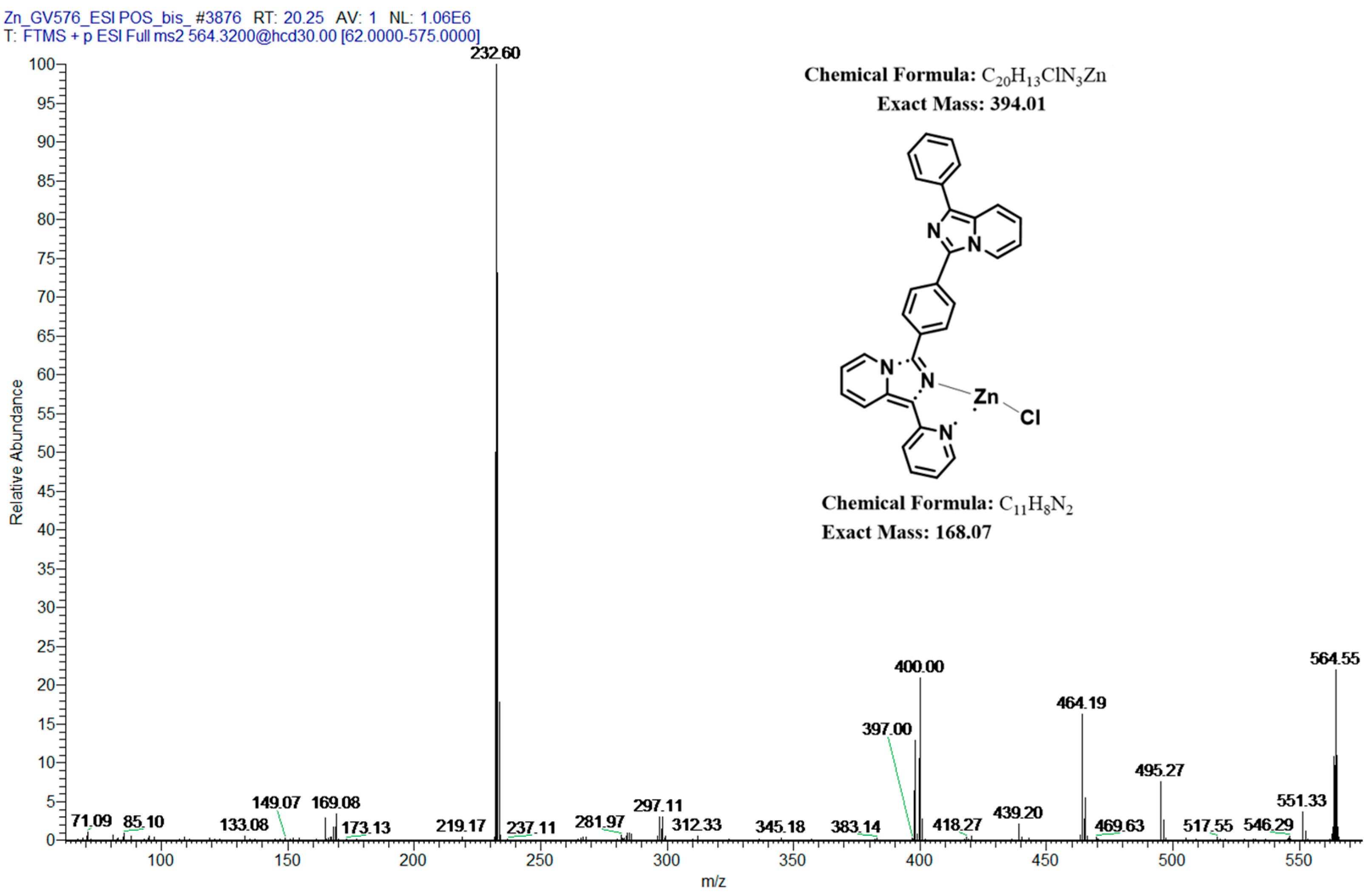
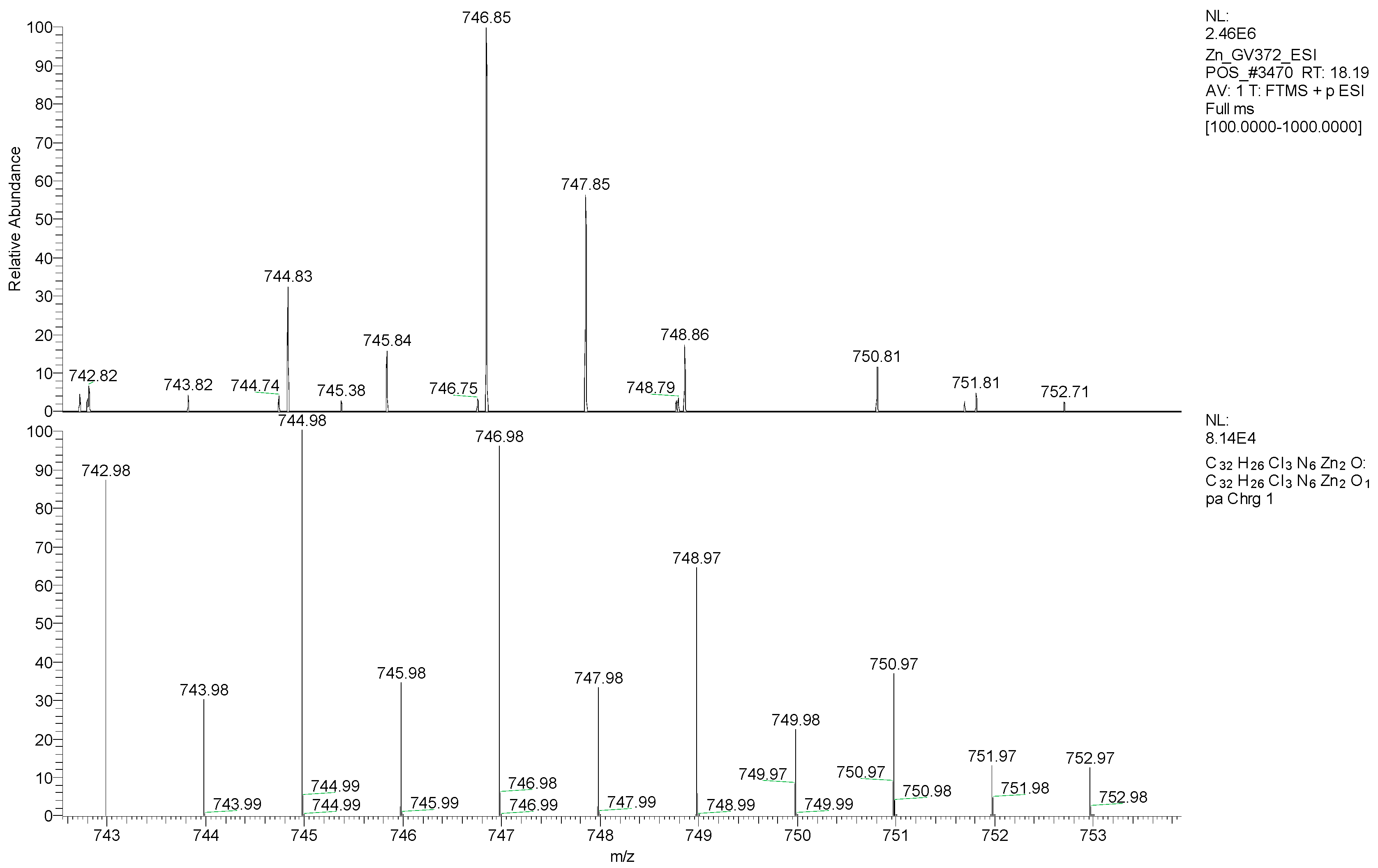
2.5. Mass Spectrometry
3. Experimental Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dumur, F. Zinc Complexes in OLEDs: An Overview. Synth. Met. 2014, 195, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Sagara, Y.; Nomura, H.; Nakamura, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Miyazaki, H.; Adachi, C. Zinc Complexes Exhibiting Highly Efficient Thermally Activated Delayed Fluorescence and Their Application to Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3181–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janghouri, M.; Adineh, M. Color Optimization of Red Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs) through Dihydroxyphenyl-Substituted Zinc Porphyrins Emitters. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 341, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.C.; Douglas, P.; Winscom, C.J. Coordination Complexes Exhibiting Room-Temperature Phosphorescence: Evaluation of Their Suitability as Triplet Emitters in Organic Light Emitting Diodes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 2093–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, K.; Komatsu, K.; Nagano, T. Zinc Sensing for Cellular Application. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2004, 8, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, S.; Reineck, P.; Vidanapathirana, A.K.; Pullen, B.J.; Drumm, D.W.; Ritter, L.J.; Schwarz, N.; Bonder, C.S.; Psaltis, P.J.; Thompson, J.G.; et al. Rationally Designed Probe for Reversible Sensing of Zinc and Application in Cells. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 6201–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strianese, M.; Brenna, S.; Ardizzoia, G.A.; Guarnieri, D.; Lamberti, M.; D’Auria, I.; Pellecchia, C. Imidazo-Pyridine-Based Zinc(II) Complexes as Fluorescent Hydrogen Sulfide Probes. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 17075–17085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Clark, R.J.; Zhu, L. Highly Sensitive Fluorescent Probes for Zinc Ion Based on Triazolyl-Containing Tetradentate Coordination Motifs. