Ultrahigh Water Permeance of a Reduced Graphene Oxide Membrane for Separation of Dyes in Wastewater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
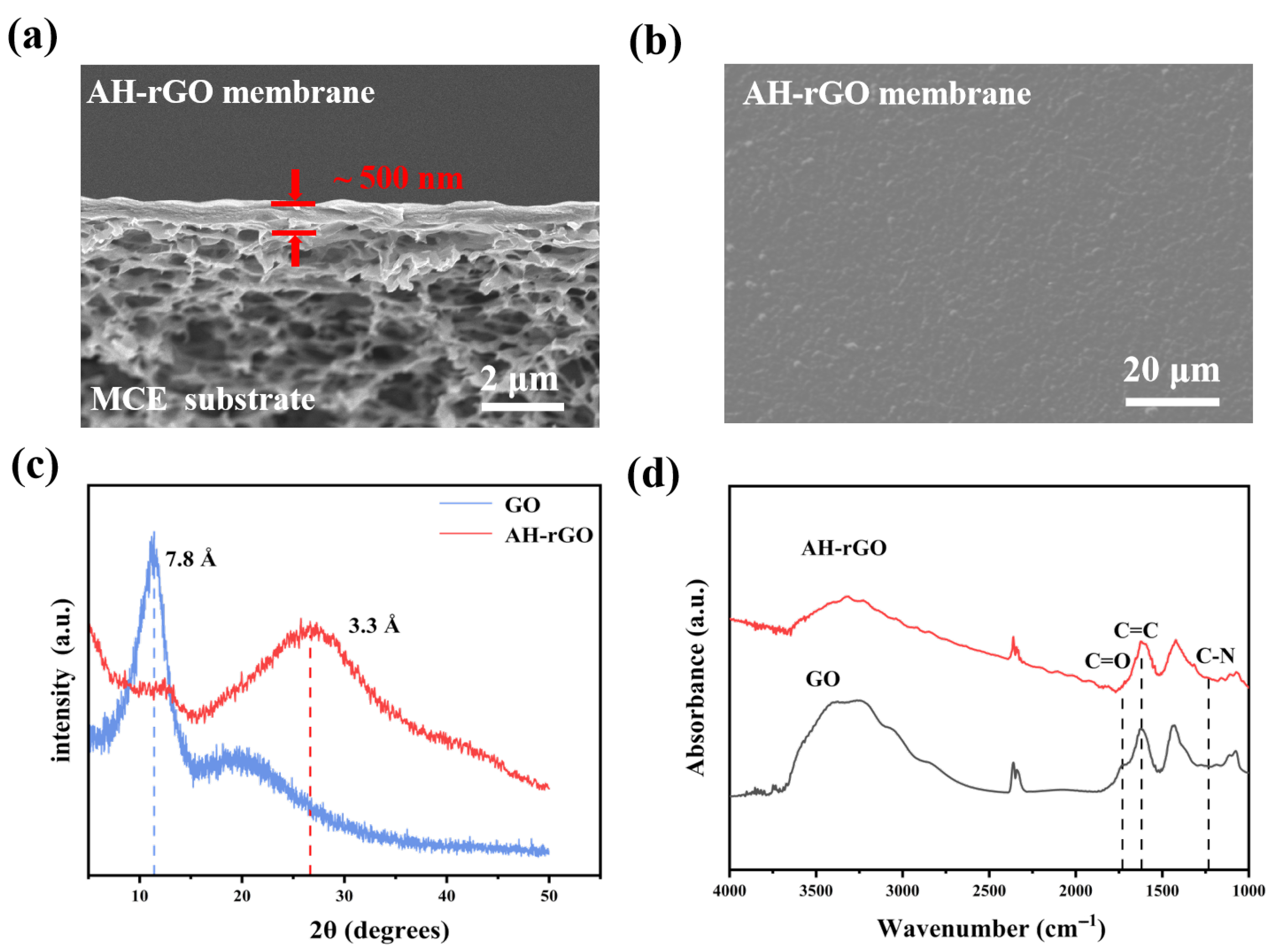
2.1. Characteristics of the rGO Membranes
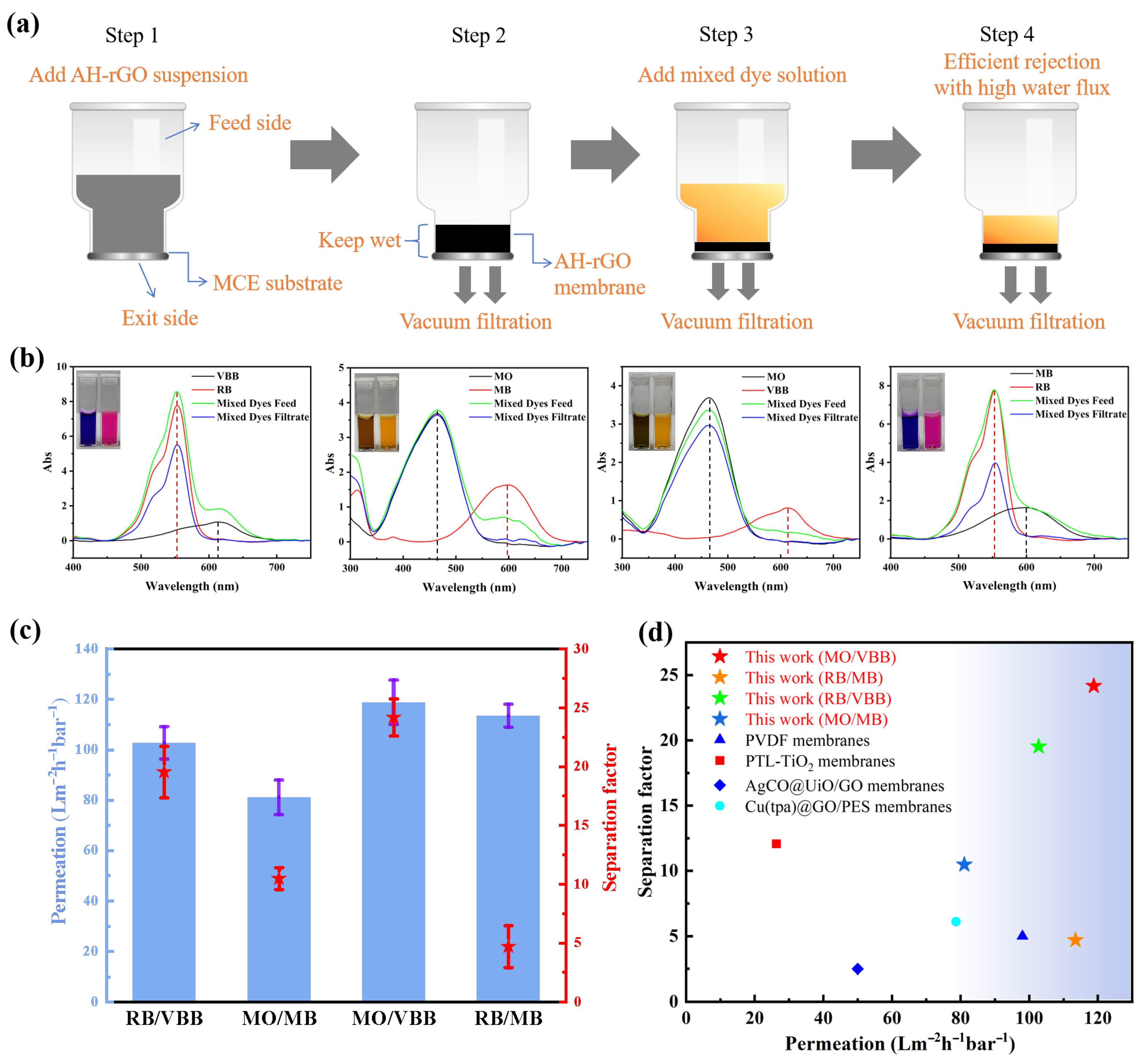
2.2. Separation Performance of the AH-rGO Membrane
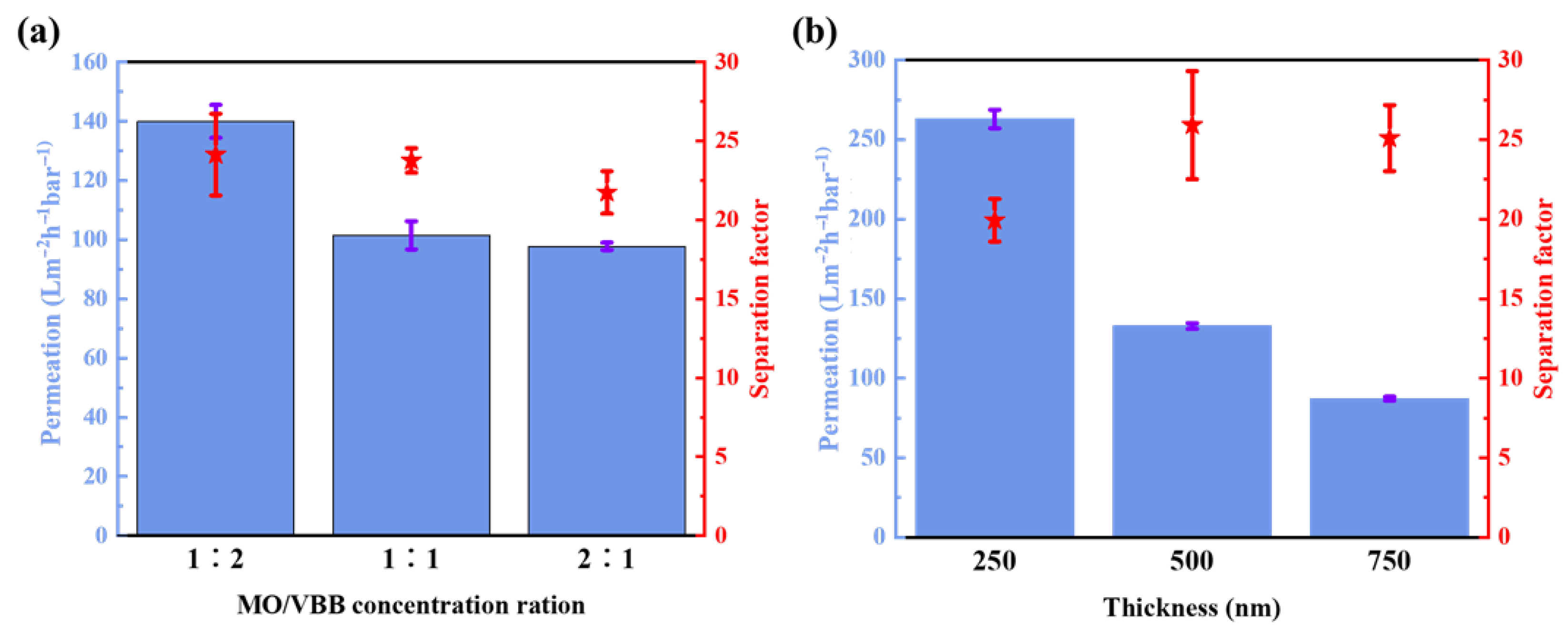
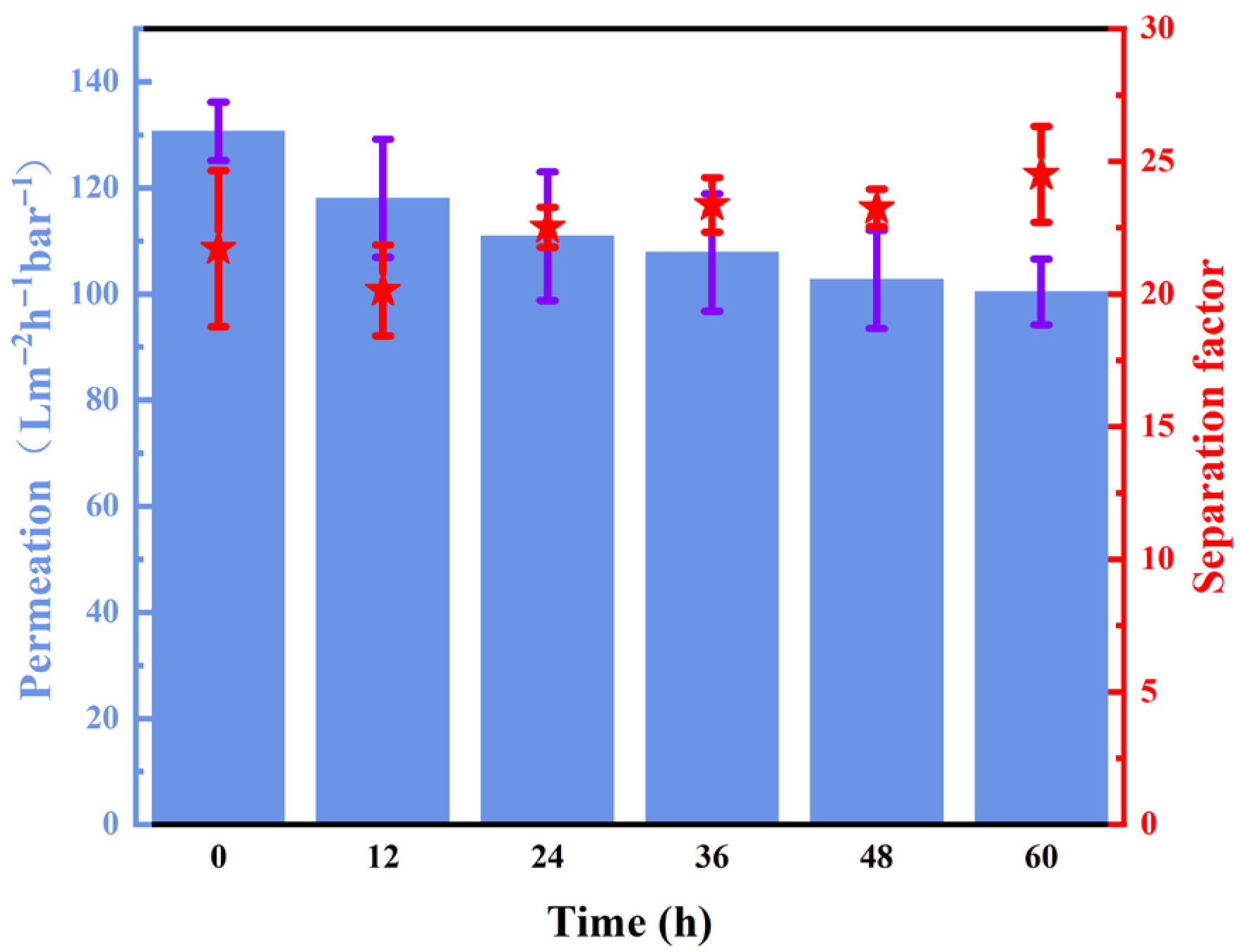
2.3. Performance of the AH-rGO Membranes
2.4. Potential Application in Dye Separation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of AH-rGO Suspension
3.3. Separation Experiments
3.4. Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MO | Methyl Orange |
| VBB | Victoria Blue B |
| MB | Methylene Blue |
| RB | Rhodamine B |
| NBB | Naphthol Blue Black |
| CR | Congo Red |
References
- Moradihamedani, P. Recent advances in dye removal from wastewater by membrane technology: A review. Polym. Bull. 2021, 79, 2603–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khader, E.H.; Khudhur, R.H.; Abbood, N.S.; Albayati, T.M. Decolourisation of Anionic Azo Dye in Industrial Wastewater Using Adsorption Process: Investigating Operating Parameters. Environ. Process. 2023, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.; Singh, A.; Ambati, S.R.; Singh, R.S.; Sonwani, R.K. An overview of recent advances in treatment of complex dye-containing wastewater and its techno-economic assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akarslan, F.; Demiralay, H. Effects of Textile Materials Harmful to Human Health. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2015, 128, B-407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopape, D.A.; Ntsendwana, B.; Mabasa, F.D. Photocatalysis as a pre-discharge treatment to improve the effect of textile dyes on human health: A critical review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghany, H.A.; Ibrahim, E.M. Unexpected radiation hazard in dyes of textiles. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2014, 50, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belpaire, C.; Reyns, T.; Geeraerts, C.; Van Loco, J. Toxic textile dyes accumulate in wild European eel Anguilla anguilla. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Roy, A.; Bhasin, S.; Emran, T.B.; Khusro, A.; Eftekhari, A.; Moradi, O.; Rokni, H.; Karimi, F. Nanomaterials: An alternative source for biodegradation of toxic dyes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 164, 112996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.S.; Lee, H.-J. Nanostructured Materials for Water Purification: Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions and Organic Dyes. Polymers 2022, 14, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danouche, M.; El Arroussi, H.; El Ghachtouli, N. Mycoremediation of synthetic dyes by yeast cells: A sustainable biodegradation approach. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 4, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindhal, T.; Rakholiya, P.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Ng, H.Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater. Bioengineered 2020, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, M.M.; El Abd, Y.M. Removal and Recovery of Dyestuffs from Dyeing Wastewaters. Sep. Purif. Methods 2006, 31, 171–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Song, G.; Sun, Y.; Ding, G. A review on selective dye adsorption by different mechanisms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhikku Kandath Valappil, R.; Ghasem, N.; Al-Marzouqi, M. Current and future trends in polymer membrane-based gas separation technology: A comprehensive review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 103–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirkar, K.K. Membrane Separation Technologies: Current Developments. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2007, 157, 145–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.; Ding, Z.; Gogotsi, Y. Two-dimensional MXenes and their applications. Front. Phys. 2023, 18, 13604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutrisna, P.D.; Kurnia, K.A.; Siagian, U.W.R.; Ismadji, S.; Wenten, I.G. Membrane fouling and fouling mitigation in oil–water separation: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.B.; Kamcev, J.; Robeson, L.M.; Elimelech, M.; Freeman, B.D. Maximizing the right stuff: The trade-off between membrane permeability and selectivity. Science 2017, 356, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-Y.; Gai, Y.-N.; Gai, X.-T.; Qin, J.; Wang, Z.-G.; Cui, L.-S.; Guo, H.; Jiang, M.-Y.; Zou, Q.; Zhou, T.; et al. Interfacial synthesized covalent organic framework nanofiltration membranes for precisely ultrafast sieving. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, S.; Qian, Y.; Zuo, H.-R.; Duan, M. A loose nanofiltration membrane prepared by interfacial radical polymerization for dye/salt separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 701, 122751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nellur, U.; K S, K.; Naik, N.S.; Padaki, M. Innovation of poly(ionic liquid)-stabilized TiO2 for membrane-based dye waste remediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 483, 144268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.V.; Kumar, S.R.; Lue, S.J. Separation mechanisms of binary dye mixtures using a PVDF ultrafiltration membrane: Donnan effect and intermolecular interaction. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 575, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.-C.; Grossman, J.C. Atomistic understandings of reduced graphene oxide as an ultrathin-film nanoporous membrane for separations. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Navarro, C.; Meyer, J.C.; Sundaram, R.S.; Chuvilin, A.; Kurasch, S.; Burghard, M.; Kern, K.; Kaiser, U. Atomic Structure of Reduced Graphene Oxide. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1144–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Qian, X.; Thebo, K.H.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ren, W. Controlling reduction degree of graphene oxide membranes for improved water permeance. Sci. Bull. 2018, 63, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Yu, R.; Yi, R.; Lan, J.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, L. Ultrahigh water permeance of a reduced graphene oxide nanofiltration membrane for multivalent metal ion rejection. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 15068–15071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Z.; Sun, L.; Peng, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; Huang, L. GO-PANI nanofiltration membrane with pH response for high efficiency water purification. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 69, 106889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Yu, Z.; Shao, L.; Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhu, X. Ag2CO3@UiO-66-NH2 embedding graphene oxide sheets photocatalytic membrane for enhancing the removal performance of Cr(VI) and dyes based on filtration. Desalination 2020, 491, 114558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhetha, T.A.; Moutloali, R.M. Antifouling properties of Cu(tpa)@GO/PES composite membranes and selective dye rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.K.; Carbone, P.; Wang, F.C.; Kravets, V.G.; Su, Y.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Wu, H.A.; Geim, A.K.; Nair, R.R. Precise and Ultrafast Molecular Sieving Through Graphene Oxide Membranes. Science 2014, 343, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhou, F.; Yu, R.; Cao, L.; Chen, L. Ultrahigh Water Permeance of Reduced Graphene Oxide Membrane for Radioactive Liquid Waste Treatment. Membranes 2021, 11, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, N.; Wu, M.; Wang, H.-Q. Review of the role of ionic liquids in two-dimensional materials. Front. Phys. 2023, 18, 43601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, C.; Lu, S.; Zeng, Y.; Hua, Q.; Zhang, Y. MnO2 Nanoflower Intercalation on Ti3C2Tx MXene With Expanded Interlayer Spacing for Flexible Asymmetric Supercapacitors. Carbon Neutralization 2025, 4, e70006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Song, Z.; Wei, N.; Shi, L.; Mao, Y.; Ying, Y.; Sun, L.; Xu, Z.; Peng, X. Ultrafast viscous water flow through nanostrand-channelled graphene oxide membranes. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Hu, G.; Feng, W.; Ru, J.; Li, Y. Transport channel engineering between MXene interlayers for Zn-ion hybrid microsupercapacitor with enhanced energy output and cycle stability. Carbon Neutralization 2023, 2, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Fan, X.; Wang, J.; Yuan, G.; Song, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Z. Study on the separation performance of the multi-channel reduced graphene oxide membranes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 384, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöche, S.; Hong, N.; Khorasaninejad, M.; Ambrosio, A.; Orabona, E.; Maddalena, P.; Capasso, F. Optical properties of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide determined by spectroscopic ellipsometry. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 421, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xia, X.; Wei, Y.; Sun, H.; Yao, H.; Zhu, J.; Liu, C.; Cao, L.; Lan, J.; Liu, X.; et al. Rapid and efficient separation of radioactive cesium ion/other radioactive ions by reduced graphene oxide membrane. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dabbs, D.M.; Liu, L.-M.; Aksay, I.A.; Car, R.; Selloni, A. Combined Effects of Functional Groups, Lattice Defects, and Edges in the Infrared Spectra of Graphene Oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 18167–18176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, K.; Cheng, D.; Pang, W.-L.; Lv, J.; Chen, X.; Zang, H.-Y.; Wu, X.-L.; Tan, H.-Q.; Wang, Y.-H.; et al. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon: Highly efficient trifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reversible catalysis and nitrogen reduction reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 7762–7769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, A.; Wei, M.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y. Influence of membrane hydrophilicity on water permeability: An experimental study bridging simulations. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 604, 118087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.R.; Wu, H.A.; Jayaram, P.N.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Geim, A.K. Unimpeded Permeation of Water Through Helium-Leak–Tight Graphene-Based Membranes. Science 2012, 335, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamang, S.; Rai, S.; Bhujel, R.; Bhattacharyya, N.K.; Swain, B.P.; Biswas, J. A concise review on GO, rGO and metal oxide/rGO composites: Fabrication and their supercapacitor and catalytic applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 947, 169588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhu, H. Cation–π Interactions in Graphene-Containing Systems for Water Treatment and Beyond. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Zhou, F.; Chen, J.; Liang, S.; Chen, L.; Fang, H. Ultrahigh water permeation with a high multivalent metal ion rejection rate through graphene oxide membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 10672–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Fu, C.-F.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Cui, P.; Ran, J.; Yang, J.; Xu, T. 2D Heterostructured Nanofluidic Channels for Enhanced Desalination Performance of Graphene Oxide Membranes. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 7586–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, N.; Qi, W.X.; Jiang, E.; Bao, J.J.; Zhang, X.P.; Zheng, W.J.; An, B.G.; et al. Low-pressure loose GO composite membrane intercalated by CNT for effective dye/salt separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 256, 117839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Fan, Y.; Yu, R.; Dai, F.; Lan, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, L. Robust reduced graphene oxide membranes with high water permeance enhanced by K+ modification. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 635, 119437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otitoju, T.A.; Ahmadipour, M.; Li, S.; Shoparwe, N.F.; Jie, L.X.; Owolabi, A.L. Influence of nanoparticle type on the performance of nanocomposite membranes for wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yan, S.; He, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Hou, R.; Chen, L.; Chen, J. A photo-Fenton self-cleaning membrane based on NH2-MIL-88B (Fe) and graphene oxide to improve dye removal performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 626, 119192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Hu, S.; Li, S.; Zhuge, H.; Mu, L.; Jiang, J.; Li, P.; Chen, L. Ultrahigh Water Permeance of a Reduced Graphene Oxide Membrane for Separation of Dyes in Wastewater. Inorganics 2025, 13, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13080251
Wu C, Hu S, Li S, Zhuge H, Mu L, Jiang J, Li P, Chen L. Ultrahigh Water Permeance of a Reduced Graphene Oxide Membrane for Separation of Dyes in Wastewater. Inorganics. 2025; 13(8):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13080251
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chengju, Shouyuan Hu, Shoupeng Li, Hangxiang Zhuge, Liuhua Mu, Jie Jiang, Pei Li, and Liang Chen. 2025. "Ultrahigh Water Permeance of a Reduced Graphene Oxide Membrane for Separation of Dyes in Wastewater" Inorganics 13, no. 8: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13080251
APA StyleWu, C., Hu, S., Li, S., Zhuge, H., Mu, L., Jiang, J., Li, P., & Chen, L. (2025). Ultrahigh Water Permeance of a Reduced Graphene Oxide Membrane for Separation of Dyes in Wastewater. Inorganics, 13(8), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13080251