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 4999–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janghouri, M. White-Light-Emitting Devices Based on Nile Red and π Electron Rich [Zn4core] Complex. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2017, 49, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-de-Luzuriaga, J.M.; Monge, M.; Olmos, M.E. Luminescent Aryl–Group Eleven Metal Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 2046–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housecroft, C.E.; Constable, E.C. Solar Energy Conversion Using First Row D-Block Metal Coordination Compound Sensitizers and Redox Mediators. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 1225–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Wang, Z.-B.; Li, Y.; Kozera, D.J.; Lu, Z.-H.; Song, D. Syntheses, Structures, and Luminescent Properties of Dipyridylamine-Functionalized Anthracene and Its Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 7039–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozada, I.B.; Braun, J.D.; Williams, J.A.G.; Herbert, D.E. Yellow-Emitting, Pseudo-Octahedral Zinc Complexes of Benzannulated N^N^O Pincer-Type Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 17568–17578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elzaher, M.M. Spectroscopic Characterization of Some Tetradentate Schiff Bases and Their Complexes with Nickel, Copper and Zinc. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2001, 48, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzoia, G.A.; Brenna, S.; Durini, S.; Therrien, B.; Veronelli, M. Synthesis, Structure, and Photophysical Properties of Blue-Emitting Zinc(II) Complexes with 3-Aryl-Substituted 1-Pyridylimidazo[1,5-a]Pyridine Ligands: Blue-Emitting Zinc(II) Complexes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2014, 4310–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzoia, G.A.; Brenna, S.; Durini, S.; Therrien, B. Synthesis and Characterization of Luminescent Zinc(II) Complexes with a N,N-Bidentate 1-Pyridylimidazo[1,5-a]Pyridine Ligand. Polyhedron 2015, 90, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciupa, A.; Mahon, M.F.; Paul, A.; Caggiano, L. Simple Pyrazoline and Pyrazole “Turn on” Fluorescent Sensors Selective for Cd2+ and Zn2+ in MeCN. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 8753–8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, E.; Shibahara, F.; Murai, T. 1-Alkynyl- and 1-Alkenyl-3-Arylimidazo[1,5-a]Pyridines: Synthesis, Photophysical Properties, and Observation of a Linear Correlation between the Fluorescent Wavelength and Hammett Substituent Constants. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 6146–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohbiya, D.R.; Sekar, N. Tuning ‘Stokes Shift’ and ICT Character by Varying the Donor Group in Imidazo[1,5 a]Pyridines: A Combined Optical, DFT, TD-DFT and NLO Approach. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 1635–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, G.; Laurenti, E.; Rabezzana, R. Imidazopyridine Family: Versatile and Promising Heterocyclic Skeletons for Different Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, G.; Rabezzana, R. Imidazo[1,5-a]Pyridine Derivatives: Useful, Luminescent and Versatile Scaffolds for Different Applications. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 5737–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durini, S.; Ardizzoia, G.A.; Therrien, B.; Brenna, S. Tuning the Fluorescence Emission in Mononuclear Heteroleptic Trigonal Silver(i) Complexes. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 3006–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, G.; Garino, C.; Conterosito, E.; Barolo, C.; Gobetto, R.; Viscardi, G. Facile Synthesis of Novel Blue Light and Large Stoke Shift Emitting Tetradentate Polyazines Based on Imidazo[1,5-a]Pyridine. Dye. Pigment. 2016, 128, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, G.; Garino, C.; Priola, E.; Diana, E.; Gobetto, R.; Buscaino, R.; Viscardi, G.; Barolo, C. Facile Synthesis of Novel Blue Light and Large Stoke Shift Emitting Tetradentate Polyazines Based on Imidazo[1,5-a]Pyridine—Part 2. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 143, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, G.; Magnano, G.; Benesperi, I.; Saccone, D.; Priola, E.; Gianotti, V.; Milanesio, M.; Conterosito, E.; Barolo, C.; Viscardi, G. One Pot Synthesis of Low Cost Emitters with Large Stokes’ Shift. Dye. Pigment. 2017, 137, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guckian, A.L.; Doering, M.; Ciesielski, M.; Walter, O.; Hjelm, J.; O’Boyle, N.M.; Henry, W.; Browne, W.R.; McGarvey, J.J.; Vos, J.G. Assessment of Intercomponent Interaction in Phenylene Bridged Dinuclear Ruthenium(II) and Osmium(II) Polypyridyl Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2004, 23, 3943–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, N.; Abtab, S.M.T.; Kundu, S.; Endo, A.; Teat, S.J.; Chaudhury, M. Triple-Stranded Helicates of Zinc(II) and Cadmium(II) Involving a New Redox-Active Multiring Nitrogenous Heterocyclic Ligand: Synthesis, Structure, and Electrochemical and Photophysical Properties. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 2652–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, N.; Maity, M.; Chatterjee, P.B.; Teat, S.J.; Endo, A.; Chaudhury, M. Reporting a Unique Example of Electronic Bistability Observed in the Form of Valence Tautomerism with a Copper(II) Helicate of a Redox-Active Nitrogenous Heterocyclic Ligand. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20104–20107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzoia, G.A.; Colombo, G.; Therrien, B.; Brenna, S. Tuning the Fluorescence Emission and HOMO-LUMO Band Gap in Homoleptic Zinc(II) Complexes with N,O-Bidentate (Imidazo[1,5-a]Pyrid-3-Yl)Phenols. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renno, G.; Cardano, F.; Volpi, G.; Barolo, C.; Viscardi, G.; Fin, A. Imidazo[1,5-a]Pyridine-Based Fluorescent Probes: A Photophysical Investigation in Liposome Models. Molecules 2022, 27, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dyers, L.; Mason, R.; Amoyaw, P.; Bu, X.R. Highly Efficient and Direct Heterocyclization of Dipyridyl Ketone to N,N-Bidentate Ligands. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 2353–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, V.; Volpi, G.; Priola, E.; Giordana, A.; Garino, C.; Rabezzana, R.; Diana, E. Mono-, Bis-, and Tris-Chelate Zn(II) Complexes with Imidazo[1,5-a]Pyridine: Luminescence and Structural Dependence. Molecules 2023, 28, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpi, G.; Priola, E.; Garino, C.; Daolio, A.; Rabezzana, R.; Benzi, P.; Giordana, A.; Diana, E.; Gobetto, R. Blue Fluorescent Zinc(II) Complexes Based on Tunable Imidazo[1,5-a]Pyridines. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2020, 509, 119662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibahara, F.; Kitagawa, A.; Yamaguchi, E.; Murai, T. Synthesis of 2-Azaindolizines by Using an Iodine-Mediated Oxidative Desulfurization Promoted Cyclization of N-2-Pyridylmethyl Thioamides and an Investigation of Their Photophysical Properties. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 5621–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, A.; Brenna, S.; Ardizzoia, G.A. Synthesis and Emissive Properties of a Series of Tetrahydro (Imidazo[1,5-a]Pyrid-3-Yl)Phenols: A New Class of Large Stokes Shift Organic Dyes. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 161, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, G.; Attilio Ardizzoia, G.; Brenna, S. Imidazo[1,5-a]Pyridine-Based Derivatives as Highly Fluorescent Dyes. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2022, 535, 120849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priola, E.; Conterosito, E.; Giordana, A.; Volpi, G.; Garino, C.; Andreo, L.; Diana, E.; Barolo, C.; Milanesio, M. Polymorphism and Solid State Peculiarities in Imidazo[1,5-a]Pyridine Core Deriving Compounds: An Analysis of Energetic and Structural Driving Forces. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1253, 132175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, G.; Garino, C.; Salassa, L.; Fiedler, J.; Hardcastle, K.I.; Gobetto, R.; Nervi, C. Cationic Heteroleptic Cyclometalated Iridium Complexes with 1-Pyridylimidazo[1,5-Alpha]Pyridine Ligands: Exploitation of an Efficient Intersystem Crossing. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 6415–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.D.; Garino, C.; Volpi, G.; Casamassa, E.; Milanesio, M.; Barolo, C.; Costa, R.D. Origin of a Counterintuitive Yellow Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cell Based on a Blue-Emitting Heteroleptic Copper(i) Complex. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8984–8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozel, A.E.; Kecel, S.; Akyuz, S. Vibrational Analysis and Quantum Chemical Calculations of 2,2′-Bipyridine Zinc(II) Halide Complexes. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 834–836, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postmus, C.; Ferraro, J.R.; Woznizk, W. Low-Frequency Infrared Spectra of Nitrogen-Ligand Complexes of Zinc(II) Halides. Inorg. Chem. 1967, 6, 2030–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
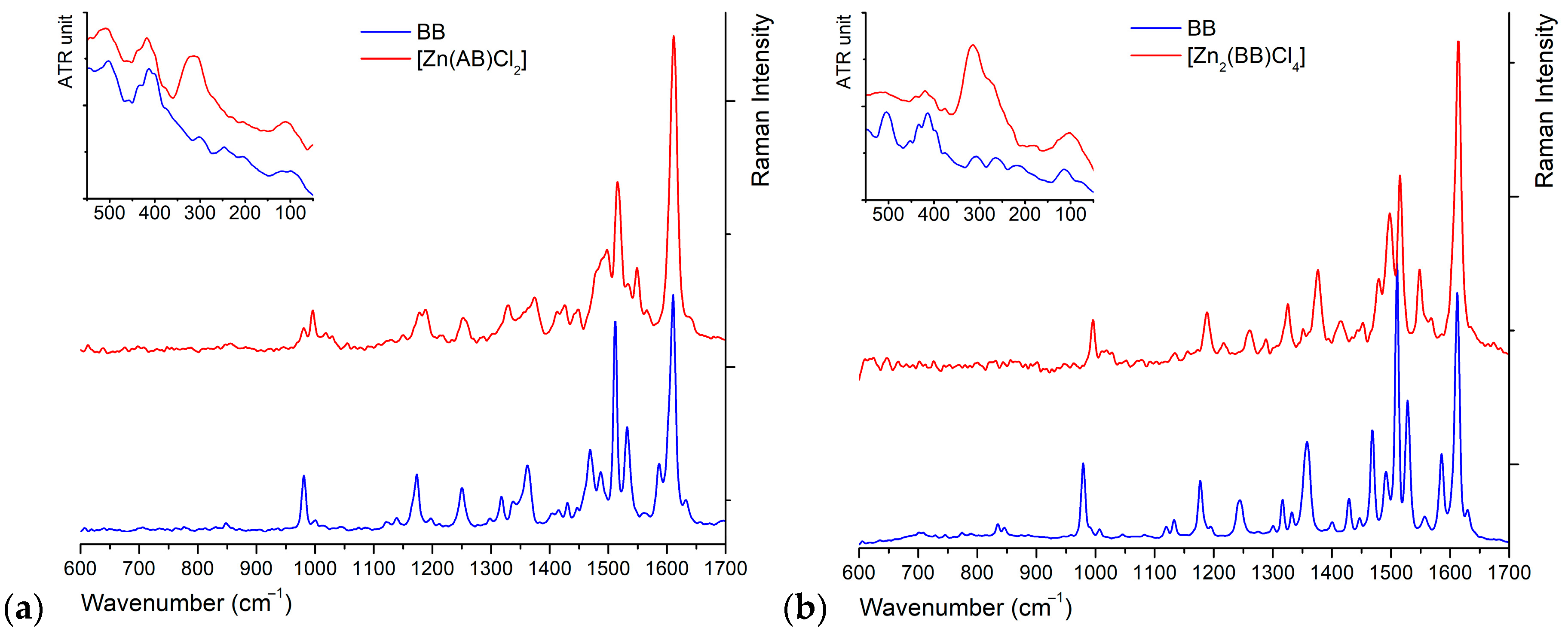
| B | [Zn(B)Cl2] | BB | [Zn2(BB)Cl4] | AB | [Zn(AB)Cl2] | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1631 m | 1638 w | 1630 w | 1635 vw | 1632 w | 1638 w,sh | νC―N, νC―C |
| 1603 s | 1604 vs | 1612 s | 1614 vs | 1611 vs | 1611 s | |
| 1588 s | 1585 m | 1586 m | ||||
| 1533 vs | 1547 s | 1548 m | 1549 m | |||
| 1523 s | 1533 s | 1528 m | 1532 m | 1533 m | ||
| 1507 s | 1513 vs | 1510 vs | 1515 m | 1511 s | 1516 m | |
| 998 w 980 m | 1023 m | 991 w 980 m | 1028 w | 1000 w 980 m | 1028 w | νC―C |
| 1018 w | 1016 w | |||||
| 1012 m | 1011 w | 996 m | ||||
| 994 s | 995 m | 980 w | ||||
| 331 s | 315 m | 324 m | νZn―Cl | |||
| 308 s | 275 w | 306 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Volpi, G.; Giordana, A.; Priola, E.; Rabezzana, R.; Diana, E. Luminescent Imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine Cores and Corresponding Zn(II) Complexes: Structural and Optical Tunability. Inorganics 2025, 13, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13090283
Volpi G, Giordana A, Priola E, Rabezzana R, Diana E. Luminescent Imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine Cores and Corresponding Zn(II) Complexes: Structural and Optical Tunability. Inorganics. 2025; 13(9):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13090283
Chicago/Turabian StyleVolpi, G., A. Giordana, E. Priola, R. Rabezzana, and E. Diana. 2025. "Luminescent Imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine Cores and Corresponding Zn(II) Complexes: Structural and Optical Tunability" Inorganics 13, no. 9: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13090283
APA StyleVolpi, G., Giordana, A., Priola, E., Rabezzana, R., & Diana, E. (2025). Luminescent Imidazo[1,5-a]pyridine Cores and Corresponding Zn(II) Complexes: Structural and Optical Tunability. Inorganics, 13(9), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13090283









